Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02658931 2014-04-11
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
=
1
GRINDING BOOM HAVING COOLING CIRCUIT
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to a grinding method and apparatus. It relates
particularly but
not exclusively to a grinding boom which can be used in high temperature
situations
such as grinding scale from exhaust systems of high temperature furnaces. It
also .
relates to sealing methods and devices for allowing equipment such as a
grinding
boom to operate in a closed environment.
Background of the Invention
Off gases from furnaces are often loaded with components which solidify aud
form
scale in exhaust systems for such furnaces. This is particularly true of flash
furnaces
generating nickel matte or other metals, particularly non-ferrous metals.
Typically such furnaces have a vertical section for taking off hot gas_ The
vertical
section communicates with a quench chamber or waste heat boiler via a
transition
member. The hot gases may be cooled by a shower of water in the quench chamber
or the heat recovered via a plurality of boiler tube bundles.
With the rapid cooling of gas as it moves from the vertical flue to the quench
chamber
or waste heat boiler, there tends to be a build up of scale or particles in
the transition.
As a result, it is generally necessary to periodically scrape the scale or
other deposits
from the transition to prevent it becoming blocked. However, with current
practices,
because of the high temperature usually present in the transition during
operation of
the furnace and the pressure differential to outside air, operation of the
furnace must
be interrupted to remove scale or other unwanted deposits from the transition
or from
other parts of the furnace construction. Typically, this may mean that a
furnace is not
operating for as much as one hour in every twenty-four.
=
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
2
Given that there is an enormous loss of revenue associated with interrupting
the
operation of a furnace on a regular basis, there is clearly a very real need
for an
alternative approach which can successfully remove scale without interrupting
the
furnace operation.
Disclosure of the Invention
The invention provides in one aspect a grinding boom conaprising,
a rotatable grinding head having a grinding surface and an underside surface,
a support arm for mounting the grinding head, and
a cooling fluid conduit extending coaxially through the support arm,
wherein the arrangement is such that cooling fluid can pass through the
cooling fluid conduit to cool the undersize surface of the grinding head.
By having a grinding head construction which allows the head to be cooled
while in
use, it should be possible to grind away scale or other materials in certain
situations
without stopping operation of -the furnace.
Where there is a pressure differential between the outside air and the region
where
scale is being ground away, the use of a sealing arrangement for the grinding
boom
may be appropriate to maintain the pressure differential.
Of course, given the high temperatures involved, it is highly desirable for
the cooling
fluid eg. water to be kept separate from contact with the hot gases and
accretion
materials evolved by the furnace.
Thus, the cooling fluid may be directed through the boom to impinge upon the
underside of the grinding head without ever actually coming into contact with
the hot
gases and accretion materials and furnace walls.
The cooling fluid conduit may be arranged so that it directs cooling fluid
against the
underside surface.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
3
The underside surface may be provided with an arrangement of channels which
direct
the cooling fluid over a predetermined region of the underside surface. It may
direct
the cooling fluid in spiral fashion over the underside surface. The channel
arrangement may comprise a cup shaped to fit against the underside surface.
The cup
may have a spiral divider in the form of a ridge or vane which creates a flow
channel
for the cooling fluid. Suitably the flow channel may be spiral.
The cooling fluid conduit may be rotatable with the grinding head.
A return gallery coaxial with the cooling fluid conduit may be arranged to
return
cooling fluid to an exit point from the grinding boom. The return gallery may
be
rotatable with the cooling fluid conduit.
The grinding head may comprise a generally hemispherical shell. It may
comprise a
plurality of grinding elements. The grinding elements may be set in recesses
formed
in the grinding head. The grinding elements may comprise tungsten carbide.
They
may be arranged at an acute angle with respect to a tangent taken on the
spherical
head at the location of the grinding element. The acute angle may be between
15 and
700, it may be between 35 and 500
.
A secondary cooling circuit may be provided for the grinding boom. The
secondary
cooling circuit may be arranged so as to cool the support arm. It may comprise
one or
more water galleries for cooling the support arm. The water galleries may be
arranged so as to cause water to spiral in contact with and along the support
arm.
The grinding boom may be arranged so as to be movable into and out of a
transition
member for a smelter exhaust. The transition member may be arranged to direct
hot
gases into a quench chamber or waste heat boiler. The arrangement of grinding
boom
and quench chamber or waste heat boiler may be such that the grinding boom is
arranged to penetrate through the quench chamber so that it may reach the
transition
member. For this purpose, the grinding boom may be mounted via a track-way so
that
it is movable along the track-way. It may be mounted via a robot. The robot
may be
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
4
arranged to move the grinding boom so as to bring the grinding head into
contact with
scale in the transition member. The grinding boom may pass through a sealing
device
in a wall of a chamber or enclosure so as to maintain any pressure
differential
between the outside and the interior of the chamber or enclosure.
$
In another aspect, the invention provides a method of grinding a surface in an
enclosure maintained at a pressure differential to outside air comprising
extending an
arm of a grinding apparatus from a region of normal outside air pressure
through a
seal assembly provided at a wall =of the enclosure so as to impinge a grinding
head of
to the grinding apparatus against the surface, wherein the seal assembly is
constructed
so as to allow the arm to move with respect to the wall whilst maintaining a
seal
between the wall and arm.
The seal assembly may be mounted on a carriage arranged to bring the seal
assembly
15 into an out of registry with an access port provided on the wall of the
enclosure. The
access port may have a movable cover to allow closing of the access port when
the
seal assembly is moved away fi-om the access port.
In another aspect, the invention provides a seal assembly for allowing a
grinding
20 apparatus such as the grinding boom hereinbefore described to extend
through the
wall of an enclosure comprising,
a hollow member having a part spherical outer surface,
an outer opening and an inner opening for the hollow member,
a collar for holding the hollow member about the part spherical outer surface
25 whereby the hollow member may be swivelled with respect to the collar,
and
sealing means for providing a seal between the seal assembly and an arm of
the grinding apparatus extending through the hollow member from the outer
opening
to the inner opening and into the enclosure.'
30 The seal assembly may include roller members for allowing the arm of the
grinding
apparatus to be slidable through the hollow member.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371 PCT/AU2007/001135
Preferred aspects of the invention will now be described with reference to the
accompanying drawings.
Brief Description of the Drawings
5
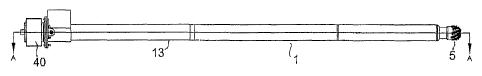
Figure 1 shows an elevational view of a . grinding boom constructed in
accordance with the invention;
Figure 2 shows a *fragmentary magnified section A-A taken through Figure 1;
Figure 3 shows a further magnified partial sectional view of a front portion
of
the grinding boom of Figure 1;
Figure 4 shows a side on elevational view of a grinding head;
Figure 5 shows a plan view of a grinding head;
Figure 6 shows section A-A taken on Figure 5;
Figure 7 shows section B-B taken on Figure 4;
Figure 8 shows an isometric view of a grinding boom and quench chamber;
Figure 9 shows a fragmentary magnified view of a portion of the quench
chamber of Figure 8;
Figure 10 shows a partially cut away view of a swivel seal; and
Figure 11 shows section A-A taken on Figure 10.
Detailed Description of the Preferred Embodiments
The various elements identified by integers in the drawings are listed in the
following
integer list.
Integer List
Grinding boom
2 Water galleries
3 Water galleries
4 Water galleries
5 Grinding head
6 Grinding elements
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
6
=
7 Fluid conduit
8 Head space
9 Connecting assembly
Bearing assembly
5 11 Bearing assembly
12 Seal assembly
13 Support arm
14 Extension member
Extension member
i0 16 Drive shaft member
17 Seat (high temperature)
18 Cavity
19 Intermediate member
Spiral cup
21 Open end
22 Spiral divider
Spiral divider
26 Spiral divider
27 Spiral divider
20 28 Outer surface
29 Underside surface
Tubular wall
32 Internal cavity
33 Inlet pipe
25 34 Outlet pipe
36 Inlet
38 Outlet
39 Rotary union
Drive unit
30 42 Mounting assembly
44 Recess
Dome
47 Screw thread
=
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371 PCT/AU2007/001135
7
50 Quench chamber
51 Transition member
52 Gas inlet
54 Outlet
56 Mounting platform
58 Trackway
59 Robot
62 Trackway "
64 Swivel seal assembly
66 Carriage
68 Access port
70 = Movable cover
72 Cool gas exhaust
74 Semi-spherical casting
75 Outer opening
76 Inner opening
78 Mounting collar
79 Low friction packing
80 Roller
. 82 Cover piece
83 Annular element
84 Cover piece
85 Annular element
86 Annular element
87 Spacer element
88 Spacer element
89 Spacer element
92 Scraper element
94 Bolts
Referring to Figures 1 to 3, there is shown a grinding boom according to the
invention generally designated 1.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO
2008/022371 PCT/AU2007/001135
8
It comprises a tubular elongate support arm 13 at the end of which is mounted
a
tubular extension member 14 in a manner which allows relative rotation between
these two members. The rotating portions of the grinding boom are identified
by
hatching in Figure 3 for clarity.
=
=
A grinding head 5 is mounted on the extension member 14. The grinding head is
hollow and has a generally hemispherical outline.
A number of grinding elements 6 comprised of high temperature high hardness
material such as tungsten carbide are provided on the grinding outer surface
28 of the
head in a manner which will be described in more detail hereinafter.
A fluid conduit 7 which extends coaxially within the support an:a 13 is
arranged to
deliver cooling fluid such as water to the grinding head. The water flows in
the
direction indicated by the arrows in the water galleries 2. The fluid conduit
is
arranged to deliver fluid to the head space 8. From there it flows through the
open
end 21 of the spiral cup 20 to impinge on the inner underside surface 29 of
the
grinding head 5. It then flows into a number of water galleries 2 defined by
the spiral
= cup 20 which nests against the underside surface of the grinding head. A
spiral
divider 22 in the fowi of a ridge spiralling around the outer surface of the
spiral cup
directs the water to move spirally through water galleries 2 around the spiral
cup
along the underside surface of the grinding head and then through a further
number of
water galleries 2 defined between the inteimediate m.ember 19 and extension
member
14.
A spiral divider 25 between the telescopic extension 14 and intermediate
member 19
defines a spiral water gallery 2 for return of cooling fluid from the grinding
head 5
after it has passed through the spiral galleries defined by the spiral cup 20.
The extension member 15 and intermediate member 19 are joined at the
connecting
assembly 9 formed at the forward end of the intermediate member by
appropriately =
located connecting bolts. In turn, the extension member is mounted on a drive
shaft
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
9
member 16. The water gallery 2 for water returning from cooling the grinding
head is
defined between the drive shaft member 16 and fluid conduit 7. ==
A cavity 18 is defined between the telescopic drive shaft 16 and fluid conduit
7 for
return of water after it has cooled the grinding head 5. This constitutes a
further
water gallery 2.
The fluid conduit, extension member 15 drive shaft 16 intermediate member 19,
extension member 14 and grinding head 5 are jointly mounted. They are all
driven to
rotate with respect to the support arm 13 by a rotary-drive assembly operating
through the end assembly 39.
Bearing assemblies 10 and 11 allow relative rotation between these components
and
the support arm. The bearing assemblies 10 and 11 are mounted between the
tubular
wall 30 and extension member 15. The seal assembly 12 and high temperature
seal
17 ensure water tightness of the water flow through the various galleries.
The tubular wall with drive shaft 16 defines an internal cavity 32.
Spiral dividers 26 and 27 are provided between the support arm 13 and tubular
wall
to provide spiral water galleries 3 and 4 for flow of cooling water to cool
the
support arm.
The water galleries 3 and 4 are arranged so that water flows counter current
through
25 adjacent galleries so that it moves forward to cool the support arrn and
then returns
with water to the galleries being supplied by the inlet pipe 33 and being
discharged
through the outlet pipe 34.
Cooling water for the fluid conduit 7 and water galleries 2 is supplied by the
inlet 36
30 and exits via the outlet 38 shown more clearly in Figure 2.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
A rotary union 39 is provided for mounting the inlet and outlet 36 and 38 and
connects to the drive unit 40 for the grinding boom. The grinding boom is
mounted
on a robot 59.
5 The connecting arm and grinding boom are in turn joined together by the
mounting
assembly 42.
Referring to Figures 4 to 7, it can be seen that the grinding head 5 comprises
a hollow
dome 45 usually formed of a heat resistant material such as steel. A large
number of
10 recesses 44 are formed on the outer surface=of the dome. These recesses
are used for
mounting of the tungSten carbide grinding elements 6 which may typically be
mounted so that they project forward at an angle of about 45 with respect to
the
tangent to the dome.
The direction of the winding elements 6 is such that they point forward in the
direction of rotation of the grinding head. Typically, they may be arranged in
rows of
grinding elements as illustrated.
A screw thread 47 is provided on the interior surface of the dome to
facilitate
attachment to the corresponding screw thread formed on the telescopic
extension
member 14.
Referring to Figures 8 and 9; there is shown a typical exhaust gas arrangement
for a
nickel smelter which incorporates a quench chamber 50.
As discussed previously, the quench chamber may include an arrangement for
spraying water down through the charriber to cool hot exhaust gases from a
nickel
matte furnace.
The hot gases after passing through a vertical flue above the furnace, are
transferred
via the transition member 51 through a gas inlet 52 in the side of the quench
chamber
50.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
11
An outlet 54 at the bottom of the quench chamber is provided for excess water
and/or
solids and a cool gas exhaust 72 is provided at the side of the quench
chamber.
A mounting platform 56 provided level with the quench chamber includes a
trackway
58 on which the robot 59 is mounted..
The robot is arranged to hold and move the grinding boom 1 so as to grind away
scale
which accumulates in the transition member.
to The grinding boom is long enough to allow it to be moved forward by the
robot along
trackway 58 so that it extends through the swivel seal assembly 64 in the side
of the
quench chamber. The scope of movement will be sufficient to allow the cutting
head
to be appropriately positioned in the transition member 51 and moved as
required to
grind off scale in the transition member_ A second trackway 62 having a
movable
carriage 66 is arranged so as to be able to move the swivel seal assembly 64
into and
out of registry with the access port 68 of the quench chamber.
When the grinding boom and swivel seal assembly 64 are fully retracted, the
access
port 68 may be covered by the movable cover 70 as and when required.
Referring to Figures 10 and 11, the swivel seal assembly 64 comprises a
semi-spherical casting 74 having an outer opening 75 for insertion of the arm
of a
grinding boom, and an inner opening 76 which extends through the access port
68 of
an enclosure such as a quench chamber.
The semi-spherical casting is mounted in a mounting collar 78 which is mounted
on
the carriage 66 described with reference to Figure 8.
Low friction packing 79 is provided between the mounting collar and outer
surface of
the semi-spherical casting 74. = The packing conforms to the circular surface
of the
semi-spherical casting allowing the semi-spherical casting to swivel with
respect to
the collar.
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
19 =
A number of rollers 80 are provided proximate the inner and outer openings 76
and
75. The rollers have a generally dished or concave surface to facilitate
smooth sliding
of the tubular arm of a grinding boom through the swivel seal assembly.
Cover pieces 82 and 84 are provided on the outer and inner openings covering
the
roller assemblies. In the case of cover piece 84, it also secures an annular
element 83
to the outlet of the inner opening 76.
A pair of annular elements 86 are secured in front of the cover piece 84..
Spacer
elements 87, 88 and 89 are provided between these annular elements, and a
scraper
element 92 for purposes to become apparent.
The scraper element 92 is mounted forward of one of the two annular elements
86
and is spaced therefrom by the sPacer element 8'7. Finally, the antaular
element 85 is
provided forward of the scraper element.
The assembly of annular elements, spacer elements and scraper element together
with
the cover piece are held by the bolts 94.
The annular elements 83, 85 and 86 may be formed of a resilient material such
as a
tough rubber or plastic material which provides a seal with the arm of the
grinding
. boom. They snugly surround the arm of a grinding boom and act to wipe off
loose
detritus which may accumulate on the arm. The spacer elements create a gap
between the annular elements through which detritus which has been wiped off
may
freely fall into the chamber or enclosure into which the arm extends.
The scraper element 92 has a forwardly protruding edge which serves to perform
an
initial cutting or slicing operation on detritus accumulating on the arm of
the boom
when the ann is retracted. The annular element 85 acts as a washer to assist
with
holding the scraper element securely in position.
With this type of arrangement, it can be seen that the cooled grinding boom
may be
used to grind away scale formed in the transition member even when the furnace
is
CA 02658931 2009-01-26
WO 2008/022371
PCT/AU2007/001135
13
operating and hot gas is passing through the transition member. Thus the
furnace can
be operated continuously_ Furthermore, the swivel seal assembly and boom/robot
are
retractable, the boom, robot and swivel seal assembly may be removed for
servicing
with closing of the movable cover 70 without interrupting the operation of the
furnace.
Whilst the above description includes the preferred embodiments of the
invention, it
is to be understood that many variations, alterations, modifications and/or
additions
may be introduced into the constructions and arrangements of parts previously
described without departing from the essential features or the spirit or ambit
of the
invention.
It will be also understood that where the word "comprise", and variations such
as
"comprises" and "comprising", are used in this specification, unless the
context
requires otherwise such use is intended to imply the inclusion of a stated
feature or
features but is not to be taken as excluding the presence of another feature
or features.
The reference to any prior art in this specification is not, and should not be
taken as,
an acknowledgement or any form of suggestion that such prior art forms part of
the
common general knowledge in Australia,