Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
New Patent Application - Canada
based upon DE 102006017305.8
Applicant: Gerd Eisenblatter GmbH
A fastening system, fastening adapter and fastening method
The invention relates to a fastening system for mounting roller-shaped tools
on a drive
shaft of a drive motor with the help of a fastening adapter, a fastening
adapter and a
method for mounting roller-shaped tools on a fastening adapter. Such roller-
shaped
tools are for example surface machining tools such as grinding or polishing
rolls. Such
tools are usually driven by means of a drive motor such as a face grinding
machine or
longitudinal grinding machine by means of a rotating drive shaft. The term
tool roller
shall also be used below alternatively for a roller-shaped tool. For the
purpose of a
torsionally rigid connection between a drive shaft and a tool roller, the
latter often
comprises a pass-through opening with a special fastening apparatus which is
adjusted
to a specific drive shaft. Drive shafts of different machines frequently
differ in their
diameter however. There are also different systems for the fastening. They can
be
based for example on screwed or plug-in connections. When a certain type of
tool roller
is to be used in a versatile manner with different drive machines it was
necessary until
now that the rollers needed to be manufactured in different configurations of
pass-
through openings and fastening apparatus.
This specialization in different drive shafts is cumbersome and causes high
costs. That
is why one has begun to produce uniform tool rollers and to provide the same
with a
special insert for the different drive shafts. It would be desirable however
when such an
insert could be reused as an adapter. Precisely one adapter would then be
sufficient for
each drive shaft, to which different tool rollers could be attached.
In view of this background it is the object of the present invention to
provide a system
for fastening a roller-shaped tool on a drive shaft of a drive motor with a
fastening
adapter, a fastening adapter and a method for mounting roller-shaped tools on
a
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
2
fastening adapter, with the fastening adapter offering a stable hold for the
tool, enabling
easy mounting and being reusable.
This object of the invention is achieved by an apparatus according to the
independent
claim 1. A fastening system in accordance with the invention comprises a
fastening
adapter, with the help of which a roller-shaped tool can be mounted on a drive
shaft of a
drive motor. A fastening adapter in accordance with the invention comprises a
hollow-
cylindrical basic body which comprises in the interior a fastening apparatus
for mounting
on a drive shaft and from which a plurality of lamellae originate which are
distributed
outwardly about the cylinder axis and are spaced from one another by slits.
The
lamellae are each tilted in their direction perpendicular to the cylinder axis
by a
predetermined angle relative to the radial direction. The outside diameter of
the
fastening adapter can be reduced elastically by exerting pressure or the
action of a
shearing force in the direction of the tilting on the lamellae. The
compression of the
fastening adapter occurs substantially in such a way that the cavities between
the
lamellae, more precisely the slits, are reduced. Depending on the material of
the
lamellae, a compression of the lamellae themselves can be involved. As a
result of the
action of shearing forces at the ends of the lamellae, which means forces
which act
tangentially on the surface in the direction of the tilting, a "smoothing" of
the lamellae is
effected. Since the lamellae are tilted relative to the radial direction in
the relaxed basic
state, the direction in which the lamellae rest on each other is already
predetermined
and the exertion of pressure on the ends of the lamellae is sufficient in
order to press
the lamellae against each other. To enable such elastic deformation of the
fastening
adapter, the lamellae can consist entirely of elastic material. An elastic
joint could also
be sufficient which enables a further tilting of a stiff lamella. The
compression of the
fastening adapter concerns an elastic deformation. When there are no longer
any
pressure or shearing forces, the lamellae will spread out again and will
assume their
original form and orientation again. The fastening adapter will then have its
original
diameter again.
Grinding or polishing devices in which the fastening adapter in accordance
with the
invention is used with roller-shaped tools are often hand-held appliances
which are
guided by a worker by hand. Such appliances usually have a preferred running
direction
for reasons of work safety. This means for the tool rollers and the fastening
adapters in
4
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
3
accordance with the invention that they are also used with a preferred
direction of
rotaticin. The lamellae are tilted in the direction of movement which is
preferred in
operation of the tool in the case of a fastening adapter in accordance with
the invention.
This leads to the advantage that the holder of the tool on the fastening
adapter is
additionally stabilized in operation during a grinding or polishing process,
as will be
explained below in closer detail. During a grinding or polishing process, the
rotational
movernent of the tool is slightly braked by friction on the tool. This braking
causes a
braking of the ends of the lamellae as a result of friction between tool
roller and
fastening adapter. If the lamellae were tilted against the running direction,
then this
would correspond to a shearing force in the direction of the tilting on the
rotating ends of
the lamellae, leading to a smoothing of the lamellae and thus a compression of
the
fastening adapter. The fixing of the roller-shaped tool would thus be loosened
at this
moment. If the lamellae are tilted in the running direction of the roller-
shaped tool, the
shearing force relative to the lamellae acts in the opposite direction. This
promotes a
stronger spreading of the lamellae. In the case of lamellae tilted in the
running direction
the larnellae will stand up more strongly, as a result of which the clamping
seat and
friction between the fastening adapter and the roller-shaped tool will be
enhanced even
further.
The stable fixing of the tool roller on the fastening adapter prevents
slippage of the tool
roller on the fastening adapter. Moreover, vibrations of the tool can thus be
prevented,
which under certain circumstances could leave chatter marks on the grinding
surfaces.
A roller-shaped tool in accordance with the invention comprises a rigid
cylindrical pass-
through opening for the fastening adapter whose inside diameter is smaller
than that of
the relaxed fastening adapter. The difference in the diameter can be in the
magnitude of
less than 1 mm, whereas the diameter itself preferably lies in the range of a
few
centimeters, e.g. between 3 and 7 cm. The inside diameter of the pass-through
opening
of the tool roller preferably corresponds to 44.75 mm, whereas the outside
diameter of
the relaxed fastening adapter is preferably 45 mm. The length of the fastening
adapter
is preferably between 80 mm and 100 mm, more preferably 90 mm. This length
corresponds appropriately also to the length of the tool roller.
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
4
The elastic deformability of the fastening adapter allows a simple mounting of
the tool
roller on the same. For this purpose, the fastening adapter is compressed at
first and
then placed in the pass-through opening of the tool roller in order to expand
there again
until it sits tightly in a clamping seat.
Suitable roller-shaped tools are for example mop wheels, mat wheels or other
grinding
or polishing tools for surface machining. They generally have a basic
cylindrical shape.
This is not necessary from a principal standpoint however. Barrel-shaped
rollers or such
profiled in a different way are also possible. The roller-shaped tools of the
fastening
adapter in accordance with the invention have a cylindrical pass-through
opening. Said
pass-through opening is rigid, so that its circular cross section is
maintained essentially
even under load.
In a preferred further development of the invention, the pass-through opening
of the tool
roller is formed by a stiff pipe with a circular cross section. Said pipe then
carries the
actual tool material. The pipe can consist for example of plastic such as PVC
or ABS, a
composite material such as Pertinax or epoxy synthetic resin, or of metal such
as
aluminum or steel. Said pipe forms the rigid pass-through opening of the tool
roller,
whereas the actual tool material is arranged outside about the pipe and is
carried by the
same. Depending on the type of tool, said tool material can be a grinding
material in the
form of pressed grinding particles, grinding lamellae, a layer of polishing
mat or the like.
For mounting a tool roller in accordance with the invention on a fastening
adapter in
accordance with the invention, the fastening adapter is compressed, as
explained
above, by means of pressure or the action of a shearing force on the lamellae
and
inserted into the pass-through opening of the tool roller. The shearing force
on the ends
of the lamellae can be exerted for example by embracing the fastening adapter
with a
twist. The embracing can occur by hand in this case. A mechanicai solution is
also
possible. Once the fastening adapter is situated in the pass-through opening
of the
roller-shaped tool, the embracement is released, whereupon the lamellae of the
fastening adapter will spread out again and press against the inside wall of
the pass-
through opening of the roller-shaped tool. As a result of the slight undersize
of the pass-
through opening with respect to the diameter of the fastening adapter, a
certain residual
compression of the fastening adapter is maintained. The thus remaining elastic
tension
I i n rll
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
in the fastening adapter increases the pressure of the ends of the lamellae
against the
inside wall of the pass-through opening. The thus increased friction between
the ends of
the Iamellae and the pass-through opening ensures a torsionally rigid seat of
the tool
roller on the fastening adapter.
The fastening adapter is equipped on its part with a pass-through opening and
a
fastening apparatus for the drive shaft for driving the fastening adapter by
the drive
shaft. The diameter of the pass-through opening and the special fastening
apparatus
are adjusted to the drive shaft to be used. Possible variants of the fastening
apparatus
are in this case an inside thread or a double groove in which a respective
drive shaft
can engage. All known variants of torsionally rigid shaft-hub connections are
principally
suitable. According to a preferred further development of the invention the
fastening
apparatus is an inside thread however. Suitable standard threads are for
example M10
threads, M14 threads or 5/8" threads.
The tool roller rotates in operation with the fastening adapter, driven by the
drive shaft.
An outwardly directed centrifugal force acts in addition on the tilted and
tensioned
lamellae by the rotation. It amplifies the pressure of the lamellae on the
inside wall of
the pass-through opening. This increases the friction between the ends of the
lamellae
and the pass-through opening. The fixing of the tool on the fastening adapter
is
stabilized in this process.
In a preferred further development, the lamellae of the fastening adapter in
accordance
with the invention consist of an elastic material. Such a material is rubber
or
polyurethane with a preferred hardness of between 60 Shore and 100 Shore. This
hardness range is especially advantageous for avoiding disturbing vibrations.
When the
entire lamellae are made of an elastic material, the compression properties of
the
fastening adapter are thus improved. On the other hand, the expansion caused
by
centrifugal force is facilitated during operation. Elastic lamellae mean for
compression
that the compression occurs not only as a result of the reduced cavities
between the
lamellae but also as a result of a compression of the lamellae themselves.
Moreover,
the construction is simplified as compared with a variant with only elastic
joints.
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
6
The lamellae are preferably also arranged in such a way that they have the
lowest cross
section at their contact point on the hollow-cylindrical basic body. In the
case of lamellae
made of a uniform elastic material this leads to the consequence that the
lamellae will
preferably bend off at such contact points for compression on the one hand and
also for
expansion on the other hand. An elastic joint thus formed in a way. The
lamellae are
also preferably arranged in such a way that in the relaxed state of the
fastening adapter
the outer ends of all lamellae jointly form a cylindrical jacket surface which
is interrupted
by slits. Relaxed state shall mean here that the fastening adapter is idle and
no
pressure or force acts upon the same. This preferred arrangement of the ends
of the
lamellae ensures that the ends of the Iamellae sit close in an especially
favorable
manner in the pass-through opening of the roller-shaped tool. The contact
surface
between the ends of the lamellae and the tool roller is then especially large.
Friction is
thus irnproved between fastening adapter and tool roller. The preferred shape
of the
lamellae with the smallest cross section at the contact point and the outer
end which
jointly form a cylinder jacket surface can be realized in such a way that the
lamellae are
subdivided by slits with respective parallel boundary walls. This form is
obtained in such
a way that even slits of constant width are cut into a hollow-cylindrical
basic body.
Reference in more detail will be made thereto in the description of the
figures.
In a preferred further development of the fastening adapter in accordance with
the
invention, its circumferential edge is chamfered on at least one of its face
sides. This
facilitates the insertion of the fastening adapters into the pass-through
opening of the
roller-shaped tool.
In an advantageous further development of the invention, the fastening adapter
is
cylindrically extended about the center with the fastening apparatus on its
face side
facing the drive motor in operation. A cylindrical excess portion is thus
formed from
which no lamellae protrude. A tool roller in accordance with the invention is
slid during
mounting only to such an extent over the fastening adapter that the
cylindrical excess
portion will just protrude. The cylindrical excess portion is then used as a
spacer
between the drive motor and the tool roller. The fastening apparatus in the
pass-through
opening of the fastening adapter appropriately continues into said extensions.
The
entire fastening adapter can be arranged in such a way that the fastening
apparatus
and the pass-through opening are situated in a cylindrical metal core around
which the
I IIY .
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
7
lamellae made of an elastic material are arranged. In this case, the excess
portion can
simply be formed by a metal core extended relative to the lamellae.
For the purpose of additional stabilization of such a fastening adapter on the
drive shaft
of a drive motor, a thread for a setscrew with a setscrew can be provided in
the
cylindrical excess portion in a further development of the invention. This
setscrew allows
additionally fixing a screwed joint and the degree of fastening. The setscrew
is then
appropriately attached on the side in the cylindrical excess portion.
In a preferred embodiment of the fastening adapter in accordance with the
invention,
the same comprises a stop ring for the tool roller at its end facing the drive
motor. Said
stop ring can consist of the material of the lamellae or of another material
such a metal.
It can be produced integrally both with the lamellae as well as the metal core
of the
fastening adapter, or it can be attached retroactively. When the fastening
adapter is
arranged with a cylindrical excess portion, the stop ring is appropriately
arranged
between the excess portion and the lamellae at the end of the lamellae. The
outside
diameter of the stop ring is larger than the inside diameter of the pass-
through opening
in the tool roller and smaller than or equal to its outside diameter. Even
when the stop
ring can be formed from an elastic material, it is not compressible to the
extent that the
tool roller can be slid over the same. The stop ring thus offers a top for the
tool roller
and is used as a spacer to the drive motor.
The object of the invention is further achieved by a fastening adapter for use
in a
fastening system as described above.
The object of the invention is also achieved by a method according to the
independent
method claim. A method in accordance with the invention for fastening a roller-
shaped
tool with a tubular pass-through opening on a fastening adapter for a drive
shaft of a
drive motor comprises the embracement of the fastening adapter with a twist,
as a
result of which the fastening adapter is compressed. The fastening adapter is
thereupon
slid in this compressed state into the pass-through opening of the tool,
whereupon the
compression is stopped, whereupon the fastening adapter expands again in the
pass-
through opening and thus forms a torsionally rigid connection with the tool by
clamping
and frictional engagement on its outer jacket surface. Twist shall be
understood here as
IY
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
8
a twisting of the outer circumference of the fastening adapter relative to its
center
marked by the pass-through opening in the direction of movement preferred in
operation. In the case of a fastening adapter in accordance with the invention
with
lamellae, this cases the lamellae to be pressed flatly in the direction of the
preferred
direction of movement. The method in accordance with the invention is
therefore
especially suitable for a fastening adapter in accordance with the invention
according to
the apparatus claims. Fastening adapters of a different structure are
principally also
possible.
The invention will now be explained in closer detail below by reference to
embodiments
shown in the drawings, wherein:
Fig. 1 shows a fastening adapter in a perspective view;
Fig. 2 shows a fastening adapter in a top view of a face side;
Fig. 3 shows one step of the method with a fastening adapter in accordance
with the
invention;
Fig. 4 shows a fastening adapter in a roller-shaped tool in a top view of a
face side, and
Fig. 5 shows a tool roller and a fastening adapter in sectional view through
the
longitudinal axis.
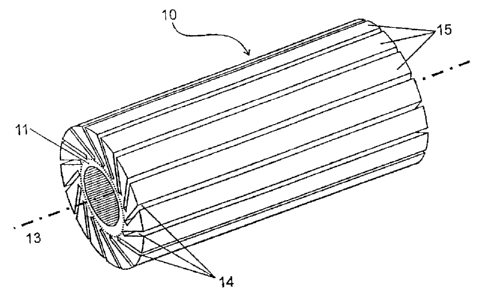
According to the Figs. 1 to 5, a fastening adapter 10 comprises a hollow-
cylindrical
basic loody 11 from which lamellae 15 protrude. The lamellae 15 and the hollow-
cylindrical basic body 11 can be made integrally or be assembled. The lamellae
15 are
separated from each other by slits 14. Both the slits 14 as well as the
lamellae 15 are
tilted relative to the radial direction by a predetermined angle a(Fig. 2).
The cross-sectional shape of the lamellae 15 is predetermined by the cross-
sectional
shape of the interposed slits 14. The slits 14 are arranged as channels with
an
approximately trapezoid cross section, with the two boundary surfaces being
parallel to
the adjacent lamellae 15. By predetermining the shape of the intermediate
spaces 14
I I I VIY
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
9
between the individual Iamellae 15, the shape of the Iamellae 15 is also
predetermined.
The intermediate spaces are arranged as slits 14 of constant width.
Accordingly, the
cross section of the lamellae 15 is similar to that of a circle sector which
increases in
width with increasing radius. The lamellae 15 are therefore cylinder sectors
which are
arranged in a tilted way from the radial direction. The widening cross section
of the
lamellae 15 which finishes outwardly with the circular arc sector is
especially
advantageous because the contact surface between lamellae 15 and the pass-
through
opening of the tool 17 is maximized. Friction between the fastening adapter 10
and the
tool roller is also maximized in this way. Based on the shape of the lamellae
15 and its
outwardly widening cross section, the tilting angle a can be defined
differently. It
assumes different values depending on the definition and the reference point.
The
values can vary in the range of approximately 150 to 900 depending on the
manner of
definition. All lamellae 15 are tilted objectively under the same angle
relative to their
respective radial direction.
The fastening adapter 10 also has a preferred operating direction which is
indicated in
Fig. 2 by arrow 20. The lamellae 15 are tilted from their radial direction in
the preferred
operating direction 20. In operation, the braking of the ends of the lamellae
by friction
between the tool roller and the fastening cylinder causes a shearing force
directed in the
opposite direction. As a result, the lamellae 15 will spread out even further,
so that the
connection between the fastening adapter and the roller-shaped tool is
stabilized even
further.
The fastening adapter is equipped with a fastening apparatus 12 for the drive
with a
drive shaft of a machine. The embodiment shown in the Figs. 2, 4 and 5
comprises an
inside thread with which it can be screwed onto a respective drive shaft. The
embodiment shown in Fig. 3 differs from that shown in Fig. 2 only in such a
way that the
fastening apparatus is arranged as a double groove instead of an inside
thread. In
addition, other cross sections are possible for respective drive shafts.
The fastening adapter can be compressed by pressure on the outer ends of the
lamellae or by action of a shearing force in the direction of the tilting of
the lamellae 15.
Fig. 3 shows how this compression can occur by embracing the fastening by
hand. In a
fastening adapter in accordance with the invention, the compression can be
achieved
Ilu.ll =
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
on the one hand by pressure on the lamellae 15 or by embracement with a twist.
The
embracement with a twist means that the center of the fastening adapter is
held tight
with the fastening apparatus 12, whereas the outer ends of the lamellae are
twisted
relative to the same. The direction of twisting is indicated by the arrow in
the hand in
Fig. 3. In this compressed state, the fastening adapter 10 has a reduced
diameter and
can thus be slid into the pass-through opening 21 of a roller-shaped tool 17.
By
releasing the adapter 10, the lamellae 15 will spread out again in the pass-
through
opening 21 of the tool 17 until they push against the inside wall of the pass-
through
opening 21 and press against the same.
Fig. 4 shows a fastening adapter 10 which is slid into the tool roller 17 and
is spread out
there. Since the inside diameter of the pass-through opening 21 is slightly
lower than
the outside diameter of the fastening adapter 10, the lamellae 15 are slightly
pressed
against each other and are tensioned. The pass-through opening 21 of tool 17
is formed
here by a PVC tube 18 which carries a ring cylinder 19 of grinding material on
its
outside. The pressure of the lamellae 15 on the PVC tube 18 increases the
friction
between the Iamellae 15 and the PVC tube 18. The pressure and thus the
friction by a
centrifugal force acting upon the lamellae 15 is increased additionally in
operation. The
fixing of the tool on the fastening adapter 10 is thus especially stable in
operation.
Fig. 5 shows a further embodiment of a fastening adapter in a tool roller in a
sectional
view through the longitudinal axis. An inside thread is provided as a
fastening apparatus
12, which inside thread is situated in a metal core of the fastening adapter
10. The
metal core is extended beyond the length of the lamellae 15 and forms a
cylindrical
excess portion 23. A thread for a setscrew 24 is additionally provided in the
cylindrical
excess portion. The screwed joint of the fastening adapter on a drive shaft
can thus be
fixed in addition. The cylindrical excess portion 23 is situated on the end of
the fastening
adapter 10 facing the drive motor. The fastening adapter 10 further comprises
a stop
ring 22 which is also made of metal like the core and is connected with the
same. A
roller tool 17 made of a PVC pipe and a slip-ring cylinder 19 is slid from the
other end of
the fastening adapter 10 over the same. In order to facilitate this step, the
fastening
adapter 10 is chamfered at said end 25. The stop ring 22 has an outside
diameter which
is larger than the inside diameter of the PVC pipe 18 and smaller than the
outside
diameter of the slip-ring cylinder 19. During the mounting of the tool roller
17 on the
. I I x 'H-
CA 02584998 2007-04-10
11
fastening adapter 10 it therefore prevents that the tool roller is slid too
far over the
fastening adapter 10. This ensures a sufficient distance between the drive
motor and
the tool roller.