Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent Application: | (11) CA 2615016 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | LASER GRAVITATIONAL FIELD FLUCTUATION DETECTOR |
| (54) French Title: | DETECTEUR LASER DE FLUCTUATIONS DU CHAMP GRAVITATIONNEL |
| Status: | Dead |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | NA |
| (74) Associate agent: | NA |
| (45) Issued: | |
| (22) Filed Date: | 2007-12-17 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 2009-06-17 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | None |
|---|
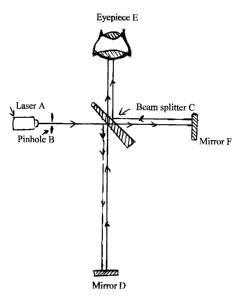
The Laser Gravitational Field Fluctuation Detector is designed to detect
gravitational
fluctuations in the Earth's gravitational field as for example when the Earth
is influenced
by the Sun or Moon's gravitation field which results in ocean tides. This
detection is
accomplished by measuring the deviation of two light beams from their normal
paths in
reference to each other when subjected to a gravitational field, due to the
fact that a
perpendicular beam is affected differently than a parallel beam. Both beams
having been
created from a single beam by means of a narrow angle glass prism beam
splitter are
affected each differently by the gravitational field. Fluctuation detection is
accomplished
by recombining both beams by means of two mirrors and the beam splitter in
order to
produce a bull`s eye type of interference pattern which can be viewed through
the eyepiece
and also recorded through the eyepiece by a camera or photocell.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Administrative Status , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Title | Date |
|---|---|
| Forecasted Issue Date | Unavailable |
| (22) Filed | 2007-12-17 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection | 2009-06-17 |
| Dead Application | 2013-12-17 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2012-12-17 | FAILURE TO REQUEST EXAMINATION | |
| 2012-12-17 | FAILURE TO PAY APPLICATION MAINTENANCE FEE |
| Fee Type | Anniversary Year | Due Date | Amount Paid | Paid Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $200.00 | 2007-12-17 | ||
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 2 | 2009-12-17 | $50.00 | 2009-12-14 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 3 | 2010-12-17 | $50.00 | 2010-10-04 |
| Maintenance Fee - Application - New Act | 4 | 2011-12-19 | $50.00 | 2011-10-18 |
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| ERDMANN, ERICH |
| ERDMANN, ADOLT |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| None |