Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
WARP-RiJT1PJER TR'IPI,E LAYER FABRIC WITH PAIRED
II'~1TPJI\\ISIC WAI1sI~' BINDERS
BACKGh.OUT\'TD OF THE II~YVEF1TIOi.r
S Field of the u~wcntion
The present invention relates to the papermaking arts. More
specifically, the present invention relates to forming fabrics for a forming
section of a paper machine.
Description of the Prior Art
During the papermaking process, a cellulosic fibrous web is formed
by depositing a fibrous slurry, that is, an aqueous dispersion of cellulose
fibers, onto a moving forming fabric in a forming section of a paper machine.
A large amount of water is drained from the slurry through the forming
fabric, leaving the cellulosic fibrous web on the surface of the forming
fabric. - -
The newly formed cellulosic fibrous web proceeds from the forming
section to a press section, which includes a series of press nips. The
cellulosic fibrous web passes through the press nips supported by a press
fabric, or, as is often the case, between two such press fabrics. In the press
nips, the cellulosic fibrous web is subjected to compressive forces which
squeeze water therefrom, and which adhere the cellulosic fibers in the web to
one another to turn the cellulosic fibrous web into a paper sheet. The water
is accepted by the press fabric or fabrics and, ideally, does not return to
the
paper sheet.
The paper sheet finally proceeds to a dryer section, which includes at
least one series of rotatable dryer drums or cylinders, which are internally
heated by steam. The newly formed paper sheet is directed in a serpentine
path sequentially around each in the series of drums by a dryer fabric, which
holds the paper sheet closely against the surfaces of the drums. The heated
drums reduce the water content of the paper sheet to a desirable level through
evaporation.
1
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
It should be appreciated that the forming, press and dryer fabrics all
take the foam of endless loops on the paper machine and function in the
manner of conveyors. It should further be appreciated that paper manufacture
is a continuous process which proceeds at considerable speeds. That is to
say, the fibrous slurry is continuously deposited onto the forming fabric in
the fomling section, while a newly manufactured paper sheet is continuously
wound onto rolls after it exits from the dryer section.
Press fabrics also participate in the finishing of the surface of the
paper sheet. That is, press fabrics are designed to have smooth surfaces and
uniformly resilient structures, so that, in the course of passing through the
press nips, a smooth, mark-free sutface is imparted to the paper.
Press fabrics accept the large quantities of water extracted from the
wet paper in the press nip. In order to fill this function, there literally
must be
space, commonly referred to as void volume, within the press fabric for the
water to go, and the fabric must have adequate permeability to water for its
entire useful life. Finally, press fabrics must be able to prevent the water
accepted from the wet paper from returning to and rewetting the paper upon
exit from the press nip.
Woven fabrics take many different forms. For example, they may be
woven endless, or flat woven and subsequently rendered into endless form
with a seam.
The present invention relates specifically to the forming fabrics used
in the forming section. Forming fabrics play a critical role during the paper
manufacturing process. One of its functions, as implied above, is to form
and convey the paper product being manufactured to the press section.
However, forming fabrics also need to address water removal and
sheet formation issues. That is, forming fabrics are designed to allow water
to pass through (i.e. control the rate of drainage) while at the same time
prevent fiber and other solids from passing through with the water. If
drainage occurs too rapidly or too slowly, the sheet quality and machine
efficiency suffers. To control drainage, the space within the forming fabric
2
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
for the water to drain, commonly referred to as void volume, must be
properly designed.
Contemporary forming fabrics are produced in a wide variety of
styles designed to meet the requirements of the paper machines on which
they are installed for the paper grades being manufactured. Generally, they
comprise a base fabric woven from monofilament and may be single-layered
or multi-layered. The yams are typically extruded from any one of several
synthetic polymeric resins, such as polyamide and polyester resins, used for
this purpose by those of ordinary skill in the paper machine clothing arts.
The design of forming fabrics additionally involves a compromise
between the desired fiber support and fabric stability. A fine mesh fabric
may provide the desired paper surface properties, but such design may lack
the desired stability resulting in a short fabric life. By contrast, coarse
mesh
fabrics provide stability and long life at the expense of fiber support. To
minimize the design tradeoff and optimize both support and stability, multi-
layer fabrics were developed. For example, in double and triple layer
fabrics, the forming side is designed for support while the wear side is
designed for stability, as well as drainage.
In addition, triple layer designs allow the forming surface of the
fabric to be woven independently of the wear surface. Because of this
independence, triple layer designs can provide a high level of fiber support
and an optimum internal void volume. Thus, triple layers may provide
significant improvement in drainage over single and double layer designs.
Essentially, triple layer fabrics consist of two fabrics, the forming
layer and the wear layer, held together by binding yams. The binding is
extremely important to the overall integrity of the fabric. One problem with
triple layer fabrics has been relative slippage between the two layers which
breaks down the fabric over time. In addition, the binding yarns can disrupt
the structure of the forming layer resulting in marking of the paper.
The present invention describes a triple-layer forming fabric having
paired intrinsic binders and wear side warp runners. The present invention
3
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
provides a solution to the problem of abrasive wear on the machine side of
the fabric while providing good fiber support with a relatively low caliper
and an appropriate void volume.
6)lJlVPJARg OF T 1tYL+ EN! yEH1 10H
Accordingly, the present invention relates to a forming fabric for use
in the forming section of a paper machine, although it may find application in
the pressing and/or drying sections of the paper machine.
The present fabric is a triple layer forming fabric having a first layer
formed of a first system of paired machine-direction (NID) warp yarns
interwoven with a first system of cross machine-direction (CD) weft yarns
and a second layer formed of a second system of MD warp yarns interwoven
with a second system of CD weft yarns. The paired MD warp yarns are
intrinsic to the first layer and are interwoven with the second system of CD
weft yarns to bind the second layer to the first layer. The second system of
MD warp yams forms long floats, or warp-runners, on an external surface of
the second layer. The first layer is a forming side of the fabric and the
second layer is a wear side of the fabric. In this manner, a triple layer
forming fabric with paired intrinsic binders and warp-runners may be
produced with improved wear side abrasion resistance.
Another aspect of the present fabric is the paired IVID warps are not
intrinsic to the second layer. The second layer paired warps help to protect
the binding point(s) between the layers. Because each wear weft passes
under at least two consecutive wear warps, the wear warps can be wrapped
more forcefully to create a greater plane difference than comparable prior art
fabrics.
Other aspects of the present invention include that the fabric may
have various weft ratios of the first system of CD weft yarns to the second
system of CD weft yarns. The long floats may be of different lengths. The
fabric may be flat woven or in endless form. Some of the yams may have
different diameters and/or shapes.
4
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
The present invention will now be described in more complete detail
with frequent reference being made to the drawing figure, which is identified
below.
BMlti;k' 1AESCYAirTIOi'~1 (Dk' 11iA+t DRAWING
For a more complete understanding of the invention, reference is
made to the following description and accompanying drawing, in which:
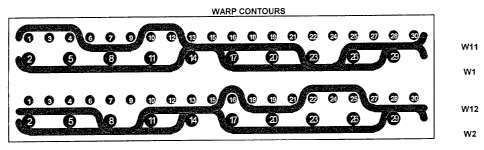
Figure 1 shows a cross-sectional view of a preferred embodiment of a
warp-bound warp-runner triple layer fabric with paired intrinsic binders and
paired warp runners in accordance with the teachings of the present
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTIOI'1 OF THE PREFERRED EMBODINIENTS
A preferred embodiment of the present invention describes a triple-
layer fabric suitable for use in the forming section of a papermaking
machine. The present fabric is comprised of-atop, nrforming; layer and a
bottom, or wear, layer. Each layer is formed of interwoven machine
direction (MD), or warp, yarns and cross-machine direction (CD), or weft
yarns. Hence, the fabric is made up of forming wefts and wear wefts with
forming warps and wear warps.
The forming layer and wear layer are bound together by the forming
warps which are interwoven with both the forming wefts and wear wefts.
These forming warps are paired together and are intrinsic to at least the
forming layer, and possibly both layers. Thus, they are referred to as paired
intrinsic binders. Here, the term intrinsic is defined to mean the yarns are
woven so as to provide fiber support to the top layer, as opposed to simply
binding one layer to another.
Another feature of the present invention is that the warps in the wear
layer of the fabric are woven so as to produce long floats on the outer wear
side surface of the triple layer fabric. Here, a "long" float means the warp
passes under at least two wefts on the wear side surface. Accordingly, such
5
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
long floats may pass under or beneath 2, 3, 4, or more yarns on the wear side.
These long floats are alternatively referred to as warp runners. The floats
are
the primary contacts between the fabric and the papermalcing machine.
Various warps or combinations of warps can also be used to form the floats;
e.g. wear side warps, or forming side warps, or both the wear side warps and
the forming warps can be used to form warp runners. Further, each of the
wear side warps and/or forming side warps or only some of them can be used
to form warp runners. The length of the floats can also be vaiied. Because
these floats run in the 1\ED and provide a relatively smooth fabric surface,
they reduce the abrasive wear on the fabric caused by contact with stationary
elements of the papermaking machine. In other words, the present fabric's
warp runners provide improved abrasion resistance. In addition, the warp
runners help reduce the load on papermaking machines running this type of
fabric.
Figure 1 shows a cross-sectional view of the preferred embodiment of
a warp-runner triple layer fabric with paired intrinsic warp binders in -
accordance with the teachings of the present invention. More specifically,
Figure 1 shows the warp contours in the forming and wear layers for a pair of
intrinsic binder yarns W 11 and W 12. Paired warps W 11 and W 12 are woven
intrinsic to the forming layer and cross to bind the wear layer. Warp W 11
binds the wear layer at weft yam 23 and warp W 12 binds the wear layer at
weft yarn 8. The fabric has a weft ratio of 2:1 as evidenced by twice as
many weft yams in the forming layer (e.g. 1, 3, 4, ...) as in the wear layer
(e.g. 2, 5, 8, ...). Wear warp WI and wear warp W2 weave the wear layer
and form paired warps with long floats from weft yarns 2 to 11 and 17 to 26.
Although a float length of 4 is illustrated in Figure 1, other float lengths
greater than 2 can be utilized. Further, the wear warps may be paired warps
and/or non-paired warps.
Additional advantages of the present fabric include a relatively high
weaving efficiency, reduced dimples on the forming surface (primarily due
to the use of binding warps rather than wefts), a relatively low caliper and
an
6
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PCT/US2005/026780
appropriate void volume. The present fabric is also relatively easy to clean,
has a relatively long life expectancy, and a relatively low drive load for
papermaking machines running this fabric due to the long wear side floats
contacting the machine elements in a perpendicular direction.
Other aspects of the present invention include that the pattern may
have forming to wear-side weft ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 3:2, or any other weft
ratio. The present fabric may also incorporate different diameter or shaped
yarns. For example, the forming side yarns may be of a smaller diameter
than the wear side yarns. Various combinations of warp and weft yam sizes
may also be used. Additionally, warp and/or weft yarns may be stacked or
not stacked. For example, the forming side wefts may be stacked or not
stacked over the wear side wefts. Note, these examples are simply
representative examples of the invention and are not meant to limit the
invention.
The fabric according to the present invention preferably comprises
only monofilament yarns. The CD and MD yarns may have a circular cross-
sectional shape with one or more different diameters. Additionally, the CD
yarns and MD yarns in the forming side and wear side may have different
diameters. It is preferable for the forming side CD and MD yarns to have
smaller diameters than the wear side CD and MD yarns. However, various
combinations of yarn diameters can be used in the present invention.
Further, in addition to a circular cross-sectional shape, one or more of the
yarns may have other cross-sectional shapes such as a rectangular cross-
sectional shape or a non-round cross-sectional shape.
The yarns may be monofilament yams of circular cross section of any
of the synthetic polymeric resins used in the production of such yarns for
paper machine clothing. Polyester and polyamide are but two examples of
such materials.
Modifications to the above would be obvious to those of ordinary
skill in the art, but would not bring the invention so modified beyond the
7
CA 02575829 2007-02-01
WO 2006/020414 PcT/US2005/026780
scope of the present invention. The claims to follow should be construed to
cover such situations.
8