Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02563488 2008-12-10
A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ABBREVIATING INFORMATION SENT TO A
VIEWING DEVICE
BACKGROUND
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to the field of data communication over a
network. More
particularly, the invention provides a system and method for abbreviating the
content and quantity
of information sent to the viewing device over a network. The information may
be an Internet or
Intranet world-wide web (WWW) page with Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
coding,
Extensible Markup Language (XML), or other types of markup languages such as
Wireless Markup
Language (WML) that utilize data frames to display information pages. The
remote viewing device
may be a handheld, laptop, or palmtop device with a limited viewing space for
the information
being received, and preferably connects to the Internet over a relatively low-
bandwidth wireless
radio network.
2. Description of the Related Art
Typically, handheld or palmtop devices have very limited viewing surfaces,
limited memory
capacity, slower processing speeds, and limited user inputs in comparison to
large desktop computer
systems. These devices may also communicate over a bandwidth-limited data
network, such as a
wireless packet data network, a cellular network using a digital packet data
protocol, or they may use
a limited speed modem to download information from a network. For these
reasons, it is desirable
to limit the data these devices receive over the network or through the modem,
particularly when
receiving large data files, such as framed web pages that may include text,
graphics, animations,
multimedia files, or other interactive elements in each frame.
A known method for limiting data transfer to such a viewing device involves
restricting the
transmittal of graphic information. By providing a specific configuration
setting available on most
-2-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
Internet browsers, a user can specify that only text information is fetched by
the browser. The
graphical portions of the web page are left behind. This method is
indiscriminate, however, and
leaves the user with little useful control; simply an on or off switch for
changing the type of
information viewed. In many cases there are pieces of text that are not
desired in the information
stream, and pieces of graphics that are desired in the information stream, but
the user has no control
over this situation. For example, in a framed page, a common frame could
provide advertisements or
a navigational toolbar. Such frames would not be desirable to a user with
limited viewing capability
and space.
Another Known method for transmitting Internet -type information to a wireless
viewing
1 o device is to "spoof' the Inter-network Protocol (IP) and Transmission
Control Protocol (TCP) so that
they partially work over the wireless link. This "spoofing" method, however,
often leads to a failure
of both the protocols and the device to display all the information.
Alternatively, several attempts have been made at using a wireless proxy to
eliminate using
both TCP and IP over the wireless network. A wireless proxy is a computer that
terminates a TCP/IP
1 5 connection on one end and a wireless connection on the other end. The most
common use of a proxy
is as a TCP/IP "firewall," which is used in most companies' networks today.
This proxy method
removes the TCP/IP protocol from running over the wireless network, but leaves
the actual data
transferred untouched. This type of proxy has limited ability to further limit
the higher-level
information being sent to the user, and in particular the bandwidth heavy
graphics and multimedia files
20 embedded in most web pages.
Still another known method for limiting information sent to a portable viewing
device is to
have users pre-define the information sites (e.g., web sites) they intend to
access using their portable
viewing device. In this method, however, a user must pick, ahead of time,
every site to be accessed
-3-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
and must select the information to be transferred when connecting with the
wireless
viewer. This selection is typically done on a desktop computer system, where
visibility, memory, CPU speed and keyboard input are not restricted. The
challenge for
the user, however, is to have foreknowledge of every site to be accessed.
In order to reduce the information contained in frames, a prior art method,
shown in Fig. 1, reduces the frame content to simple text that includes a
hypertext link.
The HTML page 10 includes three frames of information, frame A 12, frame B 14,
and
frame C 16. According to this method, page 10 is first loaded into a web proxy
server.
The proxy server interprets the HTML code of page 10 for frame identifiers,
such as the
tag <frameset>, which is a brief description of the frame. For example, the
tag
identifiers could be "Title A" for a first frame 12, "Title B" for a second
frame 14, and
"Title C" for a third frame 16. An abbreviated page 18 including just the tag
identifiers
is then sent to the viewing device as simple text with a hypertext link to the
frame 12,
14, or 16 that the tag represents. The abbreviated page 18 does not display
frame
content, but only the tag identifier for each of the frames. Thus, the user
has no idea of
what information content is included in this framed page.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A system and method for transporting abbreviated information pages from a
gateway device to a handheld viewing device is provided that includes an
information
source, a gateway device, a relay network and a handheld viewing device. The
gateway device includes a fetch and cache component, storage, and a wireless
transport
layer. The wireless transport layer delivers information from the gateway to
the
handheld viewing device. The gateway device determines whether a particular
-4-
CA 02563488 2008-12-10
information page requested by the handheld device includes frames, and, if so,
then the
gateway device creates an abbreviated version of the information page and
transmits it
to the handheld device. The abbreviated version of the information page
includes a
reduced-sized bitmap of the page and an image map that identifies the frame
regions
within the bitmap. The handheld device displays the abbreviated information
page, and
a user of the device can then manually select certain frames of data through a
user
interface.
Accordingly, in one aspect of the present invention there is provided a system
providing an information page having a plurality of frames to a viewing
device,
comprising:
means for receiving an information page request from the viewing device and
retrieving the requested information page, the requested information page
having a
plurality of frames;
means for generating an abbreviated version of the requested information page,
the abbreviated version including a graphical representation of the requested
information page and frame location data that associates a plurality of links
with the
frame locations of the plurality of frames in the graphical representation;
and
means for transmitting the abbreviated version of the requested information
page to the viewing device.
According to another aspect of the present invention there is provided a
portable
viewing device, comprising:
a transmitter for transmitting an information page request to a remote system
where the information page is stored;
a receiver for receiving an abbreviated version of the requested information
-5-
CA 02563488 2008-12-10
page in response to the information page request; and
a processor for processing the abbreviated version of the information page,
the
abbreviated version of the information page including a graphical
representation of the
requested information page and frame location data that associates a plurality
of links
with frame locations of a plurality of frames in the graphical representation.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a prior art abbreviation method for an HTML page;
FIG. 2 is a system diagram of a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a flow diagram of a preferred method for transporting information
pages according to the present invention;
FIG. 4 is a flow diagram of the preferred steps for generating an abbreviated
information page according to the present invention; and
FIG. 5 shows a graphical display for abbreviating an information page and then
interacting with the abbreviated page in order to display one frame in the
information
page.
DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
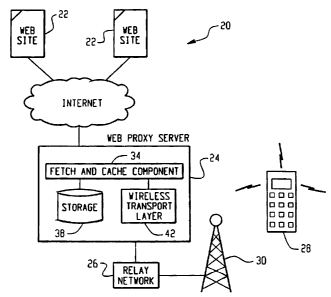
Turning now to the drawing figures that depict an example of the present
invention, FIG. 2 shows a system diagram of a preferred embodiment of the
present
invention. A system 20 includes an information source 22, such as a web site
coupled
to a communication network such as the Internet, a web proxy server 24, a
relay
network 26, a wireless network 30, and a handheld viewing device 28. The
information
source 22 could be an Internet site, an Intranet site, or even a local system.
The web
proxy server 24 is also coupled to the Internet, and communicates information
to and
from the information sources 22. The relay network 26 couples the web proxy
server
-6-
CA 02563488 2008-12-10
24 to the handheld viewing device 28 through a wireless network 30. The
viewing
device 28 is preferably a wireless handheld device, but could be any other
type of
device having a limited display screen, such as a cell phone, PDA, laptop,
etc.
An example of the handheld device 28 is a BIackBerry TM or Inter@ctiveTM
two-way Pager manufactured by Research In Motion Limited. This device is
further
described in co-owned United States Patent Nos. 6,278,442, issued on August
21, 2001
and 6,396,482, issued on May 28, 2002, both titled "Hand Held Electronic
Device with
a Keyboard Optimized for use with Thumbs" and No. 6,477,529, issued on
November
5, 2002 and titled, "Apparatus and Method for Dynamically Limiting Information
Sent
to a Viewing Device."
In this system 20, the web site 22 is a repository of the information that the
user
of the handheld device 28 desires to access for display. The web proxy server
24 is
used as a gateway to accept a connection from the relay network 26, and in
turn to
make a connection to the web site 22 to retrieve the information desired.
Preferably,
the connection between the web proxy server 24 and the information source 22
is a
TCP/IP connection and the information source 22 is a web server containing a
plurality
-7-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
of web pages. As is known in the art, a proxy server accepts a connection
request from
a device and opens another connection on behalf of the device to allow the
device to
communicate with other devices or systems indirectly. To assist the web proxy
server
24 in its task of obtaining information and preparing it for transmission to
the handheld
device 28, the web proxy server 24 includes a storage area 38. The storage
area 38 can
be located on the same machine as the web proxy server 24, in another location
across a
local area network (LAN), or even in a node cluster of fault tolerant storage
devices.
Communication across the wireless network connection 30 is facilitated on the
handheld device 28 by software operating within the handheld device 28. This
software converts requests from the user into signals that are transmitted
across the
wireless network connection 30 and understood by the web proxy server 24.
The web proxy server 24 is coupled to, and communicates with the target web
site 22 through a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) fetch and cache component
36 of the proxy server 24. The target web pages can be located on a range of
computers, computer systems, and networks. For example, the information can
be stored in local databases, on an Intranet, or on the Internet. The fetch
and cache
component 34 of the web proxy server 24 stores the web pages that are returned
-8-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
from the information source 22 in response to the user request. A wireless
transport layer 40 at the
web proxy server 24 then sends the information over the relay network 26,
through the wireless
network connection 30 to the viewing device 2S.
Referring now to Fig. 3, a flow diagram of a preferred method for transporting
abbreviated
information pages is set forth. The method begins at step 50, where the proxy
server 24 waits until
a request is received 52 from the viewing device 28. Once a page is requested,
the page is then
downloaded 54 to the web proxy server 24 using the HTTP fetch and cache
component 34, and
stored in storage 38. The proxy server 24 searches the HTML code that
describes the page for
frames in step 56. It is to be understood HTML is only used an example in this
description, other
markup languages are just as applicable such as, but not limited to, XML and
WML. If the page does
not include frames, then at step 58 the page is sent to the viewing device 28
without an abbreviation.
If the page does include frames, then the abbreviated frames method
60(described more full below
with reference to FIG. 4) is executed to form an abbreviated version of the
page and the wireless
transport layer then sends 62 the abbreviated page to the viewing device 28.
The proxy server 24 then
waits to receive additional page requests from the handheld device 28.
FIG. 4 sets forth the preferred method for generating abbreviated versions of
the information
pages having frames. The method begins at step 70 where the proxy server 24
renders the page. The
process of rendering preferably includes loading the page into a browser to
obtain the placement and
proportion of objects, such as frames, as they would appear if loaded to a
monitor. Once the page is
rendered, then a bitmap is generated at step 72 from the rendered page.
Alternatively, other forms
of graphical representations could be generated, including compressed forms of
representations. The
bitmap is a picture version of the rendered page. The bitmap is reduced at
step 74 in size from the
rendered page to a size that is viewable on the handheld device 28. Such a
reduction, could, for
-9-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
example, take a page that would display in 8(;,,r,' x 600 pixel and reduce it
to be viewed in 50 x 40 pixel
resolution.
The proportions of the frames on the rendered page are known, and this
proportion is
appropriately scaled on the bitrmy n .; 7c. F*i if a fzist frame is sized to
be 40% of the
width of a page and the full length of the page, the accompanying abbreviated
frame on the handheld
device 28 would be 40% of the width of the viewable area and the entire length
of the viewable area.
All frames from the information source 22 are similarly reduced to appropriate
proportions of the
viewable area of the handheld device 28.
Once the frame areas are determined on the reduced bitmap, then the frame
areas are assigned
i o 78 to the reduced bitmap. From the assignment of the frame areas, an image
map is generated 80. The
image map is a reference between the frame areas and the Universal Resource
Locators (URLs) that
are assigned to each frame. The image map allows a user to choose a point on
the bitmap, and then
be able to download the particular URL that is associated with that point on
the bitmap. The image
map and bitmap are packaged together 82 on the web proxy server 24 and sent
through the relay
network 26 to the viewing device 28 as shown in step 62 of Fig. 3.
The abbreviated frame method described in Fig. 4 provides the user of the
handheld device
with a graphical representation of the content of a framed web page. The bit
map reduction gives the
user perspective to determine if a particular frame contains pertinent content
that the user may want
to further examine. As shown in Fig. 5, HTML page 100 shows an example framed
web page as it
would be rendered on a desktop computer system. The HTML page 100 is divided
into three frames:
frame A 102, frame B 104, and frame C 106. Frame A 102 could, for instance, be
a story that the user
might want to read while frame B 104 and frame C 106 could be diversionary
frames that contain
links and advertisements.
-10-
CA 02563488 2006-10-20
The abbreviated frame 110 would show the bitmap representation of the page
100. The image
map for the bitmap would have three defined areas: Frame A area 112, frame B
area 114, and frame
C area 116. These image areas 112-1 16 are accessible to the user of the
viewing device 28 by input
means such as a thumbwheel located on tie view-sg device 28.''The input means
would toggle
between the image areas 112-116 to allow the user to choose a particular frame
on which to focus.
Once the user has chosen a particular frame, for instance, frame A 102 of the
HTMI, page 100, the
viewing device 28 then requests the web page having the URL associated with
frame A 102 from
the image map of the abbreviated frames page 112. This selected page is then
processed and displayed
in the same manner as described in FICis. 3 and 4. In the event, the selected
page does not contain
to frames, a single page is displayed on the viewing device 28.
The invention has been described with reference to preferred embodiments.
Those skilled in
the art will perceive improvements, changes, and modifications. Such
improvements, changes and
modifications are intended to be covered by the appended claims.
-11-