Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
Device for processing fibrous raw materials and
the method of fibrous plants processing
The subjects of the invention are: a device for processing fibrous raw
materials and the
method of fibrous plant raw materials processing. The device is used for
specific
processing of fibrous plants raw materials such as flax, hemp, kenaf, jute,
ramie and
otllers. The device enables controlled water flow and controlling pH value,
temperature
and the process time. The method enables using physico-chemical phenomena,
especially
osmosis, which run inside the stems in contact with water. The solution
enables
production of natural fibre of exceptionally good usable properties.
In the patent description CN1542198 (published 2004-11-03) the textile
ultrasonic
treatment device was presented. The ultrasonic fabric treating apparatus is
used mainly in
water washing, desizing, bleaching, dyeing and other pre-treatment. It
includes water
tank, longitudinal cloth rollers in two rows inside the water tank for the
cloth to turn to
form cloth wave, and two or more double-sided ultrasonic units set over and
below the
cloth wave. The present invention is used in treating cloth and has greatly
lowered water
consumption and power consumption, reduced water tank number and small volume.
In the patent description CN1455040 (published 2003-11-12) the ramie wet
spinning method and apparatus was presented. The present invention discloses a
ramie
wet spinning method and its equipment. It directly uses the ramie rove of
conventional
process to spin line yarn, and includes the processes of degununing ramie,
combing,
doubling and obtaining rove, making the rove pass through wet-spinning
machine,
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
2
drying, winding and baling, in which the ramie wet-spinning machine is
obtained by
improving flax wet-spinning machine, i.e. original curved frame is changed
into a
special-made breast plate which can be mounted between front and rear rollers,
their
drafting interval distance can be changed into 180-260 mm from 160 mm, and the
haimess and nep of obtained ramie yarn can be obviously reduced, its produce
quality can
be obviously raised, the yarn-forming hair is in 20/lOm, and its breaking
strength is
identical to that of dry-spun yarn, and its retentivity is above 95%.
In the patent description CN1446952 (published 2003-10-08) equipments for
processing
flax and technical method were described. An apparatus for processing flax is
composed
of electric motor, stirring wheel, the stirrer of peregal and high-speed
machine oil,
hydraulic pump, tubes, liquid tank, baker, spraying box with nozzles, and
pneumatic
pump. Its technology includes washing in cold water, washing in acid, washing
in hot
water, washing in cold water, enzyme treating for degurnrning, washing in cold
water,
baking, treating with the mixture of peregal and high-speed machine oil,
opening and
15. carding.
In the patent description JP2001164458 (published 2001-06-19) the method for
bleaching
cotton fiber product using ozone and apparatus therefore. Carrying out
bleaching of a
fiber without using chlorinated chemicals and to suppress yellowing thereof
with a lapse
of time by bringing the fabric to be bleached into contact with a gas
containing ozone and
then washing the fabric with hot water was solved. This method for bleaching
and the
apparatus therefore is that the cotton fiber after subjected to desizing and
degumming is
moistened, then brought into contact with the gas containing the ozone and
finally
washed with the hot water.
In the patent description GB2282609 (published 1995-04-12) the method for
degulmning
silk fabrics and apparatus therefore was presented. A degunvning solution is
heated in a
kier to 120 - 130 DEG C and the silk fabric is immersed in the heated solution
for 30 - 60
minutes. The kier comprises a body containing a degumming chainber and a pair
of heat
exchanger chambers communicating at their top and bottom portions with the
degurnming chamber. A lid seals the kier and an intake/exhaust pipe filled
with a valve is
used to control the pressure. In the heat exchanger chambers are two pairs of
heat
exchanger pipes and steam discharge pipes having upwardly directed nozzles,
each pair
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
3
being provided one above the other. Steam or cooling water can be supplied to
the heat
exchanger pipes to control the temperature. The top and bottom of the kier
body are in
communication through a circulation pipe which includes a pump and a heat
exchanger.
In the patent description CN1058624 (published 1992-02-12) the method and
apparatus
for comprehensive treatment of waste from biological degumrning of ramie were
presented. This invention relates to a complete set technology of combined
bacterio-
chemical degunuziing process for ramie with equipment thereof. It features
that the
refined waste gas generated in biological degumming of ramie, waste water
after flushing
machine, oiled waste liquid, condensed water of baker, partial refined water
liquid and
fermentation tail-gas treatment are used for the immersion of bacterially
degummed
ramie, beating ramie, refining, oiling, and filtering the soot of boiler, so
realizing
comprehensive treatment of waste water. Its settling tank is a plane-
rectangular diagonal
flow type. This invention has such advantages as low investment, low running
expense
and good treatment effect. The quality of treated water conforms to class-one
national
standard.
In the patent description CN1 102675 (published 1995-05-17) the method and
device for
degumming silk fabric were presented. A degumming device in which a silk
fabric can be
suspended easily and can be degununed uniforinly. Radial arms are provided in
a
cylindrical degumming lcier. A silk fabric is suspended spirally from the arms
by
attaching its top edge to hooks provided on the arms. In this state, a gap is
present
between the adjacent layers of the spirally suspended silk fabric. Since
degumming
solution can smoothly flow through the gap, the silk fabric can be degummed
uniformly.
While degununing, the arms are gradually swung upwards so that the distances
between
the adjacent arms narrow gradually. With this arrangement, the top edge of the
silk fabric
is allowed to shrink at the same rate as its bottom edge.
In the patent description CN1070021 (published 1993 -03 -17) the bleaching and
dyeing
technology for silk and tow of tussah was presented. The bleaching and dyeing
technology for tussah is comprised of degunmiing, bleaching, dyeing and silk
scrooping
agent treatment. The deguirnning includes following steps: pretreatment (0.5-2
g/1.
sodium carbonate water solution, 80-90 deg. C), water washing, boiling with
enzyme
(1.5-2.5 g/l. neutral enzyme preparation, 45-50 deg. C), water washing,
boiling with soup
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
4
(1.5-2.0 g/1. soapwater, 95 deg. C). After bleaching (5.5-7.2 g/l. H202, 60-85
deg. C.,
bath ratio 1:30) 3-4 hr., the active, neutral, and acidic dye stuffs are use
for dyeing (30-95
deg. C) and controls the dyeing rate. And fmally, the silk scrooping agent
treatment is
proceeded (concentration of water solution 4-5 g/l. 40-50 deg. C). The
technology is
reasonable, installation is simple, operation is easy, dyeing is uniform,
fastness is high
and color is lustrous.
In the patent description JP5247830 (published 1993-09-24) the apparatus and
method for
treatment of fiber product were presented. The purpose of the invention was to
provide a
safe apparatus for preventing danger, intended for the treatment, including
bleaching,
washing, dyeing, boiling, desizing, mercerizing, or the like, of textile
materials. This
apparatus has such a scheme that an applicator disposed substantially sideways
in the
direction of carrying a textile product is furnished, an aerosol jet emitted
from the nozzle
of the applicator is directed to a textile product to be treated, wherein the
applicator is
designed as a cylinder with its inlet and outlet provided on the edge face
thereof,
furthermore, there is furnished a chamber helically surrounded by a heating
element,
wherein both the chamber and the heating element are placed in a pipe.
In the patent description CN1056139 (published 1991-11-13) the technology and
apparatus for textile bleaching or pre-treatment before dyeing were presented.
This
invention belongs to the treating method before bleaching or print-dyeing of
fabrics. It
aims at that it provides the technology and equipment of shortened process and
reduced
equipment to save heat energy, water resource, auxiliary agent, man power and
lift the
product quality and quantity. Its features are: the fabric after alkali
soaking and rolling by
mercerizing range, tentering, and flush-absorbing, is steamed in cook pot,
then carry on
the following processes: flat washing, bleaching with oxygen, piling up,
tensioning flat
washing, rebleaching with oxygen, drying, bluing and whitening and stentering.
In the patent description RU2133788 (published 1999-07-27) the fibrous
material
washing apparatus was describe. The washing apparatus has conveyor for feeding
fibrous
material preliminarily loosened on scutching machine to hopper, where fibrous
material
is wetted by spray beam delivered from nozzle. Fibrous column is compacted and
fed to
carding drum for discretization of yams and removal of organic, mineral and
plant
contaminants. Preliminarily cleaned complexes are passed above pallet for
removal of
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
contaminants. Apparatus is further provided with roll for removing fibrous
material from
drum and throwing it onto conveyor. Fibrous material is washed with washing
solution
spray beam in zone between conveyor carrier run and nozzle. Fibrous material
layer
saturated with washing agent is supplied into microwave field working zone
between
5 conveyor and wave guide. Microwave energy is emitted from wave guide to
fibrous layer
so as to penetrate through it and excite it at atomic and molecular level.
Microwave field
activates microparticles of aqueous-fibrous mixture to excited state, which is
displayed
by fast heating of mixture. Heat and related electric factors facilitate
disintegration
between fibers and organic contaminants, with viscosity of organic
contaminants
suddenly decreasing. Portion of fatty substance drips into tank. Final washing
out of
contaminants is accomplished by washing solution spray beams delivered by
nozzles.
Used solution drips into tank from which it is delivered into soaking nozzle.
Cleaned
fibers are fed to roll tips and discharged from apparatus. Used solutions are
supplied from
tank to settlers for further processing and recycling.
In the patent description CA2111458 (published 1992-12-23) the method of
decorticating
flax, and flax-processing machine designed to carry out the method were
presented. The
aim of the invention is to produce, after only a short dew-retting time or
light chemical
pretreatment, a degree of decortication sufficient to form the preliminary
step of a
constant-flow fiber-digestion process. The flax is picked up as a tangled mass
and
processed in a tangential flow breaker unit and a subsequent longitudinal-flow
fiber
scutching and cleaning unit. Incorporated in the first breaker is a system of
parallel slots
and in the second breaker a peripheral gap whose axis of curvature is at right
angles to the
slots in the first breaker. The fiber scutching and cleaning unit has several
longitudinal
sections fitted with fiber-conveying and loosening means which separate and
clean the
fibers. The decorticated fibers are then compressed, in a built-on baler unit,
into bales.
In the patent description W02006032181 (published 2006-03-30) the process for
degumming the jute was presented. A process for deguimning the jute, which
includes the
following steps: (1) unpacking and stricker-up of the raw jute (2); treating
the raw jute
with a compound enzyme, which comprises adding to the container the aqueous
solution
of the compound enzyme made from pectinase and laccase so that the jute is
treated,
taking the jute out the container and patching up in a predetermined duration,
and finally
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
6
rinsing the raw jute with hot water (3); reduction bleaching, which comprises
adding to
the container a aqueous solution of reductive bleaching agent and bleaching
the jute, and
then adding a decolorizer thereto and treating the jute, finally taking the
jute out the
container after the treatments are carried out (4) beating the result jute,
and then rinsing,
oiling, dehydrating, drying sequentially, thereby the jute fiber decolorized
and impurity
free is obtained. The percentage of decoloring and the removal rate of lignin
genera are
up to 89 % and over 76 %, respectively. The shade of the jute fiber is white.
This jute
fiber can be blended or interweaved with other kinds of fibers, and the
resultant cloth can
meet the requirement in using as facing fabric in apparel industry.
Despite described above studies on obtaining new devices for processing
fibrous
plant raw materials, there is a need to build an effective and versatile
device that could be
used to conduct the technological process with the option of setting at least
several
parameters describing the process and functioning in the same time.
This invention aims at providing means that could be used to manufacture a
device improving processing fibrous plants raw materials keeping the
possibility of
parallel setting of at least several parameters, including their correlation,
without
interrupting the processing.
Performing this goal and solving problems connected with developing a device
enabling processing of fibrous plant raw materials described in the status of
the
technique, characterized also by option of processing with at least several
parameters set
have been achieved in this invention.
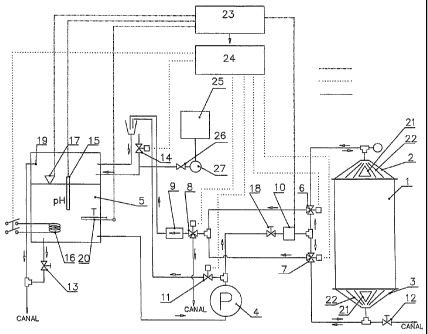
The subject of the present invention is a device for processing fibrous raw
materials
characterized in that the device is built of two tanks: a reservoir of working
fluid 5 and
working tank of the apparatus 1, of which integral parts are openable
collector 2 and
permanent collector 3 and guides 22 located in collectors 2 and 3 where
worlcing fluid
from the working fluid reservoir 5 is supplied to working tank of the
apparatus 1 by
chemical pump 4, where the working fluid is being supplied from the regulating
valve 18
to the openable collector 2 and/or permanent collector 3 of the worlcing tank
of the
apparatus 1, while the excess of liquid supplied by chemical pump 4 from the
two-way
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
7
regulating valve 11 is directed to the working fluid reservoir 5 whereas the
range of the
two-way regulating valve 11 regulation is set by a manual regulating valve 18,
where
there are heaters 16, temperature detector 20 pH detector 15 and fluid level
detector 17,
fresh water intake controlled by the water intake from the network valve 14,
and overflow
19 and drain valve 13 in working fluid reservoir 5 while particular parameters
in working
fluid reservoir 5 are read by the flow-meter 10, pH detector 15, water level
detector 17,
temperature detector 20 and are compared by the regulator 23 with the set
values, while
the deviations generate impulse to the steering device 24 starting the two-way
valve 1118
,
two-way regulating valve 11, the valve supply water form the network 14,
turning on the
heaters 16.
Preferentially, the speed of fluid flow in the working tank 1 of the apparatus
is adjusted
by the two-way regulating valve 11 from the regulator 23 by the steering
device 24, and
the working fluid is directed by.the regulating valve 18, flow-meter 10 and a
two-way
valve I 6 or a two-way valve 117 to the openable collector 2 and/or permanent
collector 3
of the apparatus working tank 1.
Preferentially, the fluid flow goes in opened cycle, where the fluid having
passed through
the apparatus working tank 1 is directed to the sewage collector by the two-
way valve III
8 or by manually controlled valve 12.
Preferentially, the fluid flow goes in closed cycle, where the fluid having
passed through
apparatus working tank 1 is guided to working fluid reservoir 5 by the two-way
valve III
8 and a filter 9, where the filter 9 is a unit prepared for particular
process.
Preferentially, pH is controlled constantly.
Preferentially, the device is equipped with ultrasound generators 21 in
collectors 2 and 3.
Preferentially, the processing is conducted by liquid water solutions of
chemicals and/or
enzymatic processing and/or biological processing and/or physical processing.
Preferentially, the processing is conducted with the use of constant water
flow by using
physico-chemical phenomena, especially osmosis.
Preferentially, the device is used for degurnrning raw materials from fibrous
plants by
using physico-chemical phenomena, especially osmosis.
Preferentially, the device is used for degumrning, washing, rinsing,
bleaching, dying,
impregnation and chemical treatment of raw materials made of fibrous plants.
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
8
Preferentially, the device is presented in Fig. 1.
The next subject of the invention is the method of processing of raw materials
obtained from fibrous plants, characterized in that the raw material is being
placed in
working tank of the apparatus 1 and the water and/or other fluid is run
through it, where
the fluid is being run through the working tank of the apparatus 1, where the
guides 22
mounted in the openable collector 2 and in the permanent collector 3 ensure
the unifonn
flow of liquid in the whole cross-section of the apparatus working tank 1, the
worlcing
fluid from the reservoir of the working fluid 5 is supplied to the apparatus
working tank 1
by the chemical pump 4, where the fluid is given its target fluid flow rate in
the working
tank of the apparatus 1 using the two-way regulating valve 11 from the
regulator 23 by
the steering unit 24, where the working fluid is directed from the two-way
regulating
valve 11 through the flow-meter 10 and two-way valve 16 or the two-way valve
117 to
the apparatus working tank collector 1, while the excess of the fluid supplied
by the
chemical pump 4 from the two-way regulating valve 11 is directed to the
working fluid
reservoir 5, where the working fluid is prepared and treated so it's
properties meet the
requirements of the process, than the values of particular parameter detected
by the flow-
meter 10, pH detector 15, fluid level detector 17, temperature detector 20 are
coinpared
with the set values by the regulator 23, while the deviations generate impulse
to the
steering unit 24, triggering the two-way valve 1118 , the two-way regulating
valve 11, the
valve supply water form the network 14 and turning-off the heaters 16.
Preferentially, the processed raw material is placed in the apparatus working
tank 1 and
the water and/or other fluid is run through it, where the fluid is being run
through the
apparatus working tank alternate in two directions.
Preferentially, pH is controlled constantly.
Preferentially, the ultra sound generator 21 helps the process.
Preferentially, the liquid water solutions of chemicals are used and/or
enzymatic
processing and/or biological processing and/or physical processing is used.
Preferentially, the processing is conducted with the use of constant water
flow by using
physico-chemical phenomena, especially osmosis.
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
9
Preferentially, the processing is conducted in an opened flow of the working
fluid and the
fluid, having passed through the apparatus working tank 1 is directed to the
sewage
collector by the two-way valve 1118.
Preferentially, the processing is conducted in close cycle of working fluid,
where the
fluid, following passing through the apparatus working tank 1 is directed on
the two-way
valve 1118, through the filter 9 to the working fluid reservoir 5 where the
filter 9 purifies
the working fluid after it has passed through the apparatus working tank 1
eliminating
substances released from processed raw materials during the process, where
purification
of the liquid enables recycling the fluid.
Preferentially, the processing of fibrous plants raw materials is periodical.
Preferentially, the processing is used for degumming raw materials from
fibrous plants by
using physico-chemical phenomena, especially osmosis.
Preferentially, the method is used for degumming, washing, rinsing, bleaching,
dying,
impregnation and chemical treatment of raw materials made of fibrous plants.
Attached figure helps the better explanation of the invention principle.
Figure 1 shows the scheme of device for processing fibrous plant raw
materials, where:
1- Apparatus working tank
2 - Openable collector
3 - Permanent collector
4-Pump
5 - Working fluid reservoir
6- Two-way valve I controlled electrically
7- Two-way valve II controlled electrically
8 - Two-way valve III
9 - Filter
10 - Flow-meter
11 - Two-way regulating valve
12 - Apparatus working tank drain valve 1
13 - Working fluid reservoir drain valve 5
14 - Water supply from the network valve
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
15 - pH detector
16 - Heaters
17 - Fluid lever detector
18 -1Vlanual regulating valve
5 19 - Overflow
- Temperature detector
21 - Ultrasound generator
22 - Guides
23 - Regulator
10 24 - Steering unit
- batching tank
26 - batching valve
27 - batching pomp
15 Presented below are examples of application of above define invention
Example 1. Deguinming flax stems.
Having opened openable container 2, 15 kg of flax stems were placed in
apparatus
working container 1 so that the stems bulk distribution was as even as
possible in whole
20 container volume which was 1.1 m high, and 0.6 m in diameter. The
parameters on the
steering unit: regulator 23 and steering device 24, were set as follows: water
pH - 6.5,
temperature - 30 C, water flow rate through the raw material set by manual
regulating
valve 18 - 20 L/min and time of change of water flow direction through the
apparatus
working tank 1 from the bottom to the top or from the top to the bottom.
Having turned
25 on the device at the steering unit: regulator 23 and steering device 24,
the worlcing fluid
reservoir 5 was automatically filled with water from the network through the
water
supply from the network valve 14, than the water was heated by heaters 16 till
set
temperature measured by the detector 20 was achieved, and having reached the
set
temperature, water was puinped over by the pump 4 from the working fluid
reservoir to
apparatus worlcing tank 1 through the electrically controlled two-way valve II
7 and
permanent collector 3. The level of water in working fluid reservoir 5 was
controlled by
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
11
the fluid level detector 17. Having pumped water over, the working fluid
reservoir 5 was
filled up with tap water through water supply from the network valve 14, water
was
heated with heaters 16 and pumped over to the apparatus worlcing tank 1 by the
pump 4
through the two-way valve II 7 and permanent collector 3. Filling up the
apparatus
working tank 1 with water took place till the moment when the working fluid
reservoir 5
and apparatus working tank 1 were completely filled. Degumming was conducted
at
constant water flow through the raw material which was directed to the
openable
collector alternate 2 from the bottom to the top of the apparatus working tank
1 by the
electrically controlled two-way valve 117 or the electrically controlled three-
way I valve
6. A uniform flow of water through the whole bulk of raw material was secured
by guides
22 in the openable collector 2 and in permanent collector 3. Having passed
through the
apparatus worlcing tank 1 water run through the two-way valve III 8 and came
back
through the filter 9 to the working fluid reservoir 5. The working fluid
reservoir 5 was
equipped with overflow 19 protecting from water overflow over its edge. The
set rate of
water flow through the apparatus working tank 1 was measured by the flow-meter
10 and
controlled by the signal from this flow-meter by electrically controlled
regulating valve
11. Degumming was conducted at constant flow of water through the raw material
for 72
hours. Having terminated the process the water working fluid from apparatus
working
tank 1 was dumped to the sewage system by the drain valve 12 and from working
fluid
reservoir 5 by the drain valve 13. Both valves, drain valve 12 and drain valve
13 were
manually controlled. Having removed the water, the stems were taken out from
the
apparatus working tank 1, than it was squeezed, dried, broken and the fiber
was
separated.
Example 2. Degumming flax steins using ultrasounds.
The example concerns using the device and the method for degumming
decorticated fibre
of such fibrous plants as flax, hemp, kenaf, jute and others Having opened
openable
container 2, 15 lcg of flax stems was placed in apparatus working container 1
so that the
stems bulk distribution was as even as possible in whole container volume
which was 1.1
m high, and 0.6 m in diameter. The parameters on the steering unit: regulator
23 and
steering device, were set as follows: water pH - 6.5, temperature - 30 C,
water flow rate
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
12
through the raw material set by manual regulating valve - 20 L/min and time of
change
of water flow direction through the apparatus working tank 1 from the bottom
to the top
or from the top to the bottom. Having turned on the device at the steering
unit: regulator
23 and steering device 24, the working fluid reservoir 5 was automatically
filled with
water from the network through the water supply from the network valve 14,
than the
water was heated by heaters 16 till set temperature measured by the detector
20 was
achieved, and having reached the set temperature, water was pumped over by the
pump 4
from the working fluid reservoir to apparatus working tank 1 through the
electrically
controlled two-way valve 117 and permanent collector 3. The level of water in
working
fluid reservoir 5 was controlled by the fluid level detector 17. Having pumped
water over,
the working fluid reservoir 5 was filled up with tap water through water
supply from the
network valve 14, water was heated with heaters 16 and pumped over to the
apparatus
working tank by the pump 4 through the two-way valve 117 and permanent
collector 3.
Filling up the apparatus working tank 1 with water took place till the moment
when the
working fluid reservoir 5 and apparatus working tank 1 were completely filled.
Having filled up the apparatus working tank 1 the ultrasound generators 2_1
were turned
on that are placed in the permanent collector 3 and in the openable collector
2. The
working time of ultrasound generators depends on the temperature and
requirements of
the process.
Deguinming was conducted at constant flow of water through the raw material,
that was
directed alternate from the bottom to the top of the apparatus working tank 1
by the
electrically controlled two-way valve 117 or by the electrically controlled
three-way I
valve 6 to the openable collector 2. Uniform flow of water through the whole
bulk of raw
material was secured by guides 22 in the openable collector 2 and in permanent
collector
3. Having passed through the apparatus working tank 1 water run through the
two-way
valve III 8 and came back through the filter 9 to the working fluid reservoir
5. The
working fluid reservoir 5 was equipped with overflow 19 protecting from water
overflow
over its edge. The set rate of water flow through the apparatus working tank 1
was
measured by the flow-meter 10 and controlled by the signal from this flow-
meter by
electrically controlled regulating valve 11. Degumming was conducted at
constant flow
of water through the raw material for 48 hours. After set time, the chemical
pump 4,
CA 02670408 2009-05-22
WO 2008/063091 PCT/PL2006/000085
13
heaters 16 and ultrasound generator 21 were turned off and two-way valve 1118
opened,
and working fluid from apparatus working tank 1 was dumped to the sewage
system by
the drain valve 12 and from working fluid reservoir 5 by drain valve 13. Both
valves, the
drain valve 12 and drain valve 13 were controlled manually. Having dumped the
water,
stems were taken out from the apparatus working tank 1 than squeezed, dried,
broken
and the fiber was separated.
15
25