Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02574762 2010-07-30
FAN BLADES AND MODIFICATIONS
Richard Michael Aynsley
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[00021 The present invention relates generally to fan blades and fan blade
modifications, and is particularly directed to an airfoil suitable for use
with a fan blade and a winglet suitable for use with a fan blade.
[00031 People who work in large structures such as warehouses and
manufacturing plants may be exposed to working conditions that range
from being uncomfortable to hazardous. The same may also apply in
agricultural settings, such as in a structure that is full of livestock. On
a hot day, the inside air temperature may reach a point where a person
or other animal is unable to maintain a healthy or otherwise desirable
body temperature. In areas where temperatures are uncomfortably or
unsafely high, it may be desirable to have a device operable to create
or enhance airflow within the area. Such airflow may, in part,
facilitate a reduction in temperature in the area.
100041 Moreover, some activities that occur in these environments, such as
welding or operating internal combustion engines, may create airborne
contaminants that can be deleterious to those exposed. The effects of
airborne contaminants may be magnified if the air flow in the area is
less than ideal. In these and similar situations, it may be desirable to
have a device operable to create or enhance airflow within the area.
Such airflow may, in part, facilitate the reduction of deleterious effects
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-2-
of contaminants, such as through dilution and/or removal of
contaminants.
[0005] In certain structures and environments, a problem may arise with heat
gathering and remaining near the ceiling of the structure. This may be
of concern where the area near the floor of the structure is relatively
cooler. Those of ordinary skill in the art will immediately recognize
disadvantages that may arise from having this or other imbalanced
air/temperature distribution. In these and similar situations, it may be
desirable to have a device operable to create or enhance airflow within
the area. Such airflow may, in part, facilitate de-stratification and the
inducement of a more ideal air/temperature distribution.
[0006] It may also be desirable to have a fan capable of reducing energy
consumption. Such a reduction of energy consumption may be
effected by having a fan that runs efficiently (e.g., less power is
required to drive the fan as compared to other fans). A reduction of
energy consumption may also be effected by having a fan that
improves air distribution, thereby reducing heating or cooling costs
associated with other devices.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0007] The accompanying drawings incorporated in and forming a part of the
specification illustrate several aspects of the present invention, and
together with the description serve to explain the principles of the
invention; it being understood, however, that this invention is not
limited to the precise arrangements shown. In the drawings, like
reference numerals refer to like elements in the several views. In the
drawings:
[0008] Fig. 1 is a plan view of a hub for mounting fan blades.
[0009] Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of an exemplary fan blade airfoil.
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-3-
[0010] Fig. 3 is a cross-sectional view of an alternative exemplary fan blade
airfoil
[0011] Fig. 4 depicts a graph showing two ellipses.
[0012] Fig. 5 depicts a portion of the graph of Fig. 4.
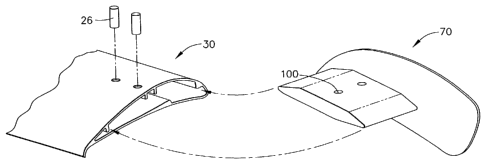
[0013] Fig. 6 is side view of an exemplary winglet fan blade modification
[0014] Fig. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the winglet of Fig. 6.
[0015] Fig. 8 is a top view of the winglet of Fig. 6.
[0016] Fig. 9 is an end view of the fan blade of Fig. 2 modified with the
winglet of Fig. 6.
[0017] Fig. 10 is an exploded perspective view of the winglet-blade assembly
of Fig. 9.
[0018] Reference will now be made in detail to the present preferred
embodiment of the invention, an example of which is illustrated in the
accompanying drawings.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF AN EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION
[0019] Referring now to the drawings in detail, wherein like numerals indicate
the same elements throughout the views, Fig. 1 shows exemplary fan hub
10, which may be used to provide a fan having fan blades 30 or 50. In
the present example, fan hub 10 includes a plurality of hub mounting
members 12 to which fan blades 30 or 50 may be mounted. In one
embodiment, fan hub 10 is coupled to a driving mechanism for rotating
fan hub 10 at selectable or predetermined speeds. A suitable hub
assembly may thus comprise hub 10 and a driving mechanism coupled to
hub 10. Of course, a hub assembly may include a variety of other
elements, including a different hub, and fan hub 10 may be driven by any
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-4-
suitable means. In addition, fan hub 10 may have any suitable number of
hub mounting members 12.
[0020] As shown in Figs. 1 through 3, each hub mounting member 12 has top
surface 14 and bottom surface 16, which terminate into leading edge 18
and trailing edge 20. In addition, each hub mounting member 12
includes opening 22 formed through top surface 14 and going through
bottom surface 16. In the present example, opening 22 is sized to receive
fastener 26. Each hub mounting member 12 is configured to receive fan
blade 30 or 50. Those of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that hub
mounting members 12 may be provided in a variety of alternative
configurations.
[0021] In one embodiment, fan blades 30 or 50 are mounted to the hub assembly
disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 6,244,821. Of course, fan blades 30 or 50
may be mounted to any other hub and/or hub assembly. A suitable hub
assembly may be operable to rotate hub 10 at any suitable angular speed.
By way of example only, such angular speed may be anywhere in the
range of approximately 7 and 108 revolutions per minute.
[0022] Fig. 2 shows a cross section of exemplary fan blade 30 having curled
trailing edge 38, mounted to hub 10. The cross section is taken along a
transverse plane located at the center of fan blade 30, looking toward hub
10. Fan blade 30 has top surface 32 and bottom surface 34, each of
which terminate into leading edge 36 and trailing edge 38. As shown,
trailing edge 38 has a slope of approximately 45 relative to portion of
top surface 32 that is proximate to trailing edge 38 and portion of bottom
surface 34 that is proximate to trailing edge 38. Of course, trailing edge
38 may have any other suitable slope, such as 0 by way of example
only, to the extent that it comprises a single, flat surface. Other suitable
trailing edge 38 configurations will be apparent to those of ordinary skill
in the art.
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-5-
[0023] In the present example, fan blade 30 is substantially hollow. A
plurality
of ribs or bosses 40 are located inside fan blade 30. As shown, when hub
mounting member 12 is inserted into fan blade 30, ribs or bosses 40 are
positioned such that they contact top surface 14, bottom surface 16,
leading edge 18, and trailing edge 20 of hub mounting member 12.
Bosses 40 thus provide a snug fit between fan blade 30 and hub
mounting member 12. Alternative configurations for fan blade 30,
including but not limited to those affecting the relationship between fan
blade (30) and hub mounting member (12), will be apparent to those of
ordinary skill in the art.
[0024] As used herein, terms such as "chord," "chord length," "maximum
thickness," "maximum camber," "angle of attack," and the like, shall
be ascribed the same meaning ascribed to those terms as used in the art
of airplane wing or other airfoil design. In one embodiment, fan blade
(30) has a chord length of approximately 6.44 inches. Fan blade (30)
has a maximum thickness of approximately 16.2% of the chord; and a
maximum camber of approximately 12.7% of the chord. The radius of
leading edge (36) is approximately 3.9% of the chord. The radius of
trailing edge (38) quadrant of bottom surface (34) is approximately
6.8% the chord. In an alternate embodiment, fan blade (30) has a
chord of approximately 7 inches. In another embodiment, fan blade
(30) has a chord of approximately 6.6875 inches. Of course, any other
suitable dimensions and/or proportions may be used.
[0025] By way of example only, fan blade (30) may display lift to drag ratios
ranging from approximately 39.8, under conditions where the
Reynolds Number is approximately 120,000, to approximately 93.3,
where the Reynolds Number is approximately 250,000. Of course,
other lift to drag ratios may be obtained with fan blade (30).
[0026] In one embodiment, fan blade (30) displays drag coefficients ranging
from approximately 0.027, under conditions where the Reynolds
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-6-
Number is approximately 75,000, to approximately 0.127, where the
Reynolds Number is approximately 112,500. Of course, other drag
coefficients may be obtained with fan blade (30).
[0027] In one example, under conditions where the Reynolds Number is
approximately 200,000, fan blade (30) moves air such that there is a
velocity ratio of approximately 1.6 at bottom surface (34) at trailing edge
(38) of fan blade (30). Other velocity ratios may be obtained with fan
blade (30).
[0028] In one embodiment, fan blade (30) provides non-stall aerodynamics for
angles of attack between approximately -1 to 7 , under conditions where
the Reynolds Number is approximately 112,000; and angles of attack
between approximately -2 to 10 , where the Reynolds number is
approximately 250,000. Of course, these values are merely exemplary.
[0029] Fig. 3 shows a cross section of another exemplary fan blade (50) having
generally elliptical top surface (52) and bottom surface (54), each of
which terminate in leading edge (56) and trailing edge (58), mounted to
hub (10). The cross section is taken along a transverse plane located at
the center of fan blade (50), looking toward hub (10). In the present
example, fan blade (50) is hollow. A plurality of bosses (60) are located
inside fan blade (50). As shown, when hub mounting member (12) is
inserted into fan blade (50), bosses (60) are positioned such that they
contact top surface (14), bottom surface (16), leading edge (18), and
trailing edge (20) of hub mounting member (12). Bosses (60) thus
provide a snug fit between fan blade (50) and hub mounting member
(12). Alternative configurations for fan blade (50), including but not
limited to those affecting the relationship between fan blade (50) and hub
mounting member (12), will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the
art.
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-7-
[0030] As shown, fan blade (50) has a lower radius of curvature toward its
leading edge (56), as compared to a higher radius of curvature toward
its trailing edge (58). The curvatures of fan blade (50) may be
obtained, at least in part, through the generation of two ellipses using
the following formulae. Those of ordinary skill in the art will
appreciate that a first ellipse, with its origin at the intersection of
Cartesian x and y axes, may be generated by these equations:
[0031] [1] x = a(COS(t)), and
[0032] [2] y = b(SIN(t)),
[0033] where
[0034] a = length of primary radius,
[0035] b = length of secondary radius, and
[0036] t = angle of rotation of a radius about the origin (e.g., in radians).
[0037] Accordingly, a first ellipse may be generated using the foregoing
equations. Similarly, a set of coordinates for the first ellipse may be
obtained using equations [1] and [2]. Exemplary first ellipse (200) is
illustrated in the graph depicted in Fig. 4, where a = 3 and b = 2.
[0038] Coordinates for a second ellipse may be obtained using these
equations:
[0039] [3] x2 = x(COS(O)) - y(SIN(O)), and
[0040] [4] y2 = y(COS(O)) - x(SIN(O)),
[0041] where
[0042] x2 = the second "x" coordinate after a counterclockwise rotation of the
first ellipse through 0 radians about the origin, and
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-8-
[0043] yz = the second "y" coordinate after a counterclockwise rotation of the
first ellipse through 0 radians about the origin.
[0044] Thus, the dimensions of the second ellipse are dependent on the
dimensions of the first ellipse. Exemplary second ellipse (300) is
illustrated in the graph depicted in Fig. 4, where 0 = 0.525 radians. It
will be appreciated that, where a first and second ellipse are plotted in
accordance with equations [1] through [4], the two ellipses may
intersect at four points ("ellipse intersections"). Fig. 4 shows four
ellipse intersections (400) between first ellipse (200) and second
ellipse (300).
[0045] The curvature of top surface (52) and bottom surface (54) may be
based, at least in part, on the curvature of the first and second ellipses
between two consecutive ellipse intersections. An example of such a
segment of first ellipse (200) and second ellipse (300) is shown in Fig.
5, which depicts the portion of ellipses (200 and 300) between
consecutive ellipse intersections (400). Accordingly, equations [1]
through [4] may be used to generate surface coordinates for at least a
portion of top surface (52) and bottom surface (54) of fan blade (50).
[0046] It will be appreciated that the chord length-to-thickness ratio of fan
blade (50) may vary with the amount of rotation, 0, relative the two
ellipses.
[0047] Of course, portions of fan blade (50) may deviate from the curvature of
the first and second ellipses. By way of example only, and as shown in
Fig. 3, leading edge (56) may be modified to have a generally circular
curvature. Other deviations will be apparent to those of ordinary skill
in the art.
[0048] In one embodiment, fan blade (50) is created using equations [1]
through [4] with a = 3 units, b = 2 units, and 0 = 0.525 radians. In this
embodiment, fan blade (50) is fit with circular leading edge (56)
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-9-
having a diameter of 3.5% of chord length. This leading (56) edge
curvature is fit tangentially to that of top surface (52) and bottom
surface (54). Such a fit may be envisioned by comparing Figs. 3 and 5.
Of course, other dimensions may be used.
[0049] In one embodiment, fan blade (50) has a chord length of approximately
7.67 inches. In another embodiment, fan blade has a chord length of
approximately 7.687 inches. Of course, fan blade (50) may have any
other suitable chord length.
[0050] In the present example, the radius of leading edge (56) is
approximately 3.5% of the chord. The maximum thickness of fan
blade (50) is approximately 14.2% of the chord. The maximum
camber of fan blade (50) is approximately 15.6% of the chord. Of
course, any other suitable dimensions and/or proportions may be used.
[0051] In one example, a fan having a 24-foot diameter and comprising ten
fan blades (50) mounted at an angle of attack of 10 produces a thrust
force of approximately 5.2 lb. when rotating at approximately 7
revolutions per minute (rpm), displacing approximately 87,302 cubic
feet per minute (cfm). When rotating at approximately 14 rpm, the fan
produces a thrust force of approximately 10.52 lb., displacing
approximately 124,174 cfm. When rotating at approximately 42 rpm,
the fan produces a thrust force of approximately 71.01 lb., displacing
approximately 322,613 cfm. Other thrust forces and/or displacement
volumes may be obtained with a fan having fan blades (50).
[0052] By way of example only, fan blade (50) having an angle of attack of
approximately 10 may display lift to drag ratios ranging from
approximately 39, under conditions where the Reynolds Number is
approximately 120,000, to approximately 60, where the Reynolds
Number is approximately 250,000. Other lift to drag ratios may be
obtained with fan blade (50).
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-10-
[0053] In one embodiment, fan blade (50) provides non-stall aerodynamics for
angles of attack between approximately 1 to 11 , under conditions
where the Reynolds Number is approximately 112,000; for angles of
attack between approximately 0 and 13 , where the Reynolds number is
approximately 200,000; and for angles of attack between approximately
1 to 13 , where the Reynolds number is approximately 250,000. Of
course, these values are merely exemplary.
[0054] In one example, a fan having a 14-foot diameter and comprising ten fan
blades (50) is rotated at approximately 25 rpm. The fan runs at
approximately 54 watts, with a torque of approximately 78.80 inch-
pounds (in.lbs.) and a flow rate of approximately 34,169 cfin. The fan
thus has an efficiency of approximately 632.76 cfm/Watt.
[0055] In another example, a fan having a 14-foot diameter and comprising ten
fan blades (50) is rotated at approximately 37.5 rpm. The fan runs at
approximately 82 watts, with a torque of approximately 187.53 inch-
pounds (in.lbs.) and a flow rate of approximately 62,421 cfm. The fan
thus has an efficiency of approximately 761.23 cfinlWatt.
[0056] In yet another example, a fan having a 14-foot diameter and comprising
ten fan blades (50) is rotated at approximately 50 rpm. The fan runs at
approximately 263 watts, with a torque of approximately 376.59 inch-
pounds (in.lbs.) and a flow rate of approximately 96,816 cfin. The fan
thus has an efficiency of approximately 368.12 cfmlWatt.
[0057] The following may be applied to any fan blade, including by way of
example only, fan blade (30) or fan blade (50):
[0058] In one embodiment, each fan blade (30 or 50) comprises a
homogenous continuum of material. By way of example only, fan
blades (30 and 50) may be constructed of extruded aluminum.
However, it will be appreciated that fan blades (30 and/or 50) may be
constructed of any other suitable material or materials, including but
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-11-
not limited to any metal and/or plastic. In addition, it will be
appreciated that fan blades (30 and/or 50) may be made by any suitable
method of manufacture, including but not limited to stamping,
bending, welding, and/or molding. Other suitable materials and
methods of manufacture will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in
the art.
[0059] When fan blade (30 or 50) is mounted to hub (10), hub mounting
members (12) may extend into fan blade (30 or 50) approximately 6
inches, by way of example only. Alternatively, hub mounting
members (12) may extend into fan blade (30 or 50) to any suitable
length. It will also be appreciated that hub (10) may have mounting.
members (12) that fit on the outside of fan blades (30 or 50), rather
than inside. Alternatively, mounting members (12) may fit both
partially inside and partially outside fan blades (30 or 50).
[0060] Fan blade (30 or 50) may also include one or more openings configured
to align with openings (22) in hub mounting member (12). In this
embodiment, when openings in fan blade (30 or 50) are aligned with
openings (22) in hub mounting member (12), fastener (26) may be
inserted through the openings to secure fan blade (30 or 50) to hub
mounting member (12). In one embodiment, fastener (26) is a bolt.
Other suitable alternatives for fastener(s) (26) will be apparent to those of
ordinary skill in the art, including but not limited to adhesives.
Accordingly, it will be understood that openings (22) are optional.
[0061] Fan blade (30 or 50) may be approximately 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13,
or 14 feet long. Alternatively, fan blade (30 or 50) may be of any other
suitable length. In one embodiment, fan blade (30 or 50) and hub (10)
are sized such that a fan comprising fan blades (30 or 50) and hub (10)
has a diameter of approximately 24 feet. In another embodiment, fan
blade (30 or 50) and hub (10) are sized such that a fan comprising fan
blades (30 or 50) and hub (10) has a diameter of approximately 14 feet.
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-12-
Other suitable dimensions will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in
the art.
[0062] It will be appreciated that all cross sections along the length of fan
blade
(30 or 50) need not be identical. In other words, the configuration of fan
blade (30 or 50) need not be uniform along the entire length of fan blade
(30 or 50). By way of example only, a portion of the "hub mounting
end" of fan blade (30 or 50) (i.e. the end of fan blade (30 or 50) that will
be mounted to hub (10)) may be removed. In one example, an oblique
cut is made to leading edge (56) of fan blade (50) to accommodate
another blade (50) on hub (10).
[0063] Alternatively, fan blade (30 or 50) may be formed or constructed such
that a portion of the hub mounting end or another portion is omitted,
relieved, or otherwise "missing." It will be appreciated that the absence
of such a portion (regardless of whether it was removed or never there to
begin with) may alleviate problems associated with blades (30 or 50)
interfering with each other at hub (10). Such interference may be caused
by a variety of factors, including but not limited to chord length of fan
blades (30 or 50). Of course, factors other than interference may
influence the removal or other absence of a portion of fan blade (30 or
50). The absent portion may comprise a portion of leading edge (36 or
56), a portion of trailing edge (38 or 58), or both.
[0064] Alternatively, to address fan blade (30 or 50) interference at hub
(10), the
diameter of hub may be increased (e.g., such as without increasing the
number of hub mounting members (12)). Altern atively, the chord of fan
blades (30 or 50) may be reduced. Still other alternatives and variations
of hub (10) and/or fan blades (30 or 50) will be apparent to those of
ordinary skill in the art.
[0065] Those of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that fan blade (30
or 50)
may have a zero or non-zero angle of attack. By way of example only,
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
- 13-
when mounted to hub mounting member (12), fan blade (30 or 50) may
have an angle of attack in the range of approximately -1 to 7 , inclusive;
between -2 and 10 , inclusive; or approximately 7 , 8 , 10 , or 13 by
way of example only. Of course, fan blade (30 or 50) may have any
other suitable angle of attack. Fan blade (30 or 50) may be substantially
straight along its length, and the angle of attack may be provided by
having hub mounting member (12) with the desired angle of attack.
[0066] Alternatively, the angle of attack of hub mounting member (12) may be
zero, and an angle of attack for fan blade (30 or 50) may be provided by a
twist in fan blade (30 or 50). In other words, fan blade (30 or 50) may be
substantially straight along the length to which hub mounting member
(12) extends in fan blade (30 or 50), and a twist may be provided to
provide an angle of attack for the remaining portion of fan blade (30 or
50). Such a twist may occur over any suitable length of fan blade (30 or
50) (e.g. the entire remainder of fan blade (30 or 50) length has a twist; or
the twist is brief, such that nearly all of the remainder of fan blade (30 or
50) is substantially straight; etc.). Still other suitable configurations and
methods for providing an angle of attack for all or part of fan blade (30)
will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art. In addition, it will
be
appreciated that all or any portion of fan blade (30 or 50) may have one
or more twists for any purpose.
[0067] Those of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that a fan blade
(e.g.,
30 or 50) may be modified in a number of ways. Such modifications
may alter the characteristics of fan performance. As illustrated in
exemplary form in Figs. 6 through 10, one such modification may
include winglet (70). While winglets (70) will be discussed in the
context of fan blades (30 and 50), it will be appreciated that winglets
(70) may be used with any other suitable fan blades.
[0068] Winglet (70) of the present example includes vertical member (72).
Vertical member (72) comprises flat inner surface (74) and rounded
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-14-
outer surface (76). Other suitable configurations for inner surface (74)
and outer surface (76) will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the
art. In the present example, the perimeter of vertical member (72) is
defined by lower edge (78), upper edge (80), and rear edge (82). Each
edge (78, 80, and 82) meets generally at respective corner (84). Thus,
in the present example, vertical member (72) has three corners (84).
As shown, each corner (84) is rounded. Accordingly, the term
"corner," as that term is used herein, shall not be read to require a
sharp angle. In other words, a corner need not be limited to a point or
region at which a pair of straight lines meet or intersect. While in the
present example vertical member (72) is described as having three
corners, it will be appreciated that vertical member (72) may have any
suitable number of corners (84).
[0069] Other variations of vertical member (72) will be apparent to those of
ordinary skill in the art.
[0070] Winglet (70) of the present example further includes winglet mounting
member (90), which extends substantially perpendicularly from inner
surface (74) of vertical member (72). As shown, winglet mounting
member (90) is configured similar to hub mounting member (12).
Winglet mounting member (90) has top surface (92) and bottom surface
(94), which each terminate into leading edge (96) and trailing edge (98).
In addition, each winglet mounting member (92) includes openings (100)
formed through top surface (92) and bottom surface (94). In the present
example, each opening (100) is sized to receive fastener (26). Winglet
mounting member (90) is configured to be inserted into an end of fan
blade (30 or 50). Those of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that
winglet mounting members (90) may be provided in a variety of
alternative configurations.
[0071] Fig. 9 shows a cross section of fan blade (30) with winglet (70)
mounted
thereto. The cross section is taken along a transverse plane located at the
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
- 15-
center of fan blade (30), looking toward winglet (70) (i.e. away from hub
(10)). In the present example, and as shown in Figs. 9 and 10, winglet
mounting member (90) is configured to fit in the end of fan blade (30 or
50). Like hub mounting member (12), winglet mounting member (90)
fits snugly against bosses (40 or 60) in fan blade (30 or 50). In the
present example, upper edge (80) of winglet (70) extends above top
surface (32 or 52) of fan blade (30 or 50), in addition to extending
beyond leading edge (36 or 56). Similarly, lower edge (78) of winglet
(70) extends below bottom surface (34 or 54) of fan blade (30 or 50).
Rear edge (82) of winglet (70) extends beyond trailing edge (38 or 58) of
fan blade (30 or 50). Of course, winglets (70) and fan blades (30 or 50)
may have any other relative sizing and/or configuration.
[00721 Fan blade (30 or 50) may have one or more openings, formed near the tip
of fan blade (30 or 50) through top surface (32 or 52) and/or bottom
surface (34 or 54), which is/are positioned to align with opening(s) (100)
in winglet mounting member (90) when winglet mounting member (90)
is inserted into fan blade (30 or 50), and which is/are sized to receive
fastener (26). Winglets (70) may thus be secured to fan blades (30 or 50)
with one or more fasteners (26). In one embodiment, fastener (26) is a
bolt. In another embodiment, fastener (26) comprises a complimentary
pair of thin head interlocking binding screws, such as screw posts
occasionally used to bind a large volume of papers together (e.g., "male"
screw with threaded outer surface configured to mate with "female"
screw having threaded inner surface). However, any other suitable
fastener(s) may be used, including but not limited to adhesives.
Accordingly, it will be appreciated that openings (100) are optional.
[00731 It will also be appreciated that winglet mounting member (90) need not
be inserted into an end of fan blade (30 or 50). In other words, and
similar to hub mounting members (12), winglet mounting member (90)
may be made to fit on the outside of fan blades (30 or 50), rather than
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-16-
inside. Alternatively, winglet mounting members (90) may fit both
partially inside and partially outside fan blades (30 or 50). Still other
configurations will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art.
[00741 In an alternate embodiment, winglet (70) lacks mounting member (90),
and instead has a recess formed in inner surface (74) of vertical
member (72). In this embodiment, the tip of fan blade (30 or 50) is
inserted into winglet (70) for attachment of winglet (70) to fan blade
(30 or 50). In yet another embodiment, fan blade (30 or 50) is
integrally formed with winglet (70). Accordingly, those of ordinary
skill in the art will appreciate that there exists a variety of
configurations for providing fan blade (30 or 50) with winglet (70).
[00751 While vertical member (72) is shown as being substantially
perpendicular to mounting member (90), it will be appreciated that
these two members may be at any suitable angle relative to each other.
Thus, and by way of example only, vertical member (72) may tilt
inward or outward when winglet (70) is attached to fan blade (30 or
50). Alternatively, vertical member (72) may comprise more than one
angle. In other words, vertical member (72) may be configured such
that the top portion of vertical member and the bottom portion of
vertical member each tilt inward when winglet is attached to fan blade
(30 or 50). Other variations of winglet (70), including but not limited
to angular variations, will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the
art.
[00761 While winglet (70) is specifically described herein as a modification
to
fan blades (30 or 50), it will be appreciated that winglet (70) may be
used to modify any other fan blades.
[00771 In one embodiment, winglet (70) is formed from homogenous continuum
of molded plastic. However, it will be appreciated that winglet (70) may
be made from a variety of materials, including but not limited to any
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
- 17-
suitable metal and/or plastic, and may comprise a plurality of pieces. In
addition, it will be appreciated that winglet may be made by any suitable
method of manufacture.
[00781 It will also be appreciated that trailing vortices that form at or near
the
tips of fan blades (30 or 50) may increase lift near the tips of fan blades
(30 or 50). Winglets (70) may inhibit the radial airflow over top surface
(32 or 52) and/or bottom surface (34 or 54) near the tips of fan blades (30
or 50). Such inhibition may force air to flow more normally from
leading edge (36 or 56) to trailing edge (38 or 58), thereby enhancing
efficiency of a fan having fan blades (30 or 50) with winglets (70), at
least at certain rotational speeds.
[00791 In one example, winglets (70) are attached to ends of fan blades (30 or
50) on a fan having a 6 foot diameter. With the addition of winglets (70),
the air flow rate of the fan is increased by 4.8% at 171 rpm.
[00801 In another example, winglets (70) are attached to ends of fan blades
(30
or 50) on a fan having a 14 foot diameter. With the addition of winglets
(70), the air flow rate of the fan is increased by 4.4% at 75 rpm.
[00811 The following two tables illustrate efficiencies that may be obtained
by
adding winglets (70) to a fan having a 14 foot diameter:
[00821 Table 1: Fan Without Winglets (70)
Speed Max. Power Avg. Power Torque Flowrate Efficiency
(rpm) (watt) (watt) (in.lbs) (cfin (cfin/watt)
12.5 54 50 17.86 0 0
25 66 54 78.80 34,169 632.76
37.5 125 82 187.53 62,421 761.23
50 339 263 376.59 96,816 368.12
62.5 700 660 564.01 110,784 167.85
75 1170 1140 839.75 129,983 114.02
CA 02574762 2007-01-22
WO 2006/022812 PCT/US2005/002703
-18-
[0083] Table 2: Fan With Winglets (70)
Speed Max. Power Avg. Power Torque Flowrate Efficiency
(rpm) (watt) (watt) (in.lbs) (cfin) (cfmlwatt)
12.5 50 42 18.56 26,815 638.45
25 58 43 18.39 46,547 1,082.49
37.5 68 49 186.00 61,661 1,258.39
50 241 198 354.61 87,552 442.18
62.5 591 528 582.78 120,859 228.90
75 980 950 847.41 136,560 143.75
[0084] Of course, other values may be realized through use of winglets (70).
In addition, suitable variations of winglets, including but not limited to
alternative winglet configurations, will be apparent to those of ordinary
skill in the art.
[0085] In summary, numerous benefits have been described which result from
employing the concepts of the invention. The foregoing description of
one or more embodiments of the invention has been presented for
purposes of illustration and description. It is not intended to be
exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise form disclosed.
Obvious modifications or variations are possible in light of the above
teachings. The one or more embodiments were chosen and described
in order to best illustrate the principles of the invention and its practical
application to thereby enable one of ordinary skill in the art to best
utilize the invention in various embodiments and with various
modifications as are suited to the particular use contemplated. It is
intended that the scope of the invention be defined by the claims
appended hereto.