Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 1 -
INTRAVENOUS SUPPORT APPARATUS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The present invention relates generally to the field of medical
equipment
and, more particularly, to an intravenous support apparatus to hang an
intravenous
liquid supply in order to enable gravity flowing of the intravenous liquids to
a patient.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] Intravenous support apparatuses which are usually referred to as I.V.
stands
or I.V. poles, are conventionally constructed having a tall slender upright
post or pole
mounted onto a relatively small-sized base, sometimes with small wheels. The
post or
pole is fitted with a hanger at the top from which the bottles or pouches of
intravenous
liquids are hung. Optionally, as I.V. pump may be supported on the post or
pole and
connected to the bottles or pouches to pump liquids. For convenience of use,
I.V.
stands are sometimes configured having the post or pole in a telescoping
configuration
in which the sections of the post or pole have a diameter smaller one than
another from
a bottom section to a top section, in order to allow adjustment of the height
level of the
bottles or pouches of the intravenous liquids for controlling the gravity
flowing of the
liquids and for convenience of access.
[0003] Also for convenience of use, the base of stands are usually relatively
small.
However, even under the regular load of the weight of the bottles or plastic
pouches
containing liquids, which are hung on the top of the post or pole, the I.V.
stands are
relatively unstable and can be rather easily knocked over. Therefore it is not
unusual for
the conventional I.V. stands to have additional support for attaching either
the pole or
the base of an I.V. stand to a bed or wheelchair, etc. on which a patient
rests while
receiving intravenous injection. Furthermore, it is not unusual for doctors
and nurses to
hang additional loads such as medical instruments, devices or other articles
on the post
or pole of an I.V. stand. Therefore, the stability of such stands and the
rigidity and
strength of the post or pole of I.V. stands are particularly important.
Another
disadvantage of conventional I.V. stands lies in that a disassembled I.V.
stand is usually
packed in a relatively large box due to the relatively large sizes of the
components,
particularly the base unit. Therefore, it is also desirable to have an I.V.
stand assembly
CA 02637581 2009-10-28
-2-
which can be disassembled into a kit package having relatively small
dimensions for
shipping and storage.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0004] In accordance with one aspect of the present invention, an intravenous
support
apparatus comprising: a pole; means attachable to the pole for hanging an
intravenous
liquid supply on the pole; a base including a plurality of disconnectable legs
having
respective inner ends joined one with another, the joined inner ends forming a
central
body of the base to defme a central passage extending vertically through the
base, the
central passage receiving a bottom end of the pole for supporting the pole in
a upright
position, each leg including a first material containing a core element of a
second
material which is heavier than the first material; and wherein the inner end
of the
respective legs is integrated with a sectorial fraction of the central body of
the base,
the sectorial fraction of each leg being of a shell-configuration and
projecting
upwardly from the inner end of the leg, thereby forming a upwardly projecting
profile
of the central body of the base in order to provide a vertical dimension for
securing
the bottom end of the pole.
[0005] In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, there is
provided a kit for an assembly of an intravenous support apparatus, the kit
comprising: a first section of a pole; a hollow second section of the pole for
receiving
the first section in a telescoping configuration; a hollow third section of
the pole; a
joint element for joining the second and third sections together; means
attachable to
the pole for hanging an intravenous liquid supply on the pole; and a plurality
of legs
to be joined to form a base for supporting the pole in an upright position,
the legs
having respective inner ends adapted for joining one with another to form a
central
body defining a central passage for receiving a bottom end of the pole, each
leg
including a first material which contains a core element of a second material
which is
heavier than the first material, the inner end of the respective legs being
integrated
with a sectorial fraction of the central body, the sectorial fraction of each
leg being of
a shell-configuration.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0006] Further features and advantages of the present invention will become
apparent from the following detailed description, taken in combination with
the
appended drawings, in which:
[0007] Figure 1 is a perspective view of an intravenous stand according to one
embodiment of the present invention;
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 3 -
[0008] Figure 2 is an exploded, perspective partial view of a pole of the
intravenous
stand of Figure 1, showing a joint member for joining upper and lower parts of
a bottom
section of the pole;
[0009] Figure 3 is a perspective bottom view of a disconnectable leg which is
part
of a base of the intravenous stand of Figure 1;
[0010] Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view of the leg of Figure 3 taken along 4-
4,
showing the two-piece configuration of the leg;
[0011] Figure 5 is a perspective view of a core element of the leg of Figure
4;
[0012] Figure 6 is a partial perspective bottom view of three legs of the
intravenous
stand of Figure 1 in an assembly procedure, showing the side connectors of
adjacent
legs for connection to each other;
[0013] Figure 7 is perspective bottom view of an assembled base of the
intravenous
stand of Figure 1, showing the legs connected one to another;
[0014] Figure 8 is a top plane view of a bottom plate used to cover the side
connectors of the connected legs from a bottom side; and
[0015] Figure 9 is a schematic illustration of a box for containing a package
of a kit
to be assembled into the intravenous stand of Figure 1.
[0016] It will be noted that throughout the appended drawings, like features
are
identified by like reference numerals.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
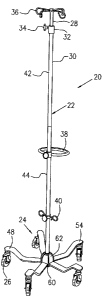
[0017] In Figure 1, an intravenous support apparatus generally referred to as
an
intravenous (I.V.) stand 20 includes a pole 22 in a substantially upright
position,
inserted into and supported by a base assembly 24 which preferably has a
plurality of
small wheels, such as wheel assemblies 26 for convenience of transportation.
[0018] Referring to Figures 1 and 2, the pole 22, according to one embodiment
of
the present invention, may include a top section 28 and a bottom section 30
which is in
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 4 -
a hollow configuration, such as of a steel tube. The top section 28 may also
be made of
a steel tube but has another diameter smaller than the inner diameter of the
bottom
section 30 so as to allow the top section 28 to be inserted into the bottom
section 30 to
form a telescoping configuration. Therefore, the top section 28 can be
extended
upwardly from or be retracted downwardly into the bottom section 30. A lock
device
may be provided to lock the top section 28 in a selected position with respect
to the
bottom section 30. The lock device for example may include a sleeve member 32
frictionally affixed on a top end of the bottom section 30 for receiving a
locking
screw 34 transversely extending through the sleeve member 32 to press against
the top
section 28 as it extends through the sleeve member 32.
[0019] Means are also provided for hanging intravenous bottles or pouches of
intravenous liquids on the pole 22. For example, hooks 36 are removably
attached to a
top end of the top section 28 as shown in Figure 1. Optionally, other
accessories such
as a patient handle 38 and additional hooks 40 may be attached to the pole,
preferably
on the bottom section 30 in a height adjustable manner, which, for example,
may be
used to support an I.V. pump if needed.
[0020] In consideration of convenience for packaging, the pole 22,
particularly the
bottom section 30 thereof, may include separable upper and lower parts 42, 44,
which
are both made from, for example, a same steel tube, therefore having
substantially equal
outer diameters and having substantially equal inner diameters greater than
the outer
diameter of the top section 28. As more clearly illustrated in Figure 2, the
upper part 42
and lower part 44 are joined end to end to form the bottom section 30 of the
pole 20. A
joint member 46 may be used to join the upper and lower parts 42, 44 together.
The
joint member 46, for example, includes a threaded bolt with a middle shoulder
(not
indicated). The shoulder preferably has an outer diameter substantially equal
to the
outer diameter of the upper and lower parts 42, 44 and the threading extends
along the
entire length of the bolt. The threads defined in the respective upper section
and lower
section of the bolt, which are separated by the middle shoulder, may have
opposite
rotational directions for convenience of engagement with complimentary inner
threads
defined in the respective upper and lower parts 42, 44 of the bottom section
30. In such
a configuration, the pole 20 can be conveniently disassembled into three
tubular sections
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 5 -
which may have roughly similar lengths for packaging, while a height
adjustment can
be easily achieved with the telescoping configuration between the top section
28 and the
upper part 42 of the bottom section 30. In a conventional multiple telescoping
configuration however, three or more sections of the pole are all connected in
telescoping configurations and the diameter of the respective telescoping
sections of the
pole from the bottom to the top is progressively smaller one than another,
which
provides height adjustability but compromises the strength and rigidity of the
pole and
thus the load bearing capacity of the I.V. stand. The embodiment of this
invention
however maintains one telescoping configuration for convenience of height
adjustment
of the pole while providing a more secure but disconnectable joining structure
between
the upper and lower parts 42, 44 of the bottom section 30 of the pole, which
advantageously and significantly increases the strength and rigidity of the
pole 22 and
thereby increases the lead bearing capacity of the intravenous stand 20.
[0021] In Figure 1 and 3-8, the base assembly 24 of the I.V. stand 20
according to
one embodiment includes a plurality of disconnectable legs 48 (five legs shown
in this
embodiment). Each leg 48 is configured, for example with a substantially flat
body 50
with an inner end 52 and an outer end 54. The outer end 54 may have a boss 56
defining a bottom surface 58 and a hole 60 which extends inwardly and upwardly
from
the bottom surface 58 for receiving a shaft (not shown) of the small wheel
assembly 26
when the wheel assembly 26 is attached to the outer end 54 of the leg 48,
abutting the
bottom surface 58.
[0022] The inner ends 52 of the respective legs 48 join one to another to form
a
central body 62 (see Figure 1) of the base assembly 24 and to define a central
passage 64 (see Figure 7) extending substantially vertically through the base
assembly 24. The central passage 64 receives a bottom end of the pole 22, for
example
the bottom end of the lower part 44 of the bottom section 30 of the pole, for
supporting
the pole 22 in an upright position as shown in Figure 1. The bottom end of the
pole 22
is secured within the central passage 64 of the central body 62 using a bottom
plate 67
(see figure 8) attached to the bottom side of the central body 62 and a screw
fastener
(not shown) inserted through a central passage 64 of the plate 67. The screw
fastener is
securely engaged with the inner thread of the bottom end of the pole 22 (the
bottom end
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 6 -
of the lower part 44 of the bottom section 30 of the pole 22 in this
embodiment). The
substantially flat body 50 of the respective legs 48 may be bent such that the
central
body 62 formed with the respective inner ends 52 of the legs 48 is positioned
at a level
which is lower than a height level of the outer ends 54 of the legs 48 when
the I.V.
stand 20 is standing upright on the ground or floor. Therefore, when the outer
ends 54
of the legs 48 are supported by the respective small wheel assemblies 26 at a
relatively
higher level with respect to the ground, the central body being in a
relatively lower
position, advantageously increases the stability of the I.V. stand 20 when the
pole 20 is
loaded.
[0023] Each of the inner ends 52 of the respective legs 48, is integrated with
a
sectorial fraction 62a of the central body 62 of the base assembly 24 (1/5 of
the central
body 62 in this embodiment). The sectorial fraction 62a which may be
configured in a
shell configuration, and projects upwardly from the inner end 52 of the leg
48, thereby
forming an upwardly projecting profile of the central body 62 when the five
legs 48 are
assembled together to form the base assembly 24. The upwardly projecting
profile of
the central body 62 provides a vertical dimension for more effectively
securing the
bottom end of the pole 22. The shell configuration of the sectorial fraction
62a of each
leg 48 may include a central wall 66 to increase the rigidity of the hollow
configuration
of the central body 60 formed by the individual shell configurations of the
sectorial
fractions 62a of the legs 48.
[0024] The inner end 52 of each leg 48 may be incorporated with a pair of side
connectors 68 and 70 which are adapted to be positioned adjacent one another
and to be
connected when the respective legs 48 are assembled together, thereby joining
the inner
ends 52 of the legs 48 and securing the respective sectorial fractions 62a in
position to
form the complete central body 62. The respective side connectors 68 and 70 of
each
leg 48 are configured substantially in a sectorial configuration and are
affixed to the
inner end 52 of the leg 48 in locations offset one to another both in
circumference and in
height with respect to the shell configuration of the sectorial fraction 62a.
For example,
side connector 68 projects circumferentially out of the shell configuration of
the
sectorial fraction 62a and is adapted to be received within the adjacent shell
configuration of sectorial fraction 62a when the legs 48 are assembled
together (see
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 7 -
Figure 6). Side connector 70, however, is substantially located within the
shell
configuration of sectorial fraction 62a at the other side thereof and at a
relatively higher
location with respect to the ground when the I.V. stand is positioned upright
on the
ground or floor, so as to match a corresponding side connector 68 of an
adjacent leg 48
which extends into a space below the side connector 70 when the adjacent leg
48 is
positioned at the other side of said leg 48. A hole (not indicated) extends
through the
respective side connectors 68 and 70 so that the hole in one side connector 68
will align
with the hole in a adjacent side connector 70, when all the legs are assembled
in position
as shown in Figure 7. Screws (not indicated) are inserted from the bottom side
of the
central body 62 into the aligned holes to engage with inner threads defined in
the hole of
the side connector 70 (the connector in the higher position), thereby securing
the side
connectors of adjacent legs 48 together.
[0025] The central body 62 formed with the sectorial fraction 62a in the shell
configuration, substantially houses the side connectors 68, 70 of the
respective legs 48
when assembled so that the side connectors 68, 70 are not visible from a top
view of the
I.V. stand 20. The side connectors 68, 70 are also not visible from a bottom
view of the
I.V. stand when the plate 67 is attached to the bottom side of the central
body 62.
[0026] It should be noted that the substantially sectorial side connector 68
may
further have an enlarged tip portion 72 (see Figure 7) which is configured to
function as
a positioning element to provide convenience of angularly positioning the legs
48 for
the assembly procedure and to substantially define a bottom opening of the
central
passage 46. A top opening of the central passage 64 is also defined by the
shell
configuration of the sectorial fractions 62a in combination, when the legs 48
are
assembled together. The top and bottom openings of the central passage 64 of
the
central body 62 have an inner diameter slightly greater than the outer
diameter of the
bottom section 30 of the pole 22 in order to ensure an appropriate fit when
the bottom
section 30 of the pole 22 is inserted into the base assembly 24. The center
wall 66 in the
shell configuration of the respective sectorial fractions 62a is configured to
not interfere
with the insertion of the bottom end 30 of the pole 22, as more clearly shown
in
Figure 4. Optionally, the bottom opening of the central passage 46 formed by
the
enlarged tip portions 72 of the sectorial side connectors 68, may have a
diameter smaller
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 8 -
than the outer diameter of the bottom section 30 of the pole 22 to prevent the
pole 22
from being over-inserted into the base assembly 24, but allowing the fastener
to pass
therethrough to secure the pole 22 to the base assembly 24.
[0027] Each leg 48 may be of an integral two-piece configuration having a
first
material containing a core element of a second material which is heavier and
stronger
than the first material. According to one embodiment as shown in Figure 4, the
leg 48
may include a steel band 74 bent in a configuration desirable for the leg 48,
as shown in
Figure 5. An outer layer composed of a second material, for example an
aluminium
alloy outer layer 76, is formed in a molding process to completely surround
the steel
band 74 in order to form the desired leg configuration. This integral two-
piece
configuration advantageously provides all the advantages of an aluminium alloy
to a
base of an I.V stand including an aesthetically pleasing appearance,
convenience of
manufacturing, resistance to rust etc., while overcoming the disadvantage of
lacking
stability because the aluminium alloy is relatively light and unable to
sustain heavy
loads in comparison with steel.
[0028] The further advantage of the I.V. stand according to the embodiments of
this
invention, lies in that the I.V. stand 20 can be completely disassembled and
packaged
into a relatively compact kit of components as described above, in contrast to
the
package size for conventional I.V. stand assemblies. Hospitals often purchase
and store
large quantities of I.V. stand assemblies. The problem with conventional
products is
that the pole cannot be collapsed to less than a length of 4.5 feet and the
base which is
typically manufactured as a complete unit cannot be disassembled and is
therefore bulky
and unwieldy. The larger size of the packages for such conventional I.V.
stands adds to
the cost of shipping and requires larger storage space and as such poses a
significant
problem. The I.V. stand 20 can be provided in a kit package contained in a
rectangular
box as shown in Figure 9, having the smaller and more compact dimensions L x W
x H
wherein L is between 34.5 inches and 34 inches, W is between 6 inches and 5.5
inches
and H is between 5 inches and 4.5 inches, which reduces shipping costs and
takes up
much less storage space.
CA 02637581 2008-07-15
- 9 -
[0029] The above description is meant to be exemplary only and one skilled in
the
art will recognize that changes may be made to the embodiments described
without
departure from the scope of the invention disclosed. For example, the core
element and
the surrounding outer layer of the legs may be made with materials other than
steel and
aluminium alloy, such as iron and plastic, etc. The connectors of the
respective legs
may be configured differently from the above-described configurations to
similarly
achieve a direct connection of adjacent legs without a separate connector, as
the
described embodiment does. Still other modifications which fall within the
scope of the
present invention will be apparent to those skilled in the art in light of a
review of this
disclosure and such modifications are intended to fall within the appended
claims.