Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
SHOCK ABSORBER FOR COSMETIC COMPACT
Field of the Invention:
The present invention relates to cosmetic product packages that include shock
absorbing means. In particular, the present invention is directed to compact
cases with solid
or semi-solid cosmetic products pressed or caste in a support pan. More
particularly, the
invention is directed to the means for isolating the product containing pan
from external
shock.
Description of the Prior Art:
Compacts for solid or semi-solid cosmetic products generally comprise a base
and a
corresponding cover. The base has at least one cavity dimensioned to receive
the cosmetic.
A shallow plastic or metal pan containing the solid or semi-solid cosmetic
product is secured
in the cavity. The solid or semi-solid cosmetic product may be, for example, a
pressed or
caste powder, a semi-solid paste, or a cake-like consistency. The category of
cosmetic may
be, for example, a powder (e.g., blush), a skin foundation, an eye shadow, a
lip cosmetic, etc.
During shipping or during the normal lifespan of the product, the compact may
be
subjected shocks or impacts, for example, when the compact is accidentally
dropped. Some
formulations of solid and semi-solid cosmetics provided in shallow trays are
susceptible to
cracking and/or crumbling when the cosmetic case is subjected to external
shock, vibration or
impact. This is particularly true for higher quality pressed powders
manufactured with less
compression to provide a softer `feel' to the user and better product payoff
onto the fingers or
an applicator. Clearly, a cracked or crumbled cosmetic product is undesirable
as it presents a
negative impression to a consumer. Furthermore, the cracked or crumbled
cosmetic may
negatively impact the performance of the product. For example, cracked or
crumbled product
may load unevenly onto an applicator (e.g., a brush or a pad). This in turn
may lead to an
undesirable and unattractive distribution of product on the user's skin.
Some attempts have been made to rectify the problem. For example, Japanese
publication No. 2006061189 discloses a cosmetic compact with a cosmetic tray
detachably
fixed in a recess by a collar such that the bottom wall of the tray and the
bottom wall of the
recess are separated by an air layer.
Japanese publication No. 2005304850 discloses a cosmetics container for
storing,
e.g., foundation and eye shadow. The container includes inner plates that form
cosmetic
storage chambers. The plates are selectively mounted at the bottom of the
container by way
of cushion members.
Japanese publication number 9-191928 discloses a shock absorbing and thin
walled
inner plate formed from a thin synthetic sheet. A second inner plate
(presumably non-shock
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
absorbing) is laid in the shock absorbing inner plate. The shock absorbing
inner plate
includes projections for coming in contact with the inner surface of the
housing bottom.
U.S. Pat. No. 5,713,471 discloses a packaging unit including a supporting
element
with a cavity for receiving a pan containing cosmetic. The pan is secured in
the cavity by
elastic holding means (e.g., an o-ring). In addition, compressible means in
the form of flexible
foam or flexible spikes may be provided beneath the pan to compensate for play
and/or
protect against vibration.
Japanese publication No. 2002-177044 discloses a container body with clearance
for
receiving an inner tray for cosmetics. Elastic arms provided in opposite sides
of the
clearance have protrusions to detachably engage recesses in the sides of the
inner tray. The
elastic arms are said to provide properties against a shock to the inner tray.
U.S. Pat. No. 1,552,173 discloses a powder box in which resilient means are
provided
beneath a false bottom to press powder on the false bottom up through a
perforated
dispensing partition.
French patent number 2691339 discloses a compact with a pan supported on
springs
provided to eject the pan from the base to effect a change of pans.
U.S. Pat. No. 1,194,187 discloses a rouge box with a rouge holding pad
yieldably held
at the top of the box by a supporting spring such that when the box is opened
the rouge is
readily accessible at all times. The rouge pad is snuggly received in the box.
Accordingly,
there does not appear to be a gap of sufficient dimension to provide for
lateral movement of
the pad in the box.
U.S. Pat. No. 2,054,004 discloses a vanity case for loose powder with springs
that
push a powder receptacle (a pan) upwardly such that an upper edge of the
receptacle
maintains contact with the underside of a cover when the case is closed, thus
preventing
leakage or spilling of the powder.
Japanese publication number 09-299138 discloses an inner tray for a cosmetic
with
protrusions formed on the outside. The protrusions match a groove on the
inside of the
compact base. The inner tray with the protrusions is said to give good shock
resistance.
Japanese publication number 06-189821 discloses a cosmetic compact with a
rubber
gasket in an annular form between a lower lid and the cosmetic tray such that
a space is
formed between the lower lid and the cosmetic tray.
None of the forgoing references disclose a cosmetic compact for pressed powder
with
a pan received in a clearance in the base of the compact such that a gap is
defined between
the pan and the base, and wherein the pan is suspended by arcuate members
across the gap
and positioned along transverse axes. Accordingly, there is a need for a cost
effective, mass
produce-able cosmetic case having shock absorber means that effectively
prevents pressed
powder cosmetics from fracturing.
2
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
Summary Of The Invention
The present invention is directed to means for dampening shocks, impacts and
vibration transmitted from the base of a cosmetic compact to a pan supported
within the
compact. The pan is adapted to contain solid or semi-solid cosmetic, e.g., a
pressed powder,
which is susceptible to damage in the form of cracking or crumbling, or in the
worst case,
release from the pan. The shock absorbing means minimizes or eliminates damage
to the
cosmetic product caused by external shock, impact or vibration. The pan is
positioned in a
clearance in the base large enough to provide for an air gap about the pan.
The shock
absorbing means comprises at least two arcuate, resilient portions extending
across the gap
to connect the pan to the base. One arcuate portion is directed along a first
axis, and the
second arcuate member is directed along a second axis transverse to the first.
The arched
portions are sufficiently resilient to allow the pan to move relative to the
base to a degree that
prevents shock, impact or vibration from being transmitted from the base to
the pan.
In a first embodiment, the arcuate portions are part of a continuous arched
web that
connects the pan to the base of the compact. Alternatively, the arched web may
include
discontinuities, such as, for example, cuts or openings, adapted to provide
more reactive and
resilient shock absorbing characteristics.
In a second embodiment, the shock absorbing device comprises a space-saving
planar
configuration, i.e., a plate within a plate, inserted between the pan and the
base of the
compact. An outer plate has a central clearance, and an inner plate is
suspended in the
central clearance such that a gap is defined between an outer edge of the
inner plate and an
inner edge of the outer plate. The inner plate is suspended in the clearance
by at least two
arcuate members. The outer plate is adapted to connect to one of the base or
the pan, and
the inner plate is adapted to connect to the other of the base or the pan.
Thus, two embodiments of a cost effective, mass produce-able shock absorbing
means are provided for a cosmetic compact case. Either embodiment can readily
be adapted
for installation in existing compact case designs. The shock absorbing means
effectively
prevent pressed powder cosmetics from fracturing.
Brief Description Of The Drawings
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a pressed powder cosmetic compact of the type
that can
incorporate either embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a perspective view of the compact of FIG. 1 illustrating the first
embodiment of the
invention;
3
CA 02655155 2011-04-28
FIG. 3 is an exploded perspective view of the compact of FIG. 2;
FIG. 4 is a sectional view taken along line 4-4 in FIG. 2 illustrating the
first embodiment;
FIG. 5 is a detail view taken from the area indicated by 5 in FIG. 3;
FIG. 5A illustrates an alternative embodiment of the upwardly directed arch
illustrated in
FIG. 5, and in particular, illustrates an inverted arch;
FIG. 5B illustrates an alternative embodiment of the upwardly directed arch
illustrated in
FIG. 5, and in particular, illustrates a wave;
FIG. 5C illustrates an alternative embodiment of the upwardly directed arch
illustrated in
FIG. 5, and in particular, illustrates a Z curve;
FIG. 5D illustrates an alternative embodiment of the upwardly directed arch
illustrated in
FIG. 5, and in particular, illustrates an S curve;
FIG. 6 is a plan view illustrating a second embodiment of the invention, a
planar shock
absorbing member;
FIG. 7 is a perspective view of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 6;
FIG. 8 is an exploded view of a compact base incorporating the second
embodiment;
FIG. 9 is a plan view of the second embodiment in a compact base;
FIG. 10 is a sectional view taken along line 10-10 in FIG. 9;
FIG. 11 is a sectional view of the second embodiment including the compact
cover, the
pan and the product; and
FIG. 12 is a plan view showing variations on the arcuate member for
illustrative purposes.
Detailed Description Of The Invention
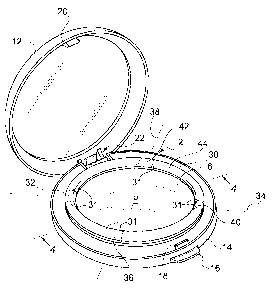
Referring now to FIGS. 1 - 3, a cosmetic compact is shown generally at
reference
number 2. The compact 2 has a cover 12 and a base 14. A button 16 on the base
is
provided to release a catch 18 from hook 20. The cover 12 is pivotable between
a closed
position (FIG. 1) and an open position (FIG. 2) by way of a hinge shown
generally at 22.
As best shown in the exploded view in FIG. 3, the compact 2 comprises a pan 6
containing a solid or semi-solid cosmetic product P. The pan 6 has a bottom
wall 8 and
4
CA 02655155 2011-04-28
a perimeter wall 10. The base 14 has a clearance 24 dimensioned to receive the
pan 6
such that a gap 28, 26 (see FIG. 4) is defined between at least one of the pan
bottom
and the base of the compact, and the perimeter wall of the pan and the base of
the
compact, respectively. In other words, the outer dimensions of the pan 6 are
sufficiently
less than the dimension of the clearance 24 to define at least one gap 28 or
26.
A shock absorbing member 30 is provided to connect the base to the pan.
In the embodiment illustrated in FIGS. 1-4, positioned along a first axis 34
the
shock absorbing member 30 has a first arcuate portion 32 extending across the
gap to connect the base to the
4a
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
pan. A second arcuate portion 36, positioned along a second axis 38 transverse
to the first
axis, extends across the gap 26 at another location to connect the base to the
pan. A third
arcuate portion 40 extends across the gap 26 to connect the base to the pan
along the first
axis 34 on a side of the pan 6 opposite from the first arcuate portion 32. A
fourth arcuate
portion 42 extends across the gap 26 along the second axis 38 on an opposite
side of the pan
6 from the second arcuate portion 36. The arcuate portions 32, 36, 40, 42 each
comprise the
area referenced between the broken lines 31 in FIGS. 2 and 3. Each of the
first, second,
third, and fourth arcuate portions is sufficiently resilient to permit
movement of the pan 6
relative to the base 14 within the clearance 26, thereby reducing transmission
of shock or
vibration from the base to the pan. The arcuate portions 32, 36, 40, 42 work
individually or in
concert to dampen and minimize the transmission of shock and/or vibration from
the base 14
to the pan 6, thus, substantially eliminating damage to the cosmetic product P
in the form of
cracking or crumbling.
While four arcuate portions are illustrated by the broken lines 31, it will be
understood
that the number of arcuate portions may vary from a minimum of two to any
suitable number
necessary to prevent damage to the contents of the pan. Preferably, at least
two arcuate
portions are provided, one directed along first axis 34 and another directed
along second axis
38 transverse to the first axis. More preferably, as illustrated, a pair of
arcuate portions, 32
and 40 is provided along axis 34, and a pair of arcuate portions 36 and 42 is
provided along
axis 38, each one of a pair on opposite sides of the pan 6.
The arcuate portions 32, 36, 40, 42 may form part of a continuous arcuate web
44, as
illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3, that connects the perimeter wall 10 of the pan 6
to the edge of
the clearance 24 in the base 14. Alternatively, the arcuate portions may
comprise individual
portions or members space apart about the perimeter of the pan 6. The
individual portions or
members may be separately formed, or may be formed by isolating parts from the
rest of the
web by slits (e.g., along the broken lines 31) or by removing portions of the
continuous web
between adjacent arcuate portions such that each arcuate portion is defined
between
openings in the web. Depending on the resilient material chosen for the
arcuate portions, the
latter arrangement may provide greater flexibility and shock absorbing
capability, particularly
in a compact containing a pan with relatively acute corners (e.g., a square,
triangular or
rectangular pan). It has been found that the continuous web arrangement works
particularly
well with pans that are substantially round or oval in plan view (as
illustrated). For pans with
acute corners (square, triangular or rectangular pans) the preferred
arrangement has
individual arcuate portions along each flat side of the pan (not shown), with
clearances in the
arched web at the acute corners of the pan.
In the first embodiment, preferably, the each arcuate portion 32, 36, 40, 42
comprises
at least one upwardly directed arch 45 (see FIG. 5). Alternatively, each
arcuate portion
5
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
comprises at least one inverted arch 47, a wave 49, a Z curve 51 or S curve 53
configuration
(see FIGS. 5A-5D).
As illustrated in the cross-sectional view in FIG. 4, the shock absorbing
member 30
has a bottom wall 46 to support the pan 6 (not shown in the FIG. 4).
Alternatively, a shock
absorbing member could be provided with a partial bottom wall or no bottom
wall. Instead, an
inner side wall 48 of the member 30 could be attached directly to the
perimeter wall 10 of the
pan 6 by, for example, mechanical or other fastening means, e.g., glue, sonic
welding, etc.
An outer side wall 50 of the shock absorbing member 30 has an annular ridge 52
for
engaging an inner edge 54 of the clearance 24 in the base 14. The member 30
may be
fastened to the base 14 by, for example, interference fit, adhesive, sonic
welding, or other
known means.
The shock absorbing member 30 may be made from any suitable plastic or
elastomer
material, such as, for example, rubber, styrene, acetal, polyethylene,
polypropylene. The
member may be made by any suitable method, such as, for example, injection
molding, die-
cutting, etc.
In another embodiment, the shock absorbing member 30 comprises a planar shock
absorbing device 130 (FIG. 6) with arcuate members defining horizontally
oriented arches, a
configuration that occupies less height in the compact. The planar shock
absorbing device
130 is adapted for insertion in the cosmetic compact 2 between the base 14 of
the compact 2
and the pan 6 received in the clearance 24 in the base. The planar device 130
comprises an
outer plate 133 with a central clearance 135, and an inner plate 137 suspended
in the central
clearance by at least two arcuate portions 132, 136. The outer plate 133, the
inner plate 137
and the at least two arcuate portions 132, 136 all lie within the same plane.
To further
minimize the height occupied by the device 130, the arch of each of the at
least two arcuate
portions also lies within the same plane as the components 133 and 137, i.e.,
each arch is
horizontally oriented within the plane as if lying on its side. The central
clearance 135 is
defined by an inner edge 139 of the outer plate. The inner plate 137 has an
outer edge 141
and is dimensioned to be received in the central clearance 135 such that a gap
126 is defined
between the outer edge 141 of the inner plate 137 and the inner edge 139 of
the outer plate
133. The outer plate is adapted to connect to one of the base or the pan, and
the inner plate
is adapted to connect to the other of the base or the pan. The base and/or the
pan may be
connected to the device by any suitable mechanical or other fastening means.
For example,
the base may be connected to the inner plate by adhering, welding (e.g.,
sonic), riveting or by
way of studs or lugs 163 in cooperative openings 165 (e.g., compression fit or
heat staking).
The pan may be connected to the outer plate by, for example, glue or similar
means.
First, second, third and fourth arcuate portions, 132, 136, 140, 142,
respectively, each
horizontally oriented with an arch within the plane occupied by the inner
plate 137 and outer
6
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
plate 133, extend across the gap to connect the outer plate 133 to the inner
plate 137. The
first and third arcuate portions, 132, 140, are positioned along a first axis
134 on opposite
sides of the inner plate. The second and fourth arcuate portions, 136, 142,
are positioned on
opposite sides of the inner plate along a second axis 138 that is transverse
to the first axis
134. Each of the arcuate portions, 132, 136, 140, 142, is sufficiently
resilient to permit
movement of the inner plate 137 relative to the outer plate 133 thereby
reducing transmission
of shock or vibration from the base 14 to the pan 6. The arcuate portions work
individually or
in concert to dampen and minimize the transmission of shock and/or vibration
from the base
to the pan, thus, substantially eliminating damage to the cosmetic product P
in the form of
cracking or crumbling.
It will be understood that the number of arcuate portions provided in the
planar shock
absorbing device 130 may vary from a minimum of two to any suitable number
necessary to
prevent damage to the contents of a pan attached to the device. Preferably, at
least two
arcuate portions are provided, one directed along a first axis 134 and another
directed along
second axis 138 transverse to the first axis. More preferably, pairs of
arcuate portions are
provided along each axis, one on each side of the inner plate 137. However,
any reasonable
number of arcuate portions may be provided.
The outer plate 133 may further comprise an upwardly directed sidewall 153
extending upwardly from a perimeter 151 of the outer plate (FIG. 8). A collar
157 including a
horizontal wall 155 and/or a depending decorative wall 159 may be provided
adjacent the top
of sidewall 153 to fill the space between the sidewall 153 and an outer wall
15 of the base 14.
The side wall 153 defines a clearance 124 dimensioned to receive the pan 6
containing
cosmetic product P. In a first configuration, the pan is attached to the outer
plate and the
inner plate is attached to the base 14 of the compact. The pan 6 may be
attached to the
outer plate by glue, as proposed above, or may be attached to the outer plate
by way of an
interference fit between the perimeter wall 10 of the pan and the upwardly
directed side wall
153 of the outer plate. The inner plate 137 may be secured to the base 14 of
the compact by
glue, or preferably by studs or lugs 163 projecting from one of the plate 137
or the base 14
and secured in cooperative openings 165 in the other of the plate 137 or the
base 14. The
studs or lugs 163 may be secured in the openings 165 by, for example,
compression fit, heat
staking, sonic welding or glue. In this first embodiment, it will be
understood that the outer
plate 133 will move relative to the base 14, and therefore the inner edge 171
of collar 157
must be in a spaced relationship with the top of the upwardly directed side
wall 153 of the
outer plate 133. Accordingly, a gap 173 is provided between the inner edge 171
and the top
of the side wall 153. In an alternative (not illustrated) to the foregoing
configuration, the pan
is attached to the inner plate and the base is attached to the outer plate. In
order to allow for
7
CA 02655155 2008-12-11
WO 2008/008682 PCT/US2007/072817
movement of the pan relative to the base, the perimeter wall 10 of the pan
must be in spaced
relationship to the sidewall 153 of the outer plate.
A channel 160 may be provided in the outer plate 133 or the inner plate 137,
or both,
to accommodate each arcuate portion 132, 136, 140,142. The channel 160 permits
the
arcuate portions to be relatively long and the inner and outer plates to have
relatively larger
surface areas for attachment to the compact base and/or pan bottom.
The arcuate portions 132, 136, 140,142 may have varying configurations. For
example, the arcuate portions may comprise a curved arch 181 (FIG. 12), an
angular arch
183 (FIG. 12), a Z shape (FIG. 5), an S shape (FIG. 5), a wavy shape 185 (FIG.
12) or a
zigzag shape (not shown), or any combination of the above. The shock absorbing
member
30 in FIG. 12 is illustrated with four differently configured arcuate portions
primarily to
illustrate the various configurations. For purposes of this application, an
arcuate portion shall
include all of the above variations as well as any member or element providing
resilience by
way of structure that approximates a curve. The variations may be used in any
combination
desired and effective in achieving the shock absorbing result.
The plate-like shock absorbing device may be formed with all its parts as a
unitary
integral piece. The outer plate, the inner plate, and the arcuate portions can
all be molded as
one piece or cut from a single pieced of base stock by, for example, injection
molding or die-
cutting, respectively. The unitary piece may comprise a part of the compact
base, e.g., the
bottom wall of an insert in the base (see FIG. 8).
In the above embodiments, the arcuate portions may also be adapted to provide
progressive dampening by varying a thickness along a length of the respective
arcuate
portion as illustrated by arcuate portion 187 in FIG. 12.
Either of the above embodiments may be made from any suitable plastic,
elastomer
(natural or synthetic) or metal by conventional methods, such as, for example,
molding or
cutting. The material should be selected to provide appropriate levels of
resilience to keep
the product from cracking. Examples of suitable materials include acetal,
polypropylene,
polyethylene, styrene and elastomer. If the shock absorbing device 130 is made
from a
plastic material, the thickness of the plates and the arcuate members is
preferably 0.5 to 2.5
mm.
It is understood that various modifications and changes in the specific form
and
construction of the various parts can be made without departing from the scope
of the
following claims.
8