Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
FLUID FLOW MACHINE
The invention is directed to a fluid flow machine.
A fluid flow machine of the type mentioned above is known, e.g., from EP 0
834 688 Al. A brush seal is also known, e.g., from DE 601 24 204 T2.
Fluid flow machines include, for example, propellers and repellers,
centrifugal
pumps and turbo machinery of any kind such as gas turbines, steam turbines and
rotary compressors such as, e.g., radial compressors and axial compressors.
The rotor in fluid flow machines such as turbo machines can be sealed by
means of labyrinth tip seals, mechanical seals or brush seals to prevent the
leakage of
fluid. In brush seals, sealing bristles (also known as brush wires) of the
brush seal
make direct contact with the rotor of the turbo machine, this rotor being
constructed,
e.g., as a shaft. The brush seal limits the amount of work fluid, e.g., the
amount of
compressor air, flowing out of a flow part of the turbo machine into a bearing
periphery of the turbo machine, for example.
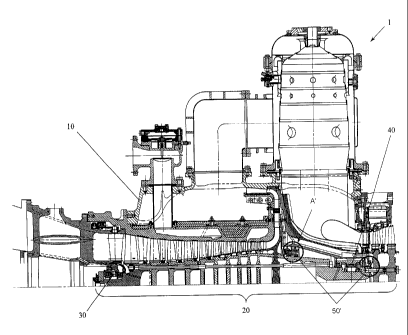
Figures 1 and 2 show a fluid flow machine 1 which is constructed as a gas
turbine. As can be seen from Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, the fluid flow machine 1 has a
stator
which is constructed in this instance as a gas turbine housing, a rotor 20
which is
supported so as to be rotatable relative to the stator 10 and which is
constructed in this
instance as a shaft, rotational bearings 30, 40 which carry out the rotatable
bearing
support of the rotor 20 in the stator 10, and two brush seals 50 which seal a
gap S
formed in radial direction RR between the stator 10 and rotor 20 to prevent
the
passage of fluid.
As can be seen particularly from Fig. 2, every brush seal 50 has a brush
holder
51 and a plurality of sealing bristles 52, each of which has a first end which
is
fastened to the brush holder 51 and a second end which contacts a sealing
surface D
which is formed in this case by an outer circumferential surface 21 of the
rotor 20, so
that a sealing bristle-on-sealing surface contact zone is formed. The sealing
surface D
is rotationally displaceable, particularly rotatable in this case, relative to
the second
ends of the respective sealing bristles 52.
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 2 -
During operation of the fluid flow machine 1, the relative movement between
the rotating rotor 20 and the brush seal 50, which is static in this case,
leads to heating
of the sealing surface D of the rotor 20 and sealing bristles 52 due to the
friction
between the sealing bristles 52 and the outer circumferential surface 21 of
the rotor
20.
However, problems arise in this conventional seal in that an uneven heating of
the sealing surface D is brought about in the absence of a state of true in
the contact
zone of the sealing surface D and sealing bristles 52. This uneven heating can
exacerbate the out-of-true state and lead to a deformation of the rotor 20
(manifesting
itself in this case as sagging between the rotational bearings 30 and 40 of
the shaft)
which impairs continued operation of the fluid flow machine 1 owing to
impermissibly strong rotor vibrations.
It is the object of the invention to provide a fluid flow machine in which the
sealing bristle-on-sealing surface contact zone is thermally decoupled in
order to
prevent a deformation in the fluid flow machine which is brought about by
introduced
heat and which impairs the operation of the fluid flow machine.
The above-stated object is met by a fluid flow machine.
According to the invention, a fluid flow machine has a stator, a rotor which
is
supported so as to be rotatable relative to the stator, and a brush seal which
seals a gap
formed between the stator and rotor in a radial direction of the rotor to
prevent the
passage of fluid. The brush seal has a brush holder and a plurality of sealing
bristles,
each of which has a first end that is fastened to the brush holder and a
second end that
contacts a sealing surface so that a sealing bristle-on-sealing surface
contact zone is
formed. The sealing surface is rotationally displaceable relative to the
second ends of
the respective sealing bristles.
The fluid flow machine according to the invention is characterized in that the
sealing surface is formed by a circumferential surface of an intermediate
sleeve or
intermediate bushing which is arranged between the stator and rotor and which
radially divides the gap.
By moving the sealing surface to an intermediate sleeve, the sealing bristle-
on-
sealing surface contact zone is thermally decoupled so as to prevent a
deformation in
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 3 -
the fluid flow machine which is brought about by introduced heat and which
impairs
the operation of the fluid flow machine.
According to the invention, the intermediate sleeve is fastened either to a
rotating part or to a stationary part of the brush seal. This fastening is
advantageously
carried out in such a way that, on the one hand, sufficient stability is
achieved and, on
the other hand, a heat transfer between the intermediate sleeve and the part
to which
the intermediate sleeve is fastened is as small as possible. The small heat
transfer can
be achieved, e.g., by means of the smallest possible contact surfaces and/or
by
providing an insulating layer between the contact surfaces of the intermediate
sleeve
and the part fastening the latter.
According to the invention, the brush holder can be arranged at the stator and
the intermediate sleeve can be arranged at the rotor so as to rotate along
with the
latter. In this case, the circumferential surface of the intermediate sleeve
forming the
sealing surface would be an outer circumferential surface. However, it is also
possible according to the invention that the brush holder is arranged at the
rotor and
the intermediate sleeve is arranged in a stationary manner at the stator so
that the
circumferential surface of the intermediate sleeve forming the sealing surface
would
be an inner circumferential surface in this case. The respective solution can
be
determined depending on the desired operating characteristics and design
factors.
Further, according to the invention, the rotor can be formed, e.g., by a shaft
rotating in a stator (e.g., in a housing) and, e.g., by a housing rotating
around a stator
(e.g., around an axle). The respective solution can be determined depending on
the
desired operating characteristics and the design factors.
According to an embodiment form of the invention, the intermediate sleeve
divides the gap radially into a first gap portion adjoining the sealing
surface and a
second gap portion adjoining a circumferential surface of the intermediate
sleeve
remote of the sealing surface, wherein a radial extension of the second gap
portion is
greater than zero.
In other words, there is an air gap between the intermediate sleeve and the
part
(e.g., the rotor or the stator) fastening this intermediate sleeve, and this
air gap
advantageously ensures additional thermal insulation between the intermediate
sleeve
and the part fastening the latter. This makes it even more difficult for heat
to transfer
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 4 -
from the sealing surface and the part fastening the intermediate sleeve so
that a
deformation of the part fastening the intermediate sleeve that is brought
about by
introduced heat is prevented in an even more reliable manner.
According to an embodiment form of the invention, the intermediate sleeve
has a flange by means of which the intermediate sleeve is mounted at a flange
mounting portion of the stator or rotor so as to be fixed with respect to
rotation
relative to it.
This construction of the invention is advantageous particularly with respect
to
ensuring the smallest possible contact surfaces between the intermediate
sleeve and
the part (in this case, particularly the stator or the rotor) fastening this
intermediate
sleeve, while at the same time ensuring that the fastening is sufficiently
stable.
According to another embodiment form of the invention, the flange is
mounted at the flange mounting portion by detachable fastening means. Such
fastening means can be, for example, screw connections, rivet connections,
clamping
connections, etc. In particular, the detachable connection facilitates the
changing of
worn intermediate sleeves, for example.
Further, the flange connection makes it possible to introduce a thermal
insulation layer between the flange and the flange mounting portion in a
simple
manner.
According to another embodiment form of the invention, the flange is
arranged at an axial end of the intermediate sleeve so that the flange has, at
the axial
end, an annular flange surface which contacts a mounting surface of the flange
mounting portion so as to be tight against fluid.
This construction of the invention reliably ensures a seal between the
intermediate sleeve and the part fastening this intermediate sleeve to prevent
the
passage of fluid.
According to another embodiment form of the invention, the rotor is formed
by a shaft and the intermediate sleeve is mounted on the rotor so as to be
fixed with
respect to rotation relative to it so that the sealing surface is formed by an
outer
circumferential surface of the intermediate sleeve, wherein the brush holder
is
arranged at the stator so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative to
it.
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 5 -
An embodiment of the invention of the kind mentioned above can be produced
in a particularly simple and dependably operating manner.
According to another embodiment form of the invention, an inner diameter of
the intermediate sleeve is greater than an outer diameter of the shaft so that
an annular
gap is formed between an inner circumferential surface of the intermediate
sleeve and
an outer circumferential surface of the shaft.
This construction of the invention achieves a thermally insulating air gap
between the intermediate sleeve and the part fastening this intermediate
sleeve in a
simple and robust manner, this part being formed in this case by the rotor
which is
constructed as a shaft.
According to embodiment forms of the invention, the fluid flow machine is
formed by a turbo machine, particularly a gas turbine or a turbo compressor.
The invention will be described in more detail in the following with reference
to preferred embodiment forms and the accompanying drawings. The drawings
show:
Fig. 1 a schematic sectional view of the basic construction of a fluid
flow
machine constructed as a gas turbine according to the prior art;
Fig. 2 an enlarged section A from Fig. 1 showing a brush seal of a fluid
flow
machine according to the prior art;
Fig. 3 a schematic sectional view of the basic construction of a fluid
flow
machine constructed as a gas turbine according to an embodiment form
of the invention; and
Fig. 4 an enlarged section A' from Fig. 3 showing a brush seal of a fluid
flow
machine according to an embodiment form of the invention.
As is shown in Figs. 3 and 4, a fluid flow machine 1 which is constructed in
this instance as a gas turbine has a stator 10 which is constructed in this
instance as a
gas turbine housing, a rotor 20 which is constructed in this instance as a
shaft which is
mounted so as to be rotatable relative to the stator 10, two rotational
bearings 30, 40
which form the rotatable bearing support of the rotor 20 in the stator 10, and
two
brush seals 50' which seal a gap S which is formed in a radial direction RR
between
the stator 10 and rotor 20 so as to be prevent the passage of fluid.
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 6 -
As can be seen particularly from Fig. 4, every brush seal 50' has a brush
holder
51 and a plurality of sealing bristles 52 each of which has a first end
fastened to the
brush holder 51 and a second end contacting a sealing surface D' so as to form
a
sealing bristle-on-sealing surface contact zone, the sealing surface D' being
displaceable with respect to rotation, particularly rotatable in this
instance, relative to
the second ends of the respective sealing bristles 52.
As can be seen from Fig. 4, the sealing surface D' is formed by an outer
circumferential surface 61 of an intermediate sleeve 60 which is arranged
between the
stator 10 and rotor 20 and which is mounted on the rotor 20 so as to be fixed
with
respect to rotation relative to it and so as to divide the gap S radially. The
brush
holder 51 is arranged at the stator 10 so as to be fixed with respect to
rotation relative
to it.
The intermediate sleeve 60 divides the gap S radially into a first gap portion
adjoining the sealing surface D' and a second gap portion adjoining an inner
circumferential surface (not shown) of the intermediate sleeve 60 remote of
the
sealing surface D'. A radial extension of the second gap portion is greater
than zero.
This means that an inner diameter of the intermediate sleeve 60 is greater
than
an outer diameter of the rotor (shaft) 20 so that an annular gap is formed
between the
inner circumferential surface of the intermediate sleeve 60 and an outer
circumferential surface 21 of the rotor 20.
In other words, an air gap (annular gap) is provided between the intermediate
sleeve 60 and the rotor 20 fastening the latter, which air gap advantageously
ensures a
thermal insulation between the intermediate sleeve 60 and the rotor 20. This
makes it
more difficult for heat to be transferred from the sealing surface D' to the
rotor 20,
which prevents a deformation of the rotor 20 fastening the intermediate sleeve
60 due
to introduced heat.
Further, as can be seen from Fig. 4, the intermediate sleeve 60 has a flange
62
by means of which the intermediate sleeve 60 is mounted at the flange mounting
portion 22 of the rotor 20 so as to be fixed with respect to rotation relative
to it. The
flange 62 is arranged at an axial end of the intermediate sleeve 60 so that
the flange
62 has, at the axial end, an annular flange surface (not designated
separately) which
contacts a recessed mounting surface (not designated separately) of the flange
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 7 -
mounting portion 22 in a fluid-tight manner. Although not shown in Fig. 4, a
flat seal
can be provided for achieving the fluid tightness and a thermal insulation
between the
annular flange surface of the flange 62 and the recessed mounting surface of
the
flange mounting portion 22.
As is shown in Fig. 4, the flange 62 is mounted at the flange mounting portion
22 of the rotor 20 by detachable fastening means which are realized in this
instance in
the form of a screw connection.
In conclusion, the rotor 20 which is constructed in this instance as a shaft
is
provided with an intermediate sleeve or intermediate bushing 60 according to
an
embodiment form of the invention. The intermediate sleeve 60 is connected to
the
rotor 20 by means of an axial flange 62 and detachable fastening means. There
is an
annular gap between the intermediate sleeve 60 and the rotor 20. The sealing
bristles
or brush wires 52 of the brush seal 50' contact the sealing surface D' formed
by the
outer circumferential surface 61 of the intermediate sleeve 60.
Accordingly, in the event of an out-of-true state of the intermediate sleeve
60,
an uneven deformation of the intermediate sleeve 60 may only aggravate the out-
of-
true state of the intermediate sleeve 60 because the rotor 20 is only
connected to the
intermediate sleeve 60 by the connection of its flange mounting portion 22 to
the
flange 62 so that a direct heating of the rotor 20 caused by heat entering the
area of
the brush seal 50' is prevented.
The solution according to the invention can be applied wherever a fluid flow
machine, e.g., a gas turbine, is to be sealed with brush seals. According to
embodiment forms of the invention, the invention can be applied, e.g., in disk
rotor
units, full rotor units and welded rotor units.
The solution according to the invention can be used to seal a bearing
periphery
of a fluid flow machine and to seal between individual stages of the fluid
flow
machine, e.g., compressor stages or turbine stages.
Apart from the flange connection described above, fastening of the
intermediate sleeve to the part which fastens or holds it can also be carried
out by
means of shrinking or welding or by means of other fastening elements.
CA 02704349 2013-06-03
- 8 -
List of Reference Numbers
1 fluid flow machine
stator
rotor
21 outer circumferential surface
22 flange mounting portion
rotational bearing
rotational bearing
brush seal
50' brush seal
51 brush holder
52 sealing bristles
intermediate sleeve
61 outer circumferential surface
62 flange
sealing surface
D' sealing surface
gap
RR radial direction