Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 CONSTRUCTIVE LIGHT WEIGHT INSULATION BLOCK
2 AND CONSTRUCTION METHOD THEREOF
3
4 TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to a constructive light weight insulation block
and
6 construction method thereof, and more particularly, to a constructive light
weight insulation block
7 on that finishes interior and exterior walls of a building by adding a
finishing material to a block
8 main body including light weight bubbling synthetic resin, thereby reducing
material costs,
9 simplifying a block building process, and reducing an energy consumption by
80-90 %
compared to a given house, and construction method thereof.
11
12 BACKGROUND ART
13 Blocks used to build walls that are conventionally manufactured by mixing
cement and
14 additive at a predetermined ratio, putting the mixture into a specific
frame, taking the mixture
from the specific frame, and hardening the mixture are mainly used for
construction and handy
16 construction such as a partition construction. Adjacent blocks are knitted
together by using
17 mortar, the blocks are piled up, and desired walls are built.
18 In this connection, although cement blocks and bricks have been known in
Korean Laid-
19 Open U.M. Publication No. 1992-15206, Korean Registration U.M. Publication
No. 346650, etc.,
when these blocks are stacked in interior and exterior walls of a building, a
separate heat
21 insulator needs to be installed in an exterior wall as a hollow wall, and a
finishing process needs
22 to be internally and externally performed.
23
24 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The above and other features and advantages of the present invention will
become more
26 apparent by describing in detail exemplary embodiments thereof with
reference to the attached
27 drawings in which:
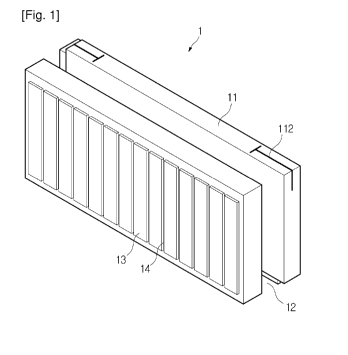
28 FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
29 to an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
31 to another embodiment of the present invention;
32 FIG. 3 is a right side view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block shown in
33 FIG. 2;
34 FIG. 4 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
to another embodiment of the present invention;
21980891.1 1
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 FIG. 5 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
2 to another embodiment of the present invention;
3 FIG. 6 is a left side view of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in
4 FIG. 5;
FIG. 7 is front, side, and plan views of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
6 shown in FIG. 1;
7 FIG. 8 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
8 to another embodiment of the present invention;
9 FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
shown in FIG. 8 taken along a line A-A;
11 FIG. 10 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
12 shown in FIG. 8;
13 FIG. 11 is a state view of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in FIG.
14 8;
FIG. 12 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block
16 according to another embodiment of the present invention;
17 FIG. 13 is a side view of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in FIG.
18 12;
19 FIG. 14 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
shown in FIG. 12;
21 FIG. 15 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat
insulation block
22 according to another embodiment of the present invention;
23 FIG. 16 is a cross-sectional view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
24 shown in FIG. 15 taken along a line B-B;
FIG. 17 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
26 shown in FIG. 15;
27 FIG. 18 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat
insulation block
28 according to another embodiment of the present invention;
29 FIG. 19 is a side view of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in FIG.
18;
31 FIG. 20 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
32 shown in FIG. 18; and
33 FIG. 21 is a perspective view for explaining a method of constructing a
constructive light
34 weight heat insulation block according to an embodiment of the present
invention.
21980891.1 2
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1
2 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
3 Technical Goal of the Invention
4 According to the conventional technology, construction efficiency is
dropped, and an
interior partition construction is accompanied by a finishing process after
blocks are stacked.
6 Also, blocks are formed of cement mortar as a whole, which increases block
manufacturing
7 costs. When the surface of a wall of a multi-storied building is
constructed, durability of the
8 multi-stored building is dropped due to the load of blocks.
9
Disclosure of the Invention
11 According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a
constructive light
12 weight heat insulation block that is stacked in interior and exterior walls
of a building is formed of
13 a bubbling synthetic resin, and comprises a coupling projection formed on
the top surface
14 thereof so that a recess is not generated when the constructive light
weight heat insulation block
is stacked, a coupling groove formed on the bottom surface thereof and
corresponding to the
16 coupling projection, and a projection portion and a groove portion formed
in the front and rear
17 surfaces thereof.
18
19 Effect of the Invention
The constructive light weight insulating block and construction method thereof
according
21 to the present invention finish interior and exterior walls of a building
by adding a finishing
22 material to a block including bubbling synthetic resin, thereby reducing
material costs, simplifying
23 a block construction process, reducing energy consumption by 80-90%
compared to a given
24 house, increasing condensation prevention and cooling and heating
efficiency owing to excellent
heat insulation thereof, and preventing a drop in the durability of the
building owing to the light
26 weight thereof.
27
28 BEST MODES FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
29 The present invention will now be described more fully with reference to
the
accompanying drawings.
31 FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
32 to an embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2 is a perspective view of
a constructive light
33 weight heat insulation block according to another embodiment of the present
invention, FIG. 3 is
34 a right side view of the constructive light weight heat insulation block
shown in FIG. 2, FIG. 4 is a
21980891.1 3
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation block
according to another
2 embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 5 is a perspective view of a
constructive light weight
3 heat insulation block according to another embodiment of the present
invention, FIG. 6 is a left
4 side view of the constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in
FIG. 5, and FIG. 7 is
front, side, and plan views of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in FIG. 1.
6 Referring to FIGS. 1 through 7, the heat insulation block 1 that is stacked
in interior and
7 exterior walls of a building is formed of a bubbling synthetic resin,
comprises a coupling
8 projection 11 formed on the top surface thereof so that a heat bridge and
moisture movement do
9 not occur due to a recess generated when stacked, a coupling groove 12
formed on the bottom
surface and corresponding to the coupling projection 11, and a projection
portion 13 and a
11 groove portion 14 formed in the front and rear surfaces.
12 An auxiliary block 6, which is in the same shape as the heat insulation
block 1, is cut to
13 the shape "L" at a part of the top portion of one surface thereof, and has
a circular insertion
14 projection 15 in the top portion of the cut member, is coupled to one side
of the heat insulation
block 1.
16 A cutting groove portion 17 is formed in the center top portion of the heat
insulation block
17 1. The circular insertion projection 15 is formed on the top portion of the
cut member.
18 A crossing block 7 in which the coupling projection 11 having one end
curved and
19 extending in the top portion thereof is formed, the coupling groove 12 is
formed on the bottom
surface thereof, the projection portion 13 and the groove portion 14 are
formed in the front and
21 rear surfaces thereof, a part of the bottom portion thereof is cut in the
shape of "1 ", and a
22 circular insertion groove 16 is formed in the top portion of the cut member
is coupled to the heat
23 insulation block 1 in which the insertion projection 15 is formed in a
lengthwise direction or at a
24 right angle.
The heat insulation block 1, the auxiliary block 6, and the crossing block 7
are coupled to
26 one another by vertically inserting the coupling projection 11 into a
vertical coupling groove 18
27 that is perpendicularly formed in one side of the bottom surface thereof.
28 The projection portion 13 formed in the front and rear surfaces of the heat
insulation
29 block 1, the auxiliary block 6, and the crossing block 7 becomes wider
towards the outer sides
and is wedge-shaped so that grouting spaces are formed in both sides of the
projection portion
31 13.
32 The projection portion 13 and the groove portion 14 formed in the front and
rear surfaces
33 of the heat insulation block 1, the auxiliary block 6, and the crossing
block 7 are in the shape of a
34 grid.
21980891.1 4
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 A plurality of the groove portions 14 that partition and divide the front
surface or the rear
2 surface of the heat insulation block 1, the auxiliary block 6, and the
crossing block 7 are formed
3 so that the finishing materials are grouted in the groove portions 14 and
are supported and fixed
4 in the front surface or the rear surface.
An adhesive agent filling groove 111 filled with an adhesive agent used for a
firm
6 coupling is formed in the top portion of the coupling projection 11 of the
heat insulation block 1.
7 A wire mesh (not shown) is inserted into the heat insulation block 1 in
order to increase
8 coupling and reinforce inner power of a masonry bond wall perpendicularly
and horizontally.
9 A filling groove 19 is horizontally formed at corners of a front plate and a
rear plate of the
heat insulation block 1.
11 The filling groove 19 is formed at each corner of the heat insulation block
1 in a
12 lengthwise direction and a grouting agent is grouted therein so that each
stacked heat insulation
13 block is fixed to each other. The grouting agent may be any one of
adhesive, cement, a plaster,
14 steel and plastic, a wood locking tool, and the like.
Locking grooves 112 are formed on both ends of the top portion of the coupling
16 projection 11 of each heat insulation block 1 so as to lock a locking steel
tool.
17 The finishing material may be formed on the surface of the front and rear
surfaces of the
18 blocks, may be any one of cement, plaster, a steel panel, a wall paper,
yellow earth, and cement
19 mixed with stone powder, and may have various colors.
In the drawings, lengths and sizes of layers and regions may be exaggerated
for clarity.
21 In addition, all terms mentioned throughout this disclosure are the ones
generally defined based
22 on the functions of what they represent in the present invention, and thus,
their definitions may
23 vary depending on user's intent or customs. Therefore, those terms should
be defined based
24 on the content of the present invention presented herein the present
disclosure.
This invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should
not be
26 construed as limited to the exemplary embodiments set forth herein. Rather,
these
27 embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and
complete, and will fully
28 convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art.
29 Referring to FIG. 1, the heat insulation block 1 that is stacked in
interior and exterior
walls of the building is formed of the bubbling synthetic resin, comprises the
coupling projection
31 11 formed on the top surface thereof so that a recess is not generated when
stacked, the
32 coupling groove 12 formed on the bottom surface and corresponding to the
coupling projection
33 11, and the projection portion 13 and the groove portion 14 formed in the
front and rear surfaces.
21980891.1 5
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 The coupling projection 11 of the heat insulation block 1 is formed
horizontally and is
2 coupled to the coupling groove 12 corresponding to the coupling projection
11 but the present
3 invention is not limited thereto. The coupling projection 11 and the
coupling groove 12 can be
4 formed in various shapes such as triangular, rectangular, semi-circular
shapes, etc.
The coupling projection 11 is formed on the top surface of the heat insulation
block 1, the
6 coupling groove 12 corresponding to the coupling projection 11 is formed in
the bottom surface
7 so that the heat insulation blocks 1 are formed in a perpendicular
direction.
8 The heat insulation block 1 is formed of a bubbling synthetic resin, i.e.,
bubbling
9 polyethylene, thereby reducing material expenses and recycling the heat
insulation block 1.
Referring to FIG. 2, the auxiliary block 6 is formed of the bubbling synthetic
resin
11 comprises the coupling projection 11 formed on the top surface thereof so
that a recess is not
12 generated when stacked, the coupling groove 12 formed on the bottom surface
and
13 corresponding to the coupling projection 11, and the projection portion 13
and the groove portion
14 14 formed in the front and rear surfaces, like the heat insulation block 1.
Referring to FIG. 5, the crossing block 7 comprises the coupling projection 11
having one
16 end of the top portion perpendicularly curved in the shape of "-1 ", the
coupling groove 12 formed
17 on the bottom surface, and the projection portion 13 and the groove portion
14 formed in the
18 front and rear surfaces.
19 A part of the bottom portion of the crossing block 7 is cut in the shape of
"1" and the
circular insertion groove 16 is formed in the top portion of the cut member.
21 Thus, the auxiliary block 6 in which a cutting portion in the shape of is
formed as
22 shown in FIG. 2, the heat insulation block 1 in which the cutting groove
portion 17 is formed in
23 the center top portion as shown in FIG. 4, and the crossing block 7 in
which the insertion groove
24 16 is formed as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6 are coupled to one another, thereby
making various
shapes such as a block coupling structure in the shape of "T" or "+".
26 One surface of the crossing block 7 in which the insertion groove 16 is
formed is round-
27 shaped, the insertion groove 16 is coupled to the insertion projection 15,
rotates, and is molded
28 so as to adjust a coupling angle so that the crossing block 7 can be
connected to the heat
29 insulation block 1.
Referring to FIG. 7, the heat insulation block 1 comprises a plurality of
groove portions 14
31 used to partition and divide the front surface or the rear surface thereof
so that the finishing
32 materials are grouted in the groove portions 14 and are supported or fixed
to the front surface or
33 the rear surface thereof. This is to prevent cement mortar used as the
finishing materials (not
34 shown) that will be described later from falling from the front surface or
the rear surface of the
21980891.1 6
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 heat insulation block 1 during a process of coating and hardening the
finishing materials to the
2 heat insulation block 1, and to prevent the hardened finishing materials
from peeling off from the
3 heat insulation block 1, so that the cement mortar is grouted in the
plurality of groove portions 14
4 and supported and firmly fixed.
The filling groove 19 is formed at each corner of the heat insulation block 1
in a
6 lengthwise direction, the grouting agent is grouted in the filling groove 19
of the heat insulation
7 block 1 so that the stacked heat insulation block 1 can be fixed to each
other in a lengthwise
8 direction and up and down directions.
9 Meanwhile, the finishing materials can be fixed to the front surface or the
rear surface of
the heat insulation block 1 by using the cement mortar, can be a cement panel
formed by
11 hardening the cement mortar, and by adding various colors to plaster, a
steel panel, a wall paper,
12 yellow earth, cement mixed with stone powder, etc.
13 The finishing materials are not limited to the plaster, the steel panel,
the wall paper,
14 yellow earth, and cement mixed with stone powder but can be adhered to the
front surface or the
rear surface of the heat insulation block 1 so as to protect the heat
insulation block 1 and
16 simultaneously create the aesthetics.
17 The grouting agent may be the cement mortar, an adhesive agent, a synthetic
resin
18 material, a steel or plastic locking tool, plaster, etc., and may create
the aesthetics by adding
19 design or color thereto.
With respect to a process of installing the constructive light weight heat
insulation block
21 according to the present embodiment, in order to finish interior and
exterior wall surfaces of the
22 building, the heat insulation block 1 is fixed to ground so as to contact a
location adjacent to the
23 interior and exterior wall surfaces or the interior and exterior wall
surfaces, the coupling groove
24 12 formed in the bottom surface of the heat insulation block 1 is inserted
into the coupling
projection 11 formed on the top surface of the heat insulation block 1, the
heat insulation block 1
26 is sequentially stacked upward and in a lengthwise direction, the grouting
agent is grouted into
27 the filling groove 19 and is fixed via the adhesive agent, etc. so that the
stacked heat insulation
28 block 1 is fixed to each other upward and downward and in a lengthwise
direction.
29 A block in which the " 1" shaped cutting portion is formed and a block in
which the cutting
groove portion 17 is formed in the center thereof are coupled to a block in
which the insertion
31 groove is formed, making a variety of shapes such as a block coupling
structure in the shape of
32 "T" or "+". When a predetermined coupling angle is necessary, one surface
of the heat
33 insulation block 1 in which the insertion groove 16 is formed is round-
shaped, the insertion
21980891.1 7
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 groove 16 and the insertion projection 15 are coupled to each other, and the
coupling angle is
2 adjusted.
3 FIG. 8 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block according
4 to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional
view of the
constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in FIG. 8 taken along a
line A-A. FIG. 10
6 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block shown in FIG. 8.
7 FIG. 11 is a state view of the constructive light weight heat insulation
block shown in FIG. 8.
8 Referring to FIGS. 8 through 11, the heat insulation block 1 that is stacked
in interior and
9 exterior walls of a building comprises a coupling projection 11 formed on
the top surface thereof
so that a recess is not generated when a plurality of heat insulation blocks
are stacked and a
11 coupling groove 12 formed on the bottom surface thereof and corresponding
to the coupling
12 projection 11, second-stepped groove portions 3 that are second-step curved
from an edge of a
13 storing portion 2 of the heat insulation block 1 in the front and rear
surfaces of the heat insulation
14 block 1, a heat proof board 4 formed of one selected from a plaster board,
a rock wool, and a
glass cotton mat, and inserted into an interior groove portion 31 disposed in
the second-step
16 groove portion 3 in an inner direction, and a finishing board 5 formed of
one selected from a
17 stone material, steel fiber reinforcement concrete, a dryvit, PVC, and
metal and inserted into an
18 exterior groove portion 32 disposed in the second-step groove portion 3 in
an exterior direction
19 and having a grouting groove 321 formed in one side thereof.
The heat insulation block 1 is formed of a light weight bubbling synthetic
resin, i.e.,
21 bubbling polyethylene, finishes interior and exterior walls of the
building, reduces material
22 expense, simplifies an operation process, and reduces a construction time.
23 The distance between the second-step groove portion 3 formed in the heat
insulation
24 block 1 and the interior groove portion 31 may be longer than that between
the second-step
groove portion 3 and the exterior groove portion 32.
26 The heat proof board 4 inserted into the interior groove portion 31 is a
light weight heat
27 proof material and is good at water proof, sound proof, and heating
efficiency. Meanwhile,
28 since the plaster board, the rock wool, and the glass cotton mat are widely
known, the present
29 invention does not repeat the specific characteristics thereof.
The characteristics of the stone material, the steel fiber reinforcement
concrete, and the
31 dryvit other than the PVC and metal that are generally used as the
finishing materials will now be
32 briefly described.
33 Although the stone material is a relatively expensive material used as an
exterior wall
34 material, the stone material is frequently used as an art decoration
component owing to a firm
21980891.1 8
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 durability and unprocessed irregular texture of the exterior wall. Although
the stone material is
2 used for the overall external wall, the stone wall can be partially mixed
with another material as a
3 substitute for a reduction in the construction costs and an individual
presentation.
4 The steel fiber reinforcement concrete irregularly arrange single phase
steel fiber instead
of traditional type steel and scatters the steel fiber in concrete so as to
prevent a crack and
6 increase durability. Since this panel is mixed with the steel fiber and has
enhanced durability,
7 the panel is not contracted due to rain, wind, and heat, and is good at
proportion intensity and
8 compression intensity.
9 The dryvit is a material having various textures that has a good durability
and no color
change by mixing acryl resin having a purity of 100% and a chemical material
and special quartz
11 sand. If the dryvit is used to finish the exterior wall, an auxiliary heat
proof and water proof
12 construction are not necessary and the wall structure is light weight,
thereby reducing structuring
13 costs. The dryvit has various textures and colors, prevents a crack owing
to its condensation
14 prevention and ordinary temperature and moisture effect, and maximizes
water proof and
durability.
16 The heat proof board 4 and the finishing board 5 of the present invention
may be
17 selected from a board having the corresponding performance necessary for a
harmony with the
18 structure of the building.
19 A process of assembling the constructive light weight heat insulation block
of the present
invention will now be described.
21 The heat proof board 4 is inserted into the interior groove portion 31
disposed in the
22 second-step groove portion 3 of the heat insulation block 1. Thereafter,
the finishing board 5 is
23 inserted into the exterior groove portion 32.
24 An inorganic adhesive agent is grouted in the grouting groove 321 formed in
one side of
the finishing board 5 so that the finishing board 5 is firmly fixed to the
heat insulation block 1. A
26 plurality of heat insulation blocks I in which the heat proof board 4 and
the finishing board 5 are
27 sequentially fixed to the front and rear surfaces thereof are stacked by
locating the coupling
28 groove 12 of the heat insulation block 1 in the coupling projection 11 of
the basic heat insulation
29 block 1.
Before describing constructive light weight heat insulation blocks according
to the
31 following embodiments of the present invention, since the characteristics
of a heat proof board
32 and a finishing board and a process of assembling blocks of the following
embodiments are the
33 same as described with reference to FIGS. 8 through 11, the specific
description will not be
34 repeated.
21980891.1 9
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 FIG. 12 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block
2 according to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 13 is a side
view of the
3 constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in FIG. 12. FIG. 14 is
a partial perspective
4 view of the constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in FIG.
12.
Referring to FIGS. 12 through 14, the heat insulation block 1 that is stacked
in interior
6 and exterior walls of a building is formed of a bubbling synthetic resin,
comprises a coupling
7 projection 11 formed on the top surface thereof so that a recess is not
generated when a
8 plurality of heat insulation blocks are stacked and a coupling groove 12
formed on the bottom
9 surface thereof and corresponding to the coupling projection 11, a circular
insertion projection 15
that is cut in the shape of in a part of one surface of the top portion
thereof and formed in
11 the top portion of the cut member, second-stepped groove portions 3 that
are second-step
12 curved from an edge of a storing portion 2 of the heat insulation block 1
in the front and rear
13 surfaces of the heat insulation block 1, a heat proof board 4 formed of one
selected from a
14 plaster board, a rock wool, and a glass cotton mat, and inserted into an
interior groove portion
31 disposed in the second-step groove portion 3 in an inner direction, and a
finishing board 5
16 formed of one selected from a stone material, steel fiber reinforcement
concrete, a dryvit, PVC,
17 and metal and inserted into an exterior groove portion 32 disposed in the
second-step groove
18 portion 3 in an exterior direction and having a grouting groove 321 formed
in one side thereof.
19 A perpendicular coupling groove 18 is perpendicularly formed in a lower one
side of the
bottom surface of the heat insulation block 1 and is coupled to the coupling
projection 11 of the
21 heat insulation block 1.
22 FIG. 15 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat
insulation block
23 according to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 16 is a
cross-sectional view of
24 the constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in FIG. 15 taken
along a line B-B. FIG.
17 is a partial perspective view of the constructive light weight heat
insulation block shown in
26 FIG. 15.
27 Referring to FIGS. 15 through 17, the heat insulation block 1 that is
stacked in interior
28 and exterior walls of a building is formed of a bubbling synthetic resin,
comprises a coupling
29 projection 11 formed on the top surface thereof so that a recess is not
generated when a
plurality of heat insulation blocks are stacked and a coupling groove 12
formed on the bottom
31 surface thereof and corresponding to the coupling projection 11, a cutting
groove portion 17
32 formed in the center top portion of the heat insulation block 1, a circular
insertion projection 2
33 formed in the top portion of the cut member, second-stepped groove portions
3 that are second-
34 step curved from an edge of a storing portion 2 of the heat insulation
block 1 in the front and rear
21980891.1 10
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 surfaces of the heat insulation block 1, a heat proof board 4 formed of one
selected from a
2 plaster board, a rock wool, and a glass cotton mat, and inserted into an
interior groove portion
3 31 disposed in the second-step groove portion 3 in an inner direction, and a
finishing board 5
4 formed of one selected from a stone material, steel fiber reinforcement
concrete, a dryvit, PVC,
and metal and inserted into an exterior groove portion 32 disposed in the
second-step groove
6 portion 3 in an exterior direction and having a grouting groove 321 formed
in one side thereof.
7 A perpendicular coupling groove 18 is perpendicularly formed in a lower one
side of the
8 bottom surface of the heat insulation block 1 and is coupled to the coupling
projection 11 of the
9 heat insulation block 1.
FIG. 18 is a perspective view of a constructive light weight heat insulation
block
11 according to another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 19 is a side
view of the
12 constructive lightweight heat insulation block shown in FIG. 18. FIG. 20 is
a partial perspective
13 view of the constructive light weight heat insulation block shown in FIG.
18.
14 Referring to FIGS. 18 through 20, the heat insulation block 1 that is
stacked in interior
and exterior walls of a building is formed of a bubbling synthetic resin,
comprises a coupling
16 projection 11 formed on the top surface thereof so that a recess is not
generated when a
17 plurality of heat insulation blocks are stacked and a coupling groove 12
formed on the bottom
18 surface thereof and corresponding to the coupling projection 11, a circular
insertion projection 15
19 that is cut in the shape of "-1 " in a part of one surface of the bottom
portion thereof and formed
in the top portion of the cut member, second-stepped groove portions 3 that
are second-step
21 curved from an edge of a storing portion 2 of the heat insulation block 1
in the front and rear
22 surfaces of the heat insulation block 1, a heat proof board 4 formed of one
selected from a
23 plaster board, a rock wool, and a glass cotton mat, and inserted into an
interior groove portion
24 31 disposed in the second-step groove portion 3 in an inner direction, and
a finishing board 5
formed of one selected from a stone material, steel fiber reinforcement
concrete, a dryvit, PVC,
26 and metal and inserted into an exterior groove portion 32 disposed in the
second-step groove
27 portion 3 in an exterior direction and having a grouting groove 321 formed
in one side thereof.
28 Meanwhile, FIG. 21 is a perspective view for explaining a method of
constructing a
29 constructive light weight heat insulation block according to an embodiment
of the present
invention. Referring to FIG. 21, the method of constructing the constructive
light weight heat
31 insulation block comprises a foundation constructing operation of
installing a plurality of steel
32 shapes 9 in a perpendicular to a foundation floor 8 of a building; stacking
a plurality of heat
33 insulation blocks 1 formed of a styrofoam material between the steel shapes
9; constructing a
34 finishing material on the interior and exterior surfaces of the stacked
heat insulation blocks 1;
21980891.1 11
CA 02701344 2010-03-31
Agent Ref: 76305/00002
1 and painting a desired color on the surface of the finishing material
constructed on the exterior
2 surface of the heat insulation blocks 1.
3 In the foundation constructing operation, the plurality of steel shapes 9 is
perpendicularly
4 installed on the foundation floor 8 of the building. The foundation floor 8
is generally formed of
concrete and is flattened so as to uniformly stack the heat insulation blocks
1.
6 The steel shapes 9 are referred to bar shaped rolled stocks having various
cross-section
7 shapes and may be H steel shapes that are mainly used for a structure of the
building.
8 The method further comprises coating an adhesive agent on the top surface of
the heat
9 insulation block 1 disposed in the lower portion thereof so as to reinforce
the coupling of the heat
insulation blocks 1 when the heat insulation blocks 1 are stacked, thereby
preventing the
11 plurality of stacked heat insulation blocks 1 from moving and increasing
the coupling force
12 thereof.
13 In the constructing the finishing material to the interior and exterior
surfaces of the
14 stacked heat insulation blocks 1, if the plurality of heat insulation
blocks 1 is completely stacked,
the finishing material is constructed on the interior and exterior surfaces of
the heat insulation
16 blocks 1 in order to protect the building from several external affects and
make a good exterior
17 of the building.
18 The finishing material uses one selected from cement, plaster, a wall
paper, yellow earth,
19 and cement mixed with stone powder.
Finally, in the painting the desired color on the surface of the finishing
material
21 constructed on the exterior surface of the heat insulation blocks 1, a
partial coloring or drawing is
22 performed in the surface of the finishing material in order to bring people
to the aesthetics when
23 the building is viewed outside.
24 While the present invention has been particularly shown and described with
reference to
exemplary embodiments thereof, it will be understood by those of ordinary
skill in the art that
26 various changes in form and details may be made therein without departing
from the spirit and
27 scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. The exemplary
embodiments
28 should be considered in a descriptive sense only and not for purposes of
limitation. Therefore,
29 the scope of the present invention is defined not by the detailed
description of the invention but
by the appended claims, and all differences within the scope of the present
invention will be
31 construed as being included in the present invention.
32
21980891.1 12