Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
HOLDING FIXTURE FOR MACHINING BEARING CAPS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to fixtures for holding wheel bearing
caps or other bearing caps in a CNC work center.
2. Background Art
Bearing caps are used to secure a bearing that journals a shaft.
Bearing caps are used in vehicles to retain axles on a vehicle frame and wheel
bearings for a wheel assembly. Bearing caps may also be provided to retain
crankshaft bearings on an engine and may also be used in other types of
machinery.
Bearing caps generally have a semi-circular body portion and flanges for
receiving
bolts that are used to secure the bearing cap to a supporting member or second
part
of a bearing retaining assembly. Bearing caps must be machined to close
tolerances
to avoid assembly problems and excessive scrap and salvage expense.
Bearing caps may be formed in a casting operation in which
tolerances are typically required to be held to +0.030 inches for castings
having a
distance between measured points of between 0 and 3 inches and + .045 between
3
and 8 inches. Castings are normally formed with a draft angle that is required
to
remove the casting from the casting mold. The unusual shape of a bearing cap
makes it difficult to properly fixture one or more bearing caps as they are
machined.
Bearing caps normally must be machined after casting to provide
uniformity from part to part. For example, at one machining center location, a
bearing cap may be fixtured while bolt holes are drilled and counterbored on
the
fastener shoulders of the bearing cap with the end faces of the bearing cap
being
milled to a tolerance of +0.010 inches.
-1-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
The relatively broad tolerance for a cast bearing cap is three times the
tolerance allowed for machining surfaces which makes it difficult to fixture
cast
bearing caps for initial machining operations. After initial machining
operations are
performed on the bearing cap, accurately machined surfaces are available to
locate
the bearing cap for subsequent machining operations.
There is a need for a fixture for machining a plurality of bearing caps
simultaneously at a work center that allows the bolt hole locations and
machined
surfaces to be accurately located. The above problems and needs are addressed
by
Applicant's invention as summarized below.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to one aspect of the invention, a holding fixture for
machining a plurality of bearing caps is provided that is easy to load and
precisely
fixtures the bearing caps to form bolt holes and milled surfaces.
According to another aspect of the invention, a holding fixture for a
bearing cap is centered relative to a generally semi-cylindrical surface of
the rough
"as cast" part. The generally semi-cylindrical surface may be the bearing bore
of
a bearing cap. The bearing bore engages a mandrel of the holding fixture that
has
a center that corresponds to the center of the bearing to be retained by the
bearing
cap. Clamps engage the outer surface of the fixtured bearing cap to retain
them on
the mandrel. The bolt holes and machined surfaces are located relative to the
partially cylindrical surface corresponding to the inner bore of the bearing
cap that
receives the bearing.
According to another aspect of the invention, a holding fixture for
machining a bearing cap is provided that permits a plurality of bearing caps
to be
fixtured relative to the cast radiused ends of the bearing cap. Floating V-
blocks that
are pivotable and shiftable may, in one embodiment, locate the ends of the
bearing
cap. The floating V-blocks may be spring loaded to move up and down and pivot
-2-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
to compensate for draft angle and cast part tolerances. The floating V-blocks
facilitate loading and also increase uniformity part-to-part for machining
operations.
According to other aspects of the present invention, the bearing caps
are retained by clamping plates that lock the bearing cap into the holding
fixture
prior to performing the desired machining operations. The clamping plates
locate
the bearing caps in the fixture at predetermined locations, and in particular,
hold the
bearing caps on the semi-circular central cast radius at the desired
circumferential
orientation relative to the mandrel.
According to another aspect of the invention, a method is disclosed
for manufacturing bearing caps using an improved fixture for "as cast" parts.
A
rough bearing cap is cast in a mold that has an as cast semi-cylindrical
bearing bore
and an outer surface. A plurality of bearing caps are assembled into a first
fixture
that has a mandrel that is received in the bearing bore. The bearing caps are
assembled onto the first fixture with clamps that engage the outer surface of
the
bearing caps. A pair of bolt shoulder portions of the bearing caps are
machined and
a bolt hole is bored into each bolt shoulder portion. The bearing caps are
removed
from the first fixture and are subsequently machined while being located using
the
bolt holes to form the finished bearing caps.
These and other features and advantages will be better understood in
view of the attached drawings and following detailed description of the
illustrated
embodiment of the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIGURE 1 is a front elevation view of a fixture for machining
bearing caps in a CNC work center shown with the bearings clamped in the
fixture
according to one embodiment of the present invention;
FIGURE 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line 2-2 in Figure
1;
-3-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
FIGURE 3 is a cross-sectional view similar to Figure 2 showing a
bearing cap prior to assembly to the fixture;
FIGURE 4 is an exploded, perspective view of a floating V-block
made in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention;
FIGURE 5 is a diagrammatic cross-sectional view showing the
degrees of freedom of movement of the floating V-block;
FIGURE 6 is a fragmentary exploded, perspective view of a mandrel
and a clamp according to one aspect of the present invention;
FIGURE 7 is a perspective view of a cast, unmachined bearing cap;
and
FIGURE 8 is a perspective view of a partially machined bearing cap.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT(S)
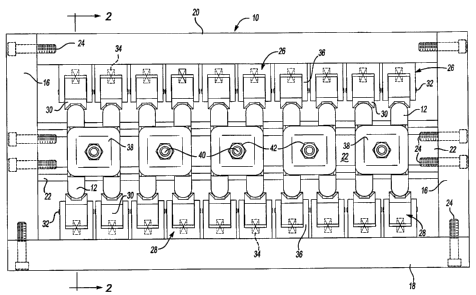
Referring to Figure 1, a fixture 10 for retaining a plurality of bearing
caps 12 is shown with ten bearing caps assembled to the fixture 10. The
fixture 10
includes two side plates 16, a base plate 18 and a top plate 20. The fixture
10 is
generally in the form of an open frame that permits machining operations to be
performed on two sides of the bearing caps 12 while assembled to the fixture
10.
A mandrel 22 extends between the side plates 16 and parallel to the base plate
18
and top plate 20. The plates and mandrel of the frame are assembled together
by
dowel pins (not shown) and socket head screws 24.
An upper floating V-block assembly 26 is assembled to the top plate
20 of the fixture 10. A lower V-block clamp assembly 28 is assembled to the
base
plate 18 of the fixture 10. Each of the V-block assemblies 26, 28 include a
jaw 30
that is mounted on a pin 32. A spring 34 resiliently biases the jaw 30
relative to a
-4-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
V-block retainer 36. The pin 32 is journalled within the V-block retainer 36
to
support the jaw 30 in a movable relationship relative to the V-block retainer
36.
A tie-down bolt 40 and nut 42 are used to secure a mandrel clamp 38.
The tie-down bolt 40 extends through the mandrel 22 between two adjacent
bearing
caps 12 so that a single clamp 38 may be used to engage the two adjacent
bearing
caps 12 to retain the bearing caps 12 in the fixture 10.
Referring to Figures 2 and 3, the relationship of the bearing cap 12,
mandrel 22 and upper and lower V-block assemblies 26, 28 is illustrated. The
mandrel 22 is secured between the side plates 16. The tie-down bolt 40 is
retained
by a backing plate 44 that holds the tie-down bolt 40 securely within the bolt
head
receptacle 46. The bolt head receptacle 46 is configured to receive the head
of the
tie-down bolt 40 in a non-rotational relationship. The tie-down bolt 40 is
received
in a bolt hole 48 formed in the mandrel 22. The tie-down bolt 40 is also
received
in a center bore 50 of the mandrel clamp 38. Mandrel clamp 38 includes
locating
fingers 52 that engage a step 54 that is formed on a reinforcing rib 56 of the
bearing
cap 12. A tubular extension 58 is formed on the mandrel clamp 38 and is
received
in a clamp receptacle opening 59. The clamp receptacle opening 59 may have a
polygonal configuration, such as a square that locates the clamp 38 in a non-
rotative
manner.
A pin receptacle 60 is provided in the V-block retainer 36 which
receives the pin 32 and holds the pin 32 stationary relative to the V-block
retainer
36. A slot 64 is provided in the jaw 30. The slot is elongated in the vertical
direction. The term "vertical direction" as used herein is the direction
defined by
a line that extends perpendicular to the base plate 18 and top plate 20. The
jaw 30
receives the pin 32 in the slot 64 so that the jaw 30 may move vertically and
pivot
relative to the V-block retainer 36. The spring 34 is received in a spring
seat 66
formed in the V-block retainer 36 and a spring receptacle 68 formed in the jaw
30.
The spring 34 biases the jaw 30 towards the mandrel 22.
-5-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
A locating face 70 of the jaw 30 is oriented to engage an outer surface
72 of the bearing cap 12. The outer surface 72 is formed with a draft angle in
the
casting process in which the bearing cap 12 is initially cast. The jaw 30 is
pivotable
relative to the V-block retainer 36 and is also vertically movable relative to
the V-
block retainer 36 to accommodate variations as a result of normal tolerances
in the
size and shape of the bearing cap 12.
When the bearing cap 12 is fixtured, the bearing cap is engaged by
the upper V-block assembly 26 and the lower V-block assembly 28 that retain
the
bearing cap relative to the mandrel 22 with the bearing bore 76, as cast,
engaging
cylindrical surfaces 78 that are formed on the mandrel 22. After the bearing
cap 12
is positioned between the upper and lower V-block assemblies 26, 28 and the
mandrel 22, the mandrel clamp 38 is placed on the tie-down bolt with the
locating
fingers 52 engaging the steps 54 of the bearing cap 12. The nut 42 is then
used to
secure the mandrel clamp 38 to the tie-down bolt 40. The tubular extension 58
of
the mandrel clamp 38 is received in the clamp receptacle opening 59.
Referring to Figure 4, the structure and function of the upper V-block
assembly 26 is described in greater detail. It should be understood that the
lower
floating clamp assembly 28 has the same structure and function as the upper V-
block
assembly 26. The upper V-block assembly 26 is assembled to the top plate 20.
In
Figure 4, two V-block retainers 36 are shown secured to the top plate 20. One
jaw
is shown oriented ready for assembly to the V-block retainer 36 with a second
jaw 30 being shown assembled to the V-block retainer 36. The spring 34 is
received
in the spring seat 66 that is formed in the V-block retainer 36. Dowel 32
extends
through the dowel holes 60 formed in the V-block retainer 36. Dowel 32 also
25 extends through the slot 64 formed in the jaw 30. The locating face 70
of the jaw
30 is oriented to engage an outer surface 70 of the end 74 of the bearing cap
12, as
previously described.
Referring to Figure 5, the movable mounting arrangement of the jaw
30 is shown to illustrate the available degrees of freedom of movement of the
jaw
30 30. The V-block retainer 36 is secured to the top plate 20. The jaw 30
is secured
-6-
CA 02601838 2007-09-13
to the V-block retainer 36 by the dowel 32. The circular dowel 32 allows for
limited rotational movement of the jaw 30 relative to the V-block retainer 36.
Longitudinal or vertical movement of the jaw 30 is permitted by means of the
elongated slot 64 formed in the jaw 30. When the bearing cap 12 is initially
inserted
into the fixture, the outer surface 72 of the bearing cap 12 is received by
the locating
face 70 of the jaw 30. The jaw 30 may move rotationally and vertically to
accommodate variations in the bearing cap 12. The jaws 30 initially retain the
bearing cap 12 adjacent the mandrel 22. Spring 34 provides a biasing force
against
the outer surface 72 of the bearing cap 12.
Referring to Figure 6, the mandrel 22 and mandrel clamp 38 are
illustrated to show how the mandrel clamps 38 are secured to the mandrel 22.
The
mandrel 22 has bolt head receptacles 46 that receive the head of the tie-down
bolt
40 so that it cannot rotate after insertion into the bolt head receptacle 46.
The tie-
down bolt 40 is held in the mandrel 22 by backing plate 44 that is secured by
bolts
24 to the mandrel 22. As shown in Figure 6, one tie-down bolt 40 is shown
secured
within the mandrel and a second tie-down bolt 40 is shown partially assembled
to
the mandrel 22 with the backing plate 44 being oriented for assembly to the
mandrel
22.
As shown in Figure 6, the mandrel clamp 38 is oriented for assembly
to the tie-down bolt 40. The mandrel clamp 38 has locating fingers 52 that are
oriented to engage a step 54 on the bearing cap 12. A center bore 50 is
drilled
through the mandrel clamp 38 that extends through the tubular extension 58 of
the
mandrel clamp 38. The tie-down bolt 40 receives the mandrel clamp 38 so that
the
tie-down bolt extends through the center bore 50.
Referring to Figure 7, a bearing cap 12 is shown in its as cast
configuration. The bearing cap 12 includes a reinforcing rib 56 on which a
step 54
is formed that is engaged by the locating fingers 52 of the mandrel clamp 38.
Two
faces 74 are cast on opposite ends of the bearing 12. Outer surfaces 72 of the
bearing cap 12 engage the locating face 70 of each of the jaws 30. Machine
stock
80 is provided on the bearing cap 12 that is machined in the CNC work center
with
-7-
CA 02601838 2014-01-10
t =
a face mill, or the like, to form a machined parting line 82. The bolt
shoulders 74 are
also machined while on the fixture with a bolt hole 84 being formed through
the bolt
shoulder 74. A counterbore 86 is formed on the bolt shoulder 74 to provide a
machined surface that is concentric with the bolt hole 84 on the opposite side
of the
bearing cap 12 from the cast parting line 80. The bolt hole 84 and counterbore
86 may
be formed in a single step with an appropriate combination drill.
Referring to Figure 8, a machined bearing cap 12' is illustrated. The
machined bearing cap 12' is machined with the mill from the cast parting line
80 to the
desired machined parting line 82. The machined bearing cap 12' has also been
machined on the opposite side from the parting line by boring a bolt hole 84
through
the bolt shoulder 74 and by counterboring the counterbore 86.
The scope of the claims should not be limited by the preferred
embodiments set forth in the examples, but should be given the broadest
interpretation
consistent with the description as a whole.
-8-