Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 1 -
A HYDRONIC HEATING SYSTEM, HANGER FOR TUBING
AND METHOD OF USING SAME TO INSTALL THE
HYDRONIC HEATING SYSTEM
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates generally to radiant
heating systems and, in particular, to hangers for
installing tubing in a radiant heating system.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Radiant heating systems for living and/or working
spaces are widely known. One popular type of radiant
heating system for these applications is the hydronic
heating system wherein a heated fluid such as water is
pumped through an endless tubing loop installed under a
floor ("RFH" or Radiant Floor Heating) or inside a wall
("RWH" or Radiant Wall Heating) . Heat is supplied to the
living area or workspace from heated fluid circulated
through the endless loop which heats the floor or wall via
natural heat transfer mechanisms, i.e. radiation,
convection and conduction. The fluid is typically heated
by a boiler which burns a carbonaceous fuel such as natural
gas or fuel oil or, alternatively, by a gas or electrical
heated water heater, or the like.
Traditionally, hydronic heating coils have been
installed between floor joists or wall studs with at least
one loop between each pair of adjacent joists or studs.
Furthermore, the endless loop has traditionally been
supported in close contact with the floor or wall surface
and heat conductive plates have been used to enhance the
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 2 -
radiation of heat from the endless loop to the undersurface
of the floor.
Prior art radiant heating systems suffer from a number
of disadvantages. First, the radiant plates which support
the heating tubes are secured directly to the floor or wall
surface. This promotes "hot spots" on the floor or wall.
Heating fluid temperatures must therefore be controlled in
order to prevent hot spots which could prove injurious or
discomforting to occupants of the heated space. Second,
plastic tubing used in hydronic heating system is
vulnerable to puncture by fasteners driven through the
flooring or the wall structure by persons who are not aware
of the hazard. Such accidental damage to the heating system
can cause water damage and potentially cause damage to the
fluid distribution pump and/or the boiler used for heating
the fluid. Third, at least one loop is required in each
inter-joist space in order to lay out the endless heating
loop efficiently as well as to provide adequate radiant
heat in most climates. Fourth, as noted above most boilers
operate at temperatures which exceed the desired
temperature of a floor surface. It is therefore necessary
to provide some mechanical arrangement to prevent fluid
heated by the boiler from circulating in an undiluted
condition through the hydronic heating system. Expensive
flow control components which must be installed by skilled
workmen are therefore required in the heating system. This
contributes to the cost of installation and maintenance of
the system.
These problems were addressed by the hydronic heating
system described in Applicant's U.S. Patent 5,542,603
(MacDuff) which issued Aug. 6, 1996. This hydronic heating
system includes a conduit for circulating heated fluid
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 3 -
beneath a floor. The conduit is suspended a predetermined
distance beneath the floor, which provides more uniform
heat transfer, eliminating unwanted hot spots. The
hydronic heating system is installed so that the conduit
runs transverse to the floor joists, i.e. the conduit
passes through holes bored in the joists.
Accordingly, it is desirable to provide an improved
hydronic heating system that facilitates installation by
permitting the fluid conduit to be run between, and
generally parallel to, the floor joists to facilitate
installation.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is therefore an object of the invention to provide
a hydronic heating system that is rapidly and easily
installed.
The invention therefore provides a hydronic heating
system for radiant floor heating, comprising a length of
tubing defining a conduit within which a heated fluid can
be circulated; and a plurality of hangers that suspend the
tubing a predetermined distance beneath the floor, each
hanger comprising: a stem having a top end that can be
secured to the underside of the floor; and a helical hook
at a bottom end of the stem for supporting the tubing, the
helical hook having a free end that is spaced away from the
stem a distance that is about equal to an outer diameter of
the tubing, the helical hook forming an arc with respect to
the stem that does not exceed 270 to permit the hook to be
slid over a side of the tubing and rotated 90 to lock the
tubing within the hook when the hanger is secured to the
underside of the floor.
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 4 -
The invention further provides a method of installing
a hydronic heating system, the method comprising: extending
a tubing beneath a floor to be heated; sliding a helical
hook at a bottom end of a hanger over the tubing, the
helical hook having a free end that is spaced away from a
stem of the hanger by a distance that is about equal to an
outer diameter of the tubing, the helical hook forming an
arc with respect to the stem that does not exceed 270 to
permit the hook to be slid over a side of the tubing and
rotated 90 to lock the tubing within the hook when the
hanger is secured to the underside of the floor; and,
sliding the hangers over the tubing at predetermined
intervals and securing the respective hangers to an
underside of the floor to suspend the tubing a
predetermined distance below the underside of the floor.
The invention further provides a hanger for suspending
a tubing for circulating a heated fluid in a hydronic
heating system. The hanger comprises a stem having a top
end securable to an underside of a floor; and a helical
hook at a bottom end of the stem, the hook having a free
end that is spaced from the stem by a distance that is
about equal to an outer diameter of the tubing, the helix
forming an arc with respect to the stem that does not
exceed 270 to permit the hook to be slid over a side of
the tubing and rotated 90 to lock the tubing within the
hook when the hanger is secured to the underside of the
floor.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further features and advantages of the present
invention will become apparent from the following detailed
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 5 -
description, taken in combination with the appended
drawings, in which:
FIG. 1 is a schematic plan view of a hydronic heating
system in accordance with an embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 2 is a front elevational view of a hanger for use
in the hydronic heating in accordance with the invention;
FIG. 3 is a side view of the hanger shown in FIG. 2,
with a fastener for fastening the hanger to an underside of
a floor;
FIG. 4 is a front view of the hanger shown in FIG. 2;
FIG. 5 is a top plan view of the hanger shown in
FIG. 2;
FIG. 6 is an isometric view of the hanger shown in
FIG. 2, preassembled with a fastener; and
FIG. 7 is a perspective view of a section of tubing
supported by the hanger shown in FIGs. 2-6.
It should be noted that throughout the appended
drawings, like features are identified by like reference
numerals.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The invention provides a hydronic heating system and a
hanger that facilitates installation of fluid distribution
tubing for the hydronic heating system.
FIG. 1 is a schematic plan view of a hydronic heating
system, generally designated by reference numeral 10, in
accordance with an embodiment of the invention. As shown
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 6 -
in FIG. 1, the hydronic heating system 10 transfers radiant
heat from a fluid heated by a boiler 12 or other heater for
heating the fluid, e.g., water. A pump 14, can be located
upstream or downstream of the boiler 12, although, as is
known in the art, the system will perform more efficiently
if the pump is located upstream of the boiler, as shown in
FIG. 1. The boiler 12 and the pump 14 can be separate
units, as shown, or different subcomponents of the same
unit.
As shown in FIG. 1, the pump 14 circulates the heated
fluid through a tubing that defines a conduit 16. In one
embodiment, the conduit is made of a composite tubing which
includes plastic and aluminum components to prevent the
intrusion of atmospheric oxygen into the heating fluid,
which can corrode boiler parts and even attack the plastic
tubing at elevated temperatures. This type of composite
tubing is well known and commercially available from a
number of suppliers.
As shown in FIG. 1, the hydronic heating system may
optionally include a return manifold 18 and a distribution
manifold 20. The return manifold 18 has a plurality of
inlet ports 22 and the distribution manifold 20 has a
plurality of outlet ports 24 for connecting to other
conduits 26, 28 that convey the heated fluid to other
heating zones. These manifolds therefore permit several
heating circuits (or "heating loops") to be connected to a
single boiler loop.
The hydronic heating system 10 typically includes a
zone valve 30 for regulating the fluid flow through the
conduit 16. The zone valve 30 is controlled by a
thermostat (not shown), which opens the zone valve 30 when
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 7 -
the thermostat demands heat and closes the zone valve 30
when heat is no longer required. Typically, the thermostat
also controls the boiler 12 and pump 14.
As shown in FIG. 1, the conduit 16 loops back and
forth under a floor 42 of a zone 40 and runs between and
generally parallel to the floor joists 44. In other words,
the conduit 16 passes through the "inter-joist spaces"
beneath the floor 42. As shown, the tubing is pulled
through holes 46 drilled in ends the joists to enable the
tubing to be extended into an adjacent inter-joist space.
A plurality of heat-radiating fins 50 which promote
heat transfer from the tubing/conduit 16, are connected to
the tubing 16 at predefined intervals, as described in
Applicant's U.S. Patent 5,542,603 (MacDuff) entitled
HYDRONIC HEATING SYSTEM.
As shown in FIG. 1, the hydronic heating system 10
further includes a plurality of hangers 100 in accordance
with the invention. As will be described in greater detail
below, the hangers 100 suspend the tubing (conduit) 16 a
predetermined distance beneath an underside of the floor 42
in order to provide uniform heat transfer to the floor and
to thus preclude the creation of any unwanted hot spots on
the floor. It should be expressly understood that the
distribution and spacing of the hangers 100 or the heat
radiating fins 50 shown schematically in FIG. 1 are not
intended to reflect a distribution and spacing that would
actually be used to suspend the tubing.
It should also be expressly understood that although
the invention is illustrated with reference to a floor
CA 02560383 2006-11-14
14060-9CA
- 8 -
supported by floor joists through which holes may be bored,
the invention is equally adapted to be used with floors
constructed with open or "space joist" systems, well known
in the art, stressed-skin panels, reinforced concrete, or
any other flooring system that presents a relatively flat
floor underside into which fasteners can be driven.
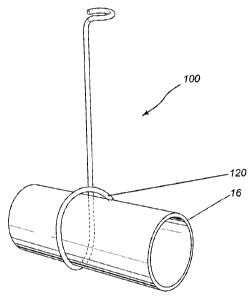
FIGS. 2-5 illustrate the hanger 100 in accordance with
an embodiment of the invention. The hanger 100 includes a
stem 102 having a top end 104 connectable to an underside
41 of a floor 42, e.g. a sub floor. In one embodiment, the
top end 104 includes an upper loop 106 formed integrally
with the stem 102. The upper loop 106 defines an passage
108 (shown in the top view of FIG. 5) through which a
fastener 110 (shown in FIG. 2) can be inserted for securing
the hanger 100 to the underside 41 of the floor 42. In one
embodiment, the fastener 110 is a threaded fastener having
a head 112 substantially larger than the passage 108
defined by the upper loop 106 and threads 114.
The hanger 100 further includes a helical hook 120 at
a bottom end 122 of the stem 102. The hook 120 has a free
end 124 that is spaced apart from the stem 102 by a
distance 126 that is about equal to an outer diameter of
the tubing 16. The helical hook spirals away from the stem
102 and forms an arc with respect to the stem that does not
exceed 270 (see FIG. 2) to provide a substantially
circular seat 128 for supporting the tubing 16. The
geometry of the helical hook 120 facilitates the sliding of
the helical hook 120 over the tubing 16 and ensures that
the retention of the tubing 16 by the hook when the hanger
100 is fastened to the underside 41 of the floor 42.
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 9 -
In one embodiment, the helical hook 120 is integrally
formed with the stem 102. In one embodiment, the stem 102
(including the upper loop 106) and the hook 120 are
integrally formed from a single piece of metal wire,
stainless steel for example. The hanger 100 can be
constructed to accommodate any size of tubing. The length
of the stem 102 positions the tubing a desired distance
beneath the floor, such as, for example, three inches.
As illustrated in FIG. 6, the hanger can also be
preassembled with a fastener 150 having a narrow neck
region 152, in accordance with another embodiment of the
invention. The narrow neck region 152 is rotatably
restrained within the passage 108 defined by the upper
loop 106. In other words, the fastener 150 is rotatably
restrained within the loop 106 to further facilitate the
task of hanging the tubing 16 to provide a hydronic heating
system.
FIG. 7 illustrates a section of tubing 16 supported by
the helical hook 120 of the hanger 100. The tubing is not
tightly or snugly gripped by the hanger 100. Rather, there
is enough play to permit the tubing to slide longitudinally
through the hanger 100.
The hydronic heating system 10 can be installed by
extending or "pulling" a tubing 16 beneath a floor 42 to be
heated. The tubing 16 is positioned between and generally
parallel to floor joists 44 as was shown in FIG. 1.
Holes 46 are drilled in the ends of the joists 44 to enable
the tubing 16 to be looped in a continuous circuit beneath
the floor 42. The tubing 16 is then suspended or hung
using the hangers 100, which are secured by fastening each
one to an underside of the floor using, for example, a
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 10 -
threaded fastener 110. The suspension of the tubing 16 is
rapidly accomplished and the installation of the hydronic
heating system 10 is greatly facilitated. It should be
understood that although the hydronic heating system is
shown installed between joists in FIG. 1, if an open joist
system or a stressed skin panel flooring system is used,
the hydronic heating system in accordance with the
invention can be installed transversely to joists or beams
supporting the floor.
During installation, each successive hanger 100 is
slipped over the tubing 16 by passing the tubing through
the gap 126 and rotating the hanger 100 about 90 before
fastening the hanger 100 to the underside 41 of the
floor 42 using a threaded fastener 110, for example. In
one embodiment, the hangers 100 are secured to the
underside of the floor 42 midway between adjacent joists 44
to ensure uniform heat transfer to the floor 42.
Once all of the tubing 16 is hung for the zone 40, the
tubing 16 is connected to the boiler 12 and pump 14, or, if
there are other zones, to the return and distribution
manifolds 18, 20, as described earlier.
The heat-radiating fins 50 are attached to the tubing
16 in order to promote heat transfer from the tubing 16 to
the floor 42. The heat-radiating fins 50 may be attached
to the tubing 16 after the tubing is threaded through the
respective joists and either before or after the hangers
100 are installed to support the tubing 16.
The embodiments of the invention described above are
intended to be exemplary only. The scope of the invention
CA 02560383 2006-09-21
14060-9CA
- 11 -
is therefore intended to be limited solely by the scope of
the appended claims.