Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02596196 2011-03-10
52262-6
WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, METHOD, AND TANGIBLE
MACHINE-READABLE MEDIUM THEREOF FOR TRANSMITTING
DATA BASED ON A FRAME STRUCTURE OF A MULTI-HOP RELAY
STANDARD
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a wireless communication system, a method,
and a_
tangible machine-readable medium thereof. More particularly, the present
invention relates to
a wireless communication system, a method, and a tangible machine-readable
medium thereof
for transmitting data based on a frame structure of a multi-hop relay
standard.
Descriptions of the Related Art
With the rapid development of computer networks, various broadband information
services are becoming more essential for the information industry. However,
due to high
costs, only a fraction of all computer users can afford high speed wired
broadband services,
such as digital subscriber line (DSL) and cable broadband access services. In
addition,
network telecommunication service providers are looking to expand the coverage
range of
their wired broadband networks. However, the relevant infrastructure costs for
building these
wired network prevents them doing so. As a result, many broadband wireless
techniques
have, hence, become an important alternative. In terms of communication
distance, current
wireless networks can be classified as follows: wide area network (WAN),
metropolitan area
network (MAN), local area network (LAN), and personal area network (PAN).
To set up a radio transmission standard for MAN to provide wireless broadband
connection as "the last mile" for the telecommunication industry, the IEEE
802.16, a
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX), was developed as a
wireless
transmission standard. After continuous improvement, the IEEE 802.16 has been
able to
address more market demands, such as various mobile and high speed broadband
applications. Moreover, in comparison to other communication techniques, such
as Wi-Fi and
the third generation mobile communication (3G) technique, the IEEE 802.16 has
a larger
1
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
network bandwidth, lower construction costs, better service quality, better
expansibility, and
extended usage modes at Wi-Fi hot spots.
Even with its advantages, the communication range and signal quality provided
by the
IEEE 802.16 are still limited. As a result, the IEEE 802.16j standard Working
Group
established a mobile multi-hop relay study group in July 2005 for building a
mobile multi-hop
relay standard (MMR-RS), to establish a multi-hop relay standard (MMR-RS)
under the
existing IEEE 802.16j standard.
A conventional two-hop relay wireless communication system 1 based on the MMR-
RS
defined in IEEE 802.16j is illustrated in FIG 1. The two-hop relay wireless
communication
system 1 comprises a base station (BS) 101, a relay station (RS) 103, and a
plurality of mobile
stations (MSs) 105, 107. For brevity, the MSs will be denoted hereinafter as
the first MS 105
and second MS 107. One type of frame structure 2 utilized in the aforesaid two-
hop relay
wireless communication system 1 is illustrated in FIG. 2. The frame structure
2 is allocated
by a wireless communication apparatus, such as the BS 101, the RS 103, the
first MS 105, or
the second MS 107. The frame structure 2 is adapted for data transmission.
The frame structure 2 of the two-hop relay wireless communication system 1
comprises
an MS downlink sub-frame 211, an RS downlink sub-frame 213, an MS uplink sub-
frame
221, and an RS uplink sub-frame 223. Each of these sub-frames can be used for
downlink or
uplink data transmission in the two-hop relay wireless communication system 1.
The x-axis
in FIG 2 represents the time axis of the frame structure 2, while the y-axis
represents the
frequency axis.
The MS downlink sub-frame 211 further comprises a pilot message 2111, a frame
control
header 2113, a downlink MAP 2115, an uplink MAP 2117, and a downlink data
allocation
2119. The pilot message 2111 is configured for synchronization between the BS
101 and the
second MS 107 or synchronization between the RS 103 and the first MS 105. The
frame
control header 2113 is configured to describe various parameters of the frame
structure 2.
The downlink MAP 2115 is configured to broadcast some parameters used for
downlink data
transmission in the two-hop relay wireless communication system 1, such as
connection
identifications (CIDs), sub-channel offsets, or time offsets. Similarly, the
uplink MAP 2117 is
configured to broadcast some parameters used for uplink data transmission in
the two-hop
relay wireless communication system 1. The downlink data allocation 2119 is
configured to
transmit data from the BS 101 to the second MS 107 or to transmit data from
the RS 103 to
the first MS 105. After data transmission of the downlink data allocation
2119, there is a
BS/RS-transmission transition gap (BS/RS-TTG) 23 that occurs thereafter.
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
The RS downlink sub-frame 213 is configured to transmit data from the BS 101
to the
RS 103. After transmission of the data of the RS downlink sub-frame 213, there
is an RS-
receive transition gap (RS-RTG) 24, which occurs after the data transmission.
The MS uplink sub-frame 221 is configured to transmit data from the second MS
107 to
the BS 101 or from the first MS 105 to the RS 103. After transmission of the
data from the
MS uplink sub-frame 221, there is a BS/RS-receive transition gap (BS/RS-RTG)
25 that
occurs thereafter.
The RS uplink sub-frame 223 is configured to transmit data from the RS 103 to
the BS
101. After transmission of the data of the RS uplink sub-frame 223, the BS-RTG
26 occurs
thereafter.
With the frame structure described above, data transmission can proceed
successfully in
accordance with the IEEE 802.16j standard. For example, the BS 101 and the RS
103 can
transmit data respectively via the MS downlink sub-frame 211 and the RS
downlink sub-
frame 213. However, because data transmission may interfere with other
frequency bands at
any time, data transmission may be interrupted and thus, not transmitted
correctly.
Accordingly, it is important for the mobile communication providers and the
mobile
communication apparatus manufacturers to find a solution for improving signal
immunity
against interference and ensuring correct data transmission to extend the
communication
range of networks using the multi-hop relay standard under IEEE 802.16j.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
One objective of this invention is to provide a method for transmitting data
based on a
frame structure of a multi-hop relay standard. The method comprises the
following steps:
allocating a relay station map (RS-MAP) frame in the frame structure to
describe the frame
structure; and allocating an MS sub-frame in the frame structure according to
information of
the RS-MAP frame. The MS sub-frame transmits the first data between a BS and
an MS, as
well as the second data between an RS and the MS, wherein a part of the second
data is the
same as the first data.
Another objective of this invention is to provide a wireless communication
system for
transmitting data based on a frame structure of a multi-hop relay standard.
The wireless
communication system comprises a BS, an MS, and an RS. The frame structure
comprises an
RS-MAP frame and an MS sub-frame. The RS-MAP frame describes the frame
structure.
The MS sub-frame which is allocated by information of the RS-MAP frame
transmits the first
data between the BS and MS, as well as the second data between the RS and MS
according to
3
CA 02596196 2011-03-10
52262-6
information of the RS-MAP frame. A part of the second data is the same as the
first data.
Yet a further objective of this invention is to provide a tangible
machine-readable medium having executable code to cause a machine to perform
a method for transmitting data based on a frame structure of a multi-hop relay
standard. The method comprises the following steps: allocating an
RS-MAP frame in the frame structure to describe the frame structure; and
allocating an MS sub-frame in the frame structure according to information of
the
RS-MAP frame. The MS sub-frame transmits the first data between a BS and an
MS, as well as the second data between an RS and the MS. A part of the second
data is the same as the first data.
The aforesaid method can be executed by wireless communication
apparatus, such as a BS, an RS, or an MS in the wireless communication system.
By transmitting data based on a frame structure of a multi-hop relay standard,
and
transmitting a part of the data from both a BS and an RS to an MS, this
invention
can prevent data transmission failure or forced transmission interruption due
to
signal interference. As a result, signal immunity is improved.
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
method for transmitting data based on a frame structure of a multi-hop relay
standard, the method comprising steps of: allocating a relay station map
(RS-MAP) frame in the frame structure to describe the frame structure; and
allocating a mobile station (MS) sub-frame in the frame structure according to
information of the RS-MAP frame, the MS sub-frame is configured to be used for
transmitting a first data between a base station (BS) and an MS, and for
transmitting a second data between a relay station (RS) and the MS; wherein a
part of the second data is the same as the first data.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a wireless communication system for transmitting data based on a
frame
structure of a multi-hop relay standard, the wireless communication system
4
CA 02596196 2011-03-10
52262-6
comprising a base station (BS), a mobile station (MS) and a relay station
(RS),
and the frame structure comprising: a relay station map (RS-MAP) frame for
describing the frame structure; and a mobile station (MS) sub-frame according
to
information of the RS-MAP frame, the MS sub-frame is configured to be used for
transmitting a first data between the BS and the MS, and for transmitting a
second
data between the RS and the MS; wherein a part of the second data is the same
as the first data.
According to still another aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a computer readable medium having stored thereon a plurality of
computer executable instructions which, when executed by a computer process,
cause a computer processor to perform a method for transmitting data, the
method comprising steps of: allocating a relay station map (RS-MAP) frame in
the
frame structure to describe the frame structure; and allocating a mobile
station
(MS) sub-frame in the frame structure according to information of the
RS-MAP frame, the MS sub-frame is configured to be used for transmitting a
first
data between a base station (BS) and an MS and for transmitting a second data
between a relay station (RS) and the MS; wherein a part of the second data is
the
same as the first data.
The detailed technology and preferred embodiments implemented
for the subject invention are described in the following paragraphs
accompanying
the appended drawings for people skilled in this field to well appreciate the
features of the claimed invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a conventional two-hop
relay wireless communication system based on the MMR-RS defined in
IEEE 802.16j;
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating the frame structure of the
conventional two-hop relay wireless communication system;
4a
CA 02596196 2011-03-10
52262-6
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating the first embodiment of this
invention;
FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram illustrating a BS frame structure
employed in the BS of the first embodiment;
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram illustrating an RS frame structure
employed in the RS of the first embodiment; and
FIG. 6 is a flow chart of the second embodiment of this invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
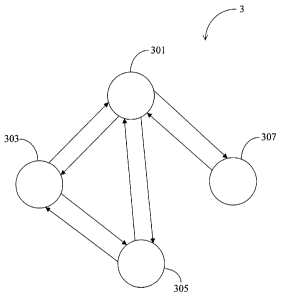
As illustrated in FIG. 3, a first embodiment of this invention is a two-
hop relay wireless communication system 3 based on the multi-hop relay
standard
defined in IEEE 802.16] (one of the multi-hop relay standards). The two-hop
relay
wireless communication system 3
4b
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
comprises a BS 301, an RS 303, and a plurality of MSs 305, 307. For brevity,
the MSs 305,
307 will be denoted hereinafter as a first MS 305 and second MS 307. One type
of BS frame
structure 4 utilized in the BS 301 is shown in FIG 4, while one type of RS
frame structure 5
utilized in the aforesaid RS 303 is shown in FIG 5. The frame structures 4, 5,
of both are
transparent RS frame structures or other kinds of frame structures and are
allocated by a
wireless communication apparatus (i.e., the BS 301, the RS 303, the first MS
305, or the
second MS 307), for transmitting data.
The BS frame structure 4 comprises an RS downlink receiving sub-frame 411, an
MS
downlink receiving sub-frame 413, an MS uplink transmitting sub-frame 421, and
an RS
uplink transmitting sub-frame 423. The MS downlink receiving sub-frame 413 and
the MS
uplink transmitting sub-frame 421 form an MS sub-frame, and the RS downlink
receiving
sub-frame 411 and the RS uplink transmitting sub-frame 423 form an RS sub-
frame. Each of
these sub-frames can be used by the BS 301 for downlink or uplink data
transmission in the
two-hop relay wireless communication system 3. The x-axis in FIG 4 represents
the time
axis of the BS frame structure 4, while the y-axis represents the frequency
axis.
The BS frame structure 4 further comprises a pilot message 4111, a frame
control header
4113, a downlink MAP 4115, an uplink MAP 4117, and an RS-MAP frame 4119. The
pilot
message 4111 is configured for synchronization among the BS 301, the RS 303,
the first MS
305, and the second MS 307. The frame control header 4113 is configured to
describe various
parameters of the frame structure 4. The downlink MAP 4115 is configured to
broadcast
some parameters, such as CIDs, sub-channel offsets, or time offsets, used for
downlink data
transmission in the two-hop relay wireless communication system 3. Similarly,
the uplink
MAP 4117 is configured to broadcast some parameters used for uplink data
transmission in
the two-hop relay wireless communication system 3. The RS-MAP frame 4119 is
configured
to storing information for allocating the MS sub-frame and the RS sub-frame in
the BS frame
structure 4. The information not only can be stored in the RS-MAP frame 4119,
but also can
be stored in other MAPs, such as the downlink MAP 4115 or the uplink MAP 4117,
etc.
The RS downlink receiving sub-frame 411 is configured to transmit data from
the BS
301 to the RS 303. In other words, the RS downlink receiving sub-frame 411
also can be
indicated as a BS downlink transmitting sub-frame. After transmission of the
data of the RS
downlink receiving sub-frame 411, an RS-RTG 43 occurs late than the RS
downlink receiving
sub-frame 411. The MS downlink receiving sub-frame 413 is configured to
transmit data
from the BS 301 to the first MS 305 or to transmit data from the BS 301 to the
second MS
307. The MS downlink receiving sub-frame 413 is further configured to transmit
data from
.5
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
the RS 304 303 to the first MS 305. More specifically, the first MS 305 can
receive the data
transmitted by the BS 301 and the data transmitted by the RS 303 at the same
time. After data
transmission of the MS downlink receiving sub-frame 413, there is an MS-RTG
44, which
occurs thereafter.
The MS uplink transmitting sub-frame 421 is configured to transmit data from
the first
MS 305 to the BS 301 or from the second MS 307 to the BS 301. After
transmission of the
data of the MS uplink transmitting sub-frame 421, an RS-RTG 45 occurs
thereafter.
The RS uplink transmitting sub-frame 423 is configured to transmit data from
the RS
303 to the BS 301. After transmission of the data of the RS uplink
transmitting sub-frame
423, a BS-RTG 46 then occurs.
The RS frame structure 5 comprises an RS downlink receiving sub-frame 511, an
MS
downlink receiving sub-frame 513, an MS uplink transmitting sub-frame 521, and
an RS
uplink transmitting sub-frame 523. Each of these sub-frames can be used by the
RS 303 for
downlink or uplink data transmission in the two-hop relay wireless
communication system 3.
The x-axis in FIG 5 represents the time axis of the RS frame structure 5,
while the y-axis
represents the frequency axis.
The MS downlink receiving sub-frame 513 is configured to transmit data from
the RS
303 to the first MS 305. After transmission of the data of the MS downlink
receiving sub-
frame 513, an MS-RTG 54 occurs thereafter. The MS uplink transmitting sub-
frame 521 is
configured to transmit data from the first MS 305 to the RS 303. After
transmission of the
data from the MS uplink transmitting sub-frame 521, an RS-RTG 55 occurs
thereafter.
Since the RS frame structure 5 is used in the RS 303, the RS downlink
receiving sub-
frame 511 is configured to transmit data from the BS 301 to the RS 303, and
the RS uplink
transmitting sub-frame 523 is configured to transmit data from the RS 303 to
the BS 301. In
addition, similarly to the BS frame structure 4, an MS-RTG 54 and a BS-RTG 56
still remain
in the RS frame structure 5.
From FIG. 3, when a first data is to be transmitted from the BS 301 of the two-
hop relay
wireless communication system 3 to the first MS 305, it can be transmitted
directly via the
MS downlink receiving sub-frame 413 or forwarded via the RS 303. When the
first data is
selected for direct transmission to the first MS 305 via the MS downlink
receiving sub-frame
413 and forwarded via the RS 303 at the same time, the BS 301 will prepare a
second data
that is partially and/or entirely the same as the first data according to the
information of the
RS-MAP frame 4119 in the BS frame structure 4. Thus, the RS 303 can transmit
the second
data to the first MS 305 via the MS downlink receiving sub-frame 513 to
complete
6
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
transmission of the first data.
In order for the second data to be transmitted successfully to the first MS
305, the BS
301 transmits a third data containing the second data, therein, to the RS 303
via the RS
downlink receiving sub-frame 411. Subsequently, the RS 303 forwards the second
data to the
first MS 305 via the MS downlink receiving sub-frame 513 at the same time when
the BS 301
is transmitting the first data directly to the first MS 305 via the MS
downlink receiving sub-
frame 413.
Upon simultaneously receiving the first data from the BS 301 and the second
data
forwarded by the RS 303, the first MS 305 verifies the accuracy of the receive
data by
comparing the first data with the second data that is partially and/or
entirely the same as the
first data. Through such verification, an improved signal to noise rate (SNR)
can be achieved
with the first data, and a correct transmission of the first data from the BS
301 to the first MS
305 can be ensured.
Furthermore, in a multi-hop relay wireless communication system, data may also
be
transmitted by using frame structures and corresponding configurations
described in the first
embodiment. Likewise, these configurations will result in an improved SNR
regarding data
reception, and ensures correct data transmission.
A second embodiment of this invention is a method for transmitting data based
on a
frame structure of the IEEE 802.16j, which is a method applied to the two-hop
relay wireless
communication system 3 described in the first embodiment. More specifically,
the data
transmission method of the second embodiment which is illustrated in FIG 6 can
be
implemented by an application program controlling various modules of a
wireless
communication apparatus in the two-hop relay wireless communication system 3.
This
application program may be stored in a tangible machine-readable medium, such
as a read
only memory (ROM), a flash memory, a floppy disk, a hard disk, a compact disk,
a mobile
disk, a magnetic tape, a database accessible to networks, or any other storage
media with the
same function and well known to those skilled in the art.
,In step 601, an RS-MAP frame is allocated in a frame structure. Next in step
603, an
MS sub-frame is allocated in the frame structure according to information of
the RS-MAP
frame. The MS sub-frame is configured to transmit the first data between BS
and MS and the
second data between an RS and the MS in the two-hop relay wireless
communication system
3. The first data is partially and/or entirely the same as the second data.
Subsequently in step
605, an RS sub-frame is allocated in the frame structure. Then, in step 607,
an MS downlink
receiving sub-frame is allocated in the MS sub-frame. Finally in step 609, an
RS downlink
7
CA 02596196 2007-08-03
receiving sub-frame is allocated in the RS sub-frame.
In addition to the steps revealed in FIG. 6, the second embodiment can also
execute all
the operations of the first embodiment, in which those skilled in the art can
understand the
corresponding steps and operations of the second embodiment by the explanation
of the first
embodiment, and thus no unnecessary detail is given.
Accordinglyõ by simultaneously transmitting partially and/or entirely the same
data from
both a base station and a relay station to a mobile station, this invention
can prevent failure of
data transmission due to the destination or forced transmission interruption
due to signal
interference. This invention further improves signal immunity against
interference (i.e., to
improve the SNR of the mobile station experiencing data receipt) and thereby,
ensure correct
transmission of data.
The above disclosure is related to the detailed technical contents and
inventive features
thereof. People skilled in this field may proceed with a variety of
modifications and
replacements based on the disclosures and suggestions of the invention as
described without
departing from the characteristics thereof. Nevertheless, although such
modifications and
replacements are not fully disclosed in the above descriptions, they have
substantially been
covered in the following claims as appended.
a