Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
WO 2005/108895 PCT/EP2005/004574
Title: Heat exchanger
DESCRIPTION
Field of application
The present invention, in its most general aspect, refers to a heat
exchanger for the heat exchange between a first and a second fluid.
Particularly, but not exclusively, the invention concerns a heat
exchanger for the heat exchange between pressurized fluids, of the type
comprising a plurality of casings, of substantially flattened shape and of
predetermined width, arranged in a pile, with an air space defined
between adjacent casings in the pile, and each formed from two half-shells
welded along a peripheral strip, which are in fluid communication with
each other through respective holes opening into said air space.
Prior art
Heat exchanger for the heat exchange between two fluids of the type
comprising a plurality of casings or flattened tubes are known.
Each casing is formed from two half-shells on which respective holes
are open, in corresponding positions, at which adjacent casings are joined
through collectors.
In such an arrangement, each pair of adjacent casings defines an air
space through which a first flow of fluid is conveyed, whereas a second
flow of fluid at a different temperature crosses the plurality of casings.
In this way, such flows carry out a heat exchange, which is generally
made more effective by making their motion highly turbulent through the
use of small corrugated plates, or turbulators, arranged in the cavities and
inside the casings, respectively.
The aforementioned joining collectors between adjacent casings are,
according to the prior art, pieces of tubes interfacing with the half-shells
and forced, through plastic deformation, around respective conical edges
foreseen at the holes open on the casings.
Heat exchangers thus realized, although advantageous, are not free
from drawbacks, including the main one represented by the low
mechanical resistance that they possess and that impairs its use, in
particular in the case of heat exchange between flows of fluids at high
pressure values.
Such a low mechanical resistance is substantial both at the joints
between adjacent casings, where the plastic deformation does not ensure
an adequate seal, and at the half-shells which, for an effective heat
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
06-12-2005 MOVOO1BWO EP0504574
-2-
exchange between the fluids, must be realized with a small thickness.
It follows from this that heat exchangers thus realized cannot be
used, or in any case are of little industrial interest, in the case of heat
exchange between flows of fluids of which at least one is at a high
pressure value; where by high pressure value we mean a value greater
than 10-13 bar.
Prior art in US 4,379,486 discloses a heat exchanger of the aforesaid
type comprising collectors (4a, 4b) which are provided with one or more
openings and which comprise prot.rusions on the lateral faces.
Document DE 71 15 268 U discloses a heat exchanger in which the
casings (21) are locked, by pulling means (47), between, terminal elements
(29, 36) and in which the collectors (27) comprise lerigthened openings.
Summary of the invention
The ~technical problem forming the basis of the present invention is
that of devising a heat exchanger for the heat exchange .between a . first
fluid and a second fluid, of the type comprising a plurality of. casings,.of
substantially flattened shape and of predetermined::w:idth;;: arranged in a,
pile, with an air space defined between adjacent casings :-in the pile, and
each formed from two half-shells welded along a peripheral atrip; in.which
the aforementioned casings are in fluid communication with each other
through respective holes opening into the aforementioned air space,
having structural and functional characteristics such as to- overcome the
aforementioned drawbacks, in other words such as to ensure an unusual
strength and mechanical resistance.
The aforementioned problem is solved according to the invention by a
heat exchanger of the type considered above, comprising, in the
aforementioned air space, at least one spacer, substantially of the sleeve
type, abutting on at the top end and made integral with said adjacent
casings around the respective holes opening into said air space.
Advantageously, the heat exchanger comprises irregularities
associated with the aforementioned at least one spacer, which extend in
the air space to rigidify the half-shells.
Preferably, the aforementioned irregularities are radial spokes
extending radially from said at least one spacer.
Advantageously, the aforementioned radial spokes are practically
equally angularly spaced.
Again preferably, the aforementioned radial spokes are formed
integrally with the spacer, and more preferably radial spokes and spacer
are a piece of an extruded profile.
Advantageously, the aforementioned extruded profile is made from
metallic material selected from the group comprising aluminium,
aluminium alloys, copper, copper alloys and similar metallic materials.
The characteristics and further advantages of a heat exchanger
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
06-12-2005 MOV001BWO EP0504574
-3-
according to the present invention shall become clearer from the
description, made hereafter, with reference to the attached drawings given
for indicating and not limiting purposes.
Brief description of the drawings
In such drawings:
Figure 1 shows a schematic front section view of a heat exchanger in
accordance with the present invention, made along the line I-I;
Figure 2 shows a plan view of the heat exchanger of figure 1, made
according to the arrow II;
Figure 3 shows an enlarged view of a detail of the exchanger of figure
Figure 4 shows a section .view of a detail of the heat exchanger of
figure 1, made accordirig to. the line IV-IV of figure 3;
Figure 5 shows a perspective, exploded view of a portion of the
exchanger of figure 1;
Figure 6 shows the. portionof figure 5 of the heat exchanger in
accordance with a variant embodiment of the invention; :
Figure 7 shows a detail of the portion of figure 5 in accordance with a
further variant embodiment of the invention;
Figure 8 shows the detail of figure 4 in accordance with a further
variant embodiment of the invention.
Detailed description
With reference to the aforementioned figures, a heat exchanger for
the heat exchange between a first fluid, for example oil, and a second
fluid, for example air, realized according to the present invention, is
globally and schematically represented with 1.
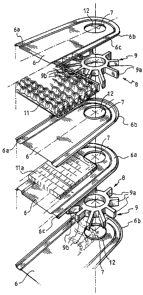
The heat exchanger 1 essentially comprises a plurality of casings 2, of
substantially flattened shape, associated together in a predetermined
distanced relationship in a pile 2a, with respective cavities 3 defmed
between casings.
The casings 2, of predetermined width L, are clamped, in a known
way, between a first plate 4 and a second plate 5, the latter provided with
joints 5a for the passage, for example, of the first of the aforernentioned
fluids.
In the example, the described exchanger has joints 5a of 1" -one
inch- (2,54 cm).
Each of the casings 2 is formed from two half-shells 6 welded along a
AMENDED SHEET
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
WO 2005/108895 PCT/EP2005/004574
-4-
peripheral strip 6a each of which is equipped, in corresponding positions,
with respective holes 7.
It should be noted that the aforementioned peripheral strip 6a has an
outer edge 6b comprising a trim 6c bent square, and that the half-shells 6
are realized in aluminium sheet of small thickness of between 0.1 and 0.4
mm, preferably 0.3 mm.
Such respective holes 7, which in the pile 2a are aligned, place the
aforementioned casings 2 in fluid communication with each other.
In such casings 2, a flow of the aforementioned first fluid is made to
flow, whereas the second fluid is made to flow in the aforementioned
cavities 3, all in a per se known way.
In accordance with a first characteristic of the invention, the heat
exchanger 1 comprises, in each of said cavities 3, a spacer 8, substantially
of the sleeve type, abutting on at the top end and made integral with the
aforementioned adjacent casings around each of the respective holes 7 of
the half-shells 6, realizing an inviolable mechanical connection between
adjacent casings.
Such spacers 8 made integral with the casings 2, for example
through brazing or welding, define, at the respective holes 7, passage
collectors for the aforementioned first fluid, communicating with the
inside of the casings 2.
In accordance with a second characteristic of the invention, the heat
exchanger 1 comprises irregularities 9 associated with each spacer 8,
which extend in each air space 3, constituting rigidifying elements of the
half-shells 6.
With particular reference to the example of figures 4 and 5, it should
be noted how such irregularities are in the form of radial spokes 9,
projecting radially towards the outside of said spacer 8 and practically
equally angularly spaced on such a spacer 8.
Advantageously and in accordance with a further characteristic of the
invention, a predetermined number of such radial spokes 9 extending
outside of the spacer 8, in the example a number equal to seven spokes
indicated with 9a, extends up to the aforementioned peripheral strip 6a.
In particular, such a predetermined number of radial spokes 9a
extends up to, and abuts upon, the aforementioned trim 6c bent square.
Again advantageously, the remaining radial spokes 9 of the same
spacer 8, in the example three spokes indicated with 9b, are sheared
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
WO 2005/108895 PCT/EP2005/004574
-5-
according to a transversal plane, indicated with T, which constitutes the
plane of reference and support for a corrugated plate, globally indicated
with 11, arranged in each of the cavities 3 and called "turbulator" by the
man skilled in the art.
Regarding this, it should also be stated that a second corrugated
plate or turbulator 11a is arranged inside each casing 2.
The aforementioned corrugated plates 11, 11a have the purpose of
increasing the efficiency of the heat exchange of the heat exchanger 1,
increasing the turbulence, by means of their corrugated surfaces, of the
flows of fluids intended for the heat exchange.
Preferably, the aforementioned radial spokes 9 are formed integrally
with the spacer 8 from which they project, and more preferably radial
spokes and spacer are a piece of an extruded profile made from a metallic
material selected from the group comprising aluminium, copper,
aluminium alloys, copper alloys and similar metallic materials.
It should be noted that the thickness s of the spacer 8 and the
thicknesses of the radial spokes 9 have values of between 2 and 4 mm,
preferably 3.5 mm.
Again preferably, each of the aforementioned respective holes 7 of
each half-shell 6 is foreseen equipped with a centring edge 12, projecting
from the half-shell 6 in the direction of the air space 3, for the alignment
of the spacer 8.
The main advantage of the heat exchanger according to the present
invention lies in its unusual strength.
Indeed, thanks to the spacers welded and made integral at the top
end on the casings, a particularly strong structure is given to the pile of
casings themselves.
In this way, an inviolable mechanical connection is realized between
adjacent casings, forming a seal and capable of withstanding violent
stresses.
In particular, the portions of exchanger that according to the prior art
were most subject to explosion are reinforced, in the exchanger according
to the invention, both through the spacers made integral with the casings
and through the radial spokes projecting from each spacer which
constitute rigidifying elements for each of the half-shells.
The heat exchanger according to the invention, in this way, is
particularly suitable for the heat exchange between pressurized flows of
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
WO 2005/108895 PCT/EP2005/004574
-6-
fluids, also for pressures of up to 35 bar and more.
Furthermore, the mechanical resistance of the exchanger is improved
by the radial spokes of the spacers, which constitute support elements for
each corrugated plate arranged in the cavities.
In this way, the corrugated plates are stably locked by the radial
spokes in an optimal position that allows an excellent increase in
turbulence of the flow of fluid that crosses the cavities, and an optimal
heat exchange in particular at high pressure values of such a flow.
In other words, the heat exchanger according to the present invention
allows a heat exchange to be carried out between a first fluid conveyed
inside the casings, and a second fluid conveyed into the cavities between
adjacent casings, in particular and at most when both of the respective
flows of such fluids are at high pressure values, thanks to the special
structure described above.
Such an unusual strength of the heat exchanger according to the
invention is achieved, advantageously, simultaneously maintaining a
compact structure of the exchanger, through half-shells realized with a
low thickness as required for an effective heat exchange.
A further advantage achieved by the heat exchanger according to the
invention lies in the minimal or negligible pressure drop that the fluids
undergo during the heat exchange, thanks to the aforementioned
mechanical connection that ensures a better seal than that which has
been provided up to now by the prior art.
It should be stated, furthermore, that radial spokes extending up to
the trim of the peripheral strip, advantageously bent square, give the heat
exchanger according to the invention an effective mechanical resistance
also against accidental knocks, preserving the heat exchanger from dents
and similar undesired damage that could derive from such knocks.
Now, with particular reference to the example of figure 6, a variant
embodiment of the present invention is described for which details and
cooperating parts having the same structure and operation as the
previous example embodiment shall be indicated with the same reference
numerals and symbols.
In such a variant embodiment, the heat exchanger comprises spacers
8, substantially shaped like a sleeve, made integral at the top end on
adjacent casings 2 and comprising radial spokes 90 projecting towards the
inside of the spacer 8.
CA 02565586 2006-11-03
WO 2005/108895 PCT/EP2005/004574
-7-
The aforementioned radial spokes 90 projecting towards the inside of
the spacer are sheared, at their free ends, so as to surround the centring
edge 12 of the respective holes 7.
Again with reference to the example of figure 6, it should be noted
that the spacer 8 comprises a first portion 80a with a curved profile, and a
second portion 80b with a squared profile constituting the reference plane
for the turbulator 11.
In such a variant embodiment it should be noted that,
advantageously, the pressure that from the inside acts upon the spacer,
due to the fluid that crosses the casings, is completely counterbalanced by
a pressure that acts from the outside on the spacer, due to the fluid that
crosses the cavities.
In the example of figure 7 a further variant embodiment of the heat
exchanger in accordance with the invention is represented.
In such a variant embodiment the heat exchanger comprises spacers
8, substantially shaped like a sleeve, each equipped with radial spokes
projecting towards the inside of the spacer, indicated with 90a, and radial
spokes projecting towards the outside of the spacer and indicated with
90b.
It can be seen that the aforementioned radial spokes 90b extending
towards the outside of the spacer 8 are in prolongation of the radial
spokes 90a extending towards the inside of the spacer.
It is important to note that, in accordance with a further variant
embodiment shown with reference to the example of figure 8, the holes 7
open on the half-shells 6 of the casings 2 are oblong.
Holes extending transversally are particularly advantageous in the
case of large widths of the exchanger, foreseen to withstand high flow
rates of the fluid circulating in the half-shells of the exchanger itself.
The man skilled in the art can bring numerous modifications to each
of the four variant embodiments of the heat exchanger described above in
order to satisfy contingent and specific requirements, all of these
modifications in any case being covered by the scope of protection of the
invention, as defined by the claims listed hereafter.