Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attomey Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
Live Media Captioning Subscription Framework for Mobile Devices
CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application claims the benefit of priority from U.S. Patent
Application entitled "Live
Media Captioning Subscription Framework for Mobile Devices", Application No.
12/191,265
filed August 13, 2008. This application claims the benefit of priority from
U.S. Patent
Application entitled "Live Media Subscription Framework for Mobile Devices",
Application No.
12/191,269 filed August 13, 2008. This application is also cross-related to
Canadian Patent
Application No. 2,560,178.
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0002] The present disclosure relates to media content, in particular live
media content that is
captioned for mobile applications and devices.
BACKGROUND
[0003] Traditional captioning devices, such as televisions and display
monitors, combine text
with a video broadcast, in which the text represents a transcribed audio
portion of the video. The
captions can be either closed captions or open captions. For closed captions,
the caption data is
embedded in a video signal, and the captions are not displayed unless they are
decoded. The text
or caption data is embedded in line 21 of the vertical blanking interval (VBI)
in analog
television. The VBI is an interval in a television signal that temporarily
suspends transmission of
the signal for an electron gun to move to the first line of a television
screen for the next screen
field. The VBI can be used to carry data, such as a test signal or the closed-
captioning data.
[0004] Closed captioned data created for analog television may use protocols
described by the
EIA (Electronics Industry Association) 608 Standard. Closed captioned
protocols for digital
television may be described in the EIA 708 Standard. In a digital
transmission, such as with
]
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
high-definition television, the EIA 708 captioning data can be encoded in user
data packets in an
MPEG compressed video stream.
[0005] When captions are decoded, the captions can be displayed on the screen.
Typically,
captions can be decoded at the display device. Open captions may be already
decoded in the
video signal and may be displayed on screen, such as subtitles in foreign
films. In broadcast
transmission systems, caption data may be transmitted to an encoder that may
include text and
control codes.
[0006] Caption data may also be provided to the internet using transcribed
data from broadcast
sources, such as broadcast radio or television signals. For instance, a
caption writer for a radio
station may transcribe a broadcast program from the radio station to post on
the radio station's
web page. In another example, a caption writer may caption the audio portion
of a television
signal and send the caption data to an encoder device at a broadcast facility
for inclusion in the
video transmission.
SUMMARY
[0007] The present disclosure describes methods, systems, and techniques for
subscription-based
services for captioned media content. Information for the captioned media
content may be
created in real time and accessible to mobile devices. The information may
include special
reports, emergency news, alerts, news updates on a variety of topics, and
reports on sports and/or
financial news. Some information may be accessible to mobile devices on a fee
basis via an
authentication mechanism utilizing user names and password protection.
Alternatively, some
information may be freely provided, as long as the mobile device user remains
a subscriber. The
content sent to the user may be individually customized based on the
subscriber's preferences.
2
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
[0008] In one general aspect, the techniques feature a system for providing
subscription services
for near-real time caption information for one or more mobile devices. The
system includes a
communication network for communicating to the one or more mobile devices, a
transcriber
connected with the communication network and configured for transcribing an
event to generate
caption data. The caption data includes transcribed data and control code
data. The system
includes a subscription gateway configured for near real time transfer of the
transcribed data over
the communication network to the one or more mobile devices. The subscription
gateway is
configured to provide access for the transcribed data to the one or more
mobile devices.
[0009] Advantageous implementations can include one or more of the following
features. The
system can be configured to transfer transcribed data to at least two mobile
devices
simultaneously. The communication network may involve the Internet, and the
subscription
gateway can be configured to send notices and alerts to subscribers using the
one or more mobile
devices based on subscriber preferences.
[0010] The system also includes an external subscription database to store
information
associated with subscribers of the near real time caption information. The use
of subscriber
preferences may involve sending transcribed event information to a mobile
device of the
subscriber based on any of an area code, a country code, and a zip code.
[0011] The system may also include a device with captioning functionality and
a display to
present caption data and a decoder to decode the caption data for presentation
on the device
comprising captioning functionality. The system may be further configured for
near real time
transfer of the caption data to the decoder.
100121 The subscription gateway may include a transcription device interface
to interact with the
transcriber, an encoder interface to interact with an external encoder that
encodes the caption
data, and a subscriber database to store information associated with
subscribers of the near real
3
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attomey Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
time caption information. The subscription gateway may also include a
subscriber database
interface to interact with an external subscriber database that is configured
to store information
associated with subscribers of the near real time caption information. The
information associated
with the subscribers may include subscriber preferences for caption
information. The
subscription gateway may have a communication network interface to interact
with the
communication network and transmit event data, as well as a server interface
to interact with an
external server. The one or more mobile devices can be configured to interact
with the external
server and the communication network.
[0013] In another general aspect, a subscription-based method for sending near
real time caption
information to one or more mobile devices involves transcribing an event to
generate device-
generated caption data having control codes, removing the control codes from
the caption data to
produce text data, searching a database of caption information subscribers to
locate one or more
subscribers subscribed to receive the text data for the event, and sending the
text data to one or
more mobile devices over a communication network.
[0014] Advantageous implementations can include one or more of the following
features. The
method may also involve receiving information associated with zip codes,
telephone country
codes, telephone number area codes, and city and state names from the one or
more mobile
devices. The method may involve comparing any of the received information with
zip codes,
telephone country codes, telephone number area codes, and city and state names
stored in the
database, and providing event data to the one or more mobile devices when
information received
from the one or more mobile devices corresponds with similar or the same
information stored in
the database.
[0015] The communication network may include any one of a satellite channel, a
telephony
channel, an optical channel, a wireless channel, a cable channel, and an
internet channel. The
4
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
event data provided may be based on a geographic region relating to any of the
zip codes and
telephone codes, in which the event data may include local news, weather
alerts, traffic reports,
and emergency information. The method may involve presenting one or more real-
time
captioning streams from one or more events to subscribers using one or more
mobile devices
based on subscriber preferences. The method may include authenticating
subscribers based on a
user name and a password stored in the database, in which the transcribing
involves using a
transcription device to add control codes to the transcribed data. The method
may involve
encrypting the text data and/or the subscriber data prior to sending the text
data to the one or
more mobile devices over the communication network. The text data and
subscriber preferences
can be displayed on the one or more mobile devices.
[0016] In another general aspect, an article including a machine-readable
medium storing
instructions operable to cause a machine to perform operations including
receiving information
from a mobile device for subscriber preferences for media content to be sent
to the mobile
device, and searching a database that has information for subscribers of media
content. The
media content involves real-time streaming data of transcribed data sent over
a communication
network. The operations include sending the transcribed data to the mobile
device, in which the
subscriber preferences include a zip code, an area code, and/or a country
code.
100171 Advantageous implementations can include one or more of the following
features. The
transcribed data may include control code data for a caption target. The
caption target may have
closed-captioning functionality. The text data can be sent to the mobile
device and the
transcribed data can be sent to the caption target simultaneously. The text
data can be sent to the
mobile device and the transcribed data is sent to the caption target in near
real time.
[0018] The operations may include selecting the media content based on any of
a zip code, an
area code, and a country code, and sending an alert to the mobile device that
media content is
5
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
available to the sent to the mobile device. The media content can include
news, weather alerts,
traffic reports, and emergency information that is specific to any of the zip
codes, area codes,
and/or country codes.
[0019] In one general aspect, the techniques feature a system for providing
near real time caption
information for one or more mobile devices. The system includes a
communication network for
communicating to the mobile devices, and a transcriber connected with the
communication
network. The transcriber is configured to transcribing audio of an event to
generate caption data,
in which the caption data includes transcribed text data and control code
data. The system is
further configured for near real time transfer of the transcribed audio text
data over the
communication network to the one or more mobile devices.
[0020] In another general aspect, the techniques feature a method for sending
near real time
caption information to one or more mobile devices. The method involves
transcribing audio to
text of an event to generate caption data having control codes, removing the
control codes from
the caption data to produce text data, and sending the text data to one or
more mobile devices
over a communication network. The event can be a broadcasted media event,
which includes
audio.
[0021] In another general aspect, the techniques feature an article that
includes a machine-
readable medium storing instructions operable to cause a machine to perform
operations. The
operations involve generating transcribed data from a transcription device,
sending text data
from the transcribed data to a mobile device using a communication network,
and sending the
transcribed data from the transcription device to a caption target. The text
data is sent to the
mobile device and the transcribed data is sent to the caption target
simultaneously. The text data
is sent to the mobile device and the transcribed data is sent to the caption
target in near real time.
6
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attomey Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
100221 In another general aspect, the techniques feature an article that
includes a machine-
readable medium storing instructions operable to cause a machine to perform
operations. The
operations involve transcribing audio data from a radio broadcast, and sending
the transcribed
audio data to at least one mobile device using a communication network. The
operation of
sending the data involves near real-time transmission of the transcribed audio
data. The
communication network is coupled to at least one mobile device.
[0023] A transcription device may be used in the operation of transcribing the
audio data. The
operations may also include using a software program to remove closed-
captioning control codes
from the transcribed audio data prior to sending the transcribed audio data to
at least one mobile
device. The transcribed audio data may involve audio data that is transcribed
into text data. The
audio data may be voice data.
[0024] In one exemplary implementation, a system includes a communication
network, such as
the Internet, and one or more mobile devices coupled to the communication
network. The
system includes a transcription device to transcribe data in real time or near
real time (e.g., real
time with a very small time delay). The transcribed data includes text data
and control code data.
The control code data is used by one or more captioning devices to display
caption data. The
control code data is removed from transcribed data, and the mobile devices
receive text data via
the communication network. The system can simultaneously send transcribed data
to one or
more captioning devices, while sending the text data to one or more mobile
devices. Subscribers
of transcribed media content can receive real time news reports, emergency
information, and
alerts on their mobile devices.
[0025] Aspects of the disclosed techniques involve a system for providing
information for one
or more mobile devices. The system includes a server for communicating to the
one or more
mobile devices for one or more users, in which the one or more mobile devices
includes Global
7
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
Positioning System (GPS) capabilities. The system includes a subscription
gateway configured
to receive a user preference for transcribed audio for an audio event
associated with a geographic
location specified by the user, the user preference comprising any of an area
code, a country
code, a zip code, a state name, a country name, a city name, a radio station
identifer, or a
television station identifier. The subscription gateway includes a subscriber
database to store
information associated with the users of the one or more mobile devices. At
least one of the
mobile devices includes a software selection for a user option to utilize the
GPS capabilities to
update the user preference based on a geographic location of the mobile device
with a selected
user option. The system includes a stenocaptioning device configured for
transcribing audio for
the audio event simultaneously with an occurrence of the audio event. The
stenocaptioning
device is further configured to generate caption data that includes
transcribed data and control
code data. The system includes a captioning device to receive the caption
data, and a software
tool configured to remove the control code data from the caption data to
generate American
Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) text data. The system is
configured for
transfer of the text data over the server to the one or more mobile devices
and transfer of caption
data to the captioning device. The system is configured for transfers of the
text data and caption
data that occur coincidentally with the transcribing of audio for the audio
event. The system is
configured for concurrent transfer of the text data to the one or more mobile
devices and the
caption data to the captioning device.
[00261 These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The system can be configured to transfer the text data to at least
two of the mobile
devices simultaneously. The system may further include a communication network
with Internet
functionality, and the subscription gateway can be configured to send notices
and alerts to users
of the one or more mobile devices based on at least one user preference. The
system can include
8
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
a subscription database that is external to the subscription gateway to store
information
associated with the users of the one or more mobile devices or the user of the
captioning device.
The user preference further can include a request for the transcribed audio.
At least one of the
devices can include an Internet Protocol (IP). The radio and television
station identifiers can be
associated with at least one audio source. The system can include a decoder to
decode the
caption data for presentation on the captioning device. The captioning device
can be a device
including captioning functionality. The stenocaptioning device can be a device
with a
stenographic keyboard, a computing device having software with captioning
functionality, or a
computing device having voice recognition software and captioning
functionality. The
subscription gateway can include: a transcription device interface to interact
with the
stenocaptioning device; an encoder interface to interact with an external
encoder that encodes the
caption data; a subscriber database interface to interact with an external
subscriber database
configured to store information associated with the users of the one or more
mobile devices or
the user of the captioning device, in which the information associated with
the any of the users
comprises subscriber preferences for the transcribed audio; a communication
network interface
to interact with a communication network; and a server interface to interact
with the server, in
which the one or more mobile devices can be configured to interact with the
server and the
communication network.
100271 In some aspects, some implementations feature a method for sending
transcribed audio
information to one or more mobile devices. The method includes communicating,
via a server,
to the one or more mobile devices for one or more users, in which the one or
more mobile
devices includes Global Positioning System (GPS) capabilities. The method
includes receiving,
via a subscription gateway, a user preference for transcribed audio for an
audio event associated
with a geographic location specified by the user. The user preference includes
any of an area
9
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
code, a country code, a zip code, a state name, a country name, a city name, a
radio station
identifier, and/or a television station identifier. The subscription gateway
includes a subscriber
database to store information associated with the users of the one or more
mobile devices, and at
least one of the mobile devices includes a software selection for a user
option to utilize the GPS
capabilities to update the user preference based on a geographic location of
the mobile device
with a selected user option. The method includes transcribing audio with a
stenocaptioning
device for the audio event simultaneously with an occurrence of the audio
event, in which the
stenocaptioning device is configured to generate caption data that comprises
transcribed data and
control code data. The method involves receiving the caption data with the
captioning device,
removing the control code data from the caption data with a software tool to
generate American
Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) text data, transferring the
text data over the
server to the one or more mobile devices, and transferring the caption data to
the captioning
device. The transfers of the text data and caption data occur coincidentally
with the transcribing
of audio for the audio event, and there is concurrent transfer of the text
data to the one or more
mobile devices and the caption data to the captioning device.
[0028] These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The user preference for transcribed audio for the audio event can
include a preference
for a type of audio event. The method may further include searching the
subscriber database to
locate one or more users subscribed to receive the text data for the audio
event. The method may
involve the following: receiving information associated with zip codes,
telephone country codes,
telephone number area codes, the city name, the state name, the country name,
the radio station
identifier, and/or the television station identifier from the one or more
mobile devices; comparing
any of the received information with zip codes, telephone country codes,
telephone number area
codes, radio station identifiers, television station identifiers, audio
sources, video sources, or city,
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
state, or country names in the database; and providing the text data to the
one or more mobile
devices when information received from the one or more mobile devices
corresponds with
similar information in the database. Any of the transfers of data may utilize
a communication
network that includes any one of a satellite channel, a telephony channel, an
optical channel, a
wireless channel, a cable channel, and an Internet channel. The data related
to the audio event
can be received based on the geographic location associated with any of the
following: zip codes,
telephone country codes, telephone number area codes, the city name, the state
name, the country
name, the radio station identifier, or the television station identifier. The
transcribed audio can
be associated with news, a weather report, a traffic report, a sporting event,
a broadcasted event,
or emergency information. The method may include presenting one or more data
streams of text
from one or more audio events to users using the one or more mobile devices
based on user
preferences. The method may involve authenticating users of the one or more
mobile devices
based on user names and passwords in one or more databases, and transferring
the text data to at
least two of the mobile devices simultaneously. The transfer to a first one of
the at least two
mobile devices can at least partially overlap in time with the transfer to a
second one of the at
least two mobile devices. The method may involve encrypting the text data
prior to transferring
the text data to the one or more mobile devices. The radio and television
station identifiers can
be associated with at least one audio source. The method can involve
transferring data to the one
or more devices for displaying the text data, the user preference, a menu of
audio events, or
geographic location information. The transfer of data to the one or more
devices can involve
transferring data to the one or more devices within an order of a few seconds
from the
occurrence of the audio event. The transfer of data to the one or more devices
can include
transferring data to the one or more devices within forty five seconds from
the occurrence of the
audio event (e.g., < 45 sec). The transfer of data to the one or more devices
can include
11
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
transferring data to the one or more devices within thirty seconds from the
occurrence of the
audio event (e.g., < 30 sec). The transfer of data to the one or more devices
can include
transferring data to the one or more devices within twenty seconds from the
occurrence of the
audio event (e.g., < 20 sec). The transfer of data to the one or more devices
can include
transferring data to the one or more devices within ten seconds from the
occurrence of the audio
event (e.g., < 10 sec). The transfer of data to the one or more devices can
include transferring
data to the one or more devices within five sections from the occurrence of
the audio event (e.g.,
< 5 sec). The method can involve receiving data at the one or more mobile
devices within an
order of a few seconds from the occurrence of the audio event. Any of the
methods described
herein can involve receiving data at the one or more mobile devices from the
occurrence of the
audio event within any particular time frame specified within this disclosure
(e.g., within 45 sec,
or 30 sec, or 20 sec, or 10 sec, or 5 sec).
[00291 In some aspects, some implementations feature an article including a
machine-readable
medium storing instructions operable to cause a machine to perform operations.
The instructions
include communicating, via a server, to one or more mobile devices for one or
more user, in
which the one or more mobile devices includes Global Positioning System (GPS)
capabilities.
The instructions include receiving, via a subscription gateway, a user
preference for transcribed
audio for an audio event associated with a geographic location specified by
the user, in which the
user preference includes any of an area code, a country code, a zip code, a
state name, a country
name, a city name, a radio station identifier, and/or a television station
identifier. The
subscription gateway includes a subscriber database to store information
associated with the
users of the one or more mobile devices, and at least one of the mobile
devices includes a
software selection for a user option to utilize the GPS capabilities to update
the user preference
based on a geographic location of the mobile device with a selected user
option. Further
12
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
instructions involve transcribing audio with a stenocaptioning device for the
audio event
simultaneously with an occurrence of the audio event, in which the
stenocaptioning device is
configured to generate caption data that includes transcribed data and control
code data. The
instructions include receiving the caption data with the captioning device,
removing the control
code data from the caption data with a software tool to generate American
Standard Code for
Information Interchange (ASCII) text data, transferring the text data over the
server to the one or
more mobile devices, and transferring the caption data to the captioning
device. The transfers of
the text data and caption data occur coincidentally with the transcribing of
audio for the audio
event, and there is concurrent transfer of the text data to the one or more
mobile devices and the
caption data to the captioning device.
[00301 These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The transcribed data can be generated from the stenocaptioning
device, a computing
device having software with captioning functionality, or a computing device
including voice
recognition software and captioning functionality. The article may include
instructions operable
to cause the machine to perform the following operations: receiving
information from one of the
mobile devices for user preferences for media content to be sent to the mobile
device; searching
one or more databases for media content, in which the media content includes
streaming ASCII
text data of the transcribed audio; and sending the text data to the mobile
device that sent the
information corresponding with the user preference. The user preference may
include a video
source identifier or an audio source identifier. The article can have
instructions for selecting the
media content based on any of the zip code, the area code, the country code,
the radio station
identifier, the television station identifier, the audio source identifier,
and/or the video source
identifier. The radio and television station identifiers can be associated
with at least one audio
source. The article may further include instructions for sending an alert or
an indicator to the
13
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
mobile device that the transcribed audio corresponding to user preferences is
available to be sent
to the mobile device. The media content can include any of the following: a
news report, a
weather report, a traffic report, a sporting event, a broadcasted event,
and/or emergency
information that is associated with any of the zip code, the area code, the
country code, the city
name, the state name, the country name, the radio station identifier, the
television station
identifier, the audio source identifier, and/or the video source identifier.
The article can include
instructions for displaying the text data on the one or more mobile devices as
the text data arrives
to the one or more mobile devices. The article may include instructions to
cause the text data to
be displayed as scrolling text, and instructions to transfer the text data via
the Internet.
[0031] In some aspects, some implementations feature a subscription gateway
for handling
transcribed audio data. The subscription gateway includes a server interface
for receiving one or
more data feeds of transcribed audio data concurrently as audio data is
transcribed into text data
for a live event. The transcribed audio data includes American Standard Code
for Information
Interchange (ASCII) text data and wrapper data, in which the wrapper data
includes one or more
client identifiers. The one or more client identifies can include a station
name, a call sign, an
area code, and/or a zip code. The subscription gateway includes a server for
communicating
with one or more mobile devices that are configured to receive the text data
based on at least one
user subscription. The server is configured for transmitting the text data to
the one or more
mobile devices concurrently with the reception of the transcribed audio data
into the server
interface. The subscription gateway includes a subscription server for
processing one or more
user preferences of users of the one or more mobile devices, and for
authenticating one or more
user subscriptions for receiving the text data on the one or more mobile
devices.
100321 These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The subscription server can be configured for authenticating one or
more subscribers
14
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
that are permitted to receive the data feeds on the one or more mobile devices
as the data feeds
are being received by the server interface. The authentication can include
utilizing at least one
user name or password. The one or more user preferences can include a user
preference for
transcribed audio data for an audio event associated with a geographic
location specified by the
user or at least one mobile device utilizing a Global Positioning System (GPS)
to specify the
geographic location. The user preference can include any of an area code, a
country code, a zip
code, a state name, a country name, a city name, a radio station identifier,
and/or a television
station identifier. The subscription gateway includes a subscriber database to
store information
associated with the users of the one or more mobile devices. The subscription
gateway can
include software to associate the user preference with the wrapper data to
associate a data feed
corresponding to the specified geographic location. The subscription server
can be configured to
execute instructions relating to a subscription status, user account
information, payment
information, or a subscription term or condition. The subscription gateway can
be configured to
interact with a communication network that is coupled to a caption target that
receives caption
data corresponding to the transcribed audio data. The transcribed audio data
and/or caption data
can be compatible with an Electronics Industry Association 708 standard (EIA
708). The
subscription server can include software to categorize any of the user
preferences. The
categorization can include geographic information, area codes, zip codes,
station identifiers,
event types, audio sources, video sources, client identifiers, news
categories, sports news or
information, and/or financial news or information. The text data can be a
product of a digital
television data stream. Alternatively, the text data can be a product of an
analog television data
transmission. The transmission of the text data via the server to the one or
more mobile devices
can involve bypassing any text data storage units (if any) during the
transmission to the one or
more mobile devices. The subscription gateway can be text data storage unit-
less (e.g., without a
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 0862 ] -0005CA2
storage unit for text data). The event can be an audio event. The subscription
gateway can
include a software tool for sending an alert or an indicator to at least one
mobile device that live
transcribed audio data for a live audio event corresponding to at least one
user preference is
available to be sent to at least the one mobile device. The transcribed audio
data can be a
product of caption data that has control codes removed from the caption data.
[0033] In some aspects, some implementations feature a method for handling
transcribed audio
data. The method can include receiving one or more data feeds of transcribed
audio data in a
server interface concurrently as audio data is transcribed into text data for
a live event. The
transcribed audio data can include American Standard Code for Information
Interchange (ASCII)
text data and wrapper data. The wrapper data can include one or more client
identifiers, in which
the one or more client identifies comprises a station name, a call sign, an
area code, or a zip
code. The method includes the following: communicating via a server with one
or more mobile
devices that are configured to receive the text data based on at least one
user subscription;
transmitting the text data via the server to the one or more mobile devices
concurrently with the
reception of the transcribed audio data into the server interface; processing
one or more user
preferences of users of the one or more mobile devices with a subscription
server; and utilizing
the subscription server to authenticate one or more user subscriptions for
receiving the text data
on the one or more mobile devices.
[0034] These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The method can include utilizing the subscription server to
authenticate one or more
subscribers that are permitted to receive the data feeds on the one or more
mobile devices as the
data feeds are being received by the server interface. The authentication can
include utilizing at
least one user name or password. The one or more user preferences can include
a user
preference for transcribed audio data for an audio event associated with a
geographic location
16
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
specified by the user or at least one mobile device utilizing a Global
Positioning System (GPS) to
specify the geographic location. The user preference can include any of an
area code, a country
code, a zip code, a state name, a country name, a city name, a radio station
identifier, or a
television station identifier. The method can involve utilizing a subscriber
database to store
information associated with the users of the one or more mobile devices. The
method can
involve associating the user preference with the wrapper data to associate a
data feed
corresponding to the specified geographic location. The method can include
executing
instructions with the subscription server relating to a subscription status,
user account
information, payment information, and/or a subscription term or condition. The
method can
include interacting with a communication network that is coupled to a caption
target that receives
caption data corresponding to the transcribed audio data. The transcribed
audio data or caption
data is compatible with an Electronics Industry Association 708 standard (EIA
708). The
method can include categorizing any of the user preferences with the
subscription server. The
categorization can include geographic information, area codes, zip codes,
station identifiers,
event types, audio sources, video sources, client identifiers, news
categories, sports news or
information, and financial news or information. The method can include
producing the text data
from a digital television data stream or an analog television data
transmission. The method can
involve transmitting the text data to the one or more mobile devices by
bypassing any text data
storage units during the transmission to the one or more mobile devices. The
method can include
sending an alert or an indicator to at least one mobile device that live
transcribed audio data for a
live audio event corresponding to at least one user preference is available to
be sent to the at least
the one mobile device. The transcribed audio data can be a product of caption
data that has
control codes removed from the caption data, and the caption data can be a
product of a
stenocaptioning device. Transmitting the text data to the one or more devices
can involve
17
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
transmitting the text data to the one or more devices within an order of a few
seconds from an
occurrence of the event that is being transcribed. Alternatively, transmitting
the text data to the
one or more devices can involve receiving the text data at the one or more
devices within an
order of a few seconds from an occurrence of the event that is being
transcribed.
[0035] In some aspects, some implementations feature an article that includes
a machine-
readable medium storing instructions operable to cause a machine to perform
operations. The
instructions include receiving one or more data feeds of transcribed audio
data in a server
interface concurrently as audio data is transcribed into text data for a live
event. The transcribed
audio data include American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
text data and
wrapper data. The wrapper data includes one or more client identifiers, in
which the one or more
client identifies includes a station name, a call sign, an area code, and/or a
zip code. The
instructions also involve the following: communicating via a server with one
or more mobile
devices that are configured to receive the text data based on at least one
user subscription;
transmitting the text data via the server to the one or more mobile devices
concurrently with the
reception of the transcribed audio data into the server interface; processing
one or more user
preferences of users of the one or more mobile devices with a subscription
server; and utilizing
the subscription server to authenticate one or more user subscriptions for
receiving the text data
on the one or more mobile devices.
100361 These and other implementations can optionally include one or more of
the following
features. The article can include instructions for utilizing the subscription
server to authenticate
one or more subscribers that are permitted to receive the data feeds on the
one or more mobile
devices as the data feeds are being received by the server interface. The
authentication can
involve utilizing at least one user name or password. The one or more user
preferences can
include a user preference for transcribed audio data for an audio event
associated with a
18
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
geographic location specified by the user or at least one mobile device
utilizing a Global
Positioning System (GPS) to specify the geographic location. The user
preference can include
any of an area code, a country code, a zip code, a state name, a country name,
a city name, a
radio station identifier, and/or a television station identifier. The article
can include instructions
for utilizing a subscriber database to store information associated with the
users of the one or
more mobile devices. The article can include instructions for associating the
user preference
with the wrapper data to associate a data feed corresponding to the specified
geographic location.
The article can include instructions for executing instructions with the
subscription server
relating to a subscription status, user account information, payment
information, and/or a
subscription term or condition. The article can include instructions for
interacting with a
communication network that is coupled to a caption target that receives
caption data
corresponding to the transcribed audio data. The transcribed audio data can be
compatible with
an Electronics Industry Association 708 standard (EIA 708). The article can
include instructions
for categorizing any of the user preferences with the subscription server. The
categorization can
include geographic information, area codes, zip codes, station identifiers,
event types, audio
sources, video sources, client identifiers, news categories, sports news or
information, and/or
financial news or information. The article can include instructions for
producing the text data
from a digital television data stream or from an analog television data
transmission. The
instructions for transmitting the text data to the one or more mobile devices
can include
instructions for bypassing any text data storage units during the transmission
to the one or more
mobile devices. The article can include comprising instructions for sending an
alert or an
indicator to at least one mobile device that live transcribed audio data for a
live audio event
corresponding to at least one user preference is available to be sent to the
at least the one mobile
device. The transcribed audio data can be a product of caption data that has
control codes
19
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
removed from the caption data. The caption data can be a product of a
stenocaptioning device.
The stenocaptioning device can include a device with a stenographic keyboard,
a computing
device having software with captioning functionality, or a computing device
having voice
recognition software and captioning functionality. The instructions for
transmitting the text data
to the one or more devices can include instructions for transmitting the text
data to the one or
more devices within an order of a few seconds from an occurrence of the event.
The text data
can be received at the one or more devices within an order of a few seconds
from an occurrence
of the event.
[0037] Details of one or more implementations are set forth in the
accompanying drawings and
the description below. Other features and advantages will be apparent from the
description and
drawings, and from the claims.
DRAWING DESCRIPTIONS
FIG I shows a block diagram of an example captioning system.
FIGS. 2A-2B show block diagrams of examples of the captioning system.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram of an example of the captioning system with voice-
recognition
software.
FIGS. 4A-4B show block diagrams of examples the captioning system with
broadcast
radio.
FIGS. 5A-5B shows block diagrams of examples of the subscription-based
captioning
system.
FIG. 6 shows a block diagram of an example of a subscription gateway.
FIG. 7 shows a block diagram of an example subscription-based captioning
system.
Like reference symbols in the various drawings indicate like elements.
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[00381 The following detailed description makes reference to the accompanying
drawings. The
following also describes tasks, techniques, systems, apparatuses, and/or
methods relating to fee
and/or advertising based, and/or subscription based service and/or framework
for closed
captioned media. Other embodiments of the present invention are possible and
modifications
may be made to the embodiments without departing from the spirit and scope of
the invention.
Therefore, the following detailed description is not meant to limit the
invention.
[0039] Moreover, for convenience in the ensuing description, some explanations
of terms are
provided herein. However, the explanations contained herein are intended to be
exemplary only.
They are not intended to limit the terms as they are described or referred to
throughout the
specification. Rather these explanations are meant to include any additional
aspects and/or
examples of the terms as described and claimed herein and/or as used by one of
skill in the art.
[00401 The following describes various tasks, techniques, and systems relating
to fee and/or
subscription-based services for closed-captioned media content. The present
disclosure
describes methods and systems that involve a fee and/or subscription-based
framework for
sending real-time caption data from a caption writer to one or more mobile
devices through a
communication network, such as the internet, while simultaneously having the
ability to send
caption data to traditional captioning devices, such as a television or
monitor that can display
captioned information.
[00411 The caption writer refers to a person, such as a stenographer, who
transcribes data from a
source presentation or an event. The data may be from a "live" event, such as
a sporting event,
an academic presentation, or a financial news report. The data can be audio
and/or video data
that is transcribed into text data. The caption writer may also transcribe the
data remotely, in
which the writer does not have to be physically present to perform the
transcription. The writer
21
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
may remotely listen to and/or watch the event using a telephone and/or a
monitor or television
set. The event may or may not be an event that is broadcasted, such as an
event using broadcast
television or radio signals.
[0042] In some implementations, a subscriber system can use a password to
authenticate a
subscriber for the service. User names and user preferences may be stored in
one or more
databases. The subscriber system can be used to alert mobile device users to
captioned data that
may be available from video and/or radio programmers. In some implementations,
the real-time
data may be created voice recognition captioning systems using stenographic
theories and/or
methodologies. The caption data can be produced in a data stream that may have
control codes
or may not have control codes. The data stream can be transmitted by a server
or server program
as Transmission Control Protocol with Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) packets to
one or more mobile
device users in real-time.
[0043] In some implementations, real-time captioned data can be sent in a real-
time data stream
to mobile devices. The real-time captioned data can be accessed by mobile
device users on a
subscription basis. Each user may have a user name and password, and the
mobile device users
may have the ability to select from among a group of content service
providers. In some
implementations, the mobile device users can enter zip codes, telephone
country codes,
telephone number area codes, city and state names by comparing zip code/phone
or country
codes preferences to the content providers zip code/ phone and complete
telephone numbers to
enables subscribers to choose from among a range of real-time captioning
streams that may be
available. Some of the captioning streams may be local and specific for a
geographic region,
such as for local news, weather alerts, traffic reports, and emergency
information. Each mobile
device user may set up individualized user preferences on the desired content.
An alert can be
sent to a subscriber if the user's preferences match the content provided by
video and/or audio
22
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
listed providers in the database. The providers may have content that is
specific for various zip
codes, country codes or area codes.
[0044] The caption information may be delivered from a provider of captioning
services or from
a content provider and a captioning service that transcribes the content
provider's information.
In some implementations, the real-time captioning/ transcription can be
provided from a content
provider to enable transmission of captioned information with caption codes to
a captioning
encoder, or to the captioning encoder and one or more mobile devices
simultaneously. Also, the
real-time captioned data from caption service providers can be sent to a
communications network
from decoded output of one or more content provider stations. The real-time
captioned data can
be verified in a database with subscriber preferences. The system can provide
for user
authentication by using user names and passwords, and can issue alerts and
notifications to
subscribers of the availability of real-time captioned data on video and/or
radio programs that
have captioned data. In some implementations, the notifications may include
notifying
subscribers of the availability of real-time captioned data on video and radio
programs that have
captioned data that is outside the preferences of the subscribers, but may be
related to the
preferences of the subscribers. For example, an alert may be issued for a
weather report of
dangerous weather conditions in a local area, and a subscriber may also be
notified that
captioned data is available for local traffic conditions in that weather.
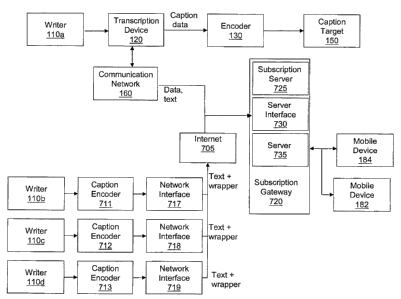
100451 As shown in Fig. 1, the captioning system can simultaneously send
caption information
to traditional captioning devices/targets 150 and mobile devices 180, 182,
184, 186. The
captioning targets 150 receive transcribed data, which includes text data
entered by the writer
110 and control code data for the captioning device 120. The mobile devices
180, 182, 184, 186
are connected to a communication network 160 and receive text data, and not
the control code
23
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
data. The control code data can be removed from the transcribed data prior to
sending data to the
communication network 160.
[0046] Fig. 1 shows a block diagram of a captioning system, in which one or
more users receive
real-time closed-caption data on one on more mobile devices. The caption
writer 110 listens to
and/or watches an event, and transcribes that event into text data using a
transcription device
120. The transcription device 120 may include a transcription-type device or a
stenographic-type
device. The transcription device 120 includes software and/or hardware to aid
in the captioning
process, and may have software to add control code data to the transcribed
data in a captioning
process. The control code data are used in traditional captioning devices for
displaying
captioned text on a monitor. The transcription device 120 may have software
and a keyboard to
enable the caption writer 110 to transcribe at rates of up to hundreds of
words per minute. For
example, the device 120 may have a stenographic keyboard or may include a
computer having
voice recognition software.
[0047] The transcribed data from the writer is sent to the transcription
device 120 that sends the
transcribed data to an encoder 130. The encoder 130 uses the control codes to
encapsulate the
transcribed data for presentation on a caption target 150. The caption target
150 can refer to a
monitor or a television with closed-captioning functionality.
[0048] Instead of or in addition to sending transcribed data to an encoder,
the transcription
device 120 may remove the control code data from the transcribed data and send
text data to a
communication network 160 to enable for one or more users to access the text
data. Examples of
communication networks include various forms or mediums of data
communications, such as a
local area network ("LAN"), a wide area network ("WAN"), a wireless local area
network
("WLAN"), and a personal area network ("PAN"). Other examples of communication
networks
include a mobile communication network using a multiple access technology,
such as a cellular
24
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
phone network with Code Division Multiple Access, ("CDMA"), a satellite
network, and the
Internet.
[0049] In sending the text data to the communication network 160, the
transcription device 120
may have software to remove the control codes from the transcribed data before
sending the data
to the communication network 160. In removing the control codes, the data that
is transmitted to
components includes text data. The text data can be sent to the communication
network 160 and
can be displayed on one or more mobile devices 180, 182, 184, 186, such as
computers, cell
phones, and personal digital assistants (PDAs). The communication network 160
interacts with a
server 165 to communicate with multiple devices. The server 165 may refer to
one or more
hardware servers, or software servers, such as a server program. The text data
may be displayed
as scrolling text data, in which the text is updated as the mobile device 180
receives text. The
devices may be internet-compatible devices and may be connected through a
cellular phone
network. As used herein, a mobile device may also refer to any general-purpose
mobile machine
that processes data according to a set of instructions that is stored
internally either temporarily or
permanently, including, but not limited to, general-purpose mobile computers,
laptop computers,
internet-compatible mobile phones, wired or wireless laptop computers. Mobile
devices also
include satellite-based transmission devices, smart client devices (that
actively fetch data and
store data locally), wireless devices, a cellular or mobile telephone, an
electronic handheld unit
for the wireless receipt and/or transmission of data, a media content playable
device, such as an
MP3 player, or the like. Each device may have a specific or unique internet
address, in which
the communication network may direct data to one or more devices based on the
device's
internet address. The system may use multicasting protocols and be configured
to broadcast the
simultaneously transcribed audio to text data streams from specific IP
addresses assigned to the
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
text data streams/feeds from each content provider, in which the text data
streams are received by
mobile devices that have users who are authorized to receive the text data
streams.
[0050) To provide for interaction with a user, each of the mobile devices 180,
182, 184, 186 uses
a display, such as a cathode ray tube (CRT) or liquid crystal display (LCD)
monitor, which
displays information to the user and a keyboard and/or a pointing device, such
as a mouse or a
trackball, to serve as input to the mobile device. The mobile device may
provide feedback to the
user with any form of sensory feedback, such as visual feedback or tactile
feedback.
100511 The communication network 160 may include a back end component, such as
a data
server, or a middleware component, such as an application server, or a front
end component,
such as a client computer having a graphical user interface, portal, or a Web
browser through
which a user can interact with an implementation of the systems and techniques
described here.
The mobile device 180 itself may have a front end component that includes a
graphical user
interface. In general, the communication network 160 and/or the mobile device
180 may use any
combination of such back end, middleware, or front end components.
[0052] The software (also known as programs, software tools or code) in the
captioning system
of Fig. 1 may include machine instructions for a programmable processor, and
can be
implemented in a high-level procedural and/or object-oriented programming
language, and/or in
assembly/machine language. The mobile device 180 may have an Application
Programming
Interface (API). For example, the mobile device 180 may also run on a Binary
Runtime
Environment for Wireless (BREW) platform, an open-source on-line application
development
platform for wireless CDMA devices from Qualcomm, Inc. of San Diego, CA. The
BREW
platform can allow application developers to write programs and scripts in
various software
languages, such as C, C++, JAVA, and XML. The mobile device 180 may have a
software
26
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
media player, such as a Windows media player, that can show the text data
and/or a video
presentation of the transcribed event.
[0053] As used herein, the term "machine-readable medium" refers to any
computer program
product, apparatus and/or device used to provide machine instructions and/or
data to a
programmable processor. The machine-readable medium refers to magnetic discs,
optical disks,
memory, Programmable Logic Devices (PLDs), and the like.
[0054] In the described system, the caption writer 110 can be located remotely
from the source
of the transcribed event. Also, the data can be sent to a mobile device using
the communication
network 160, such as the internet. Internet-compatible devices with displays
can present
captioned text in real time or near real time. The transcribed data can be
presented on a
traditional caption target 150 and a mobile device 186 simultaneously.
[0055] In one implementation, a device can allow a user to pause text streams
to receive
incoming phone calls or messages to the mobile device. A user may resume
receiving text
streams from the point at which the mobile device paused to receive an
incoming message or
phone call. Alternatively, the user may download and review text data from a
web site that has
the content of live text stream data that was saved from the point the data
stream was paused to
the time the data stream transmission was resumed to be received by the mobile
device.
[0056] Fig. 2A shows another implementation of a mobile captioning system. The
captioning
system can simultaneously send caption information to traditional captioning
devices/targets 250
and a mobile device 280. In Fig. 2A, the mobile captioning system can strip
out the control code
data in the transcribed data in the device 220 to have plain ASCII text
(American Standard Code
for Information Interchange) to be sent to the mobile device 280. Instead of
or in addition to
sending the data to the mobile device, the mobile captioning system can send
the transcribed data
with the control code data from the device 220 to an encoder 245 to provide
close captioning at a
27
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
caption target 250, such as a television or monitor. This can be performed
using remote caption
writing, and may be accomplished simultaneously and/or in real time or near
real time.
[0057] In Fig. 2A, a writer 210 transcribes the event data that they hear or
see into a device 220
that sends the data to a computer 230. The transcription device 220 includes a
computer with
software to add control code data to the text produced from the writer 210.
The event data may
or may not be broadcasted over conventional television or radio channels. The
data is sent from
the computer 230 to a communication network 240 and then to an encoder 245. As
described
above, the communication network 240 may include a modem, an internet channel,
and/or a
telephony channel. The encoder 245 encaptions the data at the caption target
250 so that the data
is put into a format for presentation on a television or a monitor, such as
utilizing line 21 of the
VBI as described above. The caption target 250 itself has a decoder to decode
the encaptioned
data from the encoder 245 prior to presenting the text on the monitor.
[0058] Alternatively and/or simultaneously, software in the computer 230
removes the control
codes from the transcribed data and sends text data to a server 260. The
server 260 may be
implemented in hardware or software. The server 260 sends the text data to the
mobile device
280. In one implementation, the server may send the text data to the mobile
device using a
communication network, such as the internet. The mobile device 280 can receive
the data from
the communication network through a router, such as a cable, DSL (Digital
Subscriber Line)
router, or a router in an enterprise or business environment.
100591 The server 260 can send the text data to the mobile device 280 via an
internet address. In
one implementation, the mobile device 280 has a particular internet address.
As the text data is
routed through the internet, the text data is routed to the internet address
of a particular mobile
device 280. In this aspect, the mobile device 280 is a client to the server
260.
28
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
100601 Instead of being located in the computer 230, the software or program
to remove the
control code data from the transcribed data can be distributed among one or
more components of
Fig. 2A. In one implementation, the control code data may be removed by
software located in
the device 220 itself, as described in Fig. 1. The transcribed data may then
be sent to the caption
target 250 and/or the text data may be sent to the mobile device 280 without
using the computer
230.
[0061] In another implementation, both the caption target 250 and the mobile
device 280 can
receive the transcribed data with the control code data. The mobile device 280
itself may have
software to remove the control code data. The device 280 can have control code
removal
abilities without having to require control-code-removing software in another
component of the
system.
100621 Fig. 2B shows another implementation of the captioning system described
with respect to
Fig. 2A. In Fig. 2B, the data is sent from the computer 230 to the encoder 245
to encaption the
data at the caption target 250. Text data is sent from the computer to the
server 260. The server
260 interacts with a mobile device 280 to present the text data on the mobile
device 280.
[0063] In an alternative implementation shown in Fig. 3, voice-recognition
software can be used
to generate caption information. Voice-recognition software 310 can be used
instead of the
writer 210 and the transcription device 220. The voice recognition software
can convert
speech/audio input into transcribed data output. The transcribed data can
include control codes
to be sent to the caption target 250. At the same time, the voice-recognition
software can output
the text of the transcribed data to be sent to the mobile device 280.
[0064] Fig. 4A shows an implementation of the captioning system in which
broadcast radio 410
is used as a source of information for the caption writer 210. In this
implementation, a caption
writer 210 listens to a radio broadcast and transcribes the broadcast
information into text data
29
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
using the transcription device 220. As described with respect to Fig. 2, the
mobile captioning
system can strip out the control code data in the transcribed data in the
device 220, or software in
the computer 230 can remove the control codes from the transcribed data before
sending the text
data to the server 260. The server 260 sends the text data to the mobile
device 280.
[0065] Fig. 4B shows another implementation of the captioning system shown in
Fig. 2A with a
radio broadcast 410 information source for the caption writer 210. The
captioning system can
simultaneously send caption information to traditional captioning
devices/targets 250 and a
mobile device 280. The mobile captioning system can strip out the control code
data in the
transcribed data in the device 220 to have text data (to be sent to the mobile
device 280).
Instead of or in addition to sending the data to the mobile device, the mobile
captioning system
can send the transcribed data with the control code data from the device 220
to an encoder 245 to
provide close captioning at a caption target 250, such as a television or
monitor. This operation
can be performed using remote caption writing, and may be accomplished
simultaneously and/or
in real time or near real time. The transcription of the radio broadcast 410
provides transcribed
data from a real time audio source.
100661 Fig. 5A shows a block diagram of a subscription-based captioning
system, in which one
or more users receive real-time closed-caption data on one on more mobile
devices for
subscribers of captioned content. As described above with respect to Fig. 1,
the captioning
system can simultaneously send caption information to traditional captioning
devices/targets 150
and mobile devices 180, 182, 184, 186. The captioning targets 150 receive
transcribed data,
which includes text data entered by the writer 110 and control code data for
the captioning
device 120. The mobile devices 180, 182, 184, 186 are connected to a
communication network
160 and receive text data, and not the control code data. Typically, the
control code data is
removed from the transcribed data prior to sending data to the communication
network 160. A
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
subscription gateway 520 receives information from the transcription device
120 and can send
transcribed data to the encoder 130 and text and subscriber data to the
communication network
160 to send to mobile devices 180, 182, 184, 186. The subscription gateway 520
may have a
database with subscriber data, subscription preferences, passwords, user
names, subscription
plans and accounts, and sources of available media and/or captioned content.
The subscription
gateway 520 may also authenticate mobile device subscribers and can be used
when subscribing
new users or unsubscribing users.
[0067] Fig. 5B shows another implementation of a subscription-based mobile
captioning system.
The captioning system can simultaneously send caption information to
traditional captioning
devices/targets 250 and a mobile device 280. In Fig. 513, the mobile
captioning system can strip
out the control code data in the transcribed data in the device 220 to have
plain ASCII text
(American Standard Code for Information Interchange) to be sent to the mobile
device 280 via
the subscription gateway 530. In some implementations, voice recognition
software can be used
to transcribe the data into ASCII text data. Instead of or in addition to
sending the data to the
mobile device, the mobile captioning system can send the transcribed data with
the control code
data from the device 220 to an encoder 245 via the subscription gateway 530 to
provide close
captioning at a caption target 250, such as a television or monitor. This can
be performed using
remote caption writing, and may be accomplished simultaneously and/or in real
time or near real
time.
[0068] In some exemplary implementations, the system may include a
communication network
240, such as the Internet, one or more mobile devices 280 coupled to the
communication
network, and a subscription gateway 530. The subscription gateway may be a
communication
network or a server program. The subscription gateway 530 can receive
transcribed data from a
transcription device 220. The data may include captioning control codes or the
control codes
31
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
may be removed by a computer using control code removal software 230. In some
implementations, the subscription gateway 530 can transmit data to a
communication network
which will distribute data to a caption encoder 245. The subscription gateway
may distribute
text data to a server device 260 that may authenticate subscriber data by a
user name and a
password. The mobile device 280 can display a menu of video, radio, and event
programming
that is currently transcribed for selection by the subscriber.
[0069] In another implementation, the transcription device can transmit data
to the subscription
gateway. The subscription gateway may be connected to a communication network
which can
transmit authentication data, user name, password data, and other subscriber
data information
from mobile device users. The subscription gateway can provide data encryption
and
authentication of subscriber-related data using the user names and password
authentication.
[0070] Fig. 6 shows an exemplary block diagram of a subscription gateway 610.
The
subscription gateway 610 includes a transcription device interface 620 to
interact with an
external transcription device 670, an encoder interface 640 to interact with
an external encoder
680, a subscriber database and data security (encryption) features 625, and a
subscriber database
interface 630 to interact with an external subscriber database 685. The
subscription gateway 610
includes a communication network interface 660 to interact with a
communication network 675.
The subscription gateway 610 includes a server interface 650 to interact with
an external server
690 and mobile devices 695 coupled to the server 690. In some implementations,
the server 690
may be part of the communication network 675. In other implementations, the
communication
network 675 may couple to one or more mobile devices 695 and/or one or more
stations, content
providers, or captioning service providers.
[0071] In one exemplary implementation, the server interface 650 can compare
user name and
password authentication information and distribute real-time transcribed
information to the
32
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
server 690. The server interface 650 can process the authenticated subscriber
information and,
according to user preferences, transmit the transcribed data to the server
690, which is connected
to one or more mobile devices 695. In one exemplary implementation, the mobile
device
user/subscriber can enter a zip code or a country code to display a menu
selection of event
programming, audio broadcasts, and/or video programming that are being
transcribed in real-
time, and are available for selection by a subscriber.
[00721 In another exemplary implementation, the server interface 650 can
compare real-time
transcribed data streams from video and radio providers, which can be inserted
in the
communication network 675 to the communication interface 660 of the
subscription gateway
610. The communication interface 660 may be implemented in hardware or
software. In some
implementations, the communication interface 660 can be used to transmit an
alert message to
subscribers of the availability of data streams of video and/or radio
programming in subscriber
profiles by zip code and/or country code. The system can allow the subscriber
to select a video
program provider for a particular zip code for emergency notifications, as
well as to enter user
names and passwords in the mobile device. The mobile devices could transmit
data via the
communication network 675 to the communication network interface 660.
Alternatively, the
mobile devices 695 could transmit data via the server 690 to the server
interface 650. In some
implementations, the communication network interface device 660 can
authenticate the user
names and password information from the external subscriber database 685
through the
subscriber data interface 630. Alternatively, the communication network
interface device 660
can authenticate the user names and password information from the internal
subscriber database
625. The listing of transcribed real-time data may be transmitted to the
server interface 650 and
to the server 690. After authentication and selection of real-time data stream
from a content
provider, the mobile device 695 can receive the selected data stream through
the communication
33
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
network 675. Mobile device users with subscriptions can be notified of
available data streams of
transcribed content from video and/or radio programmers for user-specified zip
codes, area
codes, or country codes. The notifications may be sent from communication
interface 660 with
an e-mail alert or an audible alert.
[0073] In another implementation, the communication network 675 may receive
captioned data
from the communication network interface 660. In some exemplary
implementations, the
communication network interface 660 may remove control codes, if any, and
transmit real-time
text data received from a communication network to mobile devices 695 using
the server 690
and the server interface 650. The communication network 675 may receive
captioned data from
decoded output of an encoder device at a video and/or radio program station.
The
communication network 675 may also receive caption data transcribed using
voice-recognition
technologies or through stenographic techniques of an audio broadcast. The
received data may
contain control codes or be in raw text form. Data passing through the
subscription gateway may
be encrypted by data security features 625, in which the data security
features may be
implemented in hardware or software. The data, whether encrypted or
unencrypted, can be sent
to communication network interface 660. In some implementations, subscriber
authentication by
user name and password can be performed by the subscriber data interface 630
accessing an
external subscriber database 685. Caption content subscribers on mobile
devices can enter a user
name and a password on a mobile device and access streaming data after
authentication. The
subscribers can access transcribed, captioned video and/or radio programming
being transmitted
in real-time using real-time transcription technologies, such as voice
recognition technology or
stenographic-based technology.
[0074] In other implementations, video and/or radio station programmers can
send alerts and
messages to the communication network 675. The communication network 675 may
include the
34
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
apparatuses of an internet service provider that may have the capabilities of
sending notifications
of emergency and/or special reports of captioned data being transmitted by the
station providers.
The communication network interface 660 may receive the captioned data with or
without
control codes.
[0075] In some implementations, the subscriber data interface 630 may compare
data provided
by communication network 675 with such data provided in the internal database
625 or external
database 685, and match station call sign data provided by stations to a zip
code and/or a country
code. In some implementations, the user preference data can be matched to the
call sign data of
stations of content providers to automatically match the news, messages, and
alerts of the
stations to a local zip code or country code for the subscriber. In these
implementations,
subscribers can automatically be able to receive captioned content from
stations of content
providers, such as a local news television station or a radio station. In some
implementations,
the content from the stations are not necessarily limited to the area code
where the subscriber is
located, but a subscriber may want to receive alerts and messages from
stations located in other
jurisdictions. For example the subscriber may be in one location (e.g., San
Diego, CA, area code
619) with their mobile device and may have user preferences with an area code
(e.g., Charlotte,
NC, area code 704) to receive alerts and notifications for a different
location.
[0076] In some implementations, the subscriber may have preferences for
captioned real-time
data from video and/or audio providers based on selected zip codes, area
codes, or country codes
of the video and audio providers. The subscriber data may be authenticated by
the subscriber
data interface 630. The subscriber database interface 630 may compare
subscriber preferences
and profiles, and can transmit alerts via the communication network 675 to one
or more mobile
device subscribers. In some implementations, the mobile device subscribers may
be mobile
phone subscribers. In other implementations, the mobile device subscribers may
be using
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
WiMax, the IEEE 802.16 Air Interface Standard. The mobile device subscribers
can enter a user
name and a password for authentication via the subscriber database interface
630.
[0077] In some implementations, the captioned data stream for a selected
captioned video and/or
radio program can be sent to the server interface 650 which can remove control
codes, if any,
and transmit the data to the server 690. The server can transmit TCP/IP data
of real-time
captioned data with no control codes to the communication network 675, which
can multicast the
captioned data to authenticated subscribers for receipt on one or more mobile
devices.
[0078] In some implementations, the subscribers may have a free subscription
to one or more
content providers. The content providers can interact with a caption service
provider to provide
caption and/or transcription services to subscribers. In other
implementations, the subscribers
may have a fee-based subscription to the contents providers. Alternatively,
the subscribers may
have a free subscription to some free content providers and a fee-based
subscription to fee-based
content providers. The subscribers may have free or fee-based subscriptions to
one or more
caption service providers. The content providers and/or the caption service
providers may
provide captioned and/or transcribed data free for a limited time and for a
fee at a later time.
Subscription information, accounts, payments, terms and related information on
the subscribers
may be maintained in the subscription gateway database 625 and/or the external
subscriber
database 685.
[0079) The subscription gateway 610 may be implemented in software and/or
hardware. One or
more components (e.g., communication network interface 660, subscriber
database interface 630,
server interface 650) of the subscription gateway 610 may be implemented in
software and/or
hardware. The subscriber preferences may be sent from a webpage over the
Internet to be
entered into the subscription gateway.
36
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
[0080] In analog television, a caption standard is defined by EIA-608
(Electronic Industry
Association), and in the digital domain HD-SDI, by an EIA-708 standard or a
variation of that
standard. In digital television, the digital television bit stream of
information can be
encapsulated in a transport protocol which includes video, user data bits, a
dtvcc caption channel.
In the dtvcc caption channel, caption service 1, formerly line 21 data in the
analog format, and
additional caption service data streams can be contained in the bit stream. In
some
implementations in digital transmission, the data rate for closed captioned
data can be 9600 bps,
enabling many additional features to be implemented, such as user control over
font size, color,
and other text characteristics.
[0081] FIG. 7 shows a block diagram of an example subscription-based
captioning system. In
particular, the example shown in FIG. 7 can be used with analog television
and/or digital
television (e.g., employing EIA-608 and/or EIA-708). In the Fig. 7, one or
more writers 110b,
110c, 1 lOc send multiple feeds of information to caption encoders 711, 712,
713, where the
output of the caption encoders 711, 712, 713 are sent to network interfaces
717, 718, 719. The
data sent at the output of the caption encoders 711, 712, 713 and/or the data
from the output of
the network interfaces 717, 718, 719 may be text data and a data wrapper. A
data wrapper can
include client identifiers (e.g., a station name, a call sign, an area code,
and/or a zip code, etc.), in
which the data wrapper is transmitted via the Interrlet 705 to a server
interface 730 and a
subscription server 725 in the subscription gateway 720.
[0082] In some implementations, the data from the writers 110b, 110c, 110d may
be caption data
that includes audio data that is translated into text data during the
occurrence of an audio event,
and the caption encoder 711, 712, 713 can have functionality to decode the
caption data to
produce ASCII text data. In these implementations, the caption encoders 711,
712, 713 and/or
37
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
the network interfaces 717, 718, 719 can have functionality to add a wrapper
with the ASCII text
data in a data stream to the Internet 705.
100831 The subscription gateway 720 in Fig. 7 includes the subscription server
725, the server
interface 730, and a server 735. The server 730 can have functionality to
transmit selected user
preferences and/or text feeds to/from mobile devices 182, 184. The
subscription server 725 can
store and/or categorize user preferences, such as geographic information, area
codes, zip codes,
station identifiers, event types, audio and/or video sources, client
identifiers, news categories,
sports news and information, financial news and information, as well as
authentication data. The
subscription server 725 authenticates mobile devices 182, 184, data for users
of mobile devices
182, 184, and/or requests and/or data from mobile devices 182, 184. The
subscription server 725
can interact with the server interface 730 to authorize data transmission with
one or more mobile
devices. In some implementations, data may be transmitted to/from the mobile
devices 182, 184
as a function of user preferences and/or requests from users of the mobile
devices 182, 184. The
authentication data may include passwords, user names, subscription statuses,
user account
information, payment information, subscription terms and conditions, and the
like. The
subscription server 725, server interface 730, and server 735 may be located
within one physical
unit or may be distributed servers. The servers 725, 730, 735 and/or the
subscription gateway
720 may be implemented in hardware and/or software in any combination. In some
implementations, the subscription gateway 720 may be the same subscription
gateway as FIG. 6
or similar to the subscription gateway of FIG. 6, with corresponding
components therein. The
event can be a broadcasted media event, which can include audio.
100841 The captioning system can simultaneously send caption information to
captioning
devices/targets 150 and mobile devices 180, 182. The captioning targets 150
receive transcribed
data, which includes text data entered by the writer II 0a and control code
data for the captioning
38
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
device 120. The transcription device 120 can interact with a communication
network 160, and
the communication network 160 can interact with the server interface 730 and
the Internet 705.
The communication network 160 can send or receive text and/or data to or from
the server
interface 730 and/or the Internet 705. The system can be configured for
transfer of the text data
over a server to the one or more mobile devices and transfer of caption data
to the captioning
device. The system can be configured for transfers of the text data and
caption data that occur
coincidentally with the transcribing of audio for the audio event. The system
can be configured
for concurrent transfer of the text data to the one or more mobile devices and
the caption data to
the captioning device. The system can transfer the text data to at least two
of the mobile devices
simultaneously.
[0085] In some implementations, because audio is being transcribed into text
data, the system
requires no video stream to be sent to the mobile device. In some of these
implementations,
because ASCII text data is sent to the mobile device, the system resources and
overhead required
to quickly transmit text data to the mobile device can be significantly lower
than when
transmitting video data, thus providing efficiency, low overhead, and fast
response times for the
overall system.
[0086] In some embodiments, there can be multiple writers, transcription
devices, encoders, and
caption targets in parallel that are arranged similar to writer 110a,
transcription device 120,
encoder 130, and caption target 150 in FIG. 7 or the other figures. These
parallel sources of
transcribed audio data can be transmitted to the communication network 160 and
the server
interface 730 in the subscription gateway 720.
[00871 In some implementations, a client device can encapsulate the text data,
which can
represent a text version of audio data that was simultaneously transcribed
with the occurrence of
an event. In some implementations using digital television (e.g., HD TV), the
ASCII text data
39
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
can be extracted from the encoded DTV transport bit stream as service field 1
data by using an
internal module to decode the ASCII text, and thus removing it from the
encoded TV signal.
[0088] In some implementations, the encoder may decode the EIA 608 NTSC
caption data,
which may be encapsulated in the DTV bit stream by using an internal decoder
module or an
external line 21 decoder box. The decoded text data may be output by the
encoder using a EIA
608 caption stream through an internal module in an encoder to output the text
to the client. In
other implementations, an unconverted 608 to 708 caption data stream may be
decoded by an
internal module in an encoder to output ASCII text without control codes and
to transmit via
client network.
[0089] In some implementations, a subscription system can allow users to
create and/or update
user preferences through a web portal (e.g., accessing the subscriber database
in the subscription
gateway) and/or directly from a mobile device to access the subscriber
database. In some
implementations, the mobile device may have Global Positioning System (GPS)
capability, and
the mobile device user can have the option to have the user preferences to be
automatically (e.g.,
without human intervention) and instantly updated to reflect user preference
information based
on where the mobile device is located. In some implementations, the mobile
device with the
GPS capability employing this subscription system can display all potential
audio/text feeds
coming from around the geographic area of the mobile device. The updates
and/or display of
audio/text feeds can occur automatically wherever the mobile device is located
(including any
changes in location of the mobile device).
[0090] Because the mobile device immediately receives ASCII text from
transcribed audio data
for a current/live event, no storage is required for the audio/text feeds. In
some instances, even
though some or all of the user preferences may be stored on the mobile
devices, no storage is
required at all for the audio/text feeds for operation of the subscription
system for any of the
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 0862 t-0005CA2
implementations shown herein. In some of these instances, no storage of the
audio/text feeds
(e.g., audio data, caption data, and/or ASCII text data streams) is required
anywhere in the
subscription system, including the server, communication network, subscription
gateway, and/or
the mobile devices.
[0091] In one example application, a traveler in Los Angeles might specify in
his user
preferences to have access to all news streams from areas codes for "213",
"818", or "760" if he
is travelling via airplane to New York area code "212". The mobile device user
can select the
option to have his user preferences to be automatically and instantly updated
to reflect user
preference information based on where the mobile device is located.
Accordingly, when his
plane lands in Chicago for a stop or to change planes, his user preferences
for his mobile device
can be automatically and immediately updated via GPS to have all Chicago area
codes (e.g., area
code "312") to enable live streams of text data (e.g., ASCII text from
translated audio data for a
current/live event) to be sent to his mobile device at that time in that
location.
[0092] Any of the implementations described herein can be configured for
live/current
transmission of text data from transcribed audio to multiple mobile devices
while an audio event
is occurring. For example, these implementations can be used by a live/current
media feed from
a television station to transmit live/current news, reports, announcements,
live programs, or live
sporting events to one or more mobile devices, while combining the
implementations with other
technologies to transmit pre-recorded programs, such as pre-recorded
television shows, movies,
commercials, recordings, and advertisements. The pre-recorded programs may
include audio
that was transcribed into text data at a time before an occurrence of
live/current transmission of
transcribed audio data for a live/current audio event. The pre-recorded
programming may have
audio and/or transcribed audio data that was stored on a storage unit (e.g.,
DVD, CD, tape, a
machine-readable medium) and/or storage device (e.g., memory, hard drive,
flash drive, a
41
CA 02675168 2009-08-10
Attorney Docket No.: 08621-0005CA2
machine reading data from the machine-readable medium). Any of the
implementations herein
can be used exclusively for live/current transmission of transcribed data for
a live/current audio
event to one or more mobile devices and/or one or more caption targets
simultaneously, in which
the transcribed text data may not be stored on any storage unit and/or device
before it is received
into the one or more mobile devices and/or the one or more caption targets.
[0093] Other implementations may be within the scope of the drawings and the
following
claims.
42