Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
11
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
INFLATABLE STRUCTURE FOR COVERING SPORT UTiLITY VEHICLES, BOATS
AND THE LIKE
Cross Reference to Related Application
This. application claims priority from United States Provisional Patent
Application No. 60/907,425 filed April 2, 2007 entitled Inflatable Structure
for Covering
Sport Utility Vehicles, Boats and the Like.
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to the field of inflatable structures including tents
and in
particular to an inflatable structure useful as an event venue, portable
temporary shelter, or for
covering from the elements mid to large sized vehicles including vehicles,
boats and the like.
Background of the Invention
Inflatable tents for use in camping are knowm in the prior art and are sold
commercially by for example Airzone Recreation Products of Kelowna, British
Columbia,
Canada. Such tents typically replicate camping tents available c,ommercially
which rely on
bent fibreglass poles for their support structure and instead substitute
inflatable poles which,
when bent, provide the supporting framework for the exterior fabric skin or
canopy of the tent
over which a so-called fly sheet may be mounted. In the other extreme, large
tents are known
in the prior art for use such as by the military for providing field
barra.aks, field hospitals and
various depot facilities, such tents often being made of canvas and supported
on tubular metal-
pole supporting structures.
Appticant believes that a commercial need exists for relatively large
pneumatically inflatable tent-like. structures which are larger than
conventional recreational
I
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
camping tents and smaller than military-style field tents. It is believed that
such structures will
find commercial acceptance and use by the owners of large for exam.ple sport
utility vehicles,
boats, trailers, and other wheeled vehicles or towables which ordinarily would
require a large
garage or shed for their safe storage and which are often not housed in, for
example,
conventional residential homes as not having extended. garage facilities. Also
applicant
believes that commercial acceptance and use of such larger pneumatically
inflatable tent-like
structures may include those in the field of portable corporate sponsorship
pavilions for
example for use in trade-shows, portable pneumatically inflatable recreational
and professional
sports shelters for sheltering equipment, non-engaged players, or sickly or
wounded players on
for example the side-lines of a sports field.
What is required, is a relatively larger pneumatically inflatable structure
which
may be readily transportable in that, when collapsed, the structure is not
exceedingly heavy or
overly bulky so the structure may be transported in for example the
aforementioned sport
utility vehicles, in mini-vans, or in the beds of pickup trucks and the like,
and for example may
be carried by two adult males to a convenient location for their use, and
wherein the structure
may be erected using for exarnple a high volume, low pressure air compressor
running for
example from the twelve volt power source of the vehicle used to transport the
collapsed
structure.
In the prior art applicant is aware of the following issued patents
illustrating
aspects of the state of the art in pneumatically erectable structures
including tents:
United States Patent No. 2591829 which issued. April 1952 to Katzenmeyer et
al.; United States Patent No. 2830606 which issued April 1958 to Daugherty;
United States
Patent No. 3145719 which issued August 1964 to Johnson; United States Patent
No. 3899853
which issued August 1975 to Wertman; United States Patent No. 3999333 which
issued
December 1976 to Amarantos; United States Patent No. 4068418 which issued
January 1978
to Masse; United States Patent No. 4197681 which issued April 1980 to
Holcombe; United
2
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
States Patent No. 4271642 which issued June 1981 to Karr; United States Patent
No.
4709718 which issued December 1987 to Nichols; United States Patent No.
4766918 which
issued August 1988 to Odekirk; United States Patent No. 4819389 which issued
April 1989 to
Kihn; United States Patent No. 4825892 which issued May 1989 to Norman; United
States
Patent No. 4876829 which issued October 1989 to Mattick; United States- Patent
No.
4901481 which issued February 1990 to Seeley, Jr.; United States Patent No.
4918877 which
issued April 1990 to Dutka; United States Patent No. 5005322 which issued
April 1991 to
Mattick et ai.; United States Patent No. 5007212 which issued April 1991 to
Fritts et aL;
United States Patent No. 5122400 which issued June 1992 to Stewart; United
States Patent
No. 5205086 which issued April 1993 to Heim; United States Patent No. 5247768
which
issued September 1993 to Russo; United States Patent No. 5421128 which issued
June 1995
to Shapless et al.; United States Patent No. 5570544 which issued November
1996 to Hale et
al.; United States Patent No. 5636478 which issued June 1997 to Chen; United
States Patent
No. 5987822 which issued November 1999 to McNiff et al.; United States Patent
No.
6014982 which issued January 2000 to Strevey; and United States Patent No.
6,263,617 which
issued July 2001 to Turcot.
Summary of the Invention
According to a first embodiment of the present invention there is provided a
pneumatically inflatable structure comprising first and second parallel spaced
apart pneumatic
end support tubes and at least two opposed pairs of bowed criss-crossed
pneumatic bracing
tubes and an arched canopy extending over the support tubes and bracing tubes.
Each of the
end support tubes has first and second opposed ends each mountable to a base
surface wherein
each of the end support tubes forms a vertical arch having an apex when the
structure is erect.
The pneumatic bracing tubes have first and second ends wherein each of the
first ends of the
bracing tubes are secured to one of the first or second ends of one of the
first or second end
support tubes. Each of the second ends of the pneumatic bracing tubes are
securable the apex
of an opposed of the Srst or second end support tubes.
3
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
The array of the pneumatically inflatable structure may comprise two end
suppoit
tubes and the two opposed pairs of bracing tubes may be mounted thereto and
extend
therebetween. The array may fiirther cemprise at least one intermediate
support tube forrning a
vertical arch between and in parallel to the end support tubes at a location
where one of the at
least one intermediate support tubes intersects a junction of the bracing
tubes where the bracing
tubes criss-cross. The support tubes and bracing tubes may have equal length.
The support tubes
and the bracing tnbes may be substantially identical.
The canopy may be secured to the support tubes and the bracing tubes for
example either over the top of the tubes, or under the tubes, that is the
tubes thereby forming an
exoskeleton, or as a webbing between the tubes. The pneumatically inflatable
structure may
further comprise securing means such as various fasteners for securing the
ends of the support
tubes to the base surface. The securing means may comprise a flexible or
hinged fastener, and
may also include a ground spike. The base surface may merely be the ground
surface or may
include a planar sheet, strapping, etc.
The pneumatically inflatable structure may further comprise at least two
opposed
pairs of bowed criss-crossed pneumatic bracing tubes lengthwise connected to
each other. The
support tubes and bracing tubes may advantageously be pneumaticaZly
interconnected by a
flexible air conduit extending therebetween so that the entire structure may
be inflated
simultaneously from a single source of pressurized air.
The support tubes and bracing tubes may comprise inner resilient tubes snugly
mountable within outer non-resilient straight sleeves in snugly journalled
relation therethrough.
Each sleeve of the outer non-resilient straight sleeves may have a seam
extending linearly along
its length. Each seam may be an overlapped seam having an overlapped portion
within the sleeve
due to inversion of the sleeve following forming of the seam wherein the
overlapped portion is
formed of the longitudinal edges of material forming the sleeve. The
overlapped portion may be
4
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
folded over so as to be disposed perpendicnlar to a curvature of the seam when
the support tubes
and bracing tubes become curved as they are inflated, being constrained at
their ends where
mounted to the base surface.
The support tubes and braeing tubes may be self sealing by self-sealing means
at
ends of support tubes and the bracing tubes. The self-sealing means may
comprise ends of the
inner resilient tubes which are folded over onto themselves wherein the ends
of the tubes are
anchored by anchoring means to the ends of the first and second supports. The
ends of the first
and second supports may each be formed as a flap hinge when the ends are
mounted to the tent
canopy.
The inner resilient tubes may be adapted, when mounted in the sleeves, to
contain
air pressurized up to between 8 to 12 pounds per square inch.
The pneumatically inflatable stracture may fnrther comprise a canopy vestibule
extending from an opening aperture into the pneumatically inflatable
structure.
Other aspects and features of the present invention will become apparent to
those
ordinarily skilled in the art upon review of the following description of
specific embodiments of
the invention in conjunction with the accompanying figures.
Brief Deserip-tion of the Drawings
In drawings which illustrate embodiments of the invention wherein similar
characters of reference denote corresponding parts in each view,
Figm-e 1 is a perspective view of a pneumatically inflatable structure
according to
a first embodiment of the invention.
5
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
Figure 2 is a perspective view of the pneumatically inflatable struchire of
Figure 1
with the canopy removed.
Figure 3a is a side elevation view of the pneumatically inflatable structure
of
Figure 2.
Figure 3b is a plan view of the pnemnatically inflatable structure of Figure
3a,
Figure 4 is a bottom plan view of the canopy of the inflatable structure of
Figure
1.
Figure 5 is a perspective view of a pneumatically inflatable structtm
according
to an alternative embodiment of the invention having an end vesti"bu1e.
Figure 6 is a perspective view of a pneumatically inflatable structure
according
to an alterna.tive embodiment having increased dimensions.
Figure 7 is a detailed view of the flexible end flaps of the pneumatic tubes
according to the present invention.
6
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
Detailed Descrintion of Embodiments of the Invention
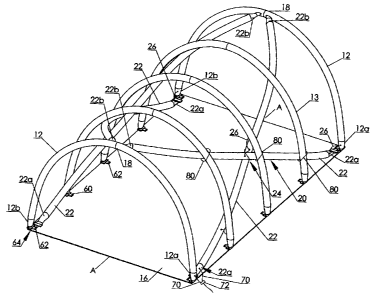
Referring to Figures 1-4, a pneumatically inflatable structure according to a
first embodiment of the invention is shown generally at 10. The pneumatically
inflatable
structure 10 includes two parallel spaced apart pneumatic end support tubes 12
and two
opposed pairs 20 of bowed and criss-crossed pneumatic bracing tubes 22 covered
by a canopy
30. ln one embodiment of the invention, end support tubes 12 and bracing tubes
22 are
substantially identical as better described below. The pneumatically
inflatable structure 10
may also include a base surface such as base sheet 16.
The pneumatic end support tubes 12 include ends 12a secured to base sheet 16
or to the ground and are bowed when inflated so as to have an apex 18 be also
downwardly
concave. The pneumatic support tubes 12 are arranged in parallel to each other
so as to define
a common opening 8 thereunder sized for mid to large sized vehicles including
vehicles, boats
and the like. The pneumatically inflatable structure 10 may also include one
or more
intermediate support tube 13 secured to the base sheet or ground which are
oriented and bowed
in parallel to the end support tubes and so as to also have an apex 18. As
illustrated in Figure
2, one intermediate support tube 13 is utilized and located at the junctions
24 of the two pairs
of the bracing tubes, although it will be appreciated that more than one
intermediate support
tube may also be utilized at different locations between the end support tubes
12.
Advantageously tubes 12 and 13 form a substantially parallel spaced apart
array of curved
supports having substantially the same height and width dimensions for each of
the curved
supports.
Each pair 20 of pneumatic bracing tubes 22 are criss-crossed at corresponding
junctions 24 in fluid communication with one another by a cooperating hollow
flexible conduit
26. The first and second opposite ends 22a and 22b, respectively of tubes 22
are mounted to
opposed pneumatic end support tubes 12, that is, to the end support tubes at
each end of
structure 10. The first ends 22a are each connected to a base 12a for example
by the use of
7
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
securing means such as flexible end flap 64 formed at the end of each of the
tubes. The second
ends 22b are each connected to apex 18 of the tube 12 at the opposite end of
structure 10, for
example by the use of flexible end flaps 64 formed at the end of each of the
tubes, so that each
tube 22 extends the length of, and generally diagonally across each lateral
side of the structure
10. The bracing tubes 22 may be secured to each other as well as to the
support tubes 12 and
13 by means of securing straps 80. Securing straps 80 may comprise of cable
ties, string,
ropes or any other suitable strap means.
Each of the pneumatic end support tubes 12 are bowed and arranged parallel to
each other so as to form a frame having downwardly concave elongate structure
defining a
common opening 8. Intermediate support tube 18 are bowed and oriented in
parallel to the end
support tubes 12 so as to support a middle portion of the canopy 30. The
pneumatic bracing
tubes 22 extend between and brace the end support tubes 12 so as to maintain
them in their
desired parallel orientation. Thus taken in combination the two opposed pairs
20 of pneumatic
bracing tubes 22 and the end support tubes 12 define an elongate open
enclosure elongate
along longitudinal axis A.
Referring to Figure 4, canopy 30 comprises a rectangular substantially planar
flexible sheet of material having first and second end edges 32 and 34,
respectively and first
and seoond side edges 36 and 38, respectively. The canopy includes a plurality
of securing
straps 40 attached to a bottom surface thereof. The securing straps 40
comprise an elongate
strip of material having first and second fastenable portions 42 and 44,
respectively. The first
and second fastenable portions may be secured to each other after the securing
strip encircles
one or more of the end or intermediate support tubes 12 or 13 or the bracing
tubes 22 and serve
to secure the canopy 30 thereto. As illustrated in Figure 1, the canopy 30
also include end
flanges 46 extending inwardly from the canopy so as to surround the support
tubes 12.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the canopy 30 includes an exterior surface 31
which
may include one or more guy loops 33 for securing a conventional pegged guy
wire 35 thereto.
8
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
It will be appreciated that the guy wires 35 will assist in the lateral
stability of the inflated
structure 10, in particular wben subjected to side loads such as wind, for
example.
In an alternative embodiment as illustrated in Figure 5, the pneumatically
inflatable structure 10 may include a vestibule 50 extending from one or more
ends. The
vestibule 50 comprises a sheet of material extending from the first or second
edge 32 or 34 of
the canopy 30 to a ground securing location 52 at a distance from the first or
second end of the
structure 10. The vestibule 50 provides increased wind resistance and security
to the structure.
The vesti-bule 50 may be formed as a oommon sheet with the canopy 30 or may be
a separate
sheet that is connected to the canopy when the structure is erected.
The inflatable structure 10 may include a base sheet 16 comprising a
rectangular sheet of material to which the ends 12a and 12b of the end support
tubes as well as
the ends of the intermediate support tubes 13 and the bracing tubes 22 may be
secured. The
base sheet 16 may provide the dimensions of the base of the inflatable
structure 10 when
erected. Alternatively the inflatable structure 10 may be secured to the
ground by passing a
fastener 60, such as for example a ground spike through an eyelet 62 in the
end flaps 64 of the
end or intermediate support tubes 12 or 13 or the bracing tubes 22, as
illustrated in Figure 7.
In a further embodiment of the present invention, one or more of the
inflatable
structures 10 as taught above may be lengthwise connected to each other to
form a common
modular elongate structure. Where more than one inflatable structure 10 are
employed
modularly and each already has a base 16 mounted to the ends of the pairs of
tubes, in a further
embodiment of the present invention, a separate spanning, joining or linking
section is
employed to join the adjacent sides of the base 16. As may be understood then,
it is not
necessary that the inflatable structure according to the present invention
merely and only is
limited to two end support tubes 12 and a single span of bracing tubes 22 as
it will be
understood that a further elongated enclosure may be constructed using two or
more pairs of
criss-crossed bracing tubes similar to pairs 20.
9
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
In a prefetred embodiment, each of the criss-crossed pneumatic bracing tubes
20 of tube pairs 22, pneumatic end support tubes 12 and pneumatic intermediate
support tubes
13 are of a design such as taught in my United States Patent No. 6,263,617 and
incorporated
herein by reference such that a resilient or at least flexible inner tube is
mounted within an
outer flexible relatively non-resilient sleeve, and wherein such a sleeve has
a folded seam
along its interior circumference folded over so that the sleeve and inner tube
may be
constructed as a linear pole which may then be bent to accommodate the
required bowed
shaped to form the inflated structure. It has been found that such inflatable
tubes for example
having approximately a twenty inch circumference which is constant along the
length of each
tube may be inflated to approximately eight to twelve pounds per square inch
(psi) and thereby
provide sufficient rigidity for an inflatable structure which may then house
wheeled vehicles or
towable trailers such as a trailer and boat combination which is not intended
to be limiting.
Thus in one embodiment, the width of the span between ends of the pneumatic
end and intermediate support tubes 12 and 13 may be approximately ten feet and
the distance
between the opposite end support tubes is approximately twenty feet.
Accordingly the height
to the apex 18 of the pneEUnatic end and intermediate support tubes 12 and 13
will be
approximately eight feet. The pneumatic end tubes and intermediate support
tubes 12 and 13
respectively and pneumatic bracing tubes 22 will thus each be approximately
twenty-four feet
long. It will be appreciated that other lengths of the pneumatic end and
intermediate support
tubes 12 and 13 and pneumatic bracing tubes 22 may also be used for other
desired dimensions
of the inflatable structure.
In a second embodiment illustrated in Figure 6, the pneumaxic end and
intermediate support tubes 12 and 13 and pneumatic bracing tubes 22 may be
sized so as to
provide a structure having internal dimensions adequate for covering the
folded wings of a
light aircraft. As illustrated in Figure 6, the pneutnatac end and
intermediate support tubes 12
and 13 and pneumatic bracing tubes 22 may be approximately 47.3 feet long.
Accordingly the
CA 02628458 2008-04-02
structure illustrated in Figare 6 may therefore be 46 feet long, 32 feet wide
and having a height
of approximately 16 feet.
An array of interconnected airlines 70 stemming from a common manifold 72
may be used to simultaneously inflate all of the tubes, where for example
separate air lines 70
are mounted in fluid communication with adjacent ends of tubes 12, 13 and 22,
and a single
source (not shown) of pressurized air is mounted to manifold 40.
Alternatively, separate air
sources may also be used for pressurizing separate zones of the structure as
defined by a
grouping of fluidically interconnected tubes. Alternatively, the structure 10
may include a
plurality of tubes 12, 13 and 22 mounted adjacent to and in parallel to each
other such that one
set of tubes 12, 13 and 22 defines a first circuit while a second set of tubes
12, 13 and 22
defines a second circuit. It will be appreciated that duplication of each tube
of the structure
permits that structure to remain erected sbould a leak occur in one of the two
circuits.
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art in the light of the foregoing
disclosure, many alterations and modifications are possible in the practice of
this invention
without departing from the spirit or scope thereof. Accordingly, the scope of
the invention is
to be construed in accordance with the substance defined by the following
claims.
11