Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
1
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS
The present invention relates to sulphonamide derivatives, to their use as
medicaments
(for example in the treatment of an inflammatory disease state), to
pharmaceutical
compositions comprising them and to processes for preparing them.
Sulphonamide derivatives are disclosed as anti-inflammatories in WO
2004/019935
and WO 2004/050631. Pharmaceutically active sulphonamides are also disclosed
in Arch.
Pharm. (1980) 313 166-173, J.Med. Chem. (2003) 46 64-73, J. Med. Chem (1997)
40 996-
1004, EP 0031954, EP 1190710 (WO 200124786), US 5861401, US 4948809, US3992441
and WO 99/33786.
It is known that certain non-steroidal compounds interact with the
glucocorticoid
receptor (GR) and, as a result of this interaction, produce a suppression of
inflammation (see,
for example, US6323199). Such compounds can show a clear dissociation between
anti-
inflammatory and metabolic actions making them superior to earlier reported
steroidal and
non-steroidal glucocorticoids. The present invention provides further non-
steroidal
compounds as modulators (for example agonists, antagonists, partial agonists
or partial
antagonists) of the glucocorticoid receptor capable of having a dissociation
between their
anti-inflammatory and metabolic actions.
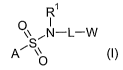
The present invention provides a compound of formula (I):
R~
~S !
,N-LW ~!)
A' ~O
wherein:
A is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, pyrazolyl,
benzthienyl, quinolinyl
or isoquinolinyl, and A is optionally substituted by halo, Ci_6 alkyl, Ci_6
alkoxy, C1_4
alkylthio, Cr_4 fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy, pyridinyloxy, benzyloxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)N(CI_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4
alkyl),
NR10Rll, phenoxy (optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, Cl_6 alkoxy,
C1_4 alkylthio, C14
fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(CI_4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)Z, NHC(O)(CI_4 alkyl) or NR14R"), phenyl
(optionally
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
2
substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 allcylthio, Ci_4
fluoroalkyl, Cl_4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2,.C(O)(C1_4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(CI_4 alkyl),
C(O)N(C1_4
allcyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NR16R17), pyridinyloxy (optionally substituted
by halo, C1_6
alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, C1_4 fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(Ci_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1_~ alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)zNH(C1_4 allcyl),
S(O)2N(C1_4 allcyl)2,
C(O)(C1_4 allcyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 allcyl), C(O)N(C1_4
alkyl)2, NHC(O)(Cl_
4 alkyl) or NR1sR19) or pyrazolyl(optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4
alkylthio, C1_4 fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)aH,
C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 allcyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4
alkyl) or
NRzoR2i);
Rio, Rll, R1a a Rls> R16 > R17 > R18, R19, R20 and Ral are, independently,
hydrogen, Cr_4 alkyl or
C3_7 cycloalkyl;
Rl is hydrogen, C1_6 alkyl, phenyl, pyridinylC(O), C3_6 cycloalkyl, (C3_6
cycloalkyl)CH2 or C3_
4 alkenyl;
L is a bond, C1_4 alkylene (optionally substituted by C1_4 allcyl or C1_4
haloalkyl), C1_4
alkylene-NH (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl),
CH2C(O)NH,
CH(CH3)C(O)NH, C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally substituted by Ci_4 alkyl or C1.4
haloalkyl), Ci_
4 alkylene-S (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl), C1_4
alkylene-S(O)
(optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl) or C1_4 alkylene-
S(O)a (optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl);
W is cyclohexyl, phenyl, methylenedioxyphenyl, thienyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl,
isoxazolyl,
pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazinyl, 1,2,3-
triazinyl, 1,2,4-triazinyl,
benzofuranyl, benzthienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, dihydroindolinyl, indazolyl,
benzimidazolyl,
benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
quinoxalinyl,
quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, [1,8]-naphthiridinyl, [1,6]-
naphthiridinyl, quinolin-
2(1H)-onyl, isoquinolin-1(2H)-onyl, phthalazin-1(2H)-onyl, 1H-indazolyl, 1,3-
dihydro-2H-
indol-2-onyl, isoindolin-l-onyl, 3,4-dihydro-lH-isochromen-l-onyl or 1H-
isochromen-l-
onyl;
W is optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio,
C1_4 fluoroalkyl, Cl_
4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, OH, C(O)ZH, C(O)2(Cl_4 alkyl), S(O)2(Cr_4
alkyl), S(O)2NH2,
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
3
S(O)2NH(C1-~ alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy, imidazolyl, C(O)(C1-4
allcyl), C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(Cl-4 allcyl), C(O)N(C1-4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl) or NR12R13;
R12 and R13 are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3-7 cycloalkyl;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Compounds of of formula (I) can exist in different isomeric forms (such as
enantiomers, diastereomers, geometric isomers or tautomers). The present
invention covers all
such isomers and mixtures thereof in all proportions.
Suitable salts include acid addition salts such as a hydrochloride,
hydrobromide,
phosphate, acetate, fumarate, maleate, tartrate, citrate, oxalate,
methanesulphonate, p-
toluenesulphonate, succinate, glutarate or malonate.
The compounds of formula (I) may exist as solvates (such as hydrates) and the
present
invention covers all such solvates.
Alkyl groups and moieties are straight or branched chain and are, for example,
methyl,
ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl or tert-butyl.
Haloalkyl comprises, for example, 1 to 6, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 halogen
(such as
fluorine or chlorine) atoms. It is, for example, CHF2, CF3, CH2CF3, C2F5 or
CH2C1.
Haloalkoxy comprises, for example, 1 to 6, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 halogen
(such as fluorine or
chlorine) atoms. It is, for example, OCHF2, OCF3, OCH2CF3, OC2F5 or OCH2C1.
Fluoroalkyl comprises, for example, 1 to 6, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluorine
atoms. It is,
for example, CHF2, CF3, CH2CF3 or C2F5. Fluoroalkoxy comprises, for example, 1
to 6, such
as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 fluorine atoms. It is, for example, OCHF2, OCF3, OCH2CF3 or
OC2F5.
Cycloalkyl is for example, cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl.
In one particular aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I),
wherein A is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, thienyl, quinolinyl or
isoquinolinyl, and A is
optionally substituted by halo, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, C1-4 alkylthio, CF3,
OCF3,
pyridinyloxy, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1-4
alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)Z, C(O)(C1-4 alkyl), C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(C1-4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1-4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl), NR10Rll, phenoxy
(optionally
substituted by halo, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, C1-4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(Ci-4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(CI-
4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1-4 allcyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 allcyl), C(O)N(Cl-4
alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-
4 alkyl) or NR14R15) or phenyl (optionally substituted by halo, Ci-6 alkyl, C1-
6 alkoxy, C1-4
alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1-4
alkyl), S(O)2NH2,
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
4
S(O)2NH(C1_4 allcyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1_4 allcyl), benzyloxy,
C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(Cl_4 allcyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NR16R17); RI ,
Ril, Ri4, Rls,
R16 and R17 are, independently, liydrogen, C1_4 allcyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; R'
is hydrogen, C1_6
alkyl, phenyl, pyridylC(O), C3_6 cycloallcyl, (C3_6 cycloalkyl)CH2 or C3_4
alkenyl; L is a bond,
C1_4 alkylene (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl), C1_4 alkylene-NH
(optionally substituted
by CI-4 alkyl), CH2C(O)NH, CH(CH3)C(O)NH, CI-4 alkylene-O (optionally
substituted by C1_
4 alkyl); C1_4 alkylene-S (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl); C1_4
allcylene-S(O) (optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl); C1_4 alkylene-S(O)2 (optionally substituted by
C1_4 alkyl); W is
phenyl, methylenedioxyphenyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl,
pyridazinyl,
pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazinyl, 1,2,3-triazinyl, 1,2,4-triazinyl, benzofuranyl,
benzthienyl, indolyl,
indolinyl, dihydroindolinyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl,
quinolinyl,
tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl,
phthalazinyl,
[1,8]-naphthiridinyl or [1,6]-naphthiridinyl; W is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl, Cl_
6 alkoxy, Cl-4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(Ci_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy, C(O)(Ci_4
alkyl), C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 allcyl) or NR12RI3; R12
and R13 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
thereof; for use as a medicament.
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I),
wherein A
is phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl, and A is optionally
substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy, CI-4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, phenoxy (optionally
substituted by
halo or C14 alkyl), phenyl (optionally substituted by halo or CI-4 alkyl),
pyridinyloxy,
benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, S(O)2NH2, C(O)(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(C1_4
alkyl) or
NR10Rll; Rl0 and R11 are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7
cycloalkyl; R' is
hydrogen, CI_6 alkyl, phenyl, pyridylC(O), cyclohexyl, cyclohexylCH2 or C3_4
alkenyl; L is a
bond, C1_4 alkylene (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl), CI-4 alkylene-NH
(optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl), CH2C(O)NH or C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally
substituted by C1_4
alkyl); W is phenyl, benzofuranyl, indolyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, thiazolyl,
pyridyl,
isoxazolyl, pyrimidinyl or 1,3,5-triazinyl, and W is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, S(O)2NH2a
C(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NR12R13; R12 and R13 are, independently,
hydrogen, C1_4
alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; for
use as a
medicament.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein:
A is phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl, and A is
optionally substituted by
halo (such as fluoro, chloro or bromo), C1_6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, nitro,
phenoxy (optionally
substituted by C1.4 alkyl), phenyl (optionally substituted by halo (such as
fluoro)),
pyridinyloxy or N(C1.4 alkyl)2; R' is hydrogen, C1_6 alkyl, phenyl,
pyridylC(O), cyclohexyl,
cyclohexylCH2 or C34 alkenyl, L is a bond, C1.4 allcylene (optionally
substituted by C1_4
alkyl), C1-4 alkylene-NH (optionally substituted by CI-4 alkyl), CH2C(O)NH or
C1_4 allcylene-
O(optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl); W is phenyl, benzofuranyl, indolyl,
tetrahydroquinolinyl, thiazolyl, pyridyl, isoxazolyl, pyrimidinyl or 1,3,5-
triazinyl, and W is
optionally substituted by halo (such as chloro or bromo), C1-6 alkyl, C1_6
alkoxy, C(O)(C1_4
alkyl), S(O)2NH2, NO2, C02(C1-4 alkyl) or N(C1.4 alkyl)2; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable
salt thereof; for use as a medicament.
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of fonnula (I)
wherein A
is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, thienyl, quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl, and A is
optionally
substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl, Ci.6 alkoxy, Ci.4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3,
pyridinyloxy,
benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1-4 allcyl),
S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1.4 alkyl)2a C(O)(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-
4 alkyl),
C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl), NR10Rll, phenoxy (optionally
substituted by halo,
C1.6 alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(Ci_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2a S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1.4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl)
or
NR14R15) or phenyl (optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 all{Y1, C1.6 alkoxy,
CI-4 alkylthio, CF3,
OCF3, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(C1_4
alkyl), S(O)2N(C1.4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1.4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4
alkyl),
C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1.4 alkyl) or NR16R17); R1o,,R1', R'4 , R15, R'6
and R17 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1-4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; R' is hydrogen, C1.6
allcyl, phenyl,
pyridylC(O), C3.6 cycloalkyl, (C3.6 cycloalkyl)CH2 or C34 alkenyl; L is a
bond, CI-4 allcylene
(optionally substituted by CI-4 alkyl), C1_4 alkylene-NH (optionally
substituted by C1.4 alkyl),
CHaC(O)NH, CH(CH3)C(O)NH, C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally substituted by C1.4
alkyl); CI-4
alkylene-S (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl); C1_4 alkylene-S(O)
(optionally substituted by
C1_4 allryl); C1_4 allcylene-S(O)2 (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl); W
is phenyl,
methylenedioxyphenyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridyl, pyrimidinyl,
pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl,
1,3,5-triazinyl, 1,2,3-triazinyl, 1,2,4-triazinyl, benzofuranyl, benzthienyl,
indolyl, indolinyl,
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
6
dihydroindolinyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl,
tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl,
phthalazinyl,
[1,8]-naphthiridinyl or [1,6]-naphthiridinyl; W is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_
6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, nitro, cyano, C(O)ZH, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy, C(O)(Ci_4
alkyl), C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) orNRIZR13; Rla and
R13 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
thereof.
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein:
A is phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, quinolinyl or isoquinolinyl, and A is
optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, phenoxy (optionally
substituted by
halo or Cl_4 alkyl), phenyl (optionally substituted by halo or Cl_4 alkyl),
pyridinyloxy,
benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, S(O)2NH2, C(O)(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(C1_4
alkyl) or
NR10R11; Rl0 and Rll are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7
cycloalkyl; R' is
hydrogen, C1_6 alkyl, phenyl, pyridylC(O), cyclohexyl, cyclohexylCH2 or C3_4
alkenyl; L is a
bond, C1_4 alkylene (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl), Cl-4 alkylene-NH
(optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl), CH2C(O)NH or C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally
substituted by C1_4
alkyl); W is phenyl, benzofuranyl, indolyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, thiazolyl,
pyridyl,
isoxazolyl, pyrimidinyl or 1,3,5-triazinyl, and W is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1_6 alkoxy, C1-4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, S(O)2NH2a
C(O)(C14 alkyl),
C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NR12R13; R 12 and R13 are, independently,
hydrogen, C1_4
alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl, C1_4 alkoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl,
Cl-4 haloalkyl, C1-4
alkoxy or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl,
C1_4 haloalkyl or
phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, Cl-4 haloalkyl,
C1_4 alkoxy or Ci_4
haloalkoxy)).
In another aspect the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein L
is C3
alkylene (substituted by C14 alkyl or Cl-4 haloalkyl), C2_4 allcylene-NH
(substituted by C1.4
alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl), CH2C(O)NH, CH(CH3)C(O)NH, C24 allcylene-O
(substituted by C1_4
alkyl or Cl-4 haloalkyl), CZ_~ alkylene-S (substituted by C1_~ alkyl or C1_4
haloalkyl), C2_4
alkylene-S(O) (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl or CI_4 haloalkyl) or C24
alkylene-S(O)a
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
7
(optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl); wherein C1_4 allcyl
is, for example,
methyl or ethyl; and C1_4 haloalkyl is, for example, CF3.
In yet another aspect the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein
L is
C3 alkylene (substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloallcyl), C2_4 alkylene-NH
(substituted by C1_4
alkyl or C14 haloallcyl) or C24 allcylene-O (substituted by C1-4 alkyl or C1_4
haloalkyl);
wherein C1_4 alkyl is, for example, methyl or ethyl; and C14 haloalkyl is, for
exainple, CF3.
In a further aspect the invention provides a compound of formula (I) wherein L
is C3
alkylene (substituted by C1-4 alkyl), C2 alkylene-NH (substituted by C1_4
allcyl) or C2 alkylene-
O(substituted by C1_4 alkyl); wherein C1_4 allcyl is, for example, methyl or
ethyl. L is, for
example, C2 allcylene-NH (substituted by C1_4 alkyl). L is, for example, C2
alkylene-0
(substituted by Cr_4 alkyl).
In a still further aspect the invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein L is
CH(CH3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration), CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-
configuration), CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2CH2
(such as
in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2NH (such as in the S-configuration),
CH(C2H5)CH2O
(such as in the S-configuration) or CH(CF3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-
configuration).
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein L
is CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-configuration) or it provides a compound of
formula (I)
wherein L is CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration).
In yet another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein W is phenyl, pyridyl, indolyl (for example indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl,
indol-6-yl or indol-
7-yl), indazolyl (for example indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl or
indazol-7-yl),
quinolinyl (for example quinolin-5-yl) or isoquinolinyl (for example
isoquinolin-5-yl).
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein
W is indolyl (for example indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl),
indazolyl (for
example indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl or indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl
(for example
quinolin-5-yl) or isoquinolinyl (for example isoquinolin-5-yl).
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein W is indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl, indol-7-yl, indazol-4-yl,
indazol-5-yl, indazol-
6-yl, indazol-7-yl, quinolin-5-yl or isoquinolin-5-yl.
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein W
is indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl, indazol-7-yl or quinolin-5-yl.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
8
In yet anotlier aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein W is optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 allcyl, CF3, C1_4
allcoxy, OCF3, phenyl
(itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, CF3, C1_4 alkoxy or
OCF3) or C(O)NH2.
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein
L is CI_4 alkylene (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl) or C1_4 alkylene-O
(optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl); for example L is CH(CH3)CH2O, CH2CH2O,
CH(CH3)(CH2)2 or
(CH2)3=
In another aspect of the invention L is C1_4 alkylene (optionally substituted
by C1_4
alkyl) or C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl).
In yet anotller aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein Rl is hydrogen.
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein W is methylenedioxyphenyl, benzofuranyl, benzthienyl, indolyl,
indolinyl,
dihydroindolinyl, benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl,
tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl,
phthalazinyl,
[1,8]-naphthiridinyl or [1,6]-naphthiridinyl, optionally substituted as
defined above. In
another aspect of the invention W is linked to L by a ring-carbon in the
benzene ring part of
its structure (see for example, Example 77, 78, 79, 80 or 83).
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein: A is phenyl, naphthyl or thienyl, and A is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1_6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, CF3, OCF3, phenoxy (optionally substituted by
halo or C1_4 alkyl),
phenyl (optionally substituted by halo or C1_4 alkyl), pyridinyloxy,
benzyloxy, nitro, cyano,
S(O)2NH2, C(O)(Cl_4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(Cl_4 allcyl) or NR10Rll; RI0 and
Rl l are,
independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; Rl is hydrogen; L is
C1_4 alkylene
(optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl) or C1_4 alkylene-O (optionally
substituted by C1_4 alkyl);
W is phenyl optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, Cl_6 alkoxy, C1_4
alkylthio, CF3, OCF3,
benzyloxy, nitro, cyano, S(O)2NH2, C(O)(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, NHC(O)(Cl_4
alkyl) or
NR1aR13; R12 and R13 are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7
cycloalkyl; or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula
(I)
wherein: A is phenyl, naphthyl or thienyl, and A is optionally substituted by
halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1_6 alkoxy, CF3, OCF3, phenoxy (optionally substituted by halo or C1.4
alkyl), phenyl
(optionally substituted by halo or C1_4 alkyl), pyridinyloxy, nitro or cyano;
R' is liydrogen; L
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
9
is C1.4 allcylene (optionally substituted by C1.4 alkyl) or C1.4 allcylene-O
(optionally
substituted by C1.4 alkyl); W is phenyl optionally substituted by halo, C1.6
alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy,
CF3, OCF3, nitro or cyano; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A
is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, pyrazolyl,
benzthienyl, quinolinyl or
isoquinolinyl, and A is optionally substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl, C1.6
alkoxy, C1.4 alkylthio,
C1.4 fluoroallcyl, C1.4 fluoroalkoxy, pyridinyloxy, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano,
C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1.4
alkyl), S(O)2(Ci.4 alleyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1.4
alkyl)2, C(O)(C1.4
alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1-4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1.4 alkyl),
NRl Rll,
phenoxy (optionally substituted by halo, C1-6 allcyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1-4
alkylthio, Cl-4
fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1.4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1-4 allcyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(Ci-4 allcyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1.4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(Cl-4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl) or NR14Rls), phenyl
(optionally
substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1.4 alkylthio, C1.4
fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1.4 allcyl), S(O)2(Ci-4 allcyl), S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(Ci.4 alkyl),
S(O)2N(C1.4 alkyl)2, C(O)(Ci.a allcyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(Cl.a
alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4
alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl) or NR16R17), pyridinyloxy (optionally substituted
by halo, C1-6
alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1-4 allcylthio, C1-4 fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1.4 allcyl),
S(O)2N(C1.4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1-4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(CI.4 alkyl)2a
NHC(O)(C1-
4 alkyl) or NR1SR19) or pyrazolyl(optionally substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl,
C1-6 allcoxy, C1.4
alkylthio, C1-4 fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-
4 allcyl),
S(O)2(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(Ci.4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1.4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1.4 alkyl)
or
NR20R21); Rlo, Ril, R14, R15, Ri6, R17, R18, R19, R20 and R21 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1.4
alkyl or C3.7 cycloalkyl; Rl is hydrogen; L is C3 alkylene (substituted by C1-
4 alkyl or C1.4
haloalkyl), C2.4 alkylene-NH (substituted by C1-4 alkyl or C1-4 haloalkyl) or
C2.4 alkylene-O
(substituted by C1-4 alkyl or C1-4 haloalkyl) {for example L is C3 alkylene
(substituted by C1.4
alkyl), C2 alkylene-NH (substituted by Ci-a alkyl) or C2 alkylene-O
(substituted by C1-4
alkyl)}; W is cyclohexyl, phenyl, methylenedioxyphenyl, thienyl, pyrazolyl,
thiazolyl,
isoxazolyl, pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazinyl,
1,2,3-triazinyl,
1,2,4-triazinyl, benzofitranyl, benzthienyl, indolyl, indolinyl,
dihydroindolinyl, indazolyl,
benzimidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl,
isoquinolinyl,
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, [1,8]-naphthiridinyl,
[1,6]-naphthiridinyl,
quinolin-2(1H)-onyl, isoquinolin-1(2H)-onyl, phthalazin-1(2H)-onyl, 1H-
indazolyl, 1,3-
dihydro-2H-indol-2-onyl, isoindolin-l-onyl, 3,4-dihydro-1H-isochromen-l-onyl
or 1H-
isochromen-l-onyl; W is optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 allcyl, C1_6
alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio,
C1_4 fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, OH, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4
allcyl), S(O)2(C1_4
alkyl), S(O)2NH2a S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(Ci_4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy,
imidazolyl, C(O)(C1_
4 alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl)
or NR12R'3;
R12 and R13 are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a
pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof {for example the compound is not in the form of a
salt}.
In yet another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl, C1_4 allcoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl,
C1_4 haloalkyl, C1_4
alkoxy or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by Cl-4 alkyl,
C1_4 haloalkyl or
phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4 haloalkyl,
C1_4 alkoxy or C1_4
haloalkoxy)); Rl is hydrogen; L is C3 alkylene (substituted by Cl-4 alkyl or
Cl_4 haloalkyl), C2-
4 alkylene-NH (substituted by C1_4 allryl or Cl-4 haloalkyl) or C2_4 alkylene-
O (substituted by
C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl) {for example L is Q alkylene (substituted by
C1_4 allcyl), C2
alkylene-NH (substituted by C1_4 alkyl) or C2 alkylene-O (substituted by C1_4
alkyl)}; W is
phenyl, pyridyl, indolyl (for example indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl or
indol-7-yl),
indazolyl (for exainple indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl or indazol-7-
yl), quinolinyl
(for example quinolin-5-yl) or isoquinolinyl (for example isoquinolin-5-yl)
{for example W is
indolyl (for example indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl),
indazolyl (for example
indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl or indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl (for
example quinolin-5-
yl) or isoquinolinyl (for example isoquinolin-5-yl)}; wherein W is optionally
substituted by
halogen, C1_4 alkyl, CF3, C1_4 alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl (itself optionally
substituted by halogen,
C1_4 alkyl, CF3, C1_4 alkoxy or OCF3) or C(O)NH2.
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein
A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4 haloallcyl,
Cl_4 alkoxy or C1_4
haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, Cl-4
haloalkyl, C1-4 alkoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl or phenyl
(itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4 haloalkyl, C1_4
alkoxy or C1_4
haloalkoxy)); Rl is liydrogen; L is C3 alkylene (substituted by Cl-4 alkyl or
C1_4 haloalkyl), C2-
4 alkylene-NH (substituted by C1_4 alkyl or C1_4 haloalkyl) or C2_4 alkylene-O
(substituted by
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
11
C1-4 alkyl or C1-4 haloalkyl) {for example L is C3 alleylene (substituted by
C1-4 allcyl), C2
allcylene-NH (substituted by C1-4 alkyl) or C2 alkylene-O (substituted by C1-4
alkyl)}; W is
indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl, indazol-6-yl, indazol-7-yl or quinolin-5-yl;
wherein W is
optionally substituted by halogen, C1-4 allcyl, CF3, C1-4 alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl
(itself optionally
substituted by halogen, C1-4 alkyl, CF3, Cl-4 alkoxy or OCF3).
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A
is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, pyrazolyl,
benzthienyl, quinolinyl or
isoquinolinyl, and A is optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1_6
alkoxy, C1-4 allcylthio,
C1-4 fluoroalkyl, Cr-4 fluoroalkoxy, pyridinyloxy, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano,
C(O)aH, C(O)2(Cl-4
allcyl), S(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)ZN(C1-4
alkyl)2, C(O)(CI-4
alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1-4 alkyl)2a NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
NRl Rll,
phenoxy (optionally substituted by halo, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, Cr-4
alkylthio, Cl-4
fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1-4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1-4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(Ci-~ alkyl), C(O)N(C1-4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl) or NR14Ris), phenyl
(optionally
substituted by halo, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, C1_4 alkylthio, C1-4
fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1-4 allcyl), S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl),
S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1-4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 alkyl),
C(O)N(Cl-4
alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4 alkyl) or NR16R17), pyridinyloxy (optionally substituted
by halo, C1-6
alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, C1-4 alkylthio, C1-4 fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(Ci-~ alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-
4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1-4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 alkyl), C(O)N(Ci-4 alkyl)2,
NHC(O)(Ci_
4 alkyl) or NR18R19) or pyrazolyl(optionally substituted by halo, Cl-6 alkyl,
Cl-6 alkoxy, C1_4
alkylthio, C1-4 fluoroalkyl, C1-4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1-
4 allcyl),
S(O)2(C1-4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(Ci-4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1-4 alkyl)a, C(O)(Ci-
4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1-4 allcyl), C(O)N(Cl-4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1-4
alkyl) or
NR2oRai); Rio, Rli, R14, R15, R16, Rl7 , Ria, R19, R20 and R21 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1-4
alkyl or C3-7 cycloallcyl; Rl is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2CH2 (such as in the
S-
configuration), CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-configuration), CH(CH3)CHaO
(such as in
the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration),
CH(C2H5)CH2NH
(such as in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2O (such as in the S-
configuration) or
CH(CF3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration); W is cyclohexyl, phenyl,
methylenedioxyphenyl, thienyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl, pyridinyl,
pyrimidinyl,
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
12
pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazinyl, 1,2,3-triazinyl, 1,2,4-triazinyl,
benzofuranyl,
benzthienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, diliydroindolinyl, indazolyl,
benziinidazolyl, benzoxazolyl,
benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, quinoxalinyl,
quinazolinyl,
cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, [1,8]-naphthiridinyl, [1,6]-naphthiridinyl, quinolin-
2(1H)-onyl,
isoquinolin-1(2H)-onyl, phthalazin-1(2H)-onyl, 1H-indazolyl, 1,3-dihydro-2H-
indol-2-onyl,
isoindolin-l-onyl, 3,4-dihydro-lH-isochromen-l-onyl or 1H-isochromen-l-onyl; W
is
optionally substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1_~ alkylthio, C1_4
fluoroalkyl, C1.4
fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, OH, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2(Cl_~ alkyl),
S(O)2NH2,
S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy, imidazolyl, C(O)(C1_4
alkyl), C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 allcyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NRr2R13; R12
and R13 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alicyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
thereof {for example the compound is not in the form of a salt}.
In yet another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1.4
haloalkyl, C1.4 alkoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 allcyl,
C1.4 haloalkyl, C1.4
allcoxy or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1.4
alkyl, C1.4 haloalkyl or
phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1.4 haloalkyl,
C1.4 alkoxy or C1.4
haloalkoxy)); Rl is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-
configuration),
CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-configuration), CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-
configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2NH
(such
as in the S-configuration), CH(CzH5)CHaO (such as in the S-configuration) or
CH(CF3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration); W is phenyl, pyridyl, indolyl
(for example
indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl), indazolyl (for example
indazol-4-yl, indazol-
5-yl, indazol-6-yl or indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl (for example quinolin-5-yl) or
isoquinolinyl
(for example isoquinolin-5-yl) {for example W is indolyl (for example indol-4-
yl, indol-5-yl,
indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl), indazolyl (for example indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl,
indazol-6-yl or
indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl (for example quinolin-5-yl) or isoquinolinyl (for
example
isoquinolin-5-yl)}; wherein W is optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4
alkyl, CF3, Cl_4
alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl,
CF3, C1_4 alkoxy or
OCF3) or C(O)NH2.
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein
A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1.4 alkyl, C1.4 haloalkyl,
C1_4 alkoxy or C1.4
haloallcoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl, C1.4 alkoxy
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
13
or C1.4 haloallcoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1.4 allcyl, C1.4
haloallcyl or phenyl
(itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1.4 allcyl, C1_4 haloallcyl, C1.4
allcoxy or C1.4
haloalkoxy)); R' is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-
configuration),
CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-configuration), CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-
configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2NH
(such
as in the S-configuration), CH(C2H5)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration) or
CH(CF3)CH2CH2 (such as in the S-configuration); W is indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-
yl, indazol-6-
yl, indazol-7-yl or quinolin-5-yl; wherein W is optionally substituted by
halogen, C1.4 alkyl,
CF3, C1_4 alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4
alkyl, CF3, C1.4
alkoxy or OCF3).
In another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A
is phenyl, naphthyl, pyridinyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, pyrazolyl,
benzthienyl, quinolinyl or
isoquinolinyl, and A is optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, C1.6
alkoxy, C1.4 alkylthio,
C1.~ fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroallcoxy, pyridinyloxy, benzyloxy, nitro, cyano,
C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1.4
alkyl), S(O)2(Ci.4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(0)2N(CI-4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(Ci.4
alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.~ alkyl), C(0)N(C1.4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
NRl Rll,
phenoxy (optionally substituted by halo, C1.6 alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1.4
alkylthio, C1_4
fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(0)2(C1.4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2a S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl), S(0)2N(CI-4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1.4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2,
C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1.4 alkyl) or NR14R1s), phenyl
(optionally
substituted by halo, C1_6 allcyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1.4 alkylthio, C1.4
fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroallcoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2(C14 alkyl), S(O)2NHa,
S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl),
S(0)2N(CI-4 alkyl)2, C(O)(C1.4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl),
C(O)N(Ci.4
alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or NR16R17), pyridinyloxy (optionally substituted
by halo, C1.6
alkyl, C1.6 alkoxy, C1_4 allcylthio, C1.4 fluoroalkyl, Cl.~ fluoroalkoxy,
nitro, cyano, C(O)2H,
C(O)2(Ci.4 alkyl), S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl), S(0)2N(CI-
4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1.4 alkyl), benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 alkyl)2,
NHC(O)(C1.
4 alkyl) or NR18R19) or pyrazolyl(optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl,
C1.6 alkoxy, Ci.4
alkylthio, C1.4 fluoroalkyl, C1.4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, C(0)2H,
C(O)2(C1.4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1.4 alkyl), S(O)2N(Cl.4 alkyl)2,
C(O)(C1_4 alkyl),
benzyloxy, C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1.4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1.4 alkyl)2a NHC(O)(C1.4 alkyl)
or
NR20R21); RIo, Rll, R14, Rls, R'6, Rl7 , Rl$, R19, R20 and R21 are,
independently, hydrogen, C1_4
allcyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; Rl is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
14
configuration) or L is CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration); W is
cyclohexyl,
phenyl, methylenedioxyphenyl, thienyl, pyrazolyl, thiazolyl, isoxazolyl,
pyridinyl,
pyrimidinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrazinyl, 1,3,5-triazinyl, 1,2,3-triazinyl, 1,2,4-
triazinyl,
benzofuranyl, benzthienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, dihydroindolinyl, indazolyl,
benzimidazolyl,
benzoxazolyl, benzthiazolyl, quinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, isoquinolinyl,
quinoxalinyl,
quinazolinyl, cinnolinyl, phthalazinyl, [1,8]-naphthiridinyl, [1,6]-
naphthiridinyl, quinolin-
2(1IH)-onyl, isoquinolin-1(2H)-onyl, phthalazin-1(2H)-onyl, 1H-indazolyl, 1,3-
dihydro-2H-
indol-2-onyl, isoindolin-l-onyl, 3,4-dihydro-lH-isochromen-l-onyl or 1H-
isochromen-l-
onyl; W is optionally substituted by halo, C1_6 alkyl, Ci_6 allcoxy, C1_4
alkylthio, Cl_4
fluoroalkyl, C1_4 fluoroalkoxy, nitro, cyano, OH, C(O)2H, C(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2(C1_4 alkyl),
S(O)2NH2, S(O)2NH(C1_4 alkyl), S(O)2N(C1_4 alkyl)2, benzyloxy, imidazolyl,
C(O)(C1_4
alkyl), C(O)NH2, C(O)NH(C1_4 alkyl), C(O)N(C1_4 alkyl)2, NHC(O)(C1_4 alkyl) or
NR12R13;
R12 and R13 are, independently, hydrogen, C1_4 alkyl or C3_7 cycloalkyl; or a
pharmaceutically
acceptable salt thereof {for exanlple the compound is not in the form of a
salt}.
In yet another aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl, Cl_4 alkoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl,
C1_4 haloalkyl, C1_4
alkoxy or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1_4
allcyl, C1_4 haloalkyl or
phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, CI-4 alkyl, C1_4 haloalkyl,
C1_4 alkoxy or C1_4
haloalkoxy)); Rl is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-
configuration) or L is
CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration); W is phenyl, pyridyl, indolyl
(for example
indol-4-yl, indol-5-yl, indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl), indazolyl (for example
indazol-4-yl, indazol-
5-yl, indazol-6-yl or indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl (for example quinolin-5-yl) or
isoquinolinyl
(for example isoquinolin-5-yl) {for exainple W is indolyl (for example indol-4-
yl, indol-5-yl,
indol-6-yl or indol-7-yl), indazolyl (for example indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl,
indazol-6-yl or
indazol-7-yl), quinolinyl (for example quinolin-5-yl) or isoquinolinyl (for
example
isoquinolin-5-yl)}; wherein W is optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4
alkyl, CF3a CI-4
alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl,
CF3, C1_4 alkoxy or
OCF3) or C(O)NH2.
In a further aspect the present invention provides a compound of formula (I)
wherein
A is phenyl (optionally substituted by halogen, CI-4 alkyl, CI-4 haloalkyl,
C1_4 alkoxy or C1_4
haloalkoxy), pyridyl (optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4 alkyl, C1_4
haloalkyl, C1_4 alkoxy
or C1_4 haloalkoxy) or pyrazolyl (optionally substituted by C1_4 alkyl, Cl_4
haloalkyl or phenyl
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
(itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1.4 alkyl, C1_4 haloallcyl, C1.4
alkoxy or C1_4
haloallcoxy)); R' is hydrogen; L is CH(CH3)CH2NH (such as in the S-
configuration) or L is
CH(CH3)CH2O (such as in the S-configuration); W is indazol-4-yl, indazol-5-yl,
indazol-6-yl,
indazol-7-yl or quinolin-5-yl; wherein W is optionally substituted by halogen,
C1.4 alkyl, CF3,
C1_4 alkoxy, OCF3, phenyl (itself optionally substituted by halogen, C1_4
alkyl, CF3, C1.4
alkoxy or OCF3).
In a still further aspect the present invention provides a compound:
4-Bromo-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Chloro-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
N-(1-Methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-4-trifluoromethoxy-b enzenesulfonamide;
4-Methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-tert-Butyl-N-(1-methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-b enzenesulfonamide;
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-4-phenoxy-benzenesulfonamide;
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (1-methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-amide;
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-4-propyl-benzenesulfonamide;
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-4-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonamide;
4-(1,1-Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(1-methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
N-(1-Methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-benzenesulfonamide;
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid (1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
4-n-Butoxy-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
N-(1-Methyl-3 -phenyl-propyl)-3-p-tolyloxy-benzenesulfonamide;
N- [2-(2, 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl] -3 -nitro-b enzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-N-[2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide;
N- {4-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethylsulfamoyl]-phenyl} -acetamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-nitro-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-N-[2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-2-methyl-
benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-methoxy-benzenesulfonamide;
N- [2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl] -4-trifluoromethoxy-
benzenesulfonamide;
4-tert-Butyl-N-[2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Cyano-N-[2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
16
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl] -4-phenoxy-benzenesulfonamide;
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid [2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-
amide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-propyl-benzenesitlfonainide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-(4-fluoro-phenoxy)-
benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-(1,1-dimethyl-propyl)-
benzenesulfonamide;
Naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid [2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-amide;
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid [2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-amide;
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid [2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-
amide;
2-Bromo-N-[2-(2,6-diinethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-inethyl-ethyl]-3-methoxy-benzenesulfonamide;
4-n-Butoxy-N-[2-(2, 6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-(pyridin-2-yloxy)-
benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-2,4,6-trimethyl-
benzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2, 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl] -3 -p-tolyloxy-b
enzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
N-(2-Phenoxy-ethyl)-4-trifluoromethoxy-benzenesulfonamide;
4-(1,1-Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (2-phenoxy-ethyl)-amide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(3 -phenyl-propyl)-b enzenesulfonamide;
N-(3 -Phenyl-propyl)-4-trifluoromethoxy-b enzenesulfonamide;
4-Methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-N-(3 -phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-tert-Butyl-N-(3 -phenyl-propyl)-b enzenesulfonamide;
4-Phenoxy-N-(3 -phenyl-propyl)-benzene sulfonamide;
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
N-(3 -Phenyl-propyl)-4-propyl-b enzene sulfonamide;
4-(4-Fluoro-phenoxy)-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
4-(1, 1 -Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide;
Naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid (3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid (3-phenyl-propyl)-amide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-(3 -phenyl-propyl)-b enzenesulfonamide;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
17
N-(3 -Phenyl-propyl)-3 -p-tolyloxy-b enz enesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(5-Isoquinolinyloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(1H-Indol-4-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-inethyl-2-(5-
quinolinyloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(l S)- 1-methyl-2-(4-
quinolinyloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1-methyl-2-(4-
quinazolinyloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2,4, 6-Trimethyl-N- [(1 S)-1-methyl-2-( 8-quinolinyloxy) ethyl]b enzene
sulfonamide;
5-Fluoro-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-5-methylbenzainide;
2-Hydroxy-6-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
5-Chloro-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-4-methylbenzamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
4-Fluoro-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl) amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
4-Chloro-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
5-Cyano-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-5-methoxybenzamide;
3-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-4-methylbenzamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-4-methoxybenzamide;
2,5-Dichloro-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]thiophene-3-
sulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1-methylethyl]-5-methyl- 1 -phenyl- 1H-
pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
1-(Difluoromethyl)-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3, 5-
dimethyl-1 H-
pyrazole-4-sulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,5-dimethylfuran-3-
sulfonamide;
2,5-Dichloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]thiopherie-3-
sulfonamide;
3-Bromo-5-chloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy) ethyl]thiophene-2-
sulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-5-[1-methyl-5-
(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-
3 -yl] thiophene-2-sulfonami de;
1-(Difluoromethyl)-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1-methylethyl]-5-methyl-
1H-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
5-Methyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-1-phenyl-1 H-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
18
-Chloro-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-inethylethyl]thiophene-2-
sulfonamide;
5-Chloro-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]thiophene-2-
sulfonamide;
Methyl4-( { [(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]amino} sulfonyl)-2,5-
dimethyl-3-
furoate;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]thiophene-3-sulfonamide;
1-Ethyl-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-1 H-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,5-Dichloro-3-thienyl)sulfonyl] amino} propyl)oxy]benzamide;
1-(Difluoromethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-
1H-pyrazole-
4-sulfonamide;
N- [(1 S)-1-Methyl-2-(quinolin- 5-yloxy) ethyl] -5 -[ 1-methyl-5 -
(trifluoromethyl)-1 H-pyrazol-3 -
yl]thiophene-2-sulfonamide;
1-Ethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5 -yloxy) ethyl]-1 H-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
2-( {(2S)-2-[( { 5-[ 1-Methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-2-thienyl}
sulfonyl)-
amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide;
2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,5-Dimethyl-3-thienyl)sulfonyl] amino} propyl)oxy]benzamide;
2, 5 -Dimethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl] furan-3 -
sulfonamide;
2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,5-Dimethyl-3-furyl)sulfonyl] amino}propyl)oxy]benzamide;
2- { [(2S)-2-( {[ 1-(Difluoromethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]sulfonyl}
amino)propyl]-
oxy}benzamide;
1-Ethyl-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3-methyl-lH-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
N- [(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5 -yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-1,3, 5 -trimethyl-1 H-
pyrazole-4-sulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylethyl]-3,5-dimethylisoxazole-4-
sulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylethyl]-2,5-dimethylthiophene-3-
sulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- {(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-[(8-methylquinolin-5-yl)amino] ethyl} -
benzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- {(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2- [(6-methylquinolin-5-yl)amino] ethyl} -
benzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(1 H-Indazol-4-ylamino)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
ylamino)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(1 H-Indazol-6-ylamino)- 1 -methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- {(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-[(2-methylquinolin-5-yl)amino] ethyl} -
benzenesulfonamide;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
19
N-[(1 S)-2-(1H-Indazol-5-ylamino)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-((1 S)-2- { [2-Chloro-4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl] amino } -1-methylethyl)-
2,4,6-
trimetllylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(4-Cyano-2,6-dimethylphenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
triinethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(3-Cyanophenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(3-Methoxyphenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(4-Cyano-2-methoxyphenoxy)-1-inethylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N- {2-[(2-Bromopyridin-3-yl)oxy]-1-methylethyl} -2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- { 1-methyl-2-[(2-methylpyridin-3-yl)oxy]
ethyl}benzenesulfonamide;
2- {2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propoxy} -N-methylbenzamide;
4- {2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propoxy}benzamide;
N- {2-[4-(lH-Imidazol-1-yl)phenoxy]-1-methylethyl} -2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-(2- {2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propoxy}phenyl)acetamide;
N- {2-[(6-Chloropyridin-3-yl)oxy]-1-methylethyl} -2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N- [(1 S)-2-(2H-Indazol-3 -yloxy)-1-methylethyl] -2,4, 6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
4-Methyl-N-[3-phenyl-l-(trifluoromethyl)propyl]benzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4-
dimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Is oquinolin-5 -yloxy)-1-methylethyl] -3,4-dimethylb
enzenesulfonamide;
N- [(1 S)-2-(Is oquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl] -2, 5-dimethylb
enzenesulfonamide;
2,4-Dimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
3,4-Dimethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,4-Dimethylphenyl)sulfonyl]amino}propyl)oxy]benzamide;
2,5-Dimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2- [((2 S)-2- {[(3,4-Dimethylphenyl) sulfonyl] amino } propyl)oxy]b enzamide;
N-(2-Anilinoethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide;
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethylphenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-4-
(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide;
N-(2-Anilinoethyl)-4'-fluorobiphenyl-4-sulfonamide;
N-(2-Anilino ethyl)-4-methoxy-2,3, 6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamid;
N-(2-Anilinoethyl)-4-bromo-2-methylbenzenesulfonamid;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-[(1S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3,5-dimethyl-
lH-
pyrazole-4-sulfonainide;
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3, 5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-lH-
pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide;
N,2,4,6-Tetramethyl-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-3-phenylpropyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- { 1-[(quinolin-5-yloxy)methyl]propyl}benzenesulfonamide;
5-Chloro-2- {2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]butoxy}benzamide;
2,4-Dichloro-6-methyl-N- [(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [4-(4-fluorophenoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl}
amino)propyl]oxy}benzamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [4-(4-inethoxyphenoxy)phenyl] sulfonyl}
amino)propyl] oxy} -
benzamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [3-(4-chlorophenoxy)phenyl] sulfonyl} amino)propyl]
oxy}benzamide;
2,4,5-Trichloro-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl] sulfonyl}
amino)propyl]oxy} -
benzamide;
3 -(4-Chlorophenoxy)-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
5 -Chloro-2- [((2S)-2-{ [(2,4-dichloro-5-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}
propyl)oxy]benzamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [3-(4-
methoxyphenoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl} amino)propyl]oxy}benzamide;
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- {[(2-methoxy-4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]
amino}propyl)oxy]benzamide;
4-(4-Fluorophenoxy)-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
5 -Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- {[(5-chloro-2-methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]
amino}propyl)oxy]benzamide;
3-Cyano-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2,4-Dichloro-5 -fluoro-N-[(1 S)- 1 -methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
2-[((2S)-2- { [(5-Bromo-2-methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl] amino}propyl)oxy]-5-
chlorobenzamide;
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- { [(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)sulfonyl] amino}
propyl)oxy]benzamide;
5-Chloro-2- { [(2S)-2-( { [4'-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-4-yl] sulfonyl}
ainino)propyl] oxy} -
benzamide;
4-(4-Methoxyphenoxy)-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- {[(6-phenoxypyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl] amino }
propyl)oxy]benzamide;
5-Bromo-6-chloro-N- [(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]pyridine-3-
sulfonamide;
5-Bromo-2-methoxy-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
N- [(1 S)- 1 -Methyl-2-(quinolin-5 -yloxy) ethyl] - 1 -benzothiophene-2-
sulfonamide;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
21
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,4-
dimethoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]amino}propyl)oxy]benzamide;
2-( {(2 S)-2-[(1-Benzothien-2-ylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-5-chlorobenzamide;
-Chloro-2-[((2 S)-2-{[(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)sulfonyl] amino}
propyl)oxy]-
benzamide;
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- { [(5-fluoro-3-methyl-1-benzothien-2-yl)sulfonyl] amino }
propyl)oxy]-
benzamide;
5-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- { [(5-chloro-3-methyl-1-benzothien-2-yl)sulfonyl]
amino}propyl)oxy]-
benzamide;
2- { [(2S)-2-( { [4-Bromo-2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl] sulfonyl}
amino)propyl]oxy}-5-
chlorobenzamide;
2,4,6-Trichloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide;
4-Methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-
benzenesulfonamide; or,
4-Bromo-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-2-(trifluoromethoxy)-
benzenesulfonamide;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
The compounds of formula (I) can be prepared using or adapting methods
disclosed in
the art, or by using or adapting the method disclosed in the Examples below.
Starting
materials for the preparative methods are either commercially available or can
be prepared by
literature methods, adapting literature, methods.
For example, a compound of the invention can be prepared by coupling a
compound
of formula (II):
0 ~Y
A~S'
0
wherein Y is a leaving group (for example chlorine), with a compound of
formula (III):
R~
I
H-L-W (III)
in a suitable solvent (such as tetrahydrofuran or N,N-dimethylformamide) at a
temperature in
the range -10 C to 50 C.
The invention further provides processes for the preparation of the compounds
of
formula (I).
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
22
Because of their ability to bind to the glucocorticoid receptor the compounds
of
formula (I) are useful as anti-inflammatory agents, and can also display
antiallergic,
immunosuppressive and anti-proliferative actions. Thus, a compound of formula
(I), or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be used as a medicament for the
treatment or
prophylaxis of one or more of the following pathologic conditions (disease
states) in a
mammal (such as a human):
(i) Lung diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= chronically obstructive lung diseases of any origin, mainly bronchial asthma
= bronchitis of different origins
= all forms of restructive lung diseases, mainly allergic alveolitis
= all forms of pulmonary edema, mainly toxic pulmonary edema
= sarcoidoses and granulomatoses, such as Boeck's disease
(ii) Rheumatic diseases/auto-immune diseases/degenerative joint diseases,
which coincide
with inflammatory, allergic and/or proliferative processes:
= all forms of rheumatic diseases, especially rlieumatoid arthritis, acute
rheumatic
fever, polymyalgia rheumatica, collagenoses
= reactive arthritis
= inflammatory soft-tissue diseases of other origins
= arthritic symptoms in degenerative joint diseases (arthroses)
= traumatic arthritides
= collagen diseases of other origins, for example systemic lupus
erythematodes,
sclerodermia, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, polyarteritis nodosa, temporal
arteritis
= Sjogren's syndrome, Still syndrome, Felty's syndrome
(iii) Allergies, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative processes:
= All forms of allergic reactions, for example Quincke's edema, hay fever,
insect
bites, allergic reactions to pharmaceutical agents, blood derivatives,
contrast
media, etc., anaphylactic shock, urticaria, contact dermatitis
(iv) Dermatological diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic
and/or
proliferative processes:
0 atopic dermatitis (mainly in children)
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
23
= psoriasis
= erythematous diseases, triggered by different noxae, for example radiation,
chemicals, burns, etc.
= acid burns
= bullous dermatoses
= diseases of the lichenoid group
= itching (for example of all ergic origins)
= seborrheal eczema
= rosacea
= pemphigus vulgaris
= erythema exudativum multiforme
= erythema nodosum
= balanitis
= vulvitis
= inflammatory hair loss, such as alopecia areata
= cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
(v) Nephropathies, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= nephrotic syndrome
= all nephritides
(vi) Liver diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= acute liver cell decomposition
= acute hepatitis of different origins, for example virally-, toxically- or
pharmaceutical agent-induced
. chronically aggressive and/or chronically intermittent hepatitis
(vii) Gastrointestinal diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic
and/or
proliferative processes:
= regional enteritis (Crohn's disease)
= ulcerative colitis
= gastroenteritis of other origins, for example native sprue
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
24
(viii) Proctological diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic
and/or proliferative
processes:
= anal eczema
= fissures
= haemorrhoids
= idiopathic proctitis
(ix) Eve diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= allergic keratitis, uvenitis iritis
= conjunctivitis
= blepharitis
= optic neuritis
= chorioiditis
= sympathetic ophthalmia
(x) Diseases of the ear-nose-throat area, which coincide with inflammatory,
allergic
and/or proliferative processes:
= allergic rhinitis, hay fever
= otitis externa, for example caused by contact dermatitis, infection, etc.
= otitis media
(xi) Neurological diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= cerebral edema, mainly tumor-induced cerebral edema
= multiple sclerosis
= acute encephalomyelitis
= different forms of convulsions, for example infantile nodding spasms
(xii) Blood diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= acquired haemolytic anemia
= idiopathic thrombocytopenia
(xiii) Tumor diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
0 acute lymphatic leukaemia
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
= malignant lymphoma
= lymphogranulomatoses
= lymphosarcoma
= extensive metastases, mainly in breast and prostate cancers
(xiv) Endocrine diseases, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes:
= endocrine orbitopathy
= thyrotoxic crisis
= de Quervain's thyroiditis
= Hashiinoto's thyroiditis
= hyperthyroidism
(xv) Transplants, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative
processes;
(xvi) Severe shock conditions, which coincide with inflammatory, allergic
and/or
proliferative processes, for example anaphylactic shock
(xvii) Substitution therapy, which coincides with inflammatory, allergic
and/or proliferative
processes, with:
= innate primary suprarenal insufficiency, for example congenital
adrenogenital
syndrome
= acquired primary suprarenal insufficiency, for example Addison's disease,
autoimmune adrenalitis, meta-infective, tumors, metastases, etc.
= innate secondary suprarenal insufficiency, for example congenital
hypopituitarism
= acquired secondary suprarenal insufficiency, for example meta-infective,
tumors,
etc.
(xviii) Emesis, which coincides with inflammatory, allergic and/or
proliferative processes:
= for example in combination with a 5-HT3-antagonist in cytostatic-agent-
induced
vomiting.
Without prejudice to the foregoing, the compounds of formula (I) can also be
used to
treat disorders such as: Conies Syndrome, primary and secondary
hyperaldosteronism,
increased sodium retention, increased magnesium and potassium excretion
(diuresis),
increased water retention, liypertension (isolated systolic and combined
systolic/diastolic),
arrhythmias, myocardial fibrosis, myocardial infarction, Bartter's Syndrome,
disorders
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
26
associated with excess catecholamine levels, diastolic and systolic congestive
heart failure
(CHF), peripheral vascular disease, diabetic nephropathy, cirrhosis with edema
and ascites,
oesophageal varicies, Addison's Disease, muscle wealcness, increased melanin
pigmentation
of the skin, weight loss, hypotension, hypoglycemia, Cushing's Syndrome,
obesity,
hypertension, glucose intolerance, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus,
osteoporosis, polyuria,
polydipsia, inflammation, autoimmune disorders, tissue rejection associated
with organ
transplant, malignancies such as leukemias and lymphomas, acute adrenal
insufficiency,
congenital adrenal hyperplasia, rheumatic fever, polyarteritis nodosa,
granulomatous
polyarteritis, inhibition of myeloid cell lines, immune
proliferation/apoptosis, HPA axis
suppression and regulation, hypercortisolemia, modulation of the Thl/Th2
cytokine balance,
chronic kidney disease, stroke and spinal cord injury, hypercalcemia,
hyperglycemia, acute
adrenal insufficiency, chronic primary adrenal insufficiency, secondary
adrenal insufficiency,
congenital adrenal hyperplasia, cerebral edema, thrombocytopenia, and Little's
syndrome,
systemic inflainmation, inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus
erythematosus, discoid
lupus erythematosus, polyartitis nodosa, Wegener's granulomatosis, giant cell
arthritis,
rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, contact
dermatitis, atopic
dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, urticaria, angioneurotic edema, chronic
obstructive
pulmonary disease, asthma, tendonitis, bursitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative
colitis,
autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, hepatitis, cinhosis, inflammatory scalp
alopecia,
panniculitis, psoriasis, inflamed cysts, pyoderma gangrenosum, pemphigus
vulgaris, bullous
pemphigoid, dermatomyositis, eosinophilic fasciitis, relapsing polychondritis,
inflammatory
vasculitis, sarcoidosis Sweet's disease, type 1 reactive leprosy, capillary
hemangiomas, lichen
planus, erythema nodosum acne, hirsutism, toxic epiderrnal necrolysis,
erythema multiform,
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, psychoses, cognitive disorders (such as memory
disturbances)
mood disorders (such as depression and bipolar disorder), anxiety disorders
and personality
disorders.
As used herein the term "congestive heart failure" (CHF) or'congestive heart
disease"
refers to a disease state of the cardiovascular system whereby the heart is
unable to efficiently
pump an adequate volume of blood to meet the requirements of the body's
tissues and organ
systems. Typically, CHF is characterized by left ventricular failure (systolic
dysfunction) and
fluid accumulation in the lungs, with the underlying cause being attributed to
one or more
heart or cardiovascular disease states including coronary artery disease,
myocardial infarction,
hypertension, diabetes, valvular heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. The term
"diastolic
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
27
congestive heart failure" refers to a state of CHF characterized by impairment
in the ability of
the heart to properly relax and fill with blood. Conversely, the term
"systolic congestive heart
failure" refers to a state of CHF characterized by impairment in the ability
of the heart to
properly contract and eject blood.
As will be appreciated by one of skill in the art, physiological disorders may
present
as a"chronic" condition, or an "acute" episode. The term "chronic", as used
herein, means a
condition of slow progress and long continuance. As such, a chronic condition
is treated
when it is diagnosed and treatment continued throughout the course of the
disease.
Conversely, the term "acute"means an exacerbated event or attack, of short
course, followed
by a period of remission. Thus, the treatment of physiological disorders
contemplates both
acute events and chronic conditions. In an acute event, compound is
administered at the onset
of symptoms and discontinued when the symptoms disappear.
In another aspect the present invention provides the use of a compound or
formula (I),
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in therapy (such as a
therapy described
above).
In yet another aspect the present invention provides the use of a compound or
formula
(I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a
medicament for use
in the treatment of a glucocorticoid receptor mediated disease state (such as
a disease state
described above).
In a further aspect the invention provides the use of a compound of formula
(I), or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament
for use in the
treatment of an inflammatory (such as an arthritic) condition.
In a still further aspect the invention provides the use of a compound of
formula (I), or
a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament
for use in the
treatment of an asthmatic or dermatological condition.
In another aspect the invention provides the use of a compound of formula (I),
or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture of a medicament
for use in the
treatment of COPD.
The present invention further provides a method of treating a glucocorticoid
receptor
mediated disease state in a mammal (such as man), which comprises
administering to a
mammal in need of such treatment an effective amount of a compound of formula
(I), or a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
28
In order to use a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable
salt
thereof, for the therapeutic treatment of a mammal, said active ingredient is
normally
formulated in accordance with standard pharmaceutical practice as a
pharmaceutical
composition.
Therefore in another aspect the present invention provides a pharmaceutical
composition comprising a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
thereof, (active ingredient) and a pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant,
diluent or carrier. In
a further aspect the present invention provides a process for the preparation
of said
composition comprising mixing the active ingredient with a pharmaceutically
acceptable
adjuvant, diluent or carrier. Depending on the mode of adininistration, the
pharmaceutical
composition can comprise from 0.05 to 99 %w (per cent by weight), for example
from 0.05 to
80 %w, such as from 0.10 to 70 %w (for example from 0.10 to 50 %w), of active
ingredient,
all percentages by weight being based on total composition.
A pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be administered in a
standard manner for the disease condition that it is desired to treat, for
example by topical
(such as to the lung and/or airways or to the skin), oral, rectal or
pa'renteral administration.
Thus, a the compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, may be
formulated into the form of, for example, an aerosol, a powder (for example
dry or
dispersible), a tablet, a capsule, a syrup, a granule, an aqueous or oily
solution or suspension,
an (lipid) emulsion, a suppository, an ointment, a cream, drops, or a sterile
injectable aqueous
or oily solution or suspension.
A suitable pharmaceutical composition of this invention is one suitable for
oral
adininistration in unit dosage form, for example a tablet or capsule
containing between 0.lmg
and 1 g of active ingredient.
In another aspect a pharmaceutical composition of the invention is one
suitable for
intravenous, subcutaneous, intraarticular or intramuscular injection.
Buffers, pharmaceutically-acceptable cosolvents such as polyethylene glycol,
polypropylene glycol, glycerol or ethanol or complexing agents such as hydroxy-
propyl (3-
cyclodextrin may be used to aid formulation.
The above formulations may be obtained by conventional procedures well known
in
the pharmaceutical art. Tablets may be enteric coated by conventional means,
for example to
provide a coating of cellulose acetate phthalate.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
29
The invention further relates to combination therapies or compositions wherein
a
compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a
pharmaceutical
composition comprising a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically
acceptable salt
tliereof, is administered concurrently (possibly in the same composition) or
sequentially with
an agent for the treatment of any one of the above disease states.
In particular, for the treatment of the inflammatory diseases (for example
rheumatoid
arthritis, COPD, asthma or allergic rhinitis) a compound of the invention can
be combined
with a TNF-a inhibitor (such as an anti-TNF monoclonal antibody (such as
Remicade, CDP-
870 and D.sub2.E.sub7.), or a TNF receptor immunoglobulin molecule (such as
Enbrel.reg.)),
a non-selective COX-1 / COX-2 inhibitor (such as piroxicam or diclofenac; a
propionic acid
such as naproxen, flubiprofen, fenoprofen, ketoprofen or ibuprofen; a fenamate
such as
mefenamic acid, indomethacin, sulindac or apazone; a pyrazolone such as
phenylbutazone; or
a salicylate such as aspirin), a COX-2 inhibitor (such as meloxicam,
celecoxib, rofecoxib,
valdecoxib or etoricoxib) low dose methotrexate, lefunomide; ciclesonide;
hydroxychloroquine, d-penicillamine or auranofin, or parenteral or oral gold.
The present invention still further relates to the combination of a compound
of the
invention together with:
= a leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor, a 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) inhibitor or a
5-
lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) antagonist, such as zileuton, ABT-761,
fenleuton, tepoxalin, Abbott-79175, Abbott-85761, an N-(5-substituted)-
thiophene-2-
alkylsulfonamide, a 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol hydrazones, a
methoxytetrahydropyran
such as Zeneca ZD-2138, SB-210661, a pyridinyl-substituted 2-cyanonaphthalene
compound such as L-739,010; a 2-cyanoquinoline compound such as L-746,530; an
indole or quinoline compound such as MK-591, MK-886 or BAY x 1005;
= a receptor antagonist for a leukotriene LTB.sub4., LTC.sub4., LTD.sub4. or
LTE.sub4. selected from the group consisting of a phenothiazin-3-one such as L-
651,392; an amidino compound such as CGS-25019c; a benzoxalamine such as
ontazolast; a benzenecarboximidamide such as BIIL 284/260; or a compound such
as
zafirlukast, ablukast, montelukast, pranlukast, verlukast (MK-679), RG-12525,
Ro-
245913, iralukast (CGP 45715A) or BAY x 7195;
= a PDE4 inhibitor including an inhibitor of the isoform PDE4D;
= an antihistaminic H.sub 1. receptor antagonist such as cetirizine,
loratadine,
desloratadine, fexofenadine, astemizole, azelastine or chlorpheniramine;
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
= a gastroprotective H.sub2. receptor antagonist;
= an a.subl.- and a.sub2.-adrenoceptor agonist vasoconstrictor sympathomimetic
agent,
such as propylhexedrine, phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, pseudoephedrine,
naphazoline hydrochloride, oxymetazoline hydrochloride, tetrahydrozoline
hydrochloride, xylometazoline hydrochloride or ethylnorepinephrine
hydrochloride;
= an anticholinergic agent such as ipratropium bromide, tiotropium bromide,
oxitropium
bromide, pirenzepine or telenzepine;
= a(3.subl.- to (3.sub4.-adrenoceptor agonist (such as (32 adrenoceptor
agonist) such as
metaproterenol, isoproterenol, isoprenaline, albuterol, salbutamol,
formoterol,
salmeterol, terbutaline, orciprenaline, bitolterol mesylate or pirbuterol, or
a
methylxanthanine including theophylline and aminophylline; sodium
cromoglycate; or
a muscarinic receptor (Ml, M2, and M3) antagonist;
= an insulin-like growth factor type I(IGF-1) mimetic;
= an inhaled glucocorticoid with reduced systemic side effects, such as
prednisone,
prednisolone, flunisolide, triamcinolone acetonide, beclomethasone
dipropionate,
budesonide, fluticasone propionate or mometasone furoate;
= an inhibitor of a matrix metalloprotease (MMP), such as a stromelysin, a
collagenase,
or a gelatinase or aggrecanase; such as collagenase-1 (MMP-1), collagenase-2
(MMP-
8), collagenase-3 (MMP-13), stromelysin-l (MMP-3), stromelysin-2 (MMP-10), and
stromelysin-3 (MMP-11) or MMP-12;
= a modulator of chemokine receptor function such as CCR1, CCR2, CCR2A, CCR2B,
CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, CCRI O and CCRl 1 (for the C-C
family); CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR5 (for the C-X-C family) and
CX3CR1 for the C-X3-C family;
= an osteoporosis agent such as roloxifene, droloxifene, lasofoxifene or
fosomax;
= an immunosuppressant agent such as FK-506, rapamycin, cyclosporine,
azathioprine
or methotrexate;
= a compound useful in the treatment of AIDS and/or HIV infection for example:
an
agent which prevents or inhibits the viral protein gp120 from engaging host
cell CD4
{such as soluble CD4 (recombinant); an anti-CD4 antibody (or modified /
recombinant antibody) for example PR0542; an anti-group120 antibody (or
modified /
recombinant antibody); or another agent which interferes with the binding of
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
31
group120 to CD4 for example BMS806}; an agent which prevents binding to a
chemokine receptor, other than CCR5, used by the HIV virus {such as a CXCR4
agonist or antagonist or an anti-CXCR4 antibody}; a coinpound which interferes
in
the fusion between the HIV viral envelope and a cell membrane {such as an anti-
group 41 antibody; enfuvirtide (T-20) or T-1249}; an inhibitor of DC-SIGN
(also
known as CD209) {such as an anti-DC-SIGN antibody or an inhibitor of DC-SIGN
binding}; a nucleoside/nucleotide analogue reverse transciptase inhibitor {for
example
zidovudine (AZT), nevirapine, didanosine (ddl), zalcitabine (ddC), stavudine
(d4T),
lamivudine (3TC), abacavir, adefovir or tenofovir (for example as free base or
as
disoproxil fumarate)}; a non-nucleoside reverse transciptase inhibitor {for
example
nevirapine, delavirdine or efavirenz}; a protease inhibitor {for example
ritonavir,
indinavir, saquinavir (for example as free base or as mesylate salt),
nelfinavir (for
example as free base or as mesylate salt), amprenavir, lopinavir or atazanavir
(for
example as free base or as sulphate salt)}; a ribonucleotide reductase
inhinbitor {for
example hydroxyurea}; or an antiretroviral {for example emtricitabine}; or,
= an existing therapeutic agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis, for
example a non-
steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (hereinafter NSAID's) such as piroxicam or
diclofenac, a propionic acid such as naproxen, flubiprofen, fenoprofen,
ketoprofen or
ibuprofen, a fenamate such as mefenamic acid, indomethacin, sulindac or
apazone, a
pyrazolone such as phenylbutazone, a salicylate such as aspirin, a COX-2
inhibitor
such as celecoxib, valdecoxib, rofecoxib or etoricoxib, an analgesic or intra-
articular
therapy such as a corticosteroid or a hyaluronic acid such as hyalgan or
synvisc, or a
P2X7 receptor antagonist.
The present invention still further relates to the combination of a compound
of the
invention together with: (i) a tryptase inhibitor; (ii) a platelet activating
factor (PAF)
antagonist; (iii) an interleukin converting enzyme (ICE) inhibitor; (iv) an
IMPDH inhibitor;
(v) an adhesion molecule inhibitor including a VLA-4 antagonist; (vi) a
cathepsin; (vii) a
MAP kinase inhibitor; (viii) a glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase inhibitor;
(ix) a kinin-
B.subl. - and B.sub2. -receptor antagonist; (x) an anti-gout agent, e.g.,
colchicine; (xi) a
xanthine oxidase inhibitor, e.g., allopurinol; (xii) an uricosuric agent,
e.g., probenecid,
sulfinpyrazone or benzbromarone; (xiii) a growth hormone secretagogue; (xiv) a
transforming
growth factor (TGF(3); (xv) a platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); (xvi) a
fibroblast growth
factor, e.g., basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF); (xvii) a granulocyte
macrophage colony
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
32
stimulating factor (GM-CSF); (xviii) a capsaicin cream; (xix) a Tachykinin
NK.subl. and
NK.sub3. receptor antagonist selected from the group consisting of NKP-608C;
SB-233412
(talnetant); and D-4418; (xx) an elastase inhibitors selected from the group
consisting of UT-
77 and ZD-0892; (xxi) a TNFoc converting enzyme inhibitor (TACE); (xxii) an
induced nitric
oxide synthase inhibitor (iNOS); or (xxiii) a chemoattractant receptor-
homologous molecule
expressed on TH2 cells (a CRTH2 antagonist).
The following compounds illustrate compounds of formula (I)
Ci \
~/ o \ / I o\o
JS~~~ ~ N
N H ~ \
O=T=O
HN H
H I o Example 3
Example 1 Example 2 d -
o,
\ 'S H ~~O
~ N
OI / O CI ~ ' ~iNH
N+A
Example 4 0
/ -
NH2 Example 5
O:::~S~
~O
N
H ~\ HII
N N- N_g1
O 0
1 - -O
~ O \ \
H
/ H
S,/, 0 O /
Example 6
xample Example 6 Example 7
W_N
q_N-S o
N H~ O
N~ O
Ci Example 10
Example 9
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
33
/ O O~, N / I N
O-N ~l N N
O o~ ~1O-N o
O - ~O S,'O
O~ N o
- Example 11 Example 12 Example 13
\ N
~ O=~S=O O
N ~ N NH S-N O
II H~
\O ~ O
N
ci ~ H ~ ~ Example 16
N N
Example 14
Example 15
The following abbreviations are used in the following preparative Examples:
THF tetrahydrofuran
TFA trifluoroacetic acid
DMSO dimethylsulfoxide
DMF N,N-dimethylformamide
TBAT N,N,N-tributylbutan-l-aminium difluoro(triphenyl)silicate
DIEA diisopropylethyl amine
NMP 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone
app approximately
sat saturated
aq aqueous
General Methods
'H NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian Mercury-VX 300 MHz instrument or
aVarian Unity 400MHz instument. The central peaks of chloroform-d (SH 7.27
ppm),
acetnitrile-d3 (8H 1.95 ppm), or DMSO-d6 (8H 2.50 ppm) were used as internal
references.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
34
Low resolution mass spectra and accurate mass determination were recorded on a
Hewlett-
Packard 1100 LC-MS system equipped with APCI ionisation chamber. Unless stated
otherwise, starting materials were commercially available. All solvents and
commercial
reagents were of laboratory grade and were used as received.
The following methods were used for LC/MS analysis
Method A: Instrument Agilent 1100; Column C18 Waters Syminetry 2.1 x 30 mm 3.5
m;
Flow rate 0.7 ml/min; Mass APCI; UV-absorption was measured at 254nm; Solvent
A: water
+ 0.1% TFA; Solvent B: acetonitrile + 0.1% TFA; Gradient 5-95%/B 8 min, 95% B
2 min.
Method B: Instrument Agilent 1100; Column Kromasil C18 3 x 100 mm 5 m; Flow
rate 1.0
ml/min; UV-absorption was measured at 254nm; Solvent A: water + 0.1% TFA;
Solvent B:
acetonitrile + 0.1 % TFA; Gradient 10-100%B 20 min, 100% B 1 min.
Example 17
4-Bromo-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
Br
N
,S;
O~"o
4-Bromo-benzenesulfonyl chloride (120 L 0.3M /THF) was mixed with 1-methyl-3-
phenyl-propylamine (100 L 0.3M/pyridine) and stirred overnight in ambient
temperature
before it was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure. The residue was
purified on
HPLC-C18 yielding 2.1mg (25%).
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.68 (ddt, J= 23.9, 8.8, 2.1 Hz, 3H), 7.30 -
7.15
(m, 3H), 7.06 (dd, J= 6.7, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 4.48 (d, J= 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.35 (q, J=
6.2 Hz, 1H),
2.57 (ddd, J= 29.9, 14.0, 7.9 Hz, 3H), 1.71 (td, J= 7.8, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.10 (d,
J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.1 min. UV 254 nm
Examples 18 - 76 were 'synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
Example 17 using the corresponding starting materials.
Example 18
4-Chloro-N-(1-methyl-3-phen y1-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
CI
1S;N
O"O
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.79 (dt, J= 9.0, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (dt, J= 8.9,
2.2 Hz,
2H), 7.30 - 7.17 (m, 3H), 7.06 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 2H), 4.46 (d, J= 7.7 Hz, 1H),
3.37 (quintet, J=
6.7 Hz, 1H), 2.57 (ddd, J= 29.9, 14.0, 7.8 Hz, 2H), 1.71 (td, J= 7.8, 6.6 Hz,
2H), 1.10 (d, J=
6.6 Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Exainple 19
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(1-inethyl-3-phen y1-propYl)-benzenesulfonamide
O, ~0
N'S / ~ -
Br
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.82 (d, J= 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.50 - 7.42 (m, 2H),
7.28 - 7.16
(m, 3H), 7.03 - 7.00 (m, 2H), 4.48 (s, 1H), 3.31 (d, J= 5.5 Hz, 1H), 2.63 (s,
3H), 2.61 - 2.45
(m, 2H), 1.76 - 1.64 (m, 2H), 1.11 (d, J= 6.4 Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.5 min. iJV 254 nm.
Example 20
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-proRyl)-4-trifluoromethoxy-benzenesulfonamide
F+F
/ O
~ ~
0 N "S
~~
O
LC (method A) rt = 6.3 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 21
4-MethoxX-2 3 6-trimethyl-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propylLbenzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
36
O
N,
S.
O'
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 6 7.26 - 7.12 (m, 3H), 7.02 - 6.97 (m, 2H), 6.58
(s, 1H),
3.87 (s, 3H), 3.30 (q, J= 6.5 Hz, 1H), 2.65 (s, 3H), 2.59 (s, 4H), 2.57 - 2.43
(m, 6H), 2.16 (s,
3H), 1.73 - 1.63 (m, 2H), 1.10 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 362.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 22
4-tert=Buty1-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
0õp
K
N
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 8 7.83 (dd, J= 6.8, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.54 (dd, J= 6.8,
1.8 Hz,
2H), 7.30 - 7.17 (m, 3H), 7.06 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 2H), 4.49 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H),
3.42 (quintet, J=
6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.58 (dtd, J= 21.9, 14.1, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 1.75 - 1.67 (m, 2H), 1.38
(s, 9H), 1.12 (d,
J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 346.3 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 23
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-4-phenoxy-benzenesulfonamide
o
N,
01'SO
APCI-MS mlz: 382.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.6 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
37
Exam-ple 24
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-amide
0S1O
N
F
JO
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 8.01 (dd, J= 6.7, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (dd, J= 6.7,
1.7 Hz,
2H), 7.70 - 7.64 (m, 2H), 7.35 - 7.23 (m, 5H), 7.15 - 7.13 (m, 2H), 4.52 (s,
OH), 3.52 (q, J=
6.4 Hz, 1H), 2.67 (ddd, J= 32.7, 14.0, 7.9 Hz, 3H), 1.81 (dd, J= 14.5, 7.9 Hz,
2H), 1.21 (d, J
= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 25 =
N-(1-Methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-4-propyl-benzenesulfonamide
O O
N
APCI-MS m/z: 332.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 26
N-(1-Methyl-3 -phenl-pro-pyl)-4-trifluoromethyl-b enzenesulfonamide
0'õ
S O
F
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) b 7.99 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (d; J= 8.3 Hz,
2H), 7.30 -
7.18 (m, 3H), 7.06 - 7.04 (m, 2H), 4.57 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.42 (dt, J= 14.9,
6.6 Hz, 1H),
2.59 (ddd, J= 29.1, 13.9, 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.77 - 1.70 (m, 2H), 1.13 (d, J= 6.4
Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.2 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
38
Example 27
4- 1 1-Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(1-methyl-3-phen y1-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
0,0
APCI-MS m/z: 360.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 7.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 28
N-(1-Methyl-3 -phMl-propyl)-3 -trifluoromethyl-b enzenesulfonamide
, N
F D\'~ O
F
F
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 8 8.16 (s, 1H), 8.05 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d,
J= 7.9 Hz,
1H), 7.66 (t, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.29 - 7.16 (m, 3H), 7.07 - 7.04 (m, 2H), 4.50
(d, J= 8.6 Hz,
1H), 3.42 (dq, J= 8.3, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 2.57 (ddd, J= 30.5, 14.1, 8.0 Hz, 2H),
1.73 (td, J= 7.8,
6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.11 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 29
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (1-methyl-3-phenyl-propyl)-amide
OS'p
( N
\ I ~
APCI-MS m/z: 366.2 [MH+]. LC (method A) rt = 6.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 30
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid (1-methtil-3-phenyl-propy)-amide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
39
0, ,,O
NS S
~Br
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.29 - 7.20 (m, 3H), 7.19 - 7.12 (m, 1H), 7.09 -
7.04 (m,
2H), 7.00 (d, J= 4.0 Hz, 1H), 4.50 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (quintet, J= 6.8
Hz, 1H), 2.58
(td, J= 7.9, 5.3 Hz, 2H), 1.72 (dd, J= 20.2, 2.2 Hz, 2H), 1.13 (d, J 6.6 Hz,
3H)
LC (method A) rt = 6.1 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 31
4-n-Butoxy-N-(1-methyl-3-phen yl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
0
N
,
q-~-
O'SO
APCI-MS m/z: 362.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.7 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 32
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-(1-methyl-3-phenyl=propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
0 ' s0
NIS
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.31 - 7.16 (m, 3H), 7.05 - 7.00 (m, 4H), 4.43
(s, 1H),
3.33 (t, J= 6.5 Hz, 1H), 2.67 (s, 6H), 2.64 - 2.47 (m, 2H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 1.75
- 1.67 (m, 2H),
1.14 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 332.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 33
N-(1-MethYl-3-phen yj-proRyl)-3-p-tolyloxy-benzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
O~S O
O N
1H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 8 7.57 - 7.53 (m, 1H), 7.29 - 7.14 (m, 6H), 7.08 -
7.04 (m,
2H), 6.91 (dt, J= 8.9, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 7.46 - 7.41 (m, 2H), 4. 5 7(s, 1 H), 3.3
8(q, J= 6.5 Hz, 1 H),
2.65 - 2.46 (m, 2H), 2.36 (s, 3H), 1.69 (td, J= 8.0, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.09 (d, J=
6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 396.2 [MH+].
LC (inethod A) rt = 6.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 34
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy -1-methyl-ethyll-3-nitro-benzenesulfonamide
0O
O
\ N~S~
~ ~N, -
\ ~ O
LC (method A) rt = 5.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 35
4-Bromo-N-[2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide
O O
~ S'N
1~
Br
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 36
N- {4-[2-(2,6-Dimethy1-phenoxY)-1-methyl-ethXlsulfamoyl]-phenyl}-acetamide
""If O
N
O
~ ooS.
O 0
APCI-MS m/z: 377.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 5.0 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
41
Example 37
N-[2-(2 6-Dimeth ,l-phenoxy -1-methyl-ethyl]-4-nitro-benzenesulfonamide
0
1 +
N,-O
O ~
~ ,S;
O p
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 38
4-Bromo-N-j2-(2 6-dimethyl-phenoxX -1-methyl-ethyl]-2-methyl-
benzenesulfonamide
S
\ O N/
/ / ~ -
Br
APCI-MS m/z: 412.1, 414.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.7 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 39
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy -1-methyl-ethyl]-4-methoxy-benzenesulfonamide
, O
O;S
O~l\N~
s ~ i
APCI-MS m/z: 350.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 5.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 40
N-r2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyll-4-trifluoromethoxy-
benzenesulfonamide
F
F I-F
~O"
/
0 N, ~ (
Dos
0
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
42
LC (method A) rt = 6.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 41
4-tert-Butyl-N-[2-(26-dimeth y1-phenoxy)-l-methyl-ethyll-benzenesulfonamide
S,
~p
APCI-MS m/z: 376.3 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 42
4-Cyano-N-[2-(2 6-dimethyl-phenoxy -l-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide
N,,
eNO
S
O 'O
LC (method A) rt = 5.7 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 43
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethYl]-4-phenoxy-benzenesulfonamide
O~N O
D O
APCI-MS m/z: 412.3 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Exam-ple 44
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid [2-(2 6-dimethyl-phenoxy -1-methyl-ethyll-
amide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
43
0 S,,0
NjO
APCI-MS m/z: 414.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 45
N-[2-(2 6-Dimeth yl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-4-propyl-benzenesulfonamide
O.õ S O j,,,~O
N
APCI-MS m/z: 362.2 [MH+].
LC (metliod A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 46
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxx)-l-methyl-ethyt]-4-(4-fluoro-phenoxyl-
benzenesulfonamide
0
O N. F
S ')- O" "
O
APCI-MS m/z: 430.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 47
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxyl-l-methyl-ethyll-4-(1 1-dimethyl-uropyl)-
benzenesulfonamide
O
~S O
~ N~:6-~-
APCI-MS I ~ m/z: 390.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 7.4 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
44
Example 48
Naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid j2-(2 6-dimethyl-phenoxy -1-methyl-ethyl]-amide
0, ,,0
S~'N-111-,
~\
~
APCI-MS mlz: 370.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 49
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid [2-(2 6-dimeth y1-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyll-amide
0 S,O
N-~,O
\ I ~ I
APCI-MS m/z: 396.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 50
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid [2-(2,6-dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyll-
amide
/ ~ )DS Br
N
.
O~ OS,O
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 51
2-Bromo-N-[2-(2 6-dimethyl-phenoxx -1-methyl-ethyl]-benzenesulfonamide
N O
Br 0'
O
APCI-MS m/z: 398.0, 400.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.2 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
Example 52
N-[2-(2,6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-3-methoxy-benzenesulfonamide
~os0
N/
APCI-MS m/z: 350.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 53
4-n-Butoxy-N- j2-(2, 6-dimethyl=phenoxy)-1-methyl-eLhyl] -b enzenesulfonamide
's~
O~N 0
O .
APCI-MS m/z: 392.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 7.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 54
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy -1-meth ~~yl]-pyridin-2-yloxy)-benzenesulfonamide
o ~-N
o o
APCI-MS m/z: 413.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 55
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxx)-1-methyl-ethyll-2 4 6-trimethyl-benzenesulfonamide
Q. . O
S
N'
~l
APCI-MS m/z: 362.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.8 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
46
Example 56
N-[2-(2 6-Dimethyl-phenoxy)-1-methyl-ethyl]-3-p-tolyloxy-benzenesulfonamide
N~
ao
,S"
910
O O
APCI-MS m/z: 426.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 7.1 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 57
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide
~, 00
S
Br
LC (method A) rt = 5.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 58
N-(2-Phenoxy-ethyl)-4-trifluoroiuethoxy-benzenesulfonamide
F
F+F
O
O--\,N,
0 S~
O
LC (method A) rt = 5.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Exam lp e 59
4-(1 1-Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(2-phenoxy-ethxl)-benzenesulfonamide
0. ,0
~ S'N~,O
I~
APCI-MS m/z: 348.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.7 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
47
Example 60
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (2-phenoxy-ethyl)-amide
0. ,0
S
/ -~
APCI-MS m/z: 354.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 mn.
Example 61
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-(2-phenoxy-ethyl)-benzenesulfonamide
N'S
O'O
APCI-MS m/z: 320.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 62
4-Bromo-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
Br
1~ ~I
,S
.
0 1, O
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 63
4-Bromo-2-methyl-N-(3-phen y1-provvl)-benzenesulfonamide
~S O
N/
Br
LC (method A) rt = 6.3 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
48
Example 64
N-(3-Phenl-pro-pyl)-4-trifluoromethoxy-benzenesulfonamide
F
F+ F
O
O
O
LC (method A) rt = 6.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 65
4-Methoxy-2 3 6-trimethyl-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
O
\~ ~A
;S'
O''O
APCI-MS m/z: 348.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.3 min. UV 254 nm.
Exam lpe66
4-tert-Butyl-N- 3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
OõO
I~ ~\
APCI-MS m/z: 332.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Exam lp e 67
4-Phenoxy-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
49
0
\S~O
N
'
~ -
APCI-MS m/z: 368.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 68
4'-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (3-pheW1-propyl)-amide
OS
I N
F/
~
~
APCI-MS m/z: 370.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 69
N-(3-Phenyl-propyl)-4- ropyl-benzenesulfonamide
o 'o
APCI-MS m/z: 318.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 70
4-(4-Fluoro-phenoxy)-3-phen yl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
0 a/,N\
s,
O' ~ O
APCI-MS m/z: 386.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.5 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
Example 71
4-(1,1-Dimethyl-propyl)-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
O,,O
S;
N
I~ ~\
~
APCI-MS m/z: 346.3 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 7.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 72
Naphthalene-2-sulfonic acid (3-phen y1-propyl -amide
o s"o
APCI-MS m/z: 326.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 73
Biphenyl-4-sulfonic acid (3-phen yl-propyl)-ainide
0,0
S
I N
\ ~ ~ \
APCI-MS m/z: 352.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 74
5-Bromo-thiophene-2-sulfonic acid (3-phenyl-propyl -amide
0 S O
NIS
Br
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
51
Example 75
2 4,6-Trimethyl-N-(3-phenyl-propyl)-benzenesulfonamide
N ;S,
q
O~ 'O
APCI-MS m/z: 318.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 76
N-(3 -Phenyl-propyl)-3 -p-tolyloxy-benzenesulfonamide
OO
~OS\NTh
APCI-MS m/z: 382.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 6.7 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 77
N-r(1S -(5-Isoquinolinylon)-1-methhyl]-2,4 6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O,SO N
N O
H Chiral
Step 1: (2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propy12,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate
L-Alaninol (4.8g, 64mmole) and 2-mesitylenesulfonyl chloride (30g, 137mmole)
were
dissolved in 200mL pyridine and stirred at room temperature overnight. The
mixture was
evaporated, dissolved in ethyl acetate(200m1) and washed with 1M HC1/aq, sat.
NaHCO3/aq.
The organic layer was dried, concentrated and purified on a silica gel column
chromatography
(heptane-ethylacetate).
APCI-MS m/z: 440.1 [MH+].
Step 2: N-[(1S)-2-(5-Isoquinolinyloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
52
(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)ainino]propy12,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate (263mg,
0.6mmole) was added to a slurry containing Cs2CO3 (487mg, 1.5mmole) and 5-
Hydroxyisoquinoline (145mg, lmmole) in 2.5mL DMF. The reaction mixture was
stirred
overnight in room teperature before it was diluted with ethyl acetate (20mL)
and washed with
1MHC1/aq. The organic layer was dried, concentrated and purified on HPLC-C18.
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) b 9.54 (s, 1H), 8.54 (d, J= 6.2 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (d,
J=
6.2 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (dd, J= 15.7, 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (t, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (d,
J= 7.3 Hz, 1H),
6.83 (d, J= 0.4 Hz, 2H), 4.04 - 3.92 (m, 2H), 3.65 (dq, J= 13.2, 6.6 Hz, 1H),
2.50 (s, 6H),
2.11 (d, J= 11.6 Hz, 3H), 1.16 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 385.1 [MH+].
Examples 78 - 83 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
Example 77 using (2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl 2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonate
and the corresponding starting materials.
Example 78
N-[(1S)-2-(1H-Indol-4-yloxy)-l-methylethyl]-2 4 6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O Chiral
N~o
H NH
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 8 10.94 (s, 1H), 7.66 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (t,
J= 2.8
Hz, 1H), 6.93 - 6.80 (m, 4H), 6.23 - 6.16 (m, 2H), 3.85 (dd, J= 9.7, 5.7 Hz,
1H), 3.69 (dd, J=
9.7, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 3.46 - 3.37 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.17 (s, 3H), 1.03 (d, J=
6.8 Hz, 2H)
APCI-MS m/z: 373.1 [MH+].
Example 79
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-j(1S)-1-methvl-2-(5-quinolinyloxy)ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
O, O " Chiral
S'N~O
H
1 N
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
53
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 9.13 (dd, J= 4.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 8.79 (dd, J= 8.4,
0.7 Hz,
1H), 7.88 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, IH), 7.65 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.83 - 7.75 (m, 2H),
7.04 (d, J= 7.7
Hz, 1H), 6.82 (s, 2H), 6.72 (s, 1H), 4.06 - 3.94 (m, 2H), 3.70 - 3.62 (m, 1H),
2.50 (s, 6H), 2.13
(s, 3H), 1.17 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 2H)
APCI-MS m/z: 385.3 [MH+].
Example 80
N-[( l S)-2-(1 3-Benzodioxol-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
Chiral
O
O~'g/ O
H
O
- o~
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) b 7.62 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (s, 2H), 6.68 (d,
J= 8.4 Hz,
1H), 6.23 (d, J= 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.08 (dd, J= 8.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 5.89 (s, 2H),
3.67 - 3.53 (m, 2H),
3.39 - 3.30 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.00 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 378.2 [MH+].
Example 81
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-[(lS -l-meth l-2- 4-quinolinLIoxylethyl]benzenesulfonamide
, O Chiral
'S" N~O
"
N
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 8.10 (dd, J= 8.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (d, J= 7.5
Hz, 1H),
7.81 (d, J= 9.5 Hz, 1H), 7.74 - 7.64 (m, 2H), 7.42 (ddd, J= 8.0, 6.3, 1.7 Hz,
1H), 6.56 (s,
2H), 6.15 (d, J= 7.5 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (dd, J=14.6, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 3.91 (dd, J=
14.7, 10.5 Hz,
1H), 3.62 (dd, J= 6.2, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 2.20 (s, 6H), 2.13 (s, 3H), 1.21 (d, J=
6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 385.1 [MH+].
Exam-ple 82
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-[(1S -1-methyl-2-(4-QUinazolinYloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
54
O, O Chiral
S, N~O
H
N~N
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.96 (dd, J= 7.9, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.82
- 7.76
(m, 1H), 7.73 (d, J= 9.4 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J= 8.0, 0.3 Hz, 1H), 7.49 (ddd, J=
8.1, 7.1, 1.1
Hz, 1H), 6.52 (s, 2H), 3.98 (dd, J= 12.7, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 3.70 - 3.53 (m, 2H),
2.36 (s, 6H), 1.91
(s, 3H), 1.13 (d, J= 6.4 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 386.2 [MH+].
Example 83
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-f(1S)-1-methyl-2-(8-quinolinylox))ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
O, , O N Chiral
S'NJ%~ O
H
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 9.14 (dd, J= 5.0, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 9.02 (d, J= 8.1
Hz, 1H),
8.04 (dd, J= 8.3, 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.82 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (t, J= 8.1 Hz,
1H), 7.41 (d, J=
7.3 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (dd, J= 0.3, 4.1 Hz, 2H), 4.21 (dd, J=10.3, 5.3 Hz, 2H),
4.04 (dd, J= 10.3,
5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.70 (dd, J= 20.9, 5.7 Hz, 1H), 2.11 (d, J= 7.0 Hz, 3H), 1.24 (d,
J= 6.8 Hz,
3H), 2.50 (s, 6H)
APCI-MS m/z: 385.1 [MH+].
Example 84
5-Fluoro-2-({(2S)-2-[(mesi lsulfonyl amino]propyl}oxy)benzamide
Chiral
S, N )"'10 ~
N F
O
(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl 2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate
L-Alaninol (4.8g, 64mmole) and 2-mesitylenesulfonyl chloride (30g, 137mmole)
were
dissolved in 200mL pyridine and stirred at room temperature overnight. The
mixture was
evaporated, dissolved in ethyl acetate (200m1) and washed with 1M HCl/aq ,
sat. NaHCO3/aq.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
The organic layer was dried, concentrated and purified on a silica gel column
chromatography
(heptane-ethyl acetate).
APCI-MS m/z: 440.1 [MH+].
Methyl 5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzoate
5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid (468mg, 3 mmole) was refluxed in methanol (20
mL
+6 drops of conc H2SO4) overnight followed by evaporation to dryness. The
product was used
in next step without further purification.
5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzamide
Methyl 5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzoate was dissolved in 37% NH3/aq ( 20inL) and
stirred
at 50 C for 60 hours. The solution was concentrated, diluted with ethylacetate
(20mL) and
washed with brine. The product was used in the next step without any further
purification.
APCI-MS m/z: 156.0 [MH+].
Aryl ether formation:
5-Fluoro-2-( {(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide
(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propy12,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate (263mg,
0.6mmole) was added to a slurry containing CsZCO3 (487mg, 1.5mmole) and 5-
fluoro-2-
hydroxybenzamide (app. lmmole) in 2.5mL DMF. The reaction mixture was stirred
overnight
in room teperature before it was diluted with ethylacetate (20mL) and washed
with 1M
HC1/aq. The organic layer was dried, concentrated and purified on HPLC-C18.
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.79 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (s, 2H), 7.50 (dd,
J= 9.5,
3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (ddd, J= 9.1, 7.7, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 6.99 - 6.88 (m, 3H), 3.87
(d, J= 5.9 Hz,
2H), 3.56 - 3.45 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 0.93 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 395.2 [MH+].
Examples 85-95 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
Example
84 using the corresponding starting materials.
Example 85
2-({(2S)-2-[(MesitYlsulfonyl)amino]propylloxy)-5-methylbenzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
56
p Chiral
p Np ~
S,
N I /
O
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 7.78 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.59 - 7.51 (m, 2H),
7.40 (s,
1H), 7.14 (mult, 1H), 6.92 (s, 2H), 6.78 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (d, J= 5.8
Hz, 2H), 3.50 (dd,
J= 8.3, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 2.18 (d, J= 3.1 Hz, 3H), 0.91
(d, J= 6.8 Hz,
3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 391.1 [MH+].
Example 86
2-HydroM-6-({(2S)-2-f(mesi lsulfonyl)aminolpropyl}oxy)benzamide
O N Chiral
O ~S ,O
" NJ,-,O
o
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 8.07 (d, J= 22.4 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (d, J= 8.4 Hz,
1H), 7.20
(t, J= 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (s, 2H), 6.39 (ddd, J= 21.5, 8.3, 0.8 Hz, 2H), 3.96 -
3.79 (m, 2H),.
3.66 - 3.52 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.19 (s, 3H), 0.88 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 393.2 [MH+].
Example 87
5-Chloro-2-( {(2S)-2-r(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide
Chiral
p /O
S" N O
N CI
O
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 7.79 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (t, J= 2.5 Hz, 1H),
7.66 -
7.60 (m, 2H), 7.39 (dd, J= 8.8, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 6.97 (d, J= 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (s,
2H), 3.90 (d, J
= 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.53 (dd, J= 20.7, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.18 (s, 3H),
0.94 (d, J= 6.8 Hz,
3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 411.1 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
57
Example 88
2-(1(25)-2-j(Mesi lsulfonyl)amino]propyl oxy)-4-methylbenzamide
O\ ~p ~ Chiral
S\N /
NO~
O
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 8 7.80 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (d, J= 7.7 Hz, 1H),
7.51 (s,
1H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 6.91 (s, 2H), 6.77 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.73 (s, 1H), 3.87
(d, J= 5.7 Hz, 2H),
3.59 - 3.45 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.17 (s, 3H), 0.92 (d, J= 6.8
Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 391.1 [MH+].
Example 89
2-({(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfon~)amino]propylloxy)benzamide
0 NChiral
1 IOI
S-N O
1H NMR (399.988 MHz, CDC13) S 8.05 (dd, J= 7.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.92 - 7.82 (m,
1H), 7.37
(s, 1H), 7.00 (t, J= 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (s, 2H), 6.80 (d, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H), 5.73 -
5.60 (m, 1H),
4.05 - 3.94 (m, 2H), 3.89 - 3.78 (m, 1H), 2.66 (s, 6H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1.13 (d,
J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 377.2 [MH+].
Example 90
4-Fluoro-2-({(2S,-2-[(mesi lsulfonyl)amino]propylloxy)benzamide
p~ sO Chiral
.S\N I O \ N F
O
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.87 - 7.79 (m, 2H), 7.49 (s, 2H), 6.94 - 6.72
(m, 4H),
3.92 - 3.87 (m, 2H), 3.54 (dd, J= 8.2, 6.7 Hz, IH), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.17 (s,
3H), 0.93 (d, J= 6.8
Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 395.2 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
58
Example 91
4-Chloro-2-(1(2S)-2-[(mesi lsulfonyl)aminolpropyl}oxy)benzamide
O\\ O ~ Chiral
S.N O ~ CI
N ~ ~
O
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 7.80 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.76 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 2H),
7.55 (s,
2H), 7.53 (s, 2H), 7.06 - 6.99 (m, 2H), 6.90 (s, 2H), 3.91 (d, J= 5.9 Hz, 2H),
3.57 - 3.48 (m,
10H), 2.50 (s, 10H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 0.94 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 411.1 [MH+].
Example 92
5-Cyano-2-(1(2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)ainino]propylloxy)benzamide
O O N O Chiral
S
Nj',~O
~
N
H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 8.27 (d, J= 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 7.69 (dd,
J= 8.6,
2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.97 - 6.91 (m, 3H), 6.85 (s, 1H), 6.04 (d, J= 7.5 Hz, 1H), 4.15
(dd, J= 9.2, 3.9
Hz, 1H), 4.06 - 3.86 (m, 2H), 2.67 (s, 6H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 1.05 (d, J= 6.6 Hz,
3H)
APCI-MS in/z: 402.1 [MH+].
Example 93
2-({(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl amino]propylloxy)-5-methoxybenzamide
O s0 Chiral
N I
O
N
O
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) 6 7.78 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.49 (s,
1H), 7.32
(d, J= 3.1 Hz, 1H), 6.95 - 6.81 (m, 4H), 3.81 (d, J= 5.7 Hz, 2H), 3.68 (s,
3H), 3.53 - 3.42 (m,
1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 0.91 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
59
APCI-MS m/z: 407.2 [MH+].
Example 94
3-({ 2S)-2-('(Mesitylsulfonyl)aminolpropylloxy)-4-methylbenzamide
O //O N Chiral
S :
\N C o
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.67 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (dd,
J= 7.6,
1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.23 - 7.17 (m, 2H), 7.10 (dd, J= 7.7, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (s, 2H),
3.75 (ddd, J=
34.1, 9.7, 5.8 Hz, 2H), 3.51 - 3.41 (m, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.16 (d, J= 6.6 Hz,
3H), 2.01 (s,
3H), 1.04 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS in/z: 391.1 [MH+].
Example 95
2-(1(2S)-2-((Mesitylsulfonyl)aminolpropylloxy)-4-methoxybenzamide
0,, ,O Chiral
S~N~p ~ O
N I /
O
1H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.84 - 7.76 (m, 2H), 7.44 (s, 1H), 7.26 (s, 1H),
6.91 (s,
2H), 6.54 (ddd, J= 8.8, 4.0, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.41 (d, J= 2.4 Hz, 1H), 3.91 - 3.86
(m, 2H), 3.74
(s, 3H), 3.54 (dd, J= 8.2, 6.5 Hz, 1H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.17 (s, 3H), 0.91 (d,
J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 407.2 [MH+].
Example 96
2 5-Dichloro-N-f(1S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-~y)-1-methylethyl]thiophene-3-
sulfonamide
Oõ O Ci
N
OH g Chiral
Ci
2- [(1 S)-2-Hydroxy-l-methylethyl] -1 H-i soindo le-1, 3(2H)- dione
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
Phthalic anhydride (50mmole, 7.4g) was dissolved in 100mL toluene together
with L-
alaninol (50mmole, 3.9mL) and DIEA (5inmole, 900 L). The mixture was refluxed
with
continues removal of water with a Dean-Stark apparatus for two hours before it
was washed
with 1M HCI/aq, sat. NaHCO3/aq. The organic layer was dried, concentrated and
used in the
next step without any further purification.
APCI-MS m/z: 206.0 [MH+].
(2S)-2-(1,3-Dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)propyl4-methylbenzenesulfonate
4-Methylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (43mmole, 8.2g) and 2-[(1S)-2-hydroxy-l-
methylethyl]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione (43mmole, 8.8g) were dissolved in
pyridine
(200mL) and stirred overnight in room temperature. The mixture was evaporated,
dissolved in
ethyl acetate (200m1) and washed with 1M HCllaq, sat. NaHCO3/aq. The organic
layer was
dried, concentrated and purified on a silica gel column chromatography
(heptane-ethyl
acetate).
APCI-MS m/z: 360.0 [MH+].
2-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl] -1 H-isoindole-1,3 (2H)-dione
(2S)-2-(1,3-Dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)propyl4-methylbenzenesulfonate
(8
mmole, 2.9g) was added to a slurry containing CsZCO3 (4g, 12mmole) and 5-
hydroxyisoquinoline (1.3g, 8.8mmole) in lOOmL DMF. The reaction mixture was
stirred for
two hours at 100 C before it was diluted with water (200mL) and extracted with
ethylacetate
(3xl5OmL). The combined organic layers were dried, concentrated and purified
on a silica gel
column chromatography (heptane-ethyl acetate).
Amine prenaration
[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl] amine
2-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
(4.7mmole, 1.56g) was dissolved in ethanol (40mL) together with hydrazine
hydrate
(14.lmmole, 684 L) and acetic acid (14.lmmole, 805 L) and refluxed for 3
hours. Solid
material was removed by filtration and the solution was concentrated and
purified on an ion
exchange column (DOWEX 50WX2-400).
APCI-MS m/z: 203.1 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
61
Sulfonamide coupling:
2,5-Dichloro-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]thiophene-3-
sulfonamide
2,5-Dichlorothiophene-3-sulfonyl chloride (100 L, 0.3M/THF) was mixed with
[(1S)-
2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]amine (100 L, 0.3M/pyridine) and stirred
overnight in
ambient temperature before it was evaporated to dryness under reduced
pressure. The residue
was purified on HPLC-Cig.
APCI-MS m/z: 349.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Examples 97 - 122 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
Example 96 using the corresponding starting materials.
Example 97
N-[(1 S)-Isoquinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyll-5-methyl-l-phenyl-lH-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide
O, Chiral
S, NJ,_.,O
N j
~ N I
N
APCI-MS m/z: 423.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.7 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 98
1 -(Difluoromethyl)-N-[(1S -iso uinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyl1-3,5-dimethyl-
lH-
pylazole-4-sulfonamide
N' F
N.N~ Chiral
F
H
O~ "0
N ss
APCI-MS m/z: 411.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Exam lp e 99
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
62
N-[(1S)-2- Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2 5-dimethylfuran-3-sulfonamide
0~ //0
N~ H~S o Chiral
APCI-MS m/z: 361.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 100
?- 5-Dichloro-N-[(1 S)-1-inethyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyllthiophene-3-
sulfonamide
CS,C Cl
N~
H S Chiral
CI
APCI-MS m/z: 416.9, 419.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 101
3-Bromo-5-chloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyllthiophene-2-
sulfonamide
0, ,,~ Br
N C~\H Chiral
S
CI
APCI-MS m/z: 460.9, 463.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.1 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 102
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-5-[ 1-methyl-5-
(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-
3 -yl] thiophene-2-sulfonainide
p, ,0 Chiral
N\ O--/~N S ~ ~ N N F
~ F
Z- F
APCI-MS m/z: 497.0 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
63
LC (method A) rt = 4.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 103
1-(Difluoromethyl)-N-[(1S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyll-5-methyl-1H-
pyrazole-4-
sulfonainide
N F Chiral
N
"N
F
O O /S\\O
APCI-MS m/z: 397.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.3 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 104
5-Methyl-N-f (l S)-1-methyl-2-(guinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide
O Chiral
S, N~O /
~ N
APCI-MS m/z: 416.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 105
5-Chloro-N-f (1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyllthiophene-2-
sulfonamide
O, ,O Chiral
N\ S
I ~ ~ CI
APCI-MS m/z: 383.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 106
5-Chloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloy)ethyllthiophene-2-sulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
64
/ O ,O Chiral
N~ I CNS S
I CI
~
APCI-MS m/z: 383.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 107
Methyl4-(f (1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyl]amino} sulfonyl)-2,5-
dimethyl-3-
furoate
Chiral
O O=
O S-N~fO
O N
APCI-MS m/z: 419.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.8 min. W 254 nm.
Example 108
N-[(1S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy -1-methylethyl]thiophene-3-sulfonamide
Chiral
~S-- N/~
O\//O O
S N
APCI-MS m/z: 349.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 109
1 -Ethyl-N-f (1 S)-2-(isoguinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyll-lH-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide
~ o Chiral
C\\ /O
S\N
r N
N
APCI-MS m/z: 361.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 2.9 min. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
Example 110
2-[((2S)-2-{r(2 5-Dichloro-3-thienl)sulfonl]aminolpro-Pyl)oxy1benzamide
N 0 = O~, ~O CiChiral
S
O~~N~
S
Ci
APCI-MS m/z: 409.0,410.9 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.7 min. TJV 254 nm.
Example 111
1-(Difluoromethyl)-3 5-dimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyll-
lH-pyrazole-
4-sulfonamide
6--- F Chiral
N
F
N
O N ~S\~O
O
APCI-MS m/z: 411.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.4 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 112
N-[(1 S)-1-Methyl-2_(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]-5-[1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethul)-
1H-pyrazol-3-
yl1thiophene-2-sulfonamide
O Chiral
~ O1f~N S N'N
N, 1
\ F
APCI-MS m/z: 497.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 113
1-Ethyl-N-f (l S)-1-methyl-2-(guinolin-5-yloxy)ethyll-lH-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
66
0\\ /p )",I0 Chiral
S~N
I
r N\N- I
N
APCI-MS m/z: 361.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 2.9 min. W 254 nm.
Example 114
2-(1(2S -2-(( f 5-[1-Methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-2-
thienyllsulfonyl)-
amino]propyl} oxy)benzamide
N 0 O.,SO N' ~ Chiral
O~/-N T/ ~ F
~ F
APCI-MS m/z: 489.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 5.1 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 115
2-[((2S)-2- { [(2,5-Dimethyl-3-thienyl)sulfonyl] amino Ipropyl)oxy]benzamide
N 0 p p Chiral
S
s
APCI-MS m/z: 369.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.4 min. W 254 nm.
Example 116
2 5-Dimethyl-N-f (1 S)-1-methyl-2-(guinolin-5-yloxy)ethy11furan-3-sulfonamide
S
0 0
N C,,/\H/
Chiral
APCI-MS m/z: 361.1 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
67
LC (method A) rt = 3.7 min. UV 254 mn.
Example 117
2-f((2S)-2-~j(2 5-Dimeth 1-~ 3-furyl)sulfonyllaminolpropyl)oxylbenzamide
N 0 = 0 0 Chiral
S
i
~o
APCI-MS m/z: 353.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.2 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 118
2-{,[(2S)-2-({(1-(Difluoromethyl)-3 5-dimethyl-lH-pyrazol-4-
yllsulfonyllamino)propyll-
oxylbenzamide
NH2 F
C H F Chiral
C,,-yN ,S\\
O
APCI-MS m/z: 403.0 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 119
1 -Ethyl-N-f (1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyll-3-methyl-IH-pyrazole-
4-
sulfonamide
0 O
's
N\ OH~ I ~N
N Chiral
APCI-MS m/z: 375.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.0 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 120
N-f (1 S)-2-(Isoguinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-1 3,5-trimethyl-lH-pyrazole-4-
sulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
68
Chiral
0
O \ O
N-S
S 'N
N I
APCI-MS m/z: 375.1 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 2.9 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 121
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3,5-diinethylisoxazole-4-
sulfonamide
Chiral
~ O 0 1
S~N/
O 1
O1~
N LN
APCI-MS m/z: 362.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.3 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 122
N-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloM)-1-methyleth3LI]-2,5-dimethylthiophene-3-
sulfonamide
N, ~S O
H s Chiral
APCI-MS m/z: 377.2 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Example 123
2 4 6-Trimethyl-N-{(1S)-1-methyl-2-f (8-methylquinolin-5-yl)aminolethyl}-
benzenesulfonamide
O, ,O Chiral
~~2N
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
69
(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propy12,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate was
prepared
as described in Example 77.
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N- {(1 S)-1-methyl-2-[(8-methylquinolin-5-yl)amino]
ethyl}benzene-
sulfonamide
(2S)-2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propyl 2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate (132mg,
0.3mmole) and 8-methylquinolin-5-amine (47mg, 0.3mmole) were dissolved in NMP
(lmL)
and heated to 130 C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was purified directly on
HPLC-C18.
1H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) S 8.80 (d, J= 5.2 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (d, J= 9.4 Hz, 1H),
7.57 (d,
J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J= 8.6, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J= 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.83
(s, 2H), 6.11 (d,
J= 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.06 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 1 H), 3.3 8(q, J= 7.1 Hz, 1H), 3.06 (dd,
J= 13.7, 8.1 Hz,
2H), 2.50 (s, 6H), 2.49 (s, 3H), 2.14 (s, 3H), 1.01 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
APCI-MS m/z: 398.1 [MH+].
Examples 124 - 129 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
Example 123 using the corresponding starting materials.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
xample 124
4 6-Trimethyl-N-{(1S)-l-methyl-2-[(6-methylquinolin-5-Y)aminolethyll-
enzenesulfonarnide
O, ,O Chiral
S, NJ",~N
N
H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) b 8.80 (d, J= 3.0 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (d, J= 7.6 Hz, 1H),
7.57 (s,
H), 7.36 (dd, J= 8.4, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J= 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.83 (s, 2H), 6.11
(d, J= 7.8 Hz,
H), 6.07 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 1H), 3.40 - 3.33 (m, 1H), 3.06 (d, J= 5.3 Hz, 2H),
2.50 (s, 6H), 2.50
3, 3H), 2.14 (s, 3H), 1.01 (d, J= 6.5 Hz, 3H)
L.PCI-MS m/z: 398.1 [MH+].
xample 125
d-[(1 S)-2 -(1 H-Indazol-4-ylamino)-1-methylethyl] -2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O Chiral
11
S'NN /
O \ ~
NN
H NMR (399.991 MHz, cd3cn) 6 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.03 (d, J= 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (t,
J= 7.8 Hz,
H), 6.81 (s, 2H), 6.21 (d, J= 7.4 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.60 -
3.49 (m, 1H), 3.21
mult, 2H), 2.51 (s, 6H), 2.18 (s, 3H), 1.14 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
PCI-MS m/z: 373.1 [MH+].
{xMle 126
4 6-Trimethyl-N-r(1S -1-methyyl-2-(q,uinolin-5-
ylamino)ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
O\ // O Chiral
S" NJI,~_,N
-H NMR (299.946 MHz, cd3cn) S 8.80 (d, J= 4.0 Hz, 1H), 8.10 (d, J= 8.6 Hz,
1H), 7.34
mult, 3H), 6.74 (s, 2H), 6.36 (d, J= 7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.68 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H),
5.23 (s, 1H), 3.57
mult, 1H), 3.18 (mult, 2H), 2.51 (s, 6H), 2.12 (s, 3H), 1.17 (d, J= 6.6 Hz,
3H)
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
71
1'CI-MS m/z: 384.1 [MH+].
,xample 127
f-[(1 S)-2-(1H-Indazol-6-ylamino -1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O Chiral
S, J,N N
N
O N
H NMR (399.991 MHz, cd3cn) 6 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.41 (d, J= 8.7 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (s,
2H), 6.38
3d, J= 8.8, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.34 (s, 1H), 5.63 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.46 (t, J=
6.5 Hz, 1H), 3.07
td, J= 13.4, 7.7 Hz, 2H), 2.56 (s, 6H), 1.10 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H), 2.17 (s, 3H)
LPCI-MS in/z: 373.1 [MH+].
xample 128
4 6-Trimethyl-N-{(1S)-1-methyl-2-[(2-methylquinolin-5-yj)amino]ethyl}-
,enzenesulfonamide
OõO
N I ~
H ~N
~ Chiral
i
H NMR (399.991 MHz, cd3cn) 6 7.99 (d, J= 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (t, J= 8.0 Hz, 1H),
7.23 (d, J
= 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (s, 2H), 6.31 (d, J= 7.7 Hz, 1H),
5.69 (d, J= 6.7
iz, 1H), 5.17 (s, 1H), 3.56 (d, J= 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.16 (mult, 2H), 2.64 (s, 3H),
2.52 (s, 6H),
.14 (s, 3H), 1.17 (d, J= 6.7 Hz, 3H)
TCI-MS m/z: 398.1 [MH+].
xample 129
1-[(1S)-2-(1H-Indazol-5-ylamino)-l-methylethyll-2 4 6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O ),"'I Chiral
oN N
N
N
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
72
Ei NMR (399.991 MHz, cd3cn) 6 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.39 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (s,
2H), 6.85 (s,
Ei), 6.83 (d, J= 2.1 Hz, 1H), 5.82 (d, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H), 3.50 (t, J= 6.4 Hz,
1H), 3.12 (mult,
EI), 2.57 (s, 6H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.06 (d, J= 6.7 Hz, 3H)
.PCI-MS m/z: 373.1 [MH+].
xample 130
[-((1 S)-2- { [2-Chloro-4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl] amino } -1-inethylethyl)-
2,4,6-
-imethylbenzenesulfonamide
0 CI Chiral
SJ\/N
O
S
O'I
H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) 6 7.63 (d, J= 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (s, 1H), 7.47 (dd, J=
8.7, 2.0
fz, 1H), 6.89 (s, 2H), 6.58 (d, J= 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.16 (t, J= 5.8 Hz, 1H), 3.22 -
3.03 (in, 6H),
.51 (s, 6H), 2.20 (s, 3H), 1.01 (d, J= 6.5 Hz, 3H)
&CI-MS m/z: 445.0 [MH+].
Examples 131-144 were prepared via the aryl ether formation as described in
Example
4, using (2S)-2-[(mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propy12,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate
and the
orresponding starting materials.
;xample 131
1-r(1 S)-4-Cyano-2 6-dimethylphenoxy)-1-methylethyll-2,4,6-
rimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O, ,O Chiral
N-U
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.76 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (s, 2H), 7.01 (s,
2H), 3.82 -
~.71 (m, OH), 3.57 - 3.37 (m, 3H), 2.55 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 2.10 (s, 6H),
1.13 (d, J= 6.6 Hz,
U)
TCI-MS m/z: 387.2[MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
73
,xample 132
1-f(1S)-2-(3-Cyano henoxy)-1-meth ly ethyl]-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
~ Chiral
0 "\ o 0
S
'_ N
II
N
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) b 7.72 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.44 - 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.03
- 6.98
m, 2H), 6.95 (s, 2H), 3.82 - 3.77 (m, 2H), 2.52 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.09
(d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
1P CI-M S m/z : 3 5 9. 2[MH+] .
;xample 133
1-[(1S)-2- 3-MethoWhenoxy)-1-meth ylethyl]-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
Chiral
O" S O O
" N
'H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.68 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (t, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H),
7.00 (s,
!H), 6.47 (ddd, J= 8.3, 2.4, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 6.28 (ddd, J= 8.2, 2.3, 0.7 Hz, 1H),
6.21 (t, J= 2.4
iz, 1H), 3.79 - 3.63 (m, 2H), 3.48 - 3.36 (m, 1H), 2.55 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H),
1.06 (d, J= 6.8
lz, 3H)
\PCI-MS mlz: 364.1 [MH+].
?xample 134
142-(3 5-Dimethoxyphenoxy -1-meth l~thyll-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O" ,o
S, N J"~O 01~1
o1-1
kPCI-MS m/z: 394.1 [MH+].
. C (method A) rt = 6.lmin. UV 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
74
>xample 135
1-F2-(4-Cyano-2-methoxyphenoxy)- l -methylethyl]-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O. ,O
~S, N O
i N
&CI-MS m/z: 389.1 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.7 inin. UV 254 nm.
;xample 136
1-{2-[(2-Bromopyridin-3-yl)oxy]-1-meth yleLhyl}-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
N Br
0N,
is~~
S
O
TCI-MS m/z: 413.1, 415.1 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.5 min. UV 254 nm.
?xample 137
,4 6-TrimethYl-N-{1-methyl-2-[(2-methylpyridin-3-yl
oxy]ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
1
i
~ ~
O ~
\ N~
S
O~ \O
\PCI-MS m/z: 349.2 [MH+].
. C (method A) rt = 3.8min. UV 254 nm:
yxample 138
>- {2-[(Mesitylsulfonl)amino]propoxyl-N-methylbenzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
N O
O
11
S,NJ\/O
O
H NMR (399.988 MHz, CDC13) 6 8.14 (dd, J= 7.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.38
(dd, J=
5.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (t, J= 7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (s, 2H), 6.82 (d, J= 8.4 Hz,
1H), 4.94 - 4.82
n, 1H), 3.99 - 3.96 (m, 2H), 3.88 - 3.78 (in, 1H), 3.06 (d, J= 4.9 Hz, 3H),
2.65 (s, 6H), 2.29
;, 3H), 1.12 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
,PCI-MS m/z: 391.2 [MH+].
,xample 139
-12-[(Mesitylsulfonl)aminolpropoxY}benzamide
N
) I / N\
O"'~f
O
H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) S 7.73 (dd, J= 6.9, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 6.91 (s, 2H), 6.77
(d, J=
.2 Hz, 2H), 5.03 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 3.89 - 3.74 (m, 2H), 3.75 - 3.63 (m, 1H),
6.16 - 5.63 (m,
H), 2.65 (s, 6H), 2.27 (s, 3H), 1.26 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
&CI-MS m/z: 377.3 [MH+].
;xample 140
1-{2-[4-(1H-Imidazol-l-yl)t2henoxy]-1-methylethl}-2 4 6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
J1,10
S, N
.
H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 69.02 (s, 1H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.46 - 7.39 (m, 3H),
6.96 (d, J=
1.3 Hz, 4H), 5.10 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (t, J= 4.2 Hz, 2H), 3.77 - 3.62
(in, 1H), 2.67 (s,
IH), 2.29 (s, 3H), 1.26 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
TCI-MS m/z: 400.2 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
76
xample 141
1-f(1S)-3 4-DimethoxyphenoxX -1-methylethyl]-2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
O'\ Chiral
S, N"I"-" O ~ O
~ ~
O
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 7.67 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (s, 2H), 6.77 (d, J=
8.8 Hz,
H), 6.29 (d, J= 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.20 (dd, J= 8.6, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 3.75 - 3.5 5(m,
9H), 2.55 (s, 6H),
.24 (s, 3H), 1.06 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 3H)
&CI-MS m/z: 394.3 [MH+].
xample 142
1-(2- {2-[(Mesitylsulfonyl)amino]propoxylphenyl)acetamide
O
O, p
S, N--k
N~ \~O
H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 6 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.41 - 8.36 (m, 1H), 6.99 - 6.93
(m, 4H),
i.75 - 6.69 (m, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 3.96 (d, J= 5.7 Hz, 1H), 3.74 (d, J= 4.6
Hz, 2H), 2.66 (s,
H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 1.09 (d, J= 6.4 Hz, 3H)
PCI-MS m/z: 391.2 [MH+].
3xample 143
1-12-r(6-Chloropyridin-3-yl oxy]-1-methylethyll-2,4,6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
CI
N~ I N~ \ ~
p-0
kPCI-MS m/z: 369.2 [MH+].
. C (method A) rt = 5.6 min. UV 254 nm.
Sxample 144
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
77
1-f(1S)-2-(2H-Indazol-3- loxy)-1-methylethyll-2 4 6-
trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
~ Chiral
/0
N-N
O
'H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) b 11.79 (s, 1H), 7.72 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (d,
J= 8.0 Hz,
. H), 7.30 (d, J= 3.5 Hz, 2H), 6.98 (dt, J= 8.0, 3.9 Hz, 1 H), 6.88 (s, 2H),
4.14 - 4.00 (m, 2H),
1.63 (quintet, J= 6.9 Hz, 1H), 2.54 (s, 6H), 2.16 (s, 3H), 1.11 (d, J= 6.7 Hz,
3H)
OCI-MS m/z: 374.1 [MH+].
,xample 145
~-Meth 1-N-r3=phenl-l-(trifluoromethyl)propyllbenzenesulfonamide
F F
F
0
S~N
O
=-Methyl-N-[(1 Z)-3-phenylpropylidene]benzenesulfonamide
A mixture of 4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (10 inmole, 1.71g), 3-phenylpropanal
10mmole, 1.34g) and sodium p-toluenesulfinate (1lmmole, 1.78g) in formic acid
(1 5mL)
nd water (15mL) was stirred over night. The resulting white precipitate was
filtered off,
vashed with water (2x10mL), pentane (10mL) and dissolved in dichloromethane
(100mL).
4turated NaHCO3/aq (70inL) was added and the mixture was stirred vigorously
for 2 hours.
'he organic phase was decanted and the aqueous phase was extracted with
CH2C12. The
ombined phases was dried and evaporated to dryness and used in the next step
without any
urther purification.
-Methyl-N-[3-phenyl-l-(trifluoromethyl)propyl]benzenesulfonamide
TBAT (1.lmmole, 594mg) was dissolved in dry THF (l2mL) and cooled to 0 C under
iert conditions. In a separate flask 4-methyl-N-[(1Z)-3-phenylpropylidene]-
enzenesulfonamide (1 mmole, 287mg) and trimethyl(trifluoromethyl)silane
(1.2mmole,
70mg) were dissolved in dry THF (lOmL) and slowly added to the TBAT-solution.
The
iixture was stirred for 45 min at 0 C before it was quenched with sat.
NH4C1/aq (6mL) . At
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
78
:)om temperature the mixture was extracted with ethylacetate. The organic
phase was dried,
oncentrated and purified on a silica gel column chromatography (heptane-ethyl
acetate).
H NMR (299.946 MHz, DMSO) S 8.71 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dt, J= 6.5, 1.9 Hz,
2H),
.54 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.42 - 7.26 (m, 3H), 7.16 - 7.12 (m, 2H), 4.18 - 4.00
(m, 1H), 2.55 -
.34 (m, 5H), 2.06 - 1.91 (m, 1H), 1.88 - 1.70 (m, 1H)
F NMR (470.314 MHz, DMSO) 8 -74.42 (d)
xample 146
4-F(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-inethylethyl]-2,4-
dimethylbenzenesulfonamide
Chiral
N N
S=0 0
O
,4-Dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride
2,4-Dimethylbenzenesulfonic acid (lOmmole, 1.86g), DIEA (10 mmole, 1.7mL) and
yanuric chloride (10mmole,1.84g) were dissolved in acetone (40mL) and the
reaction
aixture was refluxed overnight. After cooling to room temperature the mixture
was filtered
hrough a Celite pad. Solvent was removed by evaporation under reduced
pressure. The
iroduct was used in the next step without any further purification.
1-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-2,4-dimethylbenzenesulfonamide
The sulfonamide coupling was performed as described in Example 96 using the
orresponding starting materials.
OCI-M S m/z : 3 71. 2[MH+] .
,C (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
Examples 147 to 153 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described
in
,xample 146 using the corresponding starting materials.
,xample 147
1-[(1S)-Isoquinolin-5-yloxX)-1-methylehyll-3 4-dimethylbenzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
79
Chiral
S,, N
N
LPCI-MS m/z: 371.2 [MH+].
.C (methoA) rt = 3.8 min. W 254 nm.
,xample 148
d-[(1 S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyll-2,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonamide
Chiral
0
S\N
N
PCI-MS m/z: 371.2 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 149
4-Dimethyl-N-[(1S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
Chiral
N
I
O 00 iN
PCI-MS m/z: 371.2 [MH+].
JC (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
?xample 150
4-Dimethyl-N-[(l S)-1-methyl-2-(qninolin-5-yloy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
P Chiral
S\N y
/ TCI-MS m/z: 371.2 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 3.8 min. W 254 nm.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
xample 151
-f((2S)-2-{L(2 4-Dimeth l~phenyl)sulfonyl]aminoI propyl)oxy]benzamide
Chiral
N N O
S=0 0
O
PCI-MS m/z: 363.2 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.5 min. UV 254 nm.
?xample 152
5-Dimethyl-N-[(1S)-1-methyl-2- quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
Chiral
O~~ ~j0 O
S\N
P CI-M S m/z : 3 71. 2[MH+] .
,C (method A) rt = 3.8 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 153
-f ((2S)-2-{[(3,4-Dimethylphenl)sulfonyllamino}propyl)oxylbenzamide
Chiral
S ~
J""O
0 N
C
N
PCI-MS m/z: 363.2 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.5 min. UV 254 nm.
Examples 154 to 158 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described
in
?xample 96, "Sulfonamide coupling", using the corresponding starting
materials.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
81
gmple 154
-(2-Anilinoeth)Ll,)-2 4 6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamide
N
S
O O
PCI-MS m/z: 319.4 [MH+].
C(method A) rt = 4.6 min. UV 254 nm.
xam-ple 155
_[2-(2 6-Dimethylphenoxy)-1-methylethyl]-4-
(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonainide
F
F
F
O~N~
OS
~
O
,C (method A) rt = 5.4 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 156
1-(2-Anilinoethyl)-4'-fluorobiphenyl-4-sulfonamide
0. O
PCI-MS m/z: 371.0 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.0 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 157
4-(2-Anilinoethyl)-4-methoxy-2 3 6-trimethylbenzenesulfonamid
O
~ S~~
O O
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
82
PCI-MS m/z: 349.1 [MH+].
C (method A) rt = 4.7 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 158
-(2-Anilinoethy)-4-bromo-2-methylbenzenesulfonaiuid
OI /O
N~~NI'S
I I ~
Br
.PCI-MS m/z: 369.1, 371.1 [MH+].
.C (metliod A) rt = 4.8 min. UV 254 mu.
xample 159
-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-[(1S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl1-3,5-dimethyl-
lH-
yrazole-4-sulfonamide
0 Chiral
ii
N / OH O ~ N
-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3, 5-dimethyl-1 H-pyrazole
4-Fluorophenylhydrazine hydrochloride (3mmole, 488mg) and acetylacetone
3mmole, 310 L) were refluxed in ethanol (25mL) for 1 hour before the reaction
mixture was
vaporated to dryness. The residue was used in the next step without any
purification.
-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3,5-dimethyl-lH-pyrazole-4-sulfonyl chloride
1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3,5-dimethyl-lH-pyrazole (app. 3mmole) was dissolved in
hloroform (4OmL). Chlorosulfonic acid (30mmole, 2mL) was added dropwise and
the
eaction mixture was refluxed for 2 hours. After cooling the mixture to room
temperature
ulfuryl chloride (25mmole, 2mL) was added. The reaction mixture was refluxed
for 3hours
lefore it was diluted with chloroform and washed with water. The organic phase
was dried,
oncentrated and purified on a silica gel column chromatography (heptane-ethyl
acetate).
&CI-MS m/z: 288.9 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
83
-(4-Fluorophenyl)-N-[(1 S)-2-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3,5-dimethyl-
lH-
,yrazole-4-sulfonamide
Amine preparation and Sulfonamide coupling were conducted using a method
nalogous to that described in Example 96.
H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) S 9.53 (s, 1H), 8.55 (d, J= 6.1 Hz, 1H), 8.31 (d, J=
6.1 Hz,
H), 7.99 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J= 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (t, J= 8.0 Hz, 1H),
7.36 (mult,
~H), 4.12 - 4.01 (m, 2H), 3.75 - 3.69 (m, 1H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 2.32 (s, 3H),
1.24 (t, J= 6.8 Hz,
,H)
WCI-MS m/z: 455.1 [MH+].
?xample 160
~-f (1S)-2-(Isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-1-methylethyl]-3,5-dimethyl-1-phenyl-lH-
pyrazole-4-
ulfonamide
Example 160 was synthesised using a method analogous to Example 159.
Chiral
1O
N ~ O11
H O ~ ~N
~ ~ ~ '
~
H NMR (399.99 MHz, DMSO) 8 59.50 (s, 1H), 8.53 (d, J= 6.1 Hz, 1H), 8.28 (d, J=
6.1 Hz,
H), 7.98 (d, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.82 (d, J= 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (t, J= 8.0 Hz, 1H),
7.54 - 7.43
m, 3H), 7.32 (dd, J= 6.4, 1.8 Hz, 3H), 4.06 (quintet, J= 4.7 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (q,
J= 6.4 Hz,
.H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 1.25 (d, J= 6.8 Hz, 3H)
OCI-MS m/z: 437.1 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
84
xample 161
1,2 4 6-Tetramethyl-N-j(1S)-1-methyl=3-phenylpropyl]benzenesulfonamide
Chiral
II'N
S-'-0
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl]benzenesulfonamide (109mg,
1.33minol) and potassium carbonate (272mg, 2.0mmo1) was dissolved in DMF
(1m1), the
olution was cooled to 0 C and iodomethane (41 l, 0.66mmo1) was added
dropwise. The
eaction mixture was stirred for 15h at ambient temperature, dispersed between
lichloromethane and water and extracted with dichloromethane. The coinbined
organic
hases were dried over sodium sulphate, filtered and evaporated.
H NMR (299.944 MHz, CDC13) 8 7.26 - 7.15 (m, 3H), 7.08 - 7.04 (m, 2H), 6.93
(s, 2H),
.75 (q,1H), 2.74 (s,3H), 2.58 (s, 6H), 2.56 - 2.40 (m, 2H), 2.31 (s, 3H), 1.86
-1.64 (m, 2H),
..19 (d, 3H).
JC-MS m/z: 345 [M].
,C (method B) rt =16.2 min. UV 254 nm.
3xample 162
! 4,6-Trimethyl-N-{1-[(guinolin-5-yloxy)methyl]propyl}benzenesulfonamide
O
I I N
O
S~O
I iN
The title compound was obtained from 2-mesitylenesulfonyl chloride, 2-
aminobutan-
.-ol and quinolin-5-ol by a method analogous to that described in Example 77.
-HNMR (400MHz, CDC13) S 8.96 (dd, 1H), 8.52 (d,1H), 7.74 (d,1H), 7.53 (s,1H),
7.39
m,1H), 6.83 (s,2H), 6.68 (d,1H), 5.50 (bs, 1H), 4.12 (dd, 1H), 3.98 (dd, 1H),
3,63 (m, 1H),
!.63 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.75 (m, 2H), 0.91 (t, 3H).
OCI-MS m/z: 399 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
C (method B) rt = 8.1 min. UV 254 nm.
,xample 163
-Chloro-2- ~2-r(mesitylsulfonyl)aminolbutoxY}benzamide
O N
101,N O
SO
Ci
The title compound was obtained from 2-mesitylenesulfonyl chloride, 2-
aminobutan-
-ol and 5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzamide by a method analogous to that described in
Example
7.
H NMR (400MHz, dimethylsulfoxide-d6) S 7.73 (d, 1H), 7.43 (dd, 1H), 6.97 (d,
1H), 6.93
s, 2H), 3.95 (m,2H), 3.36 (m,1H), 2.53 (s, 6H), 2.21 (s, 3H), 1.54 - 1.35 (in,
2H), 0.68 (t,
,H).
OCI-MS m/z: 425/427 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method B) rt = 11.7 inin. UV 254 nm.
Examples 164 - 184 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
xample 17 using the corresponding starting materials.
xample 164
4-Dichloro-6-methyl-N-[(1S)-1-methyyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxY)ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
= o O CI Chiral
O\%'-N~g"
Ci
VCI-MS m/z: 425/427 [MH+].
X (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm.
xample 165
i-Chloro-2-{f(2S)-2-({[4-(4-fluorophenoxy)-
phenyl]sulfonyl}amino)propylloxY}benzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
86
CI N Chiral
p F
S,,
O O
OCI-MS m/z: 479/481(3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.6 min. UV 254 nm
xample 166
-Chloro-2-{f(2S)-2-(ff4-(4-methoxy hp enox))phenyl]sulfonyl amino)propylloxy}-
-enzamide
\ Chiral
J.,i O
N
0
C \ O
~N,
O~gO i
/~'
TCI-MS m/z: 491/493 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.5 min. UV 254 nm
xample 167
~-Chloro-2-f f(2S)-2-(l[3-(4-chloro
henoxy)phenyl1sulfonyl}amino)propyl]oxy}benzamide
NI-I2 CI
~
~ Chiral
0 CI/
C N,S,' /
O"~O
PCI-MS m/z: 495/497 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.9 min. UV 254 nm
xam 1pe168
,4,5-Trichloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethl]benzenesulfonamide
CI Chiral
O% SO
N~
CI
CI
LPCI-MS m/z: 445/447 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
87
(method A) rt = 4.2 min. IJV 254 nm
ample 169
Chloro-2-{[(2S)-2-(lf3-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyllsulfonyl}anino)prop 1 oxY}-
,nzamide
NH2 Ci
O H I~ \ I CI Chiral
O~ OSO
PCI-MS m/z: 529/531 [MH+].
C(method A) rt = 6.2 min. W 254 nm
xample 170
(4-Chlorophenoxy) N-f(1S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyIlbenzenesulfonamide
0Cl ChiraO--)-N. O
S.
0-0
.PCI-MS m/z: 469/471 (3:1) [MH+].
.C (method A) rt = 4.9 min. UV 254 nm
,xample 171
-Chloro-2-[((2SZ-2- { [(2,4-dichloro-5-
fluorophenyl)sulfonyllamino}propyl)oxy]benzamide
NHz F CI
Nz~ O Chiral
O s~,
p 0 CI
~PCI-MS m/z: 455/457 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.1 min. UV 254 nm
xample 172
-Chloro-2- [(2S)-2-({[3-(4-
nethoxynhenoxy)phen~lsulfonyl} amino)propyl]oxy}benzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
88
ci N p\ Chiral
p
~p N. p ~
~O'~O
kPCI-MS m/z: 491/493 (3:1) [MH+].
. X (method A) rt = 5.5 min. TJV 254 nm
?xainple 173
5-Chloro-2-f ((2S)-2- { [(2-methoxy-4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]amino}
propyl)oxylbenzamide
H2N 0 = O. O 0--
0
H ~ Chiral
kPCI-MS m/z: 413/415 (3:1) [MH+].
-C (method A) rt = 4.8 min. UV 254 mn
,xample 174
1-(4-Fluorophenoxy)-N-[(1S)-1-meth yl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
N ~ Chiral
O O
NS
O'O
kPCI-MS m/z: 453 [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 4.6 min. UV 254 nm
Bxample 175
-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- { [(5-chloro-2-methoxypheny)sulfonyl]
amino}propyLy]benzamide
H2N 0 z p' O 0--
0 H'S
\ \ ' Chiral
CI
Ci
APCI-MS m/z: 433/435 (3:1) [MH+].
LC (method A) rt = 5.0 min. UV 254 nm
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
89
>xample 176
-Cyano-N-[(1 S)-1-methXl-2- quinolin-5-~y)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
Chiral
.S\N / I
O ~ '~
),-", O
J~ 1
&CI-MS m/z: 368 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 3.2 min. UV 254 mn
xample 177
,4-Dichloro-5-fluoro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
o F CI
~Chiral
N
,~
o 5CI
.PCI-MS m/z: 429/431 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm
3xample 178
!-F((2S)-2-{[(5-Bromo-2-methoxyphenl)sulfonyll amino} propyl)oxyl-5-
chlorobenzamide
N O O Chiral
O.,
O,NS
I ' \
CI
Br
WCI-MS m/z: 477/479 (1:1) [MH+].
. C (method A) rt = 5.0 min. UV 254 nm
xample 179
-Chloro-2-f ((2S)-2- { [(2-methoxy-5-
methylphenyl)sulfonyllamino}propylloxy]benzamide
N ~ Ã q. ,o C~Chiral
~I \ ~
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
.PCI-MS m/z: 413/415 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.8 min. UV 254 nm
xample 180
-Chloro-2- {[(2 S)-j[4'-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-4-yll sulfonyl}
amino)propyll oxy} -
enzamide
Q. . Chiral
S'N
F
F N Ci
&CI-MS m/z: 513/515 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 6.0 min. UV 254 nm
;xample 181
-(4-Methoxyphenoxyy -~f(IS -1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
\ Chiral
N 0
O ~ p
~N' ~
i
0
TCI-MS m/z: 465 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.5 min. UV 254 nm
,xam 1p e 182
;-Chloro-2-f ((2S)-2- { r(6-phenoxYpyridin-3-
yl)sulfonyl]amino}propyl)oxylbenzamide
O, ~O Chiral
Na~~' S~
NO
O'~
O /
\
N ci
~PCI-MS m/z: 462/464 (3:1) [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
91
,C (method A) rt = 5.1 min. UV 254 nm
?xample 183
i-Bromo-6-chloro-N-[(1 S)-1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyl]pyridine-3-
sulfonamide
C\\ ~p Chiral
~ N I
Br
N N
CI
VCI-MS m/z: 456/458 [MH+].
:C (metllod A) rt = 3.7 min. UV 254 mu
.xample 184
i-Broino-2-methoxy-N-f(1S -1-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-
yloxy)ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
/ OSO 0~
I C~~~N~
N~ I H Chiral
~
Br
kPCI-MS m/z: 451/453 (1:1) [MH+].
:C (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm
,xample 185
~T-[(1S -1-Methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy ethyl]-1-benzothiophene-2-sulfonamide
O p CH3 Chiral
~~ ss
S SNC
N
To a solution of (2S)-1-(quinolin-5-yloxy)propan-2-amine in DMF (100 L
).3M/DMF) was added diisopropylethylamine (120 L 0.3M /THF) followed by 1-
)enzothiophene-2-sulfonyl chloride (120 L 0.3M /THF). The reaction mixture was
stirred
wernight at ambient temperature, evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure
and purified
)n HPLC-C18.
kPCI-MS m/z: 399 [MH+].
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
92
,C (method A) rt = 3.9 min. UV 254 nm
Examples 186- 194 were synthesised by a method analogous to that described in
xample 185 using the corresponding starting materials.
>xample 186
-Chloro-2-f ((2S)-2- { [=(2,4-dimethoxyphenl)sulfonyl] aminoI
propyl)oxylbenzamide
S CH3 Chiral
/
13C'C C X ~
"
N
H2N
CI
O O
CH3
PCI-MS m/z: 429/431 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.6 min. UV 254 nm
?xample 187
-( {(2S)-2-[(1-Benzothien-2-ylsulfonyl)amino]propyl} oxy)-5-chlorobenzamide
O "O CH3 Chiral
S S~e ~N O
H2N ;)acl
O
OCI-MS m/z: 425/427 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.1 min. UV 254 nm
xample 188
>-Chloro-2-r((2S)-2- { j(4-methoxy-2,3,6-
trimethylphenY1)sulfonY1]amino~propyl)oxy]-
)enzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
93
H3C C\\ ~p CH3 Chiral
13 C SI*I N,-J~
CH3 H2 N ;)a CI
u
CH3
LPCI-MS m/z: 441/443 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.2 min. UV 254 nm
,xample 189
-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2-{r(5-fluoro-3-methyl-l-benzothien-2-
Y)sulfonyl]amino}propyl)ox ,1-,
enzamide
H3C O\' O CH3 Chiral
S O
" N
S H2N
CI
O
&CI-MS m/z: 457/459 (3:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 5.3 min. UV 254 nm
xample 190
-Chloro-2-[((2S)-2- {[(5-chloro-3-methyl-l-benzothien-2-
yI)sulfonLIlaminolpropyl oxy]-
ienzamide
H3C O // O CH3 Chiral
~N-J~O
;)acl
S H2N ~.PCI-MS m/z: 473/475 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm
xample 191
;-{[ 2S)-2-({r4-Bromo-2-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]sulfonyl}amino)propylloxy}-5-
,hlorobenzamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
94
F CH3 Chiral
+o O~ O O
F S\N
~ \ H2N CI
~
Br
PCI-MS m/z: 531/532 [MH+].
C(method A) rt = 5.5 min. UV 254 nm
xample 192
4 6-Trichloro-N-[(1S)-l-inethyl-2-(quinolin-5-ylox))ethyllbenzenesulfonamide
0 CH3 Chiral
CI C~~S ~O
~N
CI
.PCI-MS m/z: 445/447 [MH+].
C(method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm
xample 193
-Methoxy-2 3 6-trimethyl-N-[(1S)-1-methyl-2- quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyll-
benzenesulfonamide
0 CH3 Chiral
H3C C~~Ss
\ /.
1 3C
CH3 O N
CH3
&CI-M S m/z : 415 [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.0 min. UV 254 nm
;xample 194
-Bromo-N-[(1 S)-l-methyl-2-(quinolin-5-yloxy)ethyll-2-trifluoromethoxy)-
ienzenesulfonamide
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
F ~ H3C Chiral
~S\N
+ O O\ // o ON
F
Br
LPCI-MS m/z: 505/507 (1:1) [MH+].
,C (method A) rt = 4.2 min. UV 254 nm
xample 195
Iuman Glucocorticoid Receptor GR) Assay
The assay is based on a commercial kit from Panvera/Invitrogen (Part number
P2893).
he assay technology is fluorescence polarization. The kit utilises recombinant
human GR
Panvera, Part number P2812), a FluoromoneTM labelled tracer (GS Red, Panvera,
Part number
12894) and a Stabilizing Peptide IOX (Panvera, Part number P2815). The GR and
Stabilizing
eptide reagents are stored at -70 C while the GS Red is stored at -20 C. Also
included in
ne kit are 1M DTT (Panvera, Part number P2325, stored at -20 C) and GR
Screening buffer
OX (Panvera, Part number P2814, stored at -70 C initially but once thawed
stored at room
-mperature). Avoid repeated freeze/thaws for all reagents. The GR Screening
buffer lOX
omprises 100mM potassium phosphate, 200mM sodium molybdate, 1mM EDTA and 20%
)MSO.
Test compounds (l L) and controls (1 L) in 100% DMSO were added to black
olystyrene 384-well plates (Greiner low volume black flat-bottom, part number
784076).
1% control was 100%DMSO and 100% control was 10 M Dexamethasone. Background
olution (8 L; assay buffer lOX, Stabilizing Peptide, DTT and ice cold MQ
water) was added
c) the background wells. GS Red solution (7 L; assay buffer 1 X, Stabilizing
Peptide, DTT,
JS Red and ice cold water) was added to all wells except background wells. GR
solution
7 L; assay buffer l OX, Stabilizing Peptide, DTT, GR and ice cold water) was
added to all
vells. The plate was sealed and incubated in a dark at room temperature for
2hours. The
late was read in an Analyst plate reader (LTL Biosystems/Molecular Devices
Corporation) or
sther similar plate reader capable of recording fluorescence polarization
(excitation
vavelength 530nm, emission wavelength 590nM and a dichroic mirror at 561nm).
The IC50
Talues were calculated using XLfit mode1205.
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
96
Example No GRhuFL FP v2 (GR-binders)
IC50 ( M)
1 1.4
2 1.9
3 0.40
4 0.064
0.64
6 0.7
7 0.70
8 1.2
9 1.6
0.60
11 2.2
12 6.0
13 2.2
14 1.7
6.3
16 4.4
19 0.54
32 0.090
34 3.0
77 0.017
78 0.023
79 0.14
80 0.23
81 0.37
82 3.4
83 8.9
123 0.018
124 0.020
125 0.042
126 0.075
CA 02584413 2007-04-11
WO 2006/046916 PCT/SE2005/001610
97
160 0.096