Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 1 -
SUMMARY
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
An electricity generating station which uses a method
that enables the force of gravity to be transformed into
electricity.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Electricity generators are known that use or consume
alternative sources of energy, that by means of special
processes generate electricity, the energy that they use in
many cases not being renewable or with scare availability,
very costly development or which are very pollutant, to
mention some of these; nuclear energy, wind power, the wave
power of the sea tides, natural gas, liquefied or bio gas,
coal, oil or diesel, hydro-power and solar power are the
energies that are currently being used to produce
electricity which have the disadvantage of being
conditioned or limited by the existence of these as
alternative energies and which means going to their place
to obtain them for production and their conversion into
electricity.
The known technique shows some but not all of the most
used energy forms to generate electricity whose use is only
possible if they are available at the moment of being used
as is well known electricity cannot be stored therefore it
usually occurs that having the installations necessary for
the production of electricity the energies consumed by the
electricity generators are not available for reasons of
nature, for example the power stations that consume water,
wind depend on the fact that climatic conditions do not
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 2 -
change leaving their reservoirs without water or the wind
farms without wind, in the other cases when the power
stations or electricity generators that use coal, gas, oil
or nuclear power as alternative energy they depend on, as
is well known, ever reducing existences, when solar energy
is used it has the disadvantage of only being able to
produce electricity during daylight and to use the power of
the tide certain technical requirements have to be
fulfilled which are not possible everywhere and finally
when these alternative energies are not near, the
transportation of the electricity has to be resolved across
large distances so as to be used in the consumption
centres.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
This present invention shows an electricity generating
station that uses the force of gravity as alternative
energy for the production of electricity, creating the
conditions and combined elements and ways that make the
obtaining of electricity possible with this method.
Basically this electricity generating station always
has the force of gravity available as alternative energy so
as to generate electricity, considering that the force of
gravity exists everywhere, is available at all times, is
not pollutant and costs nothing. Therefore this generating
station can be built anywhere that the production of
electricity is required, mainly in the consumption centres
doing away with or reducing the transport of electricity
over long distances.
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 3 -
In order to have a better understanding of the
invention it will be described on the basis of a preferred
modality, which is shown in the drawing, which is by way of
being an illustration, without it being by way of
limitation on the scope of the invention or the dimensions
or amount of the elements which are represented in it.
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
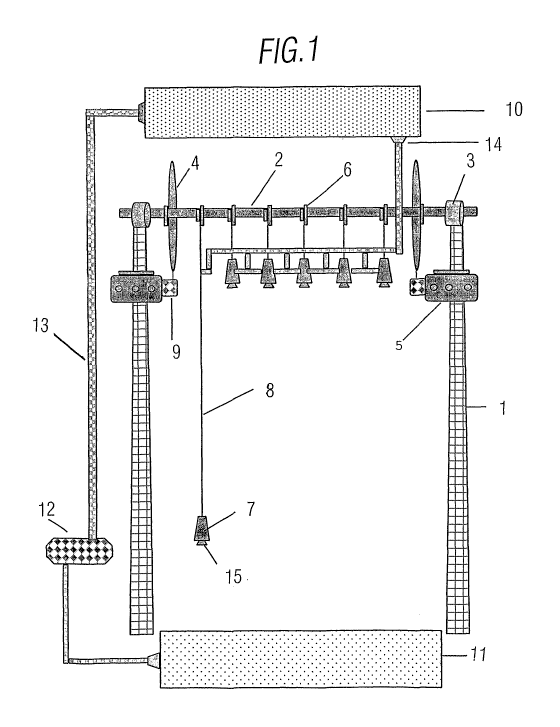
Figure 1 is a drawing of the invention, the
electricity generating station where the distribution of
its elements and its workings are shown.
A DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
As and how described in Figure 1 the elements are and
work in the following manner, two 30 metre high steel
towers (1) that support a transverse steel axle at the ends
and which has high mechanical resistance (2), this axle is
supported on the towers by means of two speed regulating
bearings (3) located on the upper part of the towers that
are used to support the axle and enable it to rotate freely
and control its speed. The towers, the axle and the
bearings are designed to support a constant load on them.
The axle bears two six-metre diameter wheels (4) at each
end, as shown in figure 1, these wheels are made from steel
that is similar to the bicycle wheels with a semi-solid
combined structure, at each end of these wheels there is a
revolution step-up gear (9) which in turn is connected to
the electricity generator (5) on the axle there are also
six direction reversers (6) one for each container with the
power of being able to reverse the rotation in an order of
the programme to rotate the opposite way of the axle
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 4 -
rotation driven by the force of gravity up and down, the
one thousand litre capacity plastic containers (7) which
are hung from these direction reversers by a thirty metre
long chain (8) that enables the container to move up and
down accordingly, the generating station additionally has a
water distribution system that consists of a ten thousand
litre steel tank (10) located at the top of the generating
station, another thirty thousand litre tank (11) located at
the bottom of the generating station and a network of PVC
conduits (13) distributed as shown in figure 1 between the
two tanks and the six one thousand litre plastic containers
and a pump (12) for raising the water to drive the water
between the different tanks and containers.
The method to generate electricity is commenced
considering that the thirty thousand and ten thousand
litres tanks have water, and start with the filling of the
one thousand litre water containers. It is carried out by
opening the valve (14) located in the upper ten thousand
litre tank and by means of the force of gravity and the PVC
conduits installed for this operation. The water goes from
the ten thousand litre tank to the six one thousand litre
plastic tanks filling these occurs when, by means of a
programme created for this method, the order is given to
the first container to move downwards brought down by the
force of gravity. This starts its downward run and by means
of the chain pulls the reverser and this makes the axle
rotate which in rotation makes the wheels rotate which
transfer the constant rotation to the revolution step-up
gear and this to the electricity generator which starts to
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 5 -
produce electricity. On the downward movement the first
container has done ninety per cent of its run the programme
determines that the second container, just like the first
container pulls the axle by means of the chain fitted for
this container so as to keep up the constant rotation of
the axle. And when the first container finishes its run the
second container maintains the rotation on the axle without
a break enabling the system to continue generating
electricity constantly. Once the first container finishes
its downward run and the second container maintains the
rotation of the axle, the programme determines the emptying
of the water from the first one thousand litre container,
an operation that is carried out by opening the back sluice
of the container (15) that is specially designed for the
automatic and rapid draining of the water. The water drawn
off goes to the thirty thousand litre tank located in the
bottom of the power station, transferring the water from
the first container to the thirty thousand litre tank the
programme gives the order to close the back sluice of the
one thousand litre tank and it instructs the reverser gear
of the first container so that it reverses the rotation and
starts to pull the container upwards pushing it by the
force that the second container is exercising on the axle
on its downward movement. At this moment we have the first
container without the one thousand litres of water going
upwards and the second container loaded with water going
downwards when this reaches ninety per cent of its run, the
programme activates the descent of the third container so
as to keep the rotation on the axle constant which starts
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 6 -
its downward run whilst the first container reaches the end
of its upward run.
The programme commences the filling of the one
thousand litres of water into the first container, an
operation that consists of opening the filling valve and
transferring the water from the upper ten thousand litre
tank to the first one thousand litre container, whilst the
second container has reached the end of its downward run
and the removal of the water starts in the same way as the
first container whilst the third container continues going
down and maintaining the rotation of the axle the second
container without water now carries out the upward process
started by the order received in the second reverser which
has reversed its rotation so as to lift the container
whilst the first container has finished the filling of the
thousand litres of water and the third container on then
reaching ninety per cent of its downward movement, the
system activates the descent of the fourth container that
starts its downward movement so as to maintain the constant
rotation on the axle while the second container reaches its
end of the upward run and the filling of the one thousand
litres of water starts in the same way as the first
container. The third container has reached the end of the
downward run and the emptying of the water from same starts
in the same way as the first container whilst the downward
run of the fourth container continues maintaining the
continuous rotation on the axle, the third container is now
carrying out the upward process started by the order
received from the third reverser gear which has inverted
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 7 -
its rotation so as to raise the container without water
while the second container has finished the filling of the
one thousand litres of water and the fourth container
having reached ninety per cent of its downward run then the
system activates the lowering of the fifth container so as
to maintain the constant rotation on the axle which starts
its run whilst the third container reaches the end of its
upward run and the filling of the one thousand litres of
water starts in the same way as the other containers. The
fourth container has reached the end of its downward run
and starts the emptying of water in just the same way as
with the other containers. Whilst the fifth container
continues the downward run maintaining the rotation on the
axle, the fourth container is now carrying out the upward
process started by the order received in the fourth
reverser which has reversed its rotation to raise the
container without water. While the third container has
finished the filling of the one thousand litres of water
and when the fifth container reaches ninety per cent of its
downward run the descent of the sixth container is
activated by the system so as to maintain the constant
rotation of the axle, which starts its downward run whilst
the fourth container reaches its upward run and starts the
filling of the one thousand litres of water in the same way
as the previous containers. The fifth container has reached
the end of its downward run and starts the emptying of the
water in the same way as the previous containers whilst the
sixth container continues its downward run and maintains
the rotation on the axle. The fifth container without water
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 8 -
is now carrying out the upward process started by the order
received from the fifth reverser which has reversed its
rotation so as to raise the container. Meanwhile the fourth
container has finished the filling of the one thousand
litres of water and the sixth container has reached ninety
per cent of its run then the system activates the descent
of the first container so as to maintain constant the
rotation on the axle and once again starting off a new
cycle that maintains the axle rotation and as a result
there is a constant generation of electricity.
when the generation of electricity is started the
electric pump (12) for raising the water is started, this
is located between the two tanks and its job is to raise
the water from the lower thirty thousand litre tank to the
upper ten thousand litre tank so as to maintain the
availability of water in the upper tank and the containers.
The power station uses a specially created programme
for the coordination of all of the movements so as to make
the entirety of the elements interact in a synchronised
manner.
TECHNICAL CONCEPTS OF THE INVENTION
The power station is able to use gravity which
attracts the container as potential energy so that it moves
downwards in this way the attraction downwards converts the
vertical movement into kinetic energy which is used to make
the axle to rotate and this latter in turn drives the
generator to produce electricity.
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 9 -
Relationship of the conversion of the revolutions
produced per minute by the method so as to generate
electricity.
1- In one minute the container will be moved 5 metres.
2- The diameter of the wheel is 6 metres
3- The diameter of the reverser is 20 centimetres.
4- The diameter of the step-up gears is 20 centimetres.
The length around the perimeter of the 6 metre wheel
is 18.84 metres;
The length around the perimeter of the 20 centimetre
direction reverser is 0.62 metres;
The length around of the 20 centimetre the step-up
gear is 0.62 metres;
Conclusions
1. We have to make the container run 5 metres in one
minute making the rotation of the axle along with this run
by means of the direction reverser whose perimeter is 0.62
metres thus the following gives 5 metres divided by 0.62
metres and the result of the rotation through which the
axle will rotate is 8.06 times by 5 metres of the container
run in one minute.
2. The axle on rotating 8.06 times the wheel that
rotates at the same rate as this but its diameter is 6
metres and its perimeter which has a length of 18.84 metres
on making contact it results in for each rotation of the
reverser it makes an increase in the revolutions that are
obtained from the multiplication of 8.06 by 18.84 this
meaning that the increase in revolutions will be 151.85
rotations.
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 10 -
3. From the above result we take the 151.85
rotations to the step-up gear whose axle is 20 centimetres
therefore the perimeter is 0.62 metres so, to complete a
rotation needs 0.62 metres and it is receiving 151.85
metres. Because of this its yield will be the division of
151.85 metres divided by 0.62 and the result is 244.91
rotations of the axle.
On applying the 244.91 rotations to the step-up gear
that is directly connected to the generator and, as its
relationship is 1 to 55, therefore the total of revolutions
from the method will be the multiplication of 244.91 by 55
and that is equal to 13,470 revolutions per minute.
The formula for the calculation of the power generated
by of the invention:
Circular trajectory, in case of motors the work is
expressed as follows:
POWER = Force x 2 x II x r, where II is a constant
(3.1416) and r is the radius of rotation (0.10)
Force = 1,000
Constant = 2
Pi = 3.1416
R = 0.10
POWER = 1,000 kilos x 2 x 3.1416 x 0.10 = 628.32 KW
Calculation of the power generated by the invention
T= D x P so P= T x N x Pi
N x Pi D
On considering this formula for the calculation of the
power we have:
T = Time 33
N = Force 1000
CA 02692619 2010-01-05
- 11 -
Pi = Constant 3.1416
D = Distance or run 165
P = T x N x Pi = 33 x 1000 x 3.1416 = 628.32 KW OF POWER
D 165