Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-1-
DESCRIPTION
DRAW FORMING METHOD AND DEVICE
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a draw forming method and
device for reducing deflection created in the center of a blank
material when the blank material is subjected to plastic working
using a press and a metal die unit.
BACKGROUND ART
Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open Publication No. H01-
153820, for example, proposes a draw forming method in which the
periphery of a blank material is held by pressure from a blank
holder, and the blank material is formed when subjected to
plastic working using a metal die unit mounted on a press. This
draw forming is described below with reference to FIGS. 13A
through 13C hereof.
In a forming method that uses a conventional drawing die
301, the periphery of a blank material B is first pressed by an
upper die holddown 303 of an upper die 302 and a lower die
holddown 305 of a lower die 304, and a section adjacent to the
center of the blank material B is pressed by a pad 306 and a
cushion 307, as shown in FIG. 13A.
Next, a first draw (cylindrical section Gl) is formed with
a punch 308, as shown in FIG. 13B.
A second draw (square base section G2) is then formed with
the cushion 307, as shown in FIG. 13C.
The first and second draws can thus be formed in a single
CA 02586049 2009-07-20
-2-
step in the conventional draw forming method.
However, although an example is given in which the punch
308 is disposed on the underside of the drawing die 301, the
punch is sometimes disposed on the topside depending on the
circumstances. In cases in which the drawing die 301 is
turned upside-down, the blank material B is set on the pad
306 to form draws, whereupon deflection is created in the
center of the blank material B. Deflection tends to occur
easily and in greater amounts particularly in cases in which
the blank material is extremely thin, or in cases in which a
thin blank material is hot-formed (including warm forming).
As a result, there is concern that the forming dimensions
will be markedly nonuniform.
In view of this, there is a need for a draw forming
technique that reduces deflection in the center of the blank
material set on the metal die unit, and that reduces
nonuniformities in the forming dimensions.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
A draw forming method is disclosed wherein a blank
material set into a metal die unit may be restrained by a
blank holder and then drawn, the method comprising the steps
of: setting the blank material into the metal die unit, the
blank material having a stretching region and a restraint
CA 02586049 2009-07-20
-3-
region set in the stated order outward and lined up with a
drawing region that is subjected to pressure from an upper
die and a lower die; restraining the restraint region of the
blank material with first holder means of the blank holder;
and applying tensile force to the drawing region and
restraining the stretching region while second holder means
of the blank holder displaces the stretching region in the
shearing direction in relation to the restraint region.
Thus, the restraint region of the blank material can be
restrained by the first holder means, and the stretching
region of the blank material may be then displaced in the
shearing direction by the second holder means, whereupon
tensile force can be applied to the stretching region of the
blank material and the drawing region in the middle, and the
deflection formed in the drawing region is removed. It is
therefore possible to reduce deflection in the middle of the
blank material set into the metal die unit.
Also disclosed is a device for draw forming a blank
material, which device may comprise: a metal die unit having
an upper die and a lower die; a blank holder for restraining
the blank material set in the metal die unit; and a press for
applying pressure to the restrained blank material, wherein
the blank holder can comprise first holder means for
restraining an outer peripheral section of the blank material
CA 02586049 2009-07-20
-4-
at a first restraining position when the press is lowered;
and second holder means disposed on the inside of the first
holder means to restrain the inside section of the outer
peripheral section of the blank material at a second
restraining position when the press is further lowered.
In the thus-arranged device, the press can operate the
first holder means, the outer peripheral section of the blank
material can be restrained by the first holder means, and the
press can then be lowered further. The second holder means
may be positioned on the inside of the first holder means
then stretches the middle of the blank material outward. As
a result, the deflection in the central section of the blank
material is extremely small, and it is possible to reduce
nonuniformities in the positional relationship between the
central section and the upper and lower dies. It is
therefore possible to reduce nonuniformities in the
dimensions of the formed article when drawing is performed.
Preferably, in the device of the present invention, the
press is a double-action press; the first restraining
position can be the position in which the first holder means
protrudes past the second holder means and in which the blank
material is held by the lowering of the double-action press;
the second restraining position can be the position in which
the double-action press is lowered further from the first
CA 02586049 2010-07-05
-5-
restraining position; the upper die is held to be capable of
sliding in relation to the second holder means, and is
disposed separate from an inner slider of the double-action
press; and the first holder means and second holder means can
be fixed to an external slider positioned on the outside of
the inner slider. As a result, tensile force can be applied
to the inside of the outer peripheral section and to the
central section of the blank material until the blank
material reaches the second restraining position while the
outer peripheral section is restrained at the first
restraining position, and deflection in the central section
of the blank material can be prevented from occurring.
Furthermore, since the first and second holder means can
be integrally fixed to the external slider of the double-
action press, there is no movement between the external
slider and the first and second holder means, and
nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article can
be reduced.
According to one aspect of the present invention there
is provided a draw forming method comprising the steps of:
providing a metal die unit having an upper die, a lower die,
and a blank holder having a first holder means and a second
holder means; providing a blank material having a restraint
region located on an outer peripheral region of the blank
CA 02586049 2010-07-05
-5a-
material, a drawing region located in a central section of
the blank material, and a stretching region located between
the restraint region and the drawing region; setting the
blank material into the metal die unit; restraining the
restraint region of the blank material to form a single plane
with the first holder means; displacing the stretching
region, which extends from the restraint region to the
drawing region, to form a subsequent single plane with the
second holder means in a shearing direction relative to the
restraint region by a predetermined distance such that the
restraint region forming the single plane and the stretching
region forming the subsequent single plane are in two
substantially different parallel planes; restraining the
stretching region with the second holder means after the
stretching region is displaced; and applying tensile force to
the drawing region.
According to another aspect of the present invention
there is provided a press device for draw forming a blank
material, comprising: a metal die unit having an upper die
and a lower die for draw forming a drawing region of the
blank material; a first holding means for holding a holding
region of the blank material surrounding the drawing region
in a first retaining position; and a second holding means for
stretching a stretching region of the blank material located
CA 02586049 2010-07-05
- 5b -
between the drawing region and the holding region in a second
retaining position, while the holding region is held by the
first holding means to apply a tensile force to the drawing
region before its draw forming, characterized in that the
first and second holding means are capable of being displaced
in such a way that, when stretching the stretching region,
the holding region in the first retaining position is
displaced in a shearing direction relative to the drawing
region in the second retaining position and surfaces of the
holding means to be engaged with the stretching region are
flat.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a draw forming
device according to a first embodiment of the present
invention;
FIG. 2 a flowchart showing the steps of a draw forming
method according to the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing the blank material used in
the draw forming method of the invention;
FIGS. 4A and 4B are schematic views showing the manner
in which the blank material is set on the metal die unit and
restrained by first holder means in the draw forming method
shown in FIG. 2;
CA 02586049 2010-07-05
- 5c -
FIGS. 5A and 5B are schematic views showing the manner
in which the press is lowered to displace the stretching
region of the blank material upward and to remove the
deflection created in the central section of the blank
material;
FIGS. 6A through 6D are schematic views showing the
manner in which a formed article is extracted after the
formed article is obtained by drawing the central section of
the blank material;
FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the draw forming
device according to a second embodiment of the present
invention;
FIGS. 8A through 8D are schematic views showing an
operation of the draw forming device according to the second
embodiment, and also showing the manner in which the formed
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-6-
article is obtained by drawing after the blank is set on a metal
die unit;
FIGS. 9A and 9B are schematic views showing the manner in
which the formed article is extracted;
FIG. 10 is a schematic view showing a modification of the
draw forming device according to the second embodiment shown in
FIG. 7;
FIGS. 11A through 11D are schematic views showing the
actions taken from the time the blank material is set until the
time the blank material is drawn in the draw forming device in
the modification;
FIGS. 12A and 12B are schematic views showing the manner in
which the formed article is extracted; and
FIGS. 13A through 13C are schematic cross-sectional views
showing a conventional draw forming device.
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Certain embodiments of the present invention will now be
described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
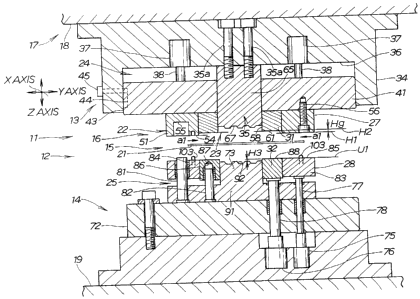
In FIG. 1, X indicates a horizontal axis in the
longitudinal direction of a blank material 15, Y indicates a
horizontal axis orthogonal to X, and Z indicates a vertical axis
orthogonal to both X and Y.
A draw forming device 11 of the first embodiment shown in
FIG. 1 is composed of a metal die unit 12 comprising an upper
metal die unit 13 and a lower metal die unit 14, and a blank
holder 16 provided to the metal die unit 12 to apply pressure to
the blank material 15. The upper metal die unit 13 is mounted
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-7-
on a ram 18 of a press 17. The lower metal die unit 14 is
mounted on a bed 19 of the press 17. The draw forming device 11
performs draw forming.
The blank holder 16 includes first holder means 22 for
restraining the outer peripheral section 21 (restraint region 98
in FIG. 3) of the blank material 15, and second holder means 23
disposed on the inside (in the direction of the arrows al, al)
of the first holder means 22. An upper cushion mechanism 24 is
mounted on the upper metal die unit 13, and a lower cushion
mechanism 25 is mounted on the lower metal die unit 14 in order
to operate the first and second holder means 22, 23.
The first holder means 22 is composed of a first upper
holddown member 27 connected to the upper cushion mechanism 24,
and a first lower holddown member 28 connected to the lower
cushion mechanism 25. Hl indicates the position in which the
first holder means 22 restrains the blank material.
The second holder means 23 is composed of a second upper
holddown member 31 connected to the upper cushion mechanism 24,
and a second lower holddown member 32 connected to the lower
cushion mechanism 25.
The position in which the second holder means 23 restrains
the blank material is indicated by H2. The restraining position
H2 is set deeper in the shearing direction (Z-axis direction)
than the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 22 by
a distance Hg.
The upper metal die unit 13 will now be described in
detail.
The upper metal die unit 13 includes an upper base member
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-8-
34 attached to the ram 18. An upper die (die) 35 is attached to
the center of the upper base member 34 by bolts 35a. A holder
placement part 36 is formed on the upper base member 34. In
other words, the upper metal die unit 13 includes the first
upper holddown member 27 and the second upper holddown member 31
of the blank holder 16.
The upper cushion mechanism 24 has third cylinders 37, 37
mounted on the upper base member 34 of the upper metal die unit
13. A cushion base 41 is mounted on rods 38, 38 of the third
cylinders 37, 37, and is fitted over the holder placement part
36 and allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. A stopper
groove 44 is formed in the left side surface 43 of the cushion
base 41. A stopper shaft 45 that fits into the stopper groove
44 is mounted on the upper base member 34. The operation of the
third cylinders 37, 37 causes the cushion base 41 to slide in
the Z-axis direction irrespective of the movement of the ram 18.
The third cylinders 37 have a structure for storing fluid,
for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such
elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the
fluid-storing cylinders. The rods 38 are used in place of pins
in this case.
The first upper holddown member 27 has a holddown main body
51. The holddown main body 51 has a pressure surface 54 formed
on the underside, and a recessed hole 55 formed in the pressure
surface 54.
The reference numeral 56 indicates a bolt for fastening the
first upper holddown member 27 to the cushion base 41.
The second upper holddown member 31 has a holddown main
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-9-
body 58 that faces the second lower holddown member 32. The
holddown main body 58 has a pressure surface 61 formed on the
underside. The pressure surface 61 is located deeper (upward)
than the pressure surface 54 of the first upper holddown member
27 by a distance Hg.
The upper die 35 has a die surface 67 formed at the bottom
of an upper die main body 65.
The lower metal die unit 14 will now be described in
detail.
The lower metal die unit 14 includes a lower base member 72
provided to the bed 19 of the press 17. The lower base member
72 includes a lower die 73 in the center of the base member. In
other words, the lower metal die unit 14 includes the first
lower holddown member 28 and second lower holddown member 32 of
the blank holder 16.
The lower cushion mechanism 25 has first cylinders 75, 75
and second cylinders 76, 76 mounted on the lower base member 72.
Rods, 77, 77, 78, 78 of the first and second cylinders 75, 76
are all connected to the first and second lower holddown members
28, 32. First guide shafts 81, 81 for guiding the first lower
holddown member 28 and second guide shaft 82 for guiding the
second lower holddown member 32 are mounted on the lower base
member 72.
The first cylinders 75 have a structure for storing fluid,
for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such
elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the
fluid-storing cylinders. The rods 77 are used in place of pins
in this case.
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 10-
The second cylinders 76 have a structure for storing fluid,
for example. Rubber, a compressed spring, or another such
elastic member (cushion member) can be used instead of the
fluid-storing cylinders. The rods 78 are used in place of pins
in this case.
The first lower holddown member 28 faces the first upper
holddown member 27, and the rods 77, 77 of the first cylinders
75, 75 are connected to the underside of a holddown main body
83. The holddown main body 83 has guide holes 84, 84 into which
the first guide shafts 81, 81 are fitted, and these shafts are
allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. The top surface of
the holddown main body 83 constitutes a pressure surface 85.
The blank material 15 is firmly held by the pressure surface 85
and the pressure surface 54 facing the pressure surface 85.
The blank is set on the first lower holddown member 28 at
the position indicated by Ul. The blank setting position Ul and
the pressure surface 85 are located higher than a die surface 92
of the lower die 73 by a distance H3.
The second lower holddown member 32 faces the second upper
holddown member 31, and the rods 78, 78 of the second cylinders
76, 76 are connected to the underside of a holddown main body
86. The holddown main body 86 has guide holes 87, 87 into which
the second guide shaft 82 are fitted, and these shafts are
allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction. The top surface of
the holddown main body 86 constitutes a pressure surface 88.
The blank material 15 is firmly held by the pressure surface 88
and the pressure surface 61 facing the pressure surface 88.
This is described in further detail hereinafter.
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-11-
The position of the pressure surface 88 is the same as that
of the pressure surface 85 of the first lower holddown member 28
located on the outside of the pressure surface 88, and is set to
the blank setting position Ul.
The die surface 92 is formed on the top surface of a lower
die main body 91 of the lower die 73. The blank material 15 is
formed into the desired shape by the die surface 92 of the lower
die 73 and the die surface 67 of the upper die 35. The second
lower holddown member 32 is raised above the die surface 92,
whereby the blank material 15 can be formed into the desired
shape as shown in FIG. 5A.
The lower die 73 has four setting shafts 103.
The number of cylinders and guide shafts (including guide
holes) in the blank holder 16 provided to the metal die unit 12
is arbitrary.
The following is a description, made with reference to FIG.
1 and FIGS. 2 through 6D, of the draw forming method performed
using the draw forming device 11.
FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of the draw forming method
according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
Step (hereinafter abbreviated as ST) 01: The blank material
15 is obtained.
ST02: The blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit
12, which is mounted on the press 17 in advance.
ST03: The metal die unit 12 is operated, and the restraint
region 98 (see FIG. 3) of the blank material 15 is restrained by
the first holder means 22 of the blank holder 16.
ST04: The first holder means 22 is lowered, whereby the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-12-
second holder means 23 displaces the stretching region 97 (see
FIG. 3) of the blank material 15 relative to the restraint
region 98 in the shearing direction, and restrains the
stretching region 97. This displacement causes tensile force to
be applied to a drawing region 96 (see FIG. 3) of the blank
material 15.
ST05: A drawing force is applied to the drawing region 96
(see FIG. 3), and the region is subjected to plastic working by
the upper die 35 and the lower die 73, whereby the blank
material 15 is formed (see FIG. 6B).
ST06: A formed article 107 is extracted (see FIG. 6D).
Details of ST01 through ST06 will now be described in
detail.
FIG. 3 shows the first step of the forming method in STO1
shown in FIG. 2.
The blank material 15 is obtained in the first step.
Specifically, the blank material 15 is a plate member (material)
including a stretching region 97 and a restraint region 98
disposed in the stated order outward from the drawing region 96
(in the direction of the arrows a3, a3) . At the same time, four
fitting holes 99 are formed in the restraint region 98. The
four aforementioned setting shafts 103 are fitted into the four
fitting holes 99. The restraint region 98 is the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15.
FIGS. 4A and 4B show the second step of the draw forming
method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of
ST02 and ST03 shown in FIG. 2.
The blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit 12 in
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 13 -
the second step shown in FIG. 4A. Specifically, the metal die
unit 12 is opened as shown in FIG. 1, the four setting shafts
103 are fitted into the four fitting holes 99 of the blank
material 15 shown in FIG. 3, and the blank material 15 is set on
the first lower holddown member 28 of the first holder means 22
and the second lower holddown member 32 of the second holder
means 23.
Next, the first holder means 22 of the blank holder 16
restrains the restraint region 98 in the second step.
Specifically, the press 17 is operated to lower the upper metal
die unit 13 by a stroke Si as shown in FIG. 4A, the first upper
holddown member 27 is pressed against the blank material 15 with
a pressure Ph, and the blank material 15 is restrained by the
first upper holddown member 27 and first lower holddown member
28 with a specific surface pressure. The closed restraining
position H1 of the first holder means 22 coincides with the
blank setting position U1 at this time.
The pressure Ph is transmitted to the first upper holddown
member 27 via the third cylinders 37, 37 of the upper cushion
mechanism 24.
When the blank material 15 is set on the blank holder 16
provided to the metal die unit 12, the central section 104 of
the blank material 15 is not supported, and deflection 105
occurs in the central section 104 as shown in FIG. 4B. As a
result, the first holder means 22 restrains the restraint region
98 of the blank material 15 in which deflection 105 has occurred
in the central section 104.
FIGS. 5A and 5B show the third step of the draw forming
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-14-
method of the first embodiment, and also show the details of
ST04 shown in FIG. 2.
In step S3, the restraint region 98 of the blank material
15 is restrained, and the second holder means 23 of the blank
holder 16 displaces the stretching region 97 in relation to the
restraint region 98 in the shearing direction (the direction of
the arrow a4, and the Z-axis direction) . Tensile force is
thereby applied to the drawing region 96 as shown by the arrow
a5, and the drawing region is then restrained. In other words,
tensile force is applied radially outward to the drawing region
96 in an amount proportional to the amount of displacement.
Specifically, the press 17 operates and lowers the first
holder means 22 while still restraining the blank material 15,
and the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is pressed
against the second lower holddown member 32. The second lower
holddown member 32 is stationary at this time. The first holder
means 22 is then lowered by a distance H4 from the blank setting
position U1, and the restraining position H1 of the first holder
means 22 is lowered by a distance H4.
In other words, the stretching region 97 is displaced by a
distance H4 from the restraining position Hl of the first holder
means 22, and the second holder means 23 is stopped at the
restraining position H2 while the second lower holddown member
32 and the second upper holddown member 31 restrain the
stretching region 97.
Thus, tensile force is applied in the directions of the
arrows a5 to the stretching region 97 and drawing region 96
shown in FIG. 5B. The drawing region 96, which is set in the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-15-
central section 104 of the blank material 15, is therefore
stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as shown by the arrows
a5, and the central section 104 is free of deflection. It is
therefore possible to reduce deflection in the central section
104 (drawing region 96) of the blank material 15 set on the
metal die unit 12.
FIGS 6A through 6D show the plastic working step in ST05
and the extraction of the formed article in ST06, shown in FIG.
2.
After the second holder means 23 restrains the stretching
region 97 of the blank material 15 as described in FIG. 5A, the
upper metal die unit 13 is lowered to lower the first and second
holder means 22, 23 by a stroke S3, as shown in FIG. 6A. At
this time, the upper metal die unit 13 is lowered against
resistance from the first cylinders 75, 75 and the second
cylinders 76, 76, and the drawing region 96 of the blank
material 15 is pressed against the die surface 92 of the lower
die 73. The upper metal die unit 13 is lowered by a stroke S3,
whereupon the first and second holder means 22, 23 come into
contact with the lower base member 72 and stop.
The upper die 35 is then lowered and pressed against the
blank material 15, whereby the blank material is drawn into the
desired shape, as shown in FIG. 6B. Specifically, the upper
base member 34 is lowered to apply a draw force Pm to the
drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 through the upper die
35, and the drawing region 96 is plastically deformed by the
lower die 73, whereby the formed article 107 is obtained.
After drawing is complete, the upper base member 34 is
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 16-
raised, whereby only the upper die 35 rises in the direction of
the arrow a6, and the upper die 35 separates from the formed
article 107.
The entire upper metal die unit 13 is then raised, whereby
the formed article 107 is lifted and separated from the lower
die 73, as shown in FIG. 6D. Consequently, the first and second
holder means 22, 23 open, and the operator is therefore able to
extract the formed article 107.
The steps described above are automated by pressing a
"start button" on the operating panel of the press 17.
A blank material 15 is obtained in the first step of the
draw forming method in the first embodiment, as described above.
This blank material includes a stretching region 97 and a
restraint region 98 disposed in the stated order outward from
the drawing region 96, as shown in FIG. 3.
In the second step, the blank material 15 is set on the
metal die unit 12, and the restraint region 98 is restrained by
the first holder means 22 of the blank holder 16, as shown in
FIG. 4A.
In the third step, the stretching region 97 is forcibly
displaced in the shearing direction by the second holder means
23 of the blank holder 16 as shown in FIG. 5A, whereby tensile
force is applied to the drawing region 96. The tensile force
does not result in deflection 105 in the drawing region 96. It
is therefore possible to reduce deflection in the central
section 104 of the blank material 15 set on the metal die unit
12.
The draw forming device 11 shown in FIG. 1 includes the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 17-
blank holder 16, which comprises the first holder means 22 for
restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank
material 15 at the first restraining position H1, and the second
holder means 23 for restraining the inner section of the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the second
restraining position H2 when the press 17 is lowered.
Therefore, after the outer peripheral section 21 is restrained,
the inner section of the outer peripheral section 21 is
restrained by the second holder means 23 so as to be displaced.
The central section 104 of the blank material 15 is thereupon
stretched outward as shown by the arrow a5 (see FIG. 5) . As a
result, deflection is reduced in the central section 104 of the
blank material 15, and drawing can be performed with minimal
nonuniformities in the formed dimensions.
The draw forming device according to a second embodiment
will now be described with reference to FIG. 7. In the draw
forming device of the second embodiment, a double-action press
217 is used as the press 17 shown in FIG. 1.
A draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment shown in
FIG. 7 is composed of a metal die unit 212 comprising an upper
metal die unit 213 and a lower metal die unit 214, and a blank
holder 216 provided to the metal die unit 212 to hold down the
blank material 15. The upper metal die unit 213 is mounted on
the double-action press 217. The lower metal die unit 214 is
mounted on a bed 219.
The double-action press 217 includes an inner slider 245
for applying pressing force in order to form the blank material
15, and an external slider 246 disposed on the outside of the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 18-
inner slider 245 to hold down the blank material 15. The
external slider 246 is raised and lowered individually by
hydraulic pressure, for example.
The upper metal die unit 213 is composed of an upper base
member 234 integrally mounted on the external slider 246 of the
double-action press 217, and an upper die 235 disposed inside an
open section 247 formed in the center of the upper base member
234.
The lower metal die unit 214 is composed of a lower base
member 272 mounted on the bed 219, and a lower die 273 fixed in
the center of the lower base member 272.
The blank holder 216 is composed of first holder means 222
for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank
material 15 shown in FIG. 3, and second holder means 223
disposed on the inside of the first holder means 222.
The first holder means 222 includes a first upper holddown
member 227 integrally fixed to the upper base member 234 by
bolts 256, and a first lower holddown member 228 that is mounted
on the lower base member 272 by first cylinders 275 and is
allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction.
The first upper holddown member 227 has a holddown member
main body 251, which is formed into a rectangular shape large
enough to come into contact with the outer peripheral section 21
of the blank material 15. The holddown member main body 251 has
a pressure surface 254 formed on the underside, and a recessed
hole 255 formed so that the pressure surface 254 is open. The
pressure surface 254 reaches the restraining position H1 of the
first holder means 222 and holds down the upper surface of the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
- 19-
outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15. The
restraining position H1 is the position in which the first
holder means 222 protrudes past the second holder means 223;
i.e., where the first holder means is lowered to hold the blank
material 15.
The first lower holddown member 228 has a holddown member
main body 283 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that
faces the holddown member main body 251 of the first upper
holddown member 227. The holddown member main body 283 has a
pressure surface 285 formed on the topside to press on the
underside of the blank material 15. The pressure surface 285 is
provided with four setting shafts 203 for setting the blank
material 15. The holddown member main body 283 also has guide
holes 284, 284 into which first guide shafts 281, 281 are fitted
and allowed to slide in the Z-axis direction by means of a
collar 283a. The first guide shafts 281, 281 are mounted on the
lower base member 272. The first cylinders 275, 275 are mounted
on the lower base member 272, and the distal ends of the rods of
the first cylinders 275, 275 are connected to the holddown
member main body 283, whereby the first lower holddown member
228 supports the underside of the blank material 15.
The first guide shafts 281, 281 guide the first lower
holddown member 228 vertically (in the Z-axis direction) The
entire lengths of the first guide shafts 281, 281 can be limited
so as to not protrude from the pressure surface 285 of the first
lower holddown member 228, for example.
The recessed hole 255 is optionally provided to the first
upper holddown member 227 to allow the insertion and withdrawal
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-20-
of the first guide shafts 281, 281.
The second holder means 223 includes a second upper
holddown member 231 integrally fixed to the upper base member
234 by bolts (not shown), and a second lower holddown member 232
that is mounted on the lower base member 272 and is allowed to
slide in the Z-axis direction by means of the lower base member
272.
The second upper holddown member 231 has a holddown member
main body 258 formed into a rectangular shape corresponding to
the size of the stretching region 97, which is an extension of
the inside of the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank
material 15 shown in FIG. 3. The underside of the holddown
member main body 258 constitutes a pressure surface 261 for
pressing on the stretching region 97.
The top of the holddown member main body 258 is provided
with a hole 263 into which a guide post 262 is fitted, first
elastic member mounting holes 265 into which elastic members 264
are fitted, and a mounting hole 269 for mounting a stopper
member 268.
The pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown
member 231 reaches the restraining position H2 of the second
holder means 223 and holds down the topside of the blank
material 15.
The mounting shape of the guide post 262 and the hole 263
for fitting the guide post 262 constitute one example, and
another possibility, for example, is to not form the hole 263
and to fasten the guide post 262 with bolts.
The pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-21-
member 231 is positioned above the pressure surface 254 of the
first upper holddown member 227 at a distance Hg.
The restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223
is the position in which the double-action press 17 is lowered
past the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222
by a stroke Sal (Sal = Hg).
The second lower holddown member 232 has a holddown member
main body 286 that is formed into a rectangular shape and that
faces the holddown member main body 258 of the second upper
holddown member 231, a pressure surface formed on the topside of
the holddown member main body 286, a guide hole 287 formed so as
to open towards the bottom of the holddown member main body 286,
and a second guide shaft 282 that fits into the guide hole 287
by means of a collar 286a.
The second guide shaft 282 is mounted on the lower base
member 272. Second cylinders 276, 276 are mounted on the lower
base member 272. The top ends of the rods of the second
cylinders 276, 276 are connected to the lower ends of the second
lower holddown member 232.
In the first holder means 22 (first upper holddown member
227 and first lower holddown member 228) and the second holder
means 223 (second upper holddown member 231 and second lower
holddown member 232), the first upper holddown member 227 and
the first lower holddown member 228 are formed into rectangular
shapes in this example. However, these shapes are arbitrary and
can also be circular. The same applies to the second upper
holddown member 231 and the second lower holddown member 232.
The upper die 235 has an upper die main body 236, which has
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-22-
a die surface 237 on the underside. A supporting member 238 is
provided in the central part of the upper die main body 236. A
guide hole 239 is formed in the supporting member 238, and the
guide post 262 is slidably fitted into the guide hole 239 by
means of a collar 240.
Second elastic member mounting holes 241 are formed in the
supporting member 238. The other ends (upper ends) of the
aforementioned elastic members 264 are fitted into the second
elastic member mounting holes 241. The supporting member 238
has a return-restricting section 242. The return-restricting
section 242 has a hole for receiving the stopper member 268.
The stopper member 268 is mounted using a bolt 243 in the
mounting hole 269 formed in the second upper holddown member
231. The topside of the upper die main body 82 constitutes a
contact surface 94 that comes into contact with the underside of
the inner slider 245.
The elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression
springs that urge the upper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into
standby mode.
With the aid of the stopper member 268, the return-
restricting section 242 holds the die surface 237 at a position
separated upward from the pressure surface 261 of the second
upper holddown member 231 by a distance M.
The lower die 273 has a die surface 292 that faces the die
surface 237 of the upper die 235.
Thus, in the draw forming device 211 of the second
embodiment, the upper die 235 is supported to be capable of
sliding in relation to the second holder means 223, and is
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-23-
disposed so as to be separated from the inner slider 245 of the
double action double-action press 217. The first and second
holder means 222, 223 are fixed to the external slider 246.
The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 8A through 8D, of the operation whereby the blank material
shown in FIG. 3 is drawn by the draw forming device 211 of
the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7.
First, the blank material 15 is set on the metal die unit
212. Specifically, the metal die unit 212 is opened, the four
10 setting shafts 203 (see FIG. 7) are fitted into the four fitting
holes 99 (see FIG. 3) in the blank material 15, and the blank
material 15 is set on the first lower holddown member 228 and
the second lower holddown member 232.
The external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is
15 lowered, whereby the first upper holddown member 227 and the
second upper holddown member 231 are lowered as shown in FIG.
8A. The first upper holddown member 227 reaches the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15, and the pressure
surface 254 on the underside of the first upper holddown member
227 presses on the outer peripheral section 21. Combining the
outputs of the double-action press 217 and the first cylinders
275 allows the first holder means 222 (first upper holddown
member 227 and first lower holddown member 228) to restrain the
outer peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 at the
restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222.
The drawing region 96 of the central section 104 in the
blank material 15 is not supported, and deflection 105 occurs in
the central section 104 of the blank material 15 as described in
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-24-
FIG. 4B.
Next, as shown in FIG. 8B, the external slider 246 further
lowers the first holder means 222 by a stroke Sal against
resistance from the output of the first cylinders 275, whereupon
a pressure surface 288 on the topside of the second lower
holddown member 232 is raised by a stroke Sal as a result, and
the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is displaced
upward from the outer peripheral section 21 by a distance H4
(see FIG. 5B) that corresponds to the stroke Sal. The output of
the second cylinders 276 at this time is greater than the output
of the double-action press 217, and the second cylinders 276
stop without being lowered.
Thus, the second lower holddown member 232 displaces the
stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 while the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained.
As was described in FIG. 5B, the drawing region 96 and the
stretching region 97 are therefore stretched in the X- and Y-
axis directions as indicated by the arrows a5, and the
deflection 105 (see FIG. 4B) is removed from in the central
section 104 of the blank material 15.
Thus, the blank material 15 is displaced, and the
stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is restrained by
the pressure surface 261 of the second upper holddown member 231
and the pressure surface 288 of the second lower holddown member
232. At this time, the output of the double-action press 217
and the second cylinders 276 allows the second holder means 223
(the second upper holddown member 231 and the second lower
holddown member 232) to restrain the blank material 15 at the
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-25-
restraining position H2 of the second holder means 223.
The second upper holddown member 231 of the second holder
means 223 does not move in the Z-axis direction independent of
the external slider 246, because the first and second holder
means 222, 223 are fixed to the external slider 246. Therefore,
nonuniformities are reduced in the dimensions of the formed
article.
When the external slider 246 is further lowered by a stroke
S2 as shown FIG. 8C, the second holder means 223 is also
lowered, and the entire drawing region 96 of the blank material
is deformed by the die surface 292 of the lower die 273. The
first lower holddown member 228 and the second lower holddown
member 232 come into contact with the lower base member 272 and
stop. The outer peripheral section 21 and stretching region 97
15 of the blank material 15 are restrained by the first holder
means 222 and the second holder means 223.
In FIG. 8D, the inner slider 245 is lowered based on
information about the position of the external slider 246,
whereupon the underside of the inner slider 245 comes into
contact with a contact surface 244 of the upper die 235, the
upper die 235 is lowered against the repulsive force of the
elastic members 264, and the upper die applies pressure to the
drawing region 96 of the blank material 15. As a result, the
drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 is drawn into the
desired shape by the die surface 237 of the upper die 235 and
the die surface 292 of the lower die 273, and the formed article
107 is obtained.
FIGS. 9A and 9B show the operation of extracting the formed
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-26-
article 107 obtained by drawing.
The inner slider 245 is raised in FIG. 9A, whereupon the
repulsive force of the elastic members 264 raises the upper die
235. The stopper member 268 comes into contact with the return-
restricting section 242, the upper die 235 reaches an upper
limit, and the device goes into standby mode. The external
slider 246 continues to apply pressure.
When the external slider 246 begins to rise in FIG. 9B, the
second lower holddown member 232 reaches an upper limit and
stops at the stroke end of the second cylinders 276, and the
second holder means 223 opens. The formed article 107 separates
from the die surface 292 of the lower die 273 in this step.
The rods of the first cylinders 275 are raised further, and
the first lower holddown member 228 stops at an upper limit at
the stroke end of the first cylinders 275. When the external
slider 246 is raised further, the first holder means 222 opens
and the operator extracts the formed article 104.
In other words, pressing the "start button" on the
operating panel of the double-action press 17 automatically
executes the operation in FIGS. 7 through 9B, and the operator
extracts the formed article 104, whereby one formation cycle is
completed.
In to the draw forming device 211 of the second embodiment
described above, tensile force is applied to the central section
104 of the blank material 15 connected to the stretching region
97. The tensile force is applied from the time the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained at
the restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222 until
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-27-
the time the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is
restrained at the restraining position H2 of the second holder
means 223. As a result, the deflection in the central section
104 of the blank material 15 can be removed.
There is no independent movement between the external
slider 246 and the first and second holder means 222, 223, and
nonuniformities in the dimensions of the formed article can be
reduced because the first and second holder means 222, 223 are
fixed to the external slider 246.
The upper die 235 is supported by the elastic members 264,
is allowed to slide (in the Z-axis direction) in relation to the
second holder means 223, and is disposed separate from the inner
slider 245 of the double-action press 217. The upper die is
therefore operated using the second holder means 223 as a
reference. Accordingly, the upper die 235 can be positioned
with greater accuracy.
FIG. 10 shows a modified example of the draw forming device
211 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7. In the
description of this drawing device in the modified example,
components identical to those in the draw forming device of the
second embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals,
and detailed descriptions are omitted.
The draw forming device 211A of the modified example has a
metal die unit 212A comprising an upper metal die unit 213A and
a lower metal die unit 214A, and also has a blank holder 216A
disposed on the metal die unit 212A to restrain the blank
material 15.
The upper metal die unit 213A has an upper die 235A
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-28-
disposed in an open section 247 formed in the upper base member
234.
The lower metal die unit 214A has a lower die 273 mounted
on a lower base member 272A, which is mounted on a bed 219. The
lower base member 272A is mounted on the bed 219.
A blank holder 216A includes first holder means 222, and
second holder means 223A disposed on the inside thereof.
The restraining position H1 of the first holder means 222
is located farther out than the second holder means 223A, and is
the position in which the blank material 15 is held. The
details are described hereinafter.
The second holder means 223A has a second lower holddown
member 232A fixed to the lower base member 272A.
The restraining position Hb2 of the second holder means
223A is the position in which the double-action press 17 is
lowered past the restraining position Hl of the first holder
means 222 by a stroke Sbl. In other words, the blank material
15 is restrained at a position that is lower by a stroke Sbl
than the restraining position Hl of the first holder means 222.
The second lower holddown member 232A has a holddown member
main body 286A formed into a rectangular shape facing the
holddown member main body 258 of the second upper holddown
member 231. The holddown member main body 286A has a pressure
surface 288 on the topside.
The first upper holddown member 227, first lower holddown
member 228, second upper holddown member 231, and second lower
holddown member 232A are rectangular in this description, but
the shapes of these components are arbitrary and may also be
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-29-
circular.
The upper die 235A has an upper die main body 236A.
The elastic members 264 are composed, e.g., of compression
springs that urge the upper die 235 in the Z-axis direction into
standby mode.
Thus, in the draw forming device 211A of the modified
example, the upper die 235A is supported to be capable of
sliding in relation to the second holder means 223A. The upper
die 235A is also disposed so as to be separated from the inner
slider 245 of the double action double-action press 217. The
first holder means 222 and second holder means 223A are fixed
integrally to the external slider 246 of the double-action press
217.
As is clear in FIG. 10, the descending stroke Sbl of the
first holder means 222 of the modified example, which is
necessary to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 of the
blank material 15, is greater than the descending stroke Sal of
the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7. Therefore, the displaced
depth H5 of the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15,
described later, is greater than the displaced depth in the
second embodiment. In other words, the amount of displacement
is greater, and the stretching region 97 and drawing region 96
of the blank material 15 are subjected to a tensile force that
corresponds to the amount of displacement. Therefore,
deflection in the central section of the blank material 15 is
reduced.
The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 11A through 11C, of the operation of drawing the blank
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-30-
material with the draw forming device of the modified example.
First, when the blank material 15 is set in the opened
metal die unit 212A as shown in FIG. 10, the blank material 15
is set on the first lower holddown member 228 and second lower
holddown member 232A as previously described.
In FIG. 11A, lowering the external slider 246 of the
double-action press 217 causes the first upper holddown member
227 and the second upper holddown member 231 to be lowered,
whereupon the first upper holddown member 227 reaches the outer
peripheral section 21 of the blank material 15, and the pressure
surface 254 of the first upper holddown member 227 applies
pressure to the outer peripheral section 21. The output of the
double-action press 217 and of the first cylinders 275 allows
the first holder means 222 to restrain the outer peripheral
section 21 of the blank material 15 at the restraining position
H1.
The blank material 15 is restrained at the external
peripheral section 21 in the restraining position H1, and is not
supported at the drawing region 96 in the central section 104.
Deflection 105 is formed in the central section 104 of the blank
material 15, as shown in FIG. 4B.
The external slider 246 of the double-action press 217 is
then lowered as shown in FIG. 11B, whereupon the first holder
means 222 for restraining the outer peripheral section 21 of the
blank material 15 is lowered by a stroke Sbl against resistance
from the output of the first cylinders 275, and the first lower
holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222 comes into
contact with the lower base member 272A and stops.
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-31-
The lowering of the first holder means 222 causes the
stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 to be displaced
upward from the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank
material 15, which is restrained by the first holder means 222.
This displacement causes the stretching region 97 and the
drawing region 96 of the blank material 15 to be stretched
outward. The stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is
then restrained by the second holder means 223A.
In other words, the second upper holddown member 231 and
the second lower holddown member 232A of the second holder means
223A restrain the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15
at the restraining position Hb2, which is set to the position in
which the external slider 246 is lowered by a stroke Sb1.
There is no deflection 105 in the central section 104 shown
in FIG. 4B, because the drawing region 96 and stretching region
97 are stretched in the X- and Y-axis directions as indicated by
the arrows a5. These regions are stretched in a process of
plastic deformation of the blank material 15 by a displacement
depth of H5 as shown in FIG. 11C, while the outer peripheral
section 21 of the blank material 15 is restrained. It is
therefore possible to reduce deflection in the drawing region 96
of the blank material 15 set in the metal die unit 212A. The
displacement depth H5 is the depth of plastic working when the
blank material is restrained at the restraining position Hb2 of
the second holder means 223A.
Thus, there is an increase in the displacement depth H5 of
the stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 based on the
lowering of the first holder means 222 in the modified example,
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-32-
and deflection in the drawing region 96 of the blank material 15
can be reduced proportionally.
The external slider 246 continues to apply pressure,
whereby the first holder means 222 and second holder means 223A
continue to restrain the outer peripheral section 21 and the
stretching region 97 of the blank material 15.
The inner slider 245 is lowered based on information about
the position of the external slider 246 as shown in FIG. 11D,
whereupon the underside of the inner slider 245 comes into
contact with the contact surface 244 of the upper die 235A, and
the upper die 235A is lowered against the repulsive force of the
external slider 246 to apply pressure to the drawing region 96
of the blank material 15. As a result, the drawing region 96 of
the blank material 15 is drawn into the desired shape by the die
surface 237 of the upper die 235A, and the die surface 292 of
the lower die 273, and a formed article 107A is obtained.
The following is a description, made with reference to
FIGS. 12A and 12B, of the operation of extracting the formed
article 107A in the draw forming device of the modified example.
When the inner slider 245 is raised in FIG. 12A, the upper
die 235A is raised against the repulsive force of the elastic
members 264, and the return-restricting section 242 comes into
contact with the stopper member 268, whereupon the upper die
235A reaches an upper limit and the device goes into standby
mode. The external slider 246 continues to apply pressure
during this time.
The external slider 246 then continues to be raised as
shown in FIG. 12B, whereupon the rods of the first cylinders 275
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-33-
are raised as well, and the first upper holddown member 227 and
first lower holddown member 228 of the first holder means 222
are raised while the outer peripheral section 21 of the blank
material 15 is restrained. As a result, the blank material 15
moves upward away from the pressure surface 288 of the second
lower holddown member 232A. The first lower holddown member 228
reaches an upper limit and stops at the stroke end of the first
cylinders 275.
The external slider 246 is then raised further, whereupon
the first holder means 222 opens as shown in FIG. 10, and the
operator therefore extracts the formed article 107A.
In other words, pressing the "start button" on the
operating panel of the double-action press 17 automatically
executes the operation beginning with drawing the blank material
15 and ending with opening the metal die unit, and the operator
extracts the formed article 107A, whereby one formation cycle is
completed.
A draw forming device of a modified example was described
above, but according to this draw forming device of the modified
example, settings are selected so that there is an increase in
the descending stroke Sbl of the first holder means 222 of the
modified example necessary to restrain the outer peripheral
section 21 of the blank material 15. The displacement of the
stretching region 97 of the blank material 15 is therefore
proportionally greater, and the stretching region 97 and drawing
region 96 of the blank material 15 are stretched farther. The
deflection in the central section of the blank material 15 is
therefore further reduced.
CA 02586049 2007-04-30
-34-
INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY
In the draw forming device of the present invention, the
outer peripheral section of a blank material is restrained by
first holder means, and the stretching region on the inside of
the outer peripheral section is displaced and restrained in the
shearing direction relative to the outer peripheral section.
Tensile force is thereby applied to the drawing region in the
middle of the blank material, and deflection in the drawing
region is reduced. Thus, when the drawing region is drawn,
formed articles having little nonuniformity in their dimensions
are obtained, which articles are usable in various industries.