Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
1
[DESCRIPTION]
CRIP TI ON]
PERFORMING IDLE MODE IN A WIRELESS ACCESS SYSTEM
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates generally to a wireless access system and, more
particularly, to
idle mode in a wireless access system.
BACKGROUND ART
1 0 A wireless access system conventionally supports an idle mode to reduce
power consumption
by a mobile station (MS). In idle mode, the MS is not yet registered to a
specific base station
(BS) and also is not handed over from one BS to another BS in a paging zone. A
paging zone is
composed of a plurality of BS areas. The MS receives a predetermined paging
message (e.g.,
MOB-PAG-ADV) to enable the MS to periodically recognize the presence or
absence of
downlink traffic destined for the MS. Such operation may reduce power
consumption by the MS.
Idle mode operation is described below. In a paging zone is a plurality of BSs
contained in a
group, called a paging group. The BSs included in the same paging group have
the same paging
cycle (e.g., Paging_Cycle) and the same paging offset (e.g., Paging_Offset).
The MS may
request the BS to enter an idle mode. The BS transmits its paging group ID
(e.g., Paging Group
ID), a paging cycle corresponding to the paging group ID, and a paging offset
to the MS to
enable the MS to enter the idle mode. In such case, the MS and the BS operate
a timer for
updating position information related to the MS that entered the idle mode.
During the idle mode, the MS receives the paging advertisement message (e.g.,
MOB-PAG-
ADV) configured as broadcast information from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined paging
time. The MS may determine whether to continuously maintain the idle mode, to
terminate the
CA 02584322 2013-02-13
74420-177
2
idle mode, or to perform a location update procedure using the received paging
advertisement
message (e.g., MOB-PAG-ADV). If uplink traffic is to be transferred from the
MS during the
idle mode, the MS may terminate the idle mode.
If downlink traffic is to be received by the MS during idle mode, the BS may
allow the MS to terminate the idle mode using the paging advertisement message
(e.g., MOB-
PAG-ADV). If the MS in the idle mode loses a synchronization point such that
it does not
receive the paging advertisement message (e.g., MOB-PAG-ADV) by a set time,
the MS
terminates the idle mode.
If the MS in the idle mode moves from a current paging group to another
paging group, or if a timer for updating position information expires, invalid
parameters are
updated according to a network re-registration procedure such that a location
update
procedure is performed. In such case, the MS does not perform removable
procedures
according to management resource information managed by the BS so that the MS
may
perform the location update procedure.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, the present invention is directed to performing idle mode in a
wireless access system that, in some embodiments, may substantially obviate
one or more
problems due to limitations and disadvantages of the related art.
Some embodiments may provide for reducing a length of a message that
provides information indicating whether an idle mode is maintained. As such,
some
embodiments may utilize downlink wireless resources more efficiently and may
minimize
power consumed when a mobile station in an idle mode processes such a message.
Additional advantages and features of some embodiments of the invention will
be set forth in part in the description which follows and in part will become
apparent to those
having ordinary skill in the art upon examination of the following or may be
learned from
practice of the invention. The objectives and other advantages of some
embodiments of the
CA 02584322 2013-02-13
74420-177
3
invention may be realized and attained by the structure particularly pointed
out in the written
description and claims hereof as well as the appended drawings.
According to one embodiment, a method for controlling an idle mode in a
mobile station comprises transmitting an idle mode request message to a
serving base station
to enter the idle mode. The method also comprises determining whether a skip
threshold
parameter has been exceeded, the skip threshold parameter associated with a
number of
paging intervals to pass before receiving a paging message with a mobile
station identifier of
the mobile station. The method also comprises transmitting a location update
request to a
base station if the skip threshold parameter has been exceeded, the location
update request
configured to update the location of the mobile terminal with respect to the
base station.
In some embodiments, the method may further comprise transmitting a skip
threshold request parameter from the mobile station and receiving the skip
threshold
parameter in response to the transmitting of the skip threshold request
parameter. In some
embodiments, the method may further comprise reinitializing the step of
determining whether
the skip threshold parameter has been exceeded in response to receiving the
paging message
with a mobile station identifier of the mobile station. In some embodiments,
the method may
further comprise receiving a paging message without a mobile station
identifier of the mobile
station from at least one base station within a paging group when there is no
downlink traffic
for the mobile station. In some embodiments, the method may further comprise
receiving a
paging message without the mobile station identifier of the mobile station
from at least one
base station within a paging group when there is no location update request.
In some embodiments, the skip threshold parameter may comprise at least one
of a MAC (Medium Access Control) address hash, an action code, and a TLV (type
length
value) parameter for a paging operation. In some embodiments, the paging
message with a
mobile station identifier of the mobile station may be a paging advertisement
message.
In another embodiment, a method for controlling an idle mode of a mobile
station in a network comprises receiving an idle mode request message from the
mobile
station to enter the idle mode. The method also comprises receiving a skip
threshold request
CA 02584322 2013-02-13
74420-177
4
parameter from the mobile station. The method also comprises transmitting a
skip threshold
parameter in response to the receiving of the skip threshold request
parameter, the skip
threshold parameter associated with a number of paging intervals to pass
before the mobile
station receives a paging message with a mobile station identifier of the
mobile station. The
method also comprises receiving a location update request from the mobile
station if the skip
threshold parameter is exceeded, the location update request configured to
update the location
of the mobile terminal.
In some embodiments, the method may further comprise transmitting a paging
message without a mobile station identifier of the mobile station to the
mobile station when
there is no downlink traffic for the mobile station and receiving the packet
data from the base
station, wherein at least two of retransmitted packet data are transmitted
from different
antennas of the base station. In some embodiments, the retransmitted packet
data are received
with information element comprising a retransmission count associated with a
number of
retransmission made by the base station.
In some embodiments, the method may further comprise transmitting a paging
message without a mobile station identifier of the mobile station to the
mobile station when
there is no location update request received from the mobile station. In some
embodiments,
the network may comprise at least one of a base station and a paging
controller, the paging
controller configured to control paging of base stations within a paging
group.
According to another embodiment, there is provided a mobile station for
controlling an idle mode in a wireless access system, the mobile station
comprising: means
for transmitting an idle mode request message to a serving base station to
enter the idle mode;
means for determining whether a skip threshold parameter has been exceeded,
the skip
threshold parameter associated with a number of paging intervals to pass
before receiving a
paging message with a mobile station identifier of the mobile station; and
means for
transmitting a location update request to a base station if the skip threshold
parameter has
been exceeded, the location update request configured to update the location
of the mobile
terminal with respect to the base station.
CA 02584322 2013-02-13
74420-177
4a
According to another embodiment, there is provided a network for controlling
an idle mode in a wireless access system, the network comprising: means for
receiving an
idle mode request message from the mobile station to enter the idle mode;
means for receiving
a skip threshold request parameter from the mobile station; means for
transmitting a skip
threshold parameter in response to the receiving of the skip threshold request
parameter, the
skip threshold parameter associated with a number of paging intervals to pass
before the
mobile station receives a paging message with a mobile station identifier of
the mobile
station; and means for receiving a location update request from the mobile
station if the skip
threshold parameter is exceeded, the location update request configured to
update the location
of the mobile terminal.
The foregoing and other features, aspects and advantages of some
embodiments of the present invention will become more apparent from the
following detailed
description of some embodiments of the present invention when taken in
conjunction with the
accompanying drawings. It is to be understood that both the foregoing general
description
1 5 and the following detailed description of some embodiments of the
present invention are
exemplary and explanatory and are intended to provide further explanation of
the invention as
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
claimed.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further
understanding of the
5 invention and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this
application, illustrate embodiments
of the invention and together with the description serve to explain the
principles of the invention.
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a paging group that includes a plurality of
base stations,
according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to an
1 0 embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to another
embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a detailed flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 3, according
to an
embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to yet
another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a first flow diagram illustrating a method for performing idle mode,
according to still
another embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a second flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 6, according
to an embodiment
2 0 of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a third flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 6, according to
an embodiment
of the present invention.
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
6
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Reference will now be made in detail to the preferred embodiments of the
present invention,
examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wherever
possible, the same
reference numbers will be used throughout the drawings to refer to the same or
like parts.
An exemplary message between base stations (BSs), e.g., a "Paging-Group-
Action" message
for constructing a paging zone is shown in the below Table 1. The Paging-Group-
Action
message may be transmitted to a target position between BSs by wire.
[Table 1]
Field Size Notes
Paging-group-action Message
Format(){
Message Type 8-bits
48- Base station unique identifier(Same number as that
Sender BS-ID
bits broadcasted on the DL-MAP message)
48- Base station unique identifier(Same number as that
Target BS-ID
bits broadcasted on the DL-MAP message)
32- Number of milliseconds since midnight GMT (set to
Time Stamp
bits Oxffffffff on the DL-MAP message)
0-Assign target BS to paging groups
4- 1-Remove target BS from paging groups
Action
bits 2-Query (which paging groups target BS belongs to?)
3-Information(Paging groups sender BS belongs to)
Num Record 4-bits Number of paging group-ID records
Field Size Notes
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
7
For(j=0; j<Num Record; j++){
16-
Paging-group-ID Paging-group-ID
bits
16- Cycle in which the paging message in
transmitted within
PAGING CYCLE
bits the paging group
PAGING OFFSET 8-bits MS PAGING OFFSET parameter
Security field = TBD A mean to authenticate this message
CRC field 2-bits IEEE CRC-32
The Paging-Group-Action message may be used in various ways, such as those
described
below, according to a combination of action bits. In a first usage, the Paging-
Group-Action
message assigns a target BS to a specific paging group, which may be denoted
by "Action=0". In
a second usage, the Paging-Group-Action message removes the target BS from the
specific
paging group, which may be denoted by "Action=1". In a third usage, the Paging-
Group-Action
message queries which paging group includes the target BS, which may be
denoted by
"Action=2". In a fourth usage, the Paging-Group-Action message indicates which
paging group
includes a sender BS, which may be denoted by "Action=3".
Since a BS may be included in one or more paging zones, the Paging-Group-
Action message
may include information associated with a plurality of paging groups. BSs may
therefore
recognize a paging cycle and a paging offset for use in each paging zone using
the Paging-Group-
Action message. Furthermore, the BSs may be dynamically assigned to a paging
group.
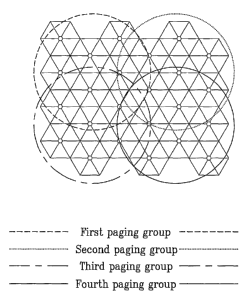
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a paging group that includes a plurality of
base stations,
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
8
according to an embodiment of the present invention. ,
Referring to FIG. 1, a plurality of BSs supporting an idle mode are included
in a paging group
to configure a paging zone. An exemplary de-registration request (e.g., DREG-
REQ) message
used when the MS is switched to idle mode is shown in the below Table 2.
[Table 2}
Syntax Size Notes
DREG-REQ_Message_Format(){
Ox00=SS de-registration request from BS
and network
Ox01=request for MS deregistration from
Management Message
8 bits Serving BS invitation of MS paging
Type=29
Availability Mode
0x02-0xFF=reserved
De-registration Request Only valid if De-Registration
Request
8 bits
Code Code=0x01
Paging Cycle Request 16 bits
TLV encoded parameter Variable
}
The MS may set the de-registration request code of the above-mentioned DREG-
REQ message
to a predetermined value of Ox01, for example, and transmit the de-
registration request code
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
9
"Ox0 1" to the BS to inform the BS that the MS will be switched to the idle
mode. After the MS is
switched to a desired paging cycle and a desired idle mode, the MS may
transmit MS
management resource information desired by the BS to the BS.
Exemplary TLV encoded parameters for the above-mentioned DREG-REQ message are
shown
in the below Table 3:
[Table 3.]
Name Type Length Value
Paging Cycle Requested cycle in which the paging message is
transmitted
Request within the paging group.
MS request for Paging Controller retention of network re-entry
related MAC management message MS service and operational
information to expedite future Network Re-entry from Idle Mode.
For each Bit location, a value of '0' indicates the information
associated with the specified MAC management message is not
requested to be retained to be retained and managed.
Idle Mode Bit#0 : Retain MS service and operational information
associated
Retain with SBC-REQ/RSP MAC management messages
Information Bit#1 : Retain MS service and operational information
associated
with PKM-REQ/RSP MAC management messages
Bit#2 : Retain MS service and operational information associated
with REG-REQ/RSP MAC messages
Bit#3 : Retain MS service and operational information associated
with Network Address
Bit#4 : Retain MS service and operational information associated
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
with Time of Day Acquisition
Bit#5 : Retain MS service and operational information associated
with TFTP MAC management messages
Bit#6: Retain MS service and operational information with Full
service (MAC state machines, CS classifier information, etc..)
After receiving the DREG-REQ message from the MS, the BS may reply using a
deregistration
command (e.g., DREG-CMD) message.
An exemplary DREG-CMD message is shown in the below Table 4.
5 [Table 4]
Syntax Size otes
DREG-CMD_Message_Format0{
Management Message Type=29 8 bits
Action Code 8 bits
TLV encoded parameters variable
}
The BS may allow the MS to switch to the idle mode using an action code of the
DREG-CMD
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
11
message, which may be denoted by "Action Code = 0x05". The BS may re-request
the switching
of the MS to the idle mode after the lapse of a predetermined time, which may
be denoted by
"Action Code = 0x06". Alternatively, the BS may not request the switching of
the MS to the idle
mode until transmitting the DREG-CMD message, which may be denoted by "Action
Code =
Ox07".
An exemplary action code of the DREG-CMD is shown in the below Table 5.
[Table 5]
Action
Action
Code
- - - - - ¨
-
MS shall immediately terminate service with BS and attempt network entry at
another
Ox00
BS
MS shall listen to the current BS but shall not transmit until an RES-CMD
message or
Ox01
DREG-CMD with Action Code Ox00 is received
MS shall listen to the current BS but only transmit on the Basic, Primary
Management
Ox02
and Secondary Management Connections.
0x03 MS shall return to normal operation and may transmit on any of its
active connections.
MS shall terminate current Normal Operation with the BS; the BS shall transmit
this
Ox04
action code only in response to any MS DREG-REQ
0x05 required MS de-registration from Serving BS and request initiation
of MS Idle Mode
The MS may retransmit the DREG-REQ message after the time duration (REQ-
0x06
duration) provided in the message
The MS shall not retransmit the DREG-REQ message and shall wait the DREG-CMD
Ox07
message
0x08- Reserved
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
12
OxFF
Using a TLV (Type Length Value) item selectively included in the DREG-CMD
message, a
paging group ID, a paging cycle (e.g., Paging_Cycle), and a paging offset
(e.g., Paging_Offset)
may be transmitted to the BS. The paging offset must be maintained by a
corresponding MS
during the idle mode.
Exemplary TLV parameters included in the DREG-CMD message are shown in the
below
Table 6.
[Table 6]
Name TypeLengthValue
- - - - - - ¨ - ¨ - - ¨
Bits 15:0 - PAGING CYCLE - Cycle in which the paging message is
transmitted within the paging group
Bits 23:16 - PAGING OFFSET - Determines the frame within the
Paging
4 cycle in which the paging message is transmitted. Must be smaller
Information
than PAGING CYCLE value
Bits 31:24- Paging-group-ID - ID of the paging group the MS is
assigned to
Waiting value for the DREG-REQ message retransmission (measured
REQ-duration 1
in frames)
This is a logical network identifier for the Serving BS or other
Paging
6 network entity retaining MS service and operational information
Controller ID
and/or administering paging activity for the MS while in IDLE Mode
Idle Mode Idle Mode Retain Information is provided as part of
this message is
1
Retain indicative only. Network Re-entry from Idle Mode
process
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
13
Information requirements may change at time of actual reentry. For
each Bit
location, a value of '0' indicates the information for the associated
reentry management messages shall not be retained and managed, a
value of '1' indicates the information for the associated re-entry
management message shall be retained and managed
Bit #0: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
SBC-REQ/RSP MAC management messages
Bit #1: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
PKM-REQ/RSP MAC management messages
Bit #2: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
REG-REQ/RSP MAC management messages
Bit #3: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
Network Address
Bit #4: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
Time of Day
Bit #5: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
TFTP MAC management messages
Bit #6: Retain MS service and operational information associated with
Full service (MAC state machines, CS classifier information, etc.)
As shown in the above Table 6, the DREG-CMD message provides a TLV parameter.
The
DREG-CMD message includes paging information, MS management resource
information
maintained by the MS after the MS is switched to the idle mode, and a paging
controller
identifier (denoted by Paging Controller ID in Table 6). A procedure for
acquiring information
units maintained by the BS when the MS is switched to the idle mode may be
removed from a
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
14
network registration procedure based on an assumption that the MS in the idle
mode terminates
the idle mode or performs the location update procedure. As a result, the MS
may be registered
in the network and position information related to the MS may be updated with
new position
information.
An exemplary paging advertisement (e.g., MOB-PAG-ADV) message is shown in the
below
Table 7.
[Table 7]
Syntax Size Notes
MOB-PAG-
ADV_Message_Format(){
Management Message Type =62 8bits
Num_Paging Group IDs 8bits Number of Paging Group IDs in this message
For(i=0;
i(Num_Paging_Group_IDs;
i++){ =
Paging Group ID 8 bits
Number of MS MAC Addresses in message may be
For(j=0; j<Num_MACs; j++){
determined from the length of the message(found in
the generic
MS MAC Address hash 24 bits
Paging action instruction to MS
Action Code 2 bits 00=No Action Required
01=Performing Ranging to establish location and
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
acknowledge message
1 0=Enter Network
1 1=reserved
Reserved 6 bits
TLV Encoded Information variableTLV specific
reserved variablePadding bits to ensure octet aligned
The MS receives the above-mentioned MOB-PAG-ADV message in a paging offset
during a
predetermined paging period and maintains or terminates idle mode,
accordingly. The MS in the
idle mode receives the paging advertisement message (e.g., MOB-PAG-ADV)
periodically
5 transmitted from the BS, such that it may determine whether to terminate
the idle mode, to
perform a location update procedure, or to maintain the idle mode.
BSs in a single paging group may command operations of idle-mode MSs included
in the
paging group using the same MOB-PAG-ADV message. In such case, a Medium Access
Control
(MAC) address hash including a predetermined length of 24 bits, for example,
may be used as an
10 identifier capable of identifying individual MSs. The idle-mode MSs may
determine whether a
paging group is changed to another paging group based on a paging group ID
parameter setup
value of the MOB-PAG-ADV message. The idle mode MSs may then find a
corresponding BS
ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, and determine
whether the idle
mode is being normally operated in the paging group.
15 If the idle-mode MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message and does not find a
corresponding
MS ID in the message, the MS may determine that a problem has occurred in idle
mode
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
16
operations and may terminate the idle mode.
Although the corresponding MS may not perform a network registration procedure
for a
location update procedure or to receive downlink traffic, the BSs included in
a paging group must
include a corresponding MS ID (e.g., MAC address hash) in the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, and
transmit the MOB-PAG-ADV message including the MS ID.
As such, BSs capable of supporting the idle mode include IDs of idle-mode MSs
belonging to
the same paging group in the MOB-PAG-ADV message. The BSs also convert the MOB-
PAG-
ADV message including the MS ID to broadcast information. Furthermore, the BSs
transmit the
broadcast information to a target MS at intervals of a paging time. Therefore,
as the number of
MSs switched to the idle mode increases, the length of the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, which
must be periodically transmitted by BSs in a corresponding paging group, also
increases in
proportion to the increased number of MSs. Furthermore, a downlink band
required to transmit
the MOB-PAG-ADV message is increased, such that BSs may not be able to
effectively use
wireless resources. Additionally, in relation to the length of the MOB-PAG-ADV
message,
processing power required for the idle-mode MS to receive and/or decode the
MOB-PAG-ADV
message is proportionally increased.
Therefore, if a corresponding MS ID (e.g., MAC address hash) is deleted when
the BS
commands the MS to maintain the idle mode using the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the
length of
the MOB-PAG-ADV message may be reduced. Furthermore, in such case, power
consumption of
wireless resources may be reduced, and a corresponding MS may update
availability of idle-
mode operation.
Various preferred embodiments for removing paging parameters from the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message are described below. The paging parameters include an MS ID (e.g., MAC
address
hash), an action code associated with the MS ID, and a TLV parameter.
In accordance with a first preferred embodiment, a type of the MOB-PAG-ADV
message is
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
17
defined, and a paging parameter associated with the idle-mode MS is included
or omitted
according to the MOB-PAG-ADV message type. The paging parameter may be removed
from
the MOB-PAG-ADV message based on a condition that the MOB-PAG-ADV message
commands all idle-mode Ms to maintain the idle mode.
In accordance with a second preferred embodiment, if the MS is switched to the
idle mode, the
BS may include a number of times that the paging parameter may be removed from
the MOB-
PAG-ADV message in the DREG-CMD message, and may transmit the DREG-CMD message
to
the MS.
In accordance with a third preferred embodiment, a method is provided for
employing a
specific flag to indicate that a paging parameter capable of maintaining the
idle mode is removed
from the MOB-PAG-ADV message. Paging parameters corresponding to some MSs may
not be
removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, while other paging parameters
corresponding to
MSs capable of generating a command required to maintain the idle mode may be
removed from
the MOB-PAG-ADV message, for example. A paging parameter associated with an MS
capable
of generating a command required to perform a location update process and a
network
registration procedure may be included in the MOB-PAG-ADV message.
In accordance with a fourth preferred embodiment, if an idle-mode MS does not
receive its ID
(e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV message for a predetermined
number of
successive times, the idle-mode MS may perform a location update procedure to
update
availability of the idle-mode operation. In such case, when the MS is switched
to the idle mode,
the BS may transmit information to indicate of the predetermined number of
successive times to
the MS using the DREG-CMD message. BSs contained in the paging group may
include a
corresponding paging parameter in the MOB-PAG-ADV message within a
predetermined time
corresponding to the predetermined number of successive times to enable the MS
to update the
availability of the idle-mode operation without performing an additional
location update
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
18
procedure. The number of times that the MS ID may be removed from the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message may be managed and/or updated by the BS or a paging controller.
An exemplary MOB-PAG-ADV message described in the above first preferred
embodiment is
shown in the below Table 8.
[Table 8]
Syntax Size Notes
MOB-PAG-
ADV_Message_FormatO {
Management Message Type=62 8 bits
Num_Paging_GroupiDs 8 bits Number of Paging Group IDs in this
message
For(i=0;
i<Num_Paging_GroupiDs; i++)
Paging Group ID 8 bits
0 : Normal type
Paging Type 1 bit
1 : Compressed type
If(Paging Type ¨ 0) {
Num_MACs 15 bits
For (j=0; j<Num_MACs; j++) {
The hash is obtained by computing a CRC24 on the
MS MAC Address hash 24 bits MS 48-bit MAC address. The polynomial
for the
calculation is Ox864CFB
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
19
Paging action instruction to MS
00=No Action Required
01=Perform Ranging to establish location and
Action Code 2 bits
acknowledge message
10=Enter Network
1 1=reserved
Reserved 6 bits
1
else {
Reserved 7 bits
}
TLV encoded Information variableTLV specific
Reserved variablePadding bits to ensure octet aligned
1
else {
Reserved 7 bits Padding bits to ensure octet aligned
1
Exemplary parameters in the DREG-CMD message according to the above second
preferred
embodiment are shown in the below Table 9.
[Table 9]
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
Name TypeLength Value
Number of skipping MS MAC address hash in the MOB-PAG-
Number of
ADV message when the value of action code associated with
skipping MAC 1
the MS is 0 (No Action). The unit is the number of MOB-PAG-
Address hash
ADV transmission.
As shown in the above Table 9, parameters indicative of the number of times of
omission
(omission times) of the MS ID may be included in the DREG-CMD message.
Exemplary parameters in the DREG-CMD message according to the above second
preferred
5 embodiment are shown in the below Table 10.
[Table 10]
Name Type Length 'Value
Indicates per which number of MOB-PAG-ADV
Interval including
transmission the BS should include MS MAC
MAC Address
1 address hash in the MOB-PAG-ADV message when
hash
the value of action code associated with the MS is 0
(No Action).
As shown in the above Table 10, parameters indicative of an interval in which
the MS ID is
included in the MOB-PAG-ADV may be included in the DREG-CMD message.
J. 0 In accordance with the above second preferred embodiment, the MOB-PAG-
ADV message for
periodically commanding operation of the idle-mode MS may include a
conventional MOB-
PAG-ADV message. However, if a corresponding MS must maintain the idle mode
according to
the number of removable times of the MS ID (e.g., the number of times that the
MSS ID may be
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
21
removed), which was transmitted by the DREG-CMD message to allow the MS to be
switched to
the idle mode, the BS may regularly remove an MS ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV
message.
Furthermore, if the MS in the idle mode receives a command to maintain the
idle mode during
a paging cycle, the corresponding MS ID may be removed. Therefore, although
the specific MS
ID is not included in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS may determine that idle-
mode
operation is functioning normally. Based on the number of removable times of
the MS ID, the
availability of the idle-mode operation may be updated using the MS ID
periodically transmitted
in the MOB-PAG-ADV message.
If the MS does not receive the MS ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message during a
predetermined time corresponding to the number of removable times of the MS ID
due to
different transmission synchronization points of the MOB-PAG-ADV message
communicated
between BSs, the MS may operate as follows. If the MS does not receive the MS
ID from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message although it repeatedly receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message
for a
predetermined number of times, the MS may determine that a problem has
occurred in idle-mode
operation. The MS may then perform a network registration procedure or a
location update
procedure. The above-mentioned predetermined number of times may be double
that of the
parameter setup value shown in the above Table 10, for example. Alternatively,
the above-
mentioned predetermined number of times may be determined to be another value
acquired when
a predetermined number of '1' is added to the parameter setup value shown in
the above Table 9
2 0 and the added result is doubled.
An exemplary MOB-PAG-ADV message according to the above third preferred
embodiment
is shown in the below Table 11.
[Table 11]
Syntax Size Notes
_ _
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
22
MOB-PAG-
ADV_Message_Format0{
Management Message Type=62 8 bits
Num_Paging_Group_IDs 8 bits Number of Paging Group IDs in this message
For (i=0;
i<Num_Paging_Group_IDs; i++)
Paging Group ID 8bits
0 : No omission of MS MAC Address hash
Omit MS MAC Address hash lbit 1 : Omission of MS MAC Address hash which
value of Action code is O.
Num_MACs 15 bits Number of MS MAC addresses
For (j=0; j<Num_MACs; j++) {
The hash is obtained by computing a CRC24 on
MS MAC Address hash 24bits the MS 48-bit MAC address. The polynomial
for
the calculation is Ox864CFB
Paging action instruction to MS
00=No Action Required
01=Perform Ranging to establish location and
Action Code 2bits
acknowledge message
10=Enter Network
11=reserved
Reserved 6 bits
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
23
TLV Encoded Information variable TLV specific
Reserved variable Padding bits to ensure octet aligned
According to the third preferred embodiment, flag information may indicate
whether
information associated with the MS required to maintain the idle mode is
removed from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message, such that the length of the MOB-PAG-ADV message may be
reduced
when there is an MS required to perform a location update procedure and a
network registration
procedure.
However, although the MS may maintain idle mode during transmission of a
plurality of
MOB-PAG-ADV messages in the above first and third preferred embodiments, the
MOB-PAG-
ADV message including IDs of all MSs (i.e., "Paging Type = 0" in Table 8 of
the first preferred
1 0 embodiment or "Omit MS MAC address hash = 0" in Table 11 of the third
preferred
embodiment), may be transmitted to the idle-mode MSs such that the MOB-PAG-ADV
message
controls the idle-mode MSs to update the availability of idle-mode operations.
An example of a parameter contained in the DREG-REQ message and the DREG-CMD
message is shown in the below Table 12.
[Table 12]
Name Type Length Value
MAC Hash
Maximum number of skipping MS MAC address hash in the
Skip
MOB-PAG-ADV message successively in case the MS shall
1
Threshold
maintain Idle Mode(i.e. Action code is 0, 'No Action Required').
The unit is the number of MOB-PAG-ADV transmission.
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
24
As shown in the above Table 12, a parameter indicative of the maximum number
of removable
times that the paging parameter removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message may be
included in
the DREG-REQ message and the DREG-CMD message is shown. The value shown in
Table 12
may indicate the maximum number of successively removable times of a
predetermined MS ID
removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message by the BS. If the MS receives the MOB-PAG-
ADV message having no MS ID, the above-mentioned parameters shown in Table 12
may be
used as a reference for the location update procedure.
According to the above fourth preferred embodiment, information related to the
MS switched
to the idle mode may be included in the DREG-REQ message shown in Table 12 in
order to
request the maximum number of successively removable times of an MS ID removed
from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message. In such case, the BS informs the MS switched to the idle
mode of the
maximum number of removable times of the MS ID removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV
message using the DREG-CMD message, as also shown in Table 12. Furthermore,
although the
MS receives the DREG-REQ message including no parameter indicative of the
maximum
number of removable times of the MS ID from the BS, the BS may include the
parameter (shown
in Table 12) indicative of the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID
in the DREG-
CMD message, and may transmit the DREG-CMD message including the above-
mentioned
parameter to the MS. The above-mentioned parameter indicative of the maximum
number of
removable times of the MS ID may be controlled by the BS or the paging
controller. BSs
contained in the same paging group may successively remove a corresponding MS
ID from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message within a predetermined time corresponding to the
determined value
(i.e., the maximum number of transmission times of the MOB-PAG-ADV message
having no MS
ID), as shown in the above Table 12.
In other words, BSs in the same paging group may set to the same value the
parameter (shown
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
in Table 12) associated with the maximum number of transmission times of the
MOB-PAG-ADV
message having no paging parameter. When the BS transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, the
BS must include the paging parameter associated with a corresponding MS one or
more times
before the determined value (i.e., the maximum number of transmission times of
the MOB-PAG-
5
ADV message having no paging parameter) shown in Table 12 is established.
Furthermore, if the
MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message including its own ID after being switched
to the idle
mode, the MS may update the availability of idle-mode operations without
performing additional
operations. If the MS successively receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message having no
MS ID
several times more than the predetermined number of times shown in Table 12,
it may perform
10
the location update procedure defined in the BS or the paging controller to
update the availability
of idle-mode operations.
The above-mentioned case in which the BS removes an ID of the MS in the idle
mode from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message may be available when an action code of a corresponding MS
commands the MS to continuously maintain the idle mode denoted by "No Action".
15
FIG. 2 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to an
embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 2, the MS transmits a DREG-CMD message to the BS for
switching to idle
mode (S201). After receiving the DREG-CMD message from the MS, the BS permits
the MS to
be switched to the idle mode (S202).
20
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S203). If the MOB-PAG-ADV message includes the MS ID (e.g., MAC
address
hash), that is, if the MOB-PAG-ADV message is determined to be a normal type
including the
MAC address hash of the MS, the MS performs an operation, such as an idle mode
maintenance
operation, a location update procedure, or a network registration operation,
associated with an
25
action code of the MOB-PAG-ADV message. In such case, the MS receives its own
ID (e.g.,
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
26
MAC address hash) and determines whether the idle mode is being normally
performed. If the
MS receives its own ID via the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS performs a network
registration procedure or a location update procedure, such that the MS may
update the
availability of idle-mode operations.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging time (S204). If the MOB-PAG-ADV message does not include the MS ID
(e.g., MAC
address hash), that is, if the MOB-PAG-ADV message is determined to be a
compressed type
having no MAC address hash equal to the MS ID, the MS determines that the
action code for
commanding successive maintenance of the idle mode has been received. In such
case, since the
MS does not receive its own ID (e.g., MAC address hash), the availability of
idle-mode
operations is not updated.
FIG. 3 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to another
embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 3, the MS transmits a DREG-REG message to the BS for
switching to idle
mode (S301). After receiving the DREG-REQ message from the MS, the BS permits
the MS to
be switched to the idle mode (S302). In such case, the BS transmits specific
information (e.g., a
predetermined number of 2) indicative of a predetermined number of removable
times related to
an idle-mode ID commonly used in the paging group to the MS.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S303). After receiving the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS
determines whether
it is normally operated in the idle mode on the basis of its ID contained in
the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, such that the MS may update the availability of idle-mode operations
accordingly.
The BS recognizes the number of removable times related to the ID of the
specific MS, and
determines whether the ID (e.g., MAC address hash) related to the specific MS
required to
maintain the idle mode is removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message at intervals of
a
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
27
predetermined paging cycle. If the MS ID is removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, the
number of removable times of the MS ID may be reduced by one.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S304). If the MS does not acquire its ID (e.g., MAC address
hash) from the MOB-
S PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the action code for commanding
idle-mode
maintenance has been received and maintains the idle mode. In such case, the
MS determines
whether a problem has occurred in the idle-mode operations =on the basis of
the number of
removable times of the MS ID received from the BS when the MS is switched to
the idle mode.
If the MS does not acquire its ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message during a
predetermined
time that is longer than a specific time corresponding to the number of
removable times of the
MS ID, the MS performs a network registration procedure or a location update
procedure in the
BS, such that the availability of idle-mode operation is updated. During the
above-mentioned
predetermined time, the MS may determine the presence or absence of the
availability of the idle
mode operation. For example, the predetermined time may be determined to be a
specific value
acquired when a predetermined number of ' 1 ' is added to the number of
removable times of the
MS ID and the added result is doubled.
If the MS must maintain the idle mode and the number of removable times of an
MS ID is
higher than a predetermined number of 1, the BS removes the MS ID (e.g., MAC
address hash)
from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, and reduces the number of removable times of the
MS ID
by one. The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined paging cycle (S305).
If the MS does not receive its ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message, the MS determines that the action code for commanding idle-mode
maintenance has
been received, such that it successively maintains the idle mode. In such
case, the MS determines
whether a problem has occurred in the idle-mode operation on the basis of the
number of
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
28
removable times of the MS ID received from the BS when the MS is switched to
the idle mode.
If the MS does not acquire its ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message during a
predetermined
time that is longer than a specific time corresponding to the number of
removable times of the
MS ID, the MS performs a network registration procedure or a location update
procedure in the
BS, such that the availability of idle-mode operation is updated. During the
above-mentioned
predetermined time, the MS may determine the presence or absence of the
availability of the idle
mode operation.
If the MS must maintain the idle mode and the number of removable times of an
MS ID is zero,
the BS includes the MS ID and an action code capable of commanding the idle
mode
maintenance in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, and then transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV
message
to the MS (S306). In such case, the BS updates the number of removable times
of the MS ID.
After receiving the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines whether the idle
mode is being
normally operated based on its own ID contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message,
such that the
MS updates the availability of idle-mode operations.
The BS transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV message to the MS, such that it commands the
MS to
perform a ranging process required for the MS location update procedure and
the availability
update procedure. If the MS performs the ranging process After receiving the
command for the
ranging process from the BS, the BS and the MS may update the number of
removable times of
the MS ID.
2 0
FIG. 4 is a detailed flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 3, according
to an
embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 4, the figure shows operations generated when the MS does
not receive its
own ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message until the number of omission times of the
MS ID
reaches the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID because the MS
moves from one
2 5 BS area to another BS area.
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
29
Referring again to FIG. 4, the MS transmits the DREG-REG message to a first BS
for
switching to idle mode (S401). After receiving the DREG-REQ message from the
MS, the first
BS permits the MS to be switched to the idle mode (S402). In such case, the
first BS transmits
specific information (e.g., a predetermined number of 2) indicative of the
number of removable
times of an idle-mode ID commonly used in the paging group to the MS.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the first BS at intervals of a
predetermined paging cycle (S403). The MS determines whether the idle mode is
being normally
operated based on its ID contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, such that the
availability of
idle-mode operations is updated.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the first BS at intervals of a
predetermined paging cycle (S404). If the MS does not acquire its ID (e.g.,
MAC address hash)
from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the action code for
commanding
idle-mode maintenance has been received and successively maintains the idle
mode.
If the MS moves from the first BS to the second BS, the MS may acquire a
downlink frame
synchronous signal associated with the second BS and receive the MOB-PAG-ADV
message
according to a paging cycle and a paging offset (S405). If the MS does not
receive its ID (e.g.,
MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the
action code
for commanding idle-mode maintenance has been received and maintains the idle
mode.
If the MOB-PAG-ADV message communicated between BSs has different transmission
2 0 synchronization points, the BSs may have different time points at which
the number of removable
times of the MS ID is updated (S406). Therefore, although a time point at
which the MS ID must
be included in the MOB-PAG-ADV message is established, the MS ID may not be
included in
the MOB-PAG-ADV message because the MS moves from one BS to another BS.
In such case, the MS determines whether a current time reaches a specific time
at which the
2 5 MS may determine the absence of the idle-mode operation availability.
The above-mentioned
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
specific time is determined to be a predetermined value acquired when a
predetermined number
of 1 is added to the number of removable times of the MS ID and the added
result is doubled. If
the specific time at which the absence of the idle-mode operation availability
is determined is not
established, the MS determines that the action code for commanding idle-mode
maintenance has
5
been received, such that the MS successively maintains the idle mode. If the
MS does not
acquire its ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message during a predetermined time during
which the
absence of the idle-mode operation availability may be determined, it performs
a network
registration procedure or a location update procedure in the BS, such that the
MS updates the
availability of idle-mode operation.
10
If the MS must maintain the idle mode and the number of removable times of the
MS ID is
zero, a second BS includes its ID and an action code capable of commanding the
idle mode
maintenance in the MOB-PAG-ADV message. The second BS then transmits the MOB-
PAG-
ADV message to the MS (S407). In such case, the BS updates the number of
removable times of
the MS ID. The MS determines whether the idle mode is being normally operated
based on its ID
15
contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, such that the MS updates the
availability of idle-
mode operations.
The above third preferred embodiment is provided to remove an ID of an MS
capable of
maintaining the idle mode from the MOB-PAG-ADV message although the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message includes information related to the MS maintaining the idle mode and
information
20
related to another MS for commanding a location update procedure and a network
registration
procedure.
FIG. 5 is a flow diagram illustrating a method of performing idle mode,
according to yet
another embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 5, the MS transmits the DREG-REG message to the BS for
switching to idle
25
mode (S501). After receiving the DREG-REQ message from the MS, the BS permits
the MS to
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
31
be switched to the idle mode (S502). The MS switched to the idle mode receives
the MOB-PAG-
ADV message from the BS at intervals of a predetermined paging cycle (S503).
In such case, if the MOB-PAG-ADV message includes all the MS IDs (e.g., MAC
address
hash), the MS maintains the idle mode according to an action code of the MOB-
PAG-ADV
message, performs a location update procedure, or performs a network
registration procedure.
Furthermore, the MS acquires its ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message, such that it is determined whether the MS is normally operated in the
idle mode. A
specific flag contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message may indicate whether the
MOB-PAG-
ADV includes all the MS IDs.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S504). If the MS receives specific information indicating that
an ID of the MS
required to maintain the idle mode is removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message
using the
above-mentioned specific flag, the ID of the MS required to maintain the idle
mode is not
included in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, and the MS does not acquire its ID (e.g.,
MAC
address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the action
code for
commanding successive maintenance of the idle mode has been received. In such
case, since the
MS does not receive its ID (e.g., MAC address hash), the availability of idle-
mode operations is
not updated. If the MS does not acquire its ID from the MOB-PAG-ADV message
including all
MS IDs after receiving the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS performs a network
registration
procedure or a location update procedure in the BS, such that the MS may
update the availability
of idle-mode operations.
FIG. 6 is a first flow diagram illustrating a method for performing idle mode,
according to still
another embodiment of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 6, the figure shows operations generated when the BS manages
the
maximum number of removable times of the MS ID. The MS transmits the DREG-REG
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
32
message to the BS for switching to idle mode (S601). In such case, the maximum
number of
transmission times of the MOB-PAG-ADV message having no MS ID may be included
in the
DREG-REQ message, and the MS may transmit the DREG-REQ message to the BS
(S601).
After receiving the DREG-REQ message from the MS, the BS permits the MS to be
switched to
the idle mode (S602). In such case, the DREG-CMD message includes information
(e.g., a
predetermined number of 4) indicative of the maximum number of transmission
times of the
MOB-PAG-ADV message having no MS ID. Although the BS may receive the DREG-REQ
message without a parameter to indicate of the maximum number of removable
times of the MS
ID, the BS may include a parameter indicative of the maximum number of
transmission times of
the MOB-PAG-ADV message having no MS ID in the DREG-CMD message. The parameter
indicative of the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID may be
managed by the BS
or the paging controller in a single paging group. The maximum number of
transmission times of
the MOB-PAG-ADV message having no MS ID is commonly used in the paging group.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S603). After receiving the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS
determines whether
the idle mode is being normally operated based on its ID contained in the MOB-
PAG-ADV
message, such that the MS updates the availability of idle-mode operations.
The BS may recognize the maximum number of removable times of an ID of a
specific MS,
and may determine whether the ID (e.g., MAC address hash) of the specific MS
required to
maintain the idle mode is removed from the MOB-PAG-ADV message at intervals of
a
predetermined paging cycle.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S604). If the MS does not acquire its ID (e.g., MAC address
hash) from the MOB-
PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the action code for commanding idle-
mode
maintenance has been received. In such case, the MS determines whether a
problem has occurred
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
33
in the idle-mode operations on the basis of the maximum number of removable
times of the MS
ID received from the BS when the MS is switched to the idle mode. If the
number of reception
times of the MS ID, which was not successively received from the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, is
equal to or less than the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID, the
MS
continuously maintains the idle mode.
If the MS must maintain the idle mode and an MS ID is successively removed
from the MOB-
PAG-ADV message within a predetermined time corresponding to the maximum
number of
removable times of the MS ID, the MS ID (e.g., MAC address hash) may be
removed from the
MOB-PAG-ADV message. The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at
intervals of a predetermined paging cycle (S605).
If the MS does not receive its ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message, the MS determines that the action code for commanding idle-mode
maintenance has
been received, such that the MS successively maintains the idle mode. In such
case, the MS
determines whether a problem has occurred in the idle-mode operation on the
basis of the
maximum number of removable times of the MS ID received from the BS when the
MS is
switched to the idle mode. If the number of successive reception times of the
MS ID received
from the MOB-PAG-ADV message is equal to or less than the maximum number of
removable
times of the MS ID, the MS continuously maintains the idle mode.
In association with the MS required to maintain the idle mode, the BS includes
the MS ID and
an action code capable of commanding the idle mode maintenance in the MOB-PAG-
ADV
message within a predetermined time corresponding to the maximum number of
removable times
of the MS ID, and transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV message including the MS ID and
the action
code (S606). In such case, the BS or the paging controller updates the maximum
number of
removable times of the MS ID. The MS determines whether the idle mode is being
normally
operated based on its own ID contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, such that
the MS
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
34
updates the availability of idle-mode operations.
The BS transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV message to the MS, such that it commands the
MS to
perform a ranging process required for the MS location update procedure and
the availability
update procedure. If the MS performs the ranging process After receiving the
command for the
ranging process from the BS, the BS and the MS may update the number of
removable times of
the MS ID.
. FIG. 7 is a second flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 6, according
to an embodiment
of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 7, the figure shows a variety of operations generated when
the MS receives
the MOB-PAG-ADV message without an MS ID, several times more than the maximum
number
of transmission times of the MOB-PAG-ADV message.
The MS transmits the DREG-REG message to the BS for switching to idle mode
(S701). After
receiving the DREG-REQ message from the MS, the BS permits the MS to be
switched to the
idle mode (S702). In such case, the BS transmits specific information (e.g., a
predetermined
number of 4) indicative of the number of removable times of an idle-mode ID
commonly used in
the paging group to the MS.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S703). The MS determines whether it is normally operated in the
idle mode on the
basis of its ID contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, such that the MS updates
the
2 0 availability of idle-mode operations.
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle at steps S704 - S706. If the MS does not receive its ID (e.g.,
MAC address hash)
from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that the action code for
commanding
idle-mode maintenance has been received. In such case, the MS determines
whether a problem
2 5 has occurred in the idle-mode operations on the basis of the maximum
number of removable
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
times of the MS ID received from the BS when the MS is switched to the idle
mode. If the
number of reception times of the MS ID which was not successively received
from the MOB-
PAG-ADV message, is equal to or less than the maximum number of removable
times of the MS
ID, the MS continuously maintains the idle mode.
5
The MS receives the MOB-PAG-ADV message from the BS at intervals of a
predetermined
paging cycle (S707). If the MS does not receive its ID (e.g., MAC address
hash) from the MOB-
PAG-ADV message at least a predetermined number of times, the MS compares the
predetermined number of reception times of the MS ID with the maximum number
of removable
times of the MS ID. If the MS does not successively receive the MS ID from the
MOB-PAG-
10
ADV message at least the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID, it
may determine
that there is no availability in the idle mode operation. In such case, the MS
performs a location
update procedure in the BS or the paging controller, such that the MS may
update the availability
of idle-mode operations. The MS transmits a ranging request to the BS to
perform a location
update procedure (S708). After receiving the ranging request from the MS, the
BS updates
15
position information related to the MS, and transmits a ranging response to
the MS, such that the
MS updates the availability of idle-mode operations (S709).
FIG. 8 is a third flow diagram illustrating the method of FIG. 6, according to
an embodiment
of the present invention.
Referring to FIG. 8 shows a variety of operations generated when the maximum
number of
20
removable times of the MS M is controlled by the paging controller. The MS
transmits the
DREG-REQ message to the BS for switching to idle mode. A parameter indicative
of the
maximum number (e.g., a parameter indicative of a MAC hash omission limitation
value) of
removable times of the MS ID may be included in the DREG-REQ message. The DREG-
REQ
message including the parameter is then transmitted to the BS (S801). The
above-mentioned
25
parameter indicative of the maximum number of removable times of the MS ID is
shown in the
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
36
above Table 12.
If the BS receives an idle mode switching request contained in the DREG-REQ
message from
the MS, the BS transmits an idle-mode information request (e.g., Idle-Info-
REQ) message, shown
in the below Table 13 to the paging controller to indicate a specific status
in which the MS is
switched to the idle mode.
An exemplary Idle-Info-REQ message is shown in the below Table 13.
[Table 13]
Field Size otes
Idle-Info-REQ message format0{
Global Message Header 12 bits
For(i----0;i<Num Records;i++){
MS MAC Address 48 bits
0000 :Idle Mode Initiation Request
0001:DL Traffic has arrived to MS
0010:MS session information
Action Code 4 bits 0011:MS re-entry complete
0100:MS has transitioned to another paging group
0101:Location Update requested
0101-1111:reserved
Reserved 4 bits
TLV encoded information variable
Security Field TBD A means to authenticate this message
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993 PCT/KR2005/003252
37
As shown in the above Table 13, the Idle-Info-REQ message includes a MAC
address of an
MS for transmitting a request to switch to the idle mode, and a MAC hash
omission limitation
TLV value (shown in Table 12) received from the MS.
After receiving the Idle-Info-REQ message, the paging controller transmits an
Idle-Info-RSP
message to the BS having transmitted the Idle-Info-REQ message (S803). An
exemplary Idle-
Info-RSP message is shown in the below Table 14.
[Table 14]
Field Size Notes
Idle-Info-RSP message format()
Global Message Header 152 bits
For(i=0; i<Num Records;i++)
MS MAC Address 48 bits
0000:MS enters Idle Mode
0001:MS exits Idle Mode
0010:MS session information
Action Code 4 bits 0011:Deliver DL Traffic to Current
Attachment BS
0100: Location Update Success
0101: Location Update Failure
0110-1111:reserved
Reserved 4 bits
TLV encoded information Variable
Security Field TBD A means to authenticate this message
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
38
As shown in the above Table 14, the Idle-Info-RSP message includes a MAC
address of a
terminal switched to the idle mode, and a MAC hash omission limitation TLV
value (shown in
Table 12). Also, although the paging controller receives the Idle-Info-REQ
message without a
parameter indicative of the MAC hash omission limitation value, the parameter
indicative of the
MAC hash omission limitation value may be included in the Idle-Info-RSP
message, such that
the Idle-Info-RSP message may be transmitted to the BS. If the BS receives the
Idle-Info-RSP
message, the BS transmits the DREG-CMD message to the MS having transmitted
the idle mode
switching request, such that the MS is switched to the idle mode according to
the DREG-CMD
message at step S804. In such case, the DREG-CMD message includes information
for
commanding the MS to be switched to the idle mode, paging information TLV
(e.g., a paging
cycle, a paging offset, and a paging group ID), a paging controller ID TLV, an
idle mode
maintenance information TLV, and a MAC hash omission limitation TLV value.
The paging controller transmits a Paging-Announcement message to a BS that
permitted the
MS to be switched to the idle mode. The Paging-Announcement message is also
transmitted to
the other BSs in the same paging group as that of the BS (S805), such that the
above-mentioned
BSs are able to transmit the MOB-PAG-ADV message capable of commanding the MS
to
perform a specific operation during the next paging interval. In such case, in
association with a
specific MS required to maintain the idle mode according to the MAC hash
omission limitation
value, the paging controller informs the BS of specific information indicating
whether the MAC
2 0 hash address is contained in the MOB-PAG-ADV message transmitted from
the BS to a plurality
of MSs. In other words, the paging controller does not include a MAC address
and an action
code of a corresponding MS in the Paging-announcement message. The paging
controller
includes a MAC address and an action code "No action Required" of the
corresponding MS in
the Paging-Announcement message in order to include the MAC address of the MS
in the MOB-
2 5 PAG-ADV message, and transmits the Paging-Announcement message to BSs
contained in the
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
39
paging group. If the MAC address of the MAC is removed from the Paging-
Announcement
message, the paging controller subtracts a predetermined number of 1 from the
MAC hash
omission limitation value associated with the MS. Otherwise, if the MAC
address of the MAC is
included in the Paging-Announcement message, the paging controller updates or
resets the MAC
hash omission limitation value.
An exemplary Paging-Announcement message is shown in the below Table 15.
[Table 15]
Field Size Notes
Paging-announce message format()
Global Message Header 152 bits
For(i=0;i<Num Records;i++){
MS MAC Address 48 bits
0000:MS shall be paged to re-enter network
0001:MS shall be paged to perform ranging
Action Code 4 bits
0010:MS needs no action required
0011-1111:reserved
Reserved 4 bits
Security Field TBD A means to authenticate this message
If the BS receives the Paging-Announcement message from the paging controller,
the BS
transmits the MOB-PAG-ADV message to the MS at intervals of a predetermined
paging cycle.
If the MS receives its ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV
message, it is
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
determined that the MS is normally operated in the idle mode. Therefore, the
MS updates the
availability of idle-mode operations, and updates the MAC hash omission
limitation value (S806).
The paging controller may remove the MAC address and action code of the MS
from the
Paging-Announcement message within a predetermined time during which the MAC
hash
5 omission limitation value does not reach a predetermined value of 0, and
may transmit the
resultant Paging-Announcement message to BSs (S807). In such case, the paging
controller
subtracts a predetermined number of 1 from the MAC hash omission limitation
value associated
with the MS having no MAC address.
If a current time reaches a predetermined paging time, the BS includes a MAC
address and an
1 0 action code of a corresponding MS, the MAC address and the action code
of which have been
included in the Paging-Announcement message received from the paging
controller, in the MOB-
PAG-ADV message. The BS configures the MOB-PAG-ADV message in the form of
broadcast
information, and then transmits the resultant MOB-PAG-ADV message. The MS
receives the
MOB-PAG-ADV message at intervals of a predetermined cycle. If the MAC address
of the MS
15 is not included in the MOB-PAG-ADV message, the MS determines that an
action code for
commanding idle mode maintenance has been received. In such case, the MS
determines
whether a problem has occurred in the idle-mode operations on the basis of the
MAC hash
omission limitation value received from the BS when the MS is switched to the
idle mode. If the
number of reception times of the MS ID, which was not successively received
from the MOB-
20 PAG-ADV message, is equal to or less than the MAC hash omission
limitation value, the MS
continuously maintains the idle mode (S808).
The paging controller may remove the MAC address and the action code of the MS
from the
Paging-Announcement message within a predetermined time corresponding to the
MAC hash
omission limitation value, and transmits the resultant Paging-Announcement
message to the BS
25 (S809).
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
41
After receiving the resultant Paging-Announcement message from the paging
controller, the
BS configures the MOB-PAG-ADV message, which was established by the Paging-
Announcement message, in the form of broadcast information, and then transmits
the resultant
MOB-PAG-ADV message at intervals of a predetermined paging cycle. Also, if the
number of
reception times of the MS ID, which was not successively received from the MOB-
PAG-ADV
message, is equal to or less than the MAC hash omission limitation value, the
MS continuously
maintains the idle mode (S810).
The paging controller transmits the Paging-Announcement message, including the
MAC
address and the action code (e.g., denoted by "No Action Required") of the MS
required to
maintain the idle mode, to BSs, such that the MAC hash omission limitation
value is updated.
The paging controller initializes the MAC hash omission limitation value to a
predetermined
value (e.g., a predetermined number of 4) (S811).
The BS configures the MOB-PAG-ADV message established by the Paging-
Announcement
message in the form of broadcast information, and transmits the resultant MOB-
PAG-ADV
message at intervals of a predetermined paging cycle. If the MS receives its
ID (e.g., MAC
address hash) from the MOB-PAG-ADV message, it is determined that the MS is
normally
operated in the idle mode, such that the availability of idle-mode operations
is updated, and the
MAC hash omission limitation value is updated (S812).
If the MS does not successively receive its ID (e.g., MAC address hash) from
the MOB-PAG-
ADV message until reaching a predetermined time corresponding to the MAC hash
omission
limitation value, the MS determines that there is no availability in the idle-
mode operations. In
such case, the MS performs a location update procedure in the paging
controller using a ranging
process, such that it may update the availability of idle-mode operations. The
MS transmits a
ranging request message to the BS to perform the location update procedure. In
such case, the
MS includes a paging controller ID and an indicator parameter indicative of
the location update
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
42
procedure in the ranging request message. After receiving the ranging request
message for the
location update procedure from the MS, the BS transmits the Idle-Info-REQ
message including a
MAC address and location update action code of a corresponding MS to the
paging controller.
The paging controller performs the location update procedure for the
corresponding MS, such
that the availability of the MS and the MAC hash omission limitation value are
updated. After
performing the above-mentioned location update procedure, the paging
controller informs the BS
of the location update result using the Idle-Info-RSP message, and transmits a
ranging response
message to the MS, such that the availability of idle-mode operations of the
MS is updated.
In one embodiment, a method for controlling an idle mode in a mobile station
comprises
transmitting an idle mode request message to a serving base station to enter
the idle mode. The
method also comprises determining whether a skip threshold parameter has been
exceeded, the
skip threshold parameter associated with a number of paging intervals to pass
before receiving a
paging message with a mobile station identifier of the mobile station. The
method also comprises
transmitting a location update request to a base station if the skip threshold
parameter has been
exceeded, the location update request configured to update the location of the
mobile terminal
with respect to the base station.
The method may further comprise transmitting a skip threshold request
parameter from the
mobile station and receiving the skip threshold parameter in response to the
transmitting of the
skip threshold request parameter. The method may further comprise
reinitializing the step of
2 0 determining whether the skip threshold parameter has been exceeded in
response to receiving the
paging message with a mobile station identifier of the mobile station. The
method may further
comprise receiving a paging message without a mobile station identifier of the
mobile station
from at least one base station within a paging group when there is no downlink
traffic for the
mobile station. The method may further comprise receiving a paging message
without the mobile
station identifier of the mobile station from at least one base station within
a paging group when
CA 02584322 2007-04-17
WO 2006/070993
PCT/KR2005/003252
43
there is no location update request.
The skip threshold parameter may comprise at least one of a MAC (Medium Access
Control)
address hash, an action code, and a TLV (type length value) parameter for a
paging operation.
The paging message with a mobile station identifier of the mobile station may
be a paging
advertisement message.
In another embodiment, a method for controlling an idle mode of a mobile
station in a network
comprises receiving an idle mode request message from the mobile station to
enter the idle mode.
The method also comprises receiving a skip threshold request parameter from
the mobile station.
The method also comprises transmitting a skip threshold parameter in response
to the receiving
of the skip threshold request parameter, the skip threshold parameter
associated with a number of
paging intervals to pass before the mobile station receives a paging message
with a mobile station
identifier of the mobile station. The method also comprises receiving a
location update request
from the mobile station if the skip threshold parameter is exceeded, the
location update request
configured to update the location of the mobile terminal.
The method may further comprise transmitting a paging message without a mobile
station
.identifier of the mobile station to the mobile station when there is no
downlink traffic for the
mobile station and receiving the packet data from the base station, wherein at
least two of
retransmitted packet data are transmitted from different antennas of the base
station. The
retransmitted packet data are received with information element comprising a
retransmission
count associated with a number of retransmission made by the base station.
The method may further comprise transmitting a paging message without a mobile
station
identifier of the mobile station to the mobile station when there is no
location update request
received from the mobile station. The network may comprise at least one of a
base station and a
paging controller, the paging controller configured to control paging of base
stations within a
paging group.
CA 02584322 2013-02-13
74420-177
44
The present invention provides for performing an idle mode in a wireless
access system to
reduce the length of a message for providing information that indicates
whether an idle mode is
maintained. Downlink wireless resources may thus be more efficiently used, and
power
consumption by the idle mode MS that processes the message may be reduced.
=
It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and
variations may be
made to the embodiments described herein. Thus,
it is intended that the present invention covers the modifications and
variations of this invention
provided they come within the scope of the appended claims and their
equivalents.
INDERSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
The present invention can be applied to a broadband wireless access system.