Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
LANSOPRAZOLE ORALLY DISINTEGRATING TABLETS
Field of the Invention
[0001] The invention is directed to enteric coated drugs, such as
Lansoprazole. In
particular, the invention is directed to an easily swallowed tablet that
readily disintegrate in
the mouth releasing enteric coated drug sub-tablets.
Background of the Invention
[0002] Lansoprazole, a substituted Benzimidazole, is an inhibitor of gastric
(H} + K+)-ATPase. Lansoprazole has been shown to be unstable under acidic
conditions,
and, thus, preferably has an enteric coating to prevent exposure of the drug
to acidic
conditions prior to absorption in the digestive system.
[0003] Enteric coated products are known. For example, U.S. Patent No.
6,706,285
discloses an enteric coated Lansoprazole, having a core and a film of an
enteric coating agent
on the surface thereof, where the core contains a complex of the Lansoprazole
and an
ion-exchange resin. Many enteric coated products are formulated as a single
monolithic unit,
such as that disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 6,706,285, while others comprise
multiple units,
where the multiple-unit formulations are formulated to improve migration in
the digestive
track, and to minimize various absorption issues. U.S. Patent 6,328,994
discloses an orally
disintegrable Lansoprazole tablet which comprises fine enteric coated
"granules," having an
average particle diameter of 400 m or less. European Patent EP 0 723 437B1
discloses an
oral pharmaceutical multiple unit tableted dosage form, comprising
individually enteric
coating layered units characterized in that the enteric coating layer has a
particular thickness,
and comprises a plasticizer an amount of 15 to 50 percent by weight of the
enteric coating
layer polymer. As a result, the compression of the individual units mixed with
the tablet
excipients into the multiple unit tableted dosage form reportedly does not
significantly affect
the acid resistance of the individually enteric coating layered units.
[0004] Many patients find almost any type of tablet hard to swallow, with or
without
water. Therefore, a need exists for a tablet comprising a drug, such as
Lansoprazole, that is
easily swallowed without exposing the drug to acidic conditions before
absorption in the
digestive track. The present invention provides such a tablet.
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
Suminary of the Invention
[0005] The present invention is directed to orally disintegrating tablets,
comprising
enteric coated sub-tablets, which comprise a drug, and to methods of preparing
such tablets
and sub-tablets, where the sub-tablets preferably have an average particle
diameter of more
than 400 m, and the enteric coat preferably comprises less than 15 percent
plasticizer by
weight of the enteric coating layer polymer. Preferably, the drug is one that
is unstable under
acidic conditions, more preferably, the drug is a Benzimidazole derivative,
such as
Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole. Most
preferably,
the drug is Lansoprazole. Preferably, orally disintegrating tablets of the
invention dissolve
rapidly in a patients mouth, releasing the enteric coated sub-tablets, which
can be swallowed
without water. As the sub-tablets are enteric coated, the sub-tablets pass
through the stomach
without exposure of the drug to acidic conditions, avoiding degradation of the
drug prior to
absorption in the patient's digestive tract. The compression of the enteric
coated sub-tablets
into the orally disintegrating tablets of the invention does not significantly
affect the acid
resistance of the individually enteric coated sub-tablets.
[0006] The orally disintegrating tablets of the invention comprise more than
one
enteric coated sub-tablet, mixed with one or more tablet excipients. The sub-
tablets comprise
an inner core, substantially free of any alkaline stabilizing agent, where
each core comprises
one or more inert core excipients and an acid sensitive drug in, on, or over
the iimer core; an
inert first coating layer, disposed over the acid sensitive drug; an alkaline
stabilizing layer,
comprising an alkaline stabilizing agent, disposed over the inner core and the
acid sensitive
drug; and an enteric coating layer, which is preferably polymeric and
plasticized with less
than 15 percent plasticizer, disposed over the alkaline stabilizing layer,
where the inert first
coating layer is substantially free of and inert with regard to both the acid
sensitive drug and
the alkaline stabilizing layer. The inert first coating layer substantially
improves the stability
of the acid sensitive drug.
[0007] The orally disintegrating tablets of the invention preferably comprise
inner
cores, having at least two sub-populations, each sub-population having a
different size
distribution. However, the inner cores can be composed of a single population,
having a
single size distribution. When placed in a mouth, the orally disintegrating
tablets of the
invention disintegrate, facilitating swallowing of the orally disintegrating
tablet by a patient.
The inner core can also be an extrusion, comprising the acid sensitive drug
and one or more
-2-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
excipients. Preferably, the acid sensitive drug comprises a Benzimidazole
derivative, such as
Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole. More
preferably,
the drug coinprises Lansoprazole. The orally disintegrating tablets of the
invention
preferably comprise no more than about 50 percent by weight sub-tablets.
[0008] As discussed above, the acid sensitive drug can be in, on, or over the
inner
core, such that the sub-tablets of the orally disintegrating tablet can
coinprise a drug layer
disposed over the inner core, where the drug layer comprises the acid
sensitive drug, the inert
first coating layer, disposed over the drug layer, and the alkaline
stabilizing layer disposed
over the inert first coating layer. At least one of the drug layer, the inert
first coating layer
and the alkaline stabilizing layer can comprise at least one of a film forming
agent and at
least one excipient.
[0009] In one embodiment, sub-tablets useful in the invention comprise an
inner, inert
core, such as sugar spheres, coated with an acid labile drug, preferably a
Benzimidazole
derivative, such as Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and
Esomeprazole,-and, more preferably, Lansoprazole, an inert first coating
layer, substantially
free of the alkaline stabilizing agent and acid labile drug, a second coating
layer, comprising
an alkaline stabilizing agent, and an outer coating, comprising an enteric
coating. However,
the materials of the inert core and the acid labile drug can be combined to
form the sub-tablet
core by, e.g., extruding a formulated particle composed of an acid labile drug
and excipients,
without departing from the scope of the invention. An orally disintegrating
tablet of the
invention, comprising such co-extruded cores, further comprises an inert first
coating layer
and an outer enteric coating.
[00010] Useful film forming agents include hypromellose, i.e., hydroxypropyl
methyleellulose, and useful excipients include talc, more preferably, extra
fine talc. The ratio
of the weight of the drug relative to the total weight of the film fomling
agent and excipient is
preferably from about 1:2 to about 2:1, and, more preferably, about 1:1. The
film forming
agent and excipient can be used in any useful relative amount, and are
preferably used in
about equal amounts by weight.
[00011] Preferably, the inert first coating layer comprises a film forming
agent and an
excipient. More preferably, the film forming agent is hypromellose and/or the
excipient is
talc, preferably, extra fine talc. The weight ratio of film forming agent to
excipient is
-3-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
preferably from about 1:1 to about 1:2, and, more preferably, is about 2:3.
The alkaline
stabilizing agent of the alkaline stabilizing layer preferably comprises a
carbonate, such as
calcium or magnesium carbonate or a mixture thereof, and, more preferably, the
alkaline
stabilizing layer further comprises a film forming agent, such as
hypromellose. The weight
ratio of the alkaline stabilizing agent to the fihn forming agent is
preferably from about 1:1 to
about 2:1, and, more preferably, is from about 1:1 to about 3:2.
[00012] Preferably, the enteric coating is polymeric, and comprises at least
one of
hypromellose phthalate and methacrylic and methacrylate copolymers. The
methacrylic and
methacrylate copolyiners are preferably selected from the group consisting of
a methacrylic
acid copolymer type B, a methacrylic acid copolymer type C, a methacrylic
acid,
methylmethacrylate, and methylmethacrylate copolymer, a methacrylate
copolymer, and
mixtures thereof. Such polymeric materials are available under the trade name
EUDRAGIT . The enteric coating can further comprises a plasticizer and/or
excipients.
When present, the plasticizer is less than 15 percent of the enteric coat
polymer. Useful
plasticizer materials include, but are not limited to, triethyl citrate, and
useful excipients
include, but are not limited to talc, preferably, extra fine talc, and
titanium dioxide.
[00013] The inner cores can be composed of a single population, having a
single size
distribution. However, the orally disintegrating tablets preferably comprise
at least first and
second sub-populations of the imler cores, where the inner cores in the first
sub-population
have smaller diameters than the inner cores of the second population. The
weight ratio of the
first and second sub-populatioiis of inner cores is preferably from about 1:1
to about 4:1,
where the ratio is the weight of the first sub-population to that of the
second sub-population.
More preferably, the weight ratio is from about 2:1 to about 3:1. Where the
acid sensitive
drug is Lansoprazole, the first sub-population preferably has a size
distribution of diameters
of from about 250 to about 350 m, and the second sub-population has a size
distribution of
diameters of from about 400 to about 500 m. Where an orally disintegrating
tablet
comprises a single population of sub-tablets, having a single size
distribution, the sized
distribution is preferably within the range of from about 250 to about 500 m.
When coated,
the diameter of the sub-tablets becomes much greater than the diameter of the
inner cores
from which they are made, and, thus, a sub-population of inner cores with an
average
diameter of 300 gm will typically become, after coating, sub-tablets with an
average diameter
in excess of 400 gin, and a sub-population of inner cores with an average
diameter of 450 m
-4-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
will typically become, after coating, sub-tablets with an average diameter in
excess of
600 m.
[00014] Preferably, the orally disintegrating tablet is a compressed tablet
comprising
the sub-tablets and tablet excipients, where at least one of the excipients
preferably functions
as a disintegrant. The tablet excipients preferably comprise at least one of a
starch or
cellulose, a hydrated sugar, and silica, where, more preferably, the starch or
cellulose is
maize starch cellulose powder, the hydrated sugar is lactose monohydrate, and
the silica is
colloidal silica. The orally disintegrating tablets can further comprise
sweeteners and
flavorings. Useful sweeteners include, but are not limited to, sugars,
aspartame, and other
commercially available artificial sweeteners. The orally disintegrating
tablets can further
comprise a lubricant or plasticizer, such as magnesium stearate.
[00015] Preferably, upon exposure of the sub-tablets to a solution having a pH
of about
3.5 for about 20 minutes, no more than about 10 percent by weight of the acid
sensitive drug
is dissolved by the solution, more preferably, no more than about 6 percent by
weight of the
acid sensitive drug is dissolved by the solution, and, most preferably, no
more than about 1
percent by weight of the acid sensitive drug is dissolved by the solution. In
a particularly
preferred embodiment, upon exposure of the sub-tablets to a solution having a
pH of about
3.5 for about 20 minutes, substantially none of the acid sensitive drug is
dissolved by the
solution, even though the enteric coating on the sub-tablets comprises less
than 15 percent,
preferably, less than 10 percent plasticizer, by weight of the enteric coating
layer polymer.
[00016] In one preferred embodiment, orally disintegrating tablets of the
invention
comprise a plurality of sub-tablets, mixed with one or more excipients, and
formed into a
tablet shape. The sub-tablets coinprise coated inner cores, coated with a
coating comprising a
drug; an inert first coating layer that is substantially free of any alkaline
stabilizing agent and
the drug, disposed over the inner core; an alkaline stabilizing layer,
comprising an alkaline
stabilizing agent, disposed over the inert first coating layer; and an outer
enteric coating
disposed over the alkaline stabilizing layer. Preferably, the inner core is
formed from any
useful material that will readily release the drug in the digestive system, is
consumable by a
patient, and does not degrade the drug. - More preferably, the inner core is
formed from
particles or granules of a sugar, such as sucrose, which can be spherical or
any other useful
shape. Preferably, the drug is an acid sensitive drug, and, more preferably,
is a
-5-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
Benzimidazole derivative, such as Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole,
Omeprazole,
and Esomeprazole. Most preferably, the drug is Lansoprazole.
[00017] In a further preferred embodiment, the orally disintegrating tablets
comprise a
plurality of sub-tablets, mixed with one or more excipients, and formed into a
tablet shape.
The sub-tablets comprise an inner core, comprising an acid sensitive' drug and
inert
excipients, but free of any alkaline stabilizing agent; an inert first coating
layer, substantially
free of the drug and alkaline stabilizing agent; an alkaline stabilizing
layer, comprising an
alkaline stabilizing agent; and an outer coating layer, comprising an enteric
coating.
Preferably, the inner core is formed from any useful material that will
readily release the drug
in the digestive system, is consumable by a patient, and does not degrade the
drug. More
preferably, the inner core is formed from a sugar, such as sucrose. Most
preferably, the drug
is a Benzimidazole derivative, such as Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole,
Rabeprazole,
Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole. Most preferably, the drug is Lansoprazole.
[00018] The invention is further directed to a method of preparing orally
disintegrating
tablets. The method comprises obtaining a plurality of inner cores, comprising
an excipient
and an acid sensitive drug, which is preferably a Benzimidazole derivative,
such as
Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole, in the
core or in a
layer over the core, applying an inert first coating layer, substantially free
of the acid
sensitive drug and alkaline stabilizing agent, over the acid sensitive drug
and the inner cores,
applying an alkaline stabilizing layer, comprising an alkaline stabilizing
agent, over the inert
first coating layer, applying an enteric coating layer, which is preferably
polymeric, over the
alkaline stabilizing layer, thereby forming enteric coated sub-tablets, and
then mixing the
enteric coated sub-tablets with one or more excipients, forming a tablet
mixture, and
compressing a portion of the resulting tablet mixture into an orally
disintegrating tablet.
Preferably, the orally disintegrating tablets comprise inner cores, having at
least two
sub-populations, the sub-populations having different size distributions, but
can be composed
of a single population, having a single size distribution.
[00019] The method of preparing orally disintegrating tablets of the invention
can
further comprise applying a layer of the acid sensitive drug over the inner
cores, and applying
the inert first coating layer over the drug layer, prior to applying the
alkaline stabilizing layer.
-6-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
[00020] Preferably, the amount of excipient in the tablet mixture is
sufficiently great
relative to the amount of enteric coated sub-tablets, and the enteric coating
layer is
sufficiently flexible, that cracking of the enteric coating during compression
of the tablet is
minimized, and upon exposure to a solution having a pH of about 3.5 for about
20 minutes,
no more than about 10 percent by weight of the acid sensitive drug is
dissolved by the
solution. Preferably, at least one of the layers is applied by spraying.
[00021] In a preferred embodiment, orally disintegrating tablets in accordance
with the
invention can be prepared by providing inner cores, and preparing separate
dispersions of the
ingredients of the drug layer, the inert first coating layer, the alkaline
stabilizing layer, and
the enteric coating, where each dispersion is formed in a solvent. For the
dispersions of the
drug layer and the inert first coating layer and the alkaline stabilizing
layer, the solvent is
preferably purified water. For the enteric layer dispersion, the solvent
preferably comprises
an organic solvent, and, more preferably, is a mixture of acetone and
isopropyl alcohol. Most
preferably, the isopropyl alcohol and acetone are used in a ratio of about
2:3. The drug layer
dispersion is applied over the inner cores, and preferably allowed to dry. The
dispersion of
the inert first coating layer is applied over the drug layer, and preferably
allowed to dry. The
dispersion of the alkaline stabilizing layer is applied over the inert first
coating layer, and
preferably allowed to dry, and the dispersion of the enteric coating is
applied over the
alkaline stabilizing layer, and preferably allowed to dry. Preferably, each
layer is applied by
spraying, and, more preferably, using a fluid bed drier. Preferably, the
amount of solvent
used in each dispersion is sufficient to allow the ready application of the
dispersion, while
miniinizing the drying time.
[00022] In a particularly preferred embodiment, the drug layer is deposited on
the
inner core, and allowed to dry, the inert first coating layer is deposited on
the drug layer, and
allowed to dry, the alkaline stabilizing layer is deposited on the inert first
coating layer, and
allowed to dry, and the enteric coating is deposited on the alkaline
stabilizing layer, and
allowed to dry. More preferably, the each layer is deposited by spraying a
dispersion of the
material used to form the layer.
[00023] The final orally disintegrating tablets are preferably formed by
mixing the
enteric coated sub-tablets with the other tablet ingredients, and, preferably,
pressing the
mixture into tablets, comprising the desired dose of the drug.
-7-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
[00024] The invention is further directed to a method of administering an acid
sensitive
drug, preferably a Benzimidazole derivative, such as, Lansoprazole,
Pantoprazole,
Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole, comprising orally administering at
least one
orally disintegrating tablet in accordance with the invention to a patient,
where the orally
disintegrating tablet at least partially disintegrates in the patients mouth,
releasing the enteric
coated sub-tablets, which are swallowed by the patient with or without the use
of water or
other fluid.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Figure 1 illustrates a cross-section of an orally disintegrating tablet of the
invention;
Figure 2 illustrates a cross-section of one preferred embodiment of a sub-
tablet of an
orally disintegrating tablet; and
Figure 3 illustrates a cross-section of a further preferred embodiment of a
sub-tablet.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Einbodiments of the Invention
[00025] As used herein, the terms "on," "disposed on," and "deposited on" mean
that a
second material is disposed or deposited directly on, and in physical contact
with a first
material. The terms "over," disposed over," and "deposited over", as used
herein, means that
a second material is outside of a first material of the orally disintegrating
tablets and
sub-tablets of the invention, and can be, but need not be, in contact with the
first material.
Instead, at least one intervening layer of material can be, but is not
necessarily, disposed or
deposited over the first material before the second materials is disposed or
deposited. The
intervening layer of material can be disposed on or disposed over the first
material.
[00026] As used here in the term "inactive excipient" refers to an excipient
that does
not reduce the effectiveness of the drug. Also as used herein, the term
"enteric" refers to a
material that is acid resistant, such that a sub-tablet coated with an enteric
material resists
dissolution in an acidic environment.
[00027] As used herein, the term "sub-tablet" refers to any pellet, granule,
powder,
minitab, and the like having the sub-tablet structure described herein.
-8-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
[00028] As used herein, the term "inert first coating layer" of a sub-tablet
refers to a
coating layer that is inert with regard to any drug, core material, and
alkaline stabilizing layer
or agent in or on a sub-tablet, and is substantially free of any drug or
alkaline stabilizing
agent.
[00029] The present invention is directed to orally disintegrating tablets
that are
formulated to readily disintegrate in the mouth of a patient, thereby
facilitating swallowing by
a patient, preferably without requiring water. Preferably, the orally
disintegrating tablets of
the invention comprise at least one Benzimidazole derivative, such as
Lansoprazole,
Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, and Esomeprazole, but can be formulated
for any
drug that can be administered orally. Tlierefore, although the invention is
described herein in
terms of Lansoprazole orally disintegrating tablets (Lansoprazole ODT), orally
disintegrating
tablets, comprising other drugs, are within the scope of the invention.
[00030] Orally disintegrating tablets in accordance with the invention
comprise a
plurality of enteric coated sub-tablets containing at least one drug, such as
Lansoprazole,
mixed with an inactive blend of excipients, and formed into a single tablet,
preferably by
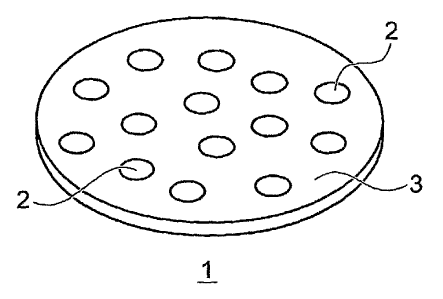
compression. An orally disintegrating tablet 1 of the invention is illustrated
in cross-section
in Figure 1. As illustrated in Figure 1, the orally disintegrating tablet 1 of
the invention,
comprises a plurality of enteric coated sub-tablets 2, preferably dispersed
within a mixture 3,
comprising excipients, flavoring, and sweeteners, and formed into the tablet
1.
[00031] Preferably, an enteric coated sub-tablet in an orally disintegrating
tablet of the
invention comprises:
a) An inner core, such as, but not limited to, sugar particles or granules,
which
can be spherical or any other useful shape, coated with a drug, preferably, an
acid sensitive drug, such as Lansoprazole, where the drug layer preferably
comprises a film forming agent, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
(hypromellose) and an excipient, such as talc, preferably, extra fine talc, in
addition to the drug;
b) A "first coating layer," Subcoat I, which is totally free of both any
alkaline
stabilizing agent and the drug, where the inert first coating layer preferably
comprises a film forming agent, such as hypromellose, and an excipient, such
as talc, preferably, extra fine talc;
-9-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
c) A "alkaline stabilizing layer," Subcoat II, that comprises an alkaline
stabilizing, agent, such as magnesium carbonate, and can further comprise a
film forming agent, such as hypromellose; and
d) An "outer coating," that comprises an enteric coating, where the enteric
coating is preferably polymeric, such as methacrylic and methacrylate
copolymers, e.g., those sold under the trade name EUDRAGIT .
[00032] A sub-tablet 5 in accordance with this embodiment of the invention is
illustrated in Figure 2. As illustrated in Figure 2, the sub-tablet 5
comprises an inner core 6, a
drug layer 7, an inert first coating layer 8, a alkaline stabilizing layer 9,
and an enteric coating
layer 10.
[00033] In a further embodiment, the inner core and the drug are combined into
a
single unit, produced, e.g., by extruding a formulated particle, comprising
the drug,
preferably, an acid sensitive drug, such as Lansoprazole, and excipients,
without departing
from the teachings of the invention. In this embodiment, the sub-tablet of the
orally
disintegrating tablet comprises: an inner core, comprising the acid sensitive
drug and
excipients, an inert first coating layer, substantially free of both the drug
and any alkaline
stabilizing agent, an alkaline stabilizing layer, comprising an alkaline
stabilizing agent, and
an outer coating agent, comprising an enteric coating.
[00034] A sub-tablet 15 in accordance with this embodiment of the invention is
illustrated in Figure 3. As illustrated in Figure 3, the sub-tablet 15
comprises a core 16,
comprising at least one inactive excipient and the acid sensitive drug, an
inert first coating
layer 17, an alkaline stabilizing layer 18, and an enteric coating layer 19.
[00035] The inner cores are preferably sugar spheres, but can have any useful
shape,
and can comprise any useful material that will readily release the drug in the
digestive
system, is consumable by a patient, and does not degrade the drug. More
preferably, the
inner core is formed from a sugar, such as sucrose. Most preferably, the drug
is a
Benzimidazole derivative, such as Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole,
Omeprazole,
and Esomeprazole. In a preferred embodiment, the drug is Lansoprazole.
[00036] Parameters preferably considered during the formulation of orally
disintegrating tablets of the invention, such as Lansoprazole ODT, include,
but are not
-10-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
necessarily limited to the composition and size distribution of the inner
cores, the material
used for the enteric coating, which is preferably polymeric, and the
excipients surrounding
the inner cores. The orally disintegrating tablets of the invention preferably
comprise two or
more populations, having different size distributions. The size distribution
of each population
and the relative amounts of the populations are preferably also considered
during formulation
of the orally disintegrating tablets.
[00037] Preferably, the orally disintegrating tablets comprise a mixture of
two
sub-populations of iimer cores, where the weight ratio of the core populations
is preferably
from about 1:1 to about 4:1, more preferably, from about 2:1 to about 3:1,
where the weight
ratio is the ratio of the total weight of the smaller cores to the total
weight of the larger cores.
For Lansoprazole ODT, one sub-population preferably has a range of diameters
of from about
250 to about 350 m, and the second sub-population preferably has a range of
diameters of
from about 400 to about 500 m. The use of two sub-populations, having
different particle
size distributions, provides a more homogeneous mixture of the coated spheres
within the
external excipients in the final tablet. Table 1 provides examples of
different ratios of the
various starting particle populations and different weights of cores per final
tablet that have
been prepared.
[00038] The following non-limiting examples are merely illustrative of the
preferred
embodiments of the present invention, and are not to be construed as limiting
the invention,
the scope of which is defined by the appended claims.
-11-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
Table 1
Materials Example Number
1 2 3 4
Core (mg) (mg) (mg) (m )
Sugar spheres 90 60 33.5 46.5
250-350 micron
Sugar spheres 30 30 16.5 23.5
400-500 micron
Total inert part 120 90 50 70
Drug Layer
Hypromellose 15 15 15 15
Talc extra fine 15 15 15 15
Lanso razole 30 30 30 30
Total Drug Layer 60 60 60 60
Subcoat I
H romellose 12 12 6 6
Talc extra fine 18 18 9 9
Total Subcoat I 30 30 15 15
Subcoat II
Hypromellose 25 16 12.5 15
Magnesium carbonate 25 24 12.5 15
Total Subcoat II 50 40 25 30
Enteric coat
Methacrylic acid 54 53 62.5 88
copolymer
Talc extra fine 22 21.5 25 36
Triethylcitrate 7 6.5 6 9
Titanium dioxide 3 3 4 7
Total Enteric coat 86 84 97.5 140
Total coated core 346 294 247.5 315
Tablet
StarLac (85% Lactose 403 374 420.5 400
monohydrate & 15%
Maize Starch)
Strawberry flavor 10 10 10 11
Aspartame 12 12 13
Colloidal Silicone 3.5 3.5 4
Dioxide (AEROSIO
Magnesium stearate 7 6.5 6.5 7
Total tablet wei ht 766 710 700 750
[00039] In the examples listed in Table 1, the total weight of inner cores per
tablet
varied between 50 mg to 120 mg. However, the final tablet weight was fairly
similar, due to
variation in the other ingredients. The weight ratios of the two populations
of cores in
-12-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
Table 1 were in the range of about 2:1 to about 3:1. As will be recognized by
those skilled in
the art, the total weight of inner cores per tablet and/or the amount of drug
per sub-tablet can
be adjusted to determine the dosage of tablets containing the sub-tablets.
[00040] The tablets exemplified in Table I were prepared as follows: An active
compound dispersion consisting of Lansoprazole, hypromellose, extra fine tale
and purified
water was prepared by stirring. First and second sub-coat dispersions were
prepared for
forming the inert first coating layer and the alkaline stabilizing layer, the
first sub-coat
dispersion comprising hypromellose, extra fine talc, and purified water, and
the second
subcoat dispersion comprising hypromellose, magnesium carbonate, and purified
water. An
outer enteric coating, comprising a dispersion of EUDRA.GIT L-100 55,
titanium dioxide,
extra fine talc, and triethyl citrate was prepared by stirring with acetone
and isopropyl alcohol
in a ratio of about 3:2. Sugar spheres were coated by consecutive spraying of
the active
dispersion subcoats (I + II) and the enteric coat layer using a fluid bed
drier equipped with a
Wurster column (bottom spray).
[00041] The polymers used for the enteric coating were also tested. As
discussed
above, Lansoprazole is unstable in an acidic environment. In order to provide
a
pharmaceutical composition for oral administration that prevents the drug from
degrading in
the stomach, the drug is provided with an enteric coating. The dosage form is
a tablet that
comprises coated particles or granules, preferably in the form of spheres,
mixed together with
excipients. In order to fully realize the advantages of the formulation, the
final tablets are
preferably formed on a conventional tablet press without damage to the enteric
coating layer
of the coated particles during compression. Preferably, to reduce or eliminate
the cracking
and crushing of the enteric coating layer, a flexible and/or malleable enteric
coating layer was
provided. To provide such a flexible enteric layer, the tablet formulation
preferably contains
one or more types of polyiner, alone or in a combination.
[00042] The flexibility and, more importantly, the robustness and integrity of
the
enteric layer was tested by comparing the dissolution release profile in acid
conditions of the
coated spheres versus the dissolution profile of compressed tablets.
Formulations using
different enteric coated polymers in different amounts and in different
combinations are
provided in Table 2. Where the enteric coat remains intact, the profile
typically remains
generally the same.
-13-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
Table 2
Materials Example Number
20 30 40 50
Core Values in mg per final Tablet
Sugar spheres 250-350 micron 46.5 46.5 46.5 46.5 46.5
Su ar spheres 400-500 micron 23.5 23.5 23.5 23.5 23.5
Total inert part 70 70 70 70 70
Drug Layer
Hypromellose 15 15 15 15 15
Talc extra fine 15 15 15 15 15
Lansoprazole 30 30 30 30 30
Total Drug La er 60 60 60 60 60
Subcoat I
Hypromellose 6 6 6 6 6
Talc extra fine 9 9 9 9 9
Total Subcoat I 15 15 15 15 15
Subcoat II
Hypromellose 15 15 15 15 15
Magnesiuin carbonate 15 15 15 15 15
Total Subcoat II 30 30 30 30 30
Enteric coat
Methacrylic acid copolymer type C - -
(EUDRAGIT L-30 D-55) 75
Methacrylate copolymer 78 50
(EUDRAGIT L-100 55)
Methacrylic acid copolymer type B - - - - 20
(EUDRAGIT S-100)
Methacrylic acid, methylmethacrylate, and - 19 - - -
methylmethacrylate copolymer
(EUDRAGIT FS)
Hypromellose phthalate (HPMCP HP-55) - - 56 80 -
Polyethylene lyco16000 - - - 8 -
Talc extra fine 31 32 - - 26
Triethylcitrate 8 11 5.5 - 7
Titanitun dioxide 5.5 3 - 2
Total Enteric coat 122.5 140 61.5 88 105
Total core 297.5 315 236.5 263 280
Tablet
StarLac (85% Lactose monohydrate & 15% 378.5 394 322
Maize Starch)
CELLACTOSE 80 (75% lactose 234 249
monohydrate
& 25% cellulose powder)
Strawberry flavor 10 10.5 8 7 8
Aspartame 12 13 10 9 10
Colloidal Silicone Dioxide (AEROSIL ) 3.5 11 9 8 8
Magnesium stearate 6.5 6.5 5 5 5
Total tablet weight 708 750 591 526 560
-14-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
[00043] Example 10 exemplifies the use of EUDRAGIT L-100 55, a methacrylate
copolymer, in a solvent, as an enteric coat, and example 20 exemplifies a
combination of two
polymers, EUDRAGIT L-30 D-55, a methacrylic acid copolymer type C, and
EUDRAGIT
FS, a methacrylic acid, methylmethacrylate, and methylmethacrylate copolymer.
In
examples 30 and 40, the enteric coat comprises hypromellose phthalate (HPMCP
HP-55), and
example 50 exemplifies a coinbination of two polymers, EUDRAGIT L-100-55 and
EUDRAGIT S-100, methacrylic acid copolyrner type B. In each of the examples,
the
amount of plasticizer was not more than 10 percent by weight.
[00044] Dissolution tests were preformed using USP apparatus II at a pH of 3.5
for 20
minutes, at which time the pH of the dissolution medium was adjusted to 5.5
for a further 40
minutes. The results of the dissolution tests are provided in Table 3.
Table 3
Mean Percentage of Drug Dissolution
Example Number
pH Sampling 10 20 30 40 50
time L-100' L-302 D-55 HPMCP HPMCP HP-55 & L-1003 55 &
(Mins.) 55 & FS HP-55 PEG S-100
3.5 10 0.0 3.0 1.0 0.0 1.0
20 0.0 5.7 6.0 1.0 3.0
5.5 30 6.0 19.8 66.0 20.0 16.0
40 58.0 61.6 69.0 65.0 34.0
50 76.0 79.0 64.0 66.0 52.0
60 74.0 72.3 52.0 60.0 56.0
1. EUDRA.GIT L-100 55
2. EUDRAGIT"' L-30D-55 & FS
3. EUDRAGIT'L-100 55 & S-100
[00045] The mean percentage drug dissolved after 20 minutes in the acid stage
was
significantly less than 10 percent by weight in each example. As discussed
above,
compression during the formation of a final tablet can result in cleavage and
crushing of the
enteric layer. There appears to be a link between the flexibility of the
enteric coating and the
dissolution of the sub-tablets in an acidic enviromnent. That is, if the layer
is not sufficiently
flexible, it can be damaged by the compression forces. As a result, acid can
penetrate into the
sphere, exposing the active compound to acidic conditions, which degrade the
drug.
[00046] As illustrated in Table 3, dissolution at a pH of 5.5 was
significantly greater
than at pH 3.5. The results of example 10 appear to indicate that EUDRAGIT L-
100 55
-15-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
provides the most flexible and/or least damage prone enteric layer, as no drug
was observed
to dissolve at a pH of 3.5 after 20 minutes of exposure to those conditions.
[00047] The orally disintegrating tablets are intended to disintegrate rapidly
in the
mouth, and, thus, the selection of the types and amounts of excipients can be
crucial to the
disintegration of the Lansoprazole ODT in the mouth of a patient. For a tablet
to disintegrate
rapidly, at least a portion of the excipients must function as a disintegrant.
The disintegrant
enables the single tablet dosage form, comprising a compressed mixture of
excipients and
sub-tablets, to disintegrate, and release the sub-tablets.
[00048] Preferred excipients include, but are not limited to a spray-dried
compound
consisting of 85 percent by weight alpha-lactose monohydrate (Ph. Eur./USP-NF)
and 15
percent by weight maize starch (Ph. Eur./USP) dry matter, such as STARLACTM,
from
ROQUETTE, and a spray-dried compound comprising 75 percent by weight alpha-
lactose
monohydrate (Ph. Eur./USP-NF/JP) and 25 percent by weight cellulose powder
(Ph. Eur.) dry
matter, such as one CELLACTOSE 80, from MEGGLE. Examples of useful
formulations
are provided in Table 4.
Table 4
Materials Example number
100 200 300 400
(mg) (mg) (mg) (mg)
Enteric coated peflets 262.5 300.0 280.0 300.0
Tablet
StarLac (85% Lactose monohydrate & 15% 335.0 408.8 - -
Maize Starch)
CELLACTOSE 80 (75% lactose - - 350.5 267.0
monohydrate & 25% cellulose powder)
Strawberry flavor 8.5 10.5 9.0 8.5
Aspartame 10.5 13.0 11.0 10.0
Colloidal Silicone Dioxide (AEROSIL ) 3.0 11.5 10.0 9.0
Magnesium stearate 5.5 7.0 6.5 5.5
Total 625.0 750.8 667.0 600.0
[00049] To enable tablet pressing without detectable damage to the enteric
coat layer
during compression, the ratio of the weight of the coated spheres to that of
the excipients in
the tablet is very important. Parameters that can affect the optimal ratio of
the weight of the
enteric coated pellets and that of the whole tablet include, but may not be
limited to the
uniformity of the content, hardness, friability and disintegration. Results of
an evaluation of
those parameters are provided in Table 5, where the Lansoprazole ODT were
prepared with
-16-
CA 02630235 2008-05-16
WO 2007/078271 PCT/US2005/046296
regard to the following specifications, an average content uiiiformity of from
about 85 to
about 115 percent by weight, a relative standard deviation (RSD) of not more
than (NMT) 6
percent, a friability of not more than 2 percent, the amount of
disintegration, and the
hardness.
Table 5
Parameters Exam le number
100 200 300 400
% Enteric coated pellets 42 40 42 50
vs. total tablet weight
Uniformity of content / RSD 106/3.3 98.5/3.3 111.5/11.9 106.2/4.8
Hardness (SCU) / Friability 9/0.8 7/4.9 9/0.5 6/0
Disinte ration (sec 80 54 67 56
[00050] According to the results provided in Tables 4 and 5, the formulations
providing the most desirable physical parameters are Formulation 100, which
contains 42
percent by weight enteric coated pellets and STARLACTM, and Formulation 400,
which
contains 50 percent by weight enteric coated pellets and CELLACTOSE .
[00051] The formulations of the invention are sufficiently stable, such that,
upon
storage at 30 C and 75 percent relative humidity for 3 months, degradation
products are
typically formed through acid reaction of the acid sensitive drug in an amount
of no more
than 0.1 percent.
[00052] While it is apparent that the invention disclosed herein is well
calculated to
fulfill the objects stated above, it will be appreciated that numerous
modifications and
embodiments may be devised by those skilled in the art. Therefore, it is
intended that the
appended claims cover all such modifications and embodiments as falling within
the true
spirit and scope of the present invention.
-17-