Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
HEAT EXCHANGER
FIELD AND BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0001] The present invention relates, in general, to the field of heat
exchangers
and, more particularly, to a heat exchanger having an integral support
structure and
a structural framework for the support thereof.
[0002] The present invention employs the teachings of U.S. Patent No.
6,336,429
to Wiener et al., the text of which is hereby incorporated by reference as
though fully
set forth herein.
[0003] To the extent that explanations of certain terminology or principles of
the
heat exchanger, boiler and/or steam generator arts may be necessary to
understand
the present invention, the reader is referred to Steam/ its -generation and
use, 40th
Edition, Stultz and Kitto, Eds., Copyright 1992, The Babcock & Wilcox
Company,
and to Steam/ its generation and use, 41st Edition, Kitto and Stultz, Eds.,
Copyright
2005, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, the texts of which are hereby incorporated
by reference as though fully set forth herein.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0004] One aspect of the present invention is drawn to a heat exchanger for
transferring heat energy into a working fluid, such as water. The heat
exchanger is
used to transform at least a portion of the water from the liquid phase into
saturated
or superheated steam.
[0005] Vertical steam/water separating devices, disclosed in the
aforementioned
U.S. Patent No. 6,336,429 to Wiener et al., are used to separate the steam
from the
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-2-
steam-water mixture. A pair of such vertical steam/water separators,
structurally
interconnected and arranged as described herein, provides an integral support
structure for the heat exchanger.
[0006] The heat exchanger of the present invention is advantageously comprised
of an arrangement of heat transfer surfaces and fluid conveying conduits
arranged in
a particular fashion to transfer a desired amount of heat energy into the
water. The
heat transfer surfaces are advantageously made of tubes arranged into panels,
and
are provided with inlet and outlet headers as required. As is known to those
skilled
in the art, heat transfer surfaces which convey steam-water mixtures are
commonly
referred to as evaporative or boiler surfaces; heat transfer surfaces which
convey
steam therethrough are commonly referred to as superheating (or reheating,
depending upon the associated steam turbine configuration) surfaces.
Regardless
of the type of heating surface, the sizes of tubes, their material, diameter,
wall
thickness, number and arrangement are based upon temperature and pressure for
service, according to applicable boiler design codes, such as the American
Society
of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section I, or
equivalent other codes as required by law. Required heat transfer
characteristics,
pressure drop, circulation ratios, spot absorption rates, mass flow rates of
the
working fluid within the tubes, etc. are also important parameters which must
be
considered. Depending upon the geographic location where the heat exchanger is
to be installed, applicable seismic loads and design codes are also
considered.
[0007] The heat exchanger is bottom supported from a base which is part of an
arrangement of interconnected rigid members that surrounds the heat exchanger
and forms a structural support framework which, together with the
aforementioned
integral support structure not only provides structural support and rigidity
for the heat
exchanger, but also a means by which the heat exchanger can be picked up and
lifted for placement at a desired location. In the case of an application of
the heat
exchanger as a solar heat energy receiver, the structural support framework
permits
the entire assembly of the heat exchanger and the framework to be assembled on
the ground and then lifted and set upon a tower during installation. The
structural
support framework remains with the heat exchanger, thereby facilitating (if
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-3-
necessary) the removal of the heat exchanger from the tower should it become
desirable to do so.
[0008] In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a heat
exchanger comprising an arrangement of heat transfer surfaces and a pair of
vertical
steam/water separators structurally interconnected to one another and
providing an
integral support structure for at least a portion of the heat transfer
surfaces of the
heat exchanger. The structural interconnection includes upper and lower
structural
members formed of heavy wall pipe and extending between the vertical
steam/water
separators. Each of the heavy wall pipes includes a pair of spaced inner
partition
walls disposed in crosswise fashion to form a central portion therein defining
a
header. The integrally supported portion of the heat transfer surfaces extends
between and is fluidically connected to the headers of the upper and lower
structural
members.
[0009] Each of the vertical steam/water separators includes four coplanar
pedestal feet positioned at the lower end of the steam/water separator, and
arranged
at equally spaced intervals about the outer periphery of the steam/water
separator.
[0010] The heat exchanger includes a structural support framework in the shape
of a rectangular parallelepiped having a top, a bottom and opposing lengthwise
sides
surrounding the heat exchanger for bottom support thereof.
[0011] The bottom of the structural support framework is comprised of four
horizontally extending parallel spaced lateral and longitudinal beams
intersecting one
another to form a grid-like structure which includes a lattice of obliquely-
disposed
web members positioned between intersecting longitudinal and lateral beams.
[0012] Two pairs of lateral braces intersect the inner two of the four
longitudinal
beams of the bottom of the structural support framework to form support bases
for
the vertical steam/water separators. The pedestal feet of the steam/water
separator
are fixedly secured to the respective support base.
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-4-
[0013] Each of the opposing lengthwise sides of the structural support
framework
has two pairs of parallel spaced vertical beams located at opposite ends of
the
structural framework and one pair of parallel spaced longitudinal beams
intersecting
the vertical beams and located at the upper end of each of the opposing sides.
A
lattice of obliquely-disposed web members is positioned between each pair of
vertical beams and the pair of longitudinal beams.
[0014] The top of the structural support framework is comprised of two lateral
beams intersecting the upper one of the pair of parallel spaced beams
extending
along each lengthwise side. The two lateral beams are located above the heat
exchanger and provide a means by which the heat exchanger and the structural
support framework can be lifted for placement at a desired location.
[0015] Another aspect of the present invention is drawn to the combination of
a
heat exchanger and the structural framework used for the support thereof. The
combination comprises an arrangement of heat transfer surfaces and a pair of
vertical steam/water separators structurally interconnected to one another and
providing an integral support structure for at least a portion of the heat
transfer
surfaces. The structural interconnection between the heat exchanger surfaces
and
the pair of vertical steam/water separators is comprised of upper and lower
heavy
wall pipes, each pipe having partitions therein defining a central header. The
integrally supported portion of the heat transfer surfaces extends between and
is
fluidically connected to the headers of the upper and lower heavy wall pipes.
Each
of the steam/water separators includes a plurality of pedestal feet positioned
at the
lower end of the steam/water separator.
[0016] The structural framework part of the combination has a top, a bottom,
and
opposing lengthwise sides surrounding the heat exchanger for bottom support
thereof. The bottom of the structural framework is comprised of four
horizontally
extending parallel spaced lateral and longitudinal beams intersecting one
another to
form a grid-like structure and includes a lattice of obliquely-disposed web
members
positioned between intersecting longitudinal and lateral beams. Two pairs of
parallel
spaced lateral braces intersect the inner two of the four longitudinal beams
at the
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-5-
bottom of the structural framework to form support bases for the vertical
steam/water
separators whose pedestal feet are fixedly secured to their respective support
bases.
Each of the opposing lengthwise sides of the structural framework has two
pairs of
parallel spaced vertical beams located at opposite ends of the structural
framework
and one pair of parallel spaced longitudinal beams intersecting the vertical
beams
and located at the upper end of each of the opposing sides. A lattice of
obliquely-
disposed web members positioned between each pair of vertical beams and the
pair
of longitudinal beams. The top of the structural framework is comprised of two
lateral beams intersecting the upper one of said pair of parallel beams. The
two
lateral beams are located above the heat exchanger and provide a means by
which
the heat exchanger and the structural framework can be lifted for placement at
a
desired location.
[0017] These and other features of the present invention will be better
understood
and its advantages will be more readily appreciated from the following
description,
especially when read with reference to the accompanying drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
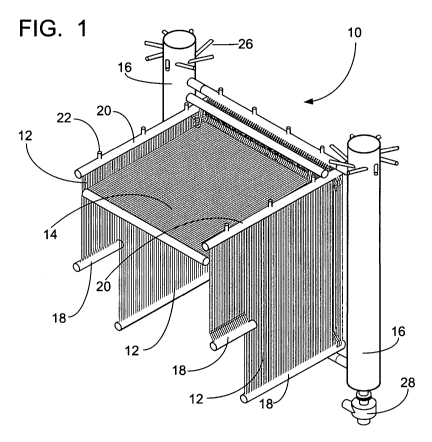
[0018] FIG. 1 is a perspective view of the heat exchanger which is shown, for
clarity, without the structural support framework of the present invention;
[0019] FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view of the heat exchanger
illustrated in
FIG. 1;
[0020] FIG. 3 is a perspective view of the pair of vertical steam/water
separators
structurally interconnected to one another to provide an integral support
structure in
accordance with the present invention; and
[0021] FIG. 4 is a perspective view of the integrally supported heat exchanger
structure of FIG. 3, together with the structural framework used to support
the heat
exchanger structure in accordance with the present invention.
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-6-
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
[0022] Reference will hereinafter be made to the accompanying drawings wherein
like numerals designate the same or functionally similar elements throughout
the
various drawings.
[0023] Referring to FIGS. 1-3, there is shown a heat exchanger 10 according to
the present invention. The heat exchanger 10 has left and right side walls 12,
a roof
portion 14, and a pair of vertical steam/water separators 16 of the type
disclosed in
the aforementioned U.S. Patent No. 6,336,429 to Wiener et al. The vertical
steam/water separators 16 of this type are particularly suited to handle large
transient swings in heat input to the heat exchanger 10 which may, in turn,
cause
large variations in water levels within the steam/water separators 16. The
side walls
12 are comprised of panels of tubes having a welded membrane between adjacent
tubes. Welded membrane tube wall panels are well known to those skilled in the
art
and will thus not be described in detail here; for additional details, the
reader is
referred to the aforementioned Steam texts. The roof portion 14 is also
comprised of
welded membrane tube wall panels. While membrane wall tube panels are
typically
employed in conventional industrial and utility furnace walls to achieve a gas-
tight
construction, the provision of the membrane between adjacent tubes in this
application also provides for structural rigidity of the panels and it is for
that purpose
that the side wall panels 12 and roof portion 14 have a membrane wall
construction.
[0024] If the heat exchanger 10 is used to provide merely saturated steam, the
side walls 12 and roof portion 14 comprise evaporative or boiler heating
surface. If
the heat exchanger 10 is used to provide superheated steam, and as will be
appreciated by those skilled in the art, some of the heating surface will have
to be
evaporative surface and other portions will have to be superheater surface. In
the
embodiment shown in FIG. 1, the side walls 12 are evaporative or boiler
surface, and
may be provided with inlet headers 18 and outlet headers 20. The steam-water
mixture generated in tubes forming the side walls 12 is collected in the
outlet
headers 20 which also serve as a mix point to even out temperature imbalances
which may exist in the steam-water mixture. Stubs 22 on the outlet headers 20
are
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-7-
interconnected via risers (not shown) to stubs 26 on upper portions of each of
the
vertical steam/water separators 16. The vertical steam/water separators 16
operate
in known fashion (see U.S. Patent No. 6,336,429 to Wiener et al.), separating
the
steam from the steam-water mixture. If the heat exchanger 10 is designed for
saturated steam production, steam outlet connections (not shown) from the top
portions of each of the separators 16 convey the steam to its downstream
location
and use. If the heat exchanger 10 is designed to produce superheated steam,
the
steam is conveyed from the separators 16 to superheater surfaces for further
heating
and eventual collection and conveyance to its downstream location and use.
Depending upon the initial steam temperature and pressure, and the desired
outlet
superheated steam temperature desired, the superheater may have to be designed
as a multiple-pass superheater in order to provide adequate mass flux rates
within
the superheater surface tubes, and such concepts are within the scope of the
present invention. Two-pass, four-pass or additional pass designs may be
required,
taking into account the temperatures of not only the tubes in the superheater,
but
also the temperature of the tubes in an adjacent structure, in order to
address
differential thermal expansion concerns. In either case, the water separated
from the
steam-water mixture is conveyed to a lower portion of each of the separators
16,
mixed with make-up feedwater, and conveyed to the evaporative surface to start
the
process over again. In order to facilitate the circulation of the water and
water-steam
mixture throughout the heat exchanger 10, circulation pumps 28 may
advantageously be provided at the lower portion of each of the separators 16
for
pumping the water back to the evaporative surface via supplies (not shown).
[0025] Referring to FIG. 2, there is shown an exploded perspective view of the
heat exchanger illustrated in FIG. 1. This view better illustrates the
relationship
between the side walls 12 and the integral support structure, generally
designated
30, comprised of the pair of vertical steam/water separators 16 structurally
interconnected to one another by means of upper and lower structural members
32.
[0026] Referring to FIG. 3, there is shown a perspective view of the pair of
vertical
steam/water separators 16 structurally interconnected to one another according
to
the present invention which provides the integral support structure 30 for the
heat
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-8-
exchanger 10. The upper and lower structural members 32 are advantageously
comprised of heavy wall pipe, rather than a structural I-beam or WF section,
for
reasons that will become apparent. One end of each member 32 is connected to
one of the vertical steam/water separators, such as by welding. The structural
members 32 do not, in and of themselves, provide any direct fluidic
interconnection
between the separators 16. The heavy wall pipe that makes up each of the
structural members 32 is fitted with inner partition walls 34 forming a
central portion
that comprises a header 36 which performs a fluid collecting/conveying
function. In
addition to providing an integral support structure for the heat exchanger 10,
the
headers 36 which are part of the upper and lower structural members 32, are
interconnected to one another by an arrangement of heating surface 38 which
extends between and is fluidically connected to the upper and lower headers
36.
Typically, the heating surface 38 is up-flowing evaporative surface, comprised
of
tubes. Tube stubs 40 provide connections for risers (not shown) which convey
the
steam-water mixture to the tube stubs 26 on the separators 16 as hereinbefore
described.
[0027] It will be noted that the heating surface 38 extends in between the
headers
36 of the upper and lower structural members 32 while providing a gap or space
42
between distal edges of the heating surface 38 and the outer wall of the
steam/water
separators 16. The side walls 12 extend into this space 42, with the distal
edges of
the heating surface 38 extending adjacent to and in close proximity with the
inside
portions of the side walls 12. However, in order to accommodate differential
thermal
expansion the heating surface 38 is not connected to the side walls 12 in any
rigid
fashion. The side walls 12 would be bottom supported from a base, in a fashion
similar to that described below with respect to the integral support structure
30. The
sidewalls 12 may also be provided with buckstays, not shown, which are well
known
to those skilled in the art as providing rigidity and support for membrane
tube wall
construction.
[0028] Referring to FIG. 4, there is shown a perspective view of a portion of
the
heat exchanger 10 according to the present invention, similar to that
illustrated in
FIG. 1, together with a structural framework 50 which supports the heat
exchanger
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-9-
10. For clarity, there is shown only the integral support structure 30
comprised of the
pair of vertical steam/water separators 16 structurally interconnected to one
another
by means of upper and lower structural members 32.
[0029] The three dimensional structural framework 50 is generally in a shape
of a
rectangular parallelepiped and is defined by the top 51, the bottom 52, and
the
lengthwise sides 55, and includes three sets of flanged beams extending in the
three
mutually orthogonal directions, eight longitudinal beams 58, six lateral beams
56,
and eight vertical beams 54.
[0030] The bottom 52 of the structural framework 50 is comprised of four
parallel
spaced longitudinal beams 58 and four parallel spaced lateral beams 56 which
connectedly intersect one another to form a grid-like structure. A lattice of
obliquely-
disposed web members 60 is positioned between the intersecting longitudinal
and
lateral beams 58 and 56 to structurally reinforce the grid-like structure
forming the
bottom 52 and to stiffen or add rigidity to the structural framework 50.
[0031] The bottom 52 of the structural framework 50 includes a pair of support
bases 53, each being formed by respective pairs of parallel spaced lateral
braces 57
connectedly intersecting the inner pair of longitudinal beams 58. Each of the
steam/water separators 16 includes four pedestal feet 59 located at or near
the
bottom of the steam/water separator. The pedestal feet 59 extend outwardly
from
the steam/water separator wall at a substantially right angle, and are
coplanar and
arranged at equally spaced intervals about the outer periphery of the
steam/water
separator 16. The pedestal feet 59 are each provided with a reinforcing gusset
61
and are fixedly secured to the support base 53.
[0032] Each of the lengthwise sides 55 of the structural framework 50 is
comprised of two pairs of parallel spaced vertical beams 54 located at
opposite ends
of the structural framework 50, and one pair of parallel spaced longitudinal
beams 58
located at the upper end of the sides 55 and connectedly intersecting the
vertical
beams 54. A lattice of obliquely-disposed web members 60 is positioned between
CA 02712027 2010-07-13
WO 2009/091816 PCT/US2009/030978
-10-
each pair of vertical beams 54 and the longitudinal beams 58 to structurally
reinforce
the sides 55 and to stiffen the structural framework 50.
[0033] The top 51 of the structural framework 50 is comprised of two lateral
beams 56 which intersect and are connected to the upper one of each of the
pairs of
longitudinal beams 58 located at the upper end of the lengthwise sides 55. In
addition to reinforcing the top 51 and stiffening the structural framework 50,
the top
lateral beams 56 are generally located over the heat exchanger 10 and provide
a
means by which the heat exchanger 10 and the supporting structural framework
50
can be picked up and lifted for placement at a desired location.
[0034] Although the present invention has been described above with reference
to particular means, materials, and embodiments, it is to be understood that
this
invention may be varied in many ways without departing from the spirit and
scope
thereof, and therefore is not limited to these disclosed particulars but
extends instead
to all equivalents within the scope of the following claims.