Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02637079 2008-07-03
Docket No.: KMC-724
Inventors: Jeffrey T. Mergy
Anthony D. Serrano
Eric V. Cole
MULTIPLE MATERIAL GOLF CLUB HEAD
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[001] This invention relates generally to golf equipment and, in particular,
to golf club
heads.
10021 Iron-type golf clubs are intended primarily for second and later shots
rather than
tee shots. Often they are used for hitting shots from bare ground or sand as
well as from turf.
Accordingly, conventional iron-type golf clubs are designed so that the club
head and, in
particular, the sole of the club head are made of a durable material such as
iron, stainless steel or
like. It is generally desirable for an iron-type golf club head to have
perimeter weighting to
increase its moment of inertia to resist twisting. It is also desirable for an
iron-type golf club
head to have a low center of gravity to enhance the ability of the club head
to launch the golf ball
in an appropriate trajectory and for the club head to be forgiving on off-
center hits.
Conventional iron-type golf clubs accomplish some of these goals through the
use of cavity back
club heads, tuning ports in the club heads and, more recently, lightweight
forged or rolled
titanium club head faces attached to heavier perimeter members.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
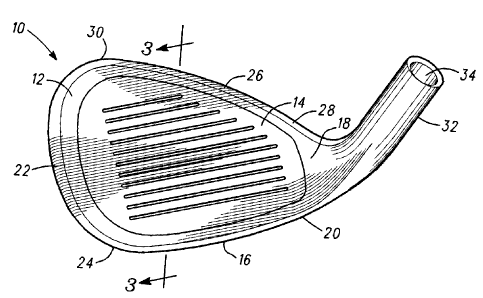
[003] Fig. 1 is a front perspective view of a golf club head incorporating
features of the
present invention;
[004] Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of one embodiment of a face plate
insert according
to the present invention;
1
CA 02637079 2008-07-03
Docket No. KMC-724
[005] Fig. 3 is a cross-sectional view of the club head of Fig. 1 taken along
line 3-3;
[006) Fig. 4 is a cross-sectional view, similar to Fig. 2, of another
embodiment of the
face plate insert; and
[007] Fig. 5 is a cross-sectional view, similar to Fig. 3, of a club head
including the face
plate insert of Fig. 4.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[008] The drawing figures are intended to illustrate the general manner of
construction
and are not necessarily to scale. In the detailed description and in the
drawing figures, specific
illustrative examples are shown and herein described in detail. It is
understood, however, that
the drawing figures and the detailed description are not intended to limit the
invention to the
particular form disclosed, but are merely illustrative and intended to teach
one of ordinary skill
how to make and/or use the invention claimed herein and for setting forth the
best mode for
carrying out the invention.
10091 With reference to Figs. 1-3, an iron golf club head 10 incorporating
features of the
present invention is preferably composed of two main components, a perimeter
member 12 and a
face plate insert 14. The perimeter member 12 is preferably composed of a
relatively dense
material such as stainless steel, carbon steel, beryllium-copper, or other
material having a density
of least 7.0 grams per cubic centimeter. The perimeter member has a sole wall
16, a heel wall 18
extending upwardly from heel end 20 of sole wal116, a toe wall 22 extending
upwardly from toe
end 24 of sole wall 16, and a top wall 26 extending from an upper end 28 of
heel wall 18 to an
upper end 30 of toe wall 22. Perimeter member 12 further comprises a hosel 32
having a hosel
bore 34 for receiving a golf club shaft (not shown).
2
CA 02637079 2008-07-03
Docket No. KMC-724
[010] Face plate insert 14 is preferably formed of a core member 36 and a
shell member
38 that encases core member 36. Preferably, core member 36 is composed of a
material such as
aluminum, thermoplastic, thermosetplastic or foam metal having a bulk density
of less than 2.7
grams per cubic centimeter. Core member 36 is preferably a solid prism having
substantially the
same shape as finished face plate insert 14 but smaller in overall size. Core
member 36
preferably has a thickness alpha (a) in the range of 0.025 to 0.040 inches,
and preferably between
0.035 and 0.040 inches.
[011] Shell member 38 comprises a metallic coating that fully encases core
member 36.
Preferably, shell member 38 comprises a nickel iron nanometal having a grain
size on the order
of 10 to 50 nanometers. Shell member 38 comprises a front wall 40, a rear wall
42 and a
perimeter wall 44. Front wall 40 has a front surface 47 arranged for impacting
a golf ball.
Preferably, front wall 40 has a thickness beta ([i) between 0.030 and 0.050
inch, rear wal142 has
a thickness gamma (y) between 0.015 and 0.025 inch, and perimeter wall 44
preferably has a
thickness delta (S) between 0.015 to 0.030 inch.
[012] Shell member 38 may be sintered onto core member 36 to form face plate
insert
14, however, shell member 38 is preferably applied to core member 36 by an
electroplating or
electroforming process such as the electroplating process for applying
nanometals practiced by
Power Metal Technologies, Inc. of Carlsbad, California. This process applies
coatings that are in
excess of 0.010 inches in thickness as opposed to conventional chrome and
other protective
coatings which are typically less than 0.001 inch thick or less than 1% of the
thickness of the part
being coated. All of the thicknesses 0, y and S are at least 1% as thick, and
preferably at least
10% as thick, as the thickness a of core member 36. As can be determined from
an examination
of Fig. 2, face plate insert 14 has an exceptionally high area moment of
inertia as a result of the
3
CA 02637079 2008-07-03
Docket No. KMC-724
displacement between front wall 40 and rear wall 42. Consequently, a face
plate insert
constructed in accordance with the teachings of the present invention is
lighter, stiffer and yet
more forgiving than prior art face plate inserts.
[013) Face plate insert 14 further includes a plurality of grooves 46 disposed
in front
wall 40. Grooves 46 are preferably U-shaped in cross-section with
substantially vertical walls
meeting the front surface 47 of face plate insert 14 along a fillet having a
radius of 0.010 0.001
inch. Because front wall 40 is formed by an electrodeposition process, rather
than casting, the
tolerance on the U-shaped grooves 46 can be held to these close tolerances
without the necessity
of secondary machining.
[014] As shown in Fig. 3, face plate insert 14 may be attached to perimeter
member 12
by any conventional means but in the illustrative embodiment is attached to
perimeter member
12 by placing face plate insert 14 into a recess 48 formed in perimeter member
12 until it comes
to rest against ledge 50. Recess 48 is formed by the sole, heel, toe and top
walls 16, 18, 22 and
26, respectively, of perimeter member 12. A deformable lip 52 is then deformed
until it presses
against shell front wall 40 to form a crimp joint that permanently retains
face plate insert 14 in
place. Face plate 14 may, however, be attached by unconventional means such as
nanobonding
in which dissimilar metals are bonded on a submicroscopic level.
[015] Referring to Figs. 4 and 5, the face plate insert 14 has been replaced
by a face
plate insert 14A. It will be understood that, in the face plate insert 14A,
the core member 36A is
sandwiched between front and rear walls 40A, 42A of a shell member 38A. The
perimeter wall
44 of the face plate insert 14 has been removed from the face plate insert
14A.
[016] Although certain illustrative embodiments and methods have been
disclosed
herein, it will be apparent from the foregoing disclosure to those skilled in
the art that variations
4
CA 02637079 2008-07-03
Docket No. KMC- 724
in modifications of such embodiments and methods may be made without departing
from the
spirit and scope of the invention. For example, although the illustrative
embodiment discloses a
single solid core, multiple cores and/or hollow cores are considered within
the scope of the
invention. Accordingly, it is intended that the invention should be limited
only to the extent
required by the appended claims and the rules and principles of applicable
law.