Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
Building supporting framework, in particular high structure supporting
framework
The invention relates to a building supporting framework, in particular a high
structure supporting framework according to the preamble of claim 1.
In principle, every building contains a supporting framework consisting of a
number
of vertical supports and a number of horizontal beams, running at right angles
to each
other in XY-directions, which are arranged in several superimposed planes. The
buildings are also individually fitted with electrical installations, water
pipes, air
conditioning systems and/or ventilation conduits etc., the fluid-transporting
conduits
being passed through shafts or building walls. Later conversions or refits are
normally associated with considerable conversion expense.
The present invention is based on the problem of creating a supporting
framework for
a building, especially for a design with multiple floors, which simplifies the
equipment of the building with fluid-transporting conduits and also enables
simple
refitting.
This problem is solved according to the invention by a supporting framework
with the
features of claim 1.
Further preferred embodiments of the inventive supporting framework form the
subject matter of the dependent claims.
The supporting framework according to the invention with integrated fluid
conduits
which can be passed in all three spatial and/or framework dimensions through
the
supporting framework, allows for a modular construction of buildings, which
can not
only be equipped in simple fashion, but can also be refitted at any time, for
example
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
-2-
for office, commercial, clinical practice, training, hotel or residential
purposes, thus
guaranteeing a broad neutrality of use and that long-term projects can be
designed.
The supply of fluids can be expanded, refitted or scaled back, and also
optimised in
terms of energy, at any time.
The invention will next be explained in more detail with the aid of the
drawings,
which show:
Fig. I an embodiment of a supporting framework for a building;
Fig. 2 in perspectival view, an intersection of the supporting framework
according to
the invention, with a vertical support, with horizontal beams, with a ceiling
construction and with fluid-transporting conduits;
Fig. 3 a horizontal section through the vertical support according to Fig. 2
above the
beams;
Fig. 4 a section along line IV-IV in Fig. 3;
Fig. 5 a section along line V-V in Fig. 3;
Fig. 6 a vertical section through the intersection according to Fig. 2,
through one of
the horizontal beams;
Fig. 7 a horizontal section through the intersection according to Fig. 2,
through both
horizontal beams; and
Fig. 8 a building section with a fluid-transporting supporting framework in
top view.
In Fig. 1 a supporting framework I for a building is shown which comprises a
number
of vertical supports 2 and a number of horizontal beams 3, 4 running at right
angles to
each other in XY-directions. The horizontal beams 3, 4 are arranged in several
levels
superimposed on each other.
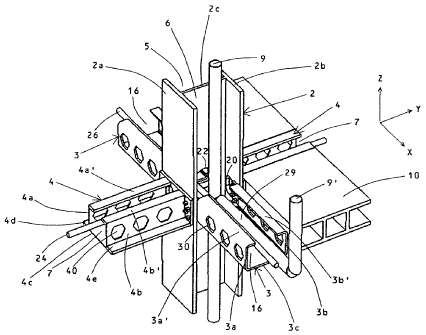
Fig. 2 shows an intersection of the supporting framework I according to the
invention
in which two beams 3 running horizontally in the X-direction and two beams 4
running horizontally in the Y-direction are attached to a vertical support 2
running in
direction Z, i.e. vertically. Obviously, only three horizontal beams 3 and 4
could be
fastened to the outer vertical supports 2 of the supporting framework 1 per
level and,
in the corner area, even just two beams 3, 4. In the embodiment shown, short
beams
also project out from the outer vertical supports 2 and/or from the corner
supports,
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
-3-
which can serve, for example, to attach lateral coverings, fa~ades, insulation
etc.
These may, however, also be omitted.
Both the vertical supports 2 as well as the beams 3, 4 are e.g. embodied as
profiles
made of metal (preferably steel) or from other suitable materials, which are
e.g.
welded together from sheets of metal, and which each at least partially
enclose at least
one cavity, which are provided according to the invention to receive fluid-
transporting
conduits, in particular electricity, water, waste water, networking,
ventilation and/or
other conduits. As can be seen in particular from Figs. 2 and 3, for example
the
vertical support 2 is embodied as a profile with an H-shaped cross-section
and, in said
H-shaped example, has two side walls 2a, 2b and a central wall 2c connecting
the side
walls 2a, 2b, as the result of which two vertical cavities 5, 6 are formed,
separated
from each other by the central wall 2c, but connected to each other as
necessary by
openings. Fluid-transporting conduits, e.g. water pipes, can be passed through
the
cavities 5, 6, in direction Z, as shown in Fig. 2 and 3 using the example of
the conduit
9 passed through the cavity 6. The vertical support 2 could also be produced
with a
cross-section made from different profiles, open or closed.
A supporting framework 4 running in Y direction is fastened on each of the
side walls
2a, 2b of the vertical support 2, preferably being screwed on or otherwise
suitably
joined, which in cross-section essentially contains a U-shaped space and has
two webs
4a, 4b and a flange 4c connecting the webs 4a, 4b, and encloses the cavity 7
which is
accessible from above and if necessary also from below (cf. Fig. 2 and 4). The
respective beam 4 is also provided with a pair of upper supporting surfaces
4a', 4b',
which point inwards toward each other from the profile webs 4a, 4b, and also
with a
pair of lower supporting surfaces 4d, 4e formed by flanges, which are directed
outwards as extension of the bottom flanges 4c connecting the webs 4a, 4b. The
supporting surfaces 4a', 4b'; 4d, 4e are used as a rest for a ceiling
construction 10 (cf.
Fig. 2 and 4). According to Fig. 4, a floor construction 11 can be laid on the
ceiling
construction 10, which has frames 12, via which the cavity 7 can be accessed
from
above, the frames 12 being closable by covers 13. The configuration of the
beam 4
can similarly also be formed by asymmetrical double-T beams or other suitable
profiles.
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
-4-
The horizontal beams 3 running in direction X are attached from within onto
the side
walls 2a, 2b of the vertical support 2. These beams 3, too, are embodied in
cross-
section to enclose an essentially U-shaped space and have two webs 3a, 3b and
a
bottom flange part 3c connecting the webs 3a, 3b, which together enclose a
cavity 16
(cf. Fig. 2 and 5). The webs 3a, 3b in turn are provided with inward-
projecting upper
supporting surfaces 3a', 3b' on which the ceiling or floor construction 12 can
be
placed. The configuration of the beam 3 can also similarly be embodied by
double-T
beams or other suitable profiles.
The cavities 7 and 16 respectively of the horizontal beams 4 and 3 are
provided to
receive fluid-transporting conduits, where according to the invention these
cavities 7,
16 are connected with each other and with the cavities 5, 6 of the vertical
supports in
such a way that the conduits can be passed in all three spatial or supporting
framework dimensions X, Y, Z through the supporting framework 1. So, for
example,
the side walls 2a, 2b of the vertical support 2 are provided with through-
openings 20
at intersections which can be seen especially clearly from Fig. 4, 6 and 7,
via which
the cavities 7 of the beam 4 oriented in Y-direction are connected to the
vertical
cavities 5, 6 in the vertical support 2. The cavities 16 of the beam 3 running
in X-
direction also open out into the vertical cavities 5, 6 in the intersections.
These
cavities 16 are in turn connected to each other via one or more through-
openings 22
made in the central wall 2c of the vertical support 2 (Fig. 2, 5 and 7).
Thus, for example, a fluid-transporting conduit 26 can be passed via the
through-
opening 22 in X-direction (transversely through the vertical cavities 5, 6)
from one
beam 3 to the other. A fluid-transporting conduit 24 passed transversely
thereto in Y-
direction is, for example, passed through one of the through-openings 20 in
the side
walls 2a, 2b of the vertical support 2 (transversely through the vertical
cavity 5).
Similarly, bifurcation in all three directions X, Y, Z is possible.
At intersections, for example, the fluid-transporting conduit 9 passed through
the
vertical cavity 6 can branch off and the fluid can, for example, go via a
conduit 29
passed through the cavity 16 which runs in X-direction to a further vertical
conduit 9'
leading out of the beam 3, which is open at the top, to a terminal unit.
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
-5-
The webs 3a, 3b and 4a, 4b of the horizontal beam 3, 4 with the space-
enclosing
cross-section are advantageously provided with a number of through-openings 30
and
40, preferably evenly distributed over the beam length, for fluid-transporting
conduits,
which connect the horizontally running cavities 16, 7 with the ceiling
construction 10.
The cavities 5, 6 of the vertical support 2 can be closed off outside the
intersection
with covers 41, 42 (Fig. 3). This applies similarly for openings in closed
vertical
support profiles. Equally, a cover partially or wholly enclosing the vertical
support
may be given larger dimensions than necessary for the cross-section of the
vertical
support, e.g. to enlarge the cavity for the benefit of the fluid-transporting
conduits.
Fig. 8 shows a sample application of the fluid-transporting supporting
framework,
with six intersections, as described above. An installation space 45 for
fluids such as
water, electricity or waste water is arranged above a beam 3 running in X-
direction to
supply, on the one side, a bathroom 46 with a washstand 47, a WC 48, a bathtub
49,
and on the other side a kitchen 50 with a cooker 51 and a sink 52. The supply
comes
via the fluid-transporting conduits 9, 24, 26, which are passed through the
supporting
framework to the installation space 45 and from this to the terminal units.
The
embodiment should be understood as applicable to every type of technical
building
installation.
The supporting framework according to the invention with the integrated fluid-
transporting conduits, which can be passed through the supporting framework in
all
three spatial or supporting framework dimensions, enables the construction of
buildings which are not only easy to equip but can also be refitted at any
time, for
example for office, commercial, clinical practice, training, hotel or
residential
purposes, thus guaranteeing a broad neutrality of use and that long-term
projects can
be designed. The supply of fluids can be expanded, refitted or scaled back,
and also
optimised in terms of energy, at any time.
CA 02621710 2008-03-07
-6-
The invention is sufficiently disclosed by the explanations clarified above.
Obviously
it could also be embodied in further variants. So, for example, the beams and
vertical
supports could be produced with closed cross-sectional formats or other
suitable
profiles. In principle, fibre-reinforced synthetics, such as carbon, could
also serve as
materials for the profiles.