Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
1
SYSTEM, METHOD AND MOBILE DEVICE FOR MANAGEMENT OF
WIRELESS CONNECTIONS
[0001] The described embodiments relate generally to a mobile device
configured to display wireless status indicators and systems and methods
therefor.
[0002] Mobile device technology has reached the point where many
mobile
devices are capable of communicating over more than one type of wireless
connection. For example, a mobile device may have a cellular connection with a
nearby cellular base station of a wireless telecommunications carrier.
Additionally, the mobile device may have one or more connections established
with other wireless devices in the immediate vicinity under a communications
protocol such as BluetoothTM. Further, the mobile device may be capable of
communicating within a wireless local area network (WLAN).
[0003] Where multiple wireless connections are available to a mobile
device, a user of the mobile device may find it inconvenient to interface with
and/or manage these connections separately.
[0004] The described embodiments attempt to address or ameliorate one
or more shortcomings of existing user interface aspects of existing mobile
device
technology, or to at least provide a useful alternative thereto.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0005] For a better understanding of the described embodiments and to
show more clearly how they may be carried into effect, reference will now be
made, by way of example, to the accompanying drawings in which:
[0006] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a mobile device in one example
implementation;
[0007] FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a communication sub-system
component of the mobile device of FIG. 1;
[0008] FIG. 3 is a block diagram of a node of a wireless network;
[0009] FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a flash memory of the mobile
device in further detail;
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
2
[0010] FIG 5. is a flowchart of a method of displaying wireless
status
indicators;
[0011] FIG. 6 is a flowchart of one step of the method of FIG. 5;
[0012] FIG. 7 is a schematic illustration of an example of the mobile
device;
[0013] FIG. 8 is an example screenshot of a manage connections display;
[0014] FIG. 9 is a further example screenshot of a manage connections
display;
[0015] FIG. 10 is a further example screenshot of a manage
connections
display;
[0016] FIG. 11 is a further example screenshot of a manage connections
display;
[0017] FIG. 12 is a further example screenshot of a manage
connections
display;
[0018] FIG. 13 is a further example screenshot of a manage
connections
display;
[0019] FIG. 14 is a further example screenshot of a manage
connections
display;
[0020] FIG. 15 is a schematic illustration of a generalized form of
the
manage connections display;
[0021] FIG. 16 is a schematic illustration of a generalized form of an
alternative manage connections display; and
[0022] FIG. 17 is a flowchart of a method of managing connections of
the
mobile device.
DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0023] The described embodiments generally make use of a mobile
station.
A mobile station may be a two-way communication device with advanced data
communication capabilities having the capability to communicate with other
computer systems and devices, and is also referred to herein generally as a
mobile device. The mobile device may also include the capability for voice
communications. Depending on the functionality provided by a mobile device, it
may be referred to as a data messaging device, a two-way pager, a cellular
telephone with data messaging capabilities, a wireless Internet appliance, a
media
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
3
player (such as an MP3 player) or a data communication device (with or without
telephony capabilities).
[0024] Certain embodiments may relate to a method of managing
wireless
connections supported by a mobile device, comprising: providing a user-
selectable icon on a display of the mobile device; receiving selection input
in
relation to the icon; and executing a connections manager application in
response
to the selection input, the connections manager application being configured
to
monitor and control a wireless connection status of each of a plurality of
wireless
communication subsystems of the mobile device. The executing step may
comprise displaying a connections manager application window on the display.
[0025] Further embodiments may relate to a method of managing
wireless
connections supported by a mobile device, comprising: providing a function-
assignable key on the mobile device; and executing a connections manager
application in response to activation of only the function-assignable key, the
connections manager application being configured to monitor and control a
wireless connection status of each of a plurality of wireless communication
subsystems of the mobile device.
[0026] Certain further embodiments may relate to a method of
providing
visual indication of wireless connection status for a plurality of wireless
connection
types supported by a mobile device, comprising: determining a wireless
connection status of each of the plurality of wireless connection types,
wherein the
wireless connection status is one of "off', "on but not connected" and "on and
connected"; and displaying in an application window on a display of the mobile
device a description of each wireless connection type and a symbolic
indication of
the wireless connection status of each wireless connection type, each symbolic
indication being visually associated with the corresponding description of the
wireless communication type on the display. The symbolic indication may
comprise a color indication. The color indication may be a first color
corresponding to the "off' connection status, a second color corresponding to
the
"on but not connected" connection status or a third color corresponding to the
"on
and connected" connection status. The first color may be red, the second color
may be yellow and the third color may be green.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
4
[0027] The symbolic indication may comprise a symbol graphically
overlaid
on the color indication. The symbol may be a negative symbol for the "off'
connection status, a neutral symbol for the "on but not connected" connection
status or a positive symbol for the "on and connected" connection status. The
negative symbol may be a cross, the neutral symbol may be a dash and the
positive symbol may be a check mark.
[0028] The method may further comprise executing a connection
manager
application on the mobile device, wherein the connection manager application
performs the determining step. The method may further comprise establishing a
monitoring process on the mobile device for each wireless connection type to
determine the occurrence of a change in connection status of the respective
wireless connection type; and repeating the displaying in response to
determination that a change in connection status has occurred.
[0029] The icon may be a connections manager application icon
displayed
in a main application icon list on a home screen of the mobile device.
Alternatively, the icon may be a wireless connection-related icon displayed on
a
home screen of the mobile device. The wireless connection-related icon may be
displayed in a banner area of the home screen. The wireless connection-related
icon may be one of a plurality of different wireless connection-related icons
displayed in the banner area. The mobile device may comprise a two-dimensional
scrolling component and the wireless connection-related icon may be accessed
using the two-dimensional scrolling component.
[0030] The method may further comprise displaying in the connection
manager application window a user-selectable master switching option; and
changing the wireless connection status of at least one of the wireless
communication subsystems in response to selection of the master switching
option. The master switching option may be one of a plurality of master
switching
options, wherein the master switching option displayed in the connections
manager application window depends on the wireless connection status of each
of the wireless communication subsystems.
[0031] If at least one of the wireless communication subsystems is
on, the
displayed master switching option is a "turn all connections off' option. When
the
"turn all connections off' option is selected, the method may further
comprise:
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
storing connection information associated with each wireless communication
subsystem that is on and connected; and turning off each wireless
communication
subsystem that was on prior to selection of the "turn all connections off'
option.
[0032] The method may further comprise displaying a "restore
connections"
5 option as the master switching option in response to the turning off.
When the
"restore connections" option is selected, the method may further comprise:
accessing the stored connection information; and turning on each wireless
communication subsystem for which connection information was stored and
attempting to establish a connection with an external system based on the
connection information. The method may further comprise, for each wireless
connection type, displaying a user-selectable connection type switching
option;
and changing the wireless connection status of the wireless communication
subsystem corresponding to the wireless connection type in response to
selection
of the respective connection type switching option.
[0033] Each connection type switching option may comprise a toggling
icon. Each connection type switching option may also comprise a toggling
description of the connection type switching option. The connection type
switching
option, the description and the symbolic indication for all wireless
connection
types may be displayed together in a portion of the connections manager
application window. The master switching option may be displayed at a top
portion of the connections manager application window. The top portion may
comprise a symbolic indication corresponding to the displayed master switching
option.
[0034] Further embodiments may relate to a mobile device comprising:
a
processor; a display responsive to the processor; a plurality of wireless
communication subsystems responsive to the processor; a user-assigned function
key that provides an output to the processor when activated; and a memory
storing program code executable by the processor for executing a connection
manager application in response to receiving the output from the user-assigned
function key, wherein a memory storing program code executable by the
processor for executing a connection manager application in response to
selection of the icon, wherein the connection manager application is
configured to
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
6
monitor and control a wireless connection status of each of the plurality of
wireless communication subsystems.
[0035] Other embodiments may relate to a mobile device comprising: a
processor; a display responsive to the processor and comprising a user-
selectable icon; a plurality of wireless communication subsystems responsive
to
the processor; and a memory storing program code executable by the processor
for executing a connection manager application in response to selection of the
icon, wherein the connection manager application is configured to monitor and
control a wireless connection status of each of the plurality of wireless
communication subsystems.
[0036] The wireless connection status may be one of "off', "on but
not
connected" and "on and connected". The memory may further comprise program
code executable by the processor for executing a user interface module, and
wherein the connection manager application, when executed by the processor, is
configured to cooperate with the user interface module to cause the display to
display in an application window a description of a wireless connection type
of
each wireless communication subsystem and a symbolic indication of the
wireless
connection status of each wireless communication subsystem, each symbolic
indication being visually associated with the corresponding description of the
wireless communication type on the display.
[0037] Each wireless connection type may be a different one of the
group
consisting of: a cellular connection, a wireless local area network
connection, a
wireless device connection and a global positioning system connection.
[0038] The symbolic indication may comprise a color indication. The
color
indication may be a first color corresponding to the "off' connection status,
a
second color corresponding to the "on but not connected" connection status or
a
third color corresponding to the "on and connected" connection status. The
first
color may be red, the second color may be yellow and the third color may be
green. The symbolic indication may comprise a symbol graphically overlaid on
the color indication. The symbol may be a negative symbol for the "off'
connection status, a neutral symbol for the "on but not connected" connection
status or a positive symbol for the "on and connected" connection status. The
negative symbol may be a cross, the neutral symbol may be a dash and the
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
7
positive symbol may be a check mark. Each wireless connection type may be a
different one of the group consisting of: a cellular connection, a wireless
local area
network connection, a wireless device connection and a global positioning
system
connection.
[0039] Further embodiments may relate to computer readable storage
storing program instructions which, when executed by a processor of a mobile
device, cause the processor to perform a method comprising the steps:
determining a wireless connection status of each of the plurality of wireless
connection types, wherein the wireless connection status is one of "off, "on
but
not connected" and "on and connected"; and displaying in an application window
on a display of the mobile device a description of each wireless connection
type
and wireless connection status of each wireless connection type, each symbolic
indication being visually associated with the corresponding description of the
wireless communication type on display.
[0040] The icon may be a connections manager application icon displayed
in a main application icon list on a home screen of the mobile device. The
icon
may be a wireless connection-related icon displayed on a home screen of the
mobile device. The wireless connection-related icon may be displayed in a
banner area of the home screen. The wireless connection-related icon may be
one of a plurality of different wireless connection-related icons displayed in
the
banner area.
[0041] The mobile device may comprise a two-dimensional scrolling
component and the wireless connection-related icon is accessed using the two-
dimensional scrolling component. The connection manager application may be
further configured to cooperate with the user interface module to display in
the
application window a user-selectable master switching option, and wherein the
connection manager application may be further configured to change the
wireless
connection status of at least one of the wireless communication subsystems in
response to selection of the master switching option.
[0042] The master switching option may be one of a plurality of master
switching options, and wherein the master switching option displayed in the
connections manager application window may depend on the wireless connection
status of each of the wireless communication subsystems. If at least one of
the
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
8
wireless communication subsystems is on, the displayed master switching option
may be a "turn all connections off' option. In response to selection of the
"turn all
connections off' option, the connection manager application may be further
configured to store connection information associated with each wireless
communication subsystem that is on and connected and to turn off each wireless
communication subsystem that was on prior to selection of the "turn all
connections off' option.
[0043] The connection manager application may be further configured
to
cooperate with the user interface module to display a "restore connections"
option
as the master switching option in response to all wireless subsystems being
turned off. In response to selection of the "restore connections" option, the
connection manager application may be further configured to access the stored
connection information, to turn on each wireless communication subsystem for
which connection information was stored and to attempt to establish a
connection
with an external system based on the connection information. The connection
manager application may be further configured to cooperate with the user
interface module to display a user selectable connection type switching option
for
each wireless connection type and to change the wireless connection status of
the
wireless communication subsystem corresponding to the wireless connection type
in response to selection of the respective connection type switching option.
Each
connection type switching option may comprise a toggling icon. Each connection
type switching option may comprise a toggling description of the connection
type
switching option.
[0044] The connection manager application may be further configured
to
cooperate with the user interface module to display the connection type
switching
option, the description and the symbolic indication for all wireless
connection
types together in a portion of the application window. The master switching
option may be displayed at a top portion of the application window. The top
portion may comprise a symbolic indication corresponding to the displayed
master
switching option.
[0045] Further embodiments may relate to computer readable storage
storing program instructions which, when executed by a processor of a mobile
device, cause the processor to perform a method comprising the steps:
providing
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
9
a user-selectable icon on a display of the mobile device; receiving a
selection
input in relation to the icon; and executing a connections manager application
in
response to the selection input, the connections manager application being
configured to monitor and control a wireless connection status of each of a
plurality of wireless communication subsystems of the mobile device.
[0046] Further embodiments may relate to computer readable storage
storing program instructions which, when executed by a processor of a mobile
device, cause the processor to perform a method comprising the steps of:
permitting user assignment of a function to a function-assignable key on the
mobile device; and executing a connections manager application in response to
actuation of only the function-assignable key, the connections manager
application being configured to monitor and control a wireless connection
status of
each of a plurality of wireless communication subsystems of the mobile device.
[0047] A wireless connections management application in the mobile
device may provide a single user interface for managing two or more wireless
communication interfaces in the mobile device in a consolidated manner.
Additionally, by using a master switch option provided by the connections
management application, a user may affect the wireless communication
interfaces
as a group through a single interaction with the user interface. The user
interface
may include a three-valued status indicator for each of the wireless
communication interfaces.
[0048] To aid the reader in understanding the structure of a mobile
device
and how it communicates with other devices, reference is first made to FIGS. 1
through 3.
[0049] Referring first to FIG. 1, a block diagram of a mobile device in one
example implementation is shown generally as 100. Mobile device 100 comprises
a number of components, the controlling component being microprocessor 102.
Microprocessor 102 controls the overall operation of mobile device 100. In
some
embodiments certain communication functions, including data and voice
communications, are performed through communication subsystem 104.
Communication subsystem 104 receives messages from and sends messages to
a wireless network 200.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
[0050] In this example implementation of mobile device 100,
communication subsystem 104 is configured for cellular communication in
accordance with the Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) and
General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) standards. The GSM/GPRS wireless
5 network is used worldwide and it is expected that these standards will be
superseded eventually by Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE) and
Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS).
[0051] New standards are still being defined, but it is believed that
they will
have similarities to the network behavior described herein, and it will also
be
10 understood by persons skilled in the art that the described embodiments
are
intended to use any other suitable standards that are developed in the future.
The
wireless link connecting communication subsystem 104 with network 200
represents one or more different Radio Frequency (RF) channels, operating
according to defined protocols specified for GSM/GPRS communications. With
newer network protocols, these channels are capable of supporting both circuit
switched voice communications and packet switched data communications.
[0052] Although the wireless network associated with mobile device
100 is
a GSM/GPRS wireless network in one example implementation of mobile device
100, other wireless networks may also be associated with mobile device 100 in
variant implementations. Different types of wireless networks that may be
employed include, for example, data-centric wireless networks, voice-centric
wireless networks, and dual-mode networks that can support both voice and data
communications over the same physical base stations. Combined dual-mode
networks include, but are not limited to, Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
or
CDMA2000 networks, GSM/GPRS networks (as mentioned above), and third-
generation (3G) networks like EDGE and UMTS. Some older examples of data-
centric networks include the MobitexTM Radio Network and the DataTACTm Radio
Network. Examples of older voice-centric data networks include Personal
Communication Systems (PCS) networks like GSM and Time Division Multiple
Access (TDMA) systems.
[0053] Microprocessor 102 also interacts with additional subsystems
such
as a Random Access Memory (RAM) 106, flash memory 108, display 110,
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
11
auxiliary input/output (I/O) subsystem 112, serial port 114, keyboard 116,
speaker
118, microphone 120, short-range communications 122 and other devices 124.
[0054] Some of the subsystems of mobile device 100 perform
communication-related functions, whereas other subsystems may provide
"resident" or on-device functions. By way of example, display 110 and keyboard
116 may be used for both communication-related functions, such as entering a
text message for transmission over network 200, and device-resident functions
such as a calculator, media player or task list. Operating system software
used
by microprocessor 102 is typically stored in a persistent store such as flash
memory 108, which may alternatively be a read-only memory (ROM) or similar
storage element (not shown). Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the
operating system, specific device applications, or parts thereof, may be
temporarily loaded into a volatile store such as RAM 106.
[0055] In some embodiments, mobile device 100 may send and receive
communication signals over network 200 after required network registration or
activation procedures have been completed. Network access is associated with a
subscriber or user of a mobile device 100. To identify a subscriber, mobile
device
100 requires a Subscriber Identity Module or "SIM" card 126 to be inserted in
a
SIM interface 128 in order to communicate with a network. SIM 126 is one type
of
a conventional "smart card" used to identify a subscriber of mobile device 100
and
to personalize the mobile device 100, among other things. Without SIM 126,
mobile device 100 is not fully operational for communication with network 200.
[0056] By inserting SIM 126 into SIM interface 128, a subscriber can
access all subscribed services. Services could include: web browsing and
messaging such as e-mail, voice mail, Short Message Service (SMS), media
transfers (such as music downloading or streaming), and Multimedia Messaging
Services (MMS). More advanced services may include: point of sale, field
service
and sales force automation. SIM 126 includes a processor and memory for
storing information. Once SIM 126 is inserted in SIM interface 128, it is
coupled
to microprocessor 102. In order to identify the subscriber, SIM 126 contains
some
user parameters such as an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). An
advantage of using SIM 126 is that a subscriber is not necessarily bound by
any
single physical mobile device. SIM 126 may store additional subscriber
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
12
information for a mobile device as well, including datebook (or calendar)
information and recent call information. In certain embodiments SIM 126 may be
a
different type of user identifier and may be integral to mobile device 100 or
not
present at all.
[0057] Mobile device 100 is a battery-powered device and includes a
battery interface 132 for receiving one or more rechargeable batteries 130.
Battery interface 132 is coupled to a regulator (not shown), which assists
battery
130 in providing power V+ to mobile device 100. Although current technology
makes use of a battery, future technologies such as micro fuel cells may
provide
the power to mobile device 100.
[0058] Microprocessor 102, in addition to its operating system
functions,
enables execution of software applications on mobile device 100. A set of
applications that control basic device operations, including data and voice
communication applications, will normally be installed in flash memory 108 (or
other non-volatile storage) on mobile device 100 during its manufacture.
[0059] Additional applications may also be loaded onto mobile device
100
through network 200, auxiliary I/O subsystem 112, serial port 114, short-range
communications subsystem 122, or any other suitable subsystem 124. This
flexibility in application installation increases the functionality of mobile
device 100
and may provide enhanced on-device functions, communication-related functions,
or both. For example, secure communication applications may enable electronic
commerce functions and other such financial transactions to be performed using
mobile device 100.
[0060] Serial port 114 enables a subscriber to set preferences
through an
external device or software application and extends the capabilities of mobile
device 100 by providing for information or software downloads to mobile device
100 other than through a wireless communication network. The alternate
download path may, for example, be used to load an encryption key onto mobile
device 100 through a direct and thus reliable and trusted connection to
provide
secure device communication.
[0061] Short-range communications subsystem 122 provides for wireless
device connections to enable communication between mobile device 100 and
different systems or devices, without the use of network 200. For example,
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
13
subsystem 122 may include an infrared device and associated circuits and
components for short-range communication. Examples of short range
communication would include standards developed by the Infrared Data
Association (IrDA), Bluetooth, and the 802.11 family of standards developed by
IEEE.
[0062] In use, a received signal such as a text message, an e-mail
message, or web page download will be processed by communication subsystem
104 and input to microprocessor 102. Microprocessor 102 will then process the
received signal for output to display 110 or alternatively to auxiliary I/O
subsystem
112. A subscriber may also compose data items, such as e-mail messages, for
example, using keyboard 116 in conjunction with display 110 and possibly
auxiliary I/O subsystem 112. Auxiliary I/O subsystem 112 may include devices
such as: a touch screen, mouse, infrared fingerprint detector, or a roller
wheel
with a dynamic button pressing capability. Further, auxiliary I/O subsystem
112
may comprise a two-dimensional navigation (or scrolling) component, such as a
track ball, a joystick or a directional pad, each optionally with a dynamic
button
pressing capability. Keyboard 116 is an alphanumeric keyboard and/or
telephone-type keypad. A composed item may be transmitted over network 200
through communication subsystem 104.
[0063] For voice communications, the overall operation of mobile device
100 is substantially similar, except that the received signals would be output
to
speaker 118, and signals for transmission would be generated by microphone
120. Alternative voice or audio I/O subsystems, such as a voice message
recording subsystem, may also be implemented on mobile device 100. Although
voice or audio signal output is accomplished primarily through speaker 118,
display 110 may also be used to provide additional information such as the
identity of a calling party, duration of a voice call, or other voice call
related
information.
[0064] Referring now to FIG. 2, a block diagram of the communication
subsystem component 104 of FIG. 1 is shown. Communication subsystem 104
comprises a receiver 150, a transmitter 152, one or more embedded or internal
antenna elements 154, 156, Local Oscillators (L0s) 158, and a processing
module such as a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) 160.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
14
[0065] The particular design of communication subsystem 104 is
dependent upon the network 200 in which mobile device 100 is intended to
operate, thus it should be understood that the design illustrated in FIG. 2
serves
only as one example. Signals received by antenna 154 through network 200 are
input to receiver 150, which may perform such common receiver functions as
signal amplification, frequency down conversion, filtering, channel selection,
and
analog-to-digital (AID) conversion. AID conversion of a received signal allows
more complex communication functions such as demodulation and decoding to be
performed in DSP 160. In a similar manner, signals to be transmitted are
processed, including modulation and encoding, by DSP 160. These DSP-
processed signals are input to transmitter 152 for digital-to-analog (D/A)
conversion, frequency up conversion, filtering, amplification and transmission
over
network 200 via antenna 156. DSP 160 not only processes communication
signals, but also provides for receiver and transmitter control. For example,
the
gains applied to communication signals in receiver 150 and transmitter 152 may
be adaptively controlled through automatic gain control algorithms implemented
in
DSP 160.
[0066] The wireless link between mobile device 100 and a network 200
may contain one or more different channels, typically different RF channels,
and
associated protocols used between mobile device 100 and network 200. A RE
channel is a limited resource that must be conserved, typically due to limits
in
overall bandwidth and limited battery power of mobile device 100.
[0067] When mobile device 100 is fully operational, transmitter 152
is
typically keyed or turned on only when it is sending to network 200 and is
otherwise turned off to conserve resources. Similarly, receiver 150 is
periodically
turned off to conserve power until it is needed to receive signals or
information (if
at all) during designated time periods.
[0068] Referring now to FIG. 3, a block diagram of a node of a
wireless
network is shown as 202. In practice, network 200 comprises one or more nodes
202. Mobile device 100 communicates with a node 202 within wireless network
200. In the example implementation of FIG. 3, node 202 is configured in
accordance with General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Global Systems for
Mobile (GSM) technologies. Node 202 includes a base station controller (BSC)
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
204 with an associated tower station 206, a Packet Control Unit (PCU) 208
added
for GPRS support in GSM, a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) 210, a Home
Location Register (HLR) 212, a Visitor Location Registry (VLR) 214, a Serving
GPRS Support Node (SGSN) 216, a Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) 218,
5 and a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 220. This list of
components
is not meant to be an exhaustive list of the components of every node 202
within a
GSM/GPRS network, but rather a list of components that are commonly used in
communications through network 200.
[0069] In a GSM network, MSC 210 is coupled to BSC 204 and to a
10 landline network, such as a Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) 222
to
satisfy circuit switched requirements. The connection through PCU 208, SGSN
216 and GGSN 218 to the public or private network (Internet) 224 (also
referred to
herein generally as a shared network infrastructure) represents the data path
for
GPRS capable mobile devices. In a GSM network extended with GPRS
15 capabilities, BSC 204 also contains a Packet Control Unit (PCU) 208 that
connects to SGSN 216 to control segmentation, radio channel allocation and to
satisfy packet switched requirements. To track mobile device location and
availability for both circuit switched and packet switched management, HLR 212
is
shared between MSC 210 and SGSN 216. Access to VLR 214 is controlled by
MSC 210.
[0070] Station 206 is a fixed transceiver station. Station 206 and
BSC 204
together form the fixed transceiver equipment. The fixed transceiver equipment
provides wireless network coverage for a particular coverage area commonly
referred to as a "cell". The fixed transceiver equipment transmits
communication
signals to and receives communication signals from mobile devices within its
cell
via station 206. The fixed transceiver equipment normally performs such
functions as modulation and possibly encoding and/or encryption of signals to
be
transmitted to the mobile device in accordance with particular, usually
predetermined, communication protocols and parameters, under control of its
controller. The fixed transceiver equipment similarly demodulates and possibly
decodes and decrypts, if necessary, any communication signals received from
mobile device 100 within its cell. Communication protocols and parameters may
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
16
vary between different nodes. For example, one node may employ a different
modulation scheme and operate at different frequencies than other nodes.
[0071] For all mobile devices 100 registered with a specific network,
permanent configuration data such as a user profile is stored in HLR 212. HLR
212 also contains location information for each registered mobile device and
can
be queried to determine the current location of a mobile device. MSC 210 is
responsible for a group of location areas and stores the data of the mobile
devices
currently in its area of responsibility in VLR 214. Further VLR 214 also
contains
information on mobile devices that are visiting other networks. The
information in
VLR 214 includes part of the permanent mobile device data transmitted from HLR
212 to VLR 214 for faster access. By moving additional information from a
remote
HLR 212 node to VLR 214, the amount of traffic between these nodes can be
reduced so that voice and data services can be provided with faster response
times and at the same time requiring less use of computing resources.
[0072] SGSN 216 and GGSN 218 are elements added for GPRS support;
namely packet switched data support, within GSM. SGSN 216 and MSC 210
have similar responsibilities within wireless network 200 by keeping track of
the
location of each mobile device 100. SGSN 216 also performs security functions
and access control for data traffic on network 200. GGSN 218 provides
internetworking connections with external packet switched networks and
connects
to one or more SGSN's 216 via an Internet Protocol (IP) backbone network
operated within the network 200. During normal operations, a given mobile
device 100 must perform a "GPRS Attach" to acquire an IP address and to access
data services. This requirement is not present in circuit switched voice
channels
as Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) addresses are used for routing
incoming and outgoing calls. Currently, all GPRS capable networks use private,
dynamically assigned IP addresses, thus requiring a DHCP server 220 connected
to the GGSN 218. There are many mechanisms for dynamic IP assignment,
including using a combination of a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
(RADIUS) server and DHCP server.
[0073] Once the GPRS Attach is complete, a logical connection is
established from a mobile device 100, through PCU 208, and SGSN 216 to an
Access Point Node (APN) within GGSN 218. The APN represents a logical end of
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
17
an IP tunnel that can either access direct Internet compatible services or
private
network connections. The APN also represents a security mechanism for network
200, insofar as each mobile device 100 must be assigned to one or more APNs
and mobile devices 100 cannot exchange data without first performing a GPRS
Attach to an APN that it has been authorized to use. The APN may be considered
to be similar to an Internet domain name such as "myconnection.wireless.com".
[0074] Once the GPRS Attach is complete, a tunnel is created and all
traffic
is exchanged within standard IP packets using any protocol that can be
supported
in IP packets. This includes tunneling methods such as IP over IP as in the
case
with some IPSecurity (IPsec) connections used with Virtual Private Networks
(VPN). These tunnels are also referred to as Packet Data Protocol (PDP)
Contexts and there are a limited number of these available in the network 200.
To
maximize use of the PDP Contexts, network 200 will run an idle timer for each
PDP Context to determine if there is a lack of activity. When a mobile device
100
is not using its PDP Context, the PDP Context can be deallocated and the IP
address returned to the IP address pool managed by DHCP server 200.
[0075] For embodiments of mobile device 100 described hereinafter,
the
mobile device 100 is equipped and configured for communication over a cellular
connection via communication subsystem 104 and with a local wireless device
using short range communications subsystem 122 with a communications
protocol specific to communication with local wireless devices, such as
BluetoothTM, for example. Mobile device 100 may also be configured for
communication in a wireless local area network (WLAN) using a communication
form commonly termed "Wi-Fi". Optionally, mobile device 100 may also be
configured for communication in a global positioning system (GPS) context. For
purposes of illustration, aspects of mobile device 100 are described below in
relation to FIGS. 4 to 17 as being configured and enabled for communication
over
three different communication types, namely a cellular connection, a WLAN
connection and a BluetoothTM connection.
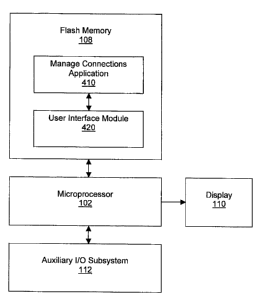
[0076] Referring now to FIG. 4, flash memory 108 is shown in further
detail.
As shown in FIG. 4, flash memory 108 comprises executable program code for
implementing a manage connections application 410 and a user interface module
420. The functions of manage connections application 410 and user interface
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
18
module 420 are performed by microprocessor 102 executing the relevant stored
program code in flash memory 108. It will be understood that flash memory 108
comprises various other program code, such as operating system software and
other software applications, although these are not specifically shown for
purposes of simplicity of illustration.
[0077] Manage connections application 410 is an application that can
be
initiated by a user of mobile device 100 in order to manage the different
wireless
connection types enabled by mobile device 100. Manage connections application
410 enables a user to readily see the connection status of each of the
wireless
connection types supported by mobile device 100 and to manage those
connections. FIGS. 8 to 14 show example screen shots of display 110 with a
manage connections applications window 710 displayed.
[0078] Manage connections application 410 also handles interfacing
between the user interface module 420 and the wireless communications
framework of device 100, including communication subsystem 104, short range
communications 122 and other communications subsystems, such as may be
provided by other device subsystems 124. In this role, manage connections
application 410 is configured to determine the connection status of each
communication subsystem in mobile device 100. The connection status may thus
be determined by manage connections application 410 as one of three statuses:
off; on but not connected; and on and connected. The functions of manage
connections application 410 are described in further detail below with
reference to
FIGS. 5 to 17.
[0079] User interface module 420 communicates with manage
connections
application 410 in order to generate a suitable visual display to be shown to
the
user of mobile device 100 on display 110, including manage connections
application window 710 and connection status indicators (as described below),
based on information received from manage connections application 410. User
interface module 420 also facilitates the receipt and interpretation of user
input in
relation to the images displayed on display 110.
[0080] Referring now to FIG. 5, a method 500 of displaying wireless
status
indicators is described. Method 500 begins at step 510, at which a user
selects a
"manage connections" icon, such as icon 705 shown in FIGS. 7 to 14 on a home
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
19
screen of mobile device 100. For example, selection of the "manage
connections"
icon may be performed by using user interface module 420 to highlight icon 705
and then actuating an auxiliary I/O device 112, such as a selection button, to
"click" on the icon.
[0081] In an alternative embodiment, step 510 involves user selection of an
icon other than the manage connections icon 705. For example, the manage
connections application 410 may be launched by user selection of a wireless
connection-related icon in the banner area of home screen 704. As shown in
FIG.
7, at a top right corner of home screen 704, a Wi-Fi icon 701, as one example
of a
WLAN connection, and an "EDGE" icon 702, as one example of a technology type
of a cellular connection, are shown. Wi-Fi icon 701 and EDGE icon 702 may be
navigated to by use of a two-dimensional navigation component, such as
trackball
706 and, upon selection by the user while Wi-Fi icon 701 or EDGE icon 702 is
emphasized, the manage connections application 410 is launched on mobile
device 100. Alternatively, selection of a Bluetooth TM icon as one example of
a
wireless personal area network technology, either in the banner or elsewhere,
may be used to launch the manage connections application 410.
[0082] In a further alternative manner of selecting manage
connections
application 410, an assignable key, sometimes called a hot key or a
convenience
key, may be assigned by the user to be associated with manage connections
application 410. Thus, when the user presses such a key, user interface module
420 interprets the key press as requiring execution of manage connections
application 410.
[0083] Once the "manage connections" icon is selected or the manage
connections application 410 is otherwise selected to be launched by the user,
manage connections application 410 is executed at step 520. In this context,
execution of manage connections application 410 is initiated (or "launched")
by
the particular launching means selected by the user.
[0084] At step 530, the manage connections application 410 queries
the
wireless framework, including wireless communications subsystems, to determine
the status of each wireless connection enabled by mobile device 100. Manage
connections application 410 then determines the status of each wireless
connection based on the responses it receives from its queries. Manage
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
connections application 410 then proceeds to display a symbolic indication of
the
wireless connection status of each wireless connection, at step 550, by
causing
user interface module 420 to generate a suitable display, examples of which
are
shown and described in relation to FIGS. 8 to 14.
5 [0085] Once manage connections application 410 has initially
determined
the status of each wireless connection, it creates listener processes to
monitor
and update the status of each wireless connection, at step 540. If the
listener
processes indicate that there is a change in the status of one of the wireless
connections, at step 560, then the changed status is communicated by the
listener
10 processes to user interface module 420 to cause an updated display to be
shown
to the user at step 550.
[0086] The listener processes established at step 540 may be
embodied as
registered call back functions. Such call back functions are registered by
manage
connections application 410 with microprocessor 102 so that, during execution
of
15 other device processes, the microprocessor checks the list of call back
functions
upon the occurrence of one or more predetermined events, such as a change in
connection status of a wireless communication subsystem. Upon the occurrence
of one or more such events, microprocessor 102 determines whether any of the
registered call back functions are applicable to the one or more events and
makes
20 a function call, as appropriate. Where an event relates to the change in
a
connection status of a wireless communication subsystem, microprocessor 102
passes the changed status and a relevant descriptor, such as a name,
technology
type or location associated with the connection, if appropriate, as parameters
in
the function call. Such call back functions are supported by functions of an
application program interface (API) of the mobile device 100.
[0087] Referring to FIG. 6, substeps of step 550 are described. Step
550
comprises a check of the status of each wireless connection type at step 610
to
determine whether the status of the relevant wireless connection type is "on".
If
not, then at step 620, the manage connections application window is caused to
display the symbolic indication for "off' for the relevant wireless connection
type.
[0088] If the wireless connection status is determined at step 610
to be
"on", then, at step 630, the manage connections application determines whether
the wireless connection is connected to a network or device, as appropriate.
If the
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
21
wireless connection status of a wireless connection is determined at step 630
to
be on but not connected, then at step 640, manage connections application
window 710 displays the symbolic indication for "on" for each connection type
to
which the status applies. The symbolic indication for "on" may also be
considered
to be a symbolic indication for "on but not connected".
[0089] If the connection status of a wireless connection is
determined to be
on and connected at step 630, then at step 650, manage connections application
window 710 is caused to display the symbolic indication for "connected" for
the
relevant wireless connections to which that status applies. The symbolic
indication for "connected" may also be considered to be a symbolic indication
for
"on and connected."
[0090] FIG. 7 is an illustration of an exemplary depiction of mobile
device
100. Mobile device 100 has a display screen 702 and user input components
such as keyboard 116, an assignable convenience key 703 and a trackball 706
(as part of auxiliary I/O subsystem 112). An exemplary home screen 704, which
is
the screen displayed in display 110 when mobile device 100 is first turned on,
and
from which most functions of mobile device 100 may be accessed, is shown in
FIG. 7. Icons representing applications of mobile device 100 are displayed in
a
main icon list 708. A user of mobile device 100 can navigate through main icon
list 708, for example using trackball 706, to manage connections icon 705.
Once
the user has navigated to manage connections icon 705, it is emphasized and a
caption 707 entitled "Manage Connections" is displayed in a lower portion of
home
screen 704. If the user selects manage connections icon 705, manage
connections application 410 is launched by microprocessor 102.
[0091] Referring now to FIG. 8, there is shown an example screen shot
comprising a manage connections application window 710 generated on display
110 by user interface module 420 based at least in part on instructions from
manage connections application 410. Manage connections application window
710 is generated by user interface module 420 based on instructions from
manage connections application 410. An example icon 705 for activating (i.e.
beginning execution of) manage connections application 410 is shown at the
left
side of the screen shot in FIG. 8.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
22
[0092] Manage connections application window 710 comprises a number
of
selectable menu options, as well as symbolic indications of the wireless
connection status of each of three types of wireless connection. These
wireless
connection types are indicated in separate rows 712, 714 and 716 of
application
window 710. In the examples illustrated in FIGS. 8 to 14, row 712 contains a
written description (label 752 in FIG. 15) of the wireless connection type
that is
"wireless" or cellular in nature, as well as a written status description
(text field
762 in FIG. 15) for that wireless connection type, which in FIG. 8 is "off".
Row 712
also has, on the right side of application window 710 a symbolic indication
722 of
the connection status of the "wireless" (cellular) wireless connection type of
row
712.
[0093] Although not clearly discernable from FIGS. 8 to 14, each of
the
symbolic indicators comprises a color indication indicative of the wireless
connection status of the row on application window 710 to which it belongs.
Thus,
rows 714 and 716 also have symbolic indications 724 and 726 on the right side
of
application window 710, indicative of the connection status of the relevant
wireless connection type. Rows 714 and 716 also contain written descriptions
of
the wireless connection types to which they relate (Wi-Fi and BluetoothTM) and
written status descriptions. If the wireless connection type of a row is "on
and
connected", the row will show a name, technology or location descriptor, as
appropriate to the connection type, in place of an "on" or "off" status
description.
[0094] Referring also to FIG. 15, there is shown a generalized form
of
manage connections application window 710, of which the screen shots shown in
FIGS. 8 to 14 are specific examples. As shown in FIG. 15, each row 712, 714,
716 comprises, from left to right, a check box, a label, a text field and a
symbolic
indication graphic. Specifically, the first, or top-most, row 712 comprises a
check
box 742, a label 752, a text field 762 and a symbolic indication (S.I.)
graphic 722.
In FIG. 8, these fields comprise the following states or contents: unchecked;
"wireless"; "off'; and red. Row 714 comprises a check box 744, label 754, text
field 764 and symbolic indication graphic 724. Row 716 has a check box 746,
label 756, text field 766 and symbolic indication graphic 726. In the example
of
FIG. 8, rows 714 and 716 have fields with similar states to those of row 712,
except that label 754 is "Wi-Fi" and label 756 is "BluetoothTm". It should be
noted
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
23
that alternative labels may be used to indicate the same connection type. For
example, in FIG. 14, label 752 is "Mobile Network", rather than "wireless".
[0095] It should be noted that rows 712, 714 and 716 each relate to
wireless connection types that can be described as relating to wireless wide
area
network (VVWAN), wireless local area network (WLAN) and wireless personal area
network (WPAN) technologies, respectively. The "wireless", "Wi-Fi" and
"Bluetooth TM" labels described herein are examples of such general
technologies.
[0096] Manage connections application window 710 has rows 712, 714
and
716 grouped together in an upper portion of application window 710 so that a
user
can easily ascertain the wireless connection status of each wireless
connection
type by looking only at the upper portion of the application window 710. In a
lower
portion of application window 710 is a list 770 comprising a plurality of
groupings
of menu items related to the wireless connection types displayed in the upper
portion of application window 710. A first grouping of menu items comprises a
first menu item 772 and a second menu item 774, which in the examples shown in
FIGS. 8 to 14 are "services status" and "setup Wi-Fi network". A second
grouping
of menu options in list 770 comprises first options item 782, second options
item
784 and third options item 786, shown in the examples of FIGS. 8 to 14 as
"wireless options", "Wi-Fi options" and "BluetoothTM options", respectively.
framework of mobile device 100, for example so that when turning on a
particular
wireless communication subsystem, manage connections application 410 can
determine whether to automatically try to establish a connection with an
external
device or service provider and, if so, on what basis such a connection should
be
established.
[0098] Manage connections icon 705 is shown in FIG. 8 and FIGS. 10 to 14
on home screen 704 as being emphasized relative to other icons in a main icon
list disposed vertically along the left hand side of home screen 704. In the
example shown in FIG. 8, manage connections application window 710 has been
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
24
launched by user selection of manage connections icon 705 while it was
emphasized on home screen 704. Manage connections application window 710
may alternatively be displayed on manage connections application 410 in
response to user selection of EDGE icon 702 (or another wireless connection
related icon adjacent EDGE icon 702) in the banner area with home screen 704.
As shown in FIG. 9, EDGE icon 702 is emphasized following user navigation
away from the main application icon list 708 to a subsidiary icon list on the
top
right of home screen 704.
[0099] Each of the example manage connections application windows 710
shown in FIGS. 8 to 14 has a master switch option, with an accompanying
written
description of the option, shown at the top of application window 710. The
master
switch option displayed in application window 710 is one of "restore
connections",
"turn all connections off' and "turn all connections on", depending on the
wireless
connection statuses of the wireless communication subsystems of the supported
wireless connection types. The master switch option can be used to turn on or
off
multiple wireless communication subsystems at the same time. Further, as
described below in relation to FIG. 17, the master switch option may be used
to
restore connections that were previously established.
[00100] Check boxes 742, 744 and 746 are shown in FIGS. 8 to 15 and
provide a further level of switching control in addition to the displayed
master
switch option. By highlighting a check box (or the row that contains that
check
box) and "clicking", the user can toggle the on/off state of the wireless
communication subsystem for the relevant wireless connection type. Thus, check
boxes 742, 744 and 746 provide user selectable control functions to manage the
wireless connections of mobile device 100, as desired.
[00101] When check boxes 742, 744 and 746 are "checked", this
corresponds to an "on" state of the corresponding wireless communication
subsystem. If any of the check boxes 742, 744 and 746 are blank, empty, or
"unchecked", this corresponds to an "off' state of the corresponding wireless
communication subsystem. Although check boxes are described herein for
providing a user selectable connection type switching option, an alternative
toggling user interface component that can be selectively toggled between two
states may be employed to a similar effect instead of the described check
boxes.
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
For example, a toggling descriptive option, such as "turn wireless radio off'
or
"turn Wi-Fi radio off' may be displayed when the corresponding wireless
communication subsystems for those connection types are on. Similarly, if
those
wireless communication subsystems are off, the descriptive option may toggle
to
5 "turn wireless radio on" or "turn Wi-Fi radio on".
[00102] Symbolic indicators 722, 724 and 726 may be one of red,
yellow and
green, corresponding to a connection state of "off', "on but not connected"
and
"on and connected", respectively. In an alternative embodiment, symbolic
indications 722, 724 and 726 may comprise symbols instead of, or in addition
to,
10 color indications. For example, for the "off', "on but not connected"
and
"on and connected" states, symbolic indications 722, 724 and 726 may comprise
a cross (or "x"), a dash and a check mark, respectively. Other symbols may be
used that tend to equivalently symbolize a negative, neutral and positive
state for
the wireless connection type, corresponding to the respective off, on but not
15 connected and on and connected states.
[00103] Also shown in FIG. 8 is a "restore connections" selectable
menu
item as the top row of application window 710. The "restore connections"
option
730 is only shown in application window 710 when all of the connection
statuses
of the available wireless connection types are off, as described in further
detail
20 below with reference to FIG. 17. To indicate that all wireless
connections are off,
a group symbolic indicator 732 (colored red) may be provided in the "restore
connections" row on the right side of application window 710 above and aligned
with symbolic indications 722, 724 and 726. Group symbolic indicator 732 may
also act as a button for selecting the "restore connections" option 730.
25 [00104] Referring now to FIG. 9, a further example screen shot
is shown, in
which the wireless connection statuses of all available connections are on,
while
the Wi-Fi connection shown in row 714 is on and connected to a wireless
carrier
via the unlicensed mobile access (UMA) technology. Accordingly, because for
rows 712 and 716 the connection status is on but not connected, the symbolic
indications 722 and 726 are colored yellow. Because the Wi-Fi connection of
row
714 is on and connected, the symbolic indication 724 is colored green.
[00105] In the example shown in FIG. 9, because all of the
connections are
on, the top row of window 710 displays an option 830 to "turn all connections
off."
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
26
[00106] Referring now to FIG. 10, a further example screen shot is
shown, in
which all wireless connection types are on and connected. Accordingly,
symbolic
indications 722, 724 and 726 are all colored green. Further, each of rows 712,
714 and 716 comprises a written description of the technology, location and/or
name of the connection types that are on and connected. Thus, for row 712, the
description of the connection type is "wireless" (cellular) and the technology
type
used for this connection is described as "EDGE". Further, for row 714, the
connection type is "Wi-Fi" (WLAN) and the location of the connection is
described
as "Starbucks hotspot". For row 716, the connection type is "Bluetooth TM" and
the name of the device with which mobile device 100 is connected is described
as
"Jabra Headset". Thus, where a connection is on and connected, further
specific
information regarding that connection is provided in the relevant row of
application
window 710 for the user's benefit.
[00107] As with the example shown in FIG. 9, the example shown in FIG.
10
has all connections shown as being on and therefore the "turn all connections
off'
option 830 is provided in the top row of application window 710. Additionally,
a
group symbolic indication 832 (colored green) of the on and connected status
is
shown on the right hand side of the row of option 830. The group symbolic
indication 832 may also act as a button for selecting option 830.
[00108] Referring now to FIG. 11, a further example screen shot is shown,
in
which alternative symbolic indications 1022, 1024 and 1026 are shown. The
example of FIG. 11 is otherwise similar to the example shown in FIG. 8.
Symbolic
indications 1022, 1024 and 1026 are colored red to indicate an off state of
the
relevant wireless connection types shown in rows 712, 714 and 716,
respectively.
In addition to the red coloration, each symbolic indication 1022, 1024 and
1026
comprises a negative symbol, shown in FIG. 11 as a cross or "x", overlaid on
the
color indication. Such symbols may serve to augment the visual information
provided to the user by the symbolic indications 1022, 1024 and 1026 and may
also serve to remove any color-related ambiguity that may be associated with
the
color indication alone. For example, for those suffering from color-blindness,
the
difference between a red color indication and a green color indication may not
be
apparent. The addition of a negative, neutral or positive symbol to the
symbolic
indication 1022, 1024 and 1026 may serve to resolve any such ambiguity. In an
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
27
alternative embodiment the negative, neutral or positive symbol may replace
the
color indication and be used as the sole form of symbolic indication of the
connection status. In addition, the on/off state of check boxes 742, 744 and
746
may be used as a supplementary symbolic indication of the connection status.
[00109] Referring now to FIG. 12, there is shown a further example screen
shot, in which the connection statuses are the same as those depicted in FIG.
8,
except that symbolic indications 1022, 1024 and 1026 are provided on the right
hand side of rows 712, 714 and 716, respectively, to indicate the connection
statuses in a symbol-augmented fashion. In particular, because the wireless
and
Bluetooth TM connections are on but not connected, the symbolic indications
1022
and 1026 are colored yellow and have a neutral symbol, in the form of a dash,
overlaid on the color indication. Because the Wi-Fl connection of row 714 is
on
and connected (via UMA technology), symbolic indication 1024 is colored green
and has a positive symbol, in the form of a check mark, overlaid on that color
indication.
[00110] Referring now to FIG. 13, a further example screen shot is
shown, in
which the wireless, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth TM connections of rows 712, 714 and
716,
respectively, are all on and connected. Accordingly, symbolic indications
1022,
1024 and 1026 are colored green and have check marks overlaid on the green
color indications. Apart from the augmentation of the color indication with
the
positive symbol of a check mark in symbolic indications 1022, 1024 and 1026,
the
example shown in FIG. 13 is otherwise similar to that shown and described in
relation to FIG. 10.
[00111] Referring now to FIG. 14, a further example screen shot is
shown, in
which all wireless communication subsystems are off. In this example, one or
more of the wireless communication subsystems is off because of having been
switched off by the user, using one or more of check boxes 742, 744 and 746.
Because of the intentional turning off of one or more of the wireless
communication subsystems by the user, the connection information for any
connections that were established with external devices or networks is cleared
from RAM 106 or flash memory 108, either only in respect of the wireless
communication subsystem that was turned off by the user, or in respect of all
such
wireless communication subsystems. Accordingly, where there is no stored
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
28
connection information for any of the wireless connection types, such as is
the
case with the example shown in FIG. 14, the "turn all connections on" option
1430
is displayed as the master switch option at the top of location window 710.
Further, in the example shown in FIG. 14, because all of the wireless
communication subsystems are off, the symbolic indications 722, 724 and 726
are
all red, symbolically indicating the off state.
[00112] A generalized form of manage connections application window
710
is described above with reference to FIG. 15 and specific examples of the
generalized form are shown and described in relation to FIGS. 8 to 14. While
FIG. 15 illustrates one particular layout of the items shown in manage
connections
application window 710, alternative layouts of such items are possible, an
example of which is illustrated in FIG. 16.
[00113] FIG. 16 shows an alternative manage connections application
window 1610 that has almost identical content to, and performs in the same way
as, manage connections application window 710, except for a rearrangement of
the items into different groupings. For example, instead of rows 712, 714 and
716
being grouped together towards the top of the application window, they are
located in distinct and separate groupings 1602, 1604 and 1606, respectively.
Each such grouping 1602, 1604 and 1606 comprises a respective one of rows
712, 714 and 716 and the corresponding one of the first, second and third
options
items 782, 784 and 786, to which the wireless connection type of the row
relates.
[00114] As shown in FIG. 16, the top grouping 1602 in application
window
1610 comprises row 712 positioned above and grouped with first options item
782, which in the examples shown in FIGS. 8 to 14 is "wireless options" or may
be
alternatively labeled "mobile network options". Second grouping 1604 is
located
in the middle of application window 1610, below the first grouping 1602.
Second
grouping 1604 comprises the second row 714 positioned above and adjacent to
second options item 784, which in the examples is "Wi-Fi options". Second
grouping 1604 also comprises second menu item 774, which relates to the
wireless connection type of row 714 and, in the examples, is "set up Wi-Fl
network". Third grouping 1606 is located toward the bottom of application
window
1610, below second grouping 1604. Third grouping 1606 comprises the third row
CA 02609503 2007-11-02
29
716 above and adjacent to third options item 786, which in the examples shown
is
"Bluetooth TM options".
[00115] Referring now to FIG. 17, there is shown a flowchart of a
method
1700 of managing all connections of mobile device 100. Like method 500,
method 1700 relies on the manage connections application being active and a
manage connections application window 710 must be displayed on display 110.
Accordingly, steps 1705 and 1710 are performed in the same manner as steps
510 and 520 described above. As shown in FIGS. 8 to 14, manage connections
application window 710 either shows a "restore connections" option 730, a
"turn
all connections on" option 1430 or a "turn all connections off" option 830 in
the top
row.
[00116] At step 1715, manage connections application 410 determines
whether all connections are off. If they are, then at step 1720, manage
connections application window 710 is displayed so as to show the "restore
connections" option 730 or the "turn all connections on" option 1430. If
connection information for a particular wireless connection type has been
stored
based on a previous connection, then the connection may be restored. In such a
case, the "restore connections" option 730 is displayed. Otherwise, the "turn
all
connections on" option 1430 is displayed. Unchecking a check box to turn off a
wireless communication subsystem also has the effect of clearing any
connection
information previously stored in relation to the relevant wireless connection
type,
which will mean that the "restore connections" option 730 cannot be displayed.
[00117] If, at step 1725, option 730 or 1430 is selected, then manage
connections application 410 accesses previously saved connection information
in
order to determine the connections to be restored, if such restoration is
possible.
If no previously saved connection information is available, then new
connections
may sought to be established or the restoration request may fail.
[00118] If previously saved connection information is available at
step 1730,
then at step 1735, manage connections application 410 attempts to restore the
previously saved states, if possible. Because of the change of connection
status
effected at step 1735, the "turn all connections off" option 830 is
subsequently
displayed on manage connections application window 710 at step 1740.
CA 02609503 2012-11-13
[00119] If, at step 1715, all connections are not off, then at step
1740, the
"turn all connections off option 830 is displayed. Option 830 may be displayed
only in the event that all connections are presently on or, optionally, in the
even
that one or more of the connections is on. If, at step 1745, option 830 is
selected,
5 then at step 1750, the connection information of all wireless connections
subsystems that are on and connected is saved, for example in a table, in RAM
106 or flash memory 108 of mobile device 100. Subsequently, at step 1755, all
connections are caused by manage connections application 410 to be turned off.
Because of the change of connection status effected by step 1355, the "restore
all
10 connections" option 730 is subsequently displayed in manage connections
application window 710 at step 1720.
[00120] Method 1700 is performed principally by manage connections
application 410, although it cooperates with user interface module 420 to
receive
user input and generate the appropriate display in manage connections
15 application window 710. Further, manage connections application 410
interfaces
with the wireless framework of mobile device 100 in order to effect the
turning on
or off or establishment of connections of the different wireless connection
types
enabled by mobile device 100.
[00121] Although certain graphical user interface examples are shown
in
20 FIGS. 7 to 14 and described in relation thereto, it should be understood
that
certain graphical re-arrangements or modifications of the graphical elements
shown in the example screen shots are possible without departing from the
scope
of the described embodiments. In particular, the orders of the rows or
groupings
of rows and options shown in manage connections application window 710 may
25 be rearranged, for example as shown in application window 1610 in FIG.
16,
described above. Similarly, the order of presentation of graphical elements
within
a row may be rearranged to provide an alternative presentation of the same
types
of information.
[00122] While the above description provides examples of the
embodiments,
30 it will be appreciated that some features and/or functions of the
described
embodiments are susceptible to modification without departing from the
principles
of operation of the described embodiments. Accordingly, what has been
CA 02609503 2012-11-13
31
described above has been intended to be illustrative of the invention and non-
limiting.