Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02577977 2007-02-23
Device for ejecting PET Preforms
The present invention concerns an ejector for an injection-molding tool for
the production of
PET preforms according to the preamble of claim 1.
Injection molding machines for the production of preforms, for example for the
production of
drinking bottles made of PET, essentially comprise an extruder unit and a
forming tool unit.
When producing thick-walled preforms of the above-mentioned kind, the cycle
time is mainly
determined by the time necessary for the preform to become inherently stable.
In order to
reduce the cycle time and, above all, the standstill periods of the plastic
injection molding
machines caused by the preforms' long cooling period, extraction devices for
taking out the
preforms are used more and more frequently. To this end, the molding tools are
opened after
the injection process and during the cooling phase respectively and the
preforms which are
not yet completely cooled are automatically taken up by those extraction
devices and kept
cooling. During this cooling period, the molding tools can be closed again and
refilled.
Such an extraction device is described, for example, in WO 97/47459. In order
to take up the
preforms after the injection molding process has been finished, the withdrawal
plate in the
opened molding tool is positioned in such a way that the individual preforms
can be drawn
into the withdrawal plate's cavities by means of low pressure produced in the
extraction
device. In those cavities they continue to cool. Thus, every single preform is
pulled off the
mold core using this extraction device. During the cooling period of those
preforms a new
molding cycle has already started.
Other similar extraction devices are described in EP-0'633'119, DE-198'48'837
or
US-6,391,244.
What they all have in common is that they are positioned in the desired way in
the opened
molding tool after the molding has been finished. In so doing, the preforms
are sucked into
the extraction device's cavities by the low pressure produced in this
apparatus in order to
continue their cooling process. However, there are different mechanisms to
remove the
preforms from the extraction devices' cavities after the cooling process. Some
eject the
cooled-down preforms using mechanical aids, while others use pressurized air
to blow them
out.
However, the disadvantage of these well-known extraction devices is that after
the injection
molding process, some preforms can easily be sucked off the mold cores into
the extraction
CA 02577977 2007-02-23
2
device while others remain stuck at the mold cores. This leads to an
interruption of the
subsequent production cycle, as the preforms remaining at the mold cores
impede the
production of new preforms.
US-4,438,065 shows a template with an appliance integrated into the form to
remove PP
injection molding pieces from this appliance. After the molding tool has been
opened, the
injection molded and cup shaped container is blown out of the form using a jet
of pressurized
air. This molding tool is used in connection with the production of cup shaped
PP forms and
therefore is not suited for PET molding tools for preforms used for the
production of drinking
bottles made of PET.
Moreover it can be shown that while producing thin-walled preforms, there is
no need for
additional cooling in the extraction device. For this reason, it is now common
practice to
equip each mold core with a device enabling the preforms to be dislodged
securely from the
mold cores, irrespective of a separate extraction device being there or not.
In particular,
molding tools have now been created that are equipped with a mechanical
stripping aid.
Furthermore, there are also molding tools for the production of PET preforms
whose molding
cores are equipped with air jets to blow the preforms off the molding core.
Unfortunately this
does not guarantee the preforms' secure removal from the molding cores,
especially when
longer preforms are being used. The reason for this is that the air jets on
those molding tools
have dedicated positions within the molding core. Due to this, when dislodging
the preform,
the air stream becomes weaker the further away the preform is piaced from the
air jet. This
disadvantage makes itself felt in particular with the production of long
preforms having to
cover a long strip-off distance. It stands to reason that preforms left over
on the molding
cores are stuck and can cant within the molding tool. This, in turn, means
that the molding
tool cannot be closed sufficiently in the course of the next cycle, leading to
leakages.
Preforms that are stuck may interrupt the entire production cycle and thus
entail time-
consuming and cost-intensive maintenance work. It has also been shown that
these air jets
can be easily over-sprayed or contaminated by oil or dust residues, which
again entails time-
consuming and cost-intensive maintenance works.
Therefore it is the aim of the present invention to provide a device that does
not have these
disadvantages. In particular, it is the aim of the present invention to create
a device with
which the preforms can be stripped off securely from their molding cores,
irrespective of their
lengths and irrespective of a separate extraction device being there or not.
Furthermore, this
device should to be easy to maintain.
CA 02577977 2007-02-23
3
According to the invention, this is achieved using an ejector according to
claim 1, and in
particular using a device having at least one air duct arranged in the molding
tool's slide rail.
The device for ejecting the PET preforms essentially comprises a slide rail
with at least one
air duct. Threaded slides are fixed to this slide rail.
This slide rail is part of a known molding tool with a clamping plate for a
molding core, as well
as a movable stripping plate. In its basic position, the stripping plate lies
flat on the mold
clamping plate, as is usual with such devices. The slide rail fixes the
preform at the thread. If
the stripping plate is moved away from the mold clamping plate, the preform is
loosened off
the molding core as well, given that the slide rails go along with the
stripping plate's
movements and fix the preform at this particular moment. The stripping plate
continues to
extend, the length of its ejecting stroke being adapted to the preform length.
Before the
maximum ejecting stroke is reached, a pressurized puff of air is applied to
the preform via the
air ducts positioned in the slide rail, blowing the preform off the molding
core. As the air ducts
are in the slide rail, they move along with the slide rail. As the air stream
is introduced at a
non-varying angle to the molding core and at a non-varying distance to the
preform, it is
ensured that the preforms are ejected steadily, irrespective of their
contours. Thus the air
impulse is effective independently of the preform's length and contour and
proves to be
extremely efficient at removing the preform from the molding core.
The benefits of the inventive device are easy to see for the expert, the main
advantage being
the ensuring of the reliable ejection of the preforms. Another advantage of
the device is that it
is very economic, because the flight curve of the preforms from the molding
tool can be
adjusted by adjusting the duration of the puff of pressurized air. This, in
turn, reduces air
consumption. Moreover, it is clear that neither oil nor dust can enter the air
ducts.
In a preferred embodiment, the air ducts in the slide rail are positioned in
such a way that the
air impulses impinge on the molding core at an angle of approx. 35 . It is
clear that there may
be several air ducts arranged in the slide rail and that these may have
differing angles to the
ejection direction.
Alternatively, the molding core's outer contours can be coated with a special
suitable
anti-stick coating.
CA 02577977 2007-02-23
4
In the following, the present invention shall be described in detail by way of
example and by
means of the illustrations. The illustrations show:
Fig. 1 A longitudinal section through a mold template with an ejector
according to the
invention for the stripping off of preforms directly after the opening of the
molding
tool.
Fig. 2 A longitudinal section through a mold template with an ejector
according to the
invention for the stripping off of preforms in a first ejection position.
Fig. 3 A longitudinal section through a mold template with an ejector
according to the
invention for the stripping off of preforms in a second ejection position.
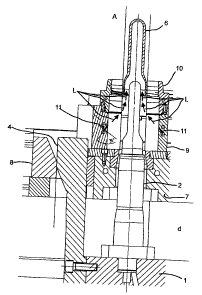
The setup of the inventive device for the ejection of preforms according to
the invention can
be seen in Fig. 1. The freshly produced preform (6) still sits solidly on the
molding core (2).
The molding tool has just been opened. The device for ejecting the preform (6)
is still in its
basic position. The molding tool has a clamping plate (1) for a molding core
(2). A movable
stripping plate (7) can be moved in the direction of the molding core and
carries along a yoke
support (8) that moves a slide rail (9) with threaded slides (10) fixed to it
using a slanted
drawing finger (4). According to the invention, the slide rail (9) has at
least one air duct (11).
Fastening means (5) secure the slanted drawing finger (4) to the mold clamping
plate (1).
The slant surfaces (12) of the yoke support (8) and the slant surfaces (13) of
the slanted
drawing finger (4) are used for the lateral opening of the slide rails (9).
According to the
invention, the device for the ejection of preforms can be operated using a
hydraulic device,
for example. In so doing the slide rail (9) is moved together with the
threaded slide (10) in the
ejection direction A. The air ducts (11) arranged in the slide rail (9) are
crucial for ejecting the
preforms.
Fig. 2 shows the ejector according to the invention in a first ejecting
position. In the ejecting
position shown here, the stripping plate (7) is distanced from the clamping
plate (1) by an
ejecting stroke a. The illustration shows that the air ducts (11) are freed by
this first
movement in the ejection direction in order to blow pressurized air directed
in between the
mold core (2) and the preform (6) in the next step. At this point in time, the
slide rails (9) and
the threaded slide (10) are only slightly open. The mechanisms needed for this
procedure
are well known to the expert and are therefore not subject of this invention.
CA 02577977 2007-02-23
As is described in Fig. 3, the stripping plate (7) is moved further away from
the mold-
clamping plate (1) in another step and this moves the yoke supports (8)
outwards due to the
corresponding slant surfaces (12,13) of the slanted drawing finger (4) and the
yoke support
(8). As a result, opening stroke a is extended and the slide rails (9) and the
threaded slides
5 (10) are opened further. In this process, the preform (6) is completely
freed. While the slide
rail (9) is opened, pressurized air (L) is blown out through at least one air
duct (11) until the
stripping plate (7) has reached the maximum ejection stroke d or the threaded
slides (10) are
opened up to their full extent. According to the invention, the air ducts (11)
are arranged in
the slide rail (9) and are inclined at an angle a with respect to the ejection
direction A. This
ensures that a targeted air stream can also be blown in an opened state
between the mold
core (2) and the preform (6). It is clear that the angle a can be varied
depending on the mold
core length. It is preferable if this angle a is inferior to 45 . A
universally well proven angle a
is approx 35 to the ejection direction A.
In a preferred development of the inventive ejector device, the slide rail (9)
has several air
ducts (11) with advantageously differing angles facing the ejection direction.
It is clear that
the mold core (2) can be fitted with an anti-stick coating on the outside.