Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PRODUCING A PRESENTATION MESSAGE
FOR A MOBILE DEVICE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of Invention
This invention relates to electronic communications and, in particular, to a
method and system for producing a presentation message for a mobile device.
2. Description of Related Art
Syndicated content, such as web feed content, can be provided by an
information publisher to a subscribing user as a XML (Extensible Markup
Language) file, which can be formatted in accordance with a syndication format
such as RSS or ATOM. RSS is a family of XML (Extensible Markup Language)
type formats, which includes formats related to Really Simple Syndication
(e.g.
RSS 0.9x, RSS 1.0, RSS 2.0). The ATOM syndicated format is a XML format
developed for web feeds as an alternative to the RSS family of XML formats.
Some mobile communications devices, including mobile telephones such
as cellular telephones and satellite telephones, personal digital assistants
and
other wireless communications devices, have installed feed reader software for
receiving RSS or ATOM format web feeds and presenting a received web feed
on a mobile communication device. However, such feed reader software must
be directed by the user to receive a web feed each time the user wishes to
receive that web feed, and such feed reader software is not able to
sequentially
present syndicated content.
Many mobile communications devices are able to receive messages
transmitted in accordance with a messaging service. Short Message Service
1 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
(SMS) permits users to receive short text messages such as text messages
limited to 140 bytes in size. Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) permits users
to receive multimedia messages containing multimedia objects such as video,
audio, images and formatted text, including multimedia messages up to 300
Kbytes in size having multimedia content specified for sequential presentation
according to specified timing.
MMS messages are often delivered to a mobile communications device
from a MMS Center, which is a telecommunications node that is typically
operated by a telecommunications provider.
International patent application publication no. W0205/091615 naming
Doyle et al. as inventors discloses a method of preparing MMS messages
suitable for transmission over a mobile phone service from PowerPoint
(trademark) multimedia presentations. The PowerPoint (trademark) multimedia
presentations include presentation slides prepared on a personal computer
(PC).
The resulting MMS messages include a SMIL layout and animated GIF images
representing presentation slides. The receiving mobile phone displays the MMS
message such that each slide in the generated MMS presentation will advance
automatically as specified within the generated SMIL layout. However, the
method of Doyle et al. cannot prepare MMS messages from syndicated content,
cannot prepare MMS messages in accordance with the media types supported
by specific mobile devices, cannot prepare MMS messages for delivery at
desired times pre-determined by users, cannot prepare MMS messages for
delivery in response to the occurrence of desired events pre-determined by
users, and cannot prepare MMS messages excluding previously delivered
information for increased transmission efficiency, for example.
2 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
SUMMARY
The above shortcomings may be addressed by providing, in accordance
with one aspect of the invention, a method of producing a presentation message
for a mobile device, the method comprising: retrieving syndicated content from
a
content source; and generating from the syndicated content the presentation
message for sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content
items of the syndicated content.
Retrieving the syndicated content from a content source may involve
retrieving the syndicated content from the content source in accordance with a
configuration parameter. Retrieving the syndicated content from a content
source may involve retrieving the syndicated content from the content source
in
accordance with a configuration parameter selected from the group consisting
of
a user selection of a web feed, an invocation parameter and a periodicity
parameter. Retrieving the syndicated content from a content source may involve
retrieving the syndicated content from the content source in accordance with a
user selection of a web feed. Retrieving the syndicated content from a content
source may involve retrieving the syndicated content from the content source
in
accordance with an invocation parameter. Retrieving the syndicated content
from a content source may involve retrieving the syndicated content from the
content source in accordance with a periodicity parameter. Retrieving the
syndicated content from the content source may involve determining whether a
current time is equal to or past a time value of the invocation parameter.
Retrieving the syndicated content from the content source may involve
determining whether an event value of the invocation parameter has occurred.
Retrieving the syndicated content from a content source may involve retrieving
the syndicated content from the content source when a current time is equal to
or
past the time value of the invocation parameter. Retrieving the syndicated
content from a content source may involve retrieving the syndicated content
from
3 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
the content source upon the occurrence of an event associated with the event
value of the invocation parameter. Retrieving the syndicated content from a
content source may involve retrieving a plurality of web feeds from one or
more
of the content sources.
Generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content may involve selecting a content item of the one or more
content items. Selecting the content item of the one or more content items may
involve selecting the content item in accordance with an item reference
associated with the syndicated content, wherein the item reference identifies
the
content item. Selecting the content item of the one or more content items may
involve selecting the content item in accordance with a configuration
parameter
selected from the group consisting of a maximum content item size parameter
and a non-redundancy parameter.
Generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content may involve determining whether the content item has been
used in generating a previous presentation message transmitted for delivery to
the mobile device. Generating from the syndicated content the presentation
message for sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content
items of the syndicated content may involve determining whether a transmission
flag associated with the content item is set to indicate previous use.
Generating
from the syndicated content the presentation message for sequentially
presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the syndicated
content may involve determining whether a transmission flag associated with
the
item reference is set to indicate previous use.
Generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content may involve converting the content item to a presentation
4 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
object. Generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content may involve converting the content item to a presentation
object in accordance with a configuration parameter. Converting the content
item
to a presentation object may involve converting the content item to the
presentation object in accordance with a configuration parameter selected from
the group consisting of a supported media types parameter, a display
dimensions
parameter and a maximum presentation size parameter. Generating from the
syndicated content the presentation message for sequentially presenting on the
mobile device one or more content items of the syndicated content may involve
converting the content item to a presentation object in accordance with a
supported media types parameter.
Generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content may involve assembling the presentation object into the
presentation message. Assembling the presentation object into the presentation
message may involve assembling the presentation object into the presentation
message in accordance with a configuration parameter. Assembling the
presentation object into the presentation message may involve assembling the
presentation object into the presentation message in accordance with a
configuration parameter selected from the group consisting of a supported
media
types parameter, a display dimensions parameter, a maximum presentation
message size parameter, and a presentation parameter. The presentation
parameter may be selected from the group consisting of a maximum number of
presentation objects parameter and a service parameter. Assembling the
presentation object into the presentation message may involve assembling the
presentation object and one or more other presentation objects associated with
the syndicated content into the presentation message. Assembling the
presentation object into the presentation message may involve assembling the
5 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
presentation object and one or more other presentation objects associated with
one or more web feeds retrieved from one or more content sources into the
presentation message.
The method may involve delivering the presentation message. Delivering
the presentation message may involve transmitting the presentation message to
a multimedia messaging service center for delivery to the mobile device.
Delivering the presentation message may involve setting the transmission flag
to
indicate previous use. Delivering the presentation message may involve setting
the transmission flag to indicate previous use of the content item associated
with
the item reference. Delivering the presentation message may involve storing
the
transmission flag in a database.
The method may involve receiving from the mobile device one or more
configuration parameters for use in producing the presentation message for
delivery to the mobile device. The method may involve obtaining one or more
configuration parameters in response to receiving a communication originating
from the mobile device. Obtaining one or more configuration parameters in
response to receiving the communication originating from the mobile device may
involve receiving user input. The method may involve storing the one or more
configuration parameters in a database.
The method may involve receiving as user input a user selection of the
syndicated content. Receiving as user input a selection of the syndicated
content may involve receiving from the mobile device a user selection of a web
feed. The method may involve storing the user selection in a database. The
method may involve presenting on the mobile device a list of one or more web
feeds associated with one or more content sources and available for selection
by
the user. The method may involve receiving as user input an invocation time.
The method may involve storing in the database a time value of an invocation
parameter associated with the invocation time. The method may involve
receiving from the mobile device a device parameter selected from the group
6 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
consisting of a supported media types parameter, a display dimensions
parameter and a maximum presentation message size parameter. Receiving
from the mobile device a device parameter selected from the group consisting
of
a supported media types parameter, a display dimensions parameter and a
maximum presentation message size parameter may involve receiving the
device parameter from the mobile device via a WAP gateway of a
telecommunications infrastructure. The method may involve determining a
presentation parameter. Determining the presentation parameter may involve
receiving as user input from the mobile device the presentation parameter.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided a
computer program product comprising computer-executable instructions
embodied in a computer-readable medium for performing one or more methods
of the present invention.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided a
system for producing a presentation message for a mobile device, the system
comprising a database; a configuration component for determining a plurality
of
configuration parameters and storing the plurality of configuration parameters
in
the database; a retrieval component for retrieving syndicated content; and a
message generating component for generating from the syndicated content the
presentation message for sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or
more content items of the syndicated content.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided a
system for producing a presentation message for a mobile device, the system
comprising configuration means for determining a plurality of configuration
parameters; database means for storing the plurality of configuration
parameters;
retrieval means for retrieving syndicated content; and message generating
means for generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content.
7 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
Other aspects and features of the present invention will become apparent
to those of ordinary skill in the art upon review of the following description
of
embodiments of the invention in conjunction with the accompanying figures and
claims.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In drawings which illustrate by way of example only embodiments of the
invention:
Figure 1 is a block diagram of a system for producing a presentation
message for a mobile device according to a first embodiment of the
invention, showing an environment of the system;
Figure 2 is a flow diagram of a method of the system shown in Figure 1 of
producing a presentation message for a mobile device;
Figure 3 is a flow diagram of a method of determining and storing a plurality
of configuration parameters of the system shown in Figure 1;
Figure 4 is a flow diagram of an exemplary method of performing the step
shown in Figure 2 of retrieving syndicated content from a content
source; and
Figure 5 is a flow diagram of an exemplary method of performing the step
shown in Figure 2 of generating a presentation message for
sequentially presenting on a mobile device on or more content
items of the syndicated content.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
A system for producing a presentation message for a mobile device
includes: configuration means for determining a plurality of configuration
parameters; database means for storing the plurality of configuration
parameters;
8 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
retrieval means for retrieving syndicated content; and message generating
means for generating from the syndicated content the presentation message for
sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content.
Referring to Figure 1, the system according to a first embodiment of the
invention is shown generally at 10. The system 10 is operable to perform
methods of the present invention, including methods of retrieving syndicated
content from a content source and generating a presentation message for
sequentially presenting on a mobile device one or more content items of the
syndicated content.
Syndicated content can include any information or data available through
syndication, including being available as all or part of a feed such as a web
feed.
Syndicated content can be obtained from any content source, including a web
feed publisher or other information publisher, or any source that has obtained
the
syndicated content from an information publisher, for example. Examples of
content sources include news websites, weblogs, podcasts, any source of
periodically or intermittently updated information, and any combination
thereof.
Typically, syndicated content is published in a standard syndication format
such as RSS (e.g. Really Simple Syndication) or ATOM. However, the scope of
the present invention is not limited to the retrieval of syndicated content in
any
particular format.
The system 10 includes a server 12 having a processing circuit, such as
the processor 14 shown in Figure 1, and a memory circuit 16. The system 10
also includes a database 18, which is shown in Figure 1 as being connected to
the server 12 by a database connection 20.
The server 12 may be any computing device such as a general purpose
computer, microcomputer, minicomputer, mainframe computer, distributed
networked computer, functionally equivalent discrete hardware components and
any combination thereof, for example.
9 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
The processor 14 is typically a processing circuit that includes one or more
circuit units, such as a central processing unit (CPU), digital signal
processor
(DSP), embedded processor, etc., and any combination thereof operating
independently or in parallel, including possibly operating redundantly. The
processor 14 may be implemented by one or more integrated circuits (IC),
including being implemented by a monolithic integrated circuit (MIC), an
Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC), a Field Programmable Gate
Array
(FPGA), etc. or any combination thereof. Additionally or alternatively, the
processor 14 may be implemented as a programmable logic controller (PLC), for
example. The processor 14 may include circuitry for storing memory, such as
digital data, and may comprise the memory circuit 16 or be in wired
communication with the memory circuit 16, for example.
Typically, the memory circuit 16 and the database 18 are each all or part
of a digital electronic integrated circuit, and may each be implemented by one
or
more integrated circuits (IC), including being implemented by a single
monolithic
integrated circuit (MIC). The memory circuit 16 and the database 18 may be
implemented as Read-Only Memory (ROM), Programmable Read-Only Memory
(PROM), Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM) or Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), flash memory, one or
more flash drives, universal serial bus (USB) connected memory units, magnetic
storage, optical storage, magneto-optical storage, and any combination
thereof,
for example. The memory circuit 16 and the database 18 may be operable to
store memory as volatile memory, non-volatile memory, dynamic memory, and
any combination thereof.
The database 18 may be implemented as part of the processor 14, the
memory circuit 16, or may be implemented separately from the server 12 as
shown in Figure 1. The database 18 typically functions to store information,
typically in the form of recordable and retrievable data for use within or by
the
system 10, including data records stored in association with other data
records.
10 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
Figure 1 shows an exemplary communications environment of the system
10. In the first embodiment, the server 12 is connected by a server connection
22 to a network such as the communications network 24 shown in Figure 1. The
communications network 24 may include any number of communications nodes,
and may include all or part of a telecommunications infrastructure, all or
part of a
data communications infrastructure, all or part of the Internet, and any
combination thereof for example. In some embodiments (not shown), the
database 18 is connected to the server 12 through the communications network
24 in addition or in the alternative to the database connection 20.
The system 10 is typically operable to run any one or more operating
systems, including time operating systems such as Windows, UNIX, Linux, etc.,
and real-time operating systems such as WinCE, Symbian, OSE, Embedded
LINUX, etc., and any combination thereof. The system 10 may be operable to
implement multi-tasking methods involving multiple threads of executable code,
for example.
Source devices 26 are shown in the exemplary arrangement of Figure 1
as being connected via source connections 28 to the communications network 24
for making syndicated content available for transmission and retrieval. In
general, the system 10 is operable to obtain syndicated content, including
receiving information feeds, from any number of content sources including web
feed sources. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to retrieve
syndicated content transmitted through the communications network 24 from any
of the source devices 26. While Figure 1 shows exemplary illustrations of
source
devices 26 as laptop computers, the system 10 is not limited by the type of a
source device 26 and is operable to retrieve syndicated content from any type
of
electronic device operable to transmit syndicated content across the
communications network 24. For example, one or more source devices 26 may
be one or more web server computers, including industry standard web servers.
11 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
Communications devices such as the mobile telephones 30 of users (not
shown) are shown in the exemplary arrangement of Figure 1 as being connected
by wireless connections 32 to the communications network 24. In the first
embodiment, the system 10 is operable to produce presentation messages for
delivery to a communications device such as any of the mobile telephones 30
shown in Figure 1. A person of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that
the
communications devices are not restricted to the mobile telephones 30 shown in
Figure 1, but can be any number of devices for receiving communications such
as cellular telephones, satellite telephones, personal digital assistants,
pagers,
wireless communications devices, or similar devices. In the first embodiment,
the system 10 is operable to effect communications with the mobile telephones
30. In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to effect communications
with the mobile telephones 30 directly from the server 12 to a given mobile
telephone 30 via the server connection 22, at least a portion of the
communications network 24, and the wireless connection 32.
Still referring to Figure 1, the system 10 in the first embodiment is operable
to effect communications with the telecommunications infrastructure 34, which
is
shown in Figure 1 connected to the communications network 24 via a
telecommunications connection 36. The telecommunications infrastructure 34 is
typically operated by a telecommunications provider, and may include
Multimedia
Messaging Service (MMS) equipment for delivering MMS messages from the
system 10 to the mobile telephones 30 and a WAP (Wireless Application
Protocol) gateway for transmitting to the system 10 communications, including
requests, received from the mobile telephones 30. For ease of illustration,
the
telecommunications infrastructure 34 is shown in Figure 1 as being separate
from the communications network 24. However, the telecommunications
infrastructure 34 may also be considered to form part of the communications
network 24.
12 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
The system 10 is operable in the first embodiment to transmit a given
message from the server 12 to the telecommunications infrastructure 34 via the
server connection 22, at least a portion of the communications network 24 and
the telecommunications connection 36. Upon receiving the given message, the
telecommunications infrastructure 34 normally forwards it (or a variant or
derived
message thereof after possible processing by the telecommunications
infrastructure 34) to a specifiable mobile telephone 30 via the
telecommunications connection 36, at least a portion of the communications
network 24, and the wireless connection 32. The portion of the communications
network 24 used for transmitting communications between the system 10 and the
telecommunications infrastructure 34 and the portion of the communications
network 24 used for transmitting communications between the
telecommunications infrastructure 34 and the mobile telephones 30 may be
identical, partly overlapping or completely separate. Thus, in at least normal
operation of the environment in which the system 10 operates, transmitting a
given message to the telecommunications infrastructure 34 results in the
delivery
of the given message to a specified mobile telephone 30.
While the database connection 20, server connection 22, source
connection 28 and telecommunications connection 36 are shown in Figure 1 as
wired connections, these connections 20, 22, 28 and 36 or portions thereof may
be any wired or wireless connection, including a copper wire link, a coaxial
cable
link, a fiber-optic transmission link, a radio link, a cellular telephone
link, a
satellite link, a line-of-sight free optical link, and any combination
thereof, for
example.
Method of Operation
Referring to Figure 2, the memory circuit 16 in accordance with the first
embodiment of the invention contains blocks of code comprising computer
13 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
executable instructions for directing the processor 14 to perform the steps of
a
method shown generally at 38. Additionally or alternatively, such blocks of
code
may form part of a computer program product comprising computer executable
instructions embodied in a signal bearing medium, which may be a recordable
computer readable medium or a signal transmission type medium, for example.
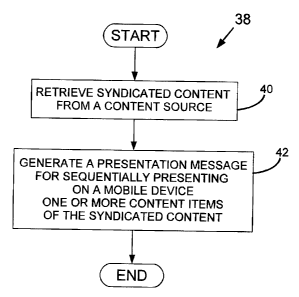
When electrical power is being supplied to the processor 14 and the
memory circuit 16, the processor 14 is directed to begin executing the
instructions of block 40. Block 40 directs the processor 14 to retrieve
syndicated
content from a content source. In the first embodiment, the system 10 (Figure
1)
is operable to cause the processor 14 to retrieve the syndicated content in
the
form of a web feed from the content source, which may be an information
publisher or a source having obtained the web feed from an information
publisher, for example.
Block 42 then directs the processor 14 to generate a presentation
message for sequentially presenting on a mobile device one or more content
items of the syndicated content. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is
operable to cause the processor 14 to generate a presentation message for
sequentially presenting on a given mobile telephone 30 one or more content
items (described further below) of the syndicated content. As described in
further
detail below, the system 10 in at least some embodiments is operable to
generate the presentation message by converting the one or more content items
to presentation objects and assembling the presentation objects into the
presentation message for delivery to the mobile telephone 30.
After block 42 has been executed, the processor 14 is then directed to end
the method 38.
Referring to Figure 3, the system 10 in the first embodiment is operable to
determine and store configuration parameters for use in executing methods of
the system 10. Such configuration parameters typically include user selections
of web feeds, device parameters and presentation parameters. An exemplary
14 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
method of determining and storing configuration parameters of the system 10 is
shown generally in Figure 3 at 44. The method 44 is preferably executed for a
given mobile telephone 30 and associated user at any time before a given
presentation message is delivered to the given mobile telephone 30. For
example, a user (not shown) may use the given mobile telephone 30, or other
device useable for communicating with the system 10 via the communications
network 24, to log into a configuration feature of the system 10 such that the
system 10 operates to determine one or more of the configuration parameters
before delivering the presentation message to the given mobile telephone 30.
The system 10 is operable then to make use of the configuration parameters in
generating the presentation message for delivery to the given mobile telephone
30.
Block 46 of the method 44 directs the processor 14 to deliver to a mobile
device, such as the given mobile telephone 30, a list of available web feeds.
In
general, the system 10 is operable to make available to any number of mobile
devices one or more lists of syndicated content, each of which may include any
number of available web feeds. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is
operable to deliver the list of web feeds to the given mobile telephone 30 via
the
communications network 24. The list may be provided in any suitable format,
including providing the list as a SMS message to the mobile telephone 30,
providing the list as a MMS message via the telecommunications infrastructure
34, making the list available for viewing on the mobile telephone 30 via a web
page of a system 10 website, and any combination thereof, for example. The
system 10 typically stores the list of available web feeds in the database 18
and
retrieves the list of web feeds from the database 18 for delivery of the list
to the
given mobile telephone 30. In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to
cause the processor 14 to effect delivery of the list of available web feeds
in
response to a reply received from the mobile telephone 30 in reply to a
message,
such as a SMS or MMS message, for example. In some embodiments, the
15 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
system 10 operates to deliver the list of available web feeds only after the
successful completion by the user of a login or similar process. The system 10
is
operable in the first embodiment to provide other information, such as
informational or promotional material, with the list of available web feeds.
Block 48 directs the processor 14 to receive from the mobile device a user
selection of a web feed. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to
receive as user input from the given mobile telephone 30 that user's selection
of
a web feed listed on the list of available web feeds. For example, the system
10
is operable to receive from the given mobile telephone 30 a URL (Uniform
Resource Locator), name or other identifying indicator associated with a web
feed source that had been typed in by a user for transmission to the system
10.
Additionally or alternatively, receiving a user selection of a web feed may
involve
receiving an indication, such as a URL or similar, of a web feed source in
response to a user selecting a "Send Me" type hyperlink button presented at a
website of the web feed source, for example. The user selection of a hyperlink
button may be received by the system 10 from any source, including receiving
the user selection of the hyperlink button from the mobile telephone 30 that
was
employed to make such selection. The system 10 is preferably operable to
determine the user selection of the web feed from the information contained
within a hyperlink button received by the system 10.
In some embodiments, the execution of block 46 to deliver to the given
mobile telephone 30 a list of available web feeds is optionally executed or
not
executed at all. In such embodiments, the system 10 is operable to receive a
communication originating from the given mobile telephone 30, such as a
communication initiated by the user selection of a hyperlink button indicating
a
requested web feed, and to obtain the user selection of the requested web feed
from the received communication, including possibly from header information
associated with the received communication.
16 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to receive a user
selection of a web feed or other syndicated content not listed on the list of
available web feeds as a syndicated content request, for example. In the first
embodiment, the system 10 is operable to fulfill such request, provided such
request is for a valid and available web feed. Typically, the user selection
is
received by the system 10 from the given mobile telephone 30 via the
communications network 24. In some embodiments, the user selection is
received via the telecommunications infrastructure 34, including via the WAP
gateway of the telecommunications infrastructure 34. Additionally or
alternatively, the user selection may be received via a SMS message
originating
from the given mobile telephone 30.
Block 50 directs the processor 14 to determine device parameters. In the
first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to determine device parameters of
the given mobile telephone 30, including a supported media types parameter, a
display dimensions parameter, a maximum presentation size parameter, other
related parameters, and any combination thereof.
The supported media types parameter indicates in the first embodiment
the types of media (e.g. ASCII text, UTF-8 encoded text, GIF images, JPG
images, PNG images, MPG videos, 3GPP videos, etc.) supported by the given
mobile telephone 30, the mobile telephone 30 generally being capable of
displaying supported media types of content.
The display dimensions parameter indicates in the first embodiment a size
of the display of the given mobile telephone 30.
The maximum presentation size parameter indicates in the first
embodiment the maximum data size, which may be measured in bytes or
multiples thereof for example, of a message, such as a MMS message, that can
be received and processed by the given mobile telephone 30.
In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to produce a
presentation message for delivery to a mobile device in accordance with the
17 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
media types supported by the mobile device, the display dimensions of the
mobile device, and such that the data size of the presentation message does
not
exceed the maximum size of a message that can be received by the mobile
device.
In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to specify the value of
one or more device parameters, such as where such device parameter value is
not obtained from a given mobile telephone 30 itself or from its user as user
input
or would otherwise exceed a system 10 maximum value or allowable range of
values for such device parameter value. In such embodiments, the system 10 is
operable to specify the value of such device parameters in accordance with
associated system 10 default values.
In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to determine the device
parameters from header information associated with communications received
from the given mobile telephone 30, including determining the device
parameters
from a UserAgentProfile parameter. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is
operable to receive the UserAgentProfile as part of a request, or response to
a
request, received from the given mobile telephone 30, which request or
response
is typically received by the system 10 via the wireless connection 32, and may
be
received via the WAP gateway of the telecommunications infrastructure 34. For
example, the UserAgentProfile may be transmitted from the given mobile
telephone 30 when transmitting the user selection of the web feed (block 48).
In
some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to receive the UserAgentProfile
by receiving a response from the given mobile telephone 30 to a request
delivered to the given mobile telephone 30. Additionally or alternatively, the
system 10 in some embodiments is operable to separately receive each of the
configuration parameters in separate communications.
In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to update one or more
device parameters when a user changes from one mobile telephone 30 to a new
18 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
mobile telephone 30, including doing so without requiring the user to create a
new user account for login purposes.
In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to accept a request that
a system 10 service be provided to a given mobile telephone 30, where such
request is received from a device other than the given mobile telephone 30. In
such embodiments, the UserAgentProfile parameter associated with the given
mobile telephone 30 typically cannot be obtained directly from such other
device.
In circumstances where the device parameters have not been previously
determined and the UserAgentProfile is not available, the system 10 is
operable
in the first embodiment to determine the device parameters in accordance with
system 10 default values. Additionally or alternatively, the system 10 is
operable
in at least some embodiments to determine the device parameters in response to
user input received from such other device. For example, such user input may
include an indication of the make and model of the given mobile telephone 30.
In
some embodiments, the system 10 is operable to provide a list of makes and
models of mobile telephones 30 for selection by the user of a specific make
and
model. In variations of embodiments, such list may include a text format list,
graphic images showing models of mobile telephones 30, and any combination
thereof for example.
Block 52 directs the processor 14 to determine one or more presentation
parameters. Presentation parameters typically indicate features, including
desired features and user-specifiable features, of the presentation message
that
are not device dependent, and may or may not be specific to a given mobile
telephone 30. For example, presentation parameters in at least some
embodiments include an invocation parameter, a periodicity parameter, an
object
display duration parameter, a maximum number of presentation objects
parameter, a maximum content item size parameter, a non-redundancy
parameter, service parameters, other related parameters, and any combination
thereof.
19 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
In the first embodiment, the value of the invocation parameter represents a
condition, such as an event or a time or times, for which the user would like
to
receive the presentation message generated on the basis of the user selected
web feed received by executing block 48. For example, the value of the
invocation parameter may indicate one or more days of the week, including one
or more groups of days of the week (e.g. weekdays, non-holiday weekdays,
weekend days, weekend days and holidays, etc.), and one or more user
specified times during such indicated days. Each specified time may be
indicated by hours and minutes (e.g. 7:00 a.m., 7:12 p.m., 19:45, etc.), for
example. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to permit a
variety
of different times to be specified in association with a variety of different
days or
groups of days. For example, the value of the invocation parameter may include
the invocation times of 7:00 a.m. and 4:30 p.m. in association with weekdays,
the
invocation times of 8:50 a.m. and 6:30 p.m. in association with Saturday, and
the
invocation time of 11:00 a.m. in association with Sunday, for example.
Additionally or alternatively, the condition represented by the value of the
invocation parameter includes in some embodiments one or more events. For
example, the value of the invocation parameter may include an indication that
a
presentation message be generated and delivered to the user's mobile telephone
30 at or after each occurrence of a new score associated with one or more
sports
events being published by a specifiable content source. In this example, a
user
may specify that a new presentation message be delivered when an updated
score for a selected sports match becomes available or when a new completed
game score for each match in a tournament or championship series becomes
available, for example.
The value of the periodicity parameter in the first embodiment indicates a
numeric periodicity in association with one or more invocation times. For
example, if the value of the invocation parameter includes the days specified
as
Tuesday and Friday, and the specified times are 7:00 and 19:00, then a
20 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
periodicity of 2 would result in invocation of presentation message generation
the
Tuesday and Friday at 7:00 and 19:00 hours of every second week, and a
periodicity of 4 would result in invocation every fourth week, or once per
month.
Other times and arrangements can be specified by the periodicity parameter and
are within the scope contemplated by the present invention.
The object display duration parameter indicates the duration of time a
given presentation object of the presentation message is to be displayed on a
given mobile telephone 30. In the first embodiment, this object display
duration
parameter is defined by the system 10 as a fixed value for all presentation
objects of all presentation messages for all mobile telephones 30, and thus
block
52 can be optionally executed in respect of this object display duration
parameter. In some embodiments, however, the system 10 is operable to
determine a value of the object display duration parameter for a given
presentation object in accordance with the type of information contained
within
that given presentation object. For example, a presentation object containing
a
large amount of text may be displayed for a longer time than a presentation
object containing less text, thereby advantageously providing a greater amount
of
time for a user to read the increased amount of text. In such embodiments, the
value of the object display duration parameter may be determined separately
for
each presentation object, specified for groups of presentation objects within
a
given presentation message, specified for all presentation objects of a given
presentation message, specified for the presentation objects of all
presentation
messages, and any combination thereof, for example.
The maximum number of presentation objects parameter indicates the
maximum number of presentation objects permitted to be included within one
presentation message. In the first embodiment, the value of the maximum
number of presentation objects parameter is defined by the system 10 as a
fixed
value for all presentation objects of all presentation messages in respect of
all
mobile telephones 30, thus block 52 can be optionally executed in respect of
this
21 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
parameter. However, in general, the value of the maximum number of
presentation objects parameter may be determined separately for each
presentation message and/or type thereof and separately in respect of each
mobile telephone 30 or group thereof, for example.
The maximum content item size parameter indicates a maximum size (e.g.
in bytes or a multiple thereof) of a content item selected for conversion to a
presentation object. In the first embodiment, the value of the maximum content
item size parameter is defined by the system 10 as a fixed value for all
content
items of all web feeds in respect of all mobile telephones 30, thus block 52
can
be optionally executed in respect of this parameter. However, in general, the
value of the maximum content item size parameter may be determined
separately for each web feed and/or type thereof and separately in respect of
each mobile telephone 30 or group thereof, for example.
The non-redundancy parameter indicates whether a content item that has
previously been processed by converting the content item to a presentation
object and assembling the presentation object into a presentation message
delivered to a given mobile telephone 30 should be processed again as it was
previously processed or excluded from processing such that presentation
messages generated and delivered by the system 10 do not include previously
delivered or otherwise redundant information. In the first embodiment, the non-
redundancy parameter is set by the system 10 to exclude redundancies in all
presentation messages for all mobile telephones 30. Avoiding redundancy in
presentation messages advantageously improves the processing efficiency of the
system 10 and, additionally or alternatively, advantageously reduces the size
of
presentation messages being delivered to mobile telephones 30, which can
reduce data transfer costs for users. In some embodiments, the value of the
non-redundancy parameter for a given mobile telephone 30 is determined from
user input received in association with the given mobile telephone 30.
22 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
Service parameters are employed by the system 10 in the first
embodiment to permit the inclusion into presentation messages of additional
information, which is typically independent of the content items associated
with
the presentation messages. A given service parameter in the first embodiment
includes the additional information to be included in a given presentation
message, or groups of presentation messages; and an associated indication of
the location or locations within the given presentation message(s) at which
the
additional information is to be added. The additional information may include
instructional information such as instructions related to the use of services
offered by the system 10, including instructions on how to upgrade or
unsubscribe to a system 10 service. Additionally or alternatively, the
additional
information may include promotional information, including advertisements, for
example. Instructional information may be injected into or otherwise added to
a
presentation message at or near its end, while promotional information may be
injected into or otherwise added to a presentation message at or near its
beginning, for example.
In some embodiments, one or more configuration parameters are user
specifiable such that determining such configuration parameters involves
receiving indications of such configuration parameters as user input and may
involve prompting users of the mobile telephones 30 for their respective
selections of indications of such configuration parameters and/or presenting a
list
of configuration parameters on the mobile telephones 30 or other
communications devices, for example. In some embodiments, the system 10 is
operable to determine the values of one or more configuration parameters in
accordance with system 10 default values, including overriding values
indicated
by a UserAgentProfile, selected by a user, or both indicated by a
UserAgentProfile and selected by a user. In some embodiments, one or more
configuration parameters are determined in accordance with system 10 default
values such that one or more steps of blocks 50 and 52 are optionally executed
23 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
or not executed at all. In some embodiments, one or more configuration
parameters are stored in the database for later retrieval and use when
generating
a given presentation message. In some embodiments, the system 10 is operable
to generate a given presentation message such that a user of the given mobile
telephone 30 is permitted to update or otherwise select indications of one or
more configuration parameters and the system 10 is operable to modify the
given
presentation message accordingly. For example, one or more steps of the
blocks 50 and 52 may be performed during execution of the method 44 (as
shown in Figure 3); during the execution of other methods of the system 10;
before, during or after the presentation of a given presentation message on a
given mobile telephone 30; and any combination thereof, for example.
Block 54 directs the processor 14 to store configuration parameters in a
database. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to store
configuration parameters in the database 18 (Figure 1). For ease of
illustration,
Figure 3 shows block 54 being executed after the execution of blocks 46 to 52.
However, each configuration parameter can, in variations of the present
invention, be stored at any time after being received, determined or otherwise
obtained by the system 10, including being stored immediately after being
obtained.
While Figure 3 shows blocks 46 to 54 in a specific order, in general the
steps of the method 44 can be executed in any order, and each step may be
repeated as may be suitable for operation of the system 10. In typical
operation
of the system 10 for a given mobile telephone 30, at least some steps of the
method 44 are executed prior to executing the method 38 (Figure 2).
Referring to Figure 4, an exemplary method of directing the processor 14
to perform steps of block 40 (Figure 2) is shown generally at 58.
Block 60 of the method 58 directs the processor 14 to determine whether
invocation should occur. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to
determine whether to invoke the retrieval of one or more web feeds or other
24 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
syndicated content. In typical operation of the system 10, determining whether
to
invoke involves determining whether the current time is equal to or past a
time
value of the invocation parameter determined by block 52 (Figure 3), whether
the
event defined by an event value of the invocation parameter has occurred, or
both whether the time and event values of the invocation parameter have
occurred. In some embodiments, determining whether to invoke involves
determining whether the current time is equal to or after a specifiable time
prior to
a time value of the invocation parameter and within a specifiable duration
before
that time value, which duration may be an estimate of the processing time
required for generating and delivering a presentation message. Determining the
time value of an invocation parameter typically involves taking into account
the
numeric value of any associated periodicity parameter, such as by defining one
or more invocation parameters in response to any associated periodicity
parameter and/or calculating one or more time values of an invocation
parameter
on the basis of any associated periodicity parameter.
If the processor 14 determines not to invoke, then the process returns to
the beginning of the method 58 for re-execution of block 60. In the first
embodiment, the system 10 is operable to wait for the appropriate invocation
time or event. For ease of illustration, Figure 4 shows that the processor 14
does
nothing other than repetitively execute block 60 until the appropriate
invocation
time or event occurs. However, the system 10 in variations of the present
invention is operable to perform other tasks while waiting for the appropriate
invocation time or event to occur. In some embodiments, the system 10 is
operable to periodically compare the current time with the time values of
invocation parameters for any number of mobile telephones 30, and operable to
periodically check for the occurrence of events defined by event values of
invocation parameters for any number of mobile telephones 30. In variations of
embodiments, the processor 12 is operable to generate and/or receive
interrupts
25 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
indicating an appropriate invocation time or event has occurred, and is
operable
to respond to any such interrupts.
If the processor 14 determines to invoke, the processor 14 is directed to
execute block 62, which directs the processor 14 to retrieve a web feed from a
web feed source. In general, the system 10 is operable in the first embodiment
to retrieve any number or amount of syndicated content from any number of
content sources. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to
retrieve
the web feeds in accordance with the user selection received by block 48. In
some embodiments, all the user selected web feeds from a given web feed
source are retrieved during a given execution of block 62. In some instances,
the
web feed or web feeds being retrieved are formatted in accordance with the RSS
format or the ATOM syndication format. However, operation of the system 10 is
not limited to these exemplary feed formats.
After block 62 has been executed, the processor 14 is directed to execute
block 64, which directs the processor 14 to determine whether there are more
web feeds. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to determine
whether there are web feeds or other syndicated content indicated by the user
selection received by block 48 (Figure 3), apart from the web feeds that have
been already retrieved by block 62.
If the processor 14 determines that there are more web feeds, the
processor 14 is directed to block 62 for the retrieval of another web feed,
including possibly retrieving another web feed from a different web feed
source.
If the processor 14 determines that there are no more web feeds for
retrieval, the processor 14 is then directed to return to the method 38 at
block 42
(Figure 2).
While Figure 4 shows the retrieval of one web feed at a time, the system
10 is operable in some embodiments to retrieve more than one web feed
simultaneously or within a single transmission, and is operable in some
26 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
embodiments to receive a plurality of web feeds from one or more web feed
sources within a single transmission, for example.
Still referring to Figure 4 and with reference to the first embodiment, the
system 10 is operable to execute blocks 62 to 64 until one or more, including
possibly all, the web feeds required to generate (e.g. in accordance with
block 42
of Figure 2) one or more, including possibly all, presentation messages
associated with one or more, including possibly all, mobile telephones 30 for
which invocation occurs in accordance with block 60.
Referring to Figure 5, an exemplary method for directing the processor 14
to perform steps of block 42 (Figure 2) in respect of a given mobile telephone
30
is shown generally at 66.
Method 66 begins execution at block 68, which directs the processor 14 to
select a content item. Such content item may be a content item of syndicated
content retrieved from a content source by block 40 (Figure 2), for example.
In
the first embodiment, selecting a content item involves selecting the content
item
as a subset of the syndicated content in accordance with an item reference.
Such item reference may take any form capable of referencing the content of a
given content item, and may include a URL, a data pointer, an item identifier
such as start and end delimiters defining the content item within retrieved
syndicated content, other related indications, and any combination thereof for
example. In some embodiments, selecting a content item involves defining start
and end points of an item in accordance with configuration parameters
associated with the given mobile telephone 30 or other parameters of the
system
10, such as default parameters, for example. Such defined start and end points
may be determined by a desired size, such as measured in bytes, of a content
item, including being determined by a fixed and/or predetermined size. For
example, such defined start and end points may be determined in accordance
with a value of the maximum content item size parameter.
27 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
Content items may be ordered such that executing the method 66 begins
by executing block 68 to select a first content item, and subsequent
executions of
block 68 cause the system 10 to select a next content item in accordance with
an
ordering scheme for the content items.
After block 68 is executed, the processor 14 is directed to execute block
70, which directs the processor 14 to determine whether the content item
selected by block 68 has already been used. In the first embodiment, the
system
is operable to determine whether the content item selected by block 68 has
already been used in a method of the system 10 to generate a presentation
10 message previously transmitted for delivery to the given mobile telephone
30. In
the first embodiment, determining whether the content item has already been
used involves determining whether a transmission flag is set to indicate
previous
use. In some embodiments, the transmission flag is associated with an item
reference identifying the content item, such that determining whether the
content
item has already been used involves determining whether the transmission flag
associated with the item reference of the content item is set to indicate
previous
use.
If the content item has already been used, then the processor 14 is
directed to execute block 68 to select a next content item. In this manner,
previously used content items are advantageously excluded from further
processing of the method 66. Excluding previously used content items from such
further processing advantageously improves the processing efficiency of the
system 10. Additionally or alternatively, excluding such content items
advantageously reduces the size of the presentation messages being delivered
to the given mobile telephone 30, which can reduce data transfer costs for the
user.
If the content item has not already been used (including possibly having
been updated or otherwise altered since a previous use), then the processor 14
is directed to execute block 72, which directs the processor 14 to convert the
28 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
content item to a presentation object in accordance with a configuration
parameter. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to convert the
content item from a web feed format, such as RSS or ATOM syndication format,
to a presentation object, such as a slide or other object, suitable for
inclusion in a
presentation message. In typical operation of the first embodiment, such
presentation message is a MMS message for sequential presentation of one or
more presentation objects converted from one or more content items. In the
first
embodiment, the system 10 is operable to convert the content item into a
presentation object that incorporates only supported media types in accordance
with the supported media types parameter and that is not of such size as to
cause a presentation message generated on the basis of the presentation object
to exceed the value of its maximum presentation size parameter, if any. In
some
embodiments, the system 10 is operable to convert the content item into a
presentation object that is compatible with the display dimensions parameter
associated with the given mobile telephone 30, including by resizing a content
item, presentation object, or both a content item and a presentation object,
or
portions thereof. Additionally or alternatively, the system 10 is operable in
some
embodiments to convert the content item into a presentation object that
incorporates one or more presentation parameters for that presentation object,
such as the object display duration parameter and/or a service parameter for
example.
While blocks 68 to 72 shown in Figure 5 accords with an exemplary
embodiment of the invention, in some embodiments block 70 is optionally
executed or not executed at all. For example, the system 10 is operable in the
first embodiment to execute block 70 if the non-redundancy parameter is set to
a
first value, such as TRUE or binary one, and to not execute block 70 if the
non-
redundancy parameter is set to a second value, such as FALSE or binary zero.
If
block 70 is not executed, then all content items selected by executing block
68,
29 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
whether already used or not, are presented for processing by block 72 as
described herein above.
The iterative nature of the method 66 advantageously permits the content
items of each web feed retrieved by block 62 (Figure 4) to be converted to
presentation objects by block 72 multiple times in accordance with different
values of configuration parameters, such as when generating presentation
messages associated with different mobile telephones 30 for which invocation
occurs in accordance with block 60 (Figure 4), without having to retrieve the
same web feed multiple times. In some embodiments, however, a given web
feed may be retrieved multiple times when used in generating different
presentation messages associated with different mobile telephones 30 for which
invocation occurs in accordance with block 60 (Figure 4).
After block 72 is executed, the processor 14 is directed to execute block
74, which directs the processor 14 to determine whether there are more content
items. If the processor 14 determines that there are more content items, the
processor 14 is directed to execute block 68 to select a next content item. In
the
exemplary operation of the method 66 of Figure 5, blocks 68, 70 and 72 are
executed until there are no further content items for selection and
conversion.
Still referring to Figure 5 and with reference to the first embodiment, the
system 10 is operable to select and convert one or more, including possibly
all,
content items required to generate one or more, including possibly all,
presentation messages associated with one or more, including possibly all,
mobile telephones 30 for which invocation occurs in accordance with block 60
(Figure 4).
In some embodiments, however, the number of content items is limited to
a specifiable maximum number of content items, including limiting the maximum
number of content items selected for conversion such that any presentation
message generated on the basis of such content items does not violate the
of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
maximum number of presentation objects parameter or other related parameter,
including any default parameter of the system 10.
If the processor 14 determines that there are no more content items, then
the processor 14 is directed to executed block 76, which directs the processor
14
to assemble the presentation object into the presentation message. Assembling
the presentation object into the presentation message typically involves
assembling all presentation objects converted from content items by block 72
into
one presentation message. However, the system 10 is operable in some
embodiments to assemble a subset of the presentation objects converted from
content items by block 72 into one presentation message. For example, the
system 10 is operable in some embodiments to assemble presentation objects
into one or more presentation messages in which each such presentation
message does not exceed the value of the maximum presentation size
parameter determined by block 52 (Figure 3). In the first embodiment, the
system 10 is operable to assemble presentation objects into one or more
presentation messages which do not contain more presentation objects than
indicated by the value of the maximum number of presentation objects parameter
associated with a given mobile telephone 30. In the first embodiment, the
system 10 is operable to assemble presentation objects into one or more
presentation messages that are compatible with the supported media types
parameter associated with the given mobile telephone 30. In the first
embodiment, the system 10 is operable to assemble presentation objects into
one or more presentation messages that are compatible with the display
dimensions parameter associated with the given mobile telephone 30, including
by resizing a presentation object or portion thereof for example. Additionally
or
alternatively, the system 10 is operable in some embodiments to assemble
presentation objects into one or more presentation messages that incorporate
one or more presentation parameters associated with the one or more
presentation messages, respectively, including assembling a presentation
object
31 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
into a presentation message in accordance with a value of the object display
duration parameter and in accordance with one or more service parameters.
Executing block 76 preferably results in at least one presentation message
that, when viewed on the given mobile telephone 30, causes the presentation
objects converted from content items by block 72 to be sequentially displayed
on
the mobile telephone 30. Sequentially displaying presentation objects on a
mobile telephone 30 may involve displaying each presentation object for a
duration of time, specified by the object display duration parameter, in a
sequence to form a slide presentation or similar other presentation message on
the mobile telephone 30. In the first embodiment, the presentation message is
a
MMS message encoded in accordance with the MMS standard. However, in
general, the presentation message may be produced in accordance with any
standard for any format and encoded in any language suitable for the
sequential
display of presentation content.
In some embodiments, the order in which blocks 74 and 76 are executed
is the reverse of that shown in Figure 5. In such embodiments, method 66
involves selecting one or more content items by executing blocks 68 and 70,
then
executing block 72 to convert one content item to a first presentation object,
then
executing block 76 to assemble that first presentation object into a given
presentation message, then executing block 74 to determine whether there are
more content items. In this manner, each presentation object is assembled into
a
given presentation message before converting another content item to the next
presentation object, thereby permitting the given presentation message to
incrementally increase in size with each newly converted content item.
After executing block 76, the processor 14 is directed to execute block 78,
which directs the processor 14 to determine whether there are more
presentation
messages. If the processor 14 determines that there are more presentation
messages, such as there being more presentation messages that can be
32 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
generated from the web feeds retrieved by block 62 (Figure 4), the processor
14
is directed to execute block 68 to select a next content item.
Still referring to Figure 5 and with reference to the first embodiment, the
system 10 is operable to assemble one or more presentation objects into one or
more, including possibly all, presentation messages associated with one or
more,
including possibly all, mobile telephones 30 for which invocation occurs in
accordance with block 60 (Figure 4).
If the processor 14 determines by executing block 78 that there are no
more presentation messages to be generated, then the processor 14 is directed
to execute block 80, which directs the processor 14 to deliver the
presentation
message. In the first embodiment, the system 10 is operable to deliver one or
more, including possibly all, presentation messages associated with one or
more,
including possibly all, mobile telephones 30 for which invocation occurs in
accordance with block 60 (Figure 4). Delivering presentation messages may
involve delivering a given presentation message to multiple mobile telephones
30, and may involve delivering a plurality of presentation messages to a given
mobile telephone 30, for example.
In the first embodiment, delivering the presentation message involves
transmitting the presentation message (or presentation messages) produced by
block 76 to the telecommunications infrastructure 34 for delivery to the given
mobile telephone 30. In general, however, the scope of the present invention
contemplates any suitable method of delivering the presentation message to the
given mobile telephone 30. In some embodiments, delivering the presentation
message includes setting the transmission flag to indicate previous use of the
content items that were converted to the presentation objects assembled into
the
presentation message being transmitted for delivery. In some embodiments,
delivering the presentation message includes storing the setting for the
transmission flag in the database 18 in association with item references
33 of 40
CA 02633177 2008-06-03
identifying the content items used in the presentation message being
transmitted
for delivery to the given mobile telephone 30.
After executing block 80, the processor 14 is directed to end the method
66 and return to the method 38 (Figure 2).
While Figure 5 shows block 80 being executed after exiting the loop
shown as containing blocks 68 to 78, in some embodiments block 80 is executed
immediately after executing block 76 and prior to executing block 78 such that
each newly generated presentation message is transmitted for delivery before
commencing to generate a next presentation message.
Referring back to Figure 2, after block 42 is executed the processor 14 is
directed to end the method 38. In some embodiments, however, the processor
14 is directed to execute block 60 of Figure 4, thereby waiting for the next
appropriate invocation time or event to occur. Additionally or alternatively,
the
processor 14 may be directed to execute the method 44 of Figure 3 in respect
of
the same or different mobile telephone 30.
Thus, there is provided a method of producing a presentation message for
a mobile device, the method comprising: retrieving syndicated content from a
content source; and generating from the syndicated content the presentation
message for sequentially presenting on the mobile device one or more content
items of the syndicated content.
While embodiments of the invention have been described and illustrated,
such embodiments should be considered illustrative of the invention only. The
invention may include variants not described or illustrated herein in detail.
Thus,
the embodiments described and illustrated herein should not be considered to
limit the invention as construed in accordance with the accompanying claims.
34 of 40