Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2568989 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | FLEXIBLE PROTECTIVE HELMET |
| (54) French Title: | CASQUE DE PROTECTION FLEXIBLE |
| Status: | Deemed expired |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | NORTON ROSE FULBRIGHT CANADA LLP/S.E.N.C.R.L., S.R.L. |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2012-08-28 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 2005-06-27 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 2006-01-19 |
| Examination requested: | 2008-09-03 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/CH2005/000355 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | WO2006/005201 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2006-12-01 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
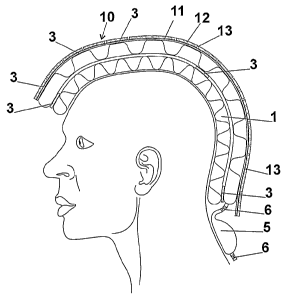
The invention relates to a protective helmet comprising an inner hood (1)
consisting of a spacer knitted fabric consisting of a monofilament yarn. Said
hood is covered by a pneumatic central layer (4) which can be pressurised by
means of compressed air and can be inflated by means of an air pump (5) which
can be, for example, removed and provided with valves (6). An outer layer (10)
consists of an inner textile layer (11) which lies over the pneumatic central
layer (4), and plates (12) which are fixed to the textile layer (11), for
example by adhesion. Said plates (12) consist, for example, of plastic,
composite materials, or natural materials. The plates (12) can be arranged in
such a way that joints (13) are created thereinbetween, the outer layer (10)
thus being provided with a certain elasticity in order to cater for different
head shapes and sizes.
L'invention concerne un casque de protection qui est composé d'une coiffe intérieure (1) constituée d'un tissu à maille à écartement en fil monofilament. Cette coiffe est recouverte d'une couche centrale pneumatique (4) qui peut être mise sous pression au moyen d'air comprimé et qui peut être gonflée à l'aide d'une pompe à air (5), par exemple amovible et équipée de soupapes (6). Une couche extérieure (10) est constituée d'une couche textile intérieure (11) posée sur la couche centrale pneumatique (4), ainsi que de plaques (12) qui sont fixées sur la couche textile (11), par exemple, par collage. Ces plaques (12) peuvent être en plastique, en matériaux composites ou en matériaux d'origine naturelle. Les plaques (12) peuvent être disposées de manière à ce que des fentes (13) soient ménagées entre elles, ce qui donne à la couche extérieure (10) une certaine élasticité permettant de prendre en compte différentes tailles et formes de tête.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Administrative Status , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Title | Date |
|---|---|
| Forecasted Issue Date | 2012-08-28 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date | 2005-06-27 |
| (87) PCT Publication Date | 2006-01-19 |
| (85) National Entry | 2006-12-01 |
| Examination Requested | 2008-09-03 |
| (45) Issued | 2012-08-28 |
| Deemed Expired | 2014-06-27 |
There is no abandonment history.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Amount Paid | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $400.00 | 2006-12-01 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 2 | 2007-06-27 | $100.00 | 2006-12-01 |
| Registration of a document - section 124 | $100.00 | 2007-04-16 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 3 | 2008-06-27 | $100.00 | 2008-05-22 |
| Request for Examination | $800.00 | 2008-09-03 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 4 | 2009-06-29 | $100.00 | 2009-06-10 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 5 | 2010-06-28 | $200.00 | 2010-06-10 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 6 | 2011-06-27 | $200.00 | 2011-06-09 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 7 | 2012-06-27 | $200.00 | 2012-05-22 |
| Final Fee | $300.00 | 2012-06-04 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| PROSPECTIVE CONCEPTS AG |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| LAUCHLI, EDITH |
| REINHARD, ANDREAS |
| SUTER, IRIS |