Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
-
H 2110 CA
A Connecting Device for Electrically Connecting a Three-Phase Motor
The invention relates to a connecting device for electrically connecting a
three-phase motor.
Three-phase motors having at least three windings and being adapted to be
connected to a three-phase network which comprises three electrical phase
lines
having phase-shifted alternating voltages are known. Such three-phase motors
are used in a star connection or in a delta connection depending on the
application. Depending on the selected connection, the ends of the windings of
the three-phase motor have to be connected in different manners known per se
to the phase lines of the three-phase network. The way of connecting the
windings to the phase lines also determines the direction of rotation of the
motor.
In the prior art, the wiring is realized manually in situ in a so-called motor
connection box into which the motor winding terminals and the phase lines are
guided. This wiring is very time-consuming and in case of a change of the
connection or of the direction of rotation of the motor, it requires a re-
plugging of
the corresponding terminals, which leads frequently to errors. Tests in which
plug
connectors are used for the coupling are also known. Here, the motor
connection
box is partially dispensed with. A change of the connection and of the
direction of
rotation however always requires a rewiring.
Document EP 2 086 066 discloses as a post-published document a
connecting device for electrically connecting a multiphase electric motor to a
power source, which is made up of a connection box and a substantially
cylindrical adapter.
Document DE 20 2006 016 472 U1 discloses a connector plug unit for three-
phase motor units having a bridge circuit module within the connector housing.
A
bridge circuit is realized in the bridge circuit module, which is required for
driving
the three-phase motor unit by means of a delta connection.
Documents US 3,525,971, FR 2617651 and DE 30 43 538 Al each disclose
plug connectors which can cause a reversal of the direction of rotation of a
motor
CA 02697839 2013-01-14
=
23292-158
2
connected to a three-phase network by a rotated mounting or by interposing an
adapter.
In some embodiments of the invention the motor connection box also known as
motor
terminal box, is unnecessary. Some embodiments of the invention permit the
electrical
connection on the cable side using a connecting device by means of which both
the direction
of rotation of the motor and the type of the connection used can be selected
in situ without a
manual re-plugging/rewiring of the motor winding ends being necessary in case
of a change
of the connection or of the direction of rotation of the motor.
According to one embodiment of the invention, there is provided a connecting
device for
electrically connecting a three-phase motor having at least three windings to
a three-phase
network, which comprises a mains connection unit for connecting the phase
lines of the
three-phase network, and a motor connection unit for connecting the at least
six winding
ends of the three-phase motor. An exchangeable coupling module is arranged
between the
mains connection unit and the motor connection unit and contains contacts and
wiring
elements electrically connecting the six winding ends in a predefined manner
to the three
phase lines of the three-phase network. A motor connection box in which re-
plugging works
are to be performed in order to change the connection is therefore no longer
necessary. The
desired connecting is realized in situ by means of the exchangeable coupling
module without
conductors having to be contacted with high expenditure.
In another embodiment of the invention, there is provided a first coupling
module which
connects the three windings of the three-phase motor in a delta connection,
and a second
coupling module which connects the three windings in a star connection. In
order to switch
from a delta connection to a star connection, it is therefore not necessary to
detach the
terminals of the winding ends on the motor side of the motor connection unit,
and the phase
terminals on the mains connection unit also remain unaffected. It is merely
necessary to
exchange the coupling module.
The coupling module, or each of the coupling modules, is adapted to be mounted
so as to be
rotated through 180 along a coupling direction, i.e. along an axis leading
from the mains
connection unit to the motor connection unit. Due to this rotation of the
coupling module, the
direction of rotation of the motor is
CA 02697839 2013-01-14
23292-158
3
reversed. The terminals on the mains connection unit and on the motor
connection unit thus remain unaffected also in case of a change of the
direction
of rotation.
Preferably, the mains connection unit has one terminal for each of the three
phase lines, the terminal branching in two parallel phase contacts in the
direction
to the coupling module, the coupling module or each of the coupling modules
each electrically contacting only one of the parallel phase contacts.
In a preferred embodiment, the motor connection unit has on the side facing
the coupling module winding contacts to the six winding ends which are
arranged
in two groups of three winding contacts each, which are point symmetric to
each
other. This can involve an arrangement on two parallel straight lines, or the
winding ends can also be arranged in a respective semicircle, the two
semicircles
being arranged so as to form a circle, for example.
In the first group, the winding beginning of a first winding, the winding end
of a
third winding, and the winding beginning of the third winding are arranged
side by
side, and in the second group, the winding end of the first winding is point
symmetric to the winding beginning of the first winding, the winding beginning
of
the second winding is point symmetric to the winding end of the third winding,
and the winding end of the second winding is point symmetric to the winding
beginning of the third winding. It is therefore ensured that in case of a
rotation of
the coupling module through 180 , the direction of rotation of the motor is
changed since other winding beginnings or winding ends thus contact the phase
lines.
In yet another embodiment the coupling module comprises an
exchangeable bridge module which contains the wiring elements. A first bridge
module is provided which contains wiring elements such that the three windings
- of the motor are connected in a delta connection. A second bridge module is
further provided which contains wiring elements such that the three motor
windings are connected in a star connection. In this embodiment, only part of
the
coupling module has to be exchanged in order to change the connection. It is
however of course also possible to exchange the entire coupling module which
is
provided with the first bridge module, for example, for a different coupling
module
which is provided with the second bridge module.
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 4 -
The mains connection unit can be mounted to the coupling module in two
positions that are rotated through 1800 with respect to each other in order to
connect the phase lines of the three-phase network. Due to the rotation of the
mains connection unit, a change of the direction of rotation of the motor can
be
produced.
The connecting device is configured in a parallelepipedal manner for both
embodiments.
The phase lines of the three-phase network are preferably firmly connected to
the mains connection unit. This is preferably realized by means of clamping
spring connections.
The connecting device is furthermore configured such that the six winding
ends on the motor connection unit are adapted to be firmly connected,
preferably
as a crimp connection.
The invention is described below with reference to two preferred
embodiments illustrated in the enclosed drawings in which:
Figure 1 shows in a schematized three-dimensional representation a motor
connection unit, a coupling module and a mains connection unit according to a
first embodiment of the invention;
Figure 2 shows in a schematized three-dimensional representation a
connecting device in accordance with Figure 1 from a different viewing
direction;
Figure 3 shows a schematized three-dimensional representation of a coupling
module and of a mains connection unit;
Figure 4a shows an electrical circuit diagram for connecting the three motor
windings to the three phase lines in a first direction of rotation in a delta
connection;
Figure 4b shows a schematized representation for realizing the connection
shown in Figure 4a using the connecting device according to Figures 1 to 3;
Figure 5a shows an electrical circuit diagram for connecting the motor
windings to the phase lines for a second direction of rotation in a delta
connection;
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 5 -
Figure 5b shows a schematized representation for realizing the connection
shown in Figure 5a using the connecting device according to Figures 1 to 3;
Figure 6a shows an electrical circuit diagram for connecting the motor
windings to the phase lines in a first direction of rotation in a star
connection;
Figure 6b shows a schematized representation for realizing the connection
shown in Figure 6a using the connecting device according to Figures 1 to 3;
Figure 7a shows an electrical circuit diagram for connecting the motor
windings to the phase lines for a second direction of rotation in a star
connection;
Figure 7b shows a schematized representation for realizing the connection
shown in Figure 7a using the connecting device according to Figures 1 to 3;
Figure 8 shows a schematized three-dimensional representation of a second
example embodiment having two exchangeable bridge modules and without the
motor connection unit;
Figure 9 shows the connecting device of Figure 8 in a mounted state without
the motor connection unit;
Figure 10 shows a schematized section through the connecting device
according to Figure 9 with the motor connection unit mounted.
First Example Embodiment
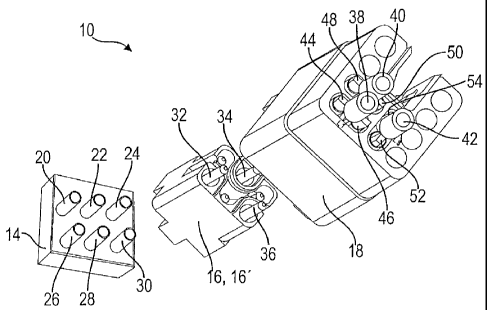
Figure 1 shows a connecting device 10 of a first example embodiment in a
schematized form. The connecting device 10 comprises a motor connection unit
14, an exchangeable coupling module 16, 16' and a mains connection unit 18
which are connected to each other by means of plug-in connections.
On its side facing the coupling module 16, 16', the motor connection unit 14
has six winding contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30. The other side of the
motor
connection unit 14 that is not visible is provided with terminals which are
electrically connected to the winding contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30 and
to
which the winding ends of a three-phase motor can be coupled, preferably via a
crimp connection. The motor windings of a three-phase motor are usually
designated by U, V and W, each motor winding having two ends. The six winding
contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30 are therefore connected to the motor
winding
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 6 -
ends U1, U2, V1, V2, W1 and W2. The six winding contacts are arranged in two
groups each having three contacts.
To explain the connecting device according to the invention, reference is
made by way of example to a three-phase motor having three windings. The
connecting device can of course also be used in multipolar machines in which
two windings respectively belong to one phase.
On its side facing the motor connection unit 14, the coupling module 16, 16'
has six winding connecting contacts which are suitable for electrically
contacting
the winding contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30. Here, the winding connecting
contacts on the coupling module and the winding contacts on the motor
connection unit are arranged in two groups such that an electrical contact is
permitted in two positions rotated through 1800 with respect to each other,
i.e. the
arrangement of the contacts must be point symmetric to an axis of rotation
extending from the side facing the motor connection unit 14 to the side of the
coupling module 16, 16' facing the mains connection unit 18 and about which
the
coupling module can be rotated. The winding connecting contacts are not
visible
in Figure 1. On the side facing the mains connection unit 18, the coupling
module
has three phase connecting contacts 32, 34, 36. The phase connecting contacts
32, 34, 36 serve to contact the phase lines L1, L2 and L3 of a three-phase
network via the mains connection unit 18. Within the coupling module 16, 16',
the
phase connecting contacts are electrically connected to the winding connecting
contacts arranged opposite thereto. Here, the two outer winding connecting
contacts of one of the groups of winding connecting contacts are connected to
the phase connecting contacts 32 and 36, and the centre winding connecting
contact of the other group is connected to the phase connecting contact 34.
The
other winding connecting contacts end as blind contacts to the outside on the
side facing the mains connection unit 18. The outer contacts of the coupling
modules 16 and 16' do not differ from each other. The coupling modules only
differ from each other in their inner wiring elements which realize a delta or
a star
connection. To easily distinguish the various coupling modules from each
other,
they can be configured in different colors so that a simple optical
distinction is
possible.
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 7 -
On its side facing away from the coupling module 16, 16', the mains
connection unit 18 has three terminals 38, 40, 42 for connecting the phase
lines
L1, L2, L3 of the three-phase network. The terminals 38, 40, 42 are preferably
configured as clamping spring connection terminals to which the phase lines
can
be coupled in a rapid and reliable manner.
As shown in Figure 1, the terminals 38, 40, 42 each branch in two parallel
terminals which are guided to the side of the mains connection unit 18 facing
the
coupling module 16, 16' and end there as phase contacts 44, 46, 48, 50, 52 and
54. In the present example, terminal 38 is provided for a connection of phase
line
L1 and branches in phase contacts 44 and 46. Terminal 40 is provided for a
connection of phase line L2 and branches in phase contacts 48 and 50. Terminal
42 is provided for a connection of phase line L3 and branches in phase
contacts
52 and 54. On its side facing the coupling module 16, 16', the mains
connection
unit 18 thus has six phase contacts 44, 46, 48, 50, 52 and 54, two parallel
terminals being respectively connected to each other within the mains
connection
unit 18 and contacting the same phase of the three-phase network.
The phase connecting contacts 32, 34, 36 of the coupling module 16, 16' and
the phase contacts 44, 46, 48, 50, 52 and 54 of the mains connection unit 18
are
configured such that one of the phase contacts that are electrically connected
in
parallel is respectively contacted by the phase connecting contacts 32, 34, 36
of
the coupling module 16, 16', and the respective other phase contact of the
phase
contacts that are electrically connected in parallel is contacted upon
rotation of
the coupling module through 180 about a longitudinal axis.
Figure 2 shows the connecting device 10 from a slightly different perspective.
Here, the motor connection unit 14 which is represented in a strongly
schematized manner in Figure 1, is shown in more detail. Three of the winding
contacts 20, 22, 24 can be seen in Figure 2, which are adapted to be
electrically
connected to the winding ends of the three-phase motor in the motor connection
unit 14 on the side facing the coupling module. The coupling module 16, 16' is
inserted into the motor connection unit 14. A coding piece 56 can be arranged
in
the motor connection unit 14 next to the coupling module 16, 16' to thus avoid
an
undesired rotation of the coupling module during insertion. As will be
explained
below, the coupling module 16, 16' can be mounted in two positions rotated
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 8 -
through 1800 with respect to each other to thus reverse the direction of
rotation of
the motor.
The mains connection unit 18 comprises the terminals 38, 40, 42 like in
Figure 1. On the side facing away from the coupling module, the mains
connection unit 18 further has additional schematically outlined terminals.
They
serve, for example, to apply ground, the protective earth, to realize a motor
braking function, and/or the neutral conductor, and are also further guided to
the
motor connection side. They are however not relevant to the function of the
connecting device according to the invention and are therefore not discussed
in
further detail.
Figure 3 shows the mains connection unit 18 as viewed from the coupling
module side, with the six phase contacts 44, 46, 48, 50, 52 and 54. A coding
piece 56 is inserted. It is marked with an "R" for right-hand rotation, and an
arrow
additionally indicates the direction of rotation of the motor. The coupling
module
16, 16' can only be inserted in one fitting position when the coding piece 56
is
inserted, as a nose 58 on the coding piece 56 cooperates with a recess 60 on
the
coupling module 16, 16'. It is of course also possible to use other coding
possibilities known to a person skilled in the art.
On the coupling module 16, 16', the winding connecting contacts are visible
which can electrically contact the winding contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30
of
the motor connection unit 14.
Depending on the application, three-phase motors are operated in a so-called
delta connection or a star connection. Invisible wiring elements in the
coupling
module 16, 16' ensure the desired connection between the motor winding ends
and the phase lines.
Figure 4a shows the electrical circuit diagram for a delta connection. The
ends of the three windings U, V and W of the three-phase motor are connected
in
a triangular shape, that means that the winding end U2 of the motor winding U
is
connected to the winding beginning W1 of the motor winding W, the winding end
W2 of the motor winding W is connected to the winding beginning V1 of the
motor
winding V, and the winding end V2 of the motor winding V is connected to the
winding beginning U1 of the motor winding U. The phase lines are connected to
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 9 -
the respective winding beginnings, which means that the phase line L1 is
connected to the winding beginning U1, the phase line L2 is connected to the
winding beginning V1, and the phase line L3 is connected to the winding
beginning W1.
Figure 4b shows in a schematic top view the phase contacts 44, 46, 48, 50,
52 and 54 of the mains connection unit 18 as circles, dotted lines 64
respectively
enclosing the two phase contacts which are electrically arranged in parallel
and
contact the same phase line. The winding contacts 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 and 30 of
the motor connection unit 14 are arranged so as to coincide with the phase
contacts of the mains connection unit 18. For a better comprehension, the
phase
lines L1, L2 und L3 associated with the phase contacts are directly inserted
in
Figure 4b just as the winding ends U1, U2, V1, V2, W1 und W2 which are
coupled to the winding contacts. The winding contacts 20 to 30 of the motor
connection unit 14 are positioned in two groups that are point symmetric to
each
other, which means that three winding contacts are respectively arranged side
by
side, and the other three winding contacts are also arranged side by side on a
straight line parallel thereto. According to Figure 4b, in the first group,
the winding
beginning U1 of the motor winding U, the winding end W2 of the motor winding
W, and the winding beginning of the motor winding W1 are arranged side by
side.
The winding end V2 of the winding V, next thereto the winding beginning V1 of
the winding V and the winding end U2 of the winding U are arranged thereabove
in a point symmetric arrangement.
In the schematic representation, a coincident representation of the phase
contacts and of the winding contacts has been chosen. In the practical
realization, the contacts need not be coincident since the electrical contact
is
realized via the coupling module arranged therebetween.
The three phase connecting contacts 32, 34, 36 of the coupling module 16
are drawn as rectangles. The fitting position shown corresponds to the fitting
position shown in Figure 1. The coupling module 16 is a coupling module for a
coupling in a delta connection. Wiring elements 62 each connecting opposite
contacts to each other are therefore contained in the coupling module.
The phase connecting contact 32 of the coupling module 16 establishes an
electrical contact to the phase contact 44 of the mains connection unit 18,
which
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 10 -
for its part is connected to the phase line L1 of the three-phase network. The
phase connecting contact 32 is electrically connected to the opposite winding
connecting contact within the coupling module 16, which is connected to the
winding beginning U1 via the motor connection unit. U1 is thus connected to
the
phase L1. U1 is further connected to V2 via a wiring element 62.
The phase connecting contact 34 of the coupling module 16 establishes an
electrical contact to the phase contact 50 of the mains connection unit 18,
which
for its part is connected to the phase line L2 of the three-phase network. The
phase connecting contact 34 is electrically connected to the opposite winding
connecting contact within the coupling module 16, which is connected to the
winding beginning V1 via the motor connection unit. V1 is thus connected to
the
phase L2. V1 is further connected to W2 via a wiring element 62.
The phase connecting contact 36 of the coupling module 16 establishes an
electrical contact to the phase contact 52 of the mains connection unit 18,
which
for its part is connected to the phase line L3 of the three-phase network. The
phase connecting contact 36 is electrically connected to the opposite winding
connecting contact within the coupling module 16, which is connected to the
winding beginning W1 via the motor connection unit. W1 is thus connected to
the
phase L3. W1 is further connected to U2 via a wiring element 62.
The contacting according to Figure 4b thus results in a connection of the
motor windings to each other and to the phases of the three-phase network
according to the circuit diagram of Figure 4a.
Figure 5a also shows the connection of the motor windings U, V and W for a
delta connection, but with a different direction of rotation. That means that
the
phase lines L1 und L2 are exchanged with respect to the representation in
Figure
4a.
Figure 5b shows the corresponding association of the contacts of the motor
connection unit 14, of the mains connection unit 18 and of the coupling module
16. As a delta connection is again involved, the same coupling module 16 as in
the connection according to Figure 4a is used. This means that the wiring
elements 62 each connect opposite contacts. In comparison with Figure 4b, the
coupling module 16 has been mounted so as to be rotated through 180 about an
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 11 -
axis extending between the motor connection unit 14 and the mains connection
18 along the coupling direction. Therefore, the phase connecting contact 36 of
the coupling module 16 now contacts the phase line L2 via the phase contact
48,
the phase connecting contact 34 of the coupling module 16 contacts the phase
contact 46 connected to the phase line L1, and the phase connecting contact 32
of the coupling module contacts the phase contact 54 of the mains connection
unit 18 which is connected to the phase line L3. The position of the winding
contacts is unchanged, i.e. the phase L2 is connected to V2 and to U1 via a
wiring element 62, the phase L1 is connected to W2 and to V1 via a wiring
element 62, and the phase L3 is connected to U2 and to W1 via a wiring element
62. The direction of rotation of the motor is therefore reversed as desired.
The
fitting position of the coupling module desired for this direction of rotation
can for
its part be fixed by means of a corresponding coding piece 56.
Figure 6a shows the electrical circuit diagram for a star connection of the
motor windings U, V and W. For this purpose, the motor winding ends U2, V2 and
W2 are electrically connected, whereas the phase line L1 is connected to the
winding beginning U1, the phase line L2 is connected to the winding beginning
V1, and the phase line L3 is connected to the winding beginning W1.
Figure 6b correspondingly shows the configuration of the connecting contacts
on the motor connection unit 14, the coupling module 16' and the mains
connection unit 18. The coupling module 16 has been replaced with a coupling
module 16' for a star connection, which externally corresponds to the coupling
module 16. The coupling module 16' contains wiring elements 66 which connect
the winding connecting contacts to each other, which are not connected to
phase
connecting contacts 32, 34, 36.
The arrangement of the winding ends U1, U2, V1, V2, W1 und W2 on the
motor connection unit 14, and of the phase lines on the mains connection unit
18
remains unchanged with respect to Figures 4b and 5b. In the fitting position
illustrated in Figure 6b, a rectangularly represented phase connecting contact
32'
of the coupling module 16 contacts the phase contact 44 of the mains
connection
unit 18 and thus the phase line L1 and the winding beginning U1 via the motor
connection unit, a phase connecting contact 34' of the coupling module 16'
contacts the phase contact 50 of the mains connection unit 18 and thus the
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
-12-
phase line L2 and the winding beginning V1, and a phase connecting contact 36'
of the coupling module 16' contacts the phase contact 52 of the mains
connection
unit 18 and thus the phase line L3 and the winding beginning W1. The winding
ends V2, W2 and U2 are not connected to a phase line, they are however
connected to each other via wiring elements 66. The electrical connection
represented in Figure 6a is therefore obtained.
Figure 7a shows the electrical circuit diagram for connecting the motor
windings U, V and W for a star connection with a reversed direction of
rotation
with respect to the connection of Figure 6a. The winding beginnings U1, V1 and
VV1 are electrically connected to each other, whereas the winding end U2 is
connected to the phase line L3, the winding end V2 to the phase line L2, and
the
winding end W2 to the phase line L1.
Figure 7b shows the contact with the coupling module 16' which has been
rotated through 1800 along an axis in the coupling direction. Therefore, the
wiring
elements 66 now electrically connect the winding beginnings U1, V1 and W1 to
each other. In the fitting position illustrated in Figure 7b, the
rectangularly
represented phase connecting contact 32' of the coupling module 16' contacts
the phase contact 54 of the mains connection unit 18 and thus the phase line
L3
and the winding end U2 via the motor connection unit, the phase connecting
contact 34' of the coupling module 16' contacts the phase contact 46 of the
mains
connection unit 18 and thus the phase line L1 and the winding end W2, and the
phase connecting contact 36' of the coupling module 16' contacts the phase
contact 48 of the mains connection unit 18 and thus the phase line L2 and the
" winding end V2.
In the present case, the orientation of the coupling module can also be fixed
by means of a coding piece 56.
It is therefore possible in a simple manner to realize a connection of the
three-
phase motor to a three-phase network without having to re-plug the connecting
lines. The distinction between the delta connection and the star connection is
realized by the selection of the appropriate coupling module 16, 16', and the
reversal of the direction of rotation is realized by the fitting position of
the coupling
module. To rotate the coupling module, the motor connection lines and the
mains
connection lines need not be detached, and it is merely necessary to extend
the
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 13 -
connecting device and to rotate the coupling module, after which the
connecting
device can be reassembled. The entire connecting device can be realized within
the cable in the form of a plug-in connection, so that a change of the
connection
and/or of the direction of rotation in situ is possible without using a tool.
Second Example Embodiment
Figure 8 shows in a schematized three-dimensional representation a second
embodiment of the connecting device according to the invention having a mains
connection unit 68, a coupling module 70 and two bridge modules 72, 72 and a
motor connection unit (not shown).
On a side facing the coupling module, the mains connection unit 68 has three
phase contacts 74, 76 and 78. Within the mains connection unit 68, the phase
contacts 74, 76 and 78 are electrically connected to three terminals (not
shown)
on the side facing away from the coupling module, to which the three phase
lines
L1, L2 and L3 of a three-phase network can be coupled. The terminal of the
phase lines L1, L2 and L3 can preferably be realized via clamping spring
connections. The mains connection unit can be fitted into the coupling module
70
in two fitting positions rotated through 180 with respect to each other in
the
direction of insertion.
The coupling module 70 has an exchangeable bridge module, Figure 8
showing a first bridge module 72 and a second bridge module 72' which can be
used alternatively. Externally, the two bridge modules have the same
structure.
They differ from each other in wiring elements that are not illustrated such
that a
delta connection is obtained by means of the bridge module 72, whereas by
means of the second bridge module 72', due to the wiring elements contained
therein, the three motor windings can be connected to each other and to the
phase lines so as to obtain a star connection.
On their side facing the coupling module 70, the bridge modules 72, 72' each
have three phase connecting contacts via which they directly electrically
contact
the three phase contacts 74, 76 and 78 of the mains connection unit 68. On the
side facing away from the coupling module 70, the bridge modules 72, 72' each
have 6 winding connecting contacts 80 to 90 or 92 to 102, respectively, which
are
suitable for electrically contacting winding contacts on the motor connection
unit
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 14 -
that is not illustrated. The winding connecting contacts 80, 82 and 84, or 92,
94
and 96, respectively, which are arranged on the top in Figure 8, are each
electrically connected to the phase connecting contacts opposite thereto,
whereas the winding connecting contacts 86, 88 and 90 or 98, 100 and 102,
respectively, which are arranged at the bottom, are connected to the winding
connecting contacts on the top in different manners depending on the bridge
module. In practice, the terminals 92, 94 and 96 can however be dispensed
with.
In the case of the bridge module 72, for example, the winding beginning U1
can be connected to the winding connecting contact 80, the winding beginning
V1
can be connected to the winding connecting contact 82, and the winding
beginning W1 can be connected to the winding connecting contact 84 via the
motor connection unit, whereas the winding connecting contact 86 contacts the
winding end W2, the winding connecting contact 88 contacts the winding end U2,
and the winding connecting contact 90 contacts the winding end V2 via the
motor
connection unit.
For a delta connection, the bridge module 72 then has a plurality of wiring
elements which connect the winding connecting contacts 80 and 86, the winding
connecting contacts 82 and 88, and the winding connecting contacts 84 and 90,
respectively, to each other to thus obtain a contact U1-W2, V1-U2 and W1-V2.
Correspondingly, for a star connection, the bridge module 72' has the winding
connecting contacts 92, 94 and 96 in an upper row, which as in the bridge
module 72 are associated with the winding beginnings U1, V1 und W1, and the
winding connecting contacts 98, 100 and 102 in a lower row which are
correspondingly associated with the terminals W2, U2 and V2. The bridge
module 72' contains wiring elements which connect the lower three winding
connecting contacts 98, 100 and 102, i.e. W2-U2-V2 to each other so that a
star
connection is obtained.
The connection of the motor winding ends on the motor connection unit thus
always remains the same, a crimp connection being preferably provided for the
connection. In this embodiment, it is also possible to switch between the
delta
connection and the star connection in a simple manner by exchanging the bridge
module without a re-plugging of the terminals being necessary.
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 15 -
For a change of the direction of rotation of the motor irrespective of the
bridge
module used, it is provided in the second embodiment that the mains connection
unit 68 can be fitted in two positions rotated through 1800 with respect to
each
other such that the reversal of the direction of rotation of the connected
three-
phase motor is thereby obtained. By way of example, the phase contact 74 is
connected to the phase line L1 via the mains connection unit 68, the phase
contact 76 is connected to the phase line L2, and the phase contact 78 is
connected to the phase line L3. In the fitted position shown in Figure 8,
using the
bridge module 72, the phase line L1 is then connected to the winding
connecting
contact 80 and thus to the winding beginning U1, the phase line L2 is
connected
to the winding connecting contact 82 and thus to the winding beginning V1, and
the phase line L3 is connected to the winding connecting contact 84 and thus
to
the winding beginning W1. Upon rotation of the mains connection unit through
180 , the phase line L1 contacts the winding beginning W1, and the phase line
L3 contacts the winding beginning U1, that means that the direction of
rotation of
the motor is reversed.
The same applies to the use of the bridge module 72'.
Figure 9 shows the connecting device according to Figure 8 in the assembled
state with a mounted bridge module 72'. The second embodiment also provides
more than the six winding terminals on the motor side, the protective earth,
the
neutral conductor and a further ground line of the three-phase network being
for
example adapted to be connected to the motor via the terminals 104, 106 and
108. These lines are not relevant to the present invention and are thus not
discussed in more detail.
Figure 10 schematically shows in a three-dimensional representation a
connecting device as represented in Figures 8 and 9, which is partially cut
open
and has a separated motor connection unit 110. Figure 10 shows the coupling
module 70 with a mains connection unit 68 inserted and a bridge module 72 or
72'. The motor connection unit 110 is connected to the coupling module and
encloses the bridge module 72, 72'. On the right-hand side of Figure 10, the
motor connection lines can thus be firmly connected to the mains connection
unit,
whereas on the left-hand side, the phase line of the three-phase network can
be
firmly connected to the mains connection unit 68.
CA 02697839 2010-03-25
- 16 -
A person skilled in the art knows different ways of connecting mains cables
and motor connection lines via plug-in connections. In both embodiments, the
phase lines are preferably connected to the mains connection unit via clamp
spring connections.
For connecting the motor lines to the motor connection unit, a crimp
connection is preferred.
Both embodiments also have in common to present a substantially
parallelepipedal structure. The invention is however not restricted to an
external
parallelepipedal shape, a cylindrical shape is for example also conceivable.
In the
first embodiment, it is in particular only decisive for the connecting
structure of the
winding ends that the terminals are arranged in two groups of three terminals
each, the terminals being point symmetric to each other such that the rotation
of
the coupling module through 180 leads to the desired reversal of the
direction of
rotation of the motor.