Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Brevet: | (11) CA 2591910 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | PLAQUE DE PLASTIQUE CONCUE POUR RECOUVRIR DES COMPOSANTS EN BETON |
| (54) Titre anglais: | PLASTIC PLATE FOR LINING CONCRETE COMPONENTS |
| Statut: | Périmé et au-delà du délai pour l’annulation |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | RICHES, MCKENZIE & HERBERT LLP |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | 2014-04-15 |
| (86) Date de dépôt PCT: | 2006-04-22 |
| (87) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 2006-10-26 |
| Requête d'examen: | 2011-04-11 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| Cédé au domaine public: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Oui |
|---|---|
| (86) Numéro de la demande PCT: | PCT/EP2006/003728 |
| (87) Numéro de publication internationale PCT: | EP2006003728 |
| (85) Entrée nationale: | 2007-06-07 |
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
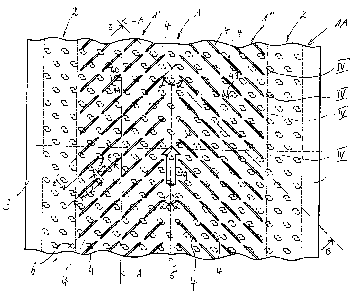
La présente invention concerne une plaque de plastique conçue pour recouvrir des composants en béton qui sont traversés par un milieu fluide. Cette plaque de plastique présente sur la face (1B) tournée vers la paroi du composant en béton une pluralité d'éléments d'ancrage (10) qui permettent de relier la plaque de plastique au composant en béton par liaison de forme. Sur la face (1A) tournée vers le milieu, la plaque de plastique présente une pluralité d'éléments d'écoulement adjacents (4) qui sont conçus sous forme de structures en saillie présentant un flanc en amont (4A) orienté dans le sens d'écoulement (9) et un flanc en aval (4B) orienté dans le sens inverse du sens d'écoulement. Les zones superficielles situées entre les éléments d'écoulement sont lisses. Il est ainsi possible d'augmenter l'action de dragage des particules entraînées dans le milieu, de manière à empêcher les dépôts de matières solides même avec une faible vitesse d'écoulement. Dans un mode de réalisation préféré, les éléments d'écoulement sont conçus sous forme de nervures étroites présentant une section transversale cunéiforme, qui sont réparties en lignes individuelles (IV) les unes à côtés des autres, transversalement à l'axe longitudinal (5) de la plaque de plastique.
The invention relates to a plastic plate for lining concrete components
through which a fluid medium flows. Said plastic plate is provided with a
plurality of anchor elements (10) which are mounted on the side (1B) thereof
oriented towards the concrete component wall and which make it possible to
positively fixe said plastic plate to the concrete component. The side (1A) of
the plastic plate oriented to a medium is provided with a plurality of
adjacent flow elements (4) which are embodied in the form of elevated
structures comprising an upstream flank (4A) oriented in a flow direction (9)
and an oppositely oriented downstream flank (4B), wherein the superficial
areas located between the flow elements are smoothly shaped. In such a manner,
it makes it possible to increase a dragging effect of medium-carried particles
in order to avoid solid deposits even at a low flowrate. In the preferred
embodiment, the flow elements are constructed in the form of narrow webs which
have a wedge-shaped cross section and are distributed in individual rows (IV)
side by side transversally to the longitudinal axis (5) of the plastic plate.
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2024-08-01 : Dans le cadre de la transition vers les Brevets de nouvelle génération (BNG), la base de données sur les brevets canadiens (BDBC) contient désormais un Historique d'événement plus détaillé, qui reproduit le Journal des événements de notre nouvelle solution interne.
Veuillez noter que les événements débutant par « Inactive : » se réfèrent à des événements qui ne sont plus utilisés dans notre nouvelle solution interne.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , Historique d'événement , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Le délai pour l'annulation est expiré | 2019-04-23 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2018-04-23 |
| Requête visant le maintien en état reçue | 2017-03-10 |
| Requête visant le maintien en état reçue | 2016-03-03 |
| Exigences relatives à la révocation de la nomination d'un agent - jugée conforme | 2015-07-29 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2015-07-29 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2015-07-29 |
| Exigences relatives à la nomination d'un agent - jugée conforme | 2015-07-29 |
| Demande visant la nomination d'un agent | 2015-06-23 |
| Demande visant la révocation de la nomination d'un agent | 2015-06-23 |
| Requête visant le maintien en état reçue | 2015-03-17 |
| Accordé par délivrance | 2014-04-15 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2014-04-14 |
| Préoctroi | 2014-02-03 |
| Inactive : Taxe finale reçue | 2014-02-03 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2013-08-12 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2013-08-12 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2013-08-12 |
| Inactive : Approuvée aux fins d'acceptation (AFA) | 2013-07-24 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2013-06-07 |
| Inactive : Dem. de l'examinateur par.30(2) Règles | 2012-12-07 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2011-05-03 |
| Exigences pour une requête d'examen - jugée conforme | 2011-04-11 |
| Toutes les exigences pour l'examen - jugée conforme | 2011-04-11 |
| Requête d'examen reçue | 2011-04-11 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive : CIB en 1re position | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2009-06-23 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2008-05-06 |
| Inactive : Notice - Entrée phase nat. - Pas de RE | 2008-04-28 |
| Demande de priorité reçue | 2008-02-01 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2007-11-29 |
| Inactive : Notice - Entrée phase nat. - Pas de RE | 2007-11-27 |
| Inactive : Déclaration des droits - Formalités | 2007-09-05 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2007-09-05 |
| Inactive : CIB en 1re position | 2007-07-21 |
| Demande reçue - PCT | 2007-07-20 |
| Exigences pour l'entrée dans la phase nationale - jugée conforme | 2007-07-07 |
| Exigences pour l'entrée dans la phase nationale - jugée conforme | 2007-06-07 |
| Demande publiée (accessible au public) | 2006-10-26 |
Il n'y a pas d'historique d'abandonnement
Le dernier paiement a été reçu le 2013-04-19
Avis : Si le paiement en totalité n'a pas été reçu au plus tard à la date indiquée, une taxe supplémentaire peut être imposée, soit une des taxes suivantes :
Les taxes sur les brevets sont ajustées au 1er janvier de chaque année. Les montants ci-dessus sont les montants actuels s'ils sont reçus au plus tard le 31 décembre de l'année en cours.
Veuillez vous référer à la page web des
taxes sur les brevets
de l'OPIC pour voir tous les montants actuels des taxes.
| Type de taxes | Anniversaire | Échéance | Date payée |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taxe nationale de base - générale | 2007-06-07 | ||
| TM (demande, 2e anniv.) - générale | 02 | 2008-04-22 | 2008-04-11 |
| TM (demande, 3e anniv.) - générale | 03 | 2009-04-22 | 2009-04-15 |
| TM (demande, 4e anniv.) - générale | 04 | 2010-04-22 | 2010-04-14 |
| TM (demande, 5e anniv.) - générale | 05 | 2011-04-22 | 2011-04-08 |
| Requête d'examen - générale | 2011-04-11 | ||
| TM (demande, 6e anniv.) - générale | 06 | 2012-04-23 | 2012-04-12 |
| TM (demande, 7e anniv.) - générale | 07 | 2013-04-22 | 2013-04-19 |
| Taxe finale - générale | 2014-02-03 | ||
| TM (brevet, 8e anniv.) - générale | 2014-04-22 | 2014-04-10 | |
| TM (brevet, 9e anniv.) - générale | 2015-04-22 | 2015-03-17 | |
| TM (brevet, 10e anniv.) - générale | 2016-04-22 | 2016-03-03 | |
| TM (brevet, 11e anniv.) - générale | 2017-04-24 | 2017-03-10 |
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| AGRU KUNSTSTOFFTECHNIK GMBH |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| WOLFGANG BERGER |