Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2591910 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | PLASTIC PLATE FOR LINING CONCRETE COMPONENTS |
| (54) French Title: | PLAQUE DE PLASTIQUE CONCUE POUR RECOUVRIR DES COMPOSANTS EN BETON |
| Status: | Expired and beyond the Period of Reversal |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | RICHES, MCKENZIE & HERBERT LLP |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2014-04-15 |
| (86) PCT Filing Date: | 2006-04-22 |
| (87) Open to Public Inspection: | 2006-10-26 |
| Examination requested: | 2011-04-11 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | Yes |
|---|---|
| (86) PCT Filing Number: | PCT/EP2006/003728 |
| (87) International Publication Number: | EP2006003728 |
| (85) National Entry: | 2007-06-07 |
| (30) Application Priority Data: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
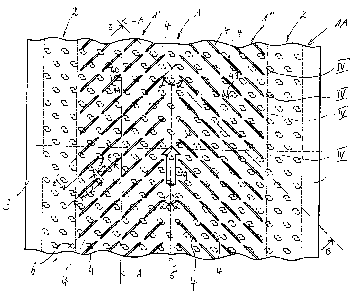
The invention relates to a plastic plate for lining concrete components
through which a fluid medium flows. Said plastic plate is provided with a
plurality of anchor elements (10) which are mounted on the side (1B) thereof
oriented towards the concrete component wall and which make it possible to
positively fixe said plastic plate to the concrete component. The side (1A) of
the plastic plate oriented to a medium is provided with a plurality of
adjacent flow elements (4) which are embodied in the form of elevated
structures comprising an upstream flank (4A) oriented in a flow direction (9)
and an oppositely oriented downstream flank (4B), wherein the superficial
areas located between the flow elements are smoothly shaped. In such a manner,
it makes it possible to increase a dragging effect of medium-carried particles
in order to avoid solid deposits even at a low flowrate. In the preferred
embodiment, the flow elements are constructed in the form of narrow webs which
have a wedge-shaped cross section and are distributed in individual rows (IV)
side by side transversally to the longitudinal axis (5) of the plastic plate.
La présente invention concerne une plaque de plastique conçue pour recouvrir des composants en béton qui sont traversés par un milieu fluide. Cette plaque de plastique présente sur la face (1B) tournée vers la paroi du composant en béton une pluralité d'éléments d'ancrage (10) qui permettent de relier la plaque de plastique au composant en béton par liaison de forme. Sur la face (1A) tournée vers le milieu, la plaque de plastique présente une pluralité d'éléments d'écoulement adjacents (4) qui sont conçus sous forme de structures en saillie présentant un flanc en amont (4A) orienté dans le sens d'écoulement (9) et un flanc en aval (4B) orienté dans le sens inverse du sens d'écoulement. Les zones superficielles situées entre les éléments d'écoulement sont lisses. Il est ainsi possible d'augmenter l'action de dragage des particules entraînées dans le milieu, de manière à empêcher les dépôts de matières solides même avec une faible vitesse d'écoulement. Dans un mode de réalisation préféré, les éléments d'écoulement sont conçus sous forme de nervures étroites présentant une section transversale cunéiforme, qui sont réparties en lignes individuelles (IV) les unes à côtés des autres, transversalement à l'axe longitudinal (5) de la plaque de plastique.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Time Limit for Reversal Expired | 2019-04-23 |
| Letter Sent | 2018-04-23 |
| Maintenance Request Received | 2017-03-10 |
| Maintenance Request Received | 2016-03-03 |
| Revocation of Agent Requirements Determined Compliant | 2015-07-29 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2015-07-29 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2015-07-29 |
| Appointment of Agent Requirements Determined Compliant | 2015-07-29 |
| Appointment of Agent Request | 2015-06-23 |
| Revocation of Agent Request | 2015-06-23 |
| Maintenance Request Received | 2015-03-17 |
| Grant by Issuance | 2014-04-15 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2014-04-14 |
| Pre-grant | 2014-02-03 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 2014-02-03 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2013-08-12 |
| Letter Sent | 2013-08-12 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2013-08-12 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 2013-07-24 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2013-06-07 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2012-12-07 |
| Letter Sent | 2011-05-03 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2011-04-11 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2011-04-11 |
| Request for Examination Received | 2011-04-11 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2008-05-06 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 2008-04-28 |
| Request for Priority Received | 2008-02-01 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2007-11-29 |
| Inactive: Notice - National entry - No RFE | 2007-11-27 |
| Inactive: Declaration of entitlement - Formalities | 2007-09-05 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2007-09-05 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2007-07-21 |
| Application Received - PCT | 2007-07-20 |
| National Entry Requirements Determined Compliant | 2007-07-07 |
| National Entry Requirements Determined Compliant | 2007-06-07 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2006-10-26 |
There is no abandonment history.
The last payment was received on 2013-04-19
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Patent fees are adjusted on the 1st of January every year. The amounts above are the current amounts if received by December 31 of the current year.
Please refer to the CIPO
Patent Fees
web page to see all current fee amounts.
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic national fee - standard | 2007-06-07 | ||
| MF (application, 2nd anniv.) - standard | 02 | 2008-04-22 | 2008-04-11 |
| MF (application, 3rd anniv.) - standard | 03 | 2009-04-22 | 2009-04-15 |
| MF (application, 4th anniv.) - standard | 04 | 2010-04-22 | 2010-04-14 |
| MF (application, 5th anniv.) - standard | 05 | 2011-04-22 | 2011-04-08 |
| Request for examination - standard | 2011-04-11 | ||
| MF (application, 6th anniv.) - standard | 06 | 2012-04-23 | 2012-04-12 |
| MF (application, 7th anniv.) - standard | 07 | 2013-04-22 | 2013-04-19 |
| Final fee - standard | 2014-02-03 | ||
| MF (patent, 8th anniv.) - standard | 2014-04-22 | 2014-04-10 | |
| MF (patent, 9th anniv.) - standard | 2015-04-22 | 2015-03-17 | |
| MF (patent, 10th anniv.) - standard | 2016-04-22 | 2016-03-03 | |
| MF (patent, 11th anniv.) - standard | 2017-04-24 | 2017-03-10 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| AGRU KUNSTSTOFFTECHNIK GMBH |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| WOLFGANG BERGER |