Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02706985 2012-12-06
P2171 DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
PISTON INJECTION UNIT FOR AN INJECTION MOLDING MACHINE
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a piston-injection unit for an injection
moulding machine.
PRIOR ART
Injection moulding machines are widely used in industry to make all kinds of
different
objects. Although a plurality of moulding machines is accordingly in use and
make it possible
to manufacture a plurality of products of the highest quality, there is still
a need to improve
the injection moulding technology.
One problem, for example, concerns the seal between the piston outer wall and
the cylinder
inner wall in a piston-injection unit. In a corresponding piston-injection
unit, the material to
be injected is pressed in a flowable state by a piston, which is guided in a
cylinder, through a
nozzle unit arranged at one end of the cylinder. On account of the
corresponding pressure, it
can happen that flowable material passes into the area between the piston
outer wall and the
cylinder inner wall. If the material remains there for too long, it can cure
or react with other
substances, thus creating undesirable foreign particles, which may on one hand
increase the
friction and wear between the piston and cylinder and, on the other, may
contaminate the
product to be made if it flows back into the moulding compound. Moreover, one
problem is
that the piston movement causes this excess material to escape uncontrollably
at the end of
the cylinder opposite the nozzle unit and thus also leads to contamination.
DE 697 06 167 T2 or the corresponding EP 0 906 180 B1 proposes an injection
apparatus,
which provides for a certain amount of clearance between the outer wall of the
piston and the
inner wall of the cylinder. The clearance is specifically matched to the
viscosity of the
material to be injected in order that rapid exchange of the material in the
clearance may occur
1
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
and thus the above-mentioned particle formation avoided. In addition, an
annular groove is
provided on the piston to prevent aspiration of air into the inner area of the
cylinder.
However, such an apparatus has further problems arising from its structural
design. Thus, in
this piston-injection unit, the material to be injected is introduced into the
cylinder from the
side, whereby the front part of the piston, which is facing the nozzle unit,
has a smaller
diameter, thus forming an annular gap through which the flowable material can
pass into the
space between the nozzle and piston prior to the actual injection process.
During the injection
process in which the piston is moved towards the nozzle to force the material
in the space
through the nozzle, the annular gap is sealed by a separate sealing element,
which is located
inside the space in front of the piston. However, the separate design of the
sealing element
(nonreturn valve) and the correspondingly small dimensions, combined with the
prevailing
injection pressure, creates the problem that the seal between the space and
the piston or the
inner wall of the cylinder is unsatisfactory. In addition, the annular gap
between the front
piston skirt and cylinder inner wall creates a large volume in which the
plasticised material
dwells for a protracted period, with no guarantee of complete, rapid exchange
through
entrainment towards the injection mould.
The piston-injection unit of DE 697 06 167 T2 further comprises a cutting
element at the end
of the cylinder or piston opposite the nozzle unit, said cutting element
cutting off the excess
moulding material which adheres to the outer wall of the piston and thus ends
up in the rear
side of the piston that is facing away from the nozzle unit. To this end, the
cutting element has
a cutting surface in the shape of a truncated cone. While this cutting element
works
satisfactorily for solid, already cured particles, adequate cleaning of the
piston is not
guaranteed in the case of material which is still partially flowable.
23
The same applies to an ejection guide, which is described in DE 699 21 059 T2
and the
corresponding EP 0992333 Bl. Here, for the purpose of removing corresponding
excess
material, an additional band heater is needed to ensure that the material has
adequate flow
properties.
DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
2
CA 02706985 2012-12-06
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a piston-
injection unit for an
injection moulding machine that easily and effectively solves the problem of
handling excess
material that can pass into the space between piston and cylinder inner wall,
whereby the
piston-injection unit, moreover, has well-balanced properties with respect to
the attainable
injection results. In particular, the piston-injection unit shall have a
simple and effective
design and be easy to use and feature simple and suitable material supply.
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
The present invention relates to a piston-injection unit comprising a
cylinder, a piston
movably guided therein and a nozzle unit arranged at one end of the cylinder.
Furthermore, in
the inventive piston-injection unit, the material to be injected is introduced
laterally into the
cylinder in the vicinity of the piston skirt. From a first aspect of the
invention, the invention
is characterised in that, at the front end of the piston, which is facing the
nozzle unit, at least a
first sealing area is provided, which has an outer surface of the piston and
an inner surface of
the cylinder, which abut each other such that they seal off this area as far
as possible. Despite
the lateral material supply in the vicinity of the piston skirt, said lateral
supply possessing
advantages in the field of machine design and the piston guide, it is
advantageous for the front
end of the piston, which comes into direct contact with the material being
injected, to be
already provided with a first sealing area in order that penetration of
material into the area
between the piston and cylinder inner wall may be avoided.
In accordance with the design comprising lateral material supply into the
cylinder, the
invention provides for a flow channel for the flowable material, which guides
the flowable
material supplied from the side of the piston to an outlet or a mouth at the
end of the piston,
whereby the mouth or the outlet can be spaced apart from the outer surface of
the piston, since
the outer surface constitutes the first sealing area. With such a design, it
is possible through
the first sealing area to isolate the space in front of the piston in which
the flowable material is
3
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
under the corresponding injection pressure from the supply region for the
flowable material,
i.e. the flow channel.
From a second aspect of the present invention for which protection is sought
independently
and in combination with the other aspects of the invention, the flow channel
is designed such
that the flow channel is fully flushed by subsequent flow material as material
is transported
from the supply opening to the space in front of the piston, such that the
dwell time of the
material to be injected in the flow channel can be kept short. This prevents
unwanted and
adverse material reactions in the flow channel. By complete flushing here is
meant especially
that no dead spaces exist in which material escapes being entrained by
subsequent material.
Complete does not mean, however, that the flow front is always straight and
stable. Rather,
differential flow rates and mixing of material in the flow channel can obtain.
Furthermore, at least one second sealing area can be provided which guarantees
an additional
5 seal between the piston and cylinder inner wall with respect to the rear
side of the piston
facing away from the nozzle unit, and in particular seals against at least
parts of the flow
channel, i.e. the supply region for the flowable material.
Accordingly, the flow channel can be provided at least partially between the
first and the
second sealing area.
The mouth of the flow channel can be provided at the end face of the piston
facing the nozzle
unit in a central region close to the longitudinal axis of the piston and in
particular
concentrically to the piston's longitudinal axis. This ensures that the end of
the piston
adjacent to the space in front of it is of a structurally favourable design
and has the
appropriate strength and leak-proofness. For uniform distribution of the
flowable material, the
mouth of the flow channel can have several openings or be shaped like a star
or cloverleaf
To prevent backflow of the flowable material transported into the space in
front of the piston
during the injection process, a check valve can be provided in the flow
channel to seal off the
flow channel, i.e. the supply region.
4
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
The check valve can be provided inside the piston and implemented in
particular by a
movable sealing body arranged in a distribution chamber of the flow channel
near the mouth,
said sealing body closing the flow channel mouth under the appropriate
pressure buildup.
The flow channel from the supply opening in the cylinder wall to the mouth at
the end face of
the piston can comprise an axial groove in the piston and an annular groove,
which can be
provided adjacent to the first sealing area. If arranged immediately adjacent
to the sealing
area, the annular groove, which cooperates with the axial groove, has the
advantage that small
amounts of the flowable material which pass through the sealing area are
collected in the
annular groove and used immediately for the next injection process.
From the annular groove, a radial connecting section can be provided that
creates the
connection to the mouth. Accordingly, the flowable material flows from the
supply opening in
the cylinder wall via the axial groove in the piston into an annular groove,
from where the
material passes via a radial connecting section into the mouth provided
centrally or
concentrically to the longitudinal axis of the piston. The radial connecting
section, which may
implemented as a radial bore, is provided preferably opposite the connection
of the axial
groove and annular groove.
To ensure easy inflow into the axial groove, the supply opening in the
cylinder wall can, in
accordance with the axial groove in the piston, have an aperture greater in
the direction of the
longitudinal axis of the piston or the cylinder, than in the transverse
direction.
The supply opening elongated in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the
piston or cylinder
to form a slot also has the effect of expanding the axial adjustability of the
piston, which
ensures that the flow channel does not form dead spaces for the supplied
plasticised material.
This provides greater variability with regard to the end position of the
piston, in which
complete enforced or self-flushing occurs. Accordingly, from a further aspect
of the present
invention, protection is sought independently for this and in conjunction with
the other
aspects.
For the material which nonetheless enters the region between the piston and
cylinder inner
wall and from there into the rear region, i.e. the region of the cylinder
facing away from the
nozzle unit, a further aspect of the invention for which protection is also
sought independently
5
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
and in combination with the other aspects of the invention provides for a
scraper part which
makes flat contact with the piston outer wall and forms on the end face a
scraper surface,
which is provided obliquely to the longitudinal axis of the piston. Through
the oblique
configuration of the scraper surface in a single plane corresponding to the
end face, both solid
and partially liquid material is transported effectively into a discharge
opening in the cylinder
wall, without need for provision of additional measures.
The scraper part is preferably formed as a cylindrical sleeve or ring with an
end face running
obliquely to the longitudinal axis. Preferably, the scraper part is made of
metal, especially
brass or an alloy thereof.
To facilitate precise adjustment of the scraper part to the piston, the
scraper part can be
accommodated with compensating clearance in the cylinder. In particular, an
annular recess
can be provided at the end of the cylinder to accommodate the scraper part,
which can be
attached in particular to a corresponding retaining part on the cylinder end.
In the inventive piston-injection unit, the plasticising unit, which may be
formed for example
by a screw extruder, can be arranged laterally offset from the longitudinal
axis of the piston or
cylinder of the piston-injection unit. Accordingly, the flowable material can
be discharged
from the plasticising unit at an angle between 00 and 180 to the piston or
cylinder
longitudinal axis.
Between plasticising unit and supply opening in the cylinder can be provided a
baffle, which
guides the flowable material from the plasticising unit to the supply opening
and especially
facilitates supply of the flowable material perpendicularly to the piston or
cylinder
longitudinal axis.
From another aspect of the present invention, for which again protection is
sought
independently and in combination with the other aspects of the present
invention, plasticising
unit and baffle are not permanently connected, but only abut one another to
form a butt
connection.
The butt connection can for example be a spherical cap connection, which is
pressed together
by the two abutting parts, i.e. plasticising unit and baffle, and held firmly
and/or under
6
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
pressure in the abutting direction. However, such a connection permits degrees
of movement
in other directions and/or about the axis of rotation, such that compensatory
movements are
possible, e.g. due to different thermal expansion.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
Further advantages, characteristics and features of the present invention will
become clear in
the following detailed description of an embodiment with reference to the
accompanying
drawings. The drawings show here in a purely schematic form in
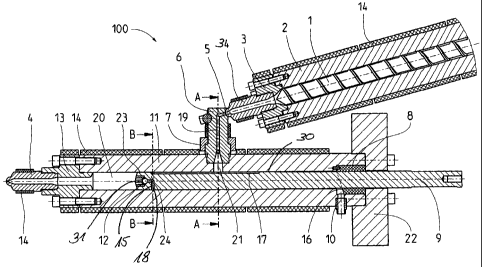
Figure 1 a cross-sectional view of an inventive piston-injection unit;
Figure 2 a cross-sectional view through the piston-injection unit from
Fig. 1 along the
cross-sectional line A-A; and in
Figure 3 a cross-sectional view through the piston-injection unit from
Fig. 1 along the
cross-sectional line BB.
Fig. 1 shows a cross-sectional view of an embodiment of a piston-injection
unit 100. The
piston-injection unit comprises a cylinder 11 in which a piston 9 is movably
arranged. At one
end of the cylinder 11 is provided a nozzle 4 through which flowable material,
which is
located inside the space 20 between nozzle 4 and the end of the piston 9
facing the nozzle,
may be pressed through the nozzle 4. Accordingly, the nozzle 4 can be
connected to an
injection mould so that the flowable material is pressed into the injection
mould.
The flowable material is plasticised in an extruder screw comprising extruder
cylinder 2 and
the screw 1 and introduced into the cylinder 11 via a baffle 6 and via a slot-
shaped supply
opening 21.
At one end of the extruder cylinder, the extruder screw has an extruder
cylinder head 3, which
is connected to an extruder die 34 so that the material transported through
the extruder die 34
by the screw may be discharged to the baffle 6. Around the extruder cylinder 2
are provided
band heaters 14, which serve to heat and maintain the temperature of the
extruder cylinder
and thus of the material contained in the extruder cylinder.
7
CA 02706985 2012-12-06
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
The extruder die 34 is connected to the baffle 6 via a spherical cap
connection 5, with a
connecting channel in the form of a connecting bore 19 being present in the
baffle 6 so that
the material received from the extruder screw may be transported into the
supply opening 21
of the cylinder 11. The extruder cylinder 2 is pressed by the ball segment
part of the extruder
longitudinal axis of the cylinder 11 or piston 9, so that it has a larger
aperture in the direction
parallel to the longitudinal axis of the piston 9 or the cylinder 11 than
transversely to it or than
the bulk of the corresponding connecting channel in the baffle. Accordingly,
the connecting
channel 19 in the area where it flows into the supply opening 21 is
correspondingly widened
The baffle 6 is permanently connected to the cylinder 11 via a clamping part
7, which is
the outer surface of the piston 9 lies flat against the inner wall of the
cylinder 11 to create a
seal through mutual contact. On the side of the sealing area 23 facing away
from the nozzle 4
is immediately a radial groove or annular groove 18, as is particularly
evident from the cross-
sectional view of Fig. 3. This annular groove 18 is on one hand connected to a
radial bore 15
8
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
the flowable or plasticised material passes into the mouth area 31 of the flow
channel formed
by the concentric bore 24, the radial connecting section 15, the annular
groove 18 and the
axial groove 17. Via the mouth 31, which has multiple branched mouth openings,
the
flowable material passes into the space 20, to be forced out again through the
nozzle 4. To
prevent backflow of the flowable material from the space 20 into the flow
channel 15, 18, 24,
17, at the end of the central bore in the mouth area is provided a check valve
12, which is
accommodated in the piston 9 and is therefore also referred to as the piston
valve.
The check valve 12 may be formed for example by a movable sealing body which
can move
in a distribution chamber of the mouth 31 such that the mouth openings are
opened when the
flowable material flows through the central bore 24 towards the mouth 31,
whereas, under
opposing pressure, the sealing body makes contact with a sealing surface at
the end of the
central bore 24 and closes it. Accordingly, given movement of the piston 9
towards the nozzle
4 and corresponding pressure build/up combined with completely filled space
20, the check
valve or the piston valve 12 prevents backflow of the flowable material
through the mouth 31
and the flow channel 15, 18, 24, 17. Moreover, since the sealing area 23 is
provided in the
area of the piston head, i.e. at that end of the piston which faces the nozzle
4, flowable
material can be prevented from passing counter to the pressing direction into
the space
between the piston 9 and cylinder inner wall. If, on account of minor leaks in
the sealing area
23, smaller quantities of flowable material pass into the space between the
piston outer wall
and cylinder inner wall, they are trapped by the annular groove 18 which is
provided in the
immediate vicinity of the sealing area 23 in the piston 9, and are used again
in the next
injection process.
To prevent backflow of the flowable material from the axial groove 17 counter
to the
injection direction or piston movement 9 in the direction of the nozzle 4, a
second sealing area
is provided, which seals the axial groove 17 against the first sealing area
23.
Should minor amounts of plasticised material pass through this sealing area 30
into the area
30 between the piston outer wall and cylinder inner wall, at that end of
the cylinder 11 which is
opposite the nozzle 4 is provided a scraper part 8, which is arranged in an
annular recess of
the cylinder 11. The scraper part 8 is formed by a circular cylindrical
sleeve, which is
preferably made of metal and particularly brass, and has an oblique end face
16 on the side
9
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
facing the nozzle. The oblique face 16 serves as a scraper surface and is
connected to a
discharge opening 10 which may be referred to as a leakage hole.
Since the inner surface of the sleeve-shaped scraper part 8 lies flat against
the outer surface of
the piston 9, excess flowable material which may be present on the outer
surface of the piston
9 is conveyed by the scraper surface 16 towards the discharge opening 10,
where it can be
collected accordingly. As a result any material to be injected which may
adhere in small
quantities to the piston outer surface is prevented from being discharged
uncontrollably at the
end of the cylinder 11 opposite the nozzle 4.
The scraper part 8 is held by a receiving part 22 in the cylinder 11, to which
the receiving part
22 is fastened by bolts.
About the circumference of the cylinder 11 and at the nozzle 4 and the
cylinder head 13
connecting the nozzle 4 and the cylinder 11 are band heaters 14 for keeping
the corresponding
components and the plasticised material carried therein at a certain
temperature, especially for
heating it so that the corresponding flowability is retained.
Although the present invention has been described in detail using a preferred
embodiment, it
is clear to a person skilled in the art that the invention is not limited to
this embodiment, but
rather that variations are possible in that the characteristics described are
implemented in
different combinations or that individual characteristics are omitted, without
departing from
the scope of the appended claims. In particular, the present invention claims
all combinations
of all presented individual characteristics.
10
CA 02706985 2010-05-28
P2171DE00
Zhafir Plastics Machinery
List of reference numerals
1 Screw
2 Extruder cylinder
3 Extruder cylinder head
4 Nozzle
5 Spherical cap
6 Baffle
7 Clamping part
8 Scraper part
9 Piston
10 Leakage bore / discharge opening
11 Cylinder
12 Piston valve / check valve
13 Cylinder head
14 Band heater
15 Radial bore / radial connecting section
16 Oblique discharge surface / end face / scraper surface
17 Axial groove
18 Radial annular groove / annular groove
19 Connecting bore / connecting channel
20 Space
21 Slot / supply opening
22 Receiving part
23 Piston-sealing surface / first sealing area
24 Centric bore
Piston-sealing surface / second sealing area
31 Mouth
34 Extruder die
30 100 Piston-injection unit
11