Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
1
Absorbent article comprising an elastic laminate
Technical field
The present invention refers to a pant type absorbent article such as a pant
diaper,
a sanitary pant or incontinence garment, said article having a core region
comprising
an absorbent core and a chassis region surrounding the core region, said
chassis region
comprising front, back and waist regions, while the core region is located at
least in a
crotch portion of the article, a liquid impermeable backsheet is arranged at
least in
the core region on the garment facing side of the absorbent core and a liquid
permeable topsheet is arranged at least in the core region on the wearer
facing
side of the absorbent core.
Background of the invention
Absorbent articles having defined core regions and chassis regions are
supposed to
have a comfortable fit about the wearer. For pant articles like pant diapers,
sanitary pants and incontinence pants it is also desirable that the articles
are
capable of being pulled up and down over the hips of the wearer to allow the
wearer or caregiver to easily put on and remove the article when it has been
soiled.
It is thus known to make such absorbent pants with elasticized stretchable
side
panels and waist portion, usually comprising elastic members, such as elastic
threads, contractably affixed between the backsheet and the topsheet.
It is further known to make portions of the chassis of absorbent articles of
an
elastic material, such as stretch-bonded laminates. Such laminates may include
a
layer of meltblown elastomeric fibers which have been stretched and sandwiched
between outer layers of spunbonded webs.
US 6,552,245 discloses an extensible outer cover for an absorbent article
which
provides a certain permanent deformation when subjected to a tensile force.
The
extensible outer cover comprises a necked laminate in the form of one film
sheet
laminated to a necked film. Both films may be non-elastic. The films may
further
be breathable.
WO 03/047488 discloses an elastic laminate comprising an elastic film which on
opposite sides is bonded to first and second non-elastic fibrous layers. The
laminate is made by bonding the non-elastic fibrous layers to the elastic film
layer
and after that stretch the composite material causing the non-elastic
materials to
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
2
break. The elastic film material may be of a breathable material. The laminate
may
be incorporated in an absorbent article.
Further examples of absorbent articles which in part are made of elastic
laminates
are found in US 6,476,289 and JP 10043235.
There is however still room for improvement with respect to comfort, fit and
cloth-
like feel of absorbent articles of the above mentioned type.
Object and most important features of the invention
The object of the present invention is to provide an absorbent article having
a core region
and a chassis region and which combines properties of comfort and fit to the
wearer's
body and a soft and cloth-like feeling close to textile materials. These and
further objects
have according to the invention been accomplished by the fact that said
article at least in
part of the chassis region comprises a outer coversheet in the form of an
elastic laminate
having a Softness (S) according to Kawabata of at least 20, wherein the
laminate is
composed of first and second layers of fibrous material and an elastic film
layer
located between said first and second fibrous layers.
Preferably the elastic laminate has a Softness (S) according to Kawabata of at
least 30
and more preferably at least 40.
According to one aspect of the invention the elastic laminate has a
Formability (F)
according to Kawabata of no more than 50, preferably no more than 30, more
preferably no more than 20 and most preferably no more than 10.
In one embodiment the elastic laminate has a Drapability (D) according to
Kawabata
of no more than 40.
In a further embodiment the elastic film layer is breathable.
In one aspect of the invention the elastic laminate has a Water Vapour
Transmission
Rate according to ASTM E96-00 Procedure D of at least 1500 g/m2 24h and
preferably
at least 3000 g/m2 24h.
According to a further embodiment a substantial part of the crotch portion of
the
article is free from said elastic laminate.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
3
According to one aspect of the invention said elastic laminate is arranged in
at least a
substantial part of the front region of the chassis, which in use is intended
to be
applied over the stomach of the wearer.
According to a further aspect of the invention the surface area of the
absorbent core
amounts to no more than 30%, preferably no more than 20% of the total surface
area
of the article as measured in a flat state as shown in Figure 2.
According to a further embodiment said elastic laminate has an elasticity in
the
transverse direction of the article of at least 30%, preferably at least 50%
and more
preferably at least 70%, when measured according to the elasticity test
specified in
the description.
For certain applications it is preferred that the waist region of the chassis
region is free
from said elastic laminate.
In one embodiment of the invention the elastic laminate constitutes both the
outer
and an inner coversheet of the article in at least a part of the chassis
region.
In a further aspect of the invention the article is a pull-up pant product
comprising
an elastic waist region, which is free from said elastic laminate, a crotch
portion
which is also free from said elastic laminate and wherein the elastic laminate
is
arranged in at least a substantial part of the front region of the chassis,
which in
use is intended to be applied over the stomach of the wearer.
According to one embodiment said elastic laminate comprises first and second
fibrous layers of spunbond material, each having a basis weight of between 10
and
g/mZ, preferably between 12 and 30 g/mz, more preferably between 15 and 25
g/m2, and a breathable elastic film layer having a basis weight between 20 and
100
30 g/mZ,preferably between 20 and 60 g/m2.
Description of drawings
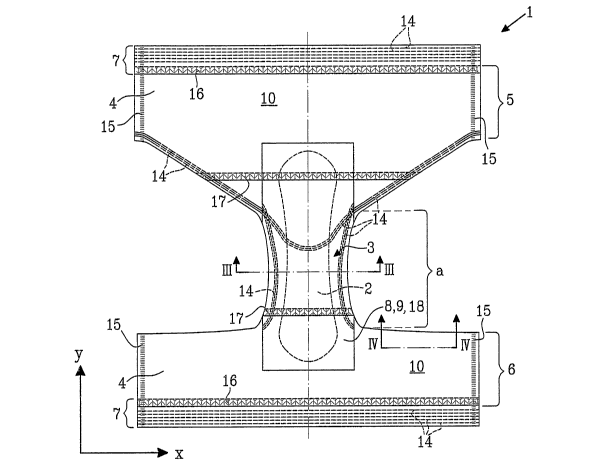
Fig. 1 shows a perspective view of a pant diaper.
Fig. 2 shows is a simplified plan view of the pant diaper in its flat,
uncontracted
35 state prior to formation.
Fig. 3 is a cross section according to the line III-III in Fig. 2.
Fig. 4 is a cross section through an elastic laminate according to the
invention.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
4
Description of preferred embodiments
The invention will in the following be closer described with reference to some
embodiments shown in the accompanying drawings.
Absorbent article
The term "absorbent article" refers to products that are placed against the
skin of the
wearer to absorb and contain body exudates, like urine, faeces and menstrual
fluid.
The invention mainly refers to disposable absorbent articles, which means
articles that
are not intended to be laundered or otherwise restored or reused as an
absorbent
article after use. According to the invention pant type absorbent articles are
referred to
having a core region and a chassis region surrounding the core region.
Examples of
such pant type absorbent articles are pant diapers, sanitary pants and
incontinence
pants.
The drawings show an embodiment of a pant diaper 1 for an infant or an
incontinent
adult. Said pant diaper typically comprises an absorbent core 2 located in a
core region
3 of the article, and a chassis region 4 surrounding the core region. The
chassis region
comprises front 5, back 6 and waist regions 7. The core region 3 is located in
the crotch
portion a of the article and extends a certain distance into the front 5 and
back regions
6. The crotch portion a is herewith defined as the narrow part of the article
intended to
be worn in the wearer's crotch between the legs. The article has a
longitudinal direction
y and a transverse direction x.
The article comprises a liquid permeable topsheet 8 and a liquid impermeable
backsheet
9 covering the core region 3. The absorbent core 2 is enclosed between the
topsheet
and the backsheet.
Topsheet
The liquid permeable topsheet 8 can consist of a nonwoven material, e g
spunbond,
meltblown, carded, hydroentangled, wetlaid etc. Suitable nonwoven materials
can be
composed of natural fibers, such as woodpulp or cotton fibres, manmade fibres,
such as
polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene, viscose etc. or from a mixture of
natural and
manmade fibres. The topsheet material may further be composed of tow fibres,
which
may be bonded to each other in a bonding pattern, as e.g. disclosed in EP-A-1
035 818.
Further examples of topsheet materials are porous foams, apertured plastic
films etc.
The materials suited as topsheet materials should be soft and non-irritating
to the skin
and intended to be penetrated by body fluid, e g urine or menstrual fluid. The
topsheet
may further be different in different parts of the absorbent article.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
Backsheet
The liquid impervious backsheet 9 covering the core region 3 on the garment
facing
side of the core, is of a liquid impervious material, such as a thin plastic
film, e.g. a
5 polyethylene or polypropylene film, a nonwoven material coated with a liquid
impervious material, a hydrophobic nonwoven material, which resists liquid
penetration
or laminates of plastic films and nonwoven materials. The core region
backsheet
material 9 may be breathable so as to allow vapour to escape from the
absorbent core,
while still preventing liquids from passing therethrough. Examples of
breathable
backsheet materials are porous polymeric films, nonwoven laminates from
spunbond
and meltblown layers, laminates from porous polymeric films and nonwovens. The
backsheet 9 is preferably inelastic.
Outer coversheet
The outer coversheet 10 covering the front and rear parts 5 and 6 of the
chassis region
4 comprises an elastic laminate 11. The laminate 11 is elastic at least in the
transverse
x-direction of the article. The elasticity in the x-direction should be at
least 30%,
preferably at least 50% and more preferably at least 70%, as measured by the
elasticity test specified below.
The elastic laminate 11 is composed of first and second outer layers of
fibrous
material 12a and 12b and a middle elastic film layer 13 located between said
fibrous layers. The outer fibrous layers 12a and 12 b are chosen to provide a
soft
and cloth-like feel to the laminate. Examples of suitable materials are carded
webs
and spunbond materials. The basis weight of the fibrous material layers should
be
between 10 and 35 g/mZ, preferably between 12 and 30 g/m2, more preferably
between 15 and 25 g/m2. Examples of suitable polymers used in the fibrous
materials are polyethylene, polypropylene and other polyolefin homopolymers
and
copolymers, polyester. Natural fibers, for example cotton, may also be used as
long
as they provide the required soft and cloth-like feel.
The middle layer 13 is according to one embodiment of the invention an
apertured
elastic film having a basis weight between 20 and 100 g/m2, preferably between
20
and 60 g/mZ. The film may be of any suitable elastic polymer, natural or
synthetic.
Some examples of suitable materials for the elastic film are low crystallinity
polyethylenes, metallocene catalyzed low crystallinity polyethylene, ethylene
vinyl
acetate copolymers (EVA), polyurethane, polyisoprene, butadiene-styrene
copolymers, styrene block copolymers, such as styrene/isoprene/styrene (SIS),
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
6
styrene/butadiene/styrene (SBS), or styrene/ethylene-butadiene/styrene block
copolymer. Blends of these polymers may also be used as well as other
modifying
elastomeric or non-elastomeric materials. One example of a suitable film is an
apertured three-layer elastomeric film of PE-SEBS-PE.
The laminate 11 may be manufactured according to a modified version of the
method disclosed in WO 03/047488, wherein one nonwoven layer 12a is applied to
the film 13 in a tacky state and will thus bond to the film layer, while the
other
nonwoven layer 12b is adhesively laminated to the film layer 13 using for
example
a pressure sensitive hot melt adhesive. The modification lies in that the
laminate is
incrementally stretched to a point below the elongation at peak load of at
least one
of the non-elastic nonwoven layers to remain some strength for at least one of
the
nonwoven layers. The other layer may also be stretched to a point below its
elongation at peak load, or to a point at which it will tear during
stretching.
The method disclosed in WO 03/047488 involves stretching of the laminate above
the
point of failure of the fibrous material, so that the non-elastic layers break
completely.
Therefore, as described in WO 03/047488, the elongation of the laminate is not
limited
by the stretch modulus of the non-elastic material.
In contrast to the method described in WO 03/047488, upon manufacture of a
laminate according to the present invention, at least one, preferably both
fibrous
layers which are bound to the elastic film are not completely torn. Selection
of
fibrous materials which have an elongation at maximum load greater than the
elongation at break of the elastic laminate allows the elastic film to stretch
during
use without being hindered by the fibrous layers.
The basis weights of the individual layers of the laminate referred to above
relate
to the basis weight in the laminate after stretching.
It is preferred that the elastic laminate 10 has a breathability (Water Vapour
Transmission Rate) according to ASTM E96-00 Procedure D of at least 1500,
preferably
at least 3000 g/m2 24h.
Absorbent core
The absorbent core 2 can be of any conventional kind. Examples of commonly
occurring
absorbent materials are cellulosic fluff pulp, tissue layers, highly absorbent
polymers
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
7
(so called superabsorbents), absorbent foam materials, absorbent nonwoven
materials
or the like. It is common to combine cellulosic fluff pulp with
superabsorbents in an
absorbent body. It is also common to have absorbent bodies comprising layers
of
different material with different properties with respect to liquid receiving
capacity,
liquid distribution capacity and storage capacity. The thin absorbent bodies,
which are
common in for example baby diapers and incontinence guards, often comprise a
compressed mixed or layered structure of cellulosic fluff pulp and
superabsorbent. The
size and absorbent capacity of the absorbent core may be varied to be suited
for
different uses such as for infants or for adult incontinent persons.
Pant diaper
The pant diaper disclosed in Fig. 1 is intended to enclose the lower part of
the wearer's
trunk like a pair of absorbent pants. It comprises a core region 3 located in
the crotch
portion a of the article and extending into the front and back regions of the
absorbent
pants. A chassis region 4 surrounds the core region 3. The core region 3 is
defined as
the surface area of the article which is occupied by the absorbent core 2 and
the areas
outside the core which are covered by the iiquid-impervious backsheet 9. The
chassis
region comprises front 5, back 6 and waist regions 7. The front 5 and back
regions 6
are joined to each other along their longitudinal edges by ultrasonic welds
15, glue
strings or the like.
According to one embodiment of the invention the surface area of the absorbent
core 2
amounts to no more than 30% of the total surface area of the article,
preferably no
more than 20% as measured during flat state of the article as shown in Fig. 2.
The elastic laminate 11 may cover the entire article, including the core
region 3
and the entire chassis region 4. However according to a preferred embodiment a
substantial part of the crotch portion of the article is free from the elastic
laminate
11. A "substantial part" used herein refers to at least 50%, preferably at
least
75%. Preferably also the waist region 7 of the chassis region is free from the
elastic
laminate 11. The waist region 7 comprises a nonwoven material that is
elasticized
by elastic members 14, such as elastic threads, contractably affixed between
material layers, such as nonwoven materials. Such elastic members 14 may also
be
arranged around the leg openings of the article. Ultrasonic welds 16, glue
strings or
the like, join the elastic laminate 11 to the elasticized nonwoven in the
waist region
7.
The liquid-impervious backsheet material 9 underlies the absorbent core 2 and
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
8
adjacent areas of the chassis region immediately outside the absorbent core 2.
The
area covered by the liquid-impervious backsheet 9 is defined as the core
region 3.
A nonwoven material 18 is arranged on the garment facing side of the liquid-
impervious backsheet 9 in the crotch portion of the article. The nonwoven
material
18 is joined to the elastic laminate 11 by means of ultrasonic welds 17, glue
strings
or the like. The elastic laminate 11 and the liquid impervious backsheet
overlap in
the outer parts of the core region 3, as seen in Fig. 2, wherein the elastic
laminate
11 is arranged on the garment facing side of the liquid impervious backsheet
9.
The elastic laminate 11 is preferably arranged as an outside coversheet
material
over a substantial part of the chassis region, except for the waist region 7.
It is
preferred that the elastic laminate is arranged at least over a substantial
part of
the front region 5 of the chassis region 4, which during use is intended to be
applied against the stomach of the wearer. A substantial part" used herein
means
at least 50% of the surface area, preferably at least 75% and most preferably
at
least 90% of the surface area of the front region 5 of the chassis. The
elastic
laminate 11 preferably also constitutes an inner coversheet of the article in
said
portions of the chassis region. Thus no additional topsheet material is
required in
these parts of the article.
No additional elasticized side panels joining the front and back regions 5 and
6 are
needed when using the elastic laminate 11 according to the invention. However,
if
desired, additional elasticized side panels may of course be provided,
especially in
cases where the elastic laminate 11 is arranged only in parts of the front
and/or
back regions.
The elastic laminate should have a Softness (S) according to Kawabata of at
least 20,
preferably at least 30 and most preferably at least 40.
It is further desired that it has a Formability (F) according to Kawabata of
no more
than 50, preferably no more than 30, more preferably no more than 20 and most
preferably no more than 10.
It is also desired that the elastic laminate has a Drapability (D) shape to
Kawabata of no
more than 40.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
9
Description of test methods
Elasticity test
The method measures how an elastic material behaves at repeated load and
unload cycles.
The sample is stretched to a predetermined elongation and a cyclic movement
between 0
and said predetermined elongation is performed. Desired load and unload forces
are
recorded. The permanent, i.e. remaining, elongation of the relaxed material is
measured.
A tensile tester, Lloyd LRX, able to perform cyclic movements and equipped
with a
printer/plotter or software presentation is used. The sample is prepared by
cutting it to a
width of 25 mm and a length that is preferably 20 mm longer than the distance
between
the clamps in the tensile tester.
The tensile tester is calibrated according to the apparatus instructions. The
parameters
needed for the test (load and unload forces) are adjusted to:
= Crosshead speed: 500 mm/min
= Clamp distance: 50 mm
= Preload: 0.05 N
The sample is placed in the clamps according to the marks and it is made sure
that the
sample is centered and fastened perpendicularly in the clamps. The tensile
tester is started
and three cycles between 0 and the predetermined elongation, equal to the
highest defined
15t load, are performed. Before the last cycle the sample is relaxed for 1
minute, then the
permanent elongation is measured by stretching the sample until a force of 0.1
N is
detected and the elongation is read.
The permanent elongation after relaxation should be less than 10% and is
measured by the
method above. Thus an elasticity of 30% is defined as that the laminate should
have a
permanent relaxation after elongation of less than 10% after being exerted to
an
elongation of 30% in the tensile tester above. An elongation of 30% means an
elongation
to a length that is 30% longer than the initial length of the sample.
Kawabata test
The Kawabata KES-FB test is a Japanese quality judgment system for used for
textile
materials and is disclosed in "The Standardization and Analysis of Hand
Evaluation (2nd
Edition), Sueo Kawabata, July 1980, The Hand Evaluation and Standardization
Committee, The Textile Machinery Society of Japan". The test used in this
invention
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
uses two of the Kawabata testing machines, KES-FB2 for measuring Bending
rigidity, B
(gf=cm2/cm), and KES-FB1 for measuring Shear stiffness, G(gf/cm=degree) and
Tensile
strain, EMT (%).
5 Bending rigidity (8) KES-F82
The slope was measured between 0.5 cm-1 and 1.5 cm-1 and -0,5 cm-1 and -1,5
cm"1.
The measurements were performed in both directions (machine direction, MD, and
cross direction, CD) with the following settings:
Total sample area: 20 x 20 cm;
10 Maximum curvature: Kmax= 2,5 cm-1;
Bending rate: 0.5 cm"1/sec;
Sample effective dimension: 20 cm length and 1 cm width;
Bending deformation is applied to the width direction.
Shear stiffness (G) KES-FBY
The slope was measured between 0.5 cm"1 and 2.5 cm-1 and -0,5 cm-1 and -2,5
cm"1.
The measurements were performed in both directions (MD and CD) with the
following
settings:
Total sample area: 20 x 20 cm;
Tension of specimen: W= W=10gf/cm;
Maximum shear angle: cp= 8 .
Sample effective dimension: 20 cm width and 5 cm length;
Shear deformation is applied to the width direction.
Tensile strain (EMT)
The measurements were performed in both directions (MD and CD) with the
following
settings:
Total sample area: 20 x 20 cm;
Maximum load: Fm= 500 gf/cm;
Tensile speed: 0.2 mm/sec.
Sample effective dimen'sion: 20 cm width and 2.5 cm length;
Tensile deformation is applied to the length direction.
Elongation sens 50 mm/1OV.
Softness (S)
The Softness (S) according to Kawabata is obtained from the formula:
S= EMTIB
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
11
Formability (F)
The Formability (F) according to Kawabata is obtained from the formula:
F=B=EMT.
Drapability (D)
The Drapability (D) according to Kawabata is obtained from the formula:
D=116+25= log(B.G/W), wherein W is the basis weight of the sample.
Example
Four different samples were measured in a Kawabata test with respect to
Bending
rigidity (B), Shear stiffness (G) and Tensile strain (EMT). From these
measured values
the Softness (S), Formability (F) and Drapability (D) were calculated.
The four samples were:
Sample laminate (SL): an elastomeric laminate according to the invention
comprising
an inner apertured three-layer elastomeric film of PE-SEBS-PE, basis weight 36
g/mZ and two outer layers of spunbond material, PP (polypropylene), each
having a
basis weight of 22 g/m2. The laminate is produced by a modified version of the
method
disclosed in WO 03/04788, wherein one spunbond layer is applied to the film in
a
tacky state and will thus bond to the film layer, while the other spunbond
layer is
adhesively laminated to the film layer using for example a pressure sensitive
hot
melt adhesive (glue amount 3 g/m2). The laminate is incrementally stretched,
at
which the non-elastic spunbond layers are stretched to a point below the
elongation at peak load to retain some strength in the spunbond layers.
The above mentioned basis weights of the layers refers to the finished
laminate
after stretching. Before stretching the basis weight of the individual layers
were:
inner film layer 40 g/mZ, outer spunbond layers 25 g/mZ each and glue layer 3
g/m2. Since it is difficult to measure the basis weights of the individual
layers after
lamination and stretching an approximation has been made from the basis
weights
of the layers before lamination and stretching. The laminate before stretching
had
a total basis weight before stretching of 93 g/mZ and after stretching it had
a basis
weight of 85 g/m2, which means a deformation of about 10%. It is then assumed
that the deformation of the individual fibrous layers and the film layer is
the same,
i.e. about 10%.
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
12
Ref. 1: Cotton-knitted goods, so called jersey with elastomeric threads.
Ref. 2: Outer coversheet of Tena Discreet incontinence pant, odour control,
size
medium, produced by SCA Hygiene Products AB,. The outer coversheet comprises
two layers of nonwoven with parallel elastic threads there between, which
wrinkle
the material.
Ref. 3: Outer coversheet material of Poise normal super incontinence pant
produced by Kimberly-Clark. The outer coversheet comprises two layers of
nonwoven with parallel elastic threads there between which wrinkle the
material.
A climate conditioning of the materials were performed in 20-C and 65% RH for
48
hours. For the pant products the absorbent core was removed and the outer
coversheet was stretched over a knitwear measuring device for 24 hours and was
then allowed to relax in the same climate during 24 hours.
The sizes of the samples were 10 x 10 cm.
All tests were made on three samples and in two material directions (machine
direction, MD, and cross direction, CD).
The following results were obtained.
Table 1
Sample B, Bending rigidity G, Shear stiffness EMT, Tensile strain (%)
(gf=cmZ/cm) (gf/cm=degree)
MD CD Mean MD CD Mean MD CD Mean
SL 0.095 0.022 0.059 1.46 1.38 1.42 208.4 92.0 150.2
Ref. 1 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.58 0.64 0.61 160.6 173.2 166.9
Ref. 2 1.05 0.09 0.57 0.87 0.68 0.77 23.9 211.7 117.8
Ref. 3 1.53 0.04 0.78 1.74 1.21 1.47 26.28 195.3 110.8
CA 02569109 2006-11-29
WO 2005/122984 PCT/SE2004/001004
13
From these results the Softness (S), the Drapability (D) and the Formability
(F)
according to Kawabata were calculated according to the formulas stated above.
These
results are stated in Table 2 below.
Table 2
Sample Softness (S) Drapability (D) Formability (F) Basis Weight (W)
EMT /B 116+25 log(B.G/W) B=EMT g/m2
SL 50 40 9 88
Ref. 1 75 13 5 231
Ref. 2 14 45 67 160
Ref. 3 12 51 87 133
The results should be interpreted in the following way:
Softness (S): a higher value indicates a softer material.
Drapability (D): a higher value indicates a stiffer material.
Formability (F): a higher value indicates that the material is less formable.
The test laminate according to the invention has a Softness (S) and a
Formability (F)
according to Kawabata which is close to cotton-knitted goods (Ref. 1). Also
the
Drapability (D) according to Kawabata is closer to the cotton-knitted
reference material
than other two tested materials, used as outer coversheets on conventional
incontinence pants. Thus the use of the elastomeric laminate as outer
coversheet
material in at least a part of the chassis region of the absorbent pant
provides a pant
article having a cloth-like feeling close to a cotton material. The pant will
also have an
excellent comfort and fit to the wearer's body. By using the elastomeric
laminate only
in those part of the pant in which the properties of the material is best
utilized, a very
economic utilization of the material is accomplished.