Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
APPARATUS FOR SATELLITE TELECOMMUNICATIONS
This invention relates to an apparatus for satellite telecommunications
and particularly to an apparatus which is arranged to reduce the ratio of
unsuccessful transmissions as compared to the total number of transmission
6 attempts primarily for purposes of power saving.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
It is known that problems are encountered in using satellite
communication devices in mountainous areas where a view of the sky can be
blocked to where the satellites are located as they move across the sky.
This is particularly applicable to low-earth orbit satellite communication
systems, including Orbcomm, Iridium and Globalstar, where the satellites
change
position relative to observers on the ground. Thus, even though a satellite is
expected to be in view above the horizon, it is in fact blocked due to the
presence of
a mountain in the direction concerned.
This can lead to many failed communication attempts which are
inconvenient and more importantly use significant power leading to drain on
portable
equipment where the power supply is a significant part of the weight and
volume of
the equipment.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is one object of the invention to provide an apparatus for satellite
telecommunications which is arranged to reduce the ratio of unsuccessful
transmissions as compared to the total number of transmission attempts.
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
2
According to one aspect of the invention there is provided an
apparatus for satellite telecommunications comprising:
a portable mobile communication device;
the mobile communication device having a first system for receiving
signals from the Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites;
the mobile communication device having a second system for
communication with a low-earth orbit communication satellite system that
contains
multiple satellites that each pass overhead, in and out of view to the
communication
device;
the first and second systems being arranged such that, at a time of
required transmission on the second system, the first system operates to
monitor the
elevation and azimuth of at least some of those GPS satellites in view so as
to
generate an elevation mask of where the sky is open at the time;
the first and second systems being arranged such that, using the
elevation mask of where the sky is open at the time, the second system
operates to
calculate from data available for the low-earth orbit communication satellite
system
and the elevation mask a prediction of whether at least one of the satellites
of the
low earth orbit communication satellite system is in view;
and the first and second systems being arranged such that the
required transmission is commenced only if the calculation prediction
indicates that
at least one of the satellites of the low earth orbit communication satellite
system is
in view.
=
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
3
Although the above refers to two systems, the apparatus may
comprise a single processor programmed with both systems as two separate
protocols operated by the same processor.
If the remote unit processor was too slow or otherwise not capable of
doing the communication system ephemeris calculation, a small file with
prediction
times and positions can be communicated to the devices in the field from time
to
time. This table could be compared to the visibility mask generated from the
GPS
when it is time to transmit. There are ways to encode the table data that are
extremely efficient and would take very little air time.
However, preferably the device includes a memory arranged such that
each low-earth orbit satellite in the low-earth orbit communication satellite
system
has an ephemeris stored in the memory wherein the ephemeris of each satellite
is
used by a satellite visibility prediction subroutine to determine when the
next visible
pass of each satellite will be, and what the azimuth and elevation of each
pass will
be.
Preferably the first and second systems are arranged such that, when
the apparatus is activated, the first system operates to constantly monitor
the
elevation and azimuth of at least some of those GPS satellites in view so as
to be
ready to generate the transmissions when required.
This concept is thus based on problems encountered in using satellite
communication device in mountainous areas but can also be applied to
situations
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
4
where a view of the sky where satellites are located is blocked for example by
buildings, equipment or even the body of the user.
Thus, for any equipment portable or fixed, it will increase the ratio of
successful transmissions as compared to the total number of transmission
attempts.
In addition, this increases system efficiency by reducing the number of
partial
transmissions and lost acknowledgement transmissions.
The system uses two separate satellite systems. The mobile
communicator on the ground can receive signals from (1) the Global Positioning
System (GPS) satellites, and can communicate with (2) a low-earth orbit
communication satellite system that contains multiple satellites that each
pass
overhead, in and out of view to the user on the ground with the communication
device.
Although it is possible to predict, using conventional systems, when
communication satellites are above the horizon and thus available for
communications, conventional systems cannot predict how much of the sky is
obscured by obstacles such as mountains, buildings, or even a user's body.
Therefore, in situations where the view of the sky is blocked, many
satellite communication attempts fail. With battery powered equipment, this is
a
particularly important problem, as a significant portion of battery capacity
is wasted
with transmission retries. This eliminates this wasted power by ensuring there
is a
view of the sky in the direction of the communication satellite before
transmission
attempts are made.
=
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
Secondly, in any type of system, be they battery powered or hard-
wired to vehicle electrical systems and thus have "unlimited" power,
transmitting
when there is a clear view of the communications satellite improves satellite
and
overall system use efficiency. This increase in efficiency is due to a lower
number of
5 partial transmissions, fewer lost transmission acknowledgements and reduced
transmission retries.
GPS satellite receivers and receiver chipsets are much more power
efficient than they used to be. Using a GPS receiver as a "sounding" system
that
provides the satellite communicator with a way to know where the sky is
visible is
much more power efficient than turning on a satellite communication receiver
subsystem and listening for satellites, or making satellite communication
transmissions "blind" in the hope they get through.
Since the GPS system has many satellites that are continuously in
view at any location, the satellite communicator can monitor the elevation and
azimuth of each GPS satellite in view. This shows the communicator where the
sky
is visible at that particular instant. Elevation and azimuth data is available
from the
GPS receiver on board the satellite communicator device.
The satellite communicator will also have the ephemeris of each low-
earth orbit satellite in the low-earth orbit communication satellite system in
memory.
The ephemeris of each satellite is used by a satellite visibility prediction
subroutine
in the satellite communicator to determine when the next visible pass of each
satellite will be, and what the azimuth and elevation of each pass will be.
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
6
Since the satellite communicator has an "elevation mask" of where the
sky is open at the present time due to the constant monitoring of GPS
satellites, the
satellite communicator can now begin communication transmissions to the low-
earth
orbit communication satellite when it is predicted to be within the "mask"
previously
calculated. This will result in a very high probability of the transmission
being
successful on the first try. This results in reduction in power use and
increased
efficiency of satellite resources.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
One embodiment of the invention will now be described in conjunction
with the accompanying drawings in which:
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of a person carrying an apparatus
for satellite telecommunications according to the present invention.
Figure 2 is a schematic illustration the apparatus of Figure 1 for
satellite telecommunications according to the present invention.
Figure 3 is a flow chart for the calculations for the apparatus for
satellite telecommunications of Figures 1 and 2.
In the drawings like characters of reference indicate corresponding
parts in the different figures.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The apparatus as shown in Figures 1 and 2 includes a portable device
10 which includes an antenna or antennas 11A and 11B for communications with
the
GPS system 18 and telecommunications system 9. The low orbit satellite
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
7
communication system includes satellites 9A to 9D. The GPS system includes
satellites 18A to 18D. As is well known, the satellites of both systems are
moving
relative to the earth surface so that at any specific time different ones are
visible by
the antennas 11A and 11B of the portable device 10 and they are at different
locations relative to the portable device 10. The portable device 10 further
includes,
a processor 12 for carrying out the communications protocols described
hereinafter,
a power supply 13 which is generally a battery, a memory 14 of the processor
containing a table 14A, an input 15 for the user to enter or enable
communications to
be transmitted and an output 16 for communicating the received communications
to
the user. Communications may be initiated on user command or may be initiated
by
an automatic system using a trigger condition such as a timer. In such case,
there
may be no user interface at all, other than a power switch.
The apparatus uses the protocols described above together with the
well known protocols necessary for GPS location detection and for two way
telecommunication with a low earth orbit communication satellite system. These
protocols are not described herein as they are well known to persons skilled
in this
art.
The method of the present invention by which transmissions to the low-
earth orbit satellite communication systems is commenced only if the above
calculation prediction indicates that at least one of the satellites of the
low earth orbit
communication satellite system is in view is shown in more detail in the flow
chart of
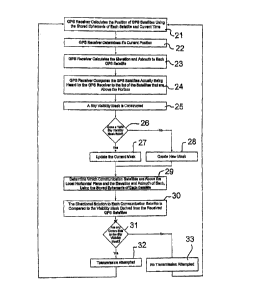
Figure 3 and described as follows:.
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
8
At step 21 the GPS receiver calculates the position of GPS satellites
around the earth using the stored ephemeris of each satellite and current
time, and
GPS receiver receiving GPS satellite signals determines the current position
of the
GPS receiver based on the GPS satellite signals received.
At step 22 and 23 the GPS receiver calculates the 2 dimensional
direction solution to each GPS satellite relative to the GPS receiver position
in terms
such as elevation degrees above the horizon and azimuth degrees from a
reference
point such as true north for each GPS satellite determined to be above local
horizontal plane of the earth or a specified offset from the local horizontal
plane of
the earth.
At step 24 the GPS receiver determines which of the satellites 18A to
18E that are above the specified local horizontal plane of the earth or the
specified
offset from the local horizontal plane of the earth are actually being heard
by the
GPS receiver.
At step 25 the processor uses the directional data for each satellite
18A, 188, 18C and 18D that is visible, and possibly in addition to directional
data for
each satellite 18E that is not visible as obstructed by a an obstruction 19,
to
construct a sky visibility mask or elevation mask 17.
As shown at steps 26, 27 and 28, if a sky visibility mask has been
previously calculated within a reasonable window of time, this previously
calculated
sky mask is updated with the new solutions, while the oldest solutions may be
dropped from the sky mask solution and a new mask created at step 28.
CA 02633051 2012-01-10
9
At step 29, using current time, the positions of communication satellites
around the earth are determined using the stored ephemeris of each satellite.
This
information is periodically downloaded into the table 14A of the memory 14.
At step 30, using current position and current time, the direction
solution to each communications satellite relative to the GPS receiver
position is
determined and the directional solution to each communication satellite is
compared
to the visibility mask derived from the received GPS satellites.
As shown at steps 31, 32 and 33, if all communication satellites are
outside the area of visibility of the visibility mask a transmission will not
be attempted
and thus a transmission is commenced only if the calculation prediction
indicates
that at least one of the satellites of the low earth orbit communication
satellite
system is in view.
If all communication satellites are outside the area of visibility of the
visibility mask a transmission will not be attempted and the estimated time to
next
visibility may be calculated. As satellites are passing regularly, the time to
the next
available transmission is generally short so that there is little or no
interference with
the communications verbal or data from the user to the low-earth orbit
satellite
communication system.