Some of the information on this Web page has been provided by external sources. The Government of Canada is not responsible for the accuracy, reliability or currency of the information supplied by external sources. Users wishing to rely upon this information should consult directly with the source of the information. Content provided by external sources is not subject to official languages, privacy and accessibility requirements.
Any discrepancies in the text and image of the Claims and Abstract are due to differing posting times. Text of the Claims and Abstract are posted:
| (12) Patent: | (11) CA 2619915 |
|---|---|
| (54) English Title: | TWO STROKE ENGINE WITH REGULAR LUBRICATION SYSTEM |
| (54) French Title: | MOTEUR A DEUX TEMPS AVEC SYSTEME DE LUBRIFICATION ORDINAIRE |
| Status: | Granted and Issued |
| (51) International Patent Classification (IPC): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventors : |
|
| (73) Owners : |
|
| (71) Applicants : |
|
| (74) Agent: | |
| (74) Associate agent: | |
| (45) Issued: | 2017-11-28 |
| (22) Filed Date: | 2008-02-14 |
| (41) Open to Public Inspection: | 2009-08-14 |
| Examination requested: | 2013-02-05 |
| Availability of licence: | N/A |
| Dedicated to the Public: | N/A |
| (25) Language of filing: | English |
| Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT): | No |
|---|
| (30) Application Priority Data: | None |
|---|
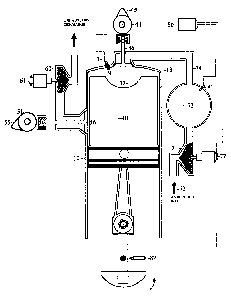
The invention is a two-stroke engine that incorporates advantages of both the
two-stroke and
four-stroke types of engines. The crankcase is sealed and uses an oil pump to
lubricate the
piston, connecting rod and crankshaft. The combustion air does not flow
through the crankcase.
Instead, the engine uses two camshafts, one for the intake valve located on
the cylinder head and
the other for the exhaust valve located on the side of the cylinder. The
engine has a compressor,
powered by the engine battery to compress ambient air before it enters into
the combustion
chamber. Additionally, the engine has an exhaust powered turbine connected to
an alternator,
which provides additional power for the engine battery. The engine is equipped
with one or
plurality of fuel-injection nozzles. The piston is of the two step type, which
reduces friction
between the piston and the cylinder.
Linvention concerne un moteur à deux temps qui comporte des avantages des types de moteurs à deux temps et à quatre temps. Le carter de moteur est scellé et utilise une pompe à huile pour lubrifier le piston, une tige de raccordement et un carter de moteur. Lair de combustion ne sécoule pas à travers le carter de moteur. Au lieu de cela, le moteur utilise deux arbres à cames, un pour la soupape dadmission située sur la tête de cylindre et lautre pour la soupape déchappement située sur le côté du cylindre. Le moteur possède un compresseur, alimenté par la batterie du moteur pour compresser lair ambiant avant quil entre dans la chambre à combustion. En outre, le moteur possède une turbine alimentée par léchappement connectée à un alternateur, laquelle offre une alimentation supplémentaire pour la batterie du moteur. Le moteur est doté dun ou dune pluralité dinjecteurs de carburant. Le piston est du type à deux temps, ce qui réduit la friction entre le piston et le cylindre.
Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
2024-08-01:As part of the Next Generation Patents (NGP) transition, the Canadian Patents Database (CPD) now contains a more detailed Event History, which replicates the Event Log of our new back-office solution.
Please note that "Inactive:" events refers to events no longer in use in our new back-office solution.
For a clearer understanding of the status of the application/patent presented on this page, the site Disclaimer , as well as the definitions for Patent , Event History , Maintenance Fee and Payment History should be consulted.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Common Representative Appointed | 2019-10-30 |
| Common Representative Appointed | 2019-10-30 |
| Grant by Issuance | 2017-11-28 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2017-11-27 |
| Inactive: Final fee received | 2017-10-13 |
| Pre-grant | 2017-10-13 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2017-06-23 |
| Letter Sent | 2017-06-23 |
| 4 | 2017-06-23 |
| Notice of Allowance is Issued | 2017-06-23 |
| Inactive: Q2 passed | 2017-06-19 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 2017-06-19 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2017-06-05 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2017-03-20 |
| Inactive: Report - QC passed | 2017-03-17 |
| Withdraw from Allowance | 2017-03-08 |
| Inactive: Adhoc Request Documented | 2017-03-07 |
| Inactive: Approved for allowance (AFA) | 2017-03-06 |
| Inactive: Q2 passed | 2017-03-06 |
| Small Entity Declaration Request Received | 2017-02-09 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2017-02-08 |
| Inactive: Adhoc Request Documented | 2016-11-07 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2016-11-07 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2016-10-05 |
| Inactive: Q2 failed | 2016-09-29 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2016-05-13 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2016-05-13 |
| Letter Sent | 2016-05-13 |
| Reinstatement Request Received | 2016-04-20 |
| Reinstatement Requirements Deemed Compliant for All Abandonment Reasons | 2016-04-20 |
| Maintenance Request Received | 2016-03-24 |
| Inactive: Reversal of dead status | 2016-03-17 |
| Inactive: Delete abandonment | 2016-03-17 |
| Deemed Abandoned - Failure to Respond to Maintenance Fee Notice | 2016-02-15 |
| Inactive: Dead - No reply to Office letter | 2015-06-19 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2014-11-27 |
| Change of Address Requirements Determined Compliant | 2014-11-27 |
| Change of Address or Method of Correspondence Request Received | 2014-11-17 |
| Inactive: Abandoned - No reply to Office letter | 2014-06-19 |
| Inactive: Correction to amendment | 2014-03-19 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2014-02-17 |
| Inactive: Adhoc Request Documented | 2014-02-17 |
| Inactive: S.30(2) Rules - Examiner requisition | 2013-08-19 |
| Letter Sent | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive: PPH closed to application | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive: Adhoc Request Documented | 2013-02-11 |
| Change of Address or Method of Correspondence Request Received | 2013-02-05 |
| Request for Examination Requirements Determined Compliant | 2013-02-05 |
| All Requirements for Examination Determined Compliant | 2013-02-05 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2013-02-05 |
| Advanced Examination Requested - PPH | 2013-02-05 |
| Request for Examination Received | 2013-02-05 |
| Maintenance Request Received | 2013-02-05 |
| Application Published (Open to Public Inspection) | 2009-08-14 |
| Inactive: Cover page published | 2009-08-13 |
| Amendment Received - Voluntary Amendment | 2009-05-08 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive: First IPC assigned | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive: IPC assigned | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - No RFE (English) | 2008-03-11 |
| Inactive: Office letter | 2008-03-11 |
| Correct Inventor Requirements Determined Compliant | 2008-03-11 |
| Inactive: Filing certificate - No RFE (English) | 2008-03-07 |
| Application Received - Regular National | 2008-03-07 |
| Small Entity Declaration Determined Compliant | 2008-02-14 |
| Abandonment Date | Reason | Reinstatement Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-04-20 | ||
| 2016-02-15 |
The last payment was received on 2017-02-09
Note : If the full payment has not been received on or before the date indicated, a further fee may be required which may be one of the following
Patent fees are adjusted on the 1st of January every year. The amounts above are the current amounts if received by December 31 of the current year.
Please refer to the CIPO
Patent Fees
web page to see all current fee amounts.
Note: Records showing the ownership history in alphabetical order.
| Current Owners on Record |
|---|
| SRDJAN PEROVIC |
| Past Owners on Record |
|---|
| None |