Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
-1-
METHOD OF EXPRESSION, RECORDING, REPRODUCTION, AND
COMMUNICATION OF COMPUTER OBJECT USING COLOR, APPARATUS FOR
RECORDING AND/OR REPRODUCTION, RECORDING MEDIUM, AND METHOD
OF PREPARATION OF CODE
DIVISIONAL APPLICATION
This application is a divisional application of
Canadian Patent Application No. 2,338,418, which was filed
on May 24, 2000.
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a method of
expression, recording or storage, reproduction, and
communication, using color, for alphanumerics, graphics,
mathematical formulas, images, sound, and other data or
information handled involving a computer in industry, daily
life, etc., an apparatus for recording and/or reproduction,
a recording medium using color, arid a method of preparation
of a code using color.
BACKGROUND ART
As conventional methods for recording various
types of information, the method of direct recording on
paper, the method of recording on floppy disks, hard disks,
compact disks (CDs), digital versatile disks (DVDs), and
other recording media involving computers, etc. are known.
Recently, along with the spread of the computer, much use
has particularly been made of such recording media.
As a method of recording several types of
information on a printed circuit board, on the other hand,
there is the method of displaying dots at suitable locations
on the printed circuit board and recording small amounts of
information by the combination of these dots. Other methods
of recording information on printed circuit boards include
the method using bar codes, the method of stamping
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
28469-4E
- 2 -
printed circuit boards with dot or check patterns, and the method
of combining these. In these cases, the recorded infoimation is
expressed by images comprised of the dots, lines, patterns, or
combinations of the same or the positions of the dots, lines, etc.
Along with the spread of the computer, the main method for
recording information has become recording information on recording
media converted to a binary format. Great strides have been made in
such recording media along with the rapid advances made in computer
hardware and software. The method of recording information on a
recording medium is now basically to link 1 bit of information with
the smallest recording unit on the recording medium (hereinafter
referred to as "1 dot", the location where the smallest recording
unit is recorded also being referred to as a "dot" ) . With the
skyrocketing amount of information for recording in recent years,
therefore, the recording capacity of recording media is rapidly being
used up.
An object of some embodiments, in view of the problem
of the limited recording capacity and taking note of the
characteristic of color, is to provide a method of expression of a
computer object using color as a medium for expressing data or
information and linking the type or difference of color printed on
a dot with a plurality of data etc, and thereby increasing the amount
of information per dot to an amount more than 1 bit (for example,
2 bits, 8 bits, 16 bits, etc.) and thereby overcoming the limitation
in the recording (or storage) capacity.
Another object of some embodiments is to provide a method
of recording, reproduction, and communication of a computer object
using the method of expression of a computer object using color.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
28469-4E
- 3 -
Another object of some embodiments is to provide an
apparatus for recording and/or reproduction of a computer object
comprised by using the method of expression of a computer object using
color.
Another object of some embodiments is to provide a
method and apparatus for recording a large amount of data or
information using general paper, plastic, or other inexpensive
recording media.
Another object of some embodiments is to provide a
recording medium using the method of recording data or information
using color.
Another object of some embodiments is to provide
a method of preparation of a code using recording of data or
information using color.
Another object of some embodiments is to provide a method
and apparatus enabling transmission of a large amount of information
by applying the recording of data or information using color as
explained above to a communications line and communications
apparatus.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
In the present invention, the concepts of color, a color entity,
computer object, etc. will be used in the following explanation.
Current computers can recognize over several million types of
printable color. Therefore, the inventors propose the technical idea
of using color to express data or information.
Here, "color" in principle is a physical manifestation which
an ordinary person can visually recognize under visible light It
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 4 -
further is assumed to include in concept a physical manifestation
under light of a frequency other than visible light so as to include
recognition by a computer.
A computer object is linked with each of the plurality of colors.
Here, a "computer object" means an alphanumeric, symbol, graphic,
mathematical formula, image, sound, or other data or information
(hereinafter referred to as "data/information's in accordance with
need) handled inside or through a computer. Such a computer object
is recorded by printing the corresponding color on a dot of the
recording medium. That is, by recording color on a recording medium,
it becomes possible to simultaneously store the computer object. Here,
the substance printed with a dot of a recording medium using color
as an attribute is referred to as a "color entity".
As explained above, the computer object is recorded by the color
of the color entity. To realize the above recording, the method of
expression of the computer object using color becomes important. The
present invention proposes such a method of expression of a computer
object using color. Various methods of recording (storage) ,
reproduction, and communications are realized according to the
present invention based on this method of expression of a computer
object. Further, an apparatus for recording and/or reproduction using
the method of expression of a computer object is proposed according
to the present invention. Further, a method of preparation of a code
using the method of expression of a computer object is proposed
according to the present invention.
Further, when recording data/information on a medium on which
color cannot be directly recorded (for example, a computer disk) or
in communication, the computer object is transmitted using a color
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 5 -
numerical value corresponding to the color.
Based on the above idea, color is linked with a computer object
and a plurality of computer objects are expressed by different colors.
As explained above, a different color is linked with each of
the plurality of computer objects handled inside a computer or through
a computer. This linked relation between a color and computer object
will be referred to as a "color-object relation". A substance having
as an attribute the color printed on one or more dots (hereinafter
referred to as "color dots") of a recording medium ( that is, a color
entity) may therefore be used to express a corresponding computer
object. A recording medium on which a color entity expressing a
computer object is recorded may be made of, for example, paper,
plastic, glass, wood, ceramic, a sheet, liquid crystal panel, a medium
able to be recorded with color, and combinations of the same.
Using the above method of expression (or method of recording)
of a computer object according to the present invention, an apparatus
for recording a computer object expressed using color may be
constructed. This recording apparatus may include a CPU (central
processing unit ) , color output device, and storage storing the
necessary data or program (main storage or auxiliary storage). This
apparatus for recording a computer object converts the computer
object to a color for recording. That is, in the apparatus for
recording a computer object, the CPU converts a computer object to
a color based on a predetermined color-object relation when there
is a command to record a certain computer object. Further, the CPU
sends a color output instruction to the color output device. The color
output device outputs and records the color entity on a recording
medium in accordance with this color output instruction. The color
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 6 -
output device is a color printer etc.
Using the above method of expression ( or method of reproduction)
of a computer object according to the present invention, an apparatus
for reproduction of a color object expressed using color may be
constructed. This reproduction apparatus includes a CPU, color input
device, and storage for storing the necessary data or program. The
apparatus for reproduction of a computer object converts color to
a computer object for reproduction. That is, in the apparatus for
reproduction of a computer object, the color input device reads the
color of a color dot on the recording medium. The color input device
includes a CCD camera, camera scanner, etc. The CPU regenerates the
computer object from the input color based on the color-object
relation. Further, the CPU displays the regenerated computer object,
outputs it as sound, outputs it as an image, prints it, stores it,
or transmits it.
It is also possible to combine an apparatus for recording and
an apparatus for reproducing a computer object to realize an apparatus
for recording and reproducing a computer object.
In the above configuration, instead of color, it is also
possible to link a different numerical value (this numerical value
being referred to as a "color numerical value") with each computer
object (the relationship of the linked color numerical values and
computer objects being referred to as "color numerical value-object
relation") and use this to express a computer object.
It is also possible to assign a color to a color numerical value
(the relation between colors and color numerical values being
referred to as a "color-color numerical value relation") and use both
of the color numerical value-object relation and color-color
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 7 -
numerical value relation to link a computer object with a color.
When converting a computer object to a color or converting a
color to a computer object, it is also possible to construct a
recording apparatus or a reproduction apparatus using both the
color-color numerical value relation and the color numerical
value-object relation instead of the color-object relation.
It is further possible to use the corresponding color numerical
value rather than the color and transmit the same over a network or
transmit the same among a plurality of computers by transfer by a
data storage medium and to use the received color numerical value
to regenerate the computer object in accordance with need using the
color numerical value-object relation and thereby keep from handling
a computer object itself on a communications path or data transfer
path.
In the method of expression, method of recording, etc. of the
computer object and recording apparatus etc., the method of setting
a color numerical value is preferably to determine a maximum allowable
range of number of elements of a color numerical value taking into
consideration the reproducibility of color and set a color numerical
value within that range.
The method of establishing a plurality of computer object groups,
preparing color numerical value-object relations having different
correspondences for each, and arranging all of the computer objects
handled in the plurality of computer object groups has been proposed.
At this time, to identify a computer object group, it is sufficient
to assign a color numerical value (inevitably a color) to each group.
This method is useful for facilitating the arrangement of computer
objects and effective when the number of computer objects handled
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 8 -
exceeds the maximum allowable range of the number of elements of the
color numerical value.
When referring to the plurality of computer object groups as
first hierarchal groups and the number of the first hierarchal groups
becomes larger, the first hierarchal groups are divided to create
a plurality of second hierarchal groups and the first hierarchal
groups are included in the second hierarchal groups. Further,
similarly, the method of preparing a third hierarchy, fourth
hierarchy, and the like and linking a color numerical value with each
of these hierarchies of groups is proposed. Due to this, it becomes
possible to more flexibly arrange computer objects and link any number
of computer objects, no matter how many, to a finite number of colors.
When converting a computer object to a color numerical value,
converting the color numerical value to a color, and converting the
color to a computer object, the color numerical value-object relation,
color-color numerical value relation, and color-object relation
(these three types of relations relating to a computer object meeting
these conditions being referred to all together as the "cyclic object
relation") are set so that a computer object after conversion becomes
the same as the computer object before conversion.
The method is also proposed of, when converting a computer
object to color or a color numerical value and transmitting,
transferring, or recording ( storing) the same, simultaneously
transmitting, transferring, and recording ( storing) the one or more
correspondences of the cyclic object relation required for
regeneration of the computer object so that even when the receiving
side does not have the relation for regeneration of the computer
object, the received color numerical value can be regenerated to the
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 9 -
computer object.
In the method of expression of a computer object according to
the present invention, an elemental computer object enabling
expression of all sorts of computer objects included in any hierarchy
of group by combinations thereof (for example, an alphanumeric or
Japanese character defined by the JIS code or something used in common
as an element of a computer object inside a computer group, such a
computer object being called a "common object") are set. It is
possible to express a series of computer objects by a common object.
A color-object relation, color numerical value-object relation,
and color-color numerical value relation are set among the common
objects and colors and color numerical values corresponding to the
same (these being called "common colors" and "common color numerical
values") (these relation relating to common objects being together
called "common object relations"). This enables a series of computer
objects to be transmitted, transferred, recorded, and regenerated
(reproduced) using only a common color numerical value or common
color.
The method has also been proposed of simultaneously adding a
common object relation when transmitting, transferring, and
recording a computer object using a common color or common color
numerical value.
The cyclic object relations include common object relations.
Using this, a series of computer objects may be converted to color
numerical values or colors and transmitted, transferred, recorded
(stored) , and regenerated (reproduced) .
The method of recording a computer object and recording
apparatus thereof assigns addresses to the recording surface of the
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 10 -
recording medium for the output of the color dots and arranges the
colors dots in accordance with those addresses.
In the above, it is preferably made possible to designate the
order of output and input of color dots by addresses.
In the method of reproduction of a computer object or
reproduction apparatus according to the present invention, it is
possible to make the shape of the recording medium or the shape of
the arrangement of color dots for output on the same a disk shape,
square shape, or other polygonal shape or any other shape. The
recording medium may be made any composition and the color dot output
surface of the storage medium may be made rotatable or movable in
any direction. Further, the color entity output surface of the storage
medium may be made movable or stoppable. Further, the recording medium
may be made detachable or may be held to enable driving, rotation,
stopping, etc. Further, the holder of the recording medium may be
made rotatable and the color dots may be made inputtable or
outputtable along with rotation of the holder.
The above recording medium may be prevented from discoloration
of the color entity by a coating etc.
The linkage in the color-object relation may be based on the
communications line and communications apparatus.
The color dots may be arranged by dividing the color dot output
surface ( display surface) of the recording medium into a control area,
storage area, security area, and other areas. The areas may be freely
set up.
The above configuration enables color dot data to be transmitted
two way and enables recording of data relating to the color dots or
checking and updating of the content of transmission.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 11 -
In the transmission, transfer, recording, and reproduction of
a computer object using the method of recording, method of
reproduction, recording apparatus, reproduction apparatus, and
recording/reproduction apparatus of a computer object according to
the present invention, all or a specific part of the series of input
colors or color numerical values may be used to judge if acceptance
is possible and perform different processing when acceptance is not
possible and when acceptance is possible (this processing is referred
to as a "color filter" ) .
The above color filter may be provided with a list of colors
or color numerical values (this list called a "filter correspondence
table") and compare an input color or color numerical value against
the filter correspondence table to judge whether acceptance is
possible.
The above color filter may function to display data for deciding
on processing when judging whether acceptance is possible for a series
of colors or color numerical values or to return data by transmission,
transfer, and reproduction or other perform other processing.
The method and apparatus for recording a computer object
according to the present invention may also comprise assigning a
specific function to one or more specific colors based on a
color-object relation or independent from a color-object relation
to give a function of designating a computer object group hierarchy,
a function of judgement and checking before converting a color entity
to a computer object, a security function, etc.
The method may further comprise using a specific color for
correcting a change in color over time or correcting a difference
in characteristics of input or output of color between color
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 12 -
input/output devices. For example, it is possible to assign one or
more color information to one specific color and output the designated
plurality of colors after a color entity as color entities. By doing
this, the side receiving the color entity as input can read one or
more corrective color entities from information designated by a
specific color and correct the difference in color due to aging or
differences in hardware by the difference in color information
designated for the read color and specific color.
In the above explanation, only color was used as the attribute
of a color entity, but it is also possible to use attributes other
than color. That is, it is possible to provide a method of expression
of a computer object, method of recording, method of reproduction,
method of communication, recording apparatus, reproduction
apparatus, or recording and reproduction apparatus linking one or
more attributes selected from the group of shapes of circles, squares,
bars, and other graphics or other printable characteristics in
addition to color as attributes of color entities ( these attributes
being referred to as "general colors" ) . When Using such composite
attributes, color numerical values may be assigned and cyclic object
relations established.
It is also possible to mix on a single recording medium (for
example, paper) a recording of computer objects by color entities
or color numerical values and a recording of computer objects not
based on the same, for example, ordinary alphanumerics etc.
Further, it is also possible to record a single computer object
using a plurality of color dots arranged continuously or in any
pattern on a recording medium. By establishing a color-object
relation or a color-color numerical value relation linking one
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 13 -
computer object or color numerical value to a combination of a
plurality of different general colors, it becomes possible to record
one computer object for a plurality of color dots arranged
continuously or in any pattern on a recording medium.
In some cases, there are color entities or color numerical
values output in advance or for which output is determined and
computer objects are linked with these colors or color numerical
values later. In this case, a new color-object relation or color
numerical value-object relation may be established and the relation
used at the time of input of colors or color numerical values.
The following effects are obtained by the method and apparatus
for expressing a computer object and recording a computer object using
a color or a color entity having a general color as an attribute.
It is possible to make the recording capacity of each dot one
of a plurality of dots up to the limit of the resolution and precision
of printing and reading of color and to thereby increase the recording
capacity ( storage capacity) . It is possible to link various types
of information such as alphanumerics , symbols, graphics,
mathematical formulas, images, and audio with each dot. A
considerable amount of information can therefore be recorded and
stored in a handy space. The available selection of recording media
also becomes broader and the recording media become inexpensive. It
further becomes possible to simplify the hardware and system for
recording and reproduction. Further, recording by a combination of
colors facilitates the recording and control of a large amount of
information. There is an equivalent action of compression of data
in the transfer and transmission of information and the storage of
books and other publications. Since information can be recorded on
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
28469-4E
- 14 -
paper etc. by the use of amounting fixture, entertainment software
and software for daily life can be prepared simply and inexpensively.
Therefore, it is possible to replace expensive large capacity storage
devices. At the same time, the invention is environmentally friendly
and energy saving in action.
The above method of expression of a computer object, method
of recording, method of reproduction, and method of communication
can be further developed and used as a method of preparing a code.
By expressing information by colors or color numerical values and
transmitting information as color numerical values, it becomes
possible to transmit a large amount of information, achieve the
function of a code, and increase the security of the information in
the middle of transmission. In preparing the codes, the information
is expressed by assigning addresses to the recording surface of
the recording medium on which the color is printed and expressing
the information with the color by designating an order of output
and input of color entities by the addresses.
Since ordinary symbols, colors and color numerical values are
selectively used, it becomes possible to reduce the amount of dots
used. Use of the correspondence table enables the colors and color
numerical values transmitted and transferred for computer objects
to be reduced.
ak 02593404 2007-07-20
. 28469-4E
-14a-
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method of recording a computer object by
a computer handling a plurality of computer objects,
comprising: converting the computer object to a color based
on a predetermined correspondence between colors and
computer objects when recording the computer object;
recording a color entity on a recording medium; using a
correspondence of colors and color numerical values and a
correspondence of color numerical values and computer
objects when converting the computer object to the color or
when converting the color to the computer object; and using
a communications means to establish links in the
correspondence between colors and computer objects.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of recording a
computer object by a computer handling a plurality of
computer objects, comprising: converting the computer object
to a color based on a predetermined correspondence between
colors and computer objects when recording the computer
object; recording a color entity on a recording medium;
using a correspondence of colors and color numerical values
and a correspondence of color numerical values and computer
objects when converting the computer object to the color or
when converting the color to the computer object; and using
color numerical values to enable two-way transmission and
reception of computer objects and enable recording of
computer objects or checking and updating of the content of
transmission.
According to still another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of communication of a
computer object among a plurality of computers, comprising:
transmitting the computer object over a network or
transferring it by a data storage medium using a color
ak 02593404 2007-07-20
= 28469-4E
-14b-
numerical value; and regenerating from a received color
numerical value the computer object or color in accordance
with need using a correspondence of color numerical values
and computer objects or correspondence of colors and color
numerical values, and thereby not handling the computer
object itself over a communication path or transfer path.
According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided an apparatus for at least one
of recording and reproducing a computer object, comprising:
a color filter for judging the possibility of acceptance by
all or a specific part of a series of colors or color
numerical values input by transmission, transfer, recording,
and reproduction of computer objects and performing
different processing when acceptance is possible and when
acceptance is not possible.
According to still a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of recording a
computer object, comprising: newly establishing a color-
object relation or color numerical value-object relation
when linking the computer object to each of a plurality of
colors or color numerical values when there are a plurality
of color entities or color numerical values output in
advance or determined for output.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a method of preparing a code,
comprising: linking different color numerical values to
information and expressing the information by the color
numerical values.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
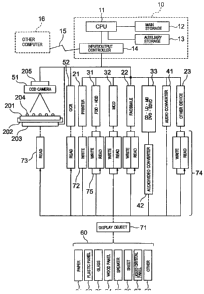
FIG. 1 shows an example of the configuration of a
computer system to which the method of the present invention
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
= 28469-4E
-14c-
for expressing a computer object using color is applied and
shows the relationship between a color entity and recording
of a display object;
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 15 -
FIG. 2 is a view of an example of the relationship between color
and a computer object by a correspondence table;
FIG. 3 is a view of an example of the relationship between color
and a color numerical value by a correspondence table;
FIG. 4 is a view of an example of the relationship between a
color numerical value and object by a correspondence table;
FIG. 5 is a view of a plurality of correspondence tables of
a color numerical values and object;
FIG. 6A is a view of the cyclic relations of a computer object,
color numerical value, and color;
FIG. 6B is a view of a pair (or set) relation including any
two components in the cyclic relations of a computer object, color
numerical value, and color;
FIG. 6C is a view of the relation between two computers when
utilizing the colors as the codes in sending/receiving information
between the two computers;
FIG. 7 is a block diagram of an example of the routine for input
and output of a computer object;
FIG. 8 is a block diagram of the configuration for selection
by a color filter;
FIG. 9 is a view of an example of a square recording media
displaying a color entity on one surface and display elements;
FIG. 10 is a view of an example of a circular recording medium
displaying a color entity on one surface and display elements;
FIG. 11 is a conceptual view of an example of the method of
arrangement of display elements on a circular recording medium;
FIG. 12 is a view of another example of the method of arrangement
of display elements on a circular recording medium and shows
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 16 -
assignment areas;
FIG. 13 is a view of an example of the display of a recording
medium displaying a color entity;
FIG. 14 is a side view of a recording medium having a first
example of a configuration for preventing discoloration of a color
entity;
FIG. 15 is a side view of a recording medium having a second
example of a configuration for preventing discoloration of a color
entity.
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Next, an explanation will be given of embodiments of the present
invention based on the attached drawings. The content of the present
invention will be made clearer by this description.
FIG. 1 shows a basic embodiment of the present invention. The
apparatus according to this embodiment (conceptually including all
apparatuses for recording and/or reproduction, that is, a recording
apparatus, reproduction device, and recording and reproduction
apparatus) shows an example of the computer system to which the method
according to the present invention for expressing a computer object
using color is applied. The block 10 shown by broken lines shows a
computer. The computer 10 is provided with an input device and output
device ( or input/output device) explained later. The system based
around the computer 10 realizes overall a specific function like for
example a printer.
The computer 10 is comprised of a CPU (central processing unit)
11, main storage 12, auxiliary storage 13, and input/output
controller 14. The computer 10 does not have to be a computer designed
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 17 -
especially for the present invention. Further, the computer does not
have to be a separate, independent unit. In the case of the present
embodiment, for example, the computer 10 is built into a printer.
Further, it is possible to give part of the computer or MPU built
into the printer the function of using the method of expression of
a computer object using color according to the present invention and
thereby record or store, reproduce, transmit ( transfer) , or otherwise
process a computer object by color. The CPU 11 has the function of
converting the computer object to color and outputting it through
the output device or conversely regenerate a color read through the
input device into a computer object. This function is realized by
providing the main storage 12 or auxiliary storage 13 with a table
having the correspondence between a plurality of computer objects
and a plurality of colors and a program executing the conversion and
input/output processing while referring to the table. Instead of the
colors, it is also possible to use color numerical values
corresponding to the colors. The auxiliary storage 13 stores the
computer objects and stores the color-object relation (Or
alternatively the color-color numerical value relation or color
numerical value-object relation) as a data base or other similar
format. The auxiliary storage 13 may be built into the computer 10
as illustrated or may be provided external to the computer 10. Further,
the auxiliary storage 13 may be constructed to be outside of the
computer 10 and connected only at the time of use. The input/output
controller 14 selects one of the plurality of input devices and
plurality of output devices connected to the computer 10 and controls
the input/output processing of the same. Further, the computer 10
is connected to another computer 16 through the input/output
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 18 -
controller 14 or through a communications device (including
communications line) 15. Therefore, the input/output controller 14
has the function of selecting the communication device 15 and
communicating with the other computer 16 through the communication
device in accordance with an instruction for communication of the
CPU 11. In FIG. 1, the communication device 15 is shown conceptually
by a line, but includes a means having a communications function.
In the above, the transfer between the input/output controller
14 and any of the input device, output device, and communications
device is not limited in the type of connection such as direct
connection or connection through a WAN or LAN or the system of
transmission such as wired, wireless, or infrared communications.
The computer 10 may be provided with various types of output
devices and input devices or input/output devices.
The output device connected to the computer 10 is for example
a device for outputting the color entity, a device for outputting
the color numerical value, or a device for outputting a regenerated
color object. As a device outputting a color entity, there are
printers 21 (color printers) , facsimiles 22, and color output devices
included in other devices 23. These color entity output devices print
the color entity on a recording medium based on an output instruction
of the computer 10. Further, as the device for outputting the color
numerical value, there are a FDD or HDD 31, MOD 32, CD, LD, MD, DVD,
SDVD 33, or storage devices included in devices 23 other than the
above. These color numerical value output devices output color
numerical values. Further, as devices for outputting regenerated
computer objects, there are audio converters 41, audio/video
converters 42, etc. in addition to the above output devices. These
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 19 -
computer object output devices output computer objects converted from
color entities or color numerical values in accordance with the
application or purpose.
In the above explanation of an output device, the example of
various types of output devices able to be connected to the computer
being connected was explained, but there is no need for all of
the above output devices to be connected at the computer 10.
The input device connected to the computer 10 is for example
a device for input of a color entity, a device for input of a color
numerical value, or a device for input of a computer object to be
recorded. As a device for input of a color entity, there are a CCD
camera 51, OCR 52, the above facsimile 22, and devices able to read
color included in other devices 23. These devices read the color of
the color entity and input it to the computer 10. As the device for
input of a color numerical value, there are the above-mentioned FDD
and HDD 31, MOD 32, CD, LD, MD, DVD, and SDVD 33, or storage device
included in devices 23 other than the above. These devices read the
color numerical values and input them to the computer 10. As a device
for inputting a computer object to be recorded, there are, in addition
to the above input devices, an audio converter 41 and audio/video
converter 42. These devices read a computer object to be recorded
into the computer 10.
In the above, a recording medium 201 is arranged under the CCD
camera 51. The recording medium 201 is held horizontal by the holding
device 202. The holding device 202 is provided with a drive 203 for
driving in the horizontal direction. A display object, that is, the
color entity 204, is displayed on the recording medium 201. The color
entity 204 is captured by the CCD camera 51. Note that the CCD camera
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 20
51 is provided with a drive controller 205.
In FIG. 1, the recording medium 60 is shown for the above-
mentioned output device, input device, and input/output device. As
the recording medium 60, paper ( ordinary paper, for example, drawings,
books, magazines, newspaper, images, etc.) 61, plastic panel (for
example, drawings, books, magazines, newspapers, images, etc.) 62,
glass 63, wood panel 64, speakers 65, sheets (for example, cards,
negotiable securities, ID certificates, books, etc.) 66, liquid
crystal panels (or PDPs, for example, drawings, books, magazines,
newspapers, images, etc.) 67, and other recording media similar to
the same (other display objects, audio, and video) 68. These recording
media record color entities or color numerical values on their
surfaces or inside them. In FIG. 1, the recorded color entity or color
numerical value is shown as a display object 71 in the recording medium
60. The recording medium 60 functions as a means for recording on
its surface or internally a display object 71 by the write operation
of the output device in the case of the output device or functions
as a means for reading the display object 71 recorded on the surface
or internally by the write operation by the input device in the case
of the input device. The computer 10 and recording medium 60 is linked
by the interaction of reading 73 through the input devices. The area
74 between the computer 10 and recording medium 60 is an area where
a relation is formed by writing and reading. In an input/output device
function as an output device and input device like an FDD or HDD 31
or facsimile 22, both write and read functions 75 are realized.
Further, when using speakers 65, the recording medium 60 is not
written for output or read from for input. An audio converter 41 is
used.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 21 -
The recording medium 60 may be used in not only the computer
outputting data to the seine, but also other computers having
similar functions. This enables data to be transferred between
computers.
The communications device 15 is a WAN ( (including a wide area
network or the Internet) using a telephone line etc. or a LAN (local
area network) . Information on the computer object is transmitted as
color numerical values or general data by these communication devices
with other computers 16 (or computer systerns ) . In the communication
by a communication device 15, it is possible to use any communications
path, communications system, or communications device. The present
invention is not limited in this respect.
The other computers 16 are not limited to any specific computers.
They need only be provided with all or part of the devices for recording
(storing) and regenerating computer objects according to the present
invention. In the computer 16, it is possible to convert data and
information by the color entity or color numerical values according
to the present invention.
Next, the method of converting a computer object to a color
entity or color numerical value and the method for conversely
regenerating a color entity or color numerical value to a computer
object will be explained.
The color-object relation is used for converting a computer
object to a color. FIG. 2 shows a color-object correspondence table
100 showing an example of the color-object relation and is expressed
in the form of a table used specifically in a computer 10. The left
column 100a of the color-object correspondence table 100 lists the
plurality of different colors used, while the right column 110b lists
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 22 -
the computer objects linked with these colors. In this example, the
colors RED 1, RED 2, ORANGE 1, ORANGE 2, and ORANGE 3 show different
colors. Linked with the colors RED 1, RED 2, ORANGE 1, ORANGE 2, and
ORANGE 3 are for example the letter "T", the Sino-Japanese character
"TANI" , the string of Sino-Japanese characters "Tani Electric
Industry Co., Ltd. " , a design drawing of a cream solder printer
identified by the drawing no. "ABC002" , and software used in the cream
solder printer identified by the code "DEF876" .
In the above color-object relation, there are limits to the
resolution of color able to be printed or read. The maximum resolution
of color is 65536 assuming a resolution corresponding to 16 bits or
just under 17 million assuming a resolution corresponding to 24 bits.
On the other hand, the number of computer objects processed by the
computer 10 is generally larger than that. At this time, it is
sufficient to divide all of the computer objects to be processed into
a plurality of groups and to establish a separate color-object
correspondence table for each group. Naturally, in these plurality
of color-object correspondence tables, the colors are common and only
the corresponding computer objects are different. At this time,
colors indicating the groups are linked with the color-object
correspondence tables. When outputting color entities, both a color
showing a group and a separate color showing the computer object are
output. In forming the groups, it is preferable to include computer
objects having a close relation and having a high possibility of being
simultaneously used into one group as much as possible.
Further, the color-object relation can be divided into two types
of relations of the color-color numerical value relation and color
numerical value-object relation by interposing the quantity called
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 23 -
the color numerical value between the colors and computer objects.
By doing this, the handling in the computer 10 becomes easier. This
will be explained with reference to FIG. 3 to FIG. 5.
FIG. 3 is a color-color numerical value correspondence table
101 expressing the color-color numerical value relation in a tabular
form, while FIG. 4 is a color numerical value-object correspondence
table expressing the color numerical value-object relation in a
tabular form. In FIG. 3, the colors of the left column 101a are the
same as the colors of the left column 100a explained in FIG. 2, while
the computer objects of the right column 102 of FIG. 4 are the same
as the computer objects of the right column 100b of FIG. 2. It is
possible to combine the two correspondence tables by color numerical
values present in both the correspondence tables 101 and 102. In the
color-color numerical value correspondence table 101, the color
numerical values are shown in the right column 101b, while in the
color numerical value-object correspondence table 102, the color
numerical values are shown in the left column 102a. The relation
between colors and computer objects obtained as a result of joining
these correspondence tables 101 and 102 is exactly the same as the
relation shown in Fig. 2.
When there are a plurality of correspondence tables in FIG.
2, as shown in FIG. 5, it is sufficient to create a plurality of (in
the illustrated example, n number in general) color numerical
value-object correspondence tables 104-1 to 104-n for one color-
color numerical value correspondence table 103. At this time, colors
are assigned to each of the color numerical value-object
correspondence tables (1 to n) 104-1 to 104-n.
If there are a large number of computer objects and the total
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 24 -
number n of the groups expressed by the color numerical value-object
correspondence table (here referred to as "first hierarchal groups")
exceeds the above-mentioned maximum color resolution, or for
convenience in arrangement of the computer objects, the first
hierarchal groups are further divided into groups ( the groups of the
first hierarchal groups being referred to as "second hierarchal
groups" and the number of first hierarchal groups included in each
of the second hierarchal groups are kept from exceeding the maximum
color resolution. When the number of computer objects becomes further
higher, third and fourth hierarchies may be suitably created. In
normal processing in the computer 10, the above color numerical values
are used. They are converted to colors only when outputting them as
color entities. Due to this, the processing in the computer 10 becomes
simpler. Further, when recording and outputting data and information
on and from the recording medium in a form other than color entities
or when transmitting them to another computer 16 through the
communications device 15, it is suitable to use color numerical
values.
FIG. 6A shows the relation among a computer object (0) , a color
numerical value (N), and a color (C) of a color entity. As shown in
FIG. 6A, the three computer object 91, color numerical value 92, and
color entity color 93 are inter-convertible. The arrows 94, 95, and
96 in the figure shows the inter-convertibilities . In the inter-
convertible relations 94, 95, and 96, the inter-convertible relation
by the arrow 95 linking the computer object 91 and the color numerical
value 92 is the above-mentioned color numerical value-object relation,
the inter-convertible relation by the arrow 94 linking the computer
object 91 and the color 93 is the above-mentioned color-object
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 25 -
relation, and the inter-convertible relation by the arrow 96 linking
the color numerical value 92 and the color 93 is the above-mentioned
color-color numerical value relation. The interrelation among the
three is called the "cyclic object relation" here.
For the above-mentioned cyclic object relation, as shown in
FIG. 6B. three sets or pairs (a, b, c) can be made by forming a set
(or pair) combining any two of the computer object (0) , the color
numerical value (N) , and the color (C) of a color entity. The set
a is one made by the computer object 91 and the color 93 based on
the color-object relation 94. The set b is one made by the computer
object 91 and the color numerical value 92 based on the color numerical
value-object relation 95. The set c is one made by the color numerical
value 92 and the color 93 based on the color-color numerical value
relation 96.
When carrying out a communication for sending/receiving data
between the computer 10 and the other computer 16 through the
communication device 15 as shown in FIG. 1, in order to utilize the
color numerical value as codes in sending/receiving the data, both
of the computers 10 and 16 must have the relations shown in FIG. 6C.
Namely, in order that data transmission from the computer 10 to the
computer 16 through the communication device 15 should be carried
out by means of the codes utilizing the color numerical values, both
of the computers 10 and 16 are necessary to have the above-mentioned
set a and the same relation defined in the conversion relation.
Further the above-mentioned relation shown in FIG. 6C is not
limited to only the relation between the computers 10 and 16, and
is further applicable to the relation between the computer 10 and
each of the printer 21 and the other devices 23 etc. being the
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 26 -
output/input device connecting to the computer 10 in the case of
sending/receiving the information as codes between them.
Selecting any one of the sets a, b, and c so that the different
computers have the same conversion relation, and selecting
combinations of the sets or the configuration of the conversion
relation based on the sets can be optional.
Further, in the communication or processing between the
computers 10 and 16, instead of the communication device 15, the other
recording media such as the FDD and HDD can be used. In this case,
the above-mentioned configuration can be used similarly.
Next, an explanation will be given, referring to FIG. 7, of
the routine in the computer 10 for converting and recording a computer
object to a color entity or color numerical value in format or
transmitting it over a communications path and regenerating the same.
When the computer 10 is given one or more sets of data or
information (data or information: alphanumerics , symbols, graphics,
mathematical formulas, images, audio, etc.) recorded on the recording
medium 60, the computer 10 reads them by the above-mentioned
input/output device 112. The data and information read by the computer
is shown as the computer object 113 in the computer 10. The computer
object 113 is either immediately processed or stored once in the
auxiliary storage 13. The block 114 in the auxiliary storage 13
computer object shows the state of storage.
Next, the CPU 11 converts the computer object 113 to a color
numerical value 115. In the CPU 11, the color numerical value-object
converter 116 is realized based on a program stored in the
above-mentioned main storage 12 (not shown in FIG. 7) . The color
numerical value-object converter 116 uses the color numerical
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 27 -
value-object correspondence table 102 stored in the auxiliary storage
13 to convert the computer object read or stored in the auxiliary
storage 13 to a color numerical value 115. When recording data and
information as a color numerical value or when transmitting
information, the color numerical value 115 itself is output or
transmitted through the input/output controller 14. That is, it is
output through the input/output controller 14 and the data
input/output controller 117 as the recorded color numerical value
118 and is output through the input/output controller 14 and
information communications unit 119 with another computer as the
transmitted color numerical value 120.
Further, when recording data and information as a color entity,
the color-color numerical value converter 121 is realized in the CPU
11 by a program stored in the main storage 12. The color-color
numerical value converter 121 uses the color-color numerical value
correspondence table 101 stored in the auxiliary storage 13 to convert
the color numerical value 115 to color and outputs the color entity
123 through the input/output controller 14 and color input/output
device 122.
Conversely, when the color entity 123 is input, the color entity
of each color dot is read by the input device portion of the color
input/output device 122, for example, a CCD camera 51 or other input
device, and input as color through the input/output controller 14.
The color-color numerical value converter 12 in the CPU 11 converts
the input color to a color numerical value 115 using the color-color
numerical value correspondence table 101 of the auxiliary storage
13. The obtained color numerical value 115 is further converted to
a computer object 113 by the color numerical value-object converter
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 28 -
116 in the CPU 11 using the color numerical value-object
correspondence table 102 of the auxiliary storage 13 and thereby
regenerated. The regenerated computer object 113 is output from the
output device 124 as the regenerated data/information 115 and
provided for use.
The color numerical value 115 converted from the color entity
123 may be recorded as it is or may be transmitted to another computer
by a communications means. Further, when regenerating a color
numerical value transmitted from another computer by communications
or a color numerical value input from the data input/output device
117 as data/information, the same type of routine is followed as when
regenerating a color numerical value converted from a color entity.
In the configuration shown in FIG. 7, the input/output device
130 of the computer object 113 includes an input device 112 and output
device 124 as explained above, but the necessary one may be used in
accordance with the application. The input/output device and
information communications unit 131 of the color entity or color
numerical value include the color input/output device 122, data
input/output device 117, and information communication unit 119 with
another computer. The necessary one can be used in accordance with
the application.
Next, an explanation will be given of the configuration relating
to "selection" referring to FIG. 8. Here, "selection" means
processing for not transmitting or not receiving unnecessary data
through the data input/output device or communications device
(including communications line) . In this selection, as shown in FIG.
8, a filter 141 called a color filter is provided in the CPU 11. FIG.
8 is a view showing the portion relating to the color filter in FIG.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 29
7. The portion of the functions shown in FIG. 7 is configured as
required. Therefore, in FIG. 8, elements substantially the same as
elements shown in FIG. 7 are assigned the same references.
The filter 141 shown in FIG. 8 selects the data input and output
as the color numerical values 118 through the data input/output device
117 at the time of input and output of data with the outside based
on the filter correspondence table 142 stored in advance in the
auxiliary storage 13. The filter correspondence table 142 stores the
color numerical values which can be received and other data. When
a series of color numerical value data are input to the CPU 11 from
the outside, the filter 141 refers to the filter correspondence table
142. When including a color numerical value not present in the filter
correspondence table 142, it judges the series of color numerical
values to be invalid and does not perform processing for conversion
to a computer object or color. Further, it is possible to insert color
numerical values which cannot be received in the filter
correspondence table 142. In this case, conversely from the above,
the filter 141 judges the series to be invalid when including a color
numerical value included in the filter correspondence table. Further
the filter correspondence table 142 may include both possible color
numerical values and impossible color numerical values. By using a
filter correspondence table having this configuration, invalid data
can be eliminated when unnecessary data is mixed in or data is modified
on the communications path, input/output path, or other paths.
In one computer object group or between a plurality of computer
object groups belonging to a higher hierarchy computer object group,
the individual items, content, properties, amounts, sizes, and other
attributes are common. Further, it is possible to designate the same
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 30 -
computer object as a "common object". By using a common object to
express a computer object, it is possible to express a computer object
more simply. At this time, the color or color numerical value
corresponding to the common object are determined as a "common color"
and "common color numerical value". The above-mentioned cyclic
relation is defined between them. Based on the cyclic relation, the
common objects, common colors, common color numerical values are
handled inter-converted.
Next, the recording medium will be explained. The recording
medium will be explained as the recording medium 60 in FIG. 1. As
an example of the recording medium 60, paper 61, plastic 62, glass
63, wood 64, etc. may be mentioned. The recording medium can take
any shape, for example, a square shape or circular shape. FIG. 9 shows
a square shaped recording medium 151, while FIG. 10 shows a circular
shaped recording medium 152. The recording surfaces of the recording
media 151 and 152 have pluralities (large numbers) of color entities
161 arranged on them. As the method of arrangement of color entities
161, arrangement in vertical and horizontal lines is the general
practice in the case of the square shaped recording medium 151 and
arrangement in a spiral array 162 as shown in FIG. 11 or in concentric
circles (or concentric ellipses) as shown in FIG. 12 the case of the
circular shaped recording medium 152. It is possible to select the
shape of the recording medium or the method of arrangement of color
entities in accordance with the characteristics of the recording
medium or input/output device used.
One recording surface of the recording medium can be used
divided into several areas in accordance with the objective. For
example, the recording media 151 and 152 shown in FIG. 9 and FIG.
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 31 -
12 are divided into the control areas 81, storage areas 82, and
security areas 83. Further, in the recording medium 152 shown in FIG.
12, an auxiliary area 84 is provided at the center portion in addition
to these three areas.
In the above the control area 81 is an area giving control
information for enabling information to be transmitted with another
computer using the recording medium alone or a telephone line or other
communications line. For example, when there are a plurality of
color-object relations or color numerical value-object relations and
a plurality of hierarchies, the information of the hierarchies or
control information on what color numerical value-object relation
is used for the data is stored in this control area 81. The storage
area 82 is an area recording the color entities .corresponding to the
computer objects. The security area 83 stores security information
for simple and easy recording and reproduction and avoiding
replication. This functions to prevent an unauthorized person from
reading and replicating the color entities. The auxiliary area 84
is an area storing the information required for recording,
reproduction, input/output, etc. of color entities. All of these
areas basically store information based on the color entities. What
meaning they are given is determined with each time of use.
FIG. 13 shows the state of color entities on a recording medium.
In FIG. 13, a square recording medium 171 is shown. The dot array
shows an example of arrangement on vertical and horizontal lines.
Individual dots are shown printed with color entities by circle marks
either hollow or containing numbers. The large number of squares 172
drawn on the surface of the recording medium 171 are divided into
several portions by the one-dot chain lines 173 to show the different
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 32 -
states of color entities. The portion shown by 174 is comprised by
a hollow circle mark. This circle mark is equivalent to the state
where there is no correspondence with a computer object and a color
entity is not printed and shows the position of a dot in which a color
entity is arranged. Circle marks with numbers (circle 1, circle 2,
etc.) show color entities linked with computer objects, that is,
specifically showing some sort of computer object. 1, 2, 3... show
the normal order of arrangement of information. In the portion shown
by 175, the color entities are arranged in their inherent order. In
this case, a series of meaningful information is obtained if reading
the color entities in the order of their arrangement. The portion
shown by 176 is an example of an arrangement different from the
inherent order of information. The information on the arrangement
is provided in the above-mentioned security area 83. When reading
color entities arranged as in portion 176, first the color of the
color entities is input in the order of arrangement, then the
arrangement order information of the security area 83 is used to
rearrange the order and thereby regenerate the original computer
object. Here, the arrangement order information stored in the
security area 83 is not limited to information directly indicating
the arrangement of the color entities. The information may also be
given as a color object and expressed as a color object. By arranging
entities as shown in the portion 176, a person not given the
arrangement order information cannot regenerate the computer object
from the color entity and therefore the same action is given as with
encoding information.
The portion shown by 177 is an example of a combination of an
attribute other than color with the color entities. The black triangle
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
- 33 -
mark 178 etc. has a shape or other attribute in addition to the color
attribute. By combining a plurality of attributes and colors in this
way, it becomes possible to increase the amount of information which
can be expressed by 1 dot.
FIG. 14 and FIG. 15 are side views of recording media showing
examples of method for preventing discoloration of color entities.
In the example shown in FIG. 14, the entire surface of the recording
medium 181 on which the color entity is printed is provided with a
discoloration prevention film 182. In the example shown in FIG. 15,
the discoloration prevention film is provided only on the portion
of the surface of the recording medium 181 printed with the color
entity.
The embodiments explained with reference to the drawings are
merely examples. The present invention is not limited to these
embodiments and may be modified in any manner within the scope of
the invention.
As clear from the above explanation, according to the present
invention, there are the following effects since one color is assigned
to each computer object and that color used to record the computer
object. It is possible to record more than 1 bit of data for the 1
dot of the minimum unit of recording and possible to easily record
a large amount of information. As the recording medium, it is possible
to use paper or another inexpensive medium. Therefore, the invention
is superior in economy. It is also possible to reduce the space for
recording or storage. Storage of paper books etc. therefore becomes
easy. In the music, image, video, and other entertainment fields,
data can be recorded and reproduced extremely inexpensively. It
becomes possible to record data and information cheaply and simply
CA 02593404 2007-07-20
=
- 34 -
per unit space. There is the advantage of a large effect of storage
and compression of information and data. Replacement of expensive
storage devices becomes inexpensive and simple as well. The
multiplexing and hierarching of the color-object relation also give
rise to an effect of data compression. Further, information cannot
be extracted without the correspondence tables, .so there is the effect
of copyright protection of the recording medium itself. By using this
recording medium, use as an external storage of a computer also
becomes possible. The invention enables transmission of a large
amount of information to a large number of receivers and free
selection of information and reduces the material sent. There is also
a large effect of reduction of the amount of dots used due to selective
use of ordinary symbols and colors and color numerical values. By
using a correspondence table, there is the large effect of reduction
of the colors and color numerical values transferred and transmitted
compared with a computer object. There is therefore the advantage
of encoding from the viewpoint of protection of data.
CAPABILITY OF UTILIZATION IN INDUSTRY
As explained above, the present invention expresses a computer
object using color, records, reproduces, transmits, and records large
amounts of information by color, and uses an inexpensive recording
medium so is more economical.