Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
P031544/WO/1
DaimlerChrysler AG
Device and method for producing a hollow section or shell
section
The invention relates to a device for producing a hollow
section or shell section according to the preamble of
patent claim 1 and to a method for this according to the
preamble of patent claim 6.
During hydroforming, contoured hollow sections or half
shells are produced from surfaces placed one on top of
the other (during "sheet blank expansion") or from
tubular blanks by the sheets or tubular blanks being
inserted in a sealing manner in a die of an HF tool and
by an introduced fluid being applied at a corresponding
high pressure to said sheets or tubular blanks in order
to form the latter. The hydroforming process is used
specifically in the production of frame structure
components in the automobile sector, for example for the
production of body members.
Such frame structure components have to be connected to
other surrounding components. In the conventional
production of frame structure components, flanges are
generally provided at the ends of the components for
connecting to the surrounding components in order to
permit an appropriate connection to other components, for
example by spot welding.
For this purpose, components produced by means of
hydroforming are subsequently subjected to further
processing steps, such as cutting or bending for example.
To this end, the hollow section or shell profile produced
must be deflected to the desired length in a separate
processing step. Whereas flat cut contours can in this
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 2 -
case still be produced by a simple saw cut running
transversely to the axial/longitudinal direction of the
hollow section or shell section, cut contours running in
three-dimensional space for flange surfaces, which are
increasingly occurring in particular in the use of frame
structure components in vehicle body construction, have
to be produced in an elaborate manner by laser or plasma -
cutting. The flanges are then produced by subsequent
bending of the material pieces or extensions still
remaining on the workpiece.
It goes without saying that such subsequent processing
steps require additional processing machines. In
addition, the components have to be transported from the
HF device to the subsequent processing stations. These
circumstances lead to an increased expenditure of time
and to considerably higher production costs.
In order to carry out cutting in an HF tool, a device is
proposed in EP 100 43 81 A2 establishing the generic
type, this device comprising die plates, integrated in
the tool and having cutting edges, and a plurality of
support plungers which bear axially against said die
plates, both the die plates and the plungers being
provided at the periphery at one end of the hollow
section blank to be formed. The end of the blank projects
from the HF tool. During the expansion of the blank by
introducing the fluid under high pressure, the periphery
of the blank butts against the cutting edges. The support
plungers, which are pushed toward the hollow section
blank via drive wedges by hydraulic or pneumatic
cylinders until they come to bear against one another,
form a small peripheral gap with the hollow section blank
in this phase, so that, by continuing the expansion, the
end of the blank is pre-cut at the cutting edges. The
drive wedge is then retracted, as a result of which the
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 3 -
plungers are lowered in the bottom tool part. In this
way, the peripheral gap in the bottom region of the blank
is markedly increased and the blank shaped into the
desired hollow section is completely cut off there at the
end at the cutting edges. However, the plungers in the
top tool part remain in their previous position due to
gravitational force, while the drive wedges move outward-.
On account of the expanding hollow section, the plungers
are pushed apart, after which the cutting edges are
exposed. Since the cutting edges, due to the lowering of
the plungers in the bottom tool part, are exposed much
earlier than in the top tool part, the trimming in the
bottom tool part is effected earlier than in the top tool
part. During the trimming, however, a pressure drop
occurs in the hollow section, so that only the bottom
peripheral region of the hollow section is severed
neatly. In the top region, either no complete parting is
effected or the parting contour of the hollow section is
at least undefined there, so that a rework operation is
inevitable in order to completely sever the initially cut
top region or to transfer the parting contour into the
desired mold profile. This is complicated for the entire
process of producing the hollow section and is affected
by production tolerances on account of the additionally
required transfer to a suitable parting or rework device.
In addition, the cut contour is in this case determined
over the periphery of the section by the shape of the
cutting edges. Since the die plates bear symmetrically
against the periphery of the HF component in the present
case, this device is only suitable for hollow sections
having a rotationally symmetrical or rectangular cross
section. However, the tongues formed on the end of the
hollow section by the trimming can be used as fastening
flanges after a resetting operation.
Based thereon, one object of the present invention is to
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 4 -
provide a device and a method for hydroforming, in which
production of HF components having joining flanges
connected to them in one piece is made possible in a
relatively simple manner.
The object is achieved according to the invention by the
features of patent claim 1 according to the device and by
the features of patent claim 6 with regard to the method.
On account of the formation of notches by means of
notching punches which are displaceable in the radial
direction relative to the hollow section or shell
section, defined parting points are created between the
lateral notch margins running in the component
longitudinal direction, these parting points being parted
by a parting device separate from the punches, with the
extension section and a cut-off component which exposes
the component to be produced being formed. After removal
of the hollow section or shell section thus produced, the
extension sections are bent over outside the HF tool to
form a flange section in each case by means of a bending
device. This constitutes a simple production method, the
acting tools forming the extension sections in a reliable
and exactly reproducible manner. By means of the notching
punches, the arrangement and shape of the notches is
relatively flexible. Thus said notching punches need not
necessarily form a rectangular shape, but rather,
according to requirements, can produce triangular or
polygonal shapes, which, according to requirements, can
have virtually any desired contour. Therefore very
diverse shapes of the component ends of a hollow section
or shell section can already be produced in the HF tool
in a highly precise manner. The notching punches may
themselves have cutting edges at their end face, with
which cutting edges they act upon the hollow section or
shell section in a cutting manner and punch a notch slug
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 5 -
out of the latter from outside into the interior of the
hollow section or shell section.
At the same time, however, it is also conceivable for the
notching punches for producing the notches to give way
relatively quickly in their passage and in the process
expose a cutting edge at the orifice opening of the
passage, this cutting edge being formed on the cavity of
the die of the HF tool. In this way, driven by the
internal high pressure, on account of the resulting
contact pressure of the hollow section or shell section
on the cavity of the die at the location of the notch to
be produced, a hole slug is cut out into the passage of
the notching punches via the cutting edge of the cavity.
The hole slug becoming jammed in the passage can be
pressed out of the passages later in a simple manner, for
example by advancing the notching punches, after removal
of the hollow section or shell section from the tool, it
being necessary to place a collecting device in the
region of the passages, which prevents the hole slugs
from falling into the empty cavity.
Care must always be taken when forming the notches to
ensure that the notching punches provide a sufficient
seal or are sealed sufficiently, so that a pressure drop
inside the hollow section or shell section is prevented,
which pressure drop would ruin a desired formation of the
notches or of the extension sections to be formed. It may
be emphasized at this point that three-dimensionally re-
created and symmetrical cuts on the hollow section or
shell section can be easily produced by a specific shape
of the cutting edge of the end face of the notching
punches or of the cavity, as a result of which the
forming of the extension sections becomes especially
variable.
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 6 -
In an especially preferred development of the invention
as claimed in claim 2, the device according to the
invention also comprises a cutting device which is
separate from the punches and is intended for initially
cutting the component along the terminating edge of the
extension section to be produced and which is arranged
inside the HF tool and directly adjoins the notching
punches in the peripheral direction of the tool cavity.
The parting device severing the component along the
initial cut is arranged outside the HF tool. A
predetermined parting point is achieved by the initial
cutting of the component effected according to the method
as claimed in claim 7, and this predetermined parting
point, if need be, is extremely thin-walled and can be
parted with the least possible effort outside the
hydroforming tool by means of a parting device of simple
construction. This may be done in such a way that the
hollow section or shell section is simply knocked off at
the thin point produced. Furthermore, the hollow section
or shell section with the component to be parted can be
removed in one piece as an entity from the HF tool, which
considerably reduces the handling and transport cost. The
cutting device in this respect may be designed, for
example, in a simple manner as a knife-like cutting edge
which plunges into the material of the hollow section or
shell section and in the process severs the hollow
section or shell section except for a thin web. The
cutting device may in this case be arranged in the same
axial position as the notching punches, since, even when
the hollow section or shell section is acted upon from
outside to inside by means of the notching punches, the
cutting device in this case in no way gets into the clip-
in region of the notching punches.
In a further preferred development of the device
according to the invention as claimed in claim 3, the
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
_ 7 _
device also comprises a cutting device which is separate
from the notching punches and is intended for cutting
through the component along the terminating edge of the
extension section to be produced except for a thin, axial
web adjoining the notch margins and which is arranged
inside the HF tool and adjoins the notching punches at a
slight distance apart in the peripheral direction of the
tool cavity. The parting device severing the component at
the location of the web is arranged outside the HF tool.
Due to the formation of a thin axial web which results
from the developed method according to the invention as
claimed in claim 8, the parting operation by means of the
parting device arranged outside the HF tool is
facilitated on account of the material to be severed to a
reduced extent. Owing to the fact that the cutting device
now largely cuts through the hollow section or shell
section, said cutting device, if it acts upon the hollow
section or shell section in the same direction as the
notching punches, would come into contact with the latter
in such a way that the notching punches and the cutting
device impair one another in an undesirable manner. Care
is therefore to be taken in the case of an axially
identical arrangement of cutting device and notching
punches that the displacement movement of the notching
punches runs in the opposite direction to the cutting
device. The hollow section or shell section is in this
case preferably cut from outside to inside by means of
the cutting device, whereas the notches, via the notching
punches giving way in the passages, are produced from
inside to outside at the cutting edge of the cavity. In
this variant, too, the component thus trimmed can also be
removed as an entity in one piece from the HF tool. In
the case where the cutting device consists of punches
which have a knife-like end face, said punches are
likewise displaceable, like the notching punches,
although in separate passages and to this end can be
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
capable of being driven mechanically, pneumatically or
hydraulically.
In an especially preferred development of the invention
as claimed in claim 4, the parting device for cutting
through the component along the terminating edge of the
extension section to be produced is arranged inside the
HF tool, in which case it directly adjoins the notching
punches in the peripheral direction of the tool cavity
but is axially offset from said notching punches in their
engagement region. This has the advantage that the
parting device is accommodated inside the HF tool in a
space-saving manner and replaces the cutting device, with
the outlay in terms of equipment and process being
considerably reduced, without losing the function of the
complete parting of the component to be cut off.
Furthermore, the development of the device according to
the invention advantageously allows the hollow section or
shell section to be acted upon in the same direction by
the notching punches and the parting device. Since the
notching and the cutting-through of the component is as
far as possible to be effected at the same time in order
to avoid the risk of a pressure drop, the fact that the
hollow section or shell section is acted upon in the same
direction due to said arrangement of the parting device
offers a considerable advantage for the process
reliability of the production of the component with
simultaneously reduced control outlay for the device. The
cutting-through of the component effected according to
the corresponding development of the method according to
the invention as claimed in claim 9 by means of the
parting device inside the HF tool along the terminating
edge of the extension section to be produced can be
carried out in a plurality of variants. In a special
configuration of the device according to the invention as
claimed in claim 5, the parting device may in this case
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 9 -
be formed by cutting punches. By means of these cutting
punches, the component can be parted linearly in a simple
manner along the abovementioned terminating edge during
or after the notching. Alternatively, however, it is
conceivable for the parting device to likewise consist of
notching punches which sever the component simultaneously
and produce notches iri the cut-off component, so that a
notching pattern with regard to a center cutting line in
the form of alternating notches is obtained. This has the
very special advantage that the cut-off component itself
is a component that can still be used and need not be
disposed of as a scrap part. The cut-off component in
this case likewise has extension sections which can be
bent over and can serve as fastening flanges. This
parting of the component, to be cut off, from the hollow
section or shell section need not necessarily be effected
at the end, but rather may also be carried out centrally
for example, in which case, if need be, identical parts
with flanges can be produced from a single workpiece
blank in a very economical manner in terms of the
process.
Apart from that, it is also conceivable for it to be
possible for such alternating notches to be formed in
such a way that a thin axial web still remains which has
to be parted outside the HF tool by means of the parting
device. The notches on the component to be cut off are in
this case made by the cutting device, which has to be of
appropriate design.
The invention is explained in more detail below with
reference to an exemplary embodiment shown in the
drawings, in which:
fig. 1 shows a cutaway lateral longitudinal section of a
hollow section in a hydroforming tool with axially
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 10 -
offset notching punches of the device according to
the invention,
fig. 2 shows the device according to the invention
according to figure 1 in a cross-sectional
illustration along section line II-II from figure 1
during the notching operation,
fig. 3 shows, in a cross section, the device according to
the invention from figure 1 along section line III-
III from figure 1 during the notching operation,
fig. 4 shows, in a lateral plan view, a segment of the
hollow section notched according to the invention
by the device from figures 1 to 3 and having an
axial web connecting the diagonally opposite
extension sections,
fig. 5 shows the hollow section from figure 4 after the
severing and exposing of the extension sections, in
a lateral plan view,
fig. 6 shows, in a cross-sectional illustration, the
hollow section from figure 5 along section line VI
VI.
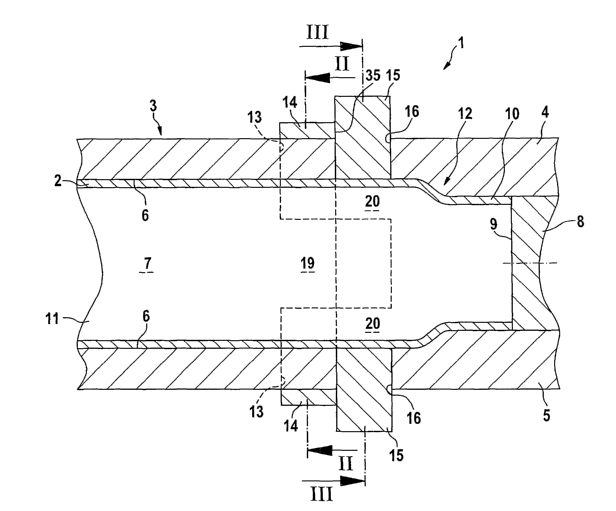
A device 1 for producing a hollow section or shell
section 2 is shown in figure 1 and contains a
hydroforming tool 3. The hydroforming (HF) tool 3 has a
top die 4 and a bottom die 5, the cavities 6 of which
define a mold space 7, into which the hollow section 2 is
inserted. For the shaping expansion of the hollow section
2, an axial plunger 8 closes the respective orifice
opening 9 of an end 10 of the hollow section 2. In the
present exemplary embodiment, the end 10 is shaped like a
bottle neck by the internal high pressure, exerted in the
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 11 -
hollow section interior 11, of a pressure fluid
introduced via the axial plunger 8. On that side of the
bottle neck 12 which is remote from the axial plunger,
passages 13 are formed in the top die 4 and the bottom
die 5, and notching punches 14 which are radially
displaceable with respect to the hollow section 2 are
arranged iri said passages 13. The notching punches 14 are
arranged offset from one another in the peripheral
direction. Adj oining the side 35 of the notching punches
14 which faces the bottle neck 12 is a cutting device
which is likewise designed as notching punches 15 and is
guided in a displaceable manner in passages 16 of the HF
tool 3 radially relative to the hollow section 2. Whereas
the notching punches 14, as can be seen in figure 2, are
arranged merely in the corner region 17 of the hollow
section 2 of box-shaped design and can act upon the
latter only at this location, the notching punches 15 of
the cutting device are arranged in the region of the
longitudinal sides 18 of the hollow section 2 in the HF
tool 3 and can only act upon said longitudinal sides 18
(figure 3). The notching punches 15 are therefore
arranged offset from the notching punches 14 in such a
way that the notching punches 15 almost completely cover
the arrangement gaps 19 between the notching punches 14
and the notching punches 14 almost completely cover the
arrangement gaps 20 between the notching punches 15.
Furthermore, the notching punches 15 are thus arranged
outside the engagement region of the notching punches 14
in such a way as to be axially offset from the latter.
However, as stated, they adjoin one another almost
directly in the peripheral direction of the tool cavity
6.
After shaping has been effected by means of internal high
pressure, the notching punches 14 are retracted suddenly
in their passages 13 in this exemplary embodiment. In the
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 12 -
process, a cutting edge 21 extending along the passage
margins and formed on the cavities 6 of the top die 4 and
the bottom die 5 is exposed, the hollow section 2 being
trimmed along said cutting edge 21, with notches 22 and
in each case an associated notch slug 23 being formed. In
this case, the notch slug 23 butts against the end face
24 of-the respective notching punch 14 and, driven by the
internal high pressure still applied, is pressed together
with said notching punch 14 into the passage 13. After
that or even at the same time, the notching punches 15
are displaced according to figure 3 toward the hollow
section 2, punch notch slugs 25 out of the latter and
plunge together with said notch slugs 25 into the hollow
section interior 11. After notching has been effected,
the notching punches 15 are retracted into their passages
16. In principle, it is also conceivable that the mode of
displacement of the notching punches 15 and 14 for
forming the notches can be kinematically reversed. The
pressure fluid is then relieved and directed out of the
hollow section interior 11. After that the HF tool 3 is
opened and the hollow section 2 thus trimmed at the
periphery at an axial distance from its end 10 is removed
from said HF tool 3. The hollow section 2 which can be
seen from figure 4 accordingly has notches 22 and notches
26 which are axially offset from one another and are in
each case spaced apart separately in the peripheral
direction. Extension sections 27 and 28 remain between
the notches 22 and between the notches 26, the extension
sections 27 being connected to the extension sections 28
at the notch margins 29 by a thin, axial web 30. On
account of its notches 26, the extension section 27 is
therefore almost completely cut through at its
terminating edge 31 and the extension section 28 is
almost completely cut through at its terminating edge 32
by the notches 22. In order to divide the hollow section
2 produced in such a way into two parts 33 and 34 in the
CA 02553622 2006-07-14
- 13 -
region of the notches 22 and 26, the hollow section 2 is
severed at the location of the webs 30 outside the HF
tool 3 by means of a parting device (not explained in any
more detail here), which results in a component 33 as can
be seen from figure 5 and figure 6. The extension
sections 27, the terminating edges 31 of which are now
completely exposed, are bent over by means of a bending
device (likewise not explained in any more detail here)
to form a flange section of the hollow section or shell
section. The webs 30 may possibly also already break off
when being cut through on account of their stretching in
the case of a very small wall thickness, so that a
separate parting device outside the hydroforming tool can
be dispensed with.