Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
Lift system
The invention relates to a lift system according to the introductory part of
claim 1.
Lift systems of this kind are known per se, for example from EP 1 329 412 Al.
The lift
system described there has two lift cages in a common lift shaft, each with a
respective
drive and with only one, common counterweight.
It is disadvantageous with this known system that inter alia each of the lift
cages, due to
the special suspension, is not balanced. This can have the consequence of
friction and
wear at guide rails if the lift cages are asymmetrically loaded. Moreover,
audible or
detectable knocks occur during travel.
It is now the task of the invention to propose a lift system of the kind
stated in the
introduction by which the disadvantages of the state of the art are avoided.
According to the invention this object is fulfilled for the lift system of the
kind stated in the
introduction by the features of independent claim 1.
Preferred developments and details of the lift system according to the
invention are
defined by the dependent claims.
Further details and advantages of the invention are described in the following
by way of
example than with reference to the drawing, in which:
Fig. 1A shows a first example of embodiment of the invention, from the side;
Fig. 1B shows the embodiment of the invention illustrated in Fig. 1A, in a
section
along the line A-A' in Fig. 1A;
Fig. 1C shows the embodiment of the invention illustrated in Fig. 1A, in a
section
along the line B-B' in Fig. 1A;
Fig. 2 shows a second example of embodiment of the invention with additional
tensioning means, in the same illustration as Fig. 1A;
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
2
Fig. 3A shows a second example of embodiment with fastening regions for the
support means strands and tensioning means stands in the same region of
the cage, for the upper cage in the lower region and for the lower cage in
the upper region;
Fig. 3B shows the upper cage illustrated in Fig. 3A, but with fastening
regions for
the support means strands and tensioning means strands in the upper
region of the cage;
Fig. 3C shows the lower cage illustrated in Fig. 3A, but with fastening
regions for
the support means strands and tensioning means strands in the lower
region of the cage;
Fig. 4 shows a third example of embodiment of the invention, with enlarged
looping angle of the support means strands about the drive pulleys, in the
same illustration as Fig. 1A and Fig. 2;
Fig. 5 shows a fourth example of embodiment of the invention, similarly with
enlarged looping angle of the support means strands around the drive
pulleys; and
Fig. 6 shows Fig. 1 B with further details, in enlarged illustration.
The following generally applies to the drawing and the further description:
- The figures are not to be regarded as true to scale.
- The same or similar constructional elements, or constructional elements with
the
same or similar function, are provided in all figures with the same reference
numerals.
- Statements such as right, left, above, below refer to the respective
arrangement in
the figures.
- Deflecting rollers and deflecting auxiliary rollers are illustrated in
sections generally
perpendicular to their axes of rotation as black circles.
- Drive pulleys are illustrated generally in sections perpendicular to their
axes of
rotation as circular or oval lines.
- Those parts or runs of support means strands and tensioning means strands,
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
3
which are disposed between one of the lift cages and an upper counterweight
deflecting roller, are illustrated by lines differently from those parts of
the support
means strands and tensioning means strands which are disposed between the
other lift cage K2 and the upper counterweight deflecting roller.
- It is additionally indicated for each run by a usual diameter signature and
with one
of the numerals 1 and 2 whether the corresponding locations respectively
relate to
a support means strand or tensioning means strand or two support means strands
or tensioning means strands; moreover it is indicated which support means
strands
or tensioning means strands are concerned.
- Looping angle of flexible support means strands around drive pulleys are in
general
indicated in multiples of 900, even when these looping angles slightly depart
from
the indicated values. The looping angles can be substantially influenced by
the
number, dimension and position of the deflecting rollers. The statements with
respect to these parameters of the deflecting rollers in the following
description and
drawings are therefore to be regarded as examples.
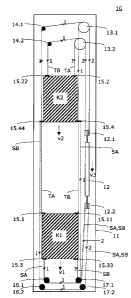
Figs. 1A, 1B and 1C show a first example of embodiment of a lift system 10
according to
the invention. These are strongly schematic side views or sections, on the
basis of which
the fundamental elements of the invention are explained. A lower lift cage K1
and an
upper lift cage K2 of the new lift system 10 are disposed one above the other
in a common
lift shaft 11, in which they can move independently of one another.
A common counterweight 12 is additionally disposed in the lift shaft 11. The
counterweight
12 is suspended at an upper counterweight deflecting roller arrangement 12.1
in a so-
termed 2:1 suspension. A roller arrangement with more than one roller is also
to be
understood by the term counterweight deflecting roller. A speed of the lower
lift cage K1 is
indicated by v1, a speed of the upper lift cage K2 by v2 and a speed of the
counterweight
12 by v3.
A first drive Ml for the lower lift cage K1 and a second drive M2 for the
upper lift cage K2
are disposed in the upper region of the lift shaft 11. A first drive pulley
13.1 is coupled with
the first drive Ml and a second drive pulley 13.2 is coupled with the second
drive M2.
In addition, a first deflecting roller 14.1 is associated with the lower lift
cage K1 and a
second deflecting roller 14.2 is associated with the upper lift cage K2, the
two deflecting
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
4
rollers being located in the upper region of the lift shaft 11.
The lower lift cage K1 has, in its upper region, a first fastening point 15.1
on the left and a
second fastening point 15.11 on the right. The upper lift cage K2 similarly
has, in its upper
region, a third fastening point 15.2 on the right and a fourth fastening point
15.22 on the
left. The lift cages K1 and K2 are suspended in a so-termed 1:1 suspension at
flexible
support means TA, TB, as is described in detail further below.
The support means substantially consist of a first support means strand TA and
a second
support means strand TB, each of which has a first and a second end. The
support
means strands TA, TB are fixed to the lift cages K1 and K2 at the fastening
points 15.1,
15.11, 15.2, 15.22 in such a manner that each of the lift cages K1 and K2 is
suspended at
each of the support means strands TA and TB. Advantageously each of the
support
means strands TA and TB is formed by two or more parallel support means
elements,
such as, for example, by two belts or two cables. Each support means strand TA
an TB
can, however, also comprise only one belt or one cable. The supporting
structure of these
support means strands TA and TB is advantageously made of steel, aramide or
Vectran.
The first support means strand TA is fastened by its first end at the first
fastening point
15.1 to the lower lift cage K1, runs from there upwardly to the first
deflecting roller 14.1 and
further to the right to the first drive pulley 13.1, around which it is led
with a looping angle
of at least 900.
The second support means strand TB is fastened by its first end at the second
fastening
point 15.11 to the lower lift cage K1 and runs from there upwardly to the
first drive pulley
13.1, around which it is led with a looping angle of at least 180 .
The two support means strands TA and TB run from the drive pulley 13.1
together in
parallel downwardly to the upper counterweight deflecting roller 12.1, where
they are
deflected through 180 .
From the upper counterweight roller 12.1 the two support means strands TA and
TB run
together upwardly in upward direction to the second drive pulley 13.2. The
first support
means strand TA is led with a looping angle of at least 180 around the second
drive
pulley 13.2. The second support means strand TB is led with a looping angle of
at least
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
900 around the second drive pulley 13.2. From the second drive pulley 13.2 the
first
support means strand TA runs downwardly to the third fastening point 15.2 at
the upper lift
cage K2, at which its second end is fastened. Similarly, from the second drive
pulley 13.2
the second support means strand TB runs to the left to the deflecting roller
14.2 and then
to the fourth fastening point 15.22 at the upper lift cage K2, at which its
second end is
fastened.
Figs. 1 C and 6 show how the force introduction takes place through the
support means
strands TA and TB for each of the lift cages K1 and K2 at least approximately
centrally
symmetrical in such a manner that a tendency of the lift cages to tip about a
horizontal tip
axis lying in the centre plane El is counteracted. This form of suspension is
here also
termed balanced suspension, which is to ensure that even in the case of
asymmetrical
loading of the lift cages K1 and K2 a tipping of the same is prevented or that
the degree of
tipping is kept within manageable limits.
Figs. 1A, 2, 3A, 4 and 5 show an advantageous arrangement of the drive pulleys
13.1 and
13.2 in the uppermost region of the lift shaft. The drive pulleys 13.1 and
13.2 are arranged
vertically, i.e. with horizontal axes Al and A2, as apparent from Fig. 6.
A particularly favourable arrangement with a conflict-free guidance of the
support means
strands TA and TB is obtained by arranging the drives Ml and M2 to be offset
in height
one above the other, wherein the offset advantageously at least corresponds
with the
radius of the drive pulleys 13.1 and 13.2.
In the case of the arrangement described above with reference to Figs. 1A, !B
and 1C the
support means strands TA, TB to a certain extent exchange their places, i.e.
the support
means strand TA is fastened to the lower lift cage Kl on the left and to the
upper lift cage
K2 on the right and the support means strand TB is fastened to the lower lift
cage K1 on
the right and to the upper lift cage K2 on the left. It is thus achieved that
the overall
lengths of the two support means strands TA, TB are not significantly
different, which is
advantageous with respect to their behaviour, particularly thermal expansion
and resilient
stretching. However, the support means strands TA, TB can also be arranged
uncrossed.
A guide device for the vertical guidance of the cages K1 and K2 in the lift
shaft 11
comprises two stationary guide rails 19 which extend vertically along opposite
sides of the
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
6
lift shaft 11 and are fastened in a manner which is not illustrated. The guide
device
additionally comprises guide bodies, which are not illustrated. Two guide
bodies which co-
operate with the respective guide rails 19 are preferably fastened in
vertically aligned
arrangement at both sides at each of the lift cages K1 and K2. The guide
bodies at each
side of the cages K1 and K2 are advantageously mounted at a largest possible
vertical
spacing.
The configuration according to the invention is such that the counterweight 12
is arranged
in the region of one of the guide rails 19 and moves, with vertical guidance,
similarly along
this guide rail 19 at counterweight guide rails (not shown), wherein the guide
rail 19 is
arranged between the cages K1 and K2 on the one hand and the counterweight 12
on the
other hand.
Fig. 2 shows a second example of embodiment of the invention. This comprises
all
constructional elements described with reference to Figs. 1 A, 1 B and 1 C as
well as an
additional device (also known as compensating cable tensioning device (ASS))
in order to
better tension the support means strands TA and TB and to better guide the
lift cages K1
and K2 as well as the counterweight 12.
The lift system 10 according to Fig. 2 comprises for this purpose a lower
counterweight
deflecting roller 12.2 which is suspended at the bottom at the counterweight
12. A fifth
fastening point 15.3 is disposed at the lower region of the lower lift cage K1
at the left
bottom and a sixth fastening point 15.33 at the right bottom. A seventh
fastening point
15.2 is disposed at the lower region of the upper lift cage K2 at the right
bottom and an
eighth fastening point 15.44 at the left bottom.
Moreover, two deflecting rollers, which are termed first auxiliary roller 16.1
and second
auxiliary roller 16.2, are located in the lower region of the shaft 11 on the
left. Moreover,
two further deflecting rollers are provided, which are termed third auxiliary
roller 17.1 and
fourth auxiliary roller 17.2. In addition, the lift system 10 according to
Fig. 2 comprises
tensioning means which substantially consist of a first tensioning means
strand SA and a
second tensioning means strand SB.
The first tensioning means strand SA is fastened by its first end at a fifth
fastening point
15.3 of the lower lift cage K1 and runs from there around the auxiliary
rollers 16.1 and
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
7
17.1. The second tensioning means strand SB is fastened at its first end at
the sixth
fastening point 15.33 of the lower lift cage K1 and runs from there around the
auxiliary
roller 17.1. The two tensioning means strands SA and SB then run together from
the
deflecting roller 17.1 to the lower counterweight deflecting roller 12.2,
where they are
deflected and subsequently led together to the auxiliary roller 17.2. Going
out from the
auxiliary roller 17.2 the first tensioning means strand SA runs upwardly to
the seventh
fastening point 15.4 of the upper lift cage K2. Similarly, going out from the
auxiliary roller
17.2 the second tensioning means strand SB runs to the auxiliary roller 16.2
and from
there upwardly to the eighth fastening point 15.44 of the upper lift cage K2.
The statement
made with respect to the change of place of the support means strands TA and
TB with
regard to Fig. 1 equally applies to a crossing of the tension means strands SA
and SB.
Advantageously, each of the tensioning means strands SA, SB is formed by two
or more
parallel tensioning means elements, such as, for example, by two belts or two
cables.
Each tensioning means strand SA, SB can, however, comprise only one belt or
one cable.
The supporting structure of these support means strands SA, SB is
advantageously made
of steel, aramide or Vectran.
Tensioning aids are preferably provided in or at the shaft 11 in the region of
the tensioning
means strands SA, SB so as to be able to mechanically tension the tensioning
means
strands SA, SB. These tensioning aids are not shown in the figures.
The first and second fastening regions 15.1, 15.11 as well as the fifth and
sixth fastening
regions 15.3, 15.33 are either located each on a lower region or an upper
region of the
cage K1, as shown in Fig. 2, or in common in the lower or upper region of the
cage K1, as
shown in Figs. 3A and 3B. If the first and second fastening regions 15.1,
15.11 are located
in the upper region of the cage K1 and the fifth and sixth fastening regions
15.3, 15.33 in
the lower region of the cage K1 then the advantage resides in the use of
shorter support
means strands TA, TB. In principle, a reverse arrangement of the first and
second
fastening regions 15.1, 15.11 in the lower region and the fifth and sixth
fastening regions
15.3, 15.33 in the upper region of the cage K1 is also possible. If the first
and second
fastening regions 15.1, 15.11 together with the fifth and sixth fastening
regions 15.3, 15.33
are located in the lower or upper region of the cage K1 the advantage resides
in the simple
construction of the cage K1. The force-introducing structure then
substantially consists of
a single beam.
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
8
Analogous arguments also apply to the third, fourth, seventh and eighth
fastening regions
15.2, 15.22, 15.4, 15.44, which are located either in common in the upper or
lower region
of the cage K2, as shown in Figs. 3A and 3C, or each in an upper region or
lower region
B2 of the cage K2, as shown in Fig. 2. If the seventh and eighth fastening
regions 15.4,
15.44 are located in the lower region B2 of the cage K2 and the third and
fourth fastening
regions 15.2, 15.22 in the upper region of the cage K2 the advantage resides
in the use of
shorter tensioning means strands SA, SB. In principle, a reverse arrangement
of the third
and fourth fastening regions 15.2, 15.22 in the lower region and the seventh
and eighth
fastening regions 15.4, 15.44 in the upper region of the cage K2 is also
possible. If the
seventh and eighth fastening regions 15.4, 15.44 together with the third and
fourth
fastening regions 15.2, 15.22 are located in the upper or lower region of the
cage K2 the
advantage resides in the simple construction of the cage K1. The force-
introducing
construction then substantially consists of a single beam.
The forms of positioning, which are shown in Figs. 2, 3A, 3B and 3C, of the
fastening
regions 15 are also analogously usable for the following examples of
embodiment shown
in Figs. 4 and 5. In addition, it will be clear to the expert that the
examples of embodiment
of Figs. 4 and 5 can similarly be equipped with an ASS system according Figs.
2, 3A, 3B,
3C.
Fig. 4 shows an example of embodiment similar to Fig. 1, in fact without the
shaft 11, but
with a different guidance of the support means strands TA and TB in order to
improve the
traction thereof or in order to ensure the traction thereof by a looping angle
of the support
means strands TA, TB around the drive pulleys of more than 900 and preferably
from 180
to 270 .
For this purpose, according to Fig. 4 the first support means strand TA runs
upwardly from
the first fastening point 15.1 to the lower lift cage K1 and around the
deflecting roller 14.1
and from there to the right to the first drive pulley 13.1. The first support
means strand TA
is then led in a first looping phase, as in the case of the arrangement
according to Fig. 1,
through 90 and subsequently through a further 90 around the first drive
pulley 13.1.
From there it passes to the left and thus back to the deflecting roller 14.1
and from this
again to the right to the first drive pulley 13.1, around which it is now
guided in a second
looping phase once more along at least 90 . The entire looping angle of the
first support
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
9
means strand TA around the first drive pulley 13.1, which according to Fig. 1
is 900, is
now, according to Fig. 4, 270 . Of that, 180 is apportioned to the first
looping phase and
90 to the second looping phase. From the first drive pulley 13.1 the first
support means
strand TA runs downwardly to the counterweight deflecting roller 12.1 and
subsequently
upwardly to the second drive pulley 13.2. The first support means strands TA
is then led
180 around the drive pulley 13.2 and finally passes to the third fastening
point 15.2 at the
upper lift cage K2.
The second support means strand TB runs from the second fastening point 15.11
at the
lower lift cage K1 around the first drive pulley 13.1, wherein its looping
angle around the
first drive pulley 13.1 is 180 . Going out from the first drive pulley 13.1
the second support
means strand TB runs, together with the first support means strand TA, to the
upper
counterweight deflecting roller 12.1 and from this upwardly to the second
drive pulley 13.2.
There the second support means strand TB is led in a first looping phase with
a looping
angle of 90 around the second drive pulley 13.2. From the second drive pulley
13.2 the
second support means strand TB then passes to the left to the deflecting
roller 14.2, where
it is deflected through 180 and is thus led back to the right to the second
drive pulley 13.2.
Here it is led in a second looping phase once more around the drive pulley
13.2 and, in
particular, this time with a looping angle of 180 . In addition, it is led
once again to the left
to the deflecting roller 14.2 and from this it finally goes downwardly to the
fourth fastening
point 15.22 of the upper lift cage K2. The entire looping angle of the second
support
means strand TB around the second drive pulley 13.2, which according to Fig. 1
is 90 , is
now, according to Fig. 4, 270 . Of that, 90 is apportioned to the first
looping phase and
180 to the second looping phase.
Fig. 5 shows a further form of embodiment of the new lift system 10 in which
similarly, as
according to Fig. 4, looping angles around the drive pulleys 13.1, 13.2 by
more than 90
are achieved, wherein this is shown in Fig. 5 merely with respect to the upper
lift cage K2
and the second drive pulley13.2. The upper lift cage K2, the counterweight 12
with the
upper counterweight deflecting roller 12.1, the deflecting roller 14.2, the
drive pulley 13.2
and those runs of the support means strands TA and TB which are disposed on
the one
hand between the fastening points 15.2 and 15.22 and the upper counterweight
deflecting
roller 12.1 are illustrated. The form of embodiment shown in Fig. 5 comprises
additional
deflecting rollers 14.3 and 14.4.
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
The first support means strand TA runs, going out from the third fastening
point 15.2,
upwardly to the deflecting roller 14.4 and further to the drive pulley 13.2,
along which it is
guided in a first looping phase through approximately 900. From there the
first support
means strand TA runs downwardly, around the deflecting roller 14.3 and back to
the drive
pulley 13.2, along which it is now led in a second looping phase through
approximately
1800. Overall, the support means TA thus encircles the drive pulley 13.2 by
270 . From
the drive pulley 13.2 the support means strand TA runs downwardly to the
counterweight
deflecting roller 12.1.
The second support means strand TB runs, going out from the fourth fastening
point 15.22
at the upper lift cage K2, upwardly to the deflecting roller 14.2 and further
to the drive
pulley 13.2, around which it is led in a first region phase through
approximately 90 . From
there the second support means strand TB runs downwardly, around the
deflecting roller
14.3 and further to the drive pulley 13.2, along which it is now led in the
second looping
phase through approximately 180 . Overall the support means strand TB thus
encircles
the drive pulley 13.2 by 270 . The second support means strand TB, together
with the first
support means strand TA, subsequently runs downwardly to the counterweight
deflecting
roller 12.1. The further course of the support means strands TA and TB is not
illustrated,
but is clearly evident to any expert from the above description.
Fig. 6 is an enlarged illustration of Fig. 1 B, in which details are shown
which do not appear
or are not clearly apparent in Fig. 1 B. Illustrated are, in particular, the
vertical centre plane
El, which is defined by the two longitudinal axes of the guide rails 19, and
the vertical
centre plane E2 oriented perpendicularly thereto. The two centre planes El and
E2
intersect at a vertical centre axis, which is visible in Fig 6 only as an
uppermost point X.
Not only the first fastening point 15.1, but also the second fastening point
15.11 at the
lower lift cage K1 are spaced from the first centre plane El and, in
particular, by paths sl
which are the same or at least approximately the same. The two fastening
points 15.1,
15.11 lie on opposite sides of the first centre plane El and the second centre
plane E2 in
order to achieve the balanced suspension of the lower lift cage K1. They are
preferably
arranged rotationally symmetrically or at least approximately rotationally
symmetrically with
respect to a point on the vertical centre axis. However, depending on the
respective
application a uniform spacing s1 in relation to the plane El suffices.
CA 02613937 2007-12-12
11
Equally, the third fastening point 15.2 and the fourth fastening point 15.22
at the upper lift
cage K2 are spaced from the first centre plane El and, in particular, by paths
s2 which are
the same or at least approximately the same. The two fastening points 15.2,
15.22 lie on
opposite sides of the first centre plane El and the second centre plane E2 and
in each
instance also on different sides of the two centre planes from the fastening
points 15.1 and
15.11. This arrangement also achieves a balanced suspension. They are
preferably
arranged rotationally symmetrically or at least approximately rotationally
symmetrically with
respect to the point X on the vertical centre axis. However, depending on the
respective
use a uniform spacing s2 with respect to the plane El suffices.
It is achieved by this special arrangement of the fastening points 15.1, 15.11
or 15.2, 15.22
that the lift cages K1 and K2 are suspended in balanced manner in such a way
that tipping
movements of the lift cages about horizontal tip axes, which lie in the
vertical centre plane
El, are largely prevented.
The first drive pulley 13.1 has a first axis Al and the second drive pulley
13.2 a second
axis A2. The deflecting roller 14.1 has a third axis A3 and the deflecting
roller 14.2 a
fourth axis A4.
The projections of the first axis Al and the second axis A2 intersect at a
point P on the first
centre plane El and include an angle W. This angle W preferably lies between
180
degrees and 90 degrees.
Due to the fact that the two cages K1, K2 are connected by way of common
support
means TA, TB with only one counterweight 12 and due to the special form of 1:1
suspension of the cages K1, K2 and the 2:1 suspension of the counterweight 12
different
speeds v1, v2 and v3 result according to the respective travel situation. If
the cage K1
moves upwardly at the speed v1 while the cage K2 is stationary the
counterweight 12 then
moves downwardly at v3 = v1/2. If the cage K2 moves downwardly at the speed v2
while
the cage K1 is stationary the counterweight 12 then moves upwardly at v3 =
v2/2. If the
cages K1, K2 move towards one another at the same speed v1 = v2 then v3 is
equal to
zero. If the cage K1 and the cage K2 move downwardly at the same speed v1 = v2
the
counterweight 12 then moves upwardly and v3 = v1 = v2.