Une partie des informations de ce site Web a été fournie par des sources externes. Le gouvernement du Canada n'assume aucune responsabilité concernant la précision, l'actualité ou la fiabilité des informations fournies par les sources externes. Les utilisateurs qui désirent employer cette information devraient consulter directement la source des informations. Le contenu fourni par les sources externes n'est pas assujetti aux exigences sur les langues officielles, la protection des renseignements personnels et l'accessibilité.
L'apparition de différences dans le texte et l'image des Revendications et de l'Abrégé dépend du moment auquel le document est publié. Les textes des Revendications et de l'Abrégé sont affichés :
| (12) Brevet: | (11) CA 2619915 |
|---|---|
| (54) Titre français: | MOTEUR A DEUX TEMPS AVEC SYSTEME DE LUBRIFICATION ORDINAIRE |
| (54) Titre anglais: | TWO STROKE ENGINE WITH REGULAR LUBRICATION SYSTEM |
| Statut: | Accordé et délivré |
| (51) Classification internationale des brevets (CIB): |
|
|---|---|
| (72) Inventeurs : |
|
| (73) Titulaires : |
|
| (71) Demandeurs : |
|
| (74) Agent: | |
| (74) Co-agent: | |
| (45) Délivré: | 2017-11-28 |
| (22) Date de dépôt: | 2008-02-14 |
| (41) Mise à la disponibilité du public: | 2009-08-14 |
| Requête d'examen: | 2013-02-05 |
| Licence disponible: | S.O. |
| Cédé au domaine public: | S.O. |
| (25) Langue des documents déposés: | Anglais |
| Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT): | Non |
|---|
| (30) Données de priorité de la demande: | S.O. |
|---|
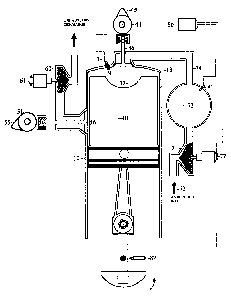
Linvention concerne un moteur à deux temps qui comporte des avantages des types de moteurs à deux temps et à quatre temps. Le carter de moteur est scellé et utilise une pompe à huile pour lubrifier le piston, une tige de raccordement et un carter de moteur. Lair de combustion ne sécoule pas à travers le carter de moteur. Au lieu de cela, le moteur utilise deux arbres à cames, un pour la soupape dadmission située sur la tête de cylindre et lautre pour la soupape déchappement située sur le côté du cylindre. Le moteur possède un compresseur, alimenté par la batterie du moteur pour compresser lair ambiant avant quil entre dans la chambre à combustion. En outre, le moteur possède une turbine alimentée par léchappement connectée à un alternateur, laquelle offre une alimentation supplémentaire pour la batterie du moteur. Le moteur est doté dun ou dune pluralité dinjecteurs de carburant. Le piston est du type à deux temps, ce qui réduit la friction entre le piston et le cylindre.
The invention is a two-stroke engine that incorporates advantages of both the
two-stroke and
four-stroke types of engines. The crankcase is sealed and uses an oil pump to
lubricate the
piston, connecting rod and crankshaft. The combustion air does not flow
through the crankcase.
Instead, the engine uses two camshafts, one for the intake valve located on
the cylinder head and
the other for the exhaust valve located on the side of the cylinder. The
engine has a compressor,
powered by the engine battery to compress ambient air before it enters into
the combustion
chamber. Additionally, the engine has an exhaust powered turbine connected to
an alternator,
which provides additional power for the engine battery. The engine is equipped
with one or
plurality of fuel-injection nozzles. The piston is of the two step type, which
reduces friction
between the piston and the cylinder.
Note : Les revendications sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
Note : Les descriptions sont présentées dans la langue officielle dans laquelle elles ont été soumises.
2024-08-01 : Dans le cadre de la transition vers les Brevets de nouvelle génération (BNG), la base de données sur les brevets canadiens (BDBC) contient désormais un Historique d'événement plus détaillé, qui reproduit le Journal des événements de notre nouvelle solution interne.
Veuillez noter que les événements débutant par « Inactive : » se réfèrent à des événements qui ne sont plus utilisés dans notre nouvelle solution interne.
Pour une meilleure compréhension de l'état de la demande ou brevet qui figure sur cette page, la rubrique Mise en garde , et les descriptions de Brevet , Historique d'événement , Taxes périodiques et Historique des paiements devraient être consultées.
| Description | Date |
|---|---|
| Représentant commun nommé | 2019-10-30 |
| Représentant commun nommé | 2019-10-30 |
| Accordé par délivrance | 2017-11-28 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2017-11-27 |
| Inactive : Taxe finale reçue | 2017-10-13 |
| Préoctroi | 2017-10-13 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2017-06-23 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2017-06-23 |
| month | 2017-06-23 |
| Un avis d'acceptation est envoyé | 2017-06-23 |
| Inactive : Q2 réussi | 2017-06-19 |
| Inactive : Approuvée aux fins d'acceptation (AFA) | 2017-06-19 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2017-06-05 |
| Inactive : Dem. de l'examinateur par.30(2) Règles | 2017-03-20 |
| Inactive : Rapport - CQ réussi | 2017-03-17 |
| Retirer de l'acceptation | 2017-03-08 |
| Inactive : Demande ad hoc documentée | 2017-03-07 |
| Inactive : Approuvée aux fins d'acceptation (AFA) | 2017-03-06 |
| Inactive : Q2 réussi | 2017-03-06 |
| Requête visant une déclaration du statut de petite entité reçue | 2017-02-09 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2017-02-08 |
| Inactive : Demande ad hoc documentée | 2016-11-07 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2016-11-07 |
| Inactive : Dem. de l'examinateur par.30(2) Règles | 2016-10-05 |
| Inactive : Q2 échoué | 2016-09-29 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2016-05-13 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2016-05-13 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2016-05-13 |
| Requête en rétablissement reçue | 2016-04-20 |
| Exigences de rétablissement - réputé conforme pour tous les motifs d'abandon | 2016-04-20 |
| Requête visant le maintien en état reçue | 2016-03-24 |
| Inactive : Renversement de l'état mort | 2016-03-17 |
| Inactive : Supprimer l'abandon | 2016-03-17 |
| Réputée abandonnée - omission de répondre à un avis sur les taxes pour le maintien en état | 2016-02-15 |
| Inactive : Morte - Aucune rép. à lettre officielle | 2015-06-19 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2014-11-27 |
| Exigences pour le changement d'adresse - jugé conforme | 2014-11-27 |
| Requête pour le changement d'adresse ou de mode de correspondance reçue | 2014-11-17 |
| Inactive : Abandon. - Aucune rép. à lettre officielle | 2014-06-19 |
| Inactive : Correction à la modification | 2014-03-19 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2014-02-17 |
| Inactive : Demande ad hoc documentée | 2014-02-17 |
| Inactive : Dem. de l'examinateur par.30(2) Règles | 2013-08-19 |
| Lettre envoyée | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive : PPH fermé pour cette demande | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2013-02-11 |
| Inactive : Demande ad hoc documentée | 2013-02-11 |
| Requête pour le changement d'adresse ou de mode de correspondance reçue | 2013-02-05 |
| Exigences pour une requête d'examen - jugée conforme | 2013-02-05 |
| Toutes les exigences pour l'examen - jugée conforme | 2013-02-05 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2013-02-05 |
| Avancement de l'examen demandé - PPH | 2013-02-05 |
| Requête d'examen reçue | 2013-02-05 |
| Requête visant le maintien en état reçue | 2013-02-05 |
| Demande publiée (accessible au public) | 2009-08-14 |
| Inactive : Page couverture publiée | 2009-08-13 |
| Modification reçue - modification volontaire | 2009-05-08 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive : CIB en 1re position | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive : CIB attribuée | 2008-05-13 |
| Inactive : Certificat de dépôt - Sans RE (Anglais) | 2008-03-11 |
| Inactive : Lettre officielle | 2008-03-11 |
| Exigences relatives à une correction d'un inventeur - jugée conforme | 2008-03-11 |
| Inactive : Certificat de dépôt - Sans RE (Anglais) | 2008-03-07 |
| Demande reçue - nationale ordinaire | 2008-03-07 |
| Déclaration du statut de petite entité jugée conforme | 2008-02-14 |
| Date d'abandonnement | Raison | Date de rétablissement |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-04-20 | ||
| 2016-02-15 |
Le dernier paiement a été reçu le 2017-02-09
Avis : Si le paiement en totalité n'a pas été reçu au plus tard à la date indiquée, une taxe supplémentaire peut être imposée, soit une des taxes suivantes :
Les taxes sur les brevets sont ajustées au 1er janvier de chaque année. Les montants ci-dessus sont les montants actuels s'ils sont reçus au plus tard le 31 décembre de l'année en cours.
Veuillez vous référer à la page web des
taxes sur les brevets
de l'OPIC pour voir tous les montants actuels des taxes.
Les titulaires actuels et antérieures au dossier sont affichés en ordre alphabétique.
| Titulaires actuels au dossier |
|---|
| SRDJAN PEROVIC |
| Titulaires antérieures au dossier |
|---|
| S.O. |