Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
DEMANDES OU BREVETS VOLUMINEUX
LA PRESENTE PARTIE DE CETTE DEMANDE OU CE BREVETS
COMPREND PLUS D'UN TOME.
CECI EST LE TOME 1 DE 2
NOTE: Pour les tomes additionels, veillez contacter le Bureau Canadien des
Brevets.
JUMBO APPLICATIONS / PATENTS
THIS SECTION OF THE APPLICATION / PATENT CONTAINS MORE
THAN ONE VOLUME.
THIS IS VOLUME 1 OF 2
NOTE: For additional volumes please contact the Canadian Patent Office.
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
PUMP SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR STORING AND DISPENSING A
PLURALITY OF PRECISELY MEASURED UNIT-DOSES OF IMIQUIMOD CREAM
Field of the Invention
[0001] The subject invention relates to unique storage and dispensing
systems that
include a pump or dispensing package pre-filled with a topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation ("pump systems") and methods for storing and
dispensing a plurality
of precisely measured unit doses of a topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation,
and more particularly to pump systems pre-filled with an imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream and
methods for delivering multiple precisely measured unit doses of an imiquimod
pharmaceutical
cream, and methods for using a controlled delivery pump to store and dispense
a plurality of
precisely measured unit doses of a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation for
use in treating a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, such as,
external genital warts
and/or perianal warts (EGWs), actinic keratosis or actinic keratoses (AK or
AKs) and superficial
basal cell carcinoma (sBCC).
Background
[0002] External genital warts and perianal warts, i.e., condylomata
acuminate, are caused
by infection with human papilloma virus (HPV), the most common sexually
transmitted virus in
the Western world. See, e.g., Lyttle PH.: Surveillance report: disease trends
at New Zealand
sexually transmitted disease clinics 1977-1993. Genitourin Med., 70:329-335
(1994); Mayeaux
EJ, Harper MB, Barksdale W, Pope JB.: Noncervical human papillomavirus genital
infections.
Am Fam Physician., 52:1137-1146 (1995); and Shah KV, Howley PM.:
Papillomaviruses. In:
Fields, BN, Knipe DM, ed Fields Virology. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Raven Press;
(2)59:1651-
1666 (1990). Approximately 1% of the sexually active population between 15 and
49 years of
age in the United States is estimated to have external genital warts. See,
e.g., Koutsky L.:
Epidemiology of human papillomavirus infection. Epidemiol Rev., 10:122-163
(1998); and
Koutsky L.: Epidemiology of genital human papillomavirus infection. Am J Med.,
102(5A):3-8
(1997). Most external genital warts are associated with HPV types 6 and 11.
See, e.g., Phelps W,
Alexander KA.: Antiviral therapy for human papillomaviruses: rationale and
prospects. Ann
Intern Med., 123:368-382 (1995). HPV types 6 and 11 are typically labeled as
low risk because
infection with these types has low oncogenic potential and usually results in
the formation of
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
condylomata and low-grade precancerous lesions. See, e.g., Gearhart, P.A. and
Randall, T.C.:
Human Papillomavirus, emedicine, pages 1-33,
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/219110
(Updated: March 8, 2010); and Fact Sheet: Human Papillomaviruses and Cancer:
Questions and
Answers, National Cancer Institute, pages.
1-11,
www.cancer.govicancertopics/factsheet/RiskHPV (Reviewed February 14, 2008).
[0003]
Specific antiviral therapy for the treatment of external genital warts and
perianal
warts is lacking, but drug and other therapies have been used. Ablative
treatment modalities
include procedures such as surgical excision, laser therapy, and cryotherapy.
Other approaches
include topical treatments, such as acetic acid, podophylline,
podophyllotoxin, and 5-fluorouracil,
which are cytodestructive, and sinecatechins, whose mechanism of action is
unknown. Each of
these therapies have disadvantages such as inconvenient regimens, pain,
burning associated with
the therapy, scarring, itching and/or high recurrence rates.
[0004]
On February 27, 1997, imiquimod 5% cream was approved for the very first time
by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of external
genital and
perianal warts, i.e., condyloma acuminate (EGW or EGWs), in patients 12 years
or older. See
Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII).
Imiquimod, an
immune response modifier that stimulates the innate and adaptive immune
response, has been
demonstrated to be an effective and safe treatment for external genital warts
and perianal warts.
Stimulation of the immune response has been shown to decrease HPV viral load,
Kreuter A,
Brockmeyer NH, Weissenborn SJ, et al.: 5% Imiquimod suppositories decrease the
DNA load of
intra-anal HPV types 6 and 11 in HIV-infected men after surgical ablation of
condylomata
acuminata [letter]. Arch Dermatol.; 142(2):243-4 (February, 2006), and thus
may decrease the
recurrence rate of visible warts, although observed rates after treatments do
vary.
[0005]
In the treatment of EGWs diagnosed in adults, the approved dosing regimen for
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is 3 times per week, for up to 16 weeks of
treatment. Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream should be applied 3 times per week to external
genital/perianal warts.
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream treatment should continue until there is total
clearance of the
genital/perianal warts or for a maximum of 16 weeks. Examples of 3 times per
week application
schedules are: Monday, Wednesday, Friday or Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday.
Aldara
2
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
(imiquimod) 5% cream should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left
on the skin for 6
-10 hours, after which time the cream should be removed by washing the area
with mild soap and
water. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to
maximize the
benefit of Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream therapy. It is recommended that
patients wash their
hands before and after applying Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream.
[0006] A study in 22 patients with genital/perianal warts comparing
Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream and vehicle shows that Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream
induces mRNA
encoding cytokines including interferon-a at the treatment site. In addition,
HPVL1 mRNA and
HPV DNA are significantly decreased following treatment. However, the clinical
relevance of
these findings is unknown.
[0007] A thin layer of Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream should be applied to
the wart area
and rubbed in until the cream is no longer visible. The application site
should not be occluded.
Following the treatment period, the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream should be
removed by
washing the treated area with mild soap and water. Local skin reactions at the
treatment site are
common. A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the
patient's discomfort or
severity caused by the treatment-related local skin reactions. Treatment may
resume once the
reactions subside. Non-occlusive dressings such as cotton gauze or cotton
underwear may be
used in the management of skin reactions. Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is
currently packaged
in single-use packets or sachets which contain sufficient cream to cover a
wart area of up to about
20 cm2. Use of excessive amounts of cream and passive transfer of the cream
should be avoided.
[0008] Actinic keratosis is a precancerous (premalignant) skin disorder
caused by or
associated with chronic exposure to radiant energy, such as sunlight. Actinic
keratosis lesions
(AKs) are small, red, rough spots or lesions occurring on sun exposed areas of
the skin. Actinic
keratosis lesions possess many of the same cellular changes observed in a skin
cancer called
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Research shows that a mutated version of the
p53 gene is found
in sun-damaged cells in the body and is present in more than about 90% of
people who have AKs
and SCC. Although most actinic keratosis lesions do not actually become
cancerous, some AKs
can become malignant.
3
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[0009] It is believed that actinic keratosis develops in skin cells
called "keratinocytes",
which are the cells that constitute about 90% of the epidermis, the outermost
layer of skin.
Chronic sun exposure, over time, generates mutations in these cells and causes
the cells to change
in size, shape, the way they are organized, and the way they behave. In
addition, the cellular
damage can even extend to the dermis, the layer of skin beneath the epidermis.
[00010] Actinic keratosis lesions generally measure in size between about
2 to about 6
millimeters in diameter. AK lesions can range in color from skin-toned to
reddish and often have
a white scale on top. On occasion, AK lesions will form into the shape of
animal horns. When
this occurs, the AKs are known as "cutaneous horns."
[00011] People who are at higher risk for developing actinic keratosis
tend to be fair-
skinned and spend significant time outdoors, e.g., at work or at play, over
the course of many
years. AKs usually develop on those areas of the body that have been
constantly exposed to the
sun for years. Additionally, the skin often becomes wrinkled, mottled, and
discolored from
chronic sun exposure. Common locations for AKs include the face, ears, lips,
balding scalp, back
of the neck, upper chest, the tops of the hands and forearms. When AKs develop
on the lips, the
condition is known as actinic cheilitis. Actinic cheilitis can be
characterized by a diffuse scaling
on the lower lip that cracks and dries. In some cases, the lips will have a
whitish discoloration on
the thickened lip.
[00012] Actinic keratosis is generally more common after age 40, because
actinic keratosis
takes years to develop. However, even younger adults may develop actinic
keratosis when living
in geographic areas that are exposed to high-intensity sunlight year round,
such as Florida and
Southern California.
[00013] Actinic keratosis has become a significant health care issue in
the United States of
America. It is estimated that over 20 million Americans suffer from actinic
keratoses, and that
that number continues to grow. In fact, actinic keratosis is so common today
that treatment for
actinic keratosis ranks as one of the most frequent reasons people consult
dermatologists.
4
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00014] Once an immunocompetent adult is diagnosed with clinically visible
AKs, a
variety of treatment options are currently available. These options include
physically removing
the AKs by (1) freezing them with liquid nitrogen, (2) using a laser to burn
the AKs, (3) scraping
the AKs off, or (4) using topical creams to treat the AKs. One such cream that
can be applied to
the skin for the treatment of AKs is Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream.
[00015] On March 2, 2004, Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream was approved by the
FDA,
under section 505(b) of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, for the
treatment of clinically
typical, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses on the face and
scalp in
immunocompetent adults. Imiquimod, an immune response modifier that stimulates
the innate
and adaptive immune response, has been demonstrated to be an effective and
safe treatment for
AKs. Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream works from within by activating the adult's
own immune
system to treat disease.
[00016] In the treatment of adults diagnosed with actinic keratosis, the
approved dosing
regimen for Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is 2 times per week, for a full 16
weeks to a defined
treatment area on the face or scalp (but not both concurrently). See Aldara
Package Insert
(Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII).
[00017] According to the approved Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised:
March 2007
(Attachment VIII), the treatment area is defined as one contiguous area of up
to approximately 25
cm2 (e.g., 5 cm x 5 cm) on the face (e.g. forehead or one cheek) or on the
scalp, and examples of
2 times per week application schedules are Monday and Thursday, or Tuesday and
Friday. The
Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII) further
instructs that
the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream should be applied to the entire treatment
area and rubbed in
until the cream is no longer visible. The Aldara Package Insert (Label)
Revised: March 2007
(Attachment VIII) cautions that no more than one packet of Aldara (imiquimod)
5% cream
should be applied to the contiguous treatment area at each application, and
the Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left
on the skin for
approximately 8 hours, after which time the cream should be removed by washing
the area with
mild soap and water.
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00018] The Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment
VIII)
further advises that prescribers should demonstrate the proper application
technique to maximize
the benefit of Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream therapy.
[00019] The Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment
VIII) also
recommends that patients should wash their hands before and after applying the
Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream as well as the treatment area with mild soap and water
and allow the area
to dry thoroughly (at least 10 minutes) before applying Aldara (imiquimod) 5%
cream.
[00020] The Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment
VIII)
further cautions that contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be
avoided and warns that
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
[00021] Because the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is currently packaged in
single-use
packets, with 12 packets supplied per box, the Aldara Package Insert (Label)
Revised: March
2007 (Attachment VIII) instructs that patients should be prescribed no more
than 3 boxes (36
packets) for the 16-week treatment period, and that unused packets should be
discarded. The
Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII) clearly
warns that
partially-used packets should be discarded and not reused.
[00022] Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is also FDA approved to treat
superficial basal
cell carcinoma (sBCC), a form of skin cancer. See, e.g., Aldara Package
Insert (Label)
Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII).
[00023] Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body. Skin cancer, however,
is most
commonly diagnosed on skin that, like with AKs, has been in constant exposure
to intense
sunlight, especially during childhood or young adulthood. According to the
American Cancer
Society, the most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma (BCC),
affecting about
800,000-900,000 Americans each year.
6
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00024] BCC develops within the basal cells, which are found within the
basal layer of the
epidermis or the top layer of the skin. Basal cells are typically small and
round and continually
divide to produce new skin cells and replace old ones.
[00025] BCC is typically a slow growing disease which can metastasize to
other areas of
the body including the lymph nodes, bone or other tissues beneath the skin if
left untreated. Basal
cell carcinoma occurs most often on sun exposed areas of the skin such as the
head or neck.
Although basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads to other parts of the body, it
may cause local tissue
destruction and it can be very destructive and disfiguring.
[00026] There are several types of BCC, including nodular basal cell
carcinoma,
superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC), small basal cell carcinoma,
morpheaform basal cell
carcinoma, infiltrating basal cell carcinoma, pigmented basal cell carcinoma,
micronodular basal
cell carcinoma and cystic basal cell carcinoma, each of which manifests a
different pattern of
behavior.
[00027] If allowed to progress without treatment, BCC can cause clinically
significant
morbidity. Because BCC most commonly affects the head and neck, cosmetic
disfigurement is
common. In addition, if there is orbital involvement, loss of vision or even
loss of an eye may
occur. BCC lesions are prone to ulceration and infection and, if there is
perineural spread or deep
and extensive skin invasion, nerve function can be lost. Death from BCC,
however, is
uncommon.
[00028] A history of chronic recreational or occupational sun exposure is
typically
observed in patients diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma. Common symptoms
presented at
diagnosis include lesions or sores that (a) won't heal, (b) vary in duration,
and (c) often bleed
when exposed to mild trauma, such as towel washing or drying.
[00029] Because there are several subtypes of BCC, it is critical for the
health care
provider to recognize and distinguish between the various subtypes in order to
prescribe
appropriate therapy. For example, aggressive therapy is often necessary for
variants such as
micronodular, infiltrating, morpheaform and superficial basal cell carcinoma.
7
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00030] Superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) is one subtype of basal
cell carcinoma.
sBCC is the most common form of skin cancer, but it is readily treatable if
identified and treated
early. sBCC is generally diagnosed by a healthcare provider after biopsy.
Typically, sBCC
slowly progresses and clinically appears as erythematous eruptions or lesions.
sBCC lesions may
appear as new growths on the skin, as open sores that fail to heal, or as
changes in appearance of
an old growth on the skin. Generally, however, the sBCC lesions are usually
not painful and may
have different shapes and colors. sBCC lesions often present as pink to red-
brown scaly patches
or papules with a whitish scale. The sBCC lesions appear multicentric wherein
clinically normal
skin and clinically involved skin often intervene or commingle. The sBCC
patches or papules
may mimic eczema or psoriasis. sBCC skin changes to look for include the
following:
= A small, smooth, shiny lump that may be pale or waxy;
= A firm, red lump;
= A sore or lump that bleeds or is covered by a scab; and/or
= A red or brown patch that is rough or scaly and may itch or become
tender.
[00031] sBCC is usually treated by surgical removal.
[00032] On July 14, 2004, the FDA approved the use of Aldara (imiquimod)
5% cream
under biopsy-confirmed, primary superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) in
inununocompetent
adults, with a maximum tumor diameter of 2.0 cm, located on the trunk
(excluding anogenital
skin), neck, or extremities (excluding hands and feet), only when surgical
methods are medically
less appropriate and patient follow-up can be reasonably assured. According to
the Aldara
Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment VIII), the histological
diagnosis of
sBCC should be established prior to treatment with Aldara (imiquimod) 5%
cream, because
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream at that time was not approved for the treatment
of other types of
basal cell carcinomas, such as nodular and morpheaform (fibrosing or
sclerosing) types.
[00033] In the treatment of sBCC diagnosed in adults, the approved dosing
regimen for
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks to a
biopsy-confirmed
superficial basal cell carcinoma. See Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised:
March 2007. An
example of a 5 times per week application schedule is to apply Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream,
8
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
once per day, Monday through Friday, for six full weeks. Aldara (imiquimod)
5% cream
should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for
approximately 8 hours,
after which time the cream should be removed by washing the area with mild
soap and water.
[00034] According to the Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March
2007, the
prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the
benefit of
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream therapy.
[00035] It is also recommended in the Aldara Package Insert (Label)
Revised: March
2007 that patients should wash their hands before and after applying Aldara
(imiquimod) 5%
cream and that the patient should wash the treatment area with mild soap and
water and allow the
area to dry thoroughly before applying the cream.
[00036] According to the Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March
2007, the target
sBCC tumor should have a maximum diameter of 2 cm and be located on the trunk
(excluding
anogenital skin), neck, or extremities (excluding hands and feet). Also
according to the Aldara
Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007, the treatment area should include
a 1 cm margin of
skin around the tumor, and that sufficient cream should be applied to cover
the treatment area,
including 1 centimeter of skin surrounding the tumor. The Aldara Package
Insert (Label)
Revised: March 2007 further instructs that the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream
should be rubbed
into the treatment area until the cream is no longer visible.
[00037] As reported in the Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March
2007, the
amount of Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream that should be used to treat sBCC is
reproduced in
Table 1 as follows.
Table 1. Amount of Aldara Cream to Use for sBCC
Target Tumor Diameter Size of Cream Droplet to be
Approximate Amount of
Used (diameter) Aldara to be Used
0.5 to < 1.0 cm 4 mm 10 mg
. 1.0 to < 1.5 cm 5 mm 25 mg
. 1.5 to 2.0 cm 7 mm 40 mg
9
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00038] According to the Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March
2007, contact
with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided and warns that Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream
is not for oral, ophthalmic or intravaginal use.
[00039] Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream is packaged in single-use packets or
sachets, with
12 packets supplied per box. Patients should be prescribed no more than 3
boxes (36 packets) for
the 6-week treatment period. Unused packets and partially-used packets should
be discarded and
not reused. See Aldara Package Insert (Label) Revised: March 2007 (Attachment
VIII).
[00040] Thus, to date, the FDA has approved imiquimod 5% cream,
commercially
available under the brand name Aldara , to treat dermal and/or mucosal-
associated conditions,
namely, the topical treatment of: (1) external genital and perianal warts,
i.e., condyloma
acuminate, in patients 12 years or older,; (2) clinically typical,
nonhyperkeratotic,
nonhypertrophic AKs on the face or scalp in immunocompetent adults; and (3)
biopsy-confirmed,
primary sBCC in immunocompetent adults.
[00041] More recently, lower dosage strength formulations of imiquimod
cream have been
developed for use in effectively treating AKs and EGWs, which contain
imiquimod in an amount
by weight of between about 1% to about 4.25%, and preferably about 2.5% or
about 3.75%. In
conjunction with these lower dosage strength formulations, the treatment
regimens for AKs and
EGW have been uniquely shortened and simplified. These reduced dosage strength
formulations
and modified treatment regimens are disclosed in (1) U.S. Patent Application
No. 12/636,613, (2)
U.S. Patent Application No. 12/771,076, (3) PCT Publication No.
WO/2010/080345, (4) PCT
International Application No. PCT/US2009/067759, (5) PCT International
Application No.
PCT/US2010/33245, (6) Canadian Patent No. 2,649,893, issued on August 3, 2010
and entitled
"Lower Dosage Strength Imiquimod Formulations and Short Dosing Regimens for
treating
Actinic Keratosis", (7) the Zyclara Package Insert (Label) (Attachment IX)
for AK treatment
with Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream, (8) the proposed Zyclara Package
Insert (Label)
(Attachment X) submitted to the FDA for EGW treatment with Zyclara
(imiquimod) 3.75%
cream, (9) the ZyclaraiD Canada Product Monograph (Attachment XI) for AK
treatment with
Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream, (10) the proposed Zyclara Canada Product
Monograph
(Attachment XII) submitted to Health Canada for EGW treatment with Zyclara
(imiquimod)
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
3.75% cream, (11) the proposed Zyclarag Package Insert (Label) (Attachment
XIII) for
submission to the FDA for AK treatment with a pump pre-filled with Zyclarag
(imiquimod)
3.75%, (12) the proposed Zyclarag Canada Product Monograph (Attachment XIV)
for
submission to Health Canada for AK treatment with a pump pre-filled with
Zyclarag
(imiquimod) 3.75%, and (13) the draft Zyclarag Package Insert (Label)
(Attachment XV) for
submission to the FDA for AK treatment with a pump pre-filled with Zyclarag
(imiquimod)
2.5% cream.
100042] As discussed in U.S. Patent Application, Serial No. 12/771,076,
and PCT
International Application No. PCT/US2010/33245, a patient diagnosed with EGW
can apply an
effective amount of a lower strength formulation of imiquimod cream, such as a
2.5% or a 3.75%
w/w formulation, to the wart area once a day for up to 8 weeks to achieve at
least partial, if not
complete, clearance of the wart.
[00043] Results from a Phase III program evaluating imiquimod 3.75% and
2.5% creams
for the treatment of EGW, applied once daily for up to 8 weeks, demonstrated
that both dosage
strengths were well-tolerated and more efficacious than placebo. According to
investigators
conducting the study, strong efficacy results with the 3.75% unique
formulation along with an
enhanced safety profile were observed. More specifically, of those who
achieved initial complete
clearance and entered the 12-week follow-up, complete clearance was sustained
in about 69.6%
of the subjects on Zyclarat? (imiquimod) 3.75% cream. As to the safety
profile, a low incidence
of treatment-related adverse events such as itching (2.5%), burning (5.8%) or
pain (6.8%) at the
application sites were observed, and no treatment-related reported systemic
adverse events of
headache or flu-like symptoms were observed. These surprising data were
included in a New
Drug Application (NDA) accepted for review by the FDA for the use of Zyclarag
(imiquimod)
3.75% cream in an eight-week treatment regimen for the treatment of EGW.
[00044] With respect to AK treatment, the FDA, on March 30, 2010, approved
a topical
3.75% imiquimod pharmaceutical cream, commercially available under the brand
name
Zyclarag, to treat clinically visible or palpable actinic keratosis lesions
(AKs), of the full face or
balding scalp in immunocompetent adults. This newly approved dosing regimen
with Zyclarag
(imiquimod) 3.75% cream to treat AKs is a novel 6-week treatment regimen
involving three
11
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
cycles, that are equal in duration. In the first cycle of the 6-week treatment
regimen, the
Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream is applied daily for two weeks to the
targeted area, i.e., the
full face or balding scalp diagnosed with AKs. In the second cycle of the 6-
week treatment
regimen designated as a rest period cycle, the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75%
cream is not applied
to the targeted area. In the third or final cycle of the 6-week treatment
regimen, the Zyclara
(imiquimod) 3.75% cream is again applied daily for two weeks to the targeted
area. This unique
6-week treatment regimen to treat AKs with Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream is
referred to as
a "2-week x 2-week x 2-week" or simply a "2 x 2 x 2" treatment regimen. See
Zyclara Package
Insert (Label) (Attachment IX) attached hereto. See also the proposed Zyclara
Package Insert
(Label) for Zyc1ara0 (imiquimod) 2.5% cream to treat AKs in accordance with
the 2 x 2 x 2"
treatment cycle (Attachment XV).
[00045] Alternatively, a unique 9-week treatment regimen may be employed
to treat AKs
with Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream or Zyclara (imiquimod) 2.5% cream,
wherein the 9
week treatment regimen involves three cycles as follows: "3-week x 3-week x 3-
week" or simply
a "3 x 3 x 3" treatment regimen. Like with the 2 x 2 x 2 treatment regimen,
the Zyclara cream
is applied daily to the targeted or treatment area in the first and third
cycles, i.e., applied daily
during the first and last 3-week cycles. However, during the second or middle
3-week cycle, it
too is a rest period wherein no Zyclara cream is applied during the second
cycle.
[00046] One of the unique benefits associated with this new and improved
treatment
regimen, the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream serendipitously treats sub-
clinical AKs (not
clinically visible ¨ not initially detected) located in the targeted treatment
area at the same time of
treatment of clinically visible AKs. Because the Zyclara ill (imiquimod) 3.75%
cream is applied
to the "entire" face or "entire" balding scalp diagnosed with clinically
visible AKs, unlike with
current Aldara treatment, the sub-clinical AKs within such treatment area are
simultaneously
treated with the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream during this "2 x 2 x 2"
treatment regimen of
the clinically visible AKs. These previously unseen AKs, that could appear
during treatment,
may therefore clear before they have a chance to develop further as a result
of this unique "2 x 2
x 2" treatment regimen with Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream.
12
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00047] The drug imiquimod, contained in both Aldara and Zyclara , is an
immune
response modifier. Chemically, imiquimod is known as 1-(2-methylpropy1)-1H-
imidazo [4,5-
c]quinolin-4- amine or 1 -isobuty1-1H-imidazo [4,5-c]-quinolin-4-amine.
Imiquimod has a
molecular formula of C141116N4 and a molecular weight of 240.3. The chemical
structural
formula for imiquimod is as follows:
N H7
113
CH .3.
[00048] Common to each of the FDA-approved treatments with imiquimod for
treating
EGWs, AKs and sBCC, the correct amount of cream or a specific unit dose to be
applied each
time by the patient is required for effective therapy. Also common to each of
such FDA-
approved treatments with imiquimod, is the inconvenient and imprecise use of
single-use packets
or sachets to apply the topical imiquimod pharmaceutical creams to the
treatment areas.
[00049] For example, if the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream or Zyclara
(imiquimod)
3.75% cream is applied too thickly or generously, the over dosage can
exacerbate unwanted site
reactions or local skin reactions, such as erosions or ulcerations, causing
pain or dysfunction (e.g.,
of the foreskin or urethra), and cause undesirable systemic absorption of the
imiquimod leading to
flu-like symptoms and headaches. Moreover, if the patient is not careful, the
patient will
inadvertently apply residual Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream or Zyclara
(imiquimod) 3.75%
cream to other areas of the body compounding over dosage issues that can
further exacerbate the
unwanted side effects.
[00050] If, however, too little imiquimod cream is applied to the targeted
areas, the patient
may not achieve the maximum level or even an effective level of therapeutic
benefit.
[00051] Also common to each of the FDA-approved treatments with imiquimod
for
treating EGW, AK and sBCC, the pharmaceutical concentration and stability of
the imiquimod
13
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
formulation provided to the patient must be maintained throughout the duration
of the treatment,
which could be for as long as 16 weeks when treating EGWs and AKs with Aldara
(imiquimod)
5% cream or for up to 8 weeks when treating EGWs with Zyclara iD 3.75%
(imiquimod) cream or
for up to 6 weeks when treating sBCC with Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream. Thus,
the storage
devices should not adversely impact the stability, uniformity, dosing
concentration or dosing
technique of the pre-filled topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation.
[00052] Each gram of Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream contains 50 mg of
imiquimod and
each gram of the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream contains 37.5 mg of
imiquimod. The
Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream and the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream are each
formulated in an off-white oil-in-water vanishing cream base consisting of
isostearic acid, cetyl
alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, polysorbate 60, sorbitan
monostearate, glycerin,
xanthan gum, purified water, benzyl alcohol, methylparaben, and propylparaben.
The Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream is packaged in single-use packets or sachets, each
containing 250 mg of
cream, equivalent to 12.5 mg of imiquimod. The Zyclaraf.? (imiquimod) 3.75%
cream is
packaged in single-use packets or sachets, each containing 250 mg of cream,
equivalent to 9.375
mg of imiquimod.
[00053] Unfortunately, single-use packets or sachets pre-filled with an
imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream are not without drawback. There are several disadvantages
associated with
providing an imiquimod pharmaceutical cream to a patient in a single-use
packet or sachet.
Single-use packets or sachets pre-filled with a topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream are, for
example, notoriously messy, difficult and clumsy to use, and more importantly
notably imprecise.
These known drawbacks can lead to needless product waste, overdosing,
inadequate dosing,
failed compliance, contamination and/or passive (unintended) transfer to other
areas of the
patients' bodies, such as the eyes, ears, nose, mouth and vagina.
[00054] To underscore these drawbacks, patients often fail to apply the
appropriate dosage
amount or to ensure that all of the imiquimod cream is squeezed out of the
single-use packet or
sachet during application to the treatment area. Consequently, patients are
frequently under-
dosed or over-dosed, which can lead to poor patient compliance.
14
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00055] This problem is recognized in the FDA-approved Labels and Health
Canada-
approved Labels for both the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream and the Zyclaraii)
(imiquimod)
3.75% cream, as well as in the proposed FDA Labels and Health Canada Labels
for the Zyclara
(imiquimod) 3.75% cream and in the draft FDA-Label for Zyclara (imiquimod)
2.5% cream.
See, for example, Attachments VIII and XV, respectively. In each of the FDA-
approved and
FDA-proposed Labels and in each of the Health Canada-approved and Health
Canada-proposed
Labels, the prescriber is clearly instructed to demonstrate the proper
application technique for the
Aldara8 (imiquimod) 5% cream, the Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream and the
Zyclara
(imiquimod) 2.5% cream, respectively, to the patients to minimize or avoid
these drawbacks.
Thus, dosing inconsistencies and product waste associated with single-use
packets or sachets pre-
filled with a topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream are problematic, common
and cause for
concern.
[00056] Another drawback associated with single-use packets or sachets pre-
filled with a
topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream concerns excessive contact with and
improper
application technique of the dispensed imiquimod pharmaceutical creams from
the single-use
packets or sachets by the patients. Because imiquimod is an immune response
modifier, minimal
patient contact and proper application technique is important to avoid
imiquimod cream
contamination, imprecise dosing, product waste, passive transfer to other
parts of the patient's
body that are outside of the treatment area, such as the eyes, ears, nose,
mouth and vagina. These
problems are also recognized in each of the FDA-approved, Health Canada-
approved and
proposed Labels wherein each Label (a) instructs the patients to thoroughly
wash their hands
"before" and "after" imiquimod cream application, (b) cautions that topical
imiquimod creams
contact with eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided, and (c) warns that
topical imiquimod
creams are not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. See Attachments VIII-
XV.
[00057] In yet another drawback, single-use packets or sachets pre-filled
with a topical
imiquimod pharmaceutical cream can be very difficult and cumbersome to use,
especially when
elderly patients are involved. Opening a single-use packet or sachet pre-
filled with a topical
imiquimod cream to dispense the imiquimod cream to "only" the targeted area
without excessive
handling or passive transfer can in some instances present real application
technique challenge to
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
those patients inflicted with, for example, limited dexterity, crippling
arthritis, vision loss and/or
visual acuity loss, which are commonly observed in elderly patients.
[00058] In still another drawback, needless product waste often occurs
with single-use
packets or sachets pre-filled with a topical imiquimod cream. Clear
instruction to patients
provides that undispensed imiquimod cream and unopened individual packets or
sachets pre-
filled with a topical imiquimod cream must be discarded. This particular
drawback is highlighted
in all Labels, the FDA-approved and proposed Labels and the Health Canada
approved and
proposed Labels for Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream and Zyclara (imiquimod)
3.75% cream,
respectively. As stated above, and according to such Labels, unopened and
partially used single-
use packets or sachets pre-filled with a topical imiquimod cream must be
discarded and not
reused. See Attachments VIII-XII. See also Attachments XIII-XV.
[00059] In yet another drawback associated with single-use packets or
sachets pre-filled
with a topical imiquimod cream, the single use packets or sachets can be
easily lost or misplaced
due to the fact that several single-use packets or sachets must be purchased
to complete a full
course of therapy. This drawback and inconvenience can cause further product
waste and
needless elevated treatment costs due to necessary product replacement. More
seriously, this
drawback and inconvenience can lead to failed patient compliance and
ineffective imiquimod
therapy.
[00060] In still another drawback associated with such single-use packets
or sachets,
imiquimod cream degradants may develop over time as a result of storage in the
single-use
packets or sachets. This drawback can cause an adverse effect on overall
efficacy and/or stability
of the imiquimod cream formulations packaged within the single-use packets or
sachets.
[00061] Thus, given the numerous drawbacks associated with single-use
imiquimod cream
packets or sachets, there is a real need for a simple, safe, clean, easy-to-
use, compact, reliable and
all-in-one storage system for dispensing topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical
formulations that: (i) can dispense a controlled and precise amount of
imiquimod cream each and
every time the topical imiquimod formulation is applied to a treatment area,
(ii) is easy and
convenient for any patient, young or old, to use; (iii) improves imiquimod
therapy compliance
16
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
and effectiveness, (iv) provides the same unit dose, such as approximately 250
mg of imiquimod
formulation, per each actuation, i.e., a reproducible dose amount, so that an
effective dose is
administered each and every time; (v) does not interfere with or hinder
imiquimod application
technique, (vi) minimizes if not eliminates product waste and product loss,
(vii) minimizes if not
eliminates excessive patient contact to avoid passive transfer; (viii)
minimizes and/or prevents
degradant formation during imiquimod formulation storage; and (ix) is
compatible for use with
topical semi-solid imiquimod formulations, for example, topical 2.5%, 3.75%
and 5% weight to
weight imiquimod creams, for treating dermal and/or mucosal-associated
conditions, such as
external genital warts, perianal warts, actinic keratoses and superficial
basal cell carcinoma.
Summary of the Invention
[00062] The present invention overcomes certain of the above-mentioned
problems and
drawbacks of the present state of the art of topical imiquimod therapy using
single-use packets or
sachets pre-filled with an imiquimod pharmaceutical cream through the
development of a novel
and unique storage and dispensing system that includes a pump or dispensing
package pre-filled
with a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation (hereinafter, a
"pump system"),
preferably a topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream, in a selected dosage
strength for
dispensing a plurality of precisely measured unit-doses of the imiquimod
formulation over pump
life, in which each precisely measured unit dose dispensed is consistent in
uniformity and
amount, for effectively treating dermal and/or mucosal-associated conditions,
such as external
genital warts or perianal warts (EGWs), actinic keratosis or actinic keratoses
(AK or AKs) or
superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC).
[00063] Uniquely, the novel pump systems of the present invention are
clean and sanitary,
safe and simple and easy to use. In addition, the novel and unique pump
systems of the present
invention are compact (hand held) and easy to store, they are reliable, they
minimize product
waste, and they improve application technique of the dispensed topical semi-
solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulations when treating dermal and/or mucosal-associated
conditions, such as
EGWs, AKs or sBCC.
[00064] In view of these and other novel and unique features of the pump
systems of the
present invention, it is believed that the effectiveness and benefits of
topical imiquimod therapy
17
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
can now be maximized and that certain if not all drawbacks associated with the
use of single-use
packets or sachets to deliver topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream can now
be minimized if
not eliminated.
[00065] The unique pump systems of the present invention include, inter
alia, a dispensing
package that has a tubular main body portion and a manually-operated airless
pumping device
mounted on the main body portion. The main body portion of the dispensing
package defines a
fluid storage chamber. The airless pumping device defines a dispensing duct
which terminates in
a self-closing discharge orifice. In alternative embodiments, the airless
pumping device can
include a cap or cover for sealing or covering the discharge orifice. The cap
or cover can be
operated automatically or manually.
[00066] The pump system of the present invention further includes a
topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, such as a topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream
formulation, which is disposed at least partially within the fluid storage
chamber defined in the
main body portion of the dispensing package. The system is constructed such
that manual
operation of the airless pumping device causes a portion of the imiquimod
cream to be withdrawn
from within the fluid storage chamber into the dispensing duct thereby causing
the self-closing
discharge orifice to open and to dispense, per actuation, a predefined,
uniform and precisely
measured unit-dose amount of a topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream
formulation from the
dispensing package.
[00067] Thus, the novel pump systems of the present invention now afford
patients with
the unique advantage of applying a consistent, precisely measured and uniform
unit-dose of a
topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation from a clean, safe,
easy and simple to
use, compact and reliable pump system to a treatment area per each
application, so that
application technique and patient compliance are improved and the
effectiveness and benefits of
topical imiquimod therapy are maximized, while minimizing (a) imprecise or
inconsistent dosing
amounts, i.e., under-dosing or over-dosing, (b) unwanted passive transfer of
the dispensed topical
imiquimod cream due to improper handling of the imiquimod cream and poor
application
technique, (c) imiquimod cream waste, and (d) unused product and/or product
loss, each of which
18
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
can contribute to poor patient compliance and less effective, if not
ineffective, topical imiquimod
therapy.
[00068] Preferably, a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation contains
imiquimod in an amount by weight of between about 1% and about 10% w/w and
more
preferably a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation contains
imiquimod in an
amount by weight of between about 1% and about 5%. Even more preferably, the
topical semi-
solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations can contain imiquimod in an amount
by weight of
between about 1% and 4.25% w/w, and most preferably, the topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulations can contain imiquimod in an amount by weight of
about 2.5%, about
3.75% or about 5%.
[00069] In a preferred embodiment, the fluid storage chamber formed in the
main body
portion of the dispensing device is adapted and configured for storing about
15 grams of a topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, namely, a topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical
cream formulation, e.g., Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream, Zyclara (imiquimod)
3.75% cream or
a 2.5% imiquimod pharmaceutical cream described herein. In alternative
constructions, the fluid
storage chamber can be adapted and configured for storing about 7.5 grams of a
topical semi-
solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, such as a topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream
formulation, namely, Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream, Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75%
cream or a
2.5% imiquimod pharmaceutical cream described herein.
[00070] It should be understood by those versed in this art that the pump
systems of the
present invention can be pre-filled with any suitable topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation, such as a cream, an ointment, a lotion, a balm, a salve or the
like, that can be
effectively dispensed there from in accordance with the teachings of the
present invention without
departing from the purpose or scope of the present invention. Thus, when the
pump systems of
the present invention are described as being pre-filled with a topical
imiquimod pharmaceutical
cream, such description is done so for exemplary purposes without intent to be
bound to any
particular topical semi-solid imiquimod dosage form or formulation.
19
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00071] It is envisioned that certain constructions of the present
invention further include a
take-up piston which is slidably disposed within the tubular main body portion
so as to partially
define the fluid storage chamber. The take-up position moves axially towards
the pumping
device when the pumping device is manually operated, so as to reduce the
volume of the fluid
storage chamber by an amount which is equivalent to the volume of imiquimod
cream
formulation dispensed from the dispensing package, i.e., the unit-dose amount.
In constructions
wherein the take-up piston defines a portion of the fluid storage chamber, it
can be positioned
during assembly to established the desired volume of the fluid storage
chamber. For example, if
it is desired to pre-fill the dispensing device with 15 g of an imiquimod
cream, the piston can be
initially positioned during the filling operation at a distance from the top
of the main body portion
of the dispensing package such that the volume of the fluid storage chamber
corresponds to the
volume required to hold 15 g of imiquimod cream. Alternatively, if 7.5 grams
of cream is to be
stored, the piston can be moved the appropriate distance towards the top of
the main body portion
of the dispensing package to accommodate 7.5 g of imiquimod cream. Of course,
it should be
appreciated by those versed in this art that the imiquimod pump systems of the
present invention
contemplate functional fluid storage chambers that can accommodate any desired
volume of
imiquimod cream, including fluid storage chambers that can hold and store
volumes greater or
lesser than 7.5 g or 15 g of imiquimod cream, so long as the objectives of the
present invention
are not defeated.
[00072] Preferably, with each operation of the pumping device, an amount
of the
imiquimod cream formulation which is within about 15% of the predefined unit
dose is
discharged from the dispending device per actuation. Still further, after
multiple operations of the
pumping device, the overall average of the dose value is within about 10% of
the predefined unit
dose per actuation. In certain constructions, it is envisioned that the
predefined unit dose amount
dispensed per actuation is about 250 mg, and more preferably about 240 mg.
[00073] It is preferred that no more than about 5 manual actuations of the
pumping device
are required to effectively prime the pumping device and start observing the
discharging of
imiquimod cream formulation from the self-closing discharge orifice.
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[00074] Following the initial operation or priming of the pumping device,
imiquimod
cream uniquely remains within the dispensing duck, i.e., the pump is now
primed. Preferably,
about 85% or more of the imiquimod cream contained within the dispensing duck
of the pumping
device following each actuation remains in the dispensing duck during storage
and prior to the next
actuation by the patient, so that the same uniform and consistent unit dose
amount is dispensed per
each actuation, even when a pump system of the present invention has been
stored (static - not
actuated) for a few days or a few weeks between actuations, consistent with
the prescribed treatment
regimens and/or rest periods taken when treating a diagnosed dermal and/or
mucosal-associated
condition, such as, external genital warts, perianal warts, actinic keratosis
or superficial basal cell
carcinoma, with a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation as
described herein.
[00075] The present invention is further directed to a pump system for
treating a subject
diagnosed with a dermal and/or mucosal-associated conditions, such as genital
warts or perianal
warts, actinic keratosis or superficial basal cell carcinoma, which includes,
inter alia, a
dispensing package that is pre-filled with a topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical
formulation, such as an imiquimod cream formulation. The dispensing package
includes a lower
subassembly and an upper subassembly. The lower subassembly has a tubular body
portion that
defines an elongated interior fluid storage chamber into which a take-up
piston element is
slidably disposed. The upper subassembly is mounted upon the lower subassembly
and includes
a dispensing head and an airless pumping mechanism. The dispensing head has an
internal fluid
passage or discharge duct formed therein which terminates in a self-closing
outlet. The
dispensing head also includes a finger-operated actuator which is operatively
associated with the
airless pumping mechanism. The dispensing package may further include a cap to
seal or cover
the dispensing head or nozzle.
[00076] The topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, e.g.,
an imiquimod
cream formulation, is disposed at least partially within the fluid storage
chamber defined in the
tubular body portion of the lower subassembly of the dispensing package.
Operation of the
finger-operated actuator causes the airless pumping mechanism to withdraw a
portion of the
imiquimod cream from within the interior chamber and to dispense the imiquimod
cream into the
internal fluid passage formed in the dispending head wherein the pressure of
the dispensed cream
21
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
causes the self-closing outlet to open thereby discharging a predetermined
final unit dose of
imiquimod cream from the dispensing head.
[00077] In certain preferred embodiments, the take-up piston is disposed
within the tubular
body portion so as to partially define the fluid storage chamber. The take-up
position is arranged
such that it moves axially towards the pumping device when the pumping device
is manually
operated, so as to reduce the volume of the fluid storage chamber by an amount
which is
equivalent to the volume of imiquimod cream dispensed from the dispensing
package, i.e., the
unit dose amount, as discussed above.
[00078] In a pump system for treating a subject diagnosed with a dermal
and/or mucosal-
associated conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC, the pump system includes a
dispensing
package that has a tubular main body portion and a manually-operated airless
pumping device
mounted on the main body portion. The main body portion of the dispensing
package defines a
fluid storage chamber which is in fluid communication with a dispending duct
which is defined in
the pumping device and that terminates in a discharge orifice.
[00079] The pump system of the present invention further includes a
mechanism for
closing the discharge orifice when the dispensing package is not in use and a
topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, e.g., an imiquimod cream formulation,
that is disposed at
least partially within the fluid storage chamber defined in main body portion
of the dispensing
package. Wherein, manual operation of the airless pumping device causes a
portion of the
imiquimod cream to be withdrawn from within the fluid storage chamber and a
predefined unit
dose of imiquimod cream to be dispensed from the discharge orifice of the
dispensing package.
Preferably, the mechanism for closing the discharge orifice when the
dispensing package is not in
use includes a shutter element that has a self-closing orifice. Alternatively
or additionally, the
mechanism for closing the discharge orifice when the dispensing package is not
in use can
include a cap, a cover or a plug.
[00080] The present invention is also directed to methods for treating
dermal and/or
mucosal-associated conditions with the novel and unique pump systems pre-
filled with topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations. Generally speaking, the
methods of the
22
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
present invention comprise treating a dermal and/or mucosal-associated
condition with a topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation dispensed from a novel and
unique imiquimod
pump system of the present invention in accordance with effective treatment
regimens, such as
those treatment regimens described herein. For example, the methods of the
present invention
comprise (1) actuating a primed dispensing pump system pre-filled with a
topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation to dispense there from an effective
precisely measured
unit-dose amount of the pre-filled topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation for
treating a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, wherein the unit-dose
amount dispensed
per each actuation is the same effective precisely measured unit-dose amount
for consistent dose
application over the course of the treatment regime, and (2) applying the
dispensed unit-dose
amount to a treatment area diagnosed with a dermal and/or mucosal-associated
condition in
accordance with the treatment regimen to treat the diagnosed dermal and/or
mucosal-associated
condition.
[00081] It of course should be understood that the methods of the present
invention
contemplate the use of any suitable topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation,
preferably imiquimod pharmaceutical creams, wherein the imiquimod is present
in an amount by
weight of about 1% to about 10% w/w, and more preferably in an amount by
weight of about 1%
to about 5% w/w, and even more preferably in an amount by weight of about 2.5%
w/w, about
3.75% w/w and about 5% w/w.
[00082] It should also be understood, as discussed above, that the methods
of the present
invention envision treatment of dermal and/or mucosal-associated conditions
such as external
genital warts and/or perianal warts (EGWs), actinic keratosis (AKs) and
superficial basal cell
carcinoma (sBCC) in accordance with effective treatment regimens such as those
described here
in throughout.
[00083] Thus, when practicing the pump systems of the present invention,
each unit-dose
amount dispensed from an imiquimod pump system per each actuation is the same
precisely
measured unit-dose amount, preferably pre-selected at the time of pump fill,
so that the same
precisely measured unit-dose amount of the pre-filled topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation is delivered to the targeted treatment area per
each application in
23
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
accordance with an effective treatment regimen, so that the effectiveness and
benefits of topical
imiquimod treatment of a treated dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition,
such as EGWs,
AKs or sBCC, are maximized and the drawbacks associated with single-use
imiquimod packets
or sachets are minimized, if not eliminated.
[00084] To further illustrate certain unique advantages of the pump
systems of the present
invention, once such a pump system pre-filled with a topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation, such as a 3.75% w/w imiquimod cream as described
herein, is
primed, each pre-selected unit-dose amount of the 3.75% w/w imiquimod cream
dispensed there
after will be repeatedly and consistently dispensed over pump life. Thus, if
the pre-selected unit-
dose amount to be delivered per actuation is about 240 mg, each single
actuation of a primed
pump system will consistently deliver about 240 mg of the 3.75% imiquimod
cream.
[00085] Of course, it should be appreciated that the number of single unit-
doses that will
be dispensed over pump life will be a function of the total pre-fill volume
and the pre-selected
unit-dose amount. Thus, if the pre-fill volume is, e.g., 15 g, and the pre-
selected unit-dose
amount per actuation or pump is about 240 mg, such a pre-filled pump will have
the ability to
deliver about 62 unit-doses of imiquimod cream at about 240 mg/pump over pump
life. If,
however, the pre-fill pump volume is, e.g., 7.5 g, such a pre-filled pump will
have the ability to
deliver about 31 unit-doses of imiquimod cream at about 240 mg/pump over pump
life.
[00086] Thus, a pump system of the present invention pre-filled with about
15 g of, for
example, a 3.75% w/w imiquimod cream or a 5% w/w imiquimod cream, can
accommodate, for
example, the following two treatment regimens for treating EGWs when each unit-
dose dispensed
is: (1) single unit doses of about 240 mg of a 3.75% imiquimod cream/pump that
is to be applied
daily for up to 8 weeks or for up to a total of about 56 single unit-doses of
3.75% imiquimod
cream (56 individual pumps) over the course of the treatment regimen; or (2)
single unit-doses of
about 240 mg of a 5% imiquimod cream/pump to be applied three times a week for
up to 16
weeks or for up to a total of about 48 single unit-doses of 5% imiquimod cream
(48 individual
pumps) over the course of the treatment regimen. On the other hand, if a pump
system of the
present invention is prefilled with about 7.5 g of, for example, a 3.75% w/w
imiquimod cream or
a 5% w/w imiquimod cream, such a pre-filled pump can accommodate the following
two
24
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
treatment regimens for treating AKs or sBCC when each unit-dose dispensed is:
(1) single unit
doses of about 240 mg of a 3.75% imiquimod cream/pump applied daily in
accordance with a 2 x
2 x 2 treatment regimen to treat AKs or for up to a total of about 28 single
unit-doses of 3.75%
imiquimod cream (28 individual pumps) over the course of the 2 x 2 x 2
treatment regimen for
AK treatment; or (2) single unit-doses of about 240 mg of a 5% imiquimod
cream/pump applied
five times a week for up to 6 weeks to treat sBCC or for up to a total of
about 30 single unit-doses
of 5% imiquimod cream (30 individual pumps) over the course of the treatment
regimen for
sBCC treatment.
[00087] It should be appreciated that the above is described when only a
single pump for
dispensing an unit-dose amount of about 240 mg/unit-dose is to be applied
during the appropriate
treatment regimen. However, when a unit-dose of about 480 mg/unit-dose is
required per
application in accordance with an appropriate treatment regimen, two pumps or
actuation will be
required (if the pre-set unit dose per pump is about 240 mg/pump) to deliver
the necessary 480
mg unit-dose per application and that at least two 7.5 g or at least two 15 g
pumps should be
prescribed and dispensed to complete the prescribed treatment regimen when
appropriate. Thus,
it should be realized by those of skill in the art that the number of pump
systems pre-filled with a
topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation that are to be
prescribed and dispensed
will, of course, depend upon (1) the pre-fill volume of the pump system, (2)
the precisely
measured amount of the unit-dose dispensed per pump or actuation, and (3) the
appropriate
treatment regimen selected to treat a treatment area diagnosed with a dermal
and/or mucosal-
associated condition, such as EGWs. AKs or sBCC.
[00088] To illustrate further, a method of the present invention
contemplates treating a
patient diagnosed with a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, such as
EGWs, AKs or
sBCC, with a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, wherein
such method
includes: (1) priming a pump system pre-filled with a topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation, e.g., an imiquimod cream, to prepare the pump
system to dispense a
plurality of predefined, precisely measured and consistent unit-doses of the
topical imiquimod
formulation to treat the diagnosed dermal and/or mucosal condition in
accordance with an
appropriate treatment regimen; (2) pumping the primed pump system no more than
twice to
dispense one of the predefined and precisely measured unit-doses onto a
treatment area diagnosed
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
with the dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition in accordance with an
appropriate treatment
regimen, (3) rubbing the dispensed unit dose amount of topical imiquimod cream
into the
treatment area until the dispensed unit-dose is no longer visible, (4) leaving
the rubbed-in unit
dose on the treatment area for a sufficient treatment period in accordance
with the appropriate
treatment regimen, for effectively treating the diagnosed dermal and/or
mucosal condition; and
(5) repeating the above-recited pumping or actuating step (2), the above-
recited rubbing step (3)
and the above-recited leaving step (4) a number of times as specified by the
appropriate treatment
regimen to effectively treat the diagnosed dermal and/or mucosal-associated
condition and to
maximize the benefit of topical imiquimod treatment.
[00089] When practicing the methods of the present invention, it is
preferable for the
patient to wash his/her hands with mild soap and water before and after
dispensing each
prescribed unit-dose from an imiquimod pump system of the present invention.
It is also
preferable to wash the treatment area diagnosed with a dermal and/or mucosal-
associated
condition with soap and water and to allow the washed treatment area to dry
before dispensing
the prescribed unit-dose from the pump system and applying such dispensed unit-
dose to the
targeted treatment area. Also, when carrying out the methods of the present,
it is preferable to
avoid contacting the dispensed unit-dose with the eyes, lips, nostrils, mouth
and/or vagina of the
patient.
[00090] More specifically, a method of the present invention comprises
applying a topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, and preferably applying a
topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream, dispensed from an airless pump system of the present
invention, equipped
with a cap for protecting the dispensing head, to a treatment area of a
patient diagnosed with a
dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition to treat the dermal and/or mucosal-
associated
condition. More particularly, this one such method comprises (a) washing a
treatment area
diagnosed with a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition to treat the
dermal and/or mucosal-
associated condition where the imiquimod cream will be applied with mild soap
and water, (b)
allowing the washed treatment area to dry, (c) washing the hands of the
patient and allowing the
washed hands to dry, (d) removing the cap from the pump system prefilled with
a topical
imiquimod pharmaceutical cream, (e) tilting the pump system for dispensing the
imiquimod
cream there from, (f) priming the pump system by firmly pressing the top of
the pump or
26
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
dispensing head all the way down up to about five times as needed until the
imiquimod cream
appears at the dispensing head outlet, (g) dispensing the primed imiquimod
cream from the
dispensing head into a paper tissue and then discarding such dispensed cream,
(h) pressing the top
of the pump system or dispensing head all of the way down up to two times as
needed to dispense
a precisely measured unit-dose of the topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream
into the hand of
the patient, (i) applying the precisely measured unit-dose of the topical
imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream to the washed and dried treatment area in accordance with
a prescribed
treatment regimen for treating the treatment area diagnosed with the dermal
and/or mucosal-
associated condition, (j) rubbing the applied unit-dose all the way into the
washed and dried
treatment area, (k) re-washing the hands of the patient after the unit-dose
has been rubbed into the
washed and dried treatment area, (1) leaving the rubbed-in imiquimod cream on
the treatment
area, without wetting or washing the treated treatment area, for up to about 8
hours to treat the
dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, (m) re-washing the treated
treatment area with soap
and water after the 8 hours has passed, and (n) repeating the said steps (h)
through (m) herein in
accordance with a prescribed treatment regimen to dispense and apply precisely
measured and
reproducible unit-doses of the topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream to
effectively treat the
diagnosed dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, wherein each said unit-
dose dispensed
from the pump system of the present invention during step (h) is a precisely
measured, consistent,
reproducible and uniform amount, so that they same dosage amount of the
topical imiquimod
pharmaceutical cream is applied each and every time over the course of the
prescribed treatment
regimen, thereby avoiding dosing inconsistencies and other drawbacks observed
or associated
with single-use packets or sachets.
[00091]
It is also a feature of the present invention to instruct prescribers and
patients as to:
(1) the correct use of the pre-filled imiquimod pump systems and treatment
regimens in order to
optimally practice the pre-filled imiquimod pump systems of the present
invention to effectively
treat dermal and/or mucosal associated conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC,
with topical
imiquimod therapy; (2) the correct way for prescribers to prescribe the pre-
filled imiquimod
pump systems, including the treatment regimens, of the present invention to
effectively treat
dermal and/or mucosal associated conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC; and
(3) the correct
way for patients in need of therapy to practice the pre-filled imiquimod pump
systems in
accordance with the present invention to effectively treat dermal and/or
mucosal associated
27
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC, and to maximize the benefits of topical
imiquimod
therapy.
[00092] The present invention also contemplates the use of instructions
provided on, for
example, a label, package insert or other communicative materials to teach
prescribers and/or
patients how to correctly and most effectively prescribe and use,
respectively, the pre-filled
imiquimod pump systems of the present invention to effectively treat dermal
and/or mucosal
associated conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC, and to maximize the benefits
of topical
imiquimod therapy.
[00093] Thus, it should now be clear that the present invention uniquely
affords a proper,
safe, convenient, easy and advantageous way to use the novel pre-filled
imiquimod pumps to
practice treatment regimens of the present invention to improve patient
compliance and to more
effectively treat dermal and/or mucosal-conditions, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC,
with topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations, such as with topical semi-
solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical creams, while mitigating, if not eliminating, the drawbacks
associated with the
use of single-use packets or sachets pre-filled with topical imiquimod
formulations to treat the
same skin disorders.
[00094] The above summary of the present invention is not intended to
describe each
disclosed embodiment or every implementation of the present invention. The
description and
examples that follow more particularly exemplify illustrative embodiments. In
several places
throughout the specification, guidance is provided through lists of examples,
which examples can
be used in various combinations. In each instance, the recited list serves
only as a representative
group and should not be interpreted as an exclusive list.
Brief Description of the Drawings
[00095] So that those having ordinary skill in the art to which the
present invention
pertains will more readily understand how to employ the pump systems and
methods of the
present invention, embodiments thereof will be described in more detail herein
below with
reference to the drawings, wherein:
28
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
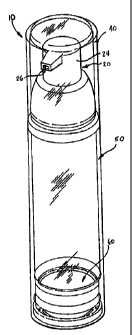
[00096] FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a dispensing package which has
been constructed
in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
[00097] FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of a lower or first subassembly
of the dispensing
package of FIG 1, which includes a hollow body along with the take-up piston
and base closure
member;
[00098] FIG. 3 is a partial cross-sectional view of an upper or second
subassembly of the
dispensing package of FIG. 1, which includes a dispensing head, a finger-
operable pump, a
holding member and a cap;
[00099] FIG. 4 provides a side elevational view of the finger-operable
pump of the upper
subassembly, and a cross-sectional view of an o-ring gasket and the hollow
body associated with
the lower subassembly;
[000100] FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of the dispensing head used in
the dispensing
package of FIG. 1, the dispensing head including a body portion and a shutter
member;
[000101] FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view of the body portion of the
dispensing head of FIG.
5;
[000102] FIG. 7 is a perspective view taken from the rear side of the
shutter member of the
dispensing head of FIG. 5;
[000103] FIG. 8-9 provide illustrate various results obtain in the examples
reported below;
and
[000104] FIG. 10-11 each illustrate a cross-sectional view of a preferred
dispensing device.
[000105] These and other aspects of the subject invention will become more
readily
apparent to those having ordinary skill in the art from the following detailed
description of the
invention taken in conjunction with the drawings and examples.
29
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Detailed Description
[000106] Disclosed herein are detailed descriptions of specific embodiments
of the devices,
systems and methods for storing and dispensing unit doses of a topical semi-
sold imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation, such as an imiquimod cream. It will be understood
that the
disclosed embodiments are merely examples of the way in which certain aspects
of the invention
can be implemented and do not represent an exhaustive list of all of the ways
the invention may
be embodied. Indeed, it will be understood that the pump systems, devices,
methods and package
assemblies described herein may be embodied in various and alternative forms.
The figures are
not necessarily to scale and some features may be exaggerated or minimized to
show details of
particular components. Well-known components, materials or methods are not
necessarily
described in great detail in order to avoid obscuring the present disclosure.
Any specific
structural and functional details disclosed herein are not to be interpreted
as limiting, but merely
as a basis for the claims and as a representative basis for teaching one
skilled in the art to
variously employ the invention.
[000107] Thus, by way of illustrating and providing a more complete
appreciation of the
present invention and many of the attendant advantages thereof, the following
detailed
description and examples are given concerning the novel methods and
compositions.
[000108] Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers expressing quantities,
ratios, and
numerical properties of ingredients, reaction conditions, and so forth used in
the specification and
claims are to be understood as being modified in all instances by the term
"about".
[000109] All parts, percentages, ratios, etc. herein are by weight unless
indicated otherwise.
[000110] As used herein, the singular forms "a" or "an" or "the" are used
interchangeably
and intended to include the plural forms as well and fall within each meaning,
unless expressly
stated otherwise. Also as used herein, "at least one" is intended to mean "one
or more" of the
listed elements. Singular word forms are intended to include plural word forms
and are likewise
used herein interchangeably where appropriate and fall within each meaning,
unless expressly
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
stated otherwise. Except where noted otherwise, capitalized and non-
capitalized forms of all
terms fall within each meaning.
[000111] The compound imiquimod is a known antiviral agent that is also
known to induce
interferon biosynthesis. It can be prepared using the method disclosed in U.S.
Pat. No.
4,689,338. The compound can be used to treat dermal and/or mucosal-associated
conditions,
such as external genital and perianal warts (EGWs), actinic keratoses (AKs) or
superficial basal
cell carcinoma (sBCC). The amount of imiquimod present in a topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation of the present invention will be an effective
amount to treat a dermal
and/or mucosal-associated condition, for example, (a) EGWs, (b) AKs or (c)
sBCC, as described
herein. An example of an effective amount of imiquimod in a formulation of the
present
invention is between about 1. percent and about 10 percent by weight based on
the total weight of
a formulation, more preferably between about 2.5% and 5%, and more preferably
about 1.25%,
1.5%, 1.75%, 2.0%, 2.25%, 2.5%, 2.75%, 3.0%, 3.25%, 3.5%, 3.75%, 4.0%, 4.25%õ
4.5%,
4.75% and 5%, even more preferably between about 2.0%, 2.25%, 2.5%, 2.75%,
3.0%, 3.25%,
3.5%, 3.75% and 4.0%, and still even more preferably between about 2.5%,
2.75%, 3.0%, 3.25%,
3.5% and 3.75%. Imiquimod formulations of the present invention that contain
about 2.5%
imiquimod, about 3.75% imiquimod or about 5% imiquimod by weight based on the
total weight
of the formulations are most preferred.
[000112] By the term "bioequivalence or bioequivalent", as used herein, it
refers to topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations in which they are
pharmaceutically equivalent
and their bioavailabilities (rate and extent of absorption) after
administration in the same molar
dosage or amount are similar to such a degree that their therapeutic effects,
as to safety and
efficacy, are essentially the same. In other words, bioequivalence or
bioequivalent means the
absence of a significant difference in the rate and extent to which imiquimod
becomes available
from such formulations at the site of imiquimod action when administered at
the same molar dose
under similar conditions, e.g., the rate at which imiquimod can leave such a
formulation and the
rate at which imiquimod can either cross the stratum corneum and/or become
available at the site
of action to treat a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition, e.g., EGWs,
AKs or sBCC. In
other words, there is a high degree of similarity in the bioavailabilities of
two topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations (of the same galenic form) from the same
molar dose,
31
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
that are unlikely to produce clinically relevant differences in therapeutic
effects, or adverse
reactions, or both. The terms "bioequivalence", as well as "pharmaceutical
equivalence" and
"therapeutic equivalence" are also used herein as defined and/or used by (a)
the FDA, (b) the
Code of Federal Regulations ("C.F.R."), Title 21, and/or (c) Health Canada.
[000113] By the term "bioavailability or bioavailable", as used herein, it
means generally
the rate and extent of absorption of imiquimod into the systemic circulation
and, more
specifically, the rate or measurements intended to reflect the rate and extent
to which imiquimod
becomes available at the site of action or is absorbed from a topical semi-
solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation and becomes available at the site of action. In
other words, and by
way of example, the extent and rate of imiquimod absorption from a topical
semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation of the present invention as reflected by
a time-
concentration curve of imiquimod in systemic circulation.
[000114] By "pharmaceutical equivalence" or "pharmaceutically equivalent",
as used
herein, it refers to topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations
of the present
invention that contain the same amount of imiquimod, in the same dosage forms,
but not
necessarily containing the same inactive ingredients, for the same route of
administration and
meeting the same or comparable compendia or other applicable standards of
identity, strength,
quality, and purity, including potency and, where applicable, content
uniformity and /or stability.
[000115] By "therapeutic equivalence" or "therapeutically equivalent", it
is meant herein to
mean those topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations which (a)
will produce the
same clinical effect and safety profile when practicing treatment regimens to
treat a dermal and/or
mucosal-associated condition, namely, EGWs, AKs or sBCC, in accordance with
the present
invention and (b) are pharmaceutical equivalents, e.g., they contain imiquimod
in the same
dosage form, they have the same route of administration; and they have the
same imiquimod
strength. In other words, therapeutic equivalence means that a chemical
equivalent of a topical
semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation of the present invention
(i.e., containing the
same amount of imiquimod in the same dosage form) when administered to the
same individuals
in the same dosage regimen will provide essentially the same efficacy and
toxicity.
32
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000116] The topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations, such
as the topical
imiquimod pharmaceutical creams, according to the present invention can be
applied to any
suitable location, for example, applied topically to dermal and/or mucosal
surfaces. In the case of
dermal application, for example, depending on the imiquimod concentration,
formulation
composition, and dermal surface, the therapeutic effect of imiquimod may
extend only to the
superficial layers of the dermal surface or to tissues below the dermal
surface. Thus, another
aspect of the present invention is directed to a method for the treatment of a
dermal and/or
mucosal-associated condition comprising applying to skin one of the imiquimod
creams via a
pump system of the present invention. As used herein, a "dermal and/or mucosal-
associated
condition" means an inflammatory, infectious, neoplastic or other condition
that involves a
dermal and/or mucosal surface or that is in sufficient proximity to a dermal
and/or mucosal
surface to be affected by a therapeutic agent topically applied to the
surface. Examples of a
dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition include warts, atopic dermatitis,
postsurgical scars,
lesions caused by a herpes virus, and epidermal neoplasias, such as for
example actinic keratosis,
pre-actinic keratosis lesions, malignant melanomas, basal cell carcinoma, and
squamous cell
carcinoma.
[000117] In some embodiments, the topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical
formulations, e.g., topical imiquimod pharmaceutical creams, are particularly
advantageous for
use with the pump systems of the present invention for dermal and/or mucosal
application for a
period of time sufficient to obtain a desired therapeutic effect without
undesired systemic
absorption of the imiquimod.
[000118] In view of the above, it should be understood by those versed in
this art that the
present invention contemplates pump systems and methods for storing and
dispensing consistent
and uniform unit dose amounts of an effective topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical
formulation, and more particularly to pump systems, pre-filled with any
effective topical semi-
solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, and methods for delivering a
precisely measured
unit dose amount of any effective topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation, and
still more particularly to pump systems pre-filled with an effective topical
semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation, and methods for using a controlled delivery pump
to store and
dispense multiple unit doses of an effective topical semi-solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical
33
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
formulation for use in treating dermal and mucosal-associated conditions, such
as, EGWs, AKs
and sBCC. It should therefore be understood by those versed in this art that
the present invention
also contemplates pump systems pre-filled with an effective topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation that is bioequivalent, pharmaceutically equivalent
and/or
therapeutically equivalent to, for example, Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream,
Zyclara
(imiquimod) 3.75% cream or a 2.5% imiquimod cream or any imiquimod formulation
set forth
herein, or which meets or has the same imiquimod bioavailability as, for
example, Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream, Zyclara (imiquimod) 3.75% cream, or a 2.5% imiquimod
cream or any
other imiquimod formulation set forth herein, as defined by the FDA, the
C.F.R. and/or Health
Canada.
[000119] For ease of description, the components of this invention are
described in an
upright operating position, and terms such as upper, lower, front, rear,
horizontal, etc., are used
with reference to this position. It will be understood, however, that the
components of this
invention may be manufactured, stored, transported, used and sold in an
orientation other than the
positions described herein.
[000120] FIGs. illustrating the components show some mechanical elements
that are known
and will be recognized by one skilled in the art. The detailed descriptions of
such elements are
not necessary to an understanding of the invention, and accordingly, are
herein presented only to
the degree necessary to facilitate an understanding of the novel and unique
features of the present
invention.
[000121] Referring now to FIG. 1, which illustrates a dispensing package
which has been
constructed in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention
and is designated
generally by the reference numeral 10. As will be discussed herein below,
package 10 is
specially adapted for storing and dispensing unit doses of a topical semi-
solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation, such as an imiquimod cream formulation.
[000122] The dispensing package 10 includes a dispensing head 20 having a
projecting,
finger-operable pump 22 (see FIGS. 3 and 4) and an external actuator button or
plunger 24. The
pump 22 is a non-venting type that has a pump chamber in which is disposed a
pressurizing
34
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
piston that can be actuated by pressing down on plunger 24, so as to dispense
a quantity of the
fluid product from a dispensing orifice or self-closing slit 26, which will be
described in greater
detail herein below.
[000123] An optional cover or cap 40 may be releasably mounted over
dispensing head 20.
The cap 40 is shown as molded from a substantially transparent material.
However, in many
applications, the cap 40 is preferably made from any suitable opaque material.
[000124] The dispensing package 10 includes a tubular structure or hollow
body 50 for
containing the imiquimod cream. The hollow body 50 is illustrated in the
figures as being made
from a substantially transparent material, such as a transparent thermoplastic
material. However,
in many applications, the body is preferably made from any suitable opaque
material.
[000125] The body 50 most typically would have a circular, transverse cross
section.
However, the hollow body 50 may have an oval shape, or some other shape,
wherein the internal,
transverse cross section is substantially uniform along most of its length.
[000126] As shown in FIG. 2, the bottom of the hollow body 50 has an open
end which is
normally closed by a base closure member 52, which defines one or more
apertures 54. The
closure member 52 has a transverse cross-section corresponding generally to
the transverse cross
section of the hollow body 50. The closure member 52 is typically secured to
the bottom of the
hollow member 50 by means of a snap-fit engagement, by adhesive, or by other
suitable means.
However, prior to securing the closure member 52 to the hollow body 50, a
follower or take-up
piston 60 is inserted into the lower, open end of the hollow body 50. The
piston sealingly engages
the interior surface of the hollow body 50 and is adapted to slidingly move
axially upwardly in
the hollow body 50. The piston 60 can thus function as a take-up piston for
moving toward the
pump 22 at the upper, discharge end of the hollow body 50.
[000127] The take-up piston 60 moves toward the pump 22 at the discharge
end of the body
50 in response to the discharge of any amount of fluid, such as imiquimod
cream, from the body
50 so as to decrease the internal volume of the body 50 by an amount equal to
the volume of the
amount of fluid product which is discharged, i.e., the unit-dose amount. The
movement of the
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
piston 60 is effected by the atmospheric pressure of the ambient air which
acts against the
exterior, bottom surfaces of the piston 60. It will be appreciated that the
vent passages 54 in the
bottom end closure member 52 insure that the ambient atmosphere will be in
continuous contact
with the exterior of the piston 60 regardless of how far the piston 60 travels
up in the hollow body
50.
[000128] The particular design and configuration of the take-up piston 60
are matters of
design choice consistent with the configuration used for the hollow body 50.
Any suitable
conventional or special piston design may be employed. The details of the
design per se of such a
piston 60 form no part of the present invention. It should be noted that the
initial position of the
piston within the hollow body 50 is dictated by the total amount of imiquimod
cream to be
supplied to the patient based on the anticipated dosing regimen. For example,
if it is desired to
dispense to the patient 15 g of imiquimod cream, the piston would be initially
located lower than
the setting for 7.5 g of cream.
[000129] The upper, discharge end of the body 50 defines a reduced-diameter
neck 56. The
upper end of the neck defines an external, peripheral shoulder 58. The side of
the neck defines an
annular, outwardly open groove 59. The distal end of the neck 56 defines an
upwardly
projecting, annular rim 57 at the inside diameter of the shoulder 58. In a
preferred embodiment,
the hollow body 50 is injection molded from a suitable thermoplastic material.
[000130] The hollow body 50, along with the take-up piston 60 and base
closure member
52, may be characterized as the lower subassembly or first subassembly.
However, in some
applications, the base closure member 52 may be omitted altogether from the
first, or lower,
subassembly. In any event, after the lower subassembly has been assembled, it
can be filled with
the imiquimod cream, and then the additional package components, comprising an
upper
subassembly or second subassembly as described below, are installed on the
filled, first
subassembly.
[000131] Referring now to FIG. 3, there is illustrated the second
subassembly or upper
subassembly, which is designed for being mounted to the lower subassembly and
comprises at
least three components; a finger operable pump 22, a dispensing head 20; and a
holding member
36
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
70. The dispensing head 20 may be regarded as part of the pump 22. Additional
components are
also preferably included in the upper subassembly, and such additional
components may include
a gasket 80 (FIG. 4) and the cap or cover 40 (FIG. 3).
[000132] The exterior of the pump 22 is designed to be mounted within the
holding member
70, along with the gasket 80 if the gasket is employed. Specifically, the pump
22 has a radially
extending mounting flange 28 (FIGS. 3 and 4). The pump 22 may also include one
or more
bosses or ribs (not shown) which are spaced above the pump flange 28 to define
an annular recess
between the flange 28 and the ribs and can be used to secure the pump 22 to
the holding member
70.
[000133] The internal pumping mechanism of the pump 22 may be of any
appropriate
conventional or special non-venting design. Typically, a conventional, non-
venting pump (air-
less), such as the pump 22 illustrated in the figures, has an interior chamber
(not visible) which
has a check valve at the lower end and in which is disposed a pressurizing
piston (not visible).
The pressurizing piston is arranged to cooperate with a hollow stem 30 which
extends out through
the top of the body of the pump 22 and which is received within the pump
actuator button 24.
[000134] The stem 30 and the piston within the pump body can move
downwardly together
in the pump chamber, but the hollow stem 30 can also move for some distance
separately relative
to the piston, so as to establish communication through the hollow stem 30
between the pump
chamber and the actuator button 24. One or more springs (not visible in the
figures) act against
the piston and/or stem 30 inside the pump body to bias the piston, stem 30,
and actuator button 24
upwardly to an elevated rest position when finger pressure is released. As
will be discussed in
more detail herein below, when the actuator button 24 is pressed, an unit-dose
amount of product
is dispensed from the pump 22.
[000135] One conventional non-venting pump that may be employed in
accordance with the
present invention is the pump designated EV09/240 and sold by Valois S.A., 50
Avenue de
L'Europe, 78160 Manly le roi, France. It will be appreciated, however, that
the detailed design
and operation of the internal components of such a pump, which may be employed
for the pump
22 described herein, form no part of the present invention.
37
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000136] The holding member 70 includes a peripheral, convex shroud 72
providing a
pleasing, external configuration. The bottom of the shroud 72 has a laterally
projecting flange or
shoulder 74. At four locations around the shroud 72 above the flange 74, there
are small,
outwardly projecting protuberances (not shown) which are adapted to establish
a snap-fit
engagement in an annular groove formed in the interior bottom of the cap or
cover 40. The cap
or cover 40 and/or the lower portion of the holding member shroud 72 are
resiliently deflectable,
so as to accommodate relative movement between the cap 40 and shroud 72 as the
cap 40 is
installed on the package. The cap 40 and/or shroud 72 deflect sufficiently so
that the cap bead
can be located below, and adjacent, the protuberances of the holding member
shroud 72. This
confronting relationship establishes the snap-fit engagement.
[000137] Projecting downwardly from the shroud 72 of the holding member 70
is an
annular sleeve 76. See FIG. 3. The sleeve 76 defines an opening, bore, or
passage for
accommodating the annular neck 56 of the hollow body 50 and for accommodating
the upwardly
projecting portion of the pump 22.
[000138] An annular flange 78 extends radially inwardly from the holding
member annular
sleeve 76 for engaging the upper surface of the pump flange 28. See FIG. 3.
The sleeve 76 also
includes an inwardly extending bead 77 for being received in the annular
groove 59 defined in the
hollow body neck 50.
[000139] Typically, the pump 22 is initially disposed in the holding member
70, along with
the gasket 80, if employed. To this end, the installation is accomplished with
the pump actuator
24 initially removed from the pump. Relative movement between the pump 22 and
the holding
member 77 is effected so as to introduce the pump into the holding member 70
from the bottom
end of the holding member.
[000140] As noted above, prior to mounting the two subassemblies together,
the lower
subassembly is filled with the topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation, such as
an imiquimod cream formulation. This can be conveniently done pursuant to a
conventional or
special filling process which is typically performed under vacuum. Preferably,
vacuum (i.e., a
38
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
reduced pressure) is created by a suitable vacuum system around the body 50.
The air below the
piston 60 within the body 50 is evacuated through the vent holes/apertures 54
in the base closure
member 52 of the body 50. Then the fluid product is discharged from a filling
machine into the
hollow body 50 through the opening in the body neck 56. Next, with vacuum
still enveloping the
components, the upper subassembly (comprising the pump 22, holding member 70,
gasket 80 if
employed, and cap 40 if employed) is moved into position on the lower
subassembly hollow body
50 so as to establish the snap-fit engagement between the hollow body 50 and
holding member
70.
[000141] The particular process and detailed operation of filling the body
50 and mounting
the upper subassembly on the lower subassembly form no part of the present
invention.
[000142] When the two subassemblies are properly mounted together as shown
in FIG. 1,
the pump flange 28 urges the gasket 80 into sealing engagement with the upper
end of the body
neck rim 57. However, depending upon the materials employed in the
construction of the pump
22 and/or body rim 57 or neck 56, the gasket 80 may either be omitted
altogether or be included
as a unitary part of either the pump flange 28 or the upper end of the body
neck 56.
[000143] The set of components provided according to the present invention
can be readily
manufactured from material which is compatible with the imiquimod cream.
Provided below are
the results of a stability studies which have been conducted to ensure certain
polymeric materials
are compatible with an imiquimod cream.
[000144] The set of components can be readily assembled to provide a
compact package
which is clean, safe, reliable, simple and easy-to-use to dispense consistent
and uniform unit-dose
amounts of a topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation, such as
an imiquimod
cream, to treat a dermal and/or mucosal-associated condition. Except for the
removable cap 40,
the components are not readily disassembled, and the completed package
protects a topical semi-
solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation from degradation, oxidation, and/or
external
contaminants.
39
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000145] Referring now to FIG. 5, it provides a cross-sectional view of
dispenser head 20.
In the embodiment shown in the FIGs., the dispenser head 20 is made up of two
component
elements, namely a body 90, FIG. 6, and a shutter 100, FIG. 7. The two
elements may be made
by injecting suitable plastics materials into appropriate molds. The body 90
is preferably made of
a plastics material that is harder or stiffer than the shutter 100.
[000146] The body 90, which is preferably integrally molded in one piece,
comprises a push
top wall 92 which serves a pusher surface against which one or more fingers of
one hand can be
applied and can exert a pressing force. In this example, the top wall 92 has a
complex shape that
is both rounded and inclined. This is an ergonomic shape for the position of a
finger with the tip
phalanx of the finger placed on the highest portion of the top wall 92. In
addition, the body 90
forms a peripheral side skirt 94 which extends from the top wall 92 downwards.
The skirt 94 has
a configuration that is also complex, but that is substantially cylindrical.
[000147] Where the top wall 92 is at its highest, the skirt 94 forms a join
surface 96 that is
exactly plane in this example. The join surface 96 is provided with plurality
of openings or slots,
as is described below. Shutter 100, described below, is designed to be mounted
on the body 90 at
the join surface 96.
[000148] The body 90 of dispensing head 20 internally defines a connection
sleeve 98
serving to receive the top end of the hollow stem 30 of pump 22. The socket
formed by the
connection sleeve 98 may be of the force-fitting type or of the snap-fastening
type. The rod-
receiving socket is extended by a dispensing duct 114 which defines an axial
inlet 116. This inlet
is disposed on a vertical longitudinal axis Y which coincides with the axis of
the dispenser
member and of its actuating rod. Naturally, the inlet 116 is open facing
downwards so as to
communicate with the socket formed by the connection sleeve 98 in which the
top end of the
hollow stem 30 of pump 22 is to be engaged.
[000149] In many cases, the body 90, and more generally the dispenser head
20, is mounted
to rotate about said vertical axis Y. The dispensing duct 114 also forms a
radial passageway 118
which opens out at the join surface 96 via an outlet 120. The outlet 120 and
the passageway 118
that connects the inlet 116 to the outlet 120 extend along a dispensing or
outlet axis X. The outlet
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
axis X extends substantially perpendicularly to the vertical longitudinal axis
Y. However, the
axis X may extend slightly or significantly upwards or downwards relative to
the axis Y.
[000150] Join surface 96 includes a circular groove 124 which extends from
the join surface
96 into the body 90 in substantially the same direction as the outlet axis X.
The groove 124 thus
forms a sort of annular trench whose depth extends horizontally.
[000151] As explained below, the function of said groove 124 is to provide
sealing with the
shutter 100. The shutter 100 forms a dispensing spout 130 internally forming
an outlet or
dispensing chamber 132. The chamber 132 terminates at self-closing slit 26
that forms a
dispensing orifice. The self-closing slit 28 has edges that are in touching
leak-tight contact in the
rest position, i.e., whenever the chamber 132 does not contain any fluid
subjected to a pressure
higher than a threshold pressure making it possible to separate the edges of
the slit and thus to
open the self-closing slit 28. In the embodiment shown in the FIGS., the
bottom surface 134 of
the dispensing chamber 132 is inclined upwards and thus constitutes a
convergence wall suitable
for directing the fluid under pressure towards the dispensing orifice.
[000152] Fixing catches 125a and 125b extend from the rear of the shutter
100 and secure
the shutter to the body 90 in snap-fit engagement. In the non-limiting
embodiment, there are a
bottom catch 125a and two side catches 125b. The three catches extend from the
rear of the
shutter 100 around the sealing lip 126.
[000153] The shutter 100 is fitted to the body 90 by causing the catches
125A and 125b to
penetrate into respective holding recesses formed in the body 90. When the
shutter 100 is fitted
to the body 90, the sealing lip 126 is caused to be pressed into the groove
124 so as to come into
leak-tight contact with the two side walls of said groove, and advantageously
also with the end-
wall thereof. Leak-tight contact is thus obtained at three points that have
very good sealing
quality, since the lip is in tight-fitting engagement between the two facing
side walls.
[000154] Once the package is filled, the priming of the actuator allows the
imiquimod
product to fill into the pump 22 and the dispensing duck 114. Once the pump 22
is fully primed
with imiquimod product, each additional actuation will cause a precise dosage
amount of the
41
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
imiquimod product to be dispensed. Moreover, each actuation causes the take-up
piston 60 to
rise until ultimately, the piston reaches the top of the package and empties
and remaining product.
[000155] A series of trials were conducted to determine the suitability of
the dispensing
device for use with topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream. A series of pump
systems were
evaluated for 2.5%, 3.75% and 5% w/w imiquimod creams targeting a pump system
that could
deliver approximately 250 mg of the product per actuation mimicking the
dosage/delivery of the
commercially available single use 250 mg packets or sachets.
[000156] Two pump system constructions were evaluated: Albion EV09/1500-30
mL
(hereinafter "Albion") and VP39/70 p1-15 mL Digital Actuator Nova Pump
EV09/150 ("Nova").
Like the previously described dispensing package, the Albion pump system
includes a tubular
base member in which a topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream is retained. The
Nova pump
system stores a topical imiquimod pharmaceutical cream in an aluminum pouch.
[000157] One difference between these two pumps are how they are designed
to operate and
the product contact materials used to manufacture the respective pump
components. In order to
determine which, if either, pump design and product contact components are
best suited for
consistently and uniformly dispensing precise unit-dose amounts of the 2.5%,
3.75% and 5% w/w
imiquimod pharmaceutical creams, even after use interruption and storage for a
period of time, a
series of performance tests, filling trials and stability studies are
conducted.
[000158] While the topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations
of the
present invention can be formulated into any form known to the art, such as a
cream, an ointment,
a gel or a lotion, it should be understood that such semi-solids may be
packaged into the multi-
dose, pump systems of the present invention for treatment of a dermal and/or
mucosal-associated
condition, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC. A packaged amount of a topical semi-
solid imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulation contemplated by the present invention includes any
suitable
packaged amount, for completing one or more treatment regimens for treating a
dermal and/or
mucosal-associated condition, such as EGWs, AKs or sBCC, such as an amount
between about 5
grams and 30 about grams, more preferably about 5 grams, about 7.5 grams,
about 10 grams,
about 12.5 grams, about 15 grams, about 17.5 grams, about 20 grams, about 22.5
grams, about 25
42
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
grams, about 27.5 grams, about 30 grams or more, and more preferably about 7.5
grams and
about 15 grams. An actuated unit-dose amount of a topical semi-solid imiquimod
formulation
that may be dispensed from a pump system of the present invention includes any
effective unit-
dose amount for treating a prescribed dermal and/or mucosal condition
discussed herein above,
such as an actuated unit dose amount of about 125 mg to about 500 mg or more,
and preferably
about 150 mg, about 175 mg, about 200 mg, about 225 mg, about 240 mg., about
250 mg, about
275 mg, about 300 mg, about 325 mg, about 350 mg, about 375 mg, about 400 mg,
about 425
mg, about 450 mg, about 500 mg or more, and more preferably about 240 mg or
about 250 mg
per actuation.
[000159] As indicated herein above, the present invention also contemplates
bioequivalent
or interchangeable topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations.
By way of an
example, bioequivalent or interchangeable dosage strength topical semi-solid
imiquimod
pharmaceutical formulations, as contemplated by the present invention, include
topical semi-solid
imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations that have respective comparable in-vivo
serum profiles,
i.e., wherein the in-vivo parameters are either the same or may vary up to
about 25% or more,
when such a 2.5%, 3.75% or 5% topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulation is
topically administered daily to the same individual in the same dosage regimen
in accordance
with dosage regimens described herein to treat a dermal and/or mucosal-
associated condition,
such as external or perianal warts, actinic keratosis or superficial basal
cell carcinoma. In other
words, two or more topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations
having the same
imiquimod concentration but different formulations will be considered
bioequivalent or
interchangeable if their respective in-vivo parameters are either the same or
vary up to about
25% or more, when such topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulations are
topically administered daily to an individual in the same dosage regimen in
accordance with
dosage regimens described herein to treat a dermal and/or mucosal-associated
condition, such as
EGWs, AKs or sBCC carcinoma.
[000160] By way of an example, bioequivalent or interchangeable 3.75%
dosage strength
topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations, as contemplated by
the present
invention, include topical semi-solid 3.75% imiquimod pharmaceutical
formulations that have
comparable in-vivo serum profiles, i.e., wherein the following in-vivo
parameters are either the
43
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
same or may vary up to about 25% or more, when approximately 500 mg of each
such
formulation (about 18.75 mg imiquimod) or less is applied daily for 21 days to
an AK treatment
area of about 200 cm2 on the face or balding scalp between about day 8 and day
14 and, selected
from one or more of the following in-vivo serum profiles:
(a) a Day 21 T.,ax of from about 4 hours to about 16 hours and preferably a
mean Tmax
of about 7.4 hours with a standard deviation ("SD") of about 3.5, a median T.
of about 9 hours
and a geometric mean Tmax of about 6.6 hours and a coefficient of variation
("CV") of about
48%;
(b) a Day 21 C. of from about 0.07 to about 0.6 ng/ml and preferably a mean
Cmax
of about 0.3 ng/ml with a standard deviation of about 0.16, a median C. of
about 0.35 and a
geometric mean C. of about 0.27 ng/ml and a coefficient of variation of about
49%;
(c) a Day 21 T1/2 of from about 9.7 to about 84 hours and preferably a mean
T1/2 of
about 29.3 hours with a standard deviation of about 17, a median T1/2 of about
25.6 hours and a
geometric mean T1/2 of about 26 hours and a coefficient of variation of about
58%;
(d) a Day 21 AUC0_24 of from about 1.1 to about 12 ng=hr/m1 and preferably
a mean
AUC0_24 of about 6 ngthr/m1 with a standard deviation of about 3, a median
AUC0_24 of about 7
neir/m1 and a geometric mean AUC0_24 of about 5 ngthr/m1 and a coefficient of
variation of about
52%;
(e) a Day 21 Az of from about 0.008 hr-1 to about 0.07 hr-1 and preferably
a mean Az of
about 0.03 hr-1 with a standard deviation of about 0.01, a median Az of about
25.6 hr' and a
geometric mean Az of about 0.03 hr-1 and a coefficient of variation of about
49%;
(f) a Day 21 C.dn of from about 0.06 to about 0.4 and preferably a mean
Cmin of about
0.20 with an SD of about 0.11, a median Cmin of about 0.19 and a geometric
mean Cmin of about
0.17 and a coefficient of variation of about 55%;
(g) at Day 14/7 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 14 over the
trough
concentration at Day 7), a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
1.09 with a 90%
confidence interval ("CI") within a range of between about 0.8 and about 1.5;
(h) at Day 21/14 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 21 over the
trough
concentration at Day 14), a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
1.33 with a 90%
confidence interval ("CI") within a range of between about 0.9 and about 1.9;
44
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
(i) at Day 22/21 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 22 over the
trough
concentration at Day 21) a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
0.93 with a 90%
confidence interval ("CI") within a range of between about 0.6 and about 1.3;
(i) a mean peak imiquimod serum concentration of about 0.323 ng/ml at Day
21;
(k) a Day 21 RAUC of from about 1 to about 7 and preferably a mean RAUC of
about
4 with a standard deviation of about 2, a median RAUC of about 3.5 and a
geometric mean
RAUC of about 3.3 and a coefficient of variation of about 56%;
a Day 21 RCmax of from about 0.5 to about 5 and preferably a mean RCmax of
about 3 with a standard deviation of about 1.5, a median RCmax of about 2.7
and a geometric
mean RCmax of about 2.4 and a coefficient of variation of about 54%;
(m) a Day 21 Lkzeff of from about 0.006 hr-1 to about 0.08 1111 and
preferably a mean
Lkzeff of about 0.02 hr-1 with a standard deviation of about 0.02, a median
Daeff of about 0.01 hr"
and a geometric mean Lkzeff of about 0.16 hr and a coefficient of variation of
about 97%; and
(n) a Day 21 TY2eff of from about 8 hr to about 110 hr and preferably a
mean TY2eff of
about 55 hr with a standard deviation of about 36, a median T1/2eff of about
50 hr and a geometric
mean TIAeff of about 42 hfl and a coefficient of variation of about 66%.
[000161] By way of another example, bioequivalent or interchangeable
topical semi-solid
3.75% imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations contemplated by the present
invention include
topical semi-solid 3.75% imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations that, when
approximately 250
mg of each such topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation'
(about 9.375 mg
imiquimod) or less is applied daily for 21 days to EGWs in the genitaPperianal
area with a total
wart area of greater than or equal to 100 mm2, provide a comparable in-vivo
serum profile
selected from one or more of the following:
(a) a Day 21 mean Tmax of about 9.7 hours with a standard deviation ("SD")
of about
4.0, a median Tmax of about 12 hours and a geometric mean T. of about 8.3
hours and a
coefficient of variation ("CV") of about 41%;
(b) a Day 21 mean C., of about 0.488 ng/ml with a standard deviation of
about
0.368, a median Cmax of about 0.45 and a geometric mean C. of about 0.39 ng/mL
and a
coefficient of variation of about 75%;
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
(c) a Day 21 Tv, of from about 6.8 to about 54 hours and preferably a mean
T1/2 of
about 24.1 hours with a standard deviation of about 12, a median T1/2, of
about 22.8 hours and a
geometric mean T. of about 21 hours and a coefficient of variation of about
51%;
(d) a Day 21 AUC0_24 of from about 1.9 to about 14 ng-hr/mL and preferably
a mean
AUC0_24 of about 6.8 ng.hr/mL with a standard deviation of about 3.6, a median
AUC0_24 of about
6.6 ng.hr/mL, and a geometric mean AUC0_24 of about 5.8 ng-hr/mL and a
coefficient of variation
of about 53%;
(e)
a Day 21 Az of from about 0.013 to about 0.102 III and preferably a mean Az
of about 0.037 hr-1 with a standard deviation of about 0.02, a median Az of
about 0.03 hr-1 and a
geometric mean Az of about 0.03 hr-1 and a coefficient of variation of about
60%;
(f) a Day 21 Cmin of from about 0.025 to about 0.47 and preferably a mean
Cm, of
about 0.158 with an SD of about 0.121, a median Cm,õ of about 0.14 and a
geometric mean Cm,
of about 0.11 and a coefficient of variation of about 77%;
(g) at Day 14/7 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 14 over the
trough
concentration at Day 7), a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
1.13 with a 90%
confidence interval ( "CI") within a range of between about 0.7 and about 1.7;
(h) at Day 21/14 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 21 over the
trough
concentration at Day 14), a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
0.84 with a 90%
confidence interval ("CI") within a range of between about 0.5 and about 1.3;
(i) at Day 22/21 (a ratio of the trough concentration at Day 22 over the
trough
concentration at Day 21) a trough concentration geometric mean ratio of about
1.12 with a 90%
confidence interval ("CI") within a range of between about 0.7 and about 1.6;
(i) a mean peak imiquimod serum concentration of about 0.488 ng/mL at
Day 21;
(k) a Day 21 RAUC of from about 0.6 to about 7 and preferably a mean
RAUC of
about 2.2 with a standard deviation of about 1.8, a median RAUC of about 1.8
and a geometric
mean RAUC of about 1.7 and a coefficient of variation of about 81%;
(1) a Day 21 RCrnax of from about 0.5 to about 5 and preferably a mean
RCmax of
about 2.3 with a standard deviation of about 1.6, a median RCrna, of about 1.7
and a geometric
mean RCina, of about 1.8 and a coefficient of variation of about 70%;
46
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
(m) a Day 21 LXzeff of from about 0.006 hr-' to about 0.09 hr' and
preferably a mean
LXzeff of about 0.04 hr-1 with a standard deviation of about 0.03, a median
LXzeff of about 0.03 hr-
1
and a geometric mean LXzeff of about 0.03 hr-1 and a coefficient of variation
of about 69%;
(n) a Day 21 T2eff of from about 8 hr to about 111 hr and preferably a mean
fAeff of
about 31 hr with a standard deviation of about 30, a median T2eff of about 22
hr and a geometric
mean T1/4eff of about 23 111 and a coefficient of variation of about 97%;
(o) a Day 21 Cmax in female patients about 61% higher in female subjects
than in male
subjects (0.676 versus 0.420 ng/mL) and total systemic exposure AUC 0-24 8%
higher in female
subjects than in male subjects (7.192 versus 6.651 ng-hr/mL) when data is not
dose normalized;
(p) a Day 21 Cm ax in female patients about 35% higher than in male
subjects (0.583
versus 0.431 ng/mL) and AUC 0-24 about 6% lower in female subjects than in
male subjects
(6.428 versus 6.858 ng-hr/mL) when using dose normalization to adjust for
differences in dosage
and reported without subjects who missed an application of study drug during
the last week of
dosing; and/or
(q) a median Tmax occurring approximately twice as quickly in female
subjects (about
6.50 hours) as in male subjects (about 12.0 hours).
[000162] In accordance with the present invention, mean peak serum
concentrations are
achieved with the topical semi-solid imiquimod pharmaceutical formulations of
the Examples
(see also Attachments I-XV) when topically applied as discussed herein
throughout. For
example, a mean peak serum concentration of about 0.488 ng/mL is achieved with
a 3.75%
dosage strength imiquimod pharmaceutical formulation 202 of Example 21 after
about 9.4 mg of
imiquimod is applied to the affected treatment area each day for up to 8
weeks.
[000163] Examples of various embodiments of the present invention will now
be further
illustrated with reference to the following examples. Thus, the following
examples are provided
to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to be limiting
thereof. Parts and
percentages are by weight unless otherwise specified. Examples of topical
imiquimod cream and
ointment compositions contemplated by the present invention are described in
U.S. Patent No.
4,689,338 and U.S. Patent No. 5,238,944. Percent modifications for, e.g.,
imiquimod and
vehicle, to generate imiquimod formulations as described herein are likewise
contemplated by the
present invention. In addition, the formulations described and disclosed in
U.S. Patent No.
47
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
7,655,672, U.S. Patent Publication No. 2007/0123558, Serial No. 11/276,324,
U.S. Patent
Publication No. 2007/0264317, U.S. Serial No. 11/433,471, U.S. Patent
Publication No.
2007/0900550 and PCT Publication No. W02008098232 (Al), are also contemplated
by the
present invention.
EXAMPLE 1
Pump Performance Attribute Tests
[000164] A series of pump performance attribute testing is conducted to
assess the best
pump design for, for example, by weight 2.5%, 3.75% and 5% w/w imiquimod
creams, such as
described in Examples 16 and 20. The performance attributes tests and
respective acceptance
criteria are described below.
A. Priming:
[000165] The purpose of this test is to determine the number of actuations
necessary to start
observing delivery of the product dispensed from the actuator. Additionally,
the number of pump
depressions, i.e., the number of depressions/actuations required until the
first full dose is
delivered is also monitored.
[000166] Acceptance Criteria: The number of actuations to start observing
delivery of the
product dispensed from the actuator must be less than or equal to 5
actuations.
B. Dosage Reproducibility:
[000167] The purpose of this test is to measure the doses restituted by the
pump and verify
the consistency of the dose value with time. Pumps are actuated manually.
[000168] Acceptance Criteria: For each pump, the average of 10 individual
dose values
must be within about 10% of the pumps nominal value of about 240 mg and each
individual dose
value must be within about 15% of the pump's nominal value of about 240 mg.
C. Sealing Integrity under Vacuum:
48
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000169] The purpose of this test is to evaluate the sealing integrity of a
specific pump and
container configuration when placed under vacuum. The sealing integrity of a
pump corresponds
to its ability to retain the product in the container and play its role in the
closure of the system.
Unprimed pump samples are filled with the product to be tested, are positioned
horizontally for
about 20 minutes at room temperature in a vacuum chamber at about 24" Hg
depression.
[000170] Acceptance Criteria: There must be no visual sign of leakage.
D. Weight Loss at Atmospheric Pressure:
[000171] The purpose of this test is to evaluate the sealing integrity of
each pump and
container configuration stored under specific conditions. For this test,
filled samples are
weighed, stored at specific conditions and then weighed again to measure for
any weight loss.
[000172] Acceptance Criteria: Weight loss values must typically not exceed
about 0.3%
after 4 weeks at room temperature and about 1.0% after about 4 weeks at about
45 C (based on the
total weight of the package).
E. Restitution Rate:
[000173] The purpose of this test is to determine the portion of product
delivered by a
package after the pump can no longer dispense any product and compare it to
the quantity of
product used to fill the package.
[000174] Acceptance Criteria: The restitution rates depend on the type of
package and the
type of filling (airless or atmospheric).
F. Dose Through Life:
[000175] This test measures the dose restituted by the pump/device
mechanism during each
actuation until the container is empty. Devices are manually actuated.
[000176] Acceptance Criteria: The overall average of the dose value must be
within about
10% of the pump's nominal dose value of about 240 mg of product. Each
individual dose value
must be within about 15% of the pump's nominal dose value. The pump is
considered to have
49
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
met the Dose through life criteria if it provides about 240 mg of product and
if it meets restitution
rate criteria.
G. Loss of Prime:
[000177] The purpose of this test is to evaluate the ability of a pump to
retain its prime over
a specific storage time. The loss of prime is defined as the amount of product
that returns from
the dose chamber back into the container after storage in an upright position.
"Shot" weights are
measured before and after storage to determine the loss of prime and the
percentage of dose
retained.
[000178] Acceptance Criteria: The pump must retain its prime during
storage. The
percentage of dose retained (ratio of dose after storage to dose before
storage) must be more than
about 85% in order to deliver a consistent, uniform and effective dosage
amount.
H. Gasket Swelling:
[000179] This test measures the change in thickness of the gasket following
storage in
contact with the product. Relevant sets of gaskets (two gaskets per set) with
the same chemical
composition and similar thickness are stored at about 45 C for about 8 weeks
containers filled
with product to be tested. The samples are stored at about 45 C at about 1,
about 4 and about 8
weeks interval are tested for the thickness of the gaskets at about room
temperature.
Additionally, the following conditions are observed: gaskets' deformation and
color change in
product or gaskets; samples will be compared with a control sample.
[000180] Acceptance Criteria: The swelling of the gasket should be not more
than about
15%. Also there should be no shrinking and no discoloration of the gasket and
the product.
I. Migration:
[000181] The purpose of this test is to check that the pigments in a
colored plastic material
do not migrate into the customer's formulation. After priming, samples will be
stored at about
45 C for about 1 week. On each day, two samples will be actuated and the
dispensed bulk will
be compared to the control sample. Additionally after about 4 weeks at about
45 C all samples
will be emptied and bulk will be compared to the control sample. The dispensed
product will be
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
examined and inspected for the presence of pigments that might have migrated
from the actuator
or for any color modification of the bulk when compared to the bulk dispensed
by the control
sample.
[000182] Acceptance Criteria: It is considered that migration has occurred
if the presence of
colored pigments is observed in the tested product when compared to the
product dispensed by
the controlled samples.
J. Corrosion of the Metal Components:
[000183] The purpose of this test is to assess the compatibility between
the active
formulation and the pump metal components after being in contact for a
specific period of time.
[000184] Corrosion of the Pump Metal Components is defined as the oxidation
of pump
metal components when exposed to the active formulation. Relevant components
(spring(s) and
stainless steel ball) will be stored in containers in intimate contact with
product, at ambient
temperature and elevated temperature (about 45 C/75% RH). Components will be
inspected at 3
days, 1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 12 weeks and 24 weeks. Components are
inspected for
oxidation on the pump metal components at each time point.
[000185] Acceptance Criteria: The results are verified against the
reference sample.
K. Discoloration of Formulation:
[000186] The purpose of this test is to assess the compatibility between
the product and the
pump components after being in contact with the product for a specific period
of time.
Discoloration of Formulation is defined as the change of color of active
formulation when in
contact with pump components for a specific amount of time. The components
will be stored in
containers at ambient temperature and elevated temperature (about 45 C/75%
RH). Change of
color in the active product will be examined at 3 days, 1 week, 2 weeks, 4
weeks, 8 weeks, 12
weeks and about 24 weeks at Room Temperature and about 45 C/75% RH.
[000187] Acceptance Criteria: The results are verified against the
reference sample.
51
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
L. Pouch Compatibility (Nova System Only):
[000188] The purpose of this test is to verify the compatibility of a pouch
foil material with
the formulation after 4 weeks of aging at about 45 C in terms of welding
resistance and physical
appearance. After aging, each sample will be cut into two 15 mm strip film and
a total of 10 test
strips is obtained. Strips will be measured for the split force using the
dynamometer. Samples
will be visually inspected to verify the absence of physical defects such as
de-lamination,
blistering or spotting.
[000189] Acceptance Criteria: Pull force that is required to split the
welded parts of the foil
must be about 1.5 Kg minimum and no physical defects are observed after
storage for about 4
weeks at 45 C.
EXAMPLE 2
Pump Filling Trials
[000190] A series of pump filling trials were conducted at two different
facilities. In both
facilities the filling process and equipment were identical. In each process,
the cream formulation
is filled under vacuum into the container barrel using volumetric dose pumps.
The barrel and the
pump head or upper assembly with the actuator is joined ("snapped on") to the
pump body under
vacuum. This packaging process enables delivery of a precise quantity of
product by depression
of the pump mechanism, avoiding any contact with air.
[000191] The filling trials as well as any salient observations and
conclusions for each trial
are described below.
A. Filling Trial #s F008-08 and F009-08 at Facility I
[000192] Initial fill trials are conducted on the Albion pump system to
determine the
capability of the filling equipment to fill the creams and also the
flowability of the cream during
the filling process. The pump body and the stem are made of polybutylene
terephthalate, the
actuator is made of polypropylene homopolymer/low density polyethylene and the
piston is made
of high density polyethylene material.
52
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000193] A fill weight of about 7.5 g and about 15 g are selected for these
trial runs. These
fill weights correspond to the quantity of cream necessary to provide a full
course of therapy to
the patient depending on which indication is being treated. The filling trial
runs prove that
Imiquimod cream about 2.5% w/w (Lot #GJB070) manufactured by 3M, Loughborough,
UK, can
successfully be packaged using the airless filling process per Valois filling
parameters.
[000194] The filling trials prove that the about 2.5% w/w cream can be
successfully filled
into the pumps. However, it is also noted that filling issues causing lower
pump delivery values,
i.e., shot weight, are caused by air bubbles entrapped in the bulk cream. This
problem is
corrected by avoiding introduction of air during the transfer of the product
from the storage drum
to the filling hopper.
[000195] All performance tests and physical stability screening data
support that the Albion
Pump Model Albion 30 ml EV09/150 pl and VP39/70 1-15 ml Digital actuator can
be
successfully filled and warrant further development.
B. Filling Trials #s 2027 through 2324 at Facility II
[000196] These series of trials focuses on selecting which Albion and/or
Nova Pump Model
to commercialize, pump fill overages that are required to ensure a about 7.5
gm and about 15 gm
pump delivery, pump actuator size, use of a cocoon tip, and contact materials
to be used in each
respective pumps. In addition, several of the package presentations are placed
on RT and
accelerated conditions to help select the most compatible pump design for
Imiquimod about
2.5%, about 3.75% and about 5% w/w cream.
[000197] The trials and corresponding observations are discussed below:
[000198] 1.) Filling #s 2022 (about 2.5%) and 2026 (about 3.75%) ¨ about
7.5 g fill
weight.
[000199] Albion 15 ml pump with standard actuator, standard piston and
about 150 11.1
dosing is filled with irniquimod cream about 2.5% w/w (lot #GJJ067) and
imiquimod cream
53
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
about 3.75% w/w (Lot #GJJ068). The piston is made of high density polyethylene
and the
position of the piston inside the pump is set to deliver about 7.5 g.
[000200] The product-components compatibility are satisfactory but the
weight loss for
about 4 weeks at about RT and loss of prime at about 1 week are not acceptable
in both trials.
[000201] 2.) Filling #s 2023 about (2.5%) and 2027 (about 3.75%) ¨ about
15 g fill
weight.
[000202] Albion 15 ml pump with standard actuator, standard piston and
about 150 I
dosing is filled with imiquimod cream about 2.5% w/w (lot #GJJ067) and
imiquimod cream
about 3.75% w/w (Lot #GJJ068). The piston is made of high density polyethylene
and the
position of the piston inside the pump was set to deliver about 15 g.
[000203] The product-components compatibility is satisfactory but loss of
prime at about 2
weeks is not acceptable in both trials.
[000204] 3.) Filling #s 2024 (about 2.5%) ¨ about 7.5 g fill weight.
[000205] Nova 15 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150 t1
is filled
with about 7.5 g of Imiquimod cream about 2.5% w/w (Lot #GJJ067).
[000206] During the testing it is observed that the pouch material is
delaminating and not
suitable for this cream product. It is theorized that the high concentration
(about 20%) of
isostearic acid in the cream formulation causes the delamination of these
pouches.
[000207] 4.) Filling #s 2025 (about 2.5%) ¨ about 15 g fill weight.
[000208] Nova 30 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150 1
with pouch
is filled with about 15 g of about 2.5% w/w of the cream (Lot #GJJ067).
54
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000209] On testing, it is observed that the pouch material is delaminating
and not suitable
for this cream product.
[000210] 5.) Filling #s 2028 (about 3.75%) ¨ about 7.5 g fill weight.
[000211] Nova 15 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150 I
with pouch
is filled with about 7.5 g of about 3.75% of the cream (Lot #GJJ068).
[000212] On testing it is observed that the pouch material is delaminating
and not suitable
for this cream product.
[000213] 6.) Filling # 2029 (about 3.75%) ¨ about 15 g fill weight.
[000214] Nova 30 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150 IA
with pouch
is filled with about 15 g of the cream (Lot #GJJ068).
[000215] On testing, it is observed that the pouch material is delaminating
and not suitable
for this cream product.
[000216] 7.) Filling # 2060 (about 5.0%) ¨ about 7.5 g fill weight.
[000217] Albion 15 ml piston pump with standard actuator dosage about 150
1 with the
position of the piston inside the pack set to deliver about 7.5 g is filled
with Aldara Cream 5%
w/w (lot #GJF033).
[000218] The product-components compatibility is satisfactory but loss of
prime at 2 week
is not acceptable.
[000219] 8.) Filling # 2061 (about 5.0%) ¨ about 15 g fill weight.
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000220] Albion 15 ml piston pump with standard actuator dosage about 150
IA with the
position of the piston inside the pack set to deliver about 15 g is filled
with Aldara Cream about
5% w/w (lot #GJF033).
[000221] The product-components compatibility is satisfactory but loss of
prime at about 1
week is not acceptable.
[000222] 9.) Filling # 2062 (about 5%) ¨ about 7.5 g fill weight.
[000223] Nova 15 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150
ill with pouch
is filled with about 7.5 g of Aldara , Cream about 5% w/w (Lot #GJF033).
[000224] Delamination of pouch material and loss of prime at about 2 weeks
are not
acceptable.
[000225] 10.) Filling # 2063 (about 5%) ¨ about 15 g fill weight.
[000226] Nova 30 ml with aluminum pouch pack standard actuator about 150 I
with pouch
is filled with about 15 g of Aldara Cream about 5% w/w (Lot #GJF033).
[000227] Delamination of pouch material and loss of prime at about 2 days
are not
acceptable.
[000228] 11.) Filling # 2084 (about 2.5%) ¨ about 15 g fill weight.
[000229] Albion 15 ml EV09/240 I pump with standard actuator dosage about
240 I to
deliver about 240 mg shot weight is filled with low strength Imiquimod cream
about 2.5% w/w
(Lot #GJJ067).
[000230] All physical test results are acceptable but there is a trend for
loss of prime to
decrease. However at about 4 weeks, the loss of prime is about 85.2% which is
at the lower limit
(about 85.0%) of the specification for loss of prime.
56
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000231] 12.) Filling #s 2085 (3.75%) - about 15 g fill weight.
[000232] Albion 15 ml EV09/ about 240 1 pump with standard actuator dosage
about 240
!Al to deliver about 40 mg shot weight is filled with low strength Imiquimod
cream about 3.75%
w/w (lot #GJJ068).
[000233] All the physical test results are acceptable; however loss of
prime at 4 weeks
testing is at about 78.2% which fails the acceptance criteria limit of about
85.0%.
[000234] 13.) Filling #2103 (5%) - about 15 g fill weight.
[000235] Albion 15 ml EV09/ about 240 I pump with standard actuator dosage
about 240
1 with the position of the piston inside the pack set to deliver about 15 g is
filled with imiquimod
cream about 5% w/w (lot #GJF033).
[000236] All the physical test results are acceptable but loss of prime at
about 4 weeks
testing is at about 79.5% and fails the acceptance criteria limit of about
85.0%.
[000237] Summary of Trials #s 2022 ¨ 2103.
[000238] Based on the results from trials # 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2026,
2027, 2028, 2029,
2060, 2061, 2062, 2063, 2084, 2085 and 2103, there is a potential for failure
for loss of prime
using the standard actuator. It is theorized that these failures are
attributable to the possibility of
drying of the cream at the exposed tip of actuator nozzle.
[000239] To prevent the potential of drying of the cream and also protect
the cream from the
atmospheric environment, a pump with shutter or cocoon actuator is
investigated. However, in
order to utilize the cocoon actuator, the pump size is adjusted to from about
15 mL to about 30
mL.
57
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000240] Pumps with a cocoon actuator in about 30 mL volume pump are
subsequently
tested. These pumps also utilize a piston made of low density polyethylene
material (standard),
while the pumps that are tested previously used high density polyethylene
pistons. Initial tests
are carried out with pumps with low density polyethylene pistons to check for
performance of the
pump with the cream.
[000241] 14.) Filling # 2274 (about 3.75%) - about 7.5g fill weight.
Filling # 2275 (about 3.75%) - about 15 g fill weight.
[000242] Albion 30 mL pump EV9/ about 240 111 equipped with a cocoon
actuator dosage
about 240 1 with the piston made up of low density polyethylene are filled at
about 7.5 g and
about 15 g fill weights using Imiquimod cream about 3.75% w/w (Lot # GJJ068).
The fill
weights are determined to be about 10.5 grams with the restitution rate of
about 7.5 g and about
18 g with the restitution rate of about 15 g as almost about 3 g of the cream
is held back in the
dosing chamber. All pumps have their piston moved to the position during the
snapping of the
actuator unit to avoid empty space on the top of the pump barrel.
[000243] Once again, Study #s 2274 and 2275 utilizing pumps with standard
piston made of
low density polyethylene material, where as all previous studies are conducted
using pistons
made up of high density polyethylene material.
[000244] All the physical test results are acceptable and loss prime at
about 4 weeks testing
is at about 95.8% and about 96.6% respectively thus possibly confirming the
earlier theory that
the failure for loss prime may be attributed to drying of the cream at nozzle
tip once actuated.
The use of the cocoon actuator or shutter surprisingly and unexpectedly, but
successfully,
corrected the loss of prime issue.
[000245] 15.) Filling #2324 (about 3.75%) ¨ about 7.5g fill weight.
[000246] This study is initiated with Albion 30 mL Pump EV9/ about 240 I
and cocoon
actuator with piston made of high density polyethylene material (the pump body
and the stem are
made of polybutylene terephthalate, the actuator is made of polypropylene
homopolymer/low
58
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
density polyethylene and the piston is made of high density polyethylene
material). The pump is
filled with Imiquimod cream about 3.75% w/w (lot #G.1J068). Based on
evaluating the restitution
rate, it is estimated that approximately 3 g of the cream is left in the pump
chamber. As a result, a
fill weight of about 10.5g is required to meet about 7.5 g Label claim.
[000247] The main goal of this study is to prove that the change of piston
material from low
density to high density polyethylene material does not affect the performance
of the pump
systems of the present invention.
EXAMPLE 3
Stress and Stability Testing Results
A. Stress Testing/Stability Results
[000248] Several observations are made during the stress testing of the
about 2.5%, about
3.75% and about 5% w/w imiquimod creams filled in the above filling trials (#
2022 to # 2029).
[000249] The observations are as follows:
[000250] 1. Delamination is observed of the Nova laminated pouch
material when it is
stored at accelerated conditions (i.e. > about 40 C). This leads to
discontinuing any further
development work with this pump model.
[000251] 2. Loss of prime in both Nova and Albion pump models is
observed after one
week of storage. This is surprisingly corrected by using the Albion pump with
cocoon actuator.
B. Stability Testing Results
[000252] Several stability programs per ICH guidelines involving a series
of pump options,
components, fill weights and imiquimod creams are initiated.
[000253] Table 2 illustrates the stability studies and the corresponding
creams that are used,
fill run number, lot number of bulk cream that is used, fill weight, pump
model and packaging
description.
59
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000254] Described below is a summary of each of the stability studies that
are conducted.
The data collected for each stability study can be found in Attachments I-IV.
Table 2. Imiquimod Cream Stability Studies
Table 2
Stability Imiquimod Fill Bulk Fill
Study (IMQ) Run Cream Lot Weight Pump Model Package
Cream # # Description
why
GW 2.5% IMQ 2022 GJJ067 ¨ 7.5 g Albion 7.5 g fill in
15 mL
805-01 2.5% EV09/150 ¨ Albion pump with
15mL 150 p.1 actuator
GW 2.5% IMQ 2023 GJJ067 ¨ 15 g Albion 15 g fill in
15 mL
805-01 2.5% EV09/150 ¨ Albion pump with
15mL 150 pi actuator
GW 2.5% IMQ 2024 GJJ067 ¨ 7.5 g Nova Pump 7.5 g fill in 15
mL
805-01 2.5% EV09/150 ¨ Nova pump with
15mL pouch 15 mL Aluminum
pouch
GW 2.5% IMQ 2025 GJJ067 ¨ 15 G Nova Pump 15 g fill in 15
mL
805-01 2.5% EV09/150 ¨ Nova pump with
30mL 30 mL Aluminum
pouch
GW 3.75% IMQ 2026 GJJ068 ¨ 7.5 g Albion 7.5 g fill in
15 mL
805-01 3.75% EV09/150 ¨ Albion pump with
15mL 150 1.11 actuator
GW 3.75% IMQ 2027 GJJ068 ¨ 15 g Albion 15 g fill in
15 mL
805-01 3.75% EV09/150 ¨ Albion pump with
15mL 150 p.1 actuator
GW 3.75% IMQ 2028 GJJ068 ¨ 7.5 g Nova Pump 7.5 g fill in 15
mL
805-01 3.75% EV09/150 ¨ Nova pump with
15mL pouch 15 mL Aluminum
pouch
GW 3.75% IMQ 2029 GJJ068 ¨ 15 g Nova Pump 15 g fill in 15
mL
805-01 3.75% EV09/150 ¨ Nova pump with
30mL pouch 30 mL Aluminum
pouch
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Table 2
Stability Imiquimod Fill Bulk Fill
Study (IMQ) Run Cream Lot Weight Pump Model Package
Cream # # Description
w/w
GW 5% Aldara 2080 GJF033 ¨ 7.5 g Albion 7.5
g fill in 15 mL
906-01 5% EV09/150 ¨
Albion pump with
15mL 150 1 actuator
GW 5% Aldara 2081 GJF033 ¨ 15 g Albion 15
g fill in 15 mL
906-01 5% EV09/150 ¨
Albion pump with
15mL 150111 actuator
GW 5% Aldara 2082 GJF033 ¨ 7.5 g Nova Pump 7.5
g fill in 15 mL
906-01 5% EV09/150 ¨
Nova pump with
15mL pouch 15
mL Aluminum
pouch
GW 5% Aldara 2083 GJF033 ¨ 15 g Nova Pump 15
g fill in 15 mL
906-01 5% EV09/150 ¨
Albion pump with
30mL pouch 30 mL Aluminum
pouch
GW 2.5% IMQ 2084 GJJ067 ¨ 15 g Albion 15
g fill in 15 mL
805-01 2.5% EV09/240 ¨
Albion pump with
15mL 240 I actuator
GW 3.75% IMQ 2085 GJJ068 ¨ 15 g Albion 15
g fill in 15 mL
907-01 3.75% EV09/240 ¨
Albion pump with
15mL 240 1 actuator
GW 5% Aldara 2103 GJF033 ¨ 15 g Albion 15
g fill in 15 mL
907-01 5% EV09/240 ¨
Albion pump with
15mL 240 I actuator
GW 3.75% IMQ 2274 GJJ068 ¨ 7.5 g Albion 15
g fill in 30 mL
907-01 3.75% EV09/240 ¨
Albion pump with
30mL with 240 1 cocoon
cocoon actuator/PEBD
piston
GW 3.75% IMQ 2275 GJJ068 ¨ 15 g Albion
Albion EV09/240 ¨
921-01 3.75% EV09/240 ¨
30mL with cocoon
30mL with actuator/PEBD
cocoon piston 15 g fill
GW 3.75% IMQ 2324 GJJ068 ¨ 7.5 g Albion
Albion EV09/240 ¨
921-01 3.75% EV09/240 ¨
30mL with cocoon
30mL with actuator/PEHD
cocoon piston 15
*The 2.5%, 3.75% and 5.0% imiquimod creams are isa cream formulation numbers
146, 202 and
61
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
16, respectively, and are the creams used in Examples 1-4 and Attachments I-
XV, respectively.
[000255] 1.) Stability Study GW 805-01- Summary.
[000256] Several observation/conclusions can be drawn from this study.
[000257] First, the delamination of the Nova pump pouch can be clearly
viewed as early as
about 2 months under accelerated conditions (about 40 C/75% RH).
[000258] All other testing (imiquimod assay, viscosity, benzyl alcohol,
methyl and propyl
parabens, pH, and 4 hydroxy imiquimod) remain well within specification and
within the trend
that is observed in the stability data for each cream in the commercial
sachets presentation. The n-
oxide testing is not performed initially as the method is not developed,
however the method is
available for testing the samples that are stored for about 9 month period at
about 25 C160 RH
and no detectable levels of n-oxide are observed.
[000259] This data can be seen in Attachment I.
[000260] 2.) Stability Study GW 906-01- Summary.
[000261] This study is conducted to determine the compatibility/stability
of the Aldara
about 5% w/w (imiquimod) cream formulation in both about 7.5 g and about 15 g
fill weight in
Albion and Nova pump systems. The stability of the formulations in both the
Albion over about
nine months and Nova pumps over about a three month period are consistent and
passes all
specifications. However, a notable difference in lower viscosities of the
formulations at about
T=0 and at subsequent time points can be observed which is due to the age ( 6
months) of the
bulk cream that is used for filling trials . Furthermore, the internal
surfaces of the pouch for the
Nova pumps that is stored at about 40 C/75% RH are observed to delaminate
after about 2
months at both fill volumes (about 7.5 and about 15 g), and are subsequently
discontinued from
testing after the about 3 month time point.
62
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000262] The stability data up to and including about 9 months, indicates
that the Albion
pump at the fill volumes of about 7.5 and about 15 g with the Aldara about 5
w/w
formulation is suitable for commercial use.
[000263] Both fill volumes (about 7.5 and about 15 g) is stored in the
Albion pumps at
about 40 C175% RH for about 3 months passes the PET test for all organisms
according to the
European Pharmacopeia and for the organism E. coli, which is an additional
requirement for the
United States Pharmacopeia.
[000264] All other testing (imiquimod assay, viscosity, benzyl alcohol,
methyl and propyl
parabens, pH, and 4 hydroxy imiquimod) remain well within specification and
within the trend
that is observed in the stability data for Aldara 5% w/w cream in the
commercial sachets
presentation.
[000265] The samples are also analyzed using the n-oxide method following
about 9 months
storage at about 25 C/60% RH and no detectable levels of n-oxide are observed.
[000266] This data is in Attachment II.
[000267] 3.) Stability Study GW 907-01- Summary.
[000268]
The stability of the formulations in the Albion pump over about six months for
all
three concentrations of imiquimod (about 2.5%, about 3.75% and about 5% w/w)
meet all
specifications (imiquimod assay, viscosity, benzyl alcohol, methyl and propyl
parabens, pH, and
4 hydroxy imiquimod) and compare well with the equivalent formulations that
are stored in
borosilicate glass vials over the same period of time. The results also
demonstrate the same
trends that are observed in the stability data for each cream in the
commercial sachet presentation.
However, a notable difference between the results in this study and those that
are observed in
other 2.5%, 3.75% and 5% w/w imiquimod creams. In the commercial sachet
presentation are
the lower viscosities of the formulations at about 1=0 and the subsequent time
points. This is the
direct result of the age of the bulk cream (z 2 months) prior to filling.
63
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000269] The samples are also analyzed using the n-oxide method following 9
months
storage at about 25 C/60% RH and no detectable levels of n-oxide are observed.
[000270] In addition, all the formulations that are stored in the Albion
pumps at about
40 C/75 RH for about 3 months passes Preservative Efficacy Test (PET) for all
organisms
according to the European Pharmacopeia and for the organism E. coli which is
an additional
requirement for the United States Pharmacopeia. This data is in Attachment
III.
[000271] 4.) Stability Study GW 921-01- Summary.
[000272] The stability of Imiquimod cream about 3.75% in Albion 30 mL EV09/
about 240
1 (the pump body and the stem are made of polybutylene terephthalate, the
actuator is made of
polypropylene homopolymer/low density polyethylene and the piston is made of
high density
polyethylene material). The pump is equipped with a cocoon actuator. The test
results for
samples that are stored for about 6 months at about 25 C/60% RH and about 40
C175 RH meet
all specifications (imiquimod assay, viscosity, benzyl alcohol, methyl and
propyl parabens, pH,
and 4 hydroxy imiquimod). In addition, the data compares well with the
equivalent formulation
that is stored in borosilicate glass vials over the same period of time and
also within the trends
that are observed in the stability data for each cream in the commercial
sachet presentation. The
data for top, middle and bottom samples that are taken for imiquimod, parabens
indicate that the
product is homogenous in the pump.
[000273] All samples are also analyzed using the n-oxide method following 6
months
storage at about 25 C/60% RH and about 40 C/75 RH. There are no detectable
levels of n-oxide
observed. This data is in Attachment IV.
EXAMPLE 4
Additional Studies Conducted
A. USP extractable Testing
[000274] The pump delivery system, Albion 30 mL EV09/ about 240 I is
equipped with a
cocoon actuator (pump body and the stem are made of polybutylene
terephthalate, the actuator is
64
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
made of polypropylene homopolymer/low density polyethylene and the piston is
made of high
density polyethylene material) that is selected for commercial use meets USP
32/NF 27 <661>
Physicochemical Tests-Plastics, and USP <281 > for Residue on Ignition.
[000275] This report is provided in Attachment V.
B. Patient in Use Test
[000276] In addition to the tests discussed in this report, Albion 30 mL
EV09/ about 240 1
with cocoon actuator (the pump body and the stem are made of polybutylene
terephthalate, the
actuator is made of polypropylene homopolymer/low density polyethylene and the
piston is made
of high density polyethylene material) is tested to simulate the patient's
clinical treatment period
for 2 weeks on 2 weeks off and 2 weeks on.
[000277] In this study, the pump is primed and actuated once every day for
2 weeks and
then left static for 2 weeks. At the end of 2 weeks of no pump actuation, the
pump is again
actuated for 2 more weeks to check if a consistent and uniform dosage amount
of cream is
available to patient for the treatment period. The results are acceptable as
the pump provides
approximately 240 mg cream for each daily application during all 4 weeks of
the treatment. The
data is provided in the Attachment VI.
C. Leak Test during stability study
[000278] During the course of the stability studies (about 12 month time
point for GW 805,
906, 907 and 9 months for GW 921), it is decided to place all pumps on their
sides to monitor
leaking and delivery performance.
[000279] There is no leaking of the product from the pumps and all pumps
delivery
performance is acceptable.
[000280] Based on the satisfactory physical, chemical and performance
testing data, Albion
30 mL EV09/ about 240 1,t1 cocoon actuator (the pump body and the stem are
made of
polybutylene terephthalate, the actuator is made of polypropylene
homopolymer/low density
polyethylene and the piston is made of high density polyethylene material) is
remarkable and
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
surprisingly acceptable and, therefore, selected for commercialization. In
addition, the NDA
registration stability batches using this pump filled at both about 7.5g and
about 15g fill using
3.75% and 5% w/w imiquimod cream are manufactured and are placed on stability
at 3M,
Loughborough, UK. This pump system is covered under Valois's DMF number 18156
"Albion
30 nil Piston Assembled Barrel + EV09/240 Pump + PR820 Cocoon Actuator + Cap".
The pump
parts, assembly and specifications are provided in Attachment VII.
EXAMPLE 5
Imiquimod Cream Formulation 5
[000281] A cream according to the present invention is prepared from the
following
ingredients in Table 3.
Table 3. Imiquimod Cream Formulation 5
Example 5 Example
5
% by Weight Amount
Oil Phase
1 -isobutv1-1H-imidazo f 4.5-cl -a uinolin-4-amine 1.0
40.0 a
Isostearic acid 10.0 400.0 g
Benzyl alcohol 2.0 80.0 g
Cetyl alcohol 2.2 88.0 g
Stearyl alcohol 3.1 124.0 g
Polysorbate 60 2.55 102.0 g
Sorbitan monostearate 0.45 18.0 g
Aqueous Phase Glycerin 2.0 80.0 g
Methylparaben 0.2 8.0 g
Propylparaben 0.02 0.8 g
Purified water 76.48 3059.2 g
[000282] The materials listed above were combined according to the
following procedure.
[000283] The glycerin, methylparaben, propylparaben and water were weighed
into a 4 liter
glass beaker then heated on a hot plate with stirring until the parabens
isostearic acid and 1-
isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-4-quinolin-4-amine were weighed into an 8 liter
stainless steel beaker
and heated on a hot plate until the amine was in solution (the temperature
reached 69 C.). The
benzyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, polysorbate 60 and sorbitan
monostearate were
added to the isostearic acid solution and heated on a hot plate until all
material was dissolved (the
66
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
temperature reached 75 C.). With both phases at approximately the same
temperature
(65 -75 C.), the water phase was added to the oil phase. The mixture was mixed
with a
homogenizer for 13 minutes then put into a cool water bath and mixed with a 3
inch propeller for
40 minutes (the temperature was 29 C.). The resulting cream was placed in
glass jars.
EXAMPLES 6-13
Imiquimod Cream Formulations 6-13
[000284] Using the general method of Example 5, the imiquimod cream
formulations shown
in Tables 4 and 5 are prepared.
Table 4. Imiquimod Cream Formulations 6-9
% by Weight
Example 6 Example 7
Example 8 Example 9
Oil Phase
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5- 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
c]quinolin-4-amine
Isostearic acid 10.0 10.0 5.0 5.0
Benzyl alcohol 2.0
Cetyl alcohol 1.7
Stearyl alcohol 2.3
Cetearyl alcohol 6.0 6.0 6.0
Polysorbate 60 2.55 2.55 2.55 2.55
Sorbitan monostearate 0.45 0.45 0.45 0.45
Brij im 30a 10.0
Aqueous Phase
Glycerin 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
Methylparaben 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Purified water 77.78 77.78 82.78 72.78
a Brirm 30 (polyoxyethylene(4) lauryl ether) is available from ICI Americas,
Inc.
Table 5. Imiquimod Cream Formulations 10-13
% by Weight
Example 10 Example 11 Example 12
Example 13
Oil Phase
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo-[4,5- 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
c]quinolin-4-amine
67
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Isostearic acid 10.0 25.0 10.0 6.0
Benzyl alcohol 2.0 2.0
Cetyl alcohol 2.2 1.7
Stearyl alcohol 3.1 2.3
Cetearyl alcohol 6.0 6.0
Polysorbate 60 2.55 3.4 2.55 2.55
Sorbitan monostearate 0.45 0.6 0.45 0.45
Brij im 30a 10.0
Aqueous Phase
Glycerin 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
Methylparaben 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Purified water 67.78 60.48 79.78 79.78
a BrijTM 30 (polyoxyethylene(4) lauryl ether) is available from ICI Americas,
Inc.
EXAMPLE 14
Imiquimod Cream Formulation 14
[000285] A cream according to the present invention is prepared from the
following
ingredients in the following Table 6.
Table 6. Imiquimod Cream Formulation 14
% by Weight Amount
Oil Phase
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo [4,5- 1.0 3.00 g
c]quinolin-4-amine
Isostearic acid 5.0 15.0 g
White petrolatum 15.0 45.0 g
Light mineral oil 12.8 38.4 g
Aluminum stearate 8.0 24.0 g
Cetyl alcohol 4.0 12.0 g
Witconollm 14a 3.0 9.00 g
Acetylated lanolin 1.0 3.0 g
Propylparaben 0.063 0.19g
Aqueous Phase
Veegumlm Kb 1.0 3.0 g
Methylparaben 0.12 0.36 g
Purified water 49.017 147.05g
aWitconollm 14 (polyglycery14 oleate) is available from Witco Chemical Corp.
Organics Division
bVeegumTM K (colloidal magnesium aluminum silicate) is available from R. T.
Vanderbilt Company Inc.
68
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
[000286] The materials listed above were combined according to the
following procedure:
The 1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine and the isostearic acid were
weighed into a
glass jar and heated with occasional stirring until the amine was dissolved
(the temperature
reached 68 C.). To this solution was added, the petrolatum, mineral oil,
aluminum stearate, cetyl
alcohol, WitconolTM 14, acetylated lanoline and propylparaben. The mixture was
heated to 75 C.
In a separate beaker, the methylparaben and water were combined and heated
until the paraben
dissolved (the temperature reached 61 C.). The VeegumTM K was added to the
aqueous solution
and heated at 75 C. for 30 minutes while mixing with a homogenizer. With both
phases at 75 C.,
the aqueous phase was slowly added to the oil phase while mixing with a
homogenizer. Mixing
was continued for 30 minutes while maintaining a temperature to about 80 C.
The jar was then
capped and the formulation was allowed to cool.
EXAMPLE 15
Imiquimod Ointment Formulation 15(a) and 15(b)
[000287] An ointment according to the present invention is prepared from
the ingredients in
the following Table 7.
Table 7. Imiquimod Ointment Formulation 15(a)
Example 15(a) Example 15(a)
% by Weight Amount
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo [4,5-c1quinolin-4-Amine 1.0 0.20 g
Isostearic acid 5.0 1.00 g
Mineral oil 12.8 2.56.g
White petrolatum 65.2 13.04g
Cetyl alcohol 4.0 080g
Acetylated lanolin 1.0 0.20 g
Witconollm 143.0 0.60g
Aluminum stearate 8.0 1.60 g
[000288] The materials listed above are combined according to the following
procedure.
[000289] The 1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quino1in-4-amine and the
isostearic acid were
placed in a glass jar and heated with stirring until the amine was dissolved.
The remaining
69
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
ingredients were added and the resulting mixture was heated to 65 C. and then
mixed while being
allowed to cool to room temperature.
[000290] Using the general procedure of Example 15, an ointment containing
the
ingredients in the following Table 8 is prepared.
Table 8. Imiquimod Ointment Formulation 15(b)
Example 15(b) Example 15(b)
% by Weight Amount
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-clquinolin-4-Amine 1.0 0.20 g
Isostearic acid 6.0 1.20 g
Polyethylene Glycol 400 55.8 11.16 g
Polyethylene Glycol 3350 32.6 6.52 g
Stearyl alcohol 4.6 0.92 g
EXAMPLES 16-18
Imiquimod Cream Formulations 16-18
[000291] Creams of the present invention are prepared using the ingredients
shown in Table
9. The Example 1 except that benzyl alcohol was used with the isostearic acid
to dissolve the 1-
isobuty1-1H-imidazo [4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine.
Table 9. Imiquimod Cream Formulations 16-18
Example 16 Example 17 Example 18
Amount % Amount % Amount %
by Weight by Weight by Weight
Oil Phase
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo [4,5-c]quinolin-4- 5.0 5.0 4.85
amine
Isostearic acid 25.0 25.0 24.3
Benzyl alcohol 2.0 2.0 1.94
Cetyl alcohol 2.2 2.2 1.16
Stearyl alcohol 3.1 3.1 1.75
Petrolatum 3.0 2.91
Polysorbate 60 3.4 3.4 4.13
Sorbitan monostearate 0.6 0.6 0.73
Stearic acid 9.71
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Aqueous Phase
Glycerin 2.0 2.0 1.94
Methylparaben 0.2 0.2 0.19
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02
EXAMPLES 19 and 20
Imiquimod Cream Formulations 19 and 20
[000292] A cream according to the present invention is prepared from the
ingredients in the
following Table 10.
Table 10. Imiquimod Cream Formulations 19 and 20
Example 19 Example 20
% by Weight % by Weight
Oil Phase Amount Amount
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-clquinolin-4-Amine 4.0 0.80g
Isostearic acid 20.0 4.00 g
Benzyl alcohol 2.0 0.40 a
Cetyl alcohol 2.2 0.49g
Stearyl alcohol 3.1 0.62 g
Polysorbate 60 3.4 0.68 g
Sorbitan mono stearate 0.6 0.12 g
Aqueous Phase
1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-clquinolin-4-amine 1.0 0.2g
Glycerin 2.0 0.4g
85% Lactic acid 1.0 0.22 g
Methylparaben 0.2 0.04 g
Propylparaben 0.02 0.004 g
Purified water 60.48 12.0 g
[000293] The materials listed above are combined according to the following
procedure:
The isostearic acid and 0.8 g of 1-isobuty1-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine
or 1-(2-
methylpropy1-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine were combined in a glass jar
and heated with
stirring until the amine had dissolved. The remaining oil phase ingredients
were added to this
solution and the mixture was heated to about 70 C. The aqueous phase
ingredients were weighed
into a separate beaker and heated with stirring until the amine and the
parabens had dissolved.
71
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
With both phases at about 70 C., the water phase was added to the oil phase
and mixed with a
propeller until the mixture cooled to room temperature.
EXAMPLE 21
Imiquimod Cream Formulations 21-254
[000294] Topical Imiquimod
Pharmaceutical Cream Formulations
[000295] Imiquimod creams are prepared in accordance with the present
invention using the
ingredients shown in Table 11 in this Example 21.
Table 11. Lower Dosage Strength Imiquimod Cream Formulations 21-254
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 21 22 23 24 25 26
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 1.00 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 68.98 66.98 64.98 61.98 60.73
60.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Total 100.00 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 27 28 29 30 31 32
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 66.98 60.98 60.98 57.08 58.98
55.78
72
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
' Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 1 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Total 100.00 100.00 , 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 33 34 35 36 _ 37 38
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 , 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 56.48 67.08 59.98 58.98 56.98
61.98
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20
0.20 . 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 39 40 41 42 43 44
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 1.00 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 68.73 66.73 64.73 61.73 60.48
60.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 45 46 47 48 49 50
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0 25.00
73
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 66.73 60.73 60.73 56.83 58.73 55.53
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.25
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 51 52 53 54 55 56
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
_
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 56.23 66.83 59.73 58.73 56.73 61.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.25 1.25 1.25 , 1.25 1.25
1.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 57 58 59 60 61 62
Fatty acid* _ 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 1.00 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 68.48 66.48 64.48 _ 61.48
60.23 60.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20
0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50
74
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100:00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 63 64 65 66 67 68
Fatty acid 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0 25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 66.48 60.48 60.48 56.58 58.48 55.28
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 69 70 71 72 73 74
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 55.98 66.58 59.48 58.48 56.48 61.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 75 . 76 77 78 79 80
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 . 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 1.00 . 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 68.23 66.23 64.23 61.23 59.98
59.98
-
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 81 82 , 83 84 85 86
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 _ 2.20 _
2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 66.23 60.23 60.23 56.33 58.23
55.03
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 87 88 89 90 91 92
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
_
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 _ 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 55.73 66.33 59.23 58.23 , 56.23
61.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
. Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 , 0.02
Imiquimod 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75 1.75
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
76
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 93 94 95 96 97 98
Fatty acid* 10.00 12.50 25.00 10.00 15.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.70 4.00 4.00 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.80 2.00 2.00 3.10
White petrolatum 5.00 5.00 3.00 3.40 2.80 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.80 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 5.00 5.00 2.00 1.00 3.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.30 0.70 0.75
Purified water 65.98 63.48 54.78 70.28 64.28
59.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 99 100 101 102 103 104
Fatty acid* 10.00 12.50 25.00 10.00 15.00
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.70 4.00 4.00 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.80 2.00 2.00 3.80
White petrolatum 5.00 5.00 3.00 3.40 2.80 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.80 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 5.00 5.00 2.00 1.00 3.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.30 0.70 0.50
Purified water 65.98 63.48 54.78 70.28 64.28
54.78
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 105 106 107 108 109 110
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
77
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 55.48 66.08 58.98 57.98 55.98 60.98
_
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 _
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 _
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 111 112 113 114 115 116 _
Fatty acid* 15.00 12.50 25.00 15.00 10.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.00 2.00 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 2.00 2.40 3.10
White petrolatum 6.00 5.00 3.00 3.40 2.80 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.00 3.40 3.80 3.80 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.20 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 5.00 5.00 2.00 3.00 3.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.30 0.30 0.75
Purified water 60.23 63.23 55.23 66.83 70.23 59.48
Benzyl alcohol 1.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 117 118 119 120 121 122
Fatty acid* 15.00 12.50 25.00 15.00 10.00 25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.00 2.00 2.70 _
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 2.00 2.40 3.80 _
White petrolatum 6.00 5.00 3.00 3.40 2.80 3.00 _
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.00 3.40 3.80 3.80 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 1.00 0.60 0.20 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 5.00 5.00 2.00 3.00 3.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.30 0.30 0.50
Purified water 60.23 63.23 55.23 66.83 70.23 54.53
_
Benzyl alcohol 1.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00 _
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
100.00 _
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 123 124 125 126 127 128
78
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 55.23 65.83 58.73 57.73 55.73
60.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25 2.25
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 129 130 131 132 133 134
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 2.50 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 65.98 65.48 63.48 60.48 59.23 59.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 135 136 137 138 139 140
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 65.48 59.48 59.48 55.58 57.48
54.28
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
79
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 141 142 143 144 145 146
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 54.98 65.58 58.48 57.48 55.48
60.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 147 148 149 150 151 152
Fatty acid* 15.00 18.00 15.00 20.00 12.50
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 , 2.00 2.20
2.20
Stearyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.40 2.40 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.40 2.80 3.40 2.80 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.80 3.00 3.00 3.40 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 1.00 0.20 . 0.20 0.60
1.00
Glycerin 3.00 2.00 1.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.30 0.70 0.70 0.30 0.50 0.75
Purified water 65.08 62.48 67.08 61.08 61.48
58.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 , 100.00
100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 153 154 155 156 157 158
Fatty acid* 15.00 18.00 15.00 20.00 12.50
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.20 2.70
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Stearyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.40 2.40 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.40 2.80 3.40 2.80 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.80 3.00 3.00 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 1.00 0.20 0.20 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 3.00 2.00 1.00 3.00 6.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.30 0.70 0.70 0.30 0.50 0.50
Purified water 65.08 62.48 67.08 61.08 61.48
53.78
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00
Total 100.00
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 159 160 161 162 163 164
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 54.48 65.08 57.98 56.98 54.98
59.98
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.00
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 165 166 167 168 169 170
Fatty acid* 15.00 20.00 15.00 20.00 10.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 4.00 4.00 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 2.00 2.40 2.40 2.40 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.40 2.80 2.50 3.40 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.80 3.40 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 0.20 1.00 1.00 0.60 1.00
Glycerin 3.00 3.00 1.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.70 0.50 0.75
Purified water 64.83 60.83 65.33 57.23 64.73
58.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
81
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Imiquimod 1 3.25 3.25 3.25 I 3.25
3.25 3.25
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 171 172 173 174 175 176
Fatty acid* 15.00 20.00 15.00 20.00
10.00 25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 4.00 4.00 2.20
2.70
Stearyl alcohol 2.00 2.40 2.40 2.40 3.10
3.80
White petrolatum 3.40 2.80 2.50 3.40 5.00
3.00
'
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.00 3.00 3.80 3.40
3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 0.20 1.00 1.00 0.60
0.60
Glycerin 3.00 3.00 1.00 3.00 5.00
2.00
Xanthan gum 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.70 0.50
0.50
Purified water 64.83 60.83 65.33 57.23 64.73
53.53
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00
2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
0.02
Imiquimod 3.25 3.25 3.25 3.25 3.25
3.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients _ %w/w %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 177 178 179 180 181 182
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20
2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10
3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00
3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40
3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60
0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00
2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50
0.50
Purified water 54.23 64.83 59.98 56.73 54.73
59.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
0.02
Imiquimod 3.25 3.25 3.25 3.25 3.25
3.25
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 183 184 185 186 187 188
Fatty acid* 15.00 10.00 12.50 19.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
2.20
Stearyl alcohol 2.40 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
3.10
White petrolatum 3.40 5.00 5.00 3.00 3.00
3.00
82
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.40 4.00 3.40 3.40 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.20 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00
Glycerin 1.00 4.00 5.00 2.00 6.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.70 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75
Purified water 66.58 65.48 61.38 60.48 56.48
58.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w
%w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 189 190 191 192 193 194
Fatty acid* 15.00 10.00 12.50 19.00 20.00
25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 2.40 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.40 5.00 5.00 3.00 3.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.40 4.00 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.20 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 1.00 4.00 5.00 2.00 6.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.70 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 66.58 65.48 61.38 60.48 56.48
53.28
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 1.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
_
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 195 196 197 198 199 200
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 53.98 64.58 57.48 56.48 54.48
59.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50 3.50
Total
100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
83
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 201 202 203 204 205 206
Fatty acid* 20.00 20.00 25.00 18.75 2000 21.25
Cetyl alcohol 4.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 2.40 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 2.80 3.00 3.00 5.00 5.00 3.75
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 1.00 2.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 5.00
Xanthan gum 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 64.53 59.23 54.23 55.48 54.23 54.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w I %w/w %w/w
Formulation 207 208 209 210 211 212 -
Fatty acid* 20.00 20.00 20.00 25.00 18.75 25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 59.23 53.23 53.23 54.33 55.48 53.03
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 i 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 213 214 215 216 217 218
Fatty acid* 25.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 21.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 4.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.40 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 5.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 1.00 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
84
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 5.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.70 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 53.73 55.73 57.23 56.23 54.23 53.23
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 219 220 221 222 223 224
Fatty acid* 20.00 25.00 22.50 20.00 20.00 22.50
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.70 2.20 4.00 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.80 3.10 2.40 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 6.00 3.00 3.00 3.40 5.00 4.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.40 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 5.00 2.00 2.00 3.00 2.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 1.00 0.70 0.50 0.50
Purified water 52.98 52.78 55.98 55.48 56.98 55.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 225 226 227 228 229 230
Fatty acid* 20.00 25.00 22.50 20.00 20.00 22.50
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.70 2.20 4.00 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.80 3.10 2.40 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 6.00 3.00 3.00 3.40 5.00 4.00
Polysorbate 60 3.00 3.40 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 1.00 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 5.00 2.00 2.00 3.00 2.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 1.00 0.70 0.50 0.50
Purified water 52.98 52.78 55.98 55.48 56.98 55.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
_
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 231 232 233 234 235 236
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.2 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 53.48 64.08 56.98 55.98 53.98 58.98
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00 4.00
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 237 238 239 240 241 242
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 20.00 15.00 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10
White petrolatum 1.00 3.00 2.00 3.00 6.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.00
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 1.00 1.00
Glycerin 2.00 2.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 3.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75 0.75
Purified water 65.73 63.73 61.73 58.73 57.48 57.48
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 243 2424 245 246 247 248
Fatty acid* 15.00 15.00 15.00 25.00 18.0 25.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.70
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.10 3.80
White petrolatum 3.00 6.00 6.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.40 3.00 3.40 3.00 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.60 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
86
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Purified water 63.73 57.73 57.73 53.83 55.73 52.53
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
Excipients %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w %w/w
Formulation 249 250 251 25 253 254
Fatty acid* 25.00 15.00 20.00 20.00 20.0 _ 20.00
Cetyl alcohol 2.20 2.00 2.20 2.20 2.20 2.20
Stearyl alcohol 3.10 2.00 3.10 3.10 _ 3.10 3.10
_
White petrolatum 3.00 3.40 5.00 3.00 5.00 3.00
Polysorbate 60 3.40 3.80 3.40 3.40 3.40 3.40
Sorbitan Monostearate 0.60 0.20 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60
Glycerin 2.00 3.00 2.00 5.00 5.00 2.00
Xanthan gum 1.00 0.30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50
Purified water 53.23 63.83 56.73 55.73 53.73 58.73
Benzyl alcohol 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00
. Methylparaben 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
_ Propylparaben 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
Imiquimod 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25 4.25
Total 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
*The Fatty acid referenced in this Table 11 can be, for example, linoleic acid
(la), stearic acid (sa), palmitic acid (pa),
isostearic acid (isa), unrefined oleic acid, (uoa), refined oleic acid, such
as super refined oleic acid (roa), or mixtures
thereof.
(000296] The materials listed below in this Example 21 are combined
according to the
following procedure to make cream formulations in the above Table 11 of this
Example 21.
[000297] The work area, all vessels and equipment is initially cleaned
prior to commencing
manufacture. A 2 L glass container and paddle stirrer blade are placed onto a
balance and the
weight is recorded. The paddle is then removed from the vessel. The isostearic
acid and benzyl
alcohol are weighed directly into the 2 L glass container. The imiquimod is
then weighed into the
2 L glass container and a spatula is used to ensure the imiquimod is wetted
with the isostearic
acid and benzyl alcohol mixture. The 2 L container is then heated in a water
bath to about 55 5
C while stirring with a Heidolph mixer (Note: aluminum foil is placed around
the top of the
vessel and the paddle for the mixer, to limit evaporation). The solution is
visually inspected to
87
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
confirm the imiquimod has fully dissolved prior to mixing with cetyl alcohol,
stearyl alcohol,
white petrolatum, polysorbate 60 and sorbitan monostearate.
[000298] Cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, polysorbate 60
and sorbitan
monostearate are then weighed directly into the 2 L container and mixing is
continued at about 55
C until the oil phase is completely in solution. Separately, about 2 L of
water are placed into
a beaker and heated to 55 5 C while stirring with a magnetic follower.
Briefly, about 500 ml
of the heated water is transferred into a 1 L beaker and placed into the water
bath maintained at
about 55 5 C.
[000299] Half of the amount of glycerin required for the final formulation
is then weighed
into the beaker along with the total amount of methylparaben and propylparaben
to the water
(where both methyl and propyl paraben are weighed into weighing boats first, a
pipette is used to
remove a portion of the heated water to wash out the weighing boats to ensure
total transfer of
both the propyl- and methylparaben into the aqueous phase). The mixture is
continuously stirred
at about 55 5 C (this is the aqueous phase).
[000300] The remaining glycerin is then added to a 28 ml vial and the
xanthan gum is added
and mixed using a small overhead mixer (1KA -Werke Lab Egg) with paddle
attachment for
about 10 mm.
[000301] The glycerin and xanthan mixture are then added slowly into the
vortex of the
aqueous phase, and a further aliquot of about 20 ml of heated water is used to
rinse the vessel out
into the water phase to ensure complete transfer.
[000302] The water phase is then heated and mixed at about 55 5 C until
the xanthan
gum mixture is fully and evenly dispersed into the aqueous phase. The
temperatures of both the
water phase and oil phase are both maintained at about 55 5 C.
[000303] The aqueous phase is then transferred into the oil phase and the
speed of the
Heidolph mixer is increased during addition. The mixture is then homogenized
on high speed for
about 3 mm and transferred immediately back to the Heidolph mixture; however,
the contents of
88
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
the homogenized sample, about 2 L, are mixed at about room temperature and
allowed to cool to
about 35 C.
[000304] The container and contents and the paddle from the overhead mixer
are then
re-weighed and the weight of the paddle and 2 L beaker, as determined above,
are subtracted to
determine the total weight of the formulation remaining.
[000305] The total weight (about 1 kg) of the cream is then made up to
weight with heated
water (Note: water evaporated during heating, which needs to be corrected at
this point). The
mixture is then transferred back onto the Heidolph mixer at about room
temperature and mixed
until the temperature of the formulation is below about 28 C. The lid of the
container is then
placed onto the vessel and stored at room temperature.
[000306] While the procedure above describes making an imiquimod cream
using isostearic
acid as the fatty acid, it is believed that this procedure may be applicable
for preparing imiquimod
creams based upon other fatty acids, such as those described in Table 11
above.
[000307] The lower dosage strength formulations of this Example 21 are
believed to be
stable and consistent with the specifications for the commercially available
Aldara (imiquimod)
5% cream. More preferably, low dosage formulations of this Example 21,
especially as to those
lower dosage strength formulations wherein the vehicle comprises an isostearic
acid as the fatty
acid, are believed to have the following:
(1) Stability. The imiquimod formulations of the present invention, when
they are
measured on HPLC at 25 C/60%RH, 30 C/65%RH and 40 C/75%RH over, one, two,
three and
six months, demonstrate stability consistent with the Aldara 5% imiquimod
cream;
(2) Degradation Products. No degradation products are detected in the
formulations
of the present invention, at its current recommended storage temperatures of
about 4-25 C. In
addition, there are no degradation products detected at any of the
temperatures or time points
mentioned under "Stability" above, when analyzed at about 318 nm.
(3) Homogeneity. The amount of imiquimod that is recovered from the
formulations
at any of the above-mentioned temperatures and time points is between about 90
to about 110%
w/w thereby demonstrating good homogeneity;
89
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
(4) Benzyl Alcohol Content. The formulations of the present invention are
also
within specifications for the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream, i.e., between 1.0
%w/w and
2.1 %w/w, at any of the above-mentioned temperatures and time points as to
benzyl alcohol
content.
(5) Microscopic Stability. There is no change in the particle size and no
crystals are
detected in the formulations of the present invention when they are stored at
25 C/60%RH and
analyzed over a six month period;
(6) Macroscopic Stability. There are no obvious physical changes in the
formulations
of the present invention when they are stored at 25 C/60%RH and analyzed over
a six month
period;
(7) Viscosity. The formulations of the present invention are within the
range of the
specifications for the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream, i.e., between 2000 cPs
and 35,000 cPs,
when they are stored at 25 C/60%RH and analyzed over a six month period; pH
Stability. The
formulations of the present invention are within the range of the
specifications for the Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream, i.e., between pH 4.0 and pH 5.5) when they are stored at
25 C/60 %RH
and analyzed over a six month period;
(8) Preservative Efficacy Test ("PET"). The formulations of the present
invention
demonstrate sufficient reductions in colony forming unit counts for each of
the organisms with
which the formulations are inoculated, i.e., S. aureus, E. coli, Ps.
Aeruginosa, C. albicans, and A.
niger, at 2-8 C and 40 C over a 28 day test period and meet the requirements
specified in both
the USP and EP;
(9) Imiquimod In vitro Release. The Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream releases
statistically significant (p<0.05) higher amounts of imiquimod over a 3 hour
time period in
comparison to the lower dosage strength formulations of the present invention
through a synthetic
membrane, e.g., Microporous polyethylene film 3M No. 9711 CoTranrm. There is
no statistical
difference (p<0.05) in the total cumulative amount of imiquimod that is
released from any of the
3.75% w/w imiquimod formulations. There is no statistical difference (p<0.05)
in the total
cumulative amount of imiquimod that is released from any of the 2.5% w/w
imiquimod
formulations. The Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream also statistically
significantly (p<0.05)
releases imiquimod at a faster rate over a 3 hour time period in comparison to
the lower dosage
strength formulations of the present invention through a synthetic membrane,
e.g., Microporous
polyethylene film 3M No. 9711 CoTranTm. There is no statistical difference
(p<0.05) between
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
the imiquimod release rates for any of the 3.75% w/w imiquimod formulations.
There is no
statistical difference (p<0.05) between the imiquimod release rates for any of
the 2.5% w/w
imiquimod formulations. Thus, the greater the amount of imiquimod in a
formulation, the faster
and greater the total amount of imiquimod that is released from such
formulation that the amount
and rate of release of imiquimod are concentration dependant and that the
rates and amounts of
release of imiquimod from the formulations of the present invention are linear
and dose
proportionate to the Aldara 5% imiquimod cream;
(10) Imiquimod In vitro Skin Permeation (Franz Cell Study). With respect to
statistical
analyses, there is no statistical difference between the lower dosage strength
formulations of the
present invention and the Aldara (imiquimod) 5% cream as to the amount of
imiquimod
recovered from the receiver fluid, epidermis and dermis combined. Nonetheless,
there is a
statistically significant (p<0.05) dose proportionate difference between the
amount of imiquimod
recovered from each of the matrices with respect to the concentration of
imiquimod in the lower
dosage strength formulations of the present invention and the Aldara
(imiquimod) 5% cream for
both un-absorbed and stratum corneum. Thus there is a linear dose release
between the amount
of imiquimod that is applied and recovered in each of the matrices, i.e.,
receiver fluid, unabsorbed
dose, stratum corneum, epidermis and dermis.
[000308] ANOVA statistical analysis at 95% confidence level is used to
analyze the
stability data generated, including the data generated for the membrane and
skin permeation
experiments.
[000309] It is also believed that the formulations of the present
invention, including the
formulations identified in this Example 21, have Hydrophilic-lipophilic
balance (HLB) values
between about 12 and 15, and more preferably between about 12.4 and about
13.4.
91
Attachment I
[000310] Stability Study GW 805-01
A. Percenta2e of imiquimod recovered from each formulation when the
formulations were stored throu2h 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Imiquimod Content Specification: 90-110% LC
Albion
Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Albion
3.75 Albion 3.75 Nova 3.75 % Nova 3.75 %
2.5
Formulations %ml)
(7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml) % (15 ml) % (7.5
ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
(15
o
99.80 99.36
100.60
t = 0 h
0
1 0.26 99.39 0.97 0.99 , 98.68 + 0.14 97.81
0.61 97.96 + 0.53 98.62 1 0.56 1.80 N.)
..]
100.09 100.60
25 C 0.95 100.70 1.91 , 1.26 99.71
0.63 99.08 0.96 99.34 0.42 99.51 0.54 97.61 1.92
w
.4
.4
t = 1 101.75 100.20 100.79
101.78
month
month 40 C t 2.22 100.67 0.53 1.53 1.46
98.72 0.79 2.96 09.98 0.27 99.78 0.87
iv
100.92 ' 102.73 ' 102.44
103.15 103.51 102.10 104.38 0
1-,
25 C 1.68 100.86 4.61 1.33 1.03 0.77
1.84 0.85 0.30 w
1
t = 2 '100.85 ' 104.52 ' 103.70 102.87
102.26 103.83 104.70 0
w
months 40 C 0.60 103.47 2.79 1.17 1.45
0.96 0.53 0.19 0.41 i
0
Not 102.12
102.53 ..]
25 C , tested , Not tested Not tested Not tested
0.53 0.72 Not tested Not tested
t = 3 Not 103.21
102.87+
months 40 C tested Not tested Not tested Not tested
0.64 0.58 Not tested Not tested
101.85 102.76 102.23+ 102.06+
102.25+ 101.07 102.28
25 C 0.38 101.31 1.95 0.34 0.35 0.27
0.92 0.25 0.36
t = 3 100.52 104.70 103.64 103.28
103.06 102.65 103.63
months 40 C 1.47 102.83 0.28 2.70
1.37 0.42 0.73 1.11 2.00
,
101.85
101.02
25 C 0.98 100.75 0.40 Not tested Not
tested 99.03 0.46 0.13 Not tested Not tested
t = 6 101.72
months, 40 C 0.80 102.58 0.20 Not
tested Not tested 99.31 0.77 101.03 + 1.01 Not tested
Not tested
1=9 101.27 102.49
101.31
months 25 C 0.60 102.94 1.81 No further
testing required 1.72 2.00 No further testing required
92
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
B. Amount (low/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each of the formulation
when the formulations were stored through 9 month
period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C175% RH
Benzyl Alcohol Specification: 1.0 to 2.1% w/w
Albion 2.5 % Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Nova 2.5
% Albion 3.75 Albion 3.75 Nova 3.75 % Nova 3.75 %
Formulations (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml) % (15 ml)
% (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
t=Oh 2.01 10.02 2.00 0.03 1.98 0.01 1.96
0.05 2.09 0.14 2.00 0.02 2.05 0.03 2.07 0.03
25 C 2.00 0.06 2.05 0.06 2.01 0.03 1.97 0.06 2.02
0.04 2.03 0.06 2.02 + 0.06 1.94 0.01
t = 1 month 40 C 1.87 0.04 1.87 0.04 1.84 0.02 1.94
0.27 1.88 0.05 1.92 0.11 1.96 1 0.18 1.91 0.04
25 C 1.86 + 0.05 1.87 0.11 1.92 0.01 1.87 0.04 1.89
0.04 1.85 0.10 1.92 0.04 1 96 0.03
t = 2 months 40 C 1.65 0.03 1.68 0.05 1.71 0.02 1.72
0.01 1.77 0.03 1.71 0.05 1.77 0.03
1.77 0.03 0
Not tested Not tested Not tested Not tested 1.87 0.03
1.87 0.03 Not tested Not tested 0
25 C
t = 3
months* 40 C Not tested Not tested Not tested Not
tested 1.71 0.06 1.76 0.05 Not tested Not tested
25 C 1.89 + 0.02 1.90 0.03 1.92 0.02 1.90 0.04 1.91
0.05 1.87 0.02 1.96 + 0.04 1.97 0.03
t = 3 months 40 C 1.61 0.03 1.64 0.01 1.66 0.03 1.68
0.03 1.79 0.02 1.77 0.02 1.78 0.01 1.80 0.05
25 C 1.86 0.02 1.87 1 0.03 Not tested Not tested 1.91
0.01 1.94 0.03 Not tested Not tested
1.43 0.02 1.40 / 0.03 Not tested Not tested 1.61 0.03 1.61
0.01 Not tested Not tested
t = 6 months 40 C
No further testing required
1.70 0.01 1.63 0.07 1.84 0.03 1.81
0.03 No further testing required
t =9 months 25 C
93
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
C. Amount (/ow/w) of methylparaben recovered from each formulation when the
formulations were stored through 9 month period
at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Methylparaben Specification: 0.18% - 0.22% w/w
Albion 2.5 % Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Albion 3.75
Albion 3.75 Nova 3.75 % Nova 3.75 %
Formulations (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml) %(15 ml)
% (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
0.194 0.194 0.193 0.192 0.199 0.191
0.193 0.196 o
t = 0 h 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.007 0.000
0.000 0.002
0.205 0.205 0.204 0.204 0.202 0.204
0.204 0.197 o
N.)
..]
25 C 0.001 0.005 0.002 0.001 0.002 0.003
0.002 0.003
w
t = 1 0206 0.203 0.201 0.213 0.202 0.206
0.208 0.199 ..]
..]
month 40 C 0.005 0.004 0.003 0.021 0.002 0.005
0.014 0.003 ..]
0.201 0.191 0.201 0.201 0.200
0.200 0.197 0205 N.)
0
25 C 0.002 0.009 0.003 0.004 _ 0.002
0.001 0.002 0.002
w
1
t = 2 0.199 0.202 0.202 0.201 0.199 0.197
0.200 0.199 o .
w
months 40 C 0.003 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.002 0.003
0.000 0.002 1
_
0
0.198 0.193
..]
25 C Not tested Not tested Not tested Not tested ,
0.003 0.005 Not tested Not tested
t = 3 0.1941 0.201
months* 40 C Not tested Not tested Not tested Not
tested _ 0.005 0.009 Not tested Not tested
0.197 0.197 0.197 0.194 0.197 0.198
0.194 0.195
25 C 0.001 0.004 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001
0.000 0.000
t = 3 0.194 0.197 0.193 0.194 0.199 0.198
0.195 0.198
months 40 C 0.003 0.001 0.000 0.004 0.002 0.001
0.002 0.004
0.208 0.209 0.205 0.205
25 C 0.003 0.002 Not tested Not tested
0.002 0.001 Not tested Not tested
t = 6 0.205 0.206 0.206 0.206
months 40 C 0.003 0.002 Not tested Not tested
0.002 0.001 Not tested Not tested
-
t = 9- 0.203 0.196 No further testing required
0.206 0.206 No further testing required
months 25 C 0.001 0.006 0.004 0.003
* Samples pulled one week earlier than 3 month time point as requested by
Graceway.
94
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
D. Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from each formulation when the
formulations were stored through 9 month period
at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Propylparaben Specification: 0.018% - 0.022% w/w
Albion 2.5 % Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Albion 3.75 % Albion
3.75 Nova 3.75 % Nova 3.75 %
Formulations (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.6 ml) (15 ml)
% (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
_
0.0185 0.0182
0.0181 0.0183 0.0184
t = 0 h 0.0183 0.000 0.000 0.0186 0.000
0.000 0.0190 0.001 0.001 0.000 0.000
0.0201 0.0186
0.0188 0.0194 0.0189 0
25 C 0.0194 0.0010.001 0.0196 0.001 0.000
0.0183 0.000 0.001 , 0.001 0.000
_
0
t = 1 0.0190 0.0203
0.0197 0.0188 0.0190 "
..]
month 40 C 0.0198 + 0.001 0.000 0.0184 0.000
0.002 0.0193 0.000 0.001 0.001 0.001
w
0.0203 0.0198
0.0196 0.0195 0.0200 ..]
..]
..]
25 C 0.0199 0.001 0.000 0.0200 0.000
0.001 0.0193 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.002
_
n.)
t = 2 0.0199 0.0198
0.0187 0.0200 0.0190 o
1-,
months 40 C i 0.0200 0.000 0.001 0.0202 0.000
0.001 0.0196 0.001 0.001 0.000 0.001 w
_ _
0.0200 0
w
i
25 C Not tested Not tested Not tested. Not
tested 0.0193 0.001 , 0.001 Not tested Not
tested o
t - 3
0.0195 .4
months* 40 C Not tested Not tested Not tested
Not tested 0.0201 0.001 0.000 Not tested Not tested
_
0.0200 0.0202
0.0201 0.0207 0.0212
25 C 0.0207 0.001 0.000 0.0204 0.001
0.000 0.0201 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.001
t = 3 0.0212 0.02101
0.0204 0.0199 0.0205
months 40 C 0.0207 0.000 0.001 0.0206 0.000
0.000 0.0205 0.001 0.000 0.001 0.001
0.0198
0.0184
25 C 0.0197 0.001 0.000 Not tested
Not tested 0.0197 0.002 , 0.001 Not tested Not tested
t = 6 0.0205
0.0188
months 40 C 0.0195 0.001 0.001 Not tested
Not tested 0.0201 0.001 0.001 Not tested Not tested
.
-
t=9 0.0203 0.0194 0.0202
0.0201
months 25 C 0.001 0.001
No further testing required 0.000
0.000 No further testing required
Attachment 1 (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
E. The pH of each formulation when stored through 9 month period at 25
C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
pH Specifications: 4.0 to 5.5
t
Formulations = 0 h
= 1 month t = 2 months t = 3 months
t = 6 months
t =-9 months t
25 C 40 C 25 C 40 C 25 C 40 C 25 C 40 C
25 C
(-)
Albion 2.5 % (15 ml) , 5.001 4.824 4.811 4.8 4.721 4.911
4.784 , 4.773 4.719 4.769
o
N.)
..]
Albion 2.5 % (7.5 ml) 4.967 4.869 4.809 4.828 4.676 ,
4.873 4.59 4.878 4.713 4.795
w
..]
Nova 2.5 % (15 ml) 5.009 4.889 4.73 4.844 4.686 4.737
4.795 N/A N/A N/A ..]
..]
Nova 2.5 % (7.5 ml) 5.017 4.834 4.758 4.818 4.68
4.693 , 4.838 N/A N/A N/A n.)
o
I-
(J)
o1
Albion 3.75 % (15 ml) 5.092 5.025 5.024 5.032 4.947 5.137
5.04 5.028 5.008 4.655 w
O
=4
Albion 3.75% (7.5 ml) 5.024 5.022 5.031 5.041 4.91 5.169
5.048 5.005 5.012 4.772
Nova 3.75% (15 ml) 5.087 5.037 4.996 5.042 _ 5.001 5.113
5.032 N/A , N/A N/A
Nova 3.75 %(7.5 ml) 5.012 5.002 5.033 4.931 4.875 5.157
5.037 N/A N/A N/A
96
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
F. The results of the viscosity measurements for the formulations stored
through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
RH
Viscosity Specification: 2,000 to 35,000 cPs for Bohlin
0
Formulation
0
t= o t=1 month t=2 months t=3 months t=6
months t = 9 months n.)
=4
1-`
25 C 40 C 25 C 40 C 25 C 40 C 25 C
40 C 25 C w
-.3
11517.5
Albion 2.5 % (15 ml) 9712 7050 9478 4218 7512 3719.5
7399.7 2394.5 5096.5
t..)
o
1-.
Albion 2.5% (7.5 ml) 11657 10344 6386.5 7489 4121
6590.5 3363 6502 2404.5 4243 w
O
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
_________________
w
o1
Nova 2.5 % (15 ml) 10653.5 12802.5 7345 7924 4726 6681.5
3727 N/A N/A N/A
-.3
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
_________________
Nova 2.5 % (7.5 ml) 10668 11685 7853.5 8296.5 4819.5
7302.5 3849.5 N/A N/A N/A
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
_________________
Albion 3.75 % (15 ml) 11632.5 13673.5 8950 10903.5 5848 9448.7
5207.5 8268 2703 6489
Albion 3.75 0/0 (7.5
12384.5 13562.5 8393 9285.5 5870 10038 5790 8709.5
2877.5 6108
ml)
Nova 3.75 % (15 ml) 12658 14657 9510.5 10222 5452
10165.5 4767 N/A N/A N/A
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
_________________
12689 13156 9510.5 10450.5 5482 9380.5
4933.5 N/A N/A N/A
Nova 3.75 % (7.5 ml)
As the bulk cream was aged at the time of filling (-2 months). the viscosity
of the cream filled in to the pump had lower viscosity
97
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
G. Amount (%w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod from each formulation stored
through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
RH
4-hydroxy Imiquimod Specification: NMT 0.3% w/w
Formulations Albion 2.5 % Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5
% Nova 2.5 % Albion 3.75 Albion 3.75 Nova 3.75 A) Nova 3.75 %
(15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml) % (15 ml)
% (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
_
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1 A NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
t = 0 h
w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w , Wiw
w/w w/w
o
25 C NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% P
w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w
w/w w/w 0
t = 1
N.)
--.1
month 40 NMT 0.1 A NMT 0.1%. NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
LA)
C W/W WAAT WiW WAV WAN WM
W/W WAN --.1
--.1
--.1
25 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% N)
C w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w
w/w w/w o
t = 2
LA)
I
months
40 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% 0
LA.)
C w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w
w/w w/w I0
--.1-
,
25 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
Not tested Not tested Not tested
Not tested Not tested Not tested
t = 3 C w/w w/w
-
_
months*
40 Not tested Not tested Not tested Not tested
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% Not tested Not tested
C w/w w/w
25 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1 %
NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1 % NMT 0.1%
C w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w
w/w w/w
t = 3
months -
40 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
C w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w w/w
w/w w/w
_
t = 6 25 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
Not tested Not tested Not tested Not tested
months C w/w w/w w/w w/w
98
40 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1 /0
Not tested Not tested Not
tested Not tested
C w/w w/w w/w w/w
t=9 25 NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1% NMT 0.1%
No further testing required No
further testing required
months C w/w w/w w/w w/w
o
0
n.)
-4
I-
(J)
-4
-4
-4
0
I-
(J)
I
0
W
I
0
-4
99
Attachment I (Continued)
Stability Study GW 805-01
H. Amount of n-oxide for the formulations stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH
Specification: Run and Record
Albion 3.75
Albion 2.5 % Albion 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Nova 2.5 % Albion 3.75 %
Nova 3.75% Nova 3.75%
Formulations /o
(15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml)
(7.5 ml)
(15 ml) (7.5 ml)
t=Oh
t=i 25 C
0
month 40 C
t = 2 25 C
months 40 C
1.)
t = 3 25 C Not tested
0
months* 40 C
0
t = 3 25 C
0
months 40 C
t = 6 25 C
months 40 C
t =9 None None None None
No further testing
No further testing required
detected
months 25 C detected detected
detected required
100
Attachment II
[000311] Stability Study GW 906-01
A. Percentage of imiquimod recovered from each formulation when the
formulations were stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Imiquimod Content Specification: 90 - 110% LC
_____________________________ _
0
Albion 5 % (15 ml) Albion 5 % (7.5 ml)
Nova 5 % (15 ml) Nova 5 % (7.5 ml)
Time point and storage temperature0
t..)
--3
t = 0 h 103.19 0.14 101.94 0.10
101.61 0.74 102.05 0.66 1-,
. _ _
w
t = 1 month
--3
25 C 101.36 1.30 98.27 + 0.86
9837 0.85 100.74 0.33 --3
--3
40 C 95.35 0.34 98.21 0.79
96.61 0.38 95.11 0.42 n.)
o
. ,
1-,
25 C 99.79 0.36 99.21 0.49
99.38 1.15 99.84 1.15 w
1
t = 2 months
o
40 C 99.66 0.08 98.76 0.46
99.71 0.55 100.66 0 I
.45 w
. _
o
t = 3 months
--3
25 C 101.33 0.91 101.87 0.68
101.92 1.30 102.24 0.93
_
40 C 101.51 0.16 101.86 0.56
102.04 0.79 102.54 1.02
.
t = 6 months
25 C 102.87 0.51 102.09 0.60
40 C 102.69 0.36 101.83 0.59
Not tested
= 9 months 25 C 105,59 0.98 105.57 0.23
t
101
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
B. Amount (%w/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each of the formulation
were stored through 9 month period at 25 C160% RH
and 40 C/75% RH
Benzyl Alcohol Specification: 1.0 to 2.1% w/w
Time point and storage temperature Albion 5 % (15 ml)
Albion 5 % (7.5 mi) Nova 5 %(15 ml) Nova 5 % (7.5 ml)
t = 0 h 1.97 0.01 1.95 0.02
1.94 0.03 1.94 0.02 0
_
25 C 1.85 0.04 1.79 0.03
1.84 0.02 1.85 0.04 0
iv
t = 1 month
.4
40 C 1.69 0.05 1.73 0.05
1.71 0.05 1.71 0.05
w
-4
-4
-4
25 C 1.74 0.01 1.73 0.01
1.73 0.02 1.73 0.01 iv
t = 2 months
o
40 C 1.56 0.02 1.54 0.01
1.58 0.01 1.57 0.01
w
i
0
w
1
25 C 1.80 0.02 1.80 0.03
1.80 0.05 1.82 0.01 0
t = 3 months
.4
40 C 158 0.02 1.56 0.01
1.58 0.02 1.57 0.01
25C 1.83 0.02 1.82 0.00
t = 6 months
40 C 1.45 1 0.02 1.42 0.05
Not tested
t =9 months 25 C 1.73 1 0.00 1.73 0.04
102
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
C. Amount (/0w/w) of methylparaben recovered from each formulation when the
formulations were stored through 9 month period
at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Methylparaben Specification: 0.18% - 0.22 w/w
o
Time point and storage temperature Albion 5 % (15 ml) _ Albion 5 %
(7.5 ml) Nova 5 %(15 ml) Nova 5 % (7.5 ml)
o
t= 0 h 0.204 0.003 0.202 0.000
0.201 0.001 0.202 0.002 "
.4
1-,
25 C 0.203 0.004 0.200 0.003
0.199 0.001 0.202 0.002 w
.4
.4
40 C 0.193 0.004 0.198 0.003
0.196 0.001 0.193 0.001 .4
t= 1 month
iv
0
1-,
25 C 0.200 0.001 0.199 0.002
0.199 0.002 0.198 0.002 w
1
0
40 C 0.202 0.000 0.202 0.002
0.201 0.000 0.201 0.001 w
1
t = 2 months
0
.4
25 C 0.207 0.002 0.207 0.002
0.207 0.005 0.206 0.002
t = 3 months
40 C 0.206 0.000 0.206 0.001
0.206 0.001 0.205 0.002
25 C 0.209 0.002 0.207 0.001
t = 6 months
40 C 0.207 0.001 0.205 0.001
Not tested
t =9 months 25 C 0.207 0.001 0.207 0.003
103
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
D. Amount (/0w/w) of prouvinaraben recovered from each formulation when
formulations were stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Propylparaben Specification: 0.018% -0.022% w/w
0
0
IV
-4
I-`
w
Time point and storage temperature Albion 5 % (15 ml) Albion 5
% (7.5 ml) Nova 5 %(15 ml) Nova 5 % (7.5 ml) ..]
..]
..]
t = 0 h 0.0202 0.001 0.0197
0.000 0.0201 0.001 0.0198 0.000 iv
0
25 C 0.0195 0.001 0.0190 0.001
0.0187 0.001 0.0190 0.001
w
t = 1 month
1
0
40 C 0.0180 0.001 0.0188 0.000
0.0180 0.000 0.0181 0.001 w
1 =
0
25 C 0.0196 0.001 0.0191 0.001
0.0190 0.001 0.0197 0.000 .4
t = 2 months
40 C 0.0194 0.001 0.0193 0.000
0.0190 0.000 0.0194 0.001
25 C 0.0197 0.001 0.0211 0.001
0.0197 0.001 0.0205 0.000
t = 3 months
40 C 0.0203 0.001 _ 0.0201 0.001
0.0204 0.000 0.0203 0.001
= 6 months 25 C 0.0203 0.001 0.0186
0.000 Not tested Not tested
t
40 C 0.0195 0.000 0.0192 0.001 Not tested Not
tested
t =9 months 25 C 0.0204 0.000 0.0206
0.001 Not tested Not tested
104
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
E. The pH of each formulation when stored throu2h 9 month period at 25
C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
pH Specifications: 4.0 to 5.5
Time point and Albion 5 % Albion 5 % Nova 5 % Nova 5 %
storage temperature (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml)
(7.5 ml)
t = 0 h 5.078 5.078 5.104 5.077
o
. 25 C 5.012 5.014 5.029 5.004
0
n.)
-.3
t = 1 month 40 C 4.958 4.955 4.958 4.98
w
-.3
25 C 5.015 5.038 4.98 5.097
-.3
t = 2 months 40 C 4.995 5.008 5.006 5.007
1\.)
0
1-,
_ 25 C 4.998 4.9353 4.954 5.043
w
o1
t = 3 months 40 C 4.841 4.805 4.942 4.864
w
o1
25 C 5.012 4.997
.4
t = 6 months 40 C 4.958 4.944 Not tested
t =9 months 25 C 5.017 4.993
105
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
F. The results of the viscosity measurements for the formulations stored
through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
FtH
Viscosity Specification: 2,000 to 35,000 cPs for Bohlin
t
Formulation t=1 month t=2 months t=3
months t=6 months = 9 0
t= 0 _____________________________________________________ months
25 C 40 C_ 25 C 40 C
25 C 40 C , 25 C 40 C 25 C 0
-4
I-`
(A)
.4
.4
0
Albion 5% (7.5 ml) 9246.5 10804.5 8784 8019.5
5115.5 8304.5 4640.5 8105 3562.5 6436.5
w
1
0
w
1
Nova 5 % (15 ml) 9299.5 11259.5 8265.5 7700.5
5161 8544.5 3814.5 Not Not Not
tested 0
tested tested .4
Nova 5 % (7.5 ml) 8900 10571.5 8228.5 7751.5 4675 8410.5
4226.5 Not Not Not tested
tested tested
_
_______________________________________________________________________________
______________
106
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
G. Amount (%w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod from each formulation stored
through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
RI!
4-hydroxy Imiquimod Specification: NMT 0.3% w/w
F
______________________________________________________________________________
Time point and Percentage (% w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod n in
the formulation
Albion 5 % Albion 5 % Nova 5 % Nova 5 %
storage 5 % ref
sample
temperature (15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
(-)
NMT NMT NMT NMT NMT
o
Iv
t = 0 h 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1%
w/w 0.1% w/w
1-`
(A)
NMT NMT NMT NMT
--3
--3
25 C 0.1% w/w 0.1 % w/w 0.1% w/w
0.1% w/w --3
t = 1
IV
NMT NMT NMT NMT
o
month
, 40 C 0.1% w/w 0,1% w/w 0.1 % w/w
0.1% w/w (J.)
O
NMT NMT NMT NMT
u.)
o1
t - 2 25 C 0.1% w/w 0.1 % w/w 0.1 % wiw w
0.1% WAN. --3
months
NMT NMT NMT NMT
40 c 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
NMT NMT NMT NMT
25 C 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
t = 3
NMT NMT NMT NMT
months
40 C 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
_
_ -
NMT NMT Not tested Not tested
OA% w/w
25 C 0.1% w/w
'
t = 6 '
NMT NMT
months Not tested Not tested
40 C 0.1% w/w 0.1% vew
_
NMT NMT
t =9 Not tested Not tested
months 25 C 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
107
Attachment II (Continued)
Stability Study GW 906-01
H. Amount of n-oxide for the formulations stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH
Specification: Run and Record
Detection of n-oxide in the formulation
Albion 5 % Albion 5 % Nova 5 % Nova 5 %
Time point and
(15 ml) (7.5 ml) (15 ml) (7.5 ml)
o
storage temperature
t = 0 h
0
n.)
..]
t=i 25 C
w
month .
..]
..]
40C
..]
n.)
t = 2 25 C
0
1-,
months
w
40 C Not tested
O
w
1
t = 3 25 C
0
..]
months
40 C
t = 6 25 C
months
40 C
t =9
25 0C None
None detected Not tested Not tested
months detected
108
Attachment III
[000312] Stability Study GW 907-01
A. Percentage of imiquimod recovered from each formulation compared to
theoretical when stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C175% RH
Imiquimod Content Specification: 90-110% LC
Temperature Formulations (% recovered
compared to theoretical)
Time point storage
o
Albion 2.5 % Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 %
Ref 2.5 % Ref 3.75 % Ref 5 % P
_
o
t = Oh 102.29 0.55 101.88 1.13
102.80 0.09 102.49 0.50 102.93 0.83 103.39
1.44 N)
--.1
l A.)
25 C 102.93 0.64 102.43 0,81
102.99 1.97 --.1
--.1
--.1
t = 1 month 40 C 102.92 1.28 100.29 0.42
102.24 0.39 N)
o
40 C (3M) 102.69 0.36 101.13 0.23
101.73 0.44 LA.)
1
-
o
25 C 102.81 1.17 102.40 1.06
102.59 0.30 LA.)
1
t = 2 months
o
--.1
40 'C 103.39 0.61 102.73 0.80 102.85
0.44
25 C 103.11 0.78 101.29 0.24 102.87
0.85
t = 3 months
40 C 102.07 1.10 101.80 0.36 100.72
2.41
25 C 104.25 1.66 100.71 4.41 103.64
0.79
t = 6 months
40 C 104.68 0.55 104.29 0.57 104.36
0.91
t = 9 months 25 C 102.59 1.25 102.75 0.10 101.81
1.08
Where Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
109
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
B. Amount (%w/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each of the formulation
when stored through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RII
and 40 C/75% RII
Benzyl Alcohol Specification: 1.0 to 2.1% w/w
Amount (%w/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each of the
Time Temperature formulation
point storage
Albion 2.5 % Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 % Ref 2.5 % Ref 3.75 1)/0 Ref 5 %
t = Oh 1.83 0.02 1.88 0.03 1.78 + 0.01
1.79 1.89+ 1.75+
0.
0.03 03 0.03
25 C 1.78 0.03 1.75 + 0.06 1.82 + 0.01
t = 1
40 C 1.77 0.02 1.74 + 0.01 1.69 0.01
month
40 C (3M) 1.76 0.02 1.85 + 0.00 1.72 0.01
t= 2 25 C 1.83 0.05 1.92 + 0.04 1.79 0.03
months 40 C 1.63 + 0.04 1.76+ 0.03 1.68 0.06
t = 3 25 C 1.75 0.01 1.82 0.01 1.74 0.01
months
40 C 1.55 0.02 1.66 0.04 1.53 + 0.88
t= 6 25 C 1.69 + 0.05 1.76 0.02 1.66 + 0.02
months
40 C 1.33 0.00 1.47 0.02 1.38 0.02
t = 9
months 25 C 1.65+ 0.01 1.74+0.02 1.65 0.03
Where Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
1 1 0
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
C. Amount (%w/vv) of methylparaben recovered from each of the formulations
when stored through 9 month period at 25 C/60%
RI! and 40 C/75% RI!
Methylparaben Specification: 0.18% - 0.22% VOW
Temperature Amount (%w/w) of methylparaben
recovered from each formulation
Time point storage
Albion 2.5 % _ Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 %
Ref 2.5 % Ref 3.75 % Ref 5 %
t = 0 h 0.201 1 0.002 0.200 0.002
0.201 0.000 0.200 0.000 0.201 0.002 0.202 0.003
_
25 C 0.195 0.002 0.192 0.001
0.191 0.004 o
o
t = 1 month 40 C 0.203 1 0.002 0.188 0.002
0.203 0.001 n.)
--3
1-,
w
40 C (3m) 0.202 0.001 0.200 0.001
0.201 0.002 --3
--3
--3
25 C 0.205 0.002 0.205 0.003
0.208 0.002 n.)
t = 2 months
0
1-,
40 C 0.204 0.002 0.204 0.001
0.205 0.003 w
1
.
o
w
25 C 0.204 0.002 0.200 0.001
0.202 0.001 1
t = 3 months .
o
-.3
40 C 0.200 0.001 0.201 0.004 0.197 0.005
25 C 0.207 0.005 0.202 0.005 0.205 0.002
t = 6 months
40 C 0.204 0.002 0.205 0.001 0.203 0.002
t = 9 months 25 C 0.211 .001 0.207 .001 0.2101.001
Where 'Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
111
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
D. Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from each formulation when
stored through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and
40 C/75% RH
Propylparaben Specification: 0.018% - 0.022% w/w
Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from each formulation
Time point Temperature storage
Albion 2.5 % Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 %
Ref 2.5 % Ref 3.75 % Ref 5 %
t = 0 h 0.0190 1 0.001 0.0185 1
0.000 0.0191 1 0.001 0.0187 1 0.000 0.0193 0.000 0.01891 0.000
C1
. .
P
25 C 0.0199 1 0.001 0.0179 1
0.000 0.0202 0.000 o
N.)
-4
t = 1 month 40 C 0.0201 0.000 0.0210 1 0.001
0.0208 1 0.001
LA.)
-4
-4
40 C (3M) 0.0194 0.000 0.0200
0.000 0.0198 1 0.001 -4
NJ
25 C 0.0196 0.001 0.0202 1
0.002 0.0202 0.002 0
1-`
t = 2 months _
LA.)
1
40 C 0.0189 1 0.001 0.0216 1
0.001 0.0183 1 0.000 0
LA.)
o1_
25 C 0.0224 0.001 0.0209
0.000 0.0200 1 0.002 -4
t = 3 months
40 C 0.0213 1 0.000 0.0202 1
0.000 0.0192 1 0.002
_
25 C 0.0194 1 0.001 0.0183
0.002 0.0188 1 0.001
t = 6 months
40 C 0.0194 1 0.000 0.0191
0.000 0.0193 1 0.000
t = 9 months 25 C 0.019110.000 0.01971.000
0.01921.000
Where 'Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps
112
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
E. The pH of each formulation when stored through 9 month period at 25
C/60% RI! and 40 C/75% RH
pH Specifications: 4.0 to 5.5
Time Temperature pH
point storage
Albion 2.5 % Albion 3.75 A Albion 5 A) Ref 2.5 A Ref 3.75 A Ref 5 %
t = 0 h 4.926 5.017 5.032 4.794 5.111 5.085
_
25 C 4.852 5.184 5.12
0
t = 1o
40 C 4.844 5.044 4.971
n.)
month
-.3
I-
40 C (3M) 4.928 5.108 5.079
w
..]
-.1
..]
t = 2 25 C 4.864 5.075 4.985
n.)
months
0
1-,
40 C 4.926 5.017 5.032
w
O
t = 3 25 C 4.471 5.130 5.163
w
o1
months
40 C 4.854 5.153 5.134
t = 6 25 C 4.774 4.969 4.985
months
40 C 4.732 4.976 4.980
t = 9
months 25 C 4.778 4.971 4.990
Where Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
113
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
F. The results of the viscosity measurements for the formulations stored
throuch 9 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
RH
Viscosity Specification: 2,000 to 35,000 cPs for Bohlin
Time Temperature Bohlin Viscosity (cPs) (based on 3M
method) o
point storage
Albion 2.5% Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 % Ref
2.5 % Ref 3.75 % Ref 5 % o
tv
t = 0 h 7955.5 9816 8521 9038 11195
9629 -4
1-,
w
25 C 8897.5 10412 8803
-4
t = 1
-4
month 40 C 8142.5 10746 8472.5
N)
o
1-,
w
o1
t = 2 25 C 9132.5 10339 8570
w
months
1
40 C 4700.5 6626.5 5498.5
0
-4
t = 3 25 C 8241 8330.5 7430
months
40 C 3513.5 5397.5 4323
t = 6 25 C 5540 7349 6580.5
months
40 C 2588 2993.5 3134
t = 9
months 25 C 3093 3622.5 4485
Where 'Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
114
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
G. Amount (%w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod from each formulation stored
through 9 month period at 25 C/60% RII and 40 C/75%
RII
4-hydroxy Imiquimod Specification: NMT 0.3% w/w
Amount (%w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod recovered from each of the formulation
Time Temperature
point storage
Albion 3.75 (1/0
Albion 2.5 % Albion 5 ')/0 Ref 2.5
% Ref 3.75 % Ref 5 %
.
(-)
t =0 h
NMT NMT NMT NMT
NMT NMT
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w o
t..)
NMT NMT NMT
..]
25 C
1-,w
t=i 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
..]
..]
month NMT NMT NMT
..]
40 C
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
n.)
o
1-,
NMT NMT NMT
w
1
25 C
t = 2 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
0
w
1
months NMT NMT NMT
0
40 C
..]
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
NMT NMT NMT
25 C
t = 3 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
months NMT NMT NMT
40 C
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
t = 6 NMT NMT NMT
months 25 C
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
NMT NMT NMT
40 C
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
t = 9
NMT NMT NMT
months 25 C
0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w 0.1% w/w
Where 'Ref samples are from the same batch of each representative formulation,
sub-aliquoted in to glass vials for comparison against pumps.
1 1 5
Attachment III (Continued)
Stability Study GW 907-01
H. Amount of n-oxide for the formulations stored through 9 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Specification: Run and Record
Time Temperature
point storage
Albion 2.5 % Albion 3.75 % Albion 5 %
t = 0 h
t=i 25 C
0
months 40C
o
n.)
t = 2 25 C Not tested
1-,
w
months
40C
-.3
=4
t = 3 25 C
n.)
o
months 40 C
w
o1
t = 6 25 C None detected None detected None
detected
w
1
months 40 C None detected None detected
None detected 0
-.3
t = 9
25 C None detected None detected None
detected
months
116
Attachment IV
[000313] Stability Study GW 921-01
A. Percentage of imiquimod recovered from each formulation compared to
theoretical when stored through 6 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Imiquimod Content Specification 90-110% LC
Time point Temperature
storage
Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 A 15 g
fill % Ref 3.75 %* o
o
t = 0 h 101.23 + 0.57 102.00 +
1.03 102.16 + 1.64 iv
-.3
1-,
25 C 102.85 0.36 102.64
0.73 102.72 0.38 w
-.3
t = 1
-.3
month
40 C 102.05 + 0.20 100.83
1.36 103.33 0.27 iv
0
25 C 101.73 1.08 100.03
0.50 101.00 0.56 w
1
t- 2
o
w
months
1
40 C 100.89 0.20 100.41 +0.41
101.94 0.39 0
-.3
t = 3 25 C 100.80 0.90 100.21
0.55 102.34 1.17
months
40 C 103.02 1.46 102.75 1.26
103.69 1.28
t = 6 25 C 100.49 0.82 101.31
0.97 101.64 1.12
months _
________________________________________
40 C 102.33 0.20 102.38
0.97 102.06 + 1.06
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
117
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
B. Amount (%w/w) of benzvl alcohol recovered from each formulation when
stored through 6 month period at 25 C160% RH and
40 C175% RH
Benzyl Alcohol Specification: 1.0 to 2.1% w/w
_____________________ _
Time Temperature
point storage
Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g fill
Ref 3.75 %* o
0185 0.
o
t= 0 h 1.85 0.03 1.89 + 0.03
1. n.)
-.3
1-,
25 C 1.89 0.03 1.88 + 0.04 1.91 + 0.03
w
-.3
t = 1
-.3
month
40 C 1.78 0.02 1.81 0.02 1.86 0.02
n.)
o
1-,
25 C 1.81 0.05 1.82 0.04 1.82 0.02
w
1
t- 2
0
w
months1
40 C 1.70 + 0.04 1.69 0.01 1.71 0.01
o
-.3
t = 3 25 C 1.80 0.02 1.80 0.07
1.77 0.20
months
40 C 1.57 0.05 1.62 0.05 1.65 0.01
t = 6 25 C 1.66 0.07 1.69 + 0.02
1.74 + 0.03
months
40 C 1.37 0.04 1.41 0.02 1.55 0.03
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
1 1 8
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
C. Amount (%w/w) of methylparaben recovered from each formulation when
stored through a 6 month period at 25 C/60% RH
and 40 C/75% RH
Methylparaben Specification: 0.18% - 0.22% w/w
Time Temperature
point storage
Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g fill %
Ref 3.75 %*
o
03205 0 .0
t = 0 h 0.201 0.000 0.203 0.002
0. 0
n.)
-.3
t
=
25 C 0.207 0.003 0.204 0.001 0.207 0.001
w
..]
month-.3
40 C 0.203 0.002 0.201 0.003 0.207 0.001
..]
n.)
o
= 25 C 0.202 0.008 0.203 0.004
0.202 0.002
t 2
w
1
months _
_________________________________________________________________________ 0
40 C 0.206 0.005 0.202 0.001 0.205 0.001
w
o1
..]
t
25 C 0.208 0.003 0.208 0.007 0.205 0.005
= 3
months
40 C 0.203 0.005 0.205 0.005 0.208 0.004
t = 6 25 C 0.199 0.006 0.203 0.004
0.204 0.003
months
40 C 0.201 0.003 0.198 0.005 0.207 0.003
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
119
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
D. Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from each formulation when
stored through a 6 month period at 25 C/60% RH
and 40 C/75% RH
Propylparaben Specification: 0.018% -0.022% W/W
Time Temperature
point storage
Albion 3.75 % 15 g fill %
Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Ref
3.75 %* o
0.0214 0.002
t = Oh 0.0189 0.001 0.0196 0.000
0
_______________________________________________________________________________
______ t..)_
-.3
month
25 C 0.0200 0.001 0.0193 0.000
0.0199 0.000
t = 1
w
-.3
-.3
40 C 0.0198 + 0.001 0.0195 + 0.000
0.0198 0.000
t..)
o
25 C 0.0202 0.001 0.0190 0.001
0.0192 + 0.001
t = 2
w
1
months0
40 C 0.0194 0.000 0.0185 0.001
0.0194 0.001 w
o1
I = 3
-.3
25 'C _ 0.0209 0.000 0.2060 0.001
0.0208 0.000
months
40 C 0.0205 + 0.002 0.0208 0.001
0.0208 0.000
t = 6 25 C 0.0195 0.000 0.0197 0.001
0.0203 0.001
months
40 C 0.0208 0.001 0.0200 0.000
0.0202 0.001
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
120
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
E. The pH of each formulation when stored through a 6 month period at 25
C/60% RH and 40 C175% RH
pH Specifications: 4.0 to 5.5
pH
Time Temperature
point storage Albion 3.75 % 7.5 Albion 3.75 % 15
g fill g fill %
Ref 3.75 A)*
t = 0 h 5.138 5.059 5.039
o
25 C 5.059 5.072
0
t = 1
n.)
-.3
month1-,
40 *C 5.052 5.052
w
..]
..]
..]
25 C 5.000 5.033
t = 2
t..)
o
months
1-,
40 C 4.991 4.921
w
O
w
25 C 4.967 5.104
1
t = 3
o
..]
months
40 C 5.016 5.030
t = 6 25 C 5.200 5.156
months
40 C 5.011 4.980
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
121
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
F. The results of the viscosity measurements for the formulation stored
through a 6 month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75%
RH
Viscosity Specification: 2,000 to 35,000 cPs for Bohlin
Bohlin Viscosity (cPs) (based on 3M method)
Time Temperature
o
point storage Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g fill "A
o
n.)
t = 0 h 10786 10027
--3
1-,
.
w
--3
25 C 9303 9138
--3
t = 1
-.3
month 40 C 7161 6956
n.)
0
1-,
.
w
25 C 8268 8340
o
tI
= 2
w
months
O
40 aC 6309 6328
--3
_
25 C 7428 6621
t = 3
months
40 c=C 6249 6613
t = 6 25 C 5450 5310
months
40 C 2808 2727
122
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
G. Amount (low/w) of 4-hydroxy Imiquimod from each formulation stored
through a 6 month period at 25 C/60% RH and
40 C/75% RH
4 -hydroxy Imiquimod Specification: NMT 0.3% WiNV
Amount (%w/w) of 4-hydroxy imiquimod recovered from
Time Temperature each formulation
point storage
Albion 3.75 % Albion 3.75 % 15
Ref 3.75 A*
7.5 g fill g fill %
n.)
t =0 h NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
25 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
t = 1
n.)
month
40 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
o
t = 2 25 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
o
months
40 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
t =3 25 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
months
40 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
t = 6 25 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
months
40 C NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w NMT 0.1% w/w
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5g and 15 g fill).
123
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
H. Imiquimod raw data (top, middle and bottom extractions)
Percentage of imiquimod recovered from each formulation (top, middle and
bottom) compared to theoretical when stored through a 6
month period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RI!
Imiquimod Content Specification: 90 to 110% LC
Formulations (% recovered compared to theoretical)
o
Temperature
Time point Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g
fill % Ref 3.75 %*
storage
o
t..)
Top Middle Bottom Top Middle-Bottom
Top Middle Bottom --3
1-,
. _
w
t = 0 h 101.89 100.94 100.86 101.58 101.23
103.17 101.78 100.74 103.95 --3
--3
--3
_ _
102.68 102.37 103.12
25 C 102.45 102.95 103.15 102.00 102.49
103.44 n.)
t = 1
o
, _ _
. 1-,
month
w
oi
40 C 102.14 101.82 102.18 99.37 102.04
101.09 103.10 103.26 103.63 ,
,
_
w
25 C 102.87 100.73 101.57 100.41 99.46
100.21 100.77 101.64 100.59 O
t = 2 . ._
-.3
months
40 C 100.94 100.67 101.06 99.94 100.65
100.63 101.53 102.30 102.00
. .
25 C 100.57 100.04 101.80 100.16 99.69
100.79 103.31 102.67 101.05
t = 3 ,
..
months
40 C 104.33 101.44 103.28 104.20 101.93
102.12 104.15 104.67 102.25
,
. . ..
25 C 100.60 101.24 99.62 101.65 102.07
100.21 102.24 100.35 102.33
t = 6 ,
months
40 C 102.50 102.38 102.10 103.47 101.62
102.04 102.18 103.06 100.94
124
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
I. Benzyl alcohol raw data (top, middle and bottom extractions)
Amount (%w/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each of the formulation (top,
middle and bottom) when stored through a 6 month
period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Benzyl Alcohol Specification: 1.0 to 2.1% w/w
0
Amount (%w/w) of benzyl alcohol recovered from each formulation
Temperature
Time point Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g
fill % Ref 3.75 %* o
n.)
storage
Top Middle Bottom Top , Middle Bottom
Top Middle Bottom -4
1-,
w
t = Oh 1.82 1.85 1.87 1.89 1.85_
-4 1.92 1.87 1.86 1.83 -4
-4
t= 1 25 C 1.85 1.91 _ 1.90 1.83 1.89
1.91 1.92 1.88 1.93 N.)
_
o
month
1-,
40 C 1.77 1.79 1.80 1.79 , 1.83
1.80 1.85 1.84 , 1.88 w
o1
t = 2 25 C 1.86 1.76 1.83 1.82 1.78
1.86 1.84 1.80 1.81 w
1
months
0
40 C 1.69 1.67 1.75 1.68 1.68
1.70 1.72 1.70 1.71 -4
_
t = 3 25 C 1.78 1.80 1.82 1.73 1.84
1.85 1.79 1.76 1.76
months
40 C 1.58 1.51 , 1.61 1.66 1.56
1.64 1.65 1.64 1.66
t = 6 25 C 1.69 1.71 1.58 1.67 1.69
1.71 1.72 1.77 , 1.73
months
40 'C 1.40 1.40 1.33 1.43 1.38
1.41 1.52 1.57 1.55
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
125
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
J. Methylparaben raw data (top, middle and bottom extractions)
Amount (%w/w) of methyluaraben recovered from each of the formulations (top,
middle and bottom) when stored through a 6 month
period at 25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RH
Methylparaben Specification: 0.18% -0.22% w/w
0
o
Amount (%w/w) of methylparaben recovered from each formulation
n.)
Temperature
-.3
Time point Albion 3.75 % 7.51 fill Albion 3.75 ' /0 15 g
fill % Ref 3.75 %*
storage
w
Top , Middle _ Bottom Top Middle
Bottom Top Middle Bottom ..]
..]
..]
t = 0 h 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 , 0.20
0.21 0.20 0.20 0.21
_ _
n.)
o
t = 1 25 C 0.20 0.21 0.21 0.20 0.20
0.21 0.21 0.21 0.21
w
month _
40 C 0.20 0.20_ w 0.20 0.20 0,20
0.20 0.21 0.21 0.21 ol
o1
t = 2 25 C 0.21 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20
0.21 0.20 0.20 0.20 ..]
_
months
40 'C 0.20 0.20_ 0.21 0.20 0.20
0.20 0.20 0.21 0.20
t = 3 25 C 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.20 , 0.21
0.21 0.21 0.20 0.20
months
40 C 0.20 0.20 0.21 0.21 0.20 ,
0.21 0.21 0.21 0.20
t = 6 25 C 0.20 0.20 0.19 0.20 0.20
0.21 0.20 0.21 0.20
_ _
months
1 40 C 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.19
0.20 0.20 0.21 0.21
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
126
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
K. Propvlparaben raw
data (top, middle and bottom extractions)
Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from each formulation (top, middle
and bottom) when stored through a 6 month period
at 25 C/60% RII and 40 C/75% RH
Propylparaben Specification: 0.018% - 0.022% w/w
0
T Amount (%w/w) of propylparaben recovered from
each formulation
emperature
o
n.)
Time point Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75 % 15 g fill
% Ref 3.75 %* ..]
storage
1-,
Top Middle Bottom Top _ Middle
Bottom Top Middle Bottom w
..]
..]
..]
t = 0 h 0.0207 0.0187 0.0184 0.0184 , 0.0192 0.0200
0.0219 0.0198 0.0195
_
n.)
o
t= 1 25 C 0.0193 0.0201 0.0205 0.0188 0.0193
0.0196 0.0200 0.0197 0.0202
w
o1
month
40 C 0.0191 0.0202 0.0193 0.0193 0.0199
0.0194 0.0196 0.0201 0.0196 w
1
_
0
=4
t = 2 25 C 0.0211 0.0200 0.0194 0.0200 , 0.0192
0.0184 0.0197 0.0187 0.0185
months
40 C 0.0187 _ 0.0191 0.0197 0.0193
0.0188 0.0195 0.0201 0.0188 0.0193
t = 3 25 C 0.0208 0.0207 0.0210 0.0195 0.0215
0.0207 0.0211 0.0204 0.0201
months
40 C , 0.0214 0.0189 0.0211 0.0217 0.0201
0.0207 0.0213 0.0209 0.0204
t = 6 25 C 0.0193 0.0199 0.0192 0.0204 0.0199
0.0187 0.0208 0.0198 0.0205
months
40 C 0.0198 0.0217 0.0208 0.0195 0.0203
0.0201 0.0196 0.0212 0.0197
* Samples from the same batch of formulation, sub-aliquoted into glass vials
for the comparison against the Albion pumps (7.5 g and 15 g fill).
127
Attachment IV (Continued)
Stability Study GW 921-01
L. N-oxide raw data (top, middle and bottom extractions)
Amount (%w/w) of n-oxide recovered from each formulation (toy, middle and
bottom) when stored through a 6 month period at
25 C/60% RH and 40 C/75% RII
Specification: Run and Record
0
o
Amount (`)/ow/w) of n oxide recovered from each formulation
n.)
Temperature
-.3
Time point Albion 3.75 % 7.5 g fill Albion 3.75
% 15 g fill % 1-,
storage
w
Top I Middle 1 Bottom Top
Middle Bottom
-.3
t = 0 h
n.)
t=i 25 C
o
1-,
w
o1
month 40 *C
w
1
t = 2 25 *C Not tested
0
..]
months 40 C
t = 3 25 *C
months 40 C
_
'None None None None None
None
t = 6 25 C detected ,detected detected detected
detected detected
months None None None None None
None
40 *C detected detected detected detected
detected detected
128
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Docket No.: 85591P2(54610)
U.S. Express Label No.:
Attachment V
[000314]
Report of Analysis
Sample ED: Albion 30 InL Pump with Cocoon
Ted Method: USP 328%1F 27 <661> Physicochemical Tots¨ Plastics
Reference Standard: Not Applicable
Test Results: See page 2
Attachment,: None
Conuneat The sample meets USP 321NF 27 specifications for thc tests
conducted.
Page 1 of 2
-
129 of 350
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment V (Continued)
TEST RESULTS
PHYSICOCIIEMICAL TESTS ¨ PLASTICS
Nonvolatile Residue US? <661>
EXTRACTAN'r TFSTI RFS11:1' SPlICIFIcATION
Residuc 911 'tuition USP <281>
Meets the USP Specifications.
Specification: it is not necessary to perform this test when the nonvolatile
residue does not exceed
mg as noted for the H20 extraction medium for plastics.
Heavy IVIetuls USP <661>
The color in the sample tube was lighter than the color m the standard tube
(less than 1 ppm).
Specification: Any brown color produced within 10 minutes in the tube
containing the extract of the
sample does not exceed that in the tube containing the standard lead solution
(I ppm).
Buffering Capacity USP <661>
Totaj (mL) _______ , 0.09
_
Specification: The total of the two volumes required for titration between
sampk and blank is not
greater than 10.0 ml,.
*** End of Report ***
Page 2 of 2 QAU Review:,
130
CA 02 7 137 7 7 2 013 - 03 - 07
Attachment VI
[000315]
ALBION 30 ml piston (LDPE) restitution 7,5m1 AIRLESS (Ai RLESSYSTEMS)
ALDARA imiquimod 3.75%
RESULTS : mg
_
TEST GliACEVVAY ,
device 062 devlce 463 devioe #134 device *65 device 066 device 087 dev)ce 068
device 069 device 070 device 071.
PRIMING 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1
dose 1 dose I doe* 1 dose
,
Day 1 235 236 233 227 234 234 228 230
232 230
. ..., ..-
,
Day 2 236 238 233 235 , 236 235 233 233
235 236
.¨
Day 3 236 241 235 235 239 234 230 235 237
237
Day 4 235 242 237 235 I 240
....._ 237 234 , 235 239
238
u j Day 5 235 240 236 235 239 236 235 235 238
238
U.1 Day 6 237 241 237 237 240 238 237 238 239
240 ,
Day? 234 242 .
235 238 , 239 236 , 235 232 235
235
- ,
CNI Day 8 240 243 239 240 , 241 239 238 236
235 241 ,
I¨ Day 9 240 242 238 236 _ 239 239 237 231
239 235
U) Day 10 239 240 237 237 243 239 239 739 239
, 238 ,
Ce
¨ Day 11 237 242 240 238 241 238 236 235 240
217 ,
1.1- ......III
Day 12 240 244 242 241 242 238 232 240 241
239
. .....
Day 13 240 , 239 , 237 235 240 237 237
239 239 237
-
Day 14 236 240 230 237 240 238 236 238 240
238
= . .
WAITING 2 WEEKS ¨,
,
1 dose I dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1
dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose
A
Day 79 237 232 235 231 232 231 230 234
233 229
__,-... ....4
(My 3u 242 244 240 210 240 237 238 , 242
242 237
0
Day 31--". 243 241 239 . 237 239 238 237 239 241
239 i
til Day 32 244 244 237 242 , 240 240 239 242
241 223
I-..1 Day 33 239 243 238 238 240 240 235 239
248 237
.___. , -
* Day 34 239 243 241 241 243 235 235 240 219
241
.. .
NI Day 35 240 240 241 240 241 240 236 239 240
238
-...- ,
õ..0 Day 36 ' 241 240 , 240 236 241 237 236 236
237 240
GDay 37 240 238 236 237 239 230 238 233 237
234
0 .
(..) Day 38 240 241 237 240 235 238 236 240237
237
-.
IA Day 39 239 226 238 240 , 238 239 230 õ .
236 231 234 .
CO Day 40 239 235 235 239 237 238 232 736 ,
223 235
¨
Day 41 na 240 237 234 239 238 234 236 237
233
Day 42 _ 238 239 ' 235 236 239 239 236 232
238 232
131
Docket No.: 85591P2(54610)
U.S. Express Label No.:
¨=¨ device #62
-41¨ device #63
, device #64 .
--A-- device #65
¨Ili¨ device #66
Evolution of the dose for 10 packagings day / day -40-device #67
ALBION 30 piston LOPE restitution 7.5m1 + EV09/240 + COCOON
lab test #2274 (conditioning under vacuum) ¨ device 469
' ¨ device #70
GRACE WAY TEST (ALDARAIMIQUIMOD 3.75%) ,
device #71
,
270
_______________________________________________________________________________
__________ .
265 =- -
i
_______________________________________________________________________________
________________ ,
, (-)
,
260 - ¨
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______ , o
, tv
-.3
255
_______________________________________________________________________________
___________ 1
¨1 1-.
(AI
-.3
250
_______________________________________________________________________________
__________ i ..3
..3
245 ________________________
. __________ i I,
0
1-
....,
E _....,---r$,,,s - ,...f., Ilrfiliier";=
: 4.=
V4p. ...z. = - -
ikt......."..;
(...,
1
e
-.
a ...",
o
id
A
225 __ .
220 ..--
215
AI
210 ___________________
205 _________ .
i
200 , I l r 1r, = T r = . I T . . , y i
. , , =
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1112 1314 15161718 19 20 21 22 232425262728 29 3031 32
3334 3536 37 38 3940 41
132 of 350
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Docket No.: 85591P2(54610)
U.S. Express Label No.:
Attachment VI (Continued)
ALBION 30 ml piston (LOPE) restitution 15ml AIRLESS IAIRLESSYSTEMS)
ALDARA imiquimod 3.75%
RESULTS: Mg
g L&Ii" ilaWAX.
d.vico 467 deo.ce 083 device 064 dove* 065 devioe NG device 067 d42.es 068 .
davica *69 deice 070 devIce 071
.... ,
PRIMING 3 3 3 3 3 , 1 9 3 3 2
_________________________________________________________________________ 4
408.1 dOse 1. 44010 1 dose 1 dole 1
...., dose 1 oose 1 , ;Jose 1 dose 1 dose 1
r . ....
Day 1 235 234 232 233 235 236 235 231 234
236
Day 2 237 239 237 237 239 235 239 235 233
238
2-- ¨ ¨.¨
Day 3 238 238 239 238 240 , 238 240 238
234 241
ICO _____________________________________________________________________
Day 4 239 234 240 236 241 240 241 237 232
239
Y Day 5 240 240 240 , 235 239 238 241 237
239 242
LLI Day 6 237 238 240 236 241 236 238 235 241
240
3 Day 7 , 239 242 240 . ...
231 .
241 238 236 237 2
237 299
, -......¨
C'd Day 8 238 243 241 243 243 239242 237
242 243
I¨ Day 9 739 239 241 739 4-
243 .
740 4
239 239 239 244
Ce Day 10 237 236. 235 240 243 240 240 241
238 244
¨ - _______________
Day 11 235 240 240 240 , 242 240 739 238
240 240
.-- ,
Day 12 238 238 244 243 243 239 242 239 740
243
Day 13 236 241 243 242 244 238 241 233 238
242
,..- .-
Day 14 238 742 240 241 247 240 241 238 239
242
MININ=M11111111111 - . -
waiting 2 weeks
1. dm 1 dose 1 , oose 1 dase 1 dose 1 dose 1 -
dose 1 dose 1 dose 1 dose 1
Diry 29 234 238 239 228 243 236 230 234 234
230
.. '
Day 30 243242 238 242 248 240 242 236 240
244
..- ___. ....... _____________________________
CO Day 31 243 244 241 242 245 240 , 242 239
242 242
Ne Day 32 241 245 ...--
242 242 247 240 242 237 , 299
244
1.1.1 .
W Day 33 241 243 241 242 250 242 242 240 240
243
r Ray 34 242 , 244 242 243 247 240 242 239
242 246 .1
Cs1 Day 35 243 243 241 242 242 239 243 241 ,
239 245
Cl .2 2
ZDay 36 240 245 241 241 243 239 242 238 241
243
O 040 37 241 239 241 _ 239 242 240 240
237 , 240 242
2-_
(2) ' Day 36 241 244 740 243 241 240 240 236
242 247
w
¨I
CO Day 3,3 . 241 244 241 242 24b 241 241 242
237 244
- 2
Day 49 241 745 , 241 742 ,. 242 240 243
236 240 244
-.2 .
040 41 242 244 242 241 242 241 243 238 241
242
b.
Day 42 242 244 242 241 243 240 241 _ 238
241 243
_ ________________________________________________________________________
133 of 350
Docket No.: 85591P2(54610)
U.S. Express Label No.:
¨48.¨ device #62
¨11¨ device #63
device #64
device #65
¨91E¨ device #66
Evolution of the dose for 10 packagings day I day -4-- device
#67
ALBION 30 piston LDPE, restitution 15mI + EV09/240 + COCOON
--- device #69
Lab test # 2275 (conditioning under vacuum)
1¨ device #70
GRACEWAY TEST (ALDARA IMIQUIMOD 3.75%) I device 471
270
_______________________________________________________________________________
____
265
_______________________________________________________________________________
____
0
260 _____
1¨`
255
_______________________________________________________________________________
____
250
N.)
245 _________________________________ 2 weeks
0
1¨`
eralf
¨;11V77114157411.1FKI
lira 240 ¨
:Wer
Ap
0
µ4,17
J 235
to 4
230 ______________________________________________________
225 __________________
220
215
_______________________________________________________________________________
_____
210 ________
205 _______________________________________________
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041
DAY
134 of 350
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Docket No.: 85591P2(54610)
U.S. Express Label No.:
Attachment VII
[000316]
AZRLES.NYSrems
PROCUCT 01111CRIP1ION
Product: SEM EV00/240 30 ALBION PP BC Pil 520 PP BC COCOON 3C CA PP BC
Componeres Materiels Suppliant
14P11 12ZU altOTAL Peirocrernicais
White volrxant standard PP00121522 Clarlani
aratislor
1P/4:O80 'Wog. Nrothontecas
I.
While colorso1 standard PP00121522 Clarlanl
ENGAGE 8401 bow CHEMICALS COMPAGNY
SL PE ER /4 POLYTECHS
61ep-on -grOTAL Pietroobeenicem
White coloranlatandird : PP00121522 Cleriant
neck pail '2174 CKNIN
OuI/Ip EV09/240 : _
body PST Vidos MX312C1M1 001 SASIC
or
PST :ORGATER /WOO PALMARCLE
Clapper PEND : HootaIen OC 7260 SMELL
Nem ipang stainless steel 1.4310 IUGITECH
itiffiat PPM W80 TOTAL Petrocheralcal4
spring holder PPH 5060 TOTAL Potrochsrale3111
plaieet PBC :Hootaleo OCT200 BASE11
Ards PPM 5060 'TOTAL Pekochemicals
+ 501corte 5111bione oils 70047 V300 BLUE STAR SILICONE
alasPRT TDAPOO Crosier PALMAROLE
or
PST : Vika HX312C-1H1C121 SABIC
135 of 350
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment VII (Continued)
e.) 1795
!!!.*¨ 01=1
mom
or
F Ur ao NIL ( PP)
flIsRREL
44
ft
0 ___________________________ 71
=
;
\\I __________________________
=te
cs=
Z,
1
>
PISTON 30101. P910
Roo
ON, ________________________ Ci
IF0N03011,11. PP)
136
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment VII (Continued)
_ CAPOT PIO ENCIAUETE PP ( PP)
OVERCAP $P30 PP
__________________________ .4
A, _________
POUSSOM 820 COCOON BRIT ( -)
_______________________ 3" BRIGHT FINISH 420 COCOON ACTUATOR
.04
+II TOURETTE ENCLIQUE1ABLE
k.VOLUTION ( PM
C+1 ,
Nt: 1 _____________________ TURRET
r)
'
f. ___________ A JOINT OE COL ( therrnopiaatore I
1 NECK GASKET
T
,4-1, ri. ___ 1=111=111114, ___
-4t. B'CUE SP 30 PMEC ( PP U)
CO
) ______________________________________ .
i SNAP CH SP30
T-i
Lei T -
co
ni PNIP EVOLuTION AIRLESS DOSE 240
( -1
,.
PI.,4AP.EV00-240
. 29,15 0.15
1.--
NO COMPRESSED NECK GASKET
137
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment VIII
[000317] Aldara (imiquimod) 5% Cream
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Aldara
safely and
effectively. See full prescribing information for Aldara .
Aldara (irniquimod) Cream
For topical use only
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
----------------------- INDICATIONS AND USAGE ----------------------------
Aldara Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of:
= Clinically typical, nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses
(AK) on
the face or scalp in immunocompetent adults (1.1)
= Biopsy-confirmed, primary superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) in
immunocompetent adults; maximum tumor diameter of 2.0 cm on trunk, neck, or
extremities (excluding hands and feet), only when surgical methods are
medically less
appropriate and patient follow-up can be reasonably assured (1.2)
= External genital and perianal warts/condyloma acuminata in patients 12
years old
or older (1.3)
Limitations of Use: Efficacy was not demonstrated for rnolluscum contagiosum
in
children aged 2-12 (1.4, 8.4)
--------------------- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ------------------------
Aldara Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.(2)
= Actinic keratosis: 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks (2.1)
= Superficial basal cell carcinoma: 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks
(2.2)
= External genital warts (EGW): 3 times per week until total clearance or a
maximum of 16 weeks (2.3)
138
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
-------------------- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS -------------------------
= Aldaraii) (imiquimod) Cream, 5%, is supplied in single-use packets (12
per
box), each of which contains 250 mg of the cream, equivalent to 12.5 mg of
imiquimod. (3)
------------------------- CONTRAINDICATIONS -----------------------------
= None (4)
--------------------- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS --------------------------
= Intense local inflammatory reactions can occur (e.g., skin weeping,
erosion).
Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.1, 6)
= Flu-like systemic signs and symptoms including malaise, fever, nausea,
myalgias
and rigors may occur. Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.2, 6)
= Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear sunscreen daily (5.3).
= Safety and efficacy have not been established for repeat courses of
treatment to
the same area for AK. (5.4)
= Aldara Cream is not recommended for treatment of BCC subtypes other than
the superficial variant, i.e., sBCC. (5.5)
= Treatment of urethral, intra-vaginal, cervical, rectal or intra-anal
viral disease is
not recommended. (5.6)
= Safety and efficacy in immunosuppressed patients have not been
established (1.5)
------------------------- ADVERSE REACTIONS ------------------------------
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >28%) are application site reactions
or local
skin reactions: itching, burning, erythema, flaking/scaling/dryness,
scabbing/crusting, edema,
induration, excoriation, erosion, ulceration. Other reported reactions (> 1%)
include fatigue,
fever, and headache (6.1, 6.2, 6.3)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Graceway Pharmaceuticals,
LLC at 1-800-328-0255 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1 088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA- approved patient
labeling.
Revised: March 2007
139
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
1.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
1.3 External Genital Warts
1.4 Limitations of Use
1.5 Unevaluated Populations
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
2.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
2.3 External Genital Warts
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Inflammatory Reactions 5.2 Systemic Reactions
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
5.4 Unevaluated Uses: Actinic Keratosis
5.5 Unevaluated Uses: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
5.6 Unevaluated Uses: External Genital Warts
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience : Actinic Keratosis
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
6.3 Clinical Trials Experience: External Genital Warts
6.4 Clinical Trials Experience: Dermal Safety Studies
6.5 Postmarketing Experience
140
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
OVER DOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
14.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
14.3 External Genital Warts
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 General Information: All Indications
17.2 Local Skin Reactions: All Indications
17.3 Systemic Reactions: All Indications
17.4 Patients Being Treated for Actinic Keratosis (AK)
141
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
17.5 Patients Being Treated for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma (sBCC)
17.6 Patients Being Treated for External Genital Warts
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not
listed.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
Alclarao Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical,
nonhyperkeratotic,
nonhypertrophic actinic keratoses on the face or scalp in immunocompetent
adults.
1.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Aldara Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of biopsy-confirmed,
primary
superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) in immunocompetent adults, with a
maximum tumor
diameter of 2.0 cm, located on the trunk (excluding anogenital skin), neck, or
extremities
(excluding hands and feet), only when surgical methods are medically less
appropriate and
patient follow-up can be reasonably assured.
The histological diagnosis of superficial basal cell carcinoma should be
established
prior to treatment, since safety and efficacy of Aldara Cream have not been
established for
other types of basal cell carcinomas, including nodular and morpheaform
(fibrosing or
sclerosing) types.
L3 External Genital Warts
Aldara Cream is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal
warts/condyloma acuminata in patients 12 years or older.
1.4 Limitations of Use
Aldara Cream has been evaluated in children ages 2 to 12 years with molluscum
contagiosum and these studies failed to demonstrate efficacy. [see Use in
Specific Populations
(8.4)].
1_5 Unevaluated Populations
142
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
The safety and efficacy of Aldara Cream in immunasuppressed patients have not
been
established.
Aldara Cream should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing
autoimmune
conditions.
The efficacy and safety of Aldara Cream have not been established for
patients with
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome or Xeroderma Pigmentosum.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINIS1RATION
The application frequency for Aldara Cream is different for each indication.
Aldara Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
Aldara Cream should be applied 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks to a
defined
treatment area on the face or scalp (but not both concurrently). The treatment
area is defined as
one contiguous area of approximately 25 cm2 (e.g., 5 cm x 5 cm) on the face
(e.g. forehead or
one cheek) or on the scalp. Examples of 2 times per week application schedules
are Monday
and Thursday, or Tuesday and Friday. Aldara Cream should be applied to the
entire treatment
area and rubbed in until the Aldara Cream is no longer visible. No more than
one packet of
Aldara Cream should be applied to the contiguous treatment area at each
application. Aldara
Cream should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin
for approximately 8
hours, after which time the Aldara Cream should be removed by washing the
area with mild
soap and water. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application
technique to
maximize the benefit of Aldara Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Aldara Cream.
Before applying the Aldara Cream, the patient should wash the treatment area
with mild
soap and water and allow the area to dry thoroughly (at least 10 minutes).
Contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are common. [see Adverse Reactions
(6.1,
6.5)] A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's
discomfort or
severity of the local skin reaction. However, the treatment period should not
be extended beyond
16 weeks due to missed doses or rest periods. Response to treatment cannot be
adequately assessed
143
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
until resolution of local skin reactions. Lesions that do not respond to
treatment should be
carefully re-evaluated and management reconsidered.
Aldara Cream is packaged in single-use packets, with 12 packets supplied per
box.
Patients should be prescribed no more than 3 boxes (36 packets) for the 16-
week treatment period.
Unused packets should be discarded. Partially-used packets should be discarded
and not reused.
2.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Aldara Cream should be applied 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks to a
biopsy-
confirmed superficial basal cell carcinoma. An example of a 5 times per week
application
schedule is to apply Aldara Cream, once per day, Monday through Friday.
Aldara Cream
should be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for
approximately 8 hours,
after which time the Aldara l3 Cream should be removed by washing the area
with mild soap
and water. The prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique
to maximize the
benefit of Aldara Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Aldara
Cream. The patient should wash the treatment area with mild soap and water
before applying the
cream, and allow the area to dry thoroughly.
The target tumor should have a maximum diameter of 2 cm and be located on the
trunk (excluding anogenital skin), neck, or extremities (excluding hands and
feet). The treatment
area should include a 1 cm margin of skin around the tumor. Sufficient cream
should be applied
to cover the treatment area, including 1 centimeter of skin surrounding the
tumor. Aldara
Cream should be rubbed into the treatment area until the cream is no longer
visible.
Table 1. Amount of Aldara Cream to Use for sBCC
Target Tumor Diameter Size of Cream Droplet to be
Approximate Amount of
Used (diameter) Aldara to be Used
0.5 to < 1.0 cm 4 mm 10 mg
. 1.0 to < 1.5 cm 5 mm 25 mg
. 1.5 to 2.0 cm 7 mm 40 mg
Contact with the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are commonisee Adverse Reactions
(6.2,
6.5)] A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's
discomfort or
severity of the local skin reaction.
144
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Early clinical clearance cannot be adequately assessed until resolution of
local skin
reactions (e.g. 12 weeks post-treatment). Local skin reactions or other
findings (e.g.
infection) may require that a patient be seen sooner than the post-treatment
assessment
for clinical clearance. If there is clinical evidence of persistent tumor at
the post-
treatment assessment for clinical clearance, a biopsy or other alternative
intervention should be
considered. Lesions that do not respond to therapy should be carefully re-
evaluated and
management reconsidered; the safety and efficacy of a repeat course of Aldara
Cream treatment
have not been established. If any suspicious lesion arises in the treatment
area at any time
after a determination of clinical clearance, the patient should seek a medical
evaluation [see
Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Aldara Cream is packaged in single-use packets, with 12 packets supplied per
box.
Patients should be prescribed no more than 3 boxes (36 packets) for the 6-week
treatment
period. Unused packets should be discarded. Partially-used packets should be
discarded and
not reused.
2.3 External Genital Warts
Aldara i3 Cream should be applied 3 times per week to external
genital/perianal warts.
Aldara Cream treatment should continue until there is total clearance of the
genital/perianal
warts or for a maximum of 16 weeks. Examples of 3 times per week application
schedules
are: Monday, Wednesday, Friday or Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday. Aldara Cream
should
be applied prior to normal sleeping hours and left on the skin for 6-10 hours,
after which time
the Aldara Cream should be removed by washing the area with mild soap and
water. The
prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the
benefit of
Aldara Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Aldara
Cream. A thin layer of Aldara Cream should be applied to the wart area and
rubbed in until
the Aldara Cream is no longer visible. The application site should not be
occluded.
Following the treatment period the Aldara Cream should be removed by washing
the
treated area with mild soap and water.
Local skin reactions at the treatment site are common. [see Adverse Reactions
(6.3,
6.5)]. A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's
discomfort or
severity of the local skin reaction. Treatment may resume once the reaction
subsides. Non-
145
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
occlusive dressings such as cotton gauze or cotton underwear may be used in
the
management of skin reactions.
Aldara Cream is packaged in single-use packets which contain sufficient
Aldara
Cream to cover a wart area of up to 20 cm2; use of excessive amounts of Aldara
Cream
should be avoided.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Aldara (imiquitnod) Cream, 5%, is supplied in single-use packets each of
which
contains 250 mg of the cream, equivalent to 12.5 mg of imiquimod. Aldara
Cream is
supplied in boxes of 12 packets each.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Inflammatory Reactions
Intense local inflammatory reactions including skin weeping or erosion can
occur after
few applications of Aldara Cream and may require an interruption of dosing.
[see Dosage and
Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. Aldara Cream has the potential
to exacerbate
inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus host
disease.
Administration of Aldara Cream is not recommended until the skin is
completely healed from
any previous drug or surgical treatment.
5.2 Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local inflammatory
reactions and may include malaise, fever, nausea, myalgias and rigors. An
interruption of
dosing should be considered. [see Adverse Reactions (6)1
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
Exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) should be avoided or minimized
during
use of Aldara Cream because of concern for heightened sunburn susceptibility.
Patients
should be warned to use protective clothing (e.g., a hat) when using Aldara
Cream. Patients
with sunburn should be advised not to use Aldara Cream until fully recovered.
Patients who
146
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
may have considerable sun exposure, e.g. due to their occupation, and those
patients with
inherent sensitivity to sunlight should exercise caution when using Aldara
Cream.
Aldara Cream shortened the time to skin tumor formation in an animal photoco-
carcinogenicity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. The enhancement of
ultraviolet
carcinogenicity is not necessarily dependent on phototoxic mechanisms.
Therefore, patients
should minimize or avoid natural or artificial sunlight exposure.
5.4 Unevaluated Uses: Actinic Keratosis
Safety and efficacy have not been established for Aldara Cream in the
treatment of
actinic keratosis with repeated use, i.e. more than one treatment course, in
the same area.
The safety of Aldara Cream applied to areas of skin greater than 25 cm2 (e.g.
5 cm X
cm) for the treatment of actinic keratosis has not been established [see
Clinical Pharmacology
( 1 2 . 3)] .
5.5 Unevaluated Uses: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
The safety and efficacy of Aldara Cream have not been established for other
types of
basal cell carcinomas (BCC), including nodular and morpheaform (fibrosing or
sclerosing) types.
Aldara Cream is not recommended for treatment of BCC subtypes other than the
superficial
variant (i.e., sBCC). Patients with sBCC treated with Aldara Cream should
have regular
follow-up of the treatment site. [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The safety and efficacy of treating sBCC lesions on the face, head and
anogenital area
have not been established.
5.6 Unevaluated Uses: External Genital Warts
Aldara Cream has not been evaluated for the treatment of urethral, intra-
vaginal,
cervical, rectal, or intra-anal human papilloma viral disease.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse
reaction
rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to
rates in the clinical
trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
61 Clinical Trials Experience: Actinic Keratosis
The data described below reflect exposure to Aldara Cream or vehicle in 436
subjects
enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies. Subjects applied
Aldara Cream or
147
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
vehicle to a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area on the face or scalp 2 times per
week for 16
weeks.
Table 2: Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 1% of Aldara -Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies
(Actinic
Keratosis)
Aklara Cream Vehicle
Preferred Term (n= 215) (n= 221)
Application Site Reaction 71 ( 33%) 32 ( 14%)
Upper Resp Tract Infection 33 ( 15%) 27 ( 12%)
Sinusitis 16 ( 7%) 14 ( 6%)
Headache 11 ( 5%) 7 ( 3%)
Carcinoma Squamous 8 ( 4%) 5 ( 2%)
Diarrhea 6 ( 3%) 2 ( 1%)
Eczema 4 ( 2%) 3 ( 1%)
Back Pain 3 ( 1%) 2 ( 1%)
Fatigue 3 ( 1%) 2 ( 1%)
Fibrillation Atrial 3 ( 1%) 2 ( 1%)
Infection Viral 3 ( 1%) 2 ( 1%)
Dizziness 3 ( 1%) 1 ( <1%)
Vomiting 3 ( 1%) 1 ( <1%)
Urinary Tract Infection 3 ( 1%) 1 ( <1%)
Fever 3 ( 1%) 0 ( 0%)
Rigors 3 ( 1%) 0 ( 0%)
Alopecia 3 ( 1%) 0 ( 0%)
Table 3: Application Site Reactions Reported by > 1% of Aldara -Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined
Studies (Actinic Keratosis)
Aldarag Cream Vehicle
n=215 n=221
Included Term
Itching 44 (20%) 17 (8%)
Burning 13 (6%) 4 (2%)
Bleeding 7 (3%) 1 (<1%)
Stinging 6 (3%) 2 (1%)
Pain 6(3%) 2(1%)
Induration 5 (2%) 3 (1%)
Tenderness 4 (2%) 3 (1%)
Irritation 4 (2%) 0 (0%)
148
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Local skin reactions were collected independently of the adverse reaction
"application site reaction" in an effort to provide a better picture of the
specific types of local
reactions that might be seen. The most frequently reported local skin
reactions were
erythema, flaking/scaling/ dryness, and scabbing/crusting. The prevalence and
severity of
local skin reactions that occurred during controlled studies are shown in the
following table.
Table 4: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the
Investigator
(Actinic Keratosis)
Aldara Cream Vehicle
(n=215) (n=220)
All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe
Erythema 209 (97%) 38 (18%) 206 (93%)
5 (2%)
Flaking/Scaling/Dryness 199 (93%) 16 (7%) 199 (91%)
7 (3%)
Scabbing/Crusting 169 (7 TA) 18 (8%) 92 (42%)
4 (2%)
Edema 106 (49%) 0 (0%) 22 (10%)
0 (0%)
Erosion/Ulceration 103 (48%) 5 (2%) 20 (9%) 0
(0%)
Weeping/Exudate 45 (22%) 0 (0%) 3 (1%) 0
(0%)
Vesicles 19 (9%) 0 (0%) 2 (1%) 0
(0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
The adverse reactions that most frequently resulted in clinical intervention
(e.g., rest
periods, withdrawal from study) were local skin and application site
reactions. Overall, in the
clinical studies, 2% (5/215) of subjects discontinued for local
skin/application site reactions. Of
the 215 subjects treated, 35 subjects (16%) on Aldara Cream and 3 of 220
subjects (1%)
on vehicle cream had at least one rest period. Of these Aldara Cream
subjects, 32 (9 1%)
resumed therapy after a rest period.
In the AK studies, 22 of 678 (3.2%) of Aldara -treated subjects developed
treatment site infections that required a rest period off Aldara ii.) Cream
and were treated with
antibiotics (19 with oral and 3 with topical).
Of the 206 Aldara subjects with both baseline and 8-week post-treatment
scarring
assessments, 6 (2.9%) had a greater degree of scarring scores at 8-weeks post-
treatment than at
baseline.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
149
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
The data described below reflect exposure to Aldara Cream or vehicle in 364
subjects
enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies. Subjects applied
Aldara Cream or
vehicle 5 times per week for 6 weeks. The incidence of adverse reactions
reported by > 1%
of subjects during the studies is summarized below.
Table 5: Selected Adverse Reactions Reported by > 1% of Aldara -Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies
(Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
Aldara Vehicle
Cream
(n= 179)
Preferred Term (n= 185) N %
N
Application Site Reaction 52 (28%) 5 ( 3%)
Headache 14 (8%) 4 (2%)
Back Pain 7 ( 4%) 1 ( <1%)
Upper Resp Tract Infection 6 ( 3%) 2 ( 1%)
Rhinitis 5 ( 3%) 1 ( <1%)
Lymphadenopathy 5 ( 3%) 1 ( <1%)
Fatigue 4 ( 2%) 2 ( 1%)
Sinusitis 4 ( 2%) 1 ( <1%)
Dyspepsia 3 ( 2%) 2 ( 1%)
Coughing 3 ( 2%) 1 ( <1%)
Fever 3 ( 2%) 0 ( 0%)
Dizziness 2 (1%) 1 (<1%)
Anxiety 2 ( 1%) 1 ( <1%)
Pharyngitis 2 ( 1%) 1 ( <1%)
Chest Pain 2 ( 1%) 0 ( 0%)
Nausea 2 ( 1%) 0 ( 0%)
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were local skin and application
site
reactions including erythema, edema, induration, erosion, flaking/scaling,
scabbing/crusting,
itching and burning at the application site. The incidence of application site
reactions reported
by > 1% of the subjects during the 6 week treatment period is summarized in
the table below.
Table 6: Application Site Reactions Reported by > 1% of Aldara -Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Vehicle in the Combined Studies
(Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
150
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Aldara Cream Vehicle
Included Term n=185 n=179
Itching 30 (16%) 1(1%)
Burning 11(6%) 2 (1%)
Pain 6 (3%) 0 (0%)
Bleeding 4 (2%) 0 (0%)
Erythema 3 (2%) 0 (0%)
Papule(s) 3 (2%) 0 (0%)
Tenderness 2 (1%) 0 (0%)
Infection 2 (1%) 0 (0%)
Local skin reactions were collected independently of the adverse reaction
"application site reaction" in an effort to provide a better picture of the
specific types of local
reactions that might be seen. The prevalence and severity of local skin
reactions that
occurred during controlled studies are shown in the following table.
Table 7: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the
Investigator
(Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma)
Aldara Cream Vehicle
n=184 n=178
All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe
Erythema 184(100%) 57(3 1%) 173 (97%) 4 (2%)
Flaking/Scaling 167 (91%) 7(4%) 135 (76%) 0 (0%)
Induration 154(84%) 11(6%) 94 (53%) 0 (0%)
Scabbing/Crusting 152(83%) 35(19%) 61(34%) 0 (0%)
Edema 143(78%) 13(7%) 64 (36%) 0
(0%)
Erosion 122 (66%) 23(13%) 25 (14%) 0 (0%)
Ulceration 73 (40%) 11(6%) 6 (3%) 0 (0%)
Vesicles 57 (3 1%) 3 (2%) 4 (2%) 0 (0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
The adverse reactions that most frequently resulted in clinical intervention
(e.g., rest
periods, withdrawal from study) were local skin and application site
reactions; 10% (19/1 85) of
subjects received rest periods. The average number of doses not received per
subject due to
151
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
rest periods was 7 doses with a range of 2 to 22 doses; 79% of subjects
(15/19) resumed
therapy after a rest period. Overall, in the clinical studies, 2% (4/185) of
subjects
discontinued for local skin/application site reactions.
In the sBCC studies, 17 of 1266 (1.3%) Aldara -treated subjects developed
treatment
site infections that required a rest period and treatment with antibiotics.
6.3 Clinical Trials Experience: External Genital Warts
In controlled clinical trials for genital warts, the most frequently reported
adverse
reactions were local skin and application site reactions.
Some subjects also reported systemic reactions. Overall, 1.2% (4/327) of the
subjects discontinued due to local skin/application site reactions. The
incidence and severity of
local skin reactions during controlled clinical trials are shown in the
following table.
Table 8: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area as Assessed by the
Investigator
(External Genital Warts)
Aldara Cream Vehicle
Females Males Females Males
n=114 n=156 n=99 n=157
All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe
Erythema 74(65%) 4(4%) 90(58%) 6(4%) 21(21%) 0(0%) 34(22%) 0(0%)
Erosion 35(31%) 1(1%) 47(30%) 2(1%) 8(8%) 0(0%) 10(6%) 0(0%)
Excoriation/ 21(18%) 0(0%) 40(26%) 1(1%)
8(8%) 0(0%) 12(8%) 0(0%)
Flaking
Edema 20(18%) 1(1%) 19(12%) 0(0%) 5(5%) 0(0%) 1(1%) 0(0%)
Scabbing 4(4%) 0(0%) 20(13%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 4(3%) 0(0%)
Induration 6(5%) 0(0%) 11(7%) 0(0%) 2(2%) 0(0%) 3(2%) 0(0%)
Ulceration 9(8%) 3(3%) 7(4%) 0(0%) 1(1%) 0(0%) 1(1%) 0(0%)
Vesicles 3(3%) 0(0%) 3(2%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 0(0%)
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
Remote site skin reactions were also reported. The severe remote site skin
reactions
reported for females were erythema (3%), ulceration (2%), and edema (1%); and
for males,
erosion (2%), and erythema, edema, induration, and excoriation/flaking (each
1%). Selected
adverse reactions judged to be probably or possibly related to Aldara Cream
are listed below.
152
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Table 9: Selected Treatment Related Reactions (External Genital Warts)
Females Males
Aldarae Aldara
Cream Vehicle Cream Vehicle
n=117 n=103 n=156 n=158
Application Site Disorders:
Application Site Reactions
Wart Site:
Itching 38(32%) 21(20%) 34(22%) 16(10%)
Burning 30(26%)
12(12%) 14(9%) 8(5%)
Pain 9(8%) 2(2%) 3(2%) 1(1%)
Soreness 3(3%) 0(0%) 0(0%) 1(1%)
Fungal Infection* 13(11%) 3(3%) 3(2%) 1(1%)
Systemic Reactions:
Headache 5(4%) 3(3%) 8(5%) 3(2%)
Influenza-like symptoms 4(3%) 2(2%) 2(1%) 0(0%)
Myalgia 1(1%) 0(0%) 2(1%) 1(1%)
*Incidences reported without regard to causality with Aldara Cream.
Adverse reactions judged to be possibly or probably related to Aldara Cream
and
reported by more than 1% of subjects included:
Application Site Disorders: burning, hypopigrnentation, irritation, itching,
pain, rash,
sensitivity, soreness, stinging, tenderness
Remote Site Reactions: bleeding, burning, itching, pain, tenderness, tinea
cruris Body
as a Whole: fatigue, fever, influenza-like symptoms
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders: headache
Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders: diarrhea
Musculo-Skeletal System Disorders: myalgia.
Provocative repeat insult patch test studies involving induction and challenge
phases
produced no evidence that Aldara Cream causes photoallergenicity or contact
sensitization in
healthy skin; however, cumulative irritancy testing revealed the potential for
Aldara Cream
to cause irritation, and application site reactions were reported in the
clinical studies [see
Adverse Reactions (6)].
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use
of
Aldara Cream. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a
population of
153
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency
or establish a
causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: angioedema.
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy,
pulmonary
edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, palpitations), chest
pain, ischemia,
myocardial infarction, syncope.
Endocrine: thyroiditis.
Hematological: decreases in red cell, white cell and platelet counts
(including idiopathic
thrombocytopenic purpura), lymphoma.
Hepatic: abnormal liver function.
Neuropsychiatric: agitation, cerebrovascular accident, convulsions (including
febrile
convulsions), depression, insomnia, multiple sclerosis aggravation, paresis,
suicide. Respiratory:
dyspnea.
Urinary System Disorders: proteinuria.
Skin and Appendages: exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multifonne,
hyperpigmentation.
Vascular: Henoch-Schonlein purpura syndrome.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
Note: The Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) was set at 2 packets per
treatment of Aldara Cream (25 mg imiquimod) for the animal multiple of human
exposure
ratios presented in this label. If higher doses than 2 packets of Aldara
Cream are used
clinically, then the animal multiple of human exposure would be reduced for
that dose. A
non-proportional increase in systemic exposure with increased dose of Aldara
Cream
was noted in the clinical pharmacokinetic study conducted in actinic keratosis
subjects
[see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The AUC after topical application of 6
packets of
Aldara Cream was 8 fold greater than the AUC after topical application of 2
packets of
Aldara Cream in actinic keratosis subjects. Therefore, if a dose of 6 packets
per treatment of
Aldara Cream was topically administered to an individual, then the animal
multiple of human
exposure would be either 1/3 of the value provided in the label (based on body
surface area
154
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
comparisons) or 1/8 of the value provided in the label (based on AUC
comparisons). The
animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on weekly dose
comparisons for
the carcinogenicity studies described in this label. The animal multiples of
human exposure
calculations were based on daily dose comparisons for the reproductive
toxicology studies
described in this label.
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits.
Oral
doses of 1, 5 and 20 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period
of
organogenesis (gestational days 6 ¨ 15) to pregnant female rats. In the
presence of maternal
toxicity, fetal effects noted at 20 mg/kg/day (577X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons)
included increased resorptions, decreased fetal body weights, delays in
skeletal ossification,
bent limb bones, and two fetuses in one litter (2 of 1567 fetuses)
demonstrated
exencephaly, protruding tongues and low-set ears. No treatment related effects
on
embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 5 mg/kg/day (98X MRHD
based on
AUC comparisons).
Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1 and 2 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during
the
period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 ¨ 18) to pregnant female rabbits.
No treatment
related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 2
mg/kg/day (1 .5X MRHD
based on BSA comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study, or 1
mg/kg/day (407X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
A combined fertility and pen- and post-natal development study was conducted
in
rats. Oral doses of 1, 1.5, 3 and 6 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered to
male rats from
70 days prior to mating through the mating period and to female rats from 14
days prior to
mating through parturition and lactation. No effects on growth, fertility,
reproduction or post-
natal development were noted at doses up to 6 mg/kg/day (87X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study. In the absence of
maternal toxicity,
bent limb bones were noted in the F 1 fetuses at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (87X
MRHD based
on AUC comparisons). This fetal effect was also noted in the oral rat
embryofetal
development study conducted with imiquimod. No treatment related effects on
teratogenicity
were noted at 3 mg/kg/day (41X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
155
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Aldara0
Cream
should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the
potential risk to the
fetus.
83 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether imiquimod is excreted in human milk following use of
AldaraS
Cream. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be
exercised when
AldaraS Cream is administered to nursing women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
AK and sBCC are not conditions generally seen within the pediatric population.
The
safety and efficacy of Aldara Cream for AK or sBCC in patients less than 18
years of age have
not been established.
Safety and efficacy in patients with external genital/perianal warts below the
age of 12
years have not been established.
AldaraS Cream was evaluated in two randomized, vehicle-controlled, double-
blind trials
involving 702 pediatric subjects with molluscurn contagiosum (MC) (470 exposed
to AldaraS
Cream; median age 5 years, range 2-12 years). Subjects applied AldaraS Cream
or vehicle 3
times weekly for up to 16 weeks. Complete clearance (no MC lesions) was
assessed at Week 18.
In Study 1, the complete clearance rate was 24% (52/2 17) in the Alclarat
Cream group compared
with 26% (28/106) in the vehicle group. In Study 2, the clearance rates were
24% (60/253) in the
AldaraS Cream group compared with 28% (3 5/126) in the vehicle group. These
studies failed
to demonstrate efficacy.
Similar to the studies conducted in adults, the most frequently reported
adverse reaction
from 2 studies in children with molluscum contagiosum was application site
reaction. Adverse
events which occurred more frequently in AldaraS-treated subjects compared
with vehicle-
treated subjects generally resembled those seen in studies in indications
approved for adults and
also included otitis media (5% AldaraS Cream vs. 3% vehicle) and
conjunctivitis (3% AldaraS
Cream vs. 2% vehicle).
Erythema was the most frequently reported local skin reaction. Severe local
skin
reactions reported by AlclaraS-treated subjects in the pediatric studies
included erythema (28%),
edema (8%), scabbing/crusting (5%), flaking/scaling (5%), erosion (2%) and
weeping/exudate
(2%).
156
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Systemic absorption of imiquimod across the affected skin of 22 subjects aged
2 to 12 years
with extensive MC involving at least 10% of the total body surface area was
observed after single
and multiple doses at a dosing frequency of 3 applications per week for 4
weeks. The investigator
determined the dose applied, either 1, 2 or 3 packets per dose, based on the
size of the treatment
area and the subject's weight. The overall median peak serum drug
concentrations at the end of
week 4 was between 0.26 and 1.06 ng/ml except in a 2-year old female who was
administered 2
packets of study drug per dose, had a Cmax of 9.66 ng/mL after multiple
dosing. Children aged
2-5 years received doses of 12.5 mg (one packet) or 25 mg (two packets) of
imiquimod and had
median multiple-dose peak serum drug levels of approximately 0.2 or 0.5 ng/mL,
respectively.
Children aged 6-12 years received doses of 12.5 mg, 25 mg, or 37.5 mg (three
packets) and had
median multiple dose serum drug levels of approximately 0.1, 0.15, or 0.3
ng/mL, respectively.
Among the 20 subjects with evaluable laboratory assessments, the median WBC
count decreased
by 1.4* 109/L and the median absolute neutrophil count decreased by 1.42*
109/L.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 215 subjects treated with Aldara Cream in the AK clinical studies, 127
subjects
(5 9%) were 65 years and older, while 60 subjects (28%) were 75 years and
older. Of the 185
subjects treated with Aldara Cream in the sBCC clinical studies , 65 subjects
(35%) were 65
years and older, while 25 subjects (14%) were 75 years and older. No overall
differences in
safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger
subjects. No other
clinical experience has identified differences in responses between the
elderly and younger
subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled
out.
OVER DOSAGE
Topical overdosing of Aldara Cream could result in an increased incidence of
severe local
skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
The most clinically serious adverse event reported following multiple oral
imiquimod
doses of >200 mg (equivalent to imiquimod content of >16 packets) was
hypotension, which
resolved following oral or intravenous fluid administration.
11 DESCRIPTION
157
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
N
I
3
CH3
Aldara (imiquimod 5%) Cream is an immune response modifier for topical
administration. Each gram contains 50 mg of imiquimod in an off-white oil-in-
water vanishing
cream base consisting of isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol,
white petrolatum,
polysorbate 60, sorbitan monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water,
benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and propylparaben.
Chemically, imiquimod is 1 -(2-methylpropy1)- 1H-imidazo,4,5-c,quinolin-4-
amine.
Imiquimod has a molecular formula of C14H16N4 and a molecular weight of 240.3.
Its structural
formula is:
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Aldara Cream in treating AK and sBCC lesions is
unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Actinic Keratosis
In a study of 18 subjects with AK comparing Aldara Cream to vehicle,
increases from
baseline in week 2 biomarker levels were reported for CD3, CD4, CD8, CD1 1 c,
and CD68
for Aldara Cream treated subjects; however, the clinical relevance of these
findings is
unknown.
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
An open label study in six subjects with sBCC suggests that treatment with
Aldara
Cream may increase the infiltration of lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and
macrophages into the
tumor lesion; however, the clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
External Genital Warts
Imiquimod has no direct antiviral activity in cell culture. A study in 22
subjects with
genital/perianal warts comparing Aldara Cream and vehicle shows that Aldara
Cream
158
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
induces mRNA encoding cytokines including interferon- at the treatment site.
In addition
HPVL1 mRNA and HPV DNA are significantly decreased following treatment
However, the
clinical relevance of these fmdings is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic absorption of imiquimod across the affected skin of 58 subjects with
AK was
observed with a dosing frequency of 3 applications per week for 16 weeks. Mean
peak serum
drug concentrations at the end of week 16 were approximately 0.1, 0.2, and 3.5
ng/mL for the
applications to face (12.5 mg imiquimod, 1 single-use packet), scalp (25 mg, 2
packets) and
hands/arms (75 mg, 6 packets), respectively.
Table 10: Mean Serum Imiquimod Concentration in Adults Following
Administration of the Last Topical Dose During Week 16 (Actinic Keratosis)
Amount of Aldara Cream applied Mean peak serum imiquimod
concentration [Cmaxi
12.5 mg (1 packet) 0.1 ng/mL
25 mg (2 packets) 0.2 ng/mL
75 mg (6 packets) 3.5 ng/mL
The application surface area was not controlled when more than one packet was
used.
Dose proportionality was not observed. However it appears that systemic
exposure may be
more dependent on surface area of application than amount of applied dose. The
apparent
half-life was approximately 10 times greater with topical dosing than the 2
hour apparent half-
life seen following subcutaneous dosing, suggesting prolonged retention of
drug in the skin.
Mean urinary recoveries of imiquimod and metabolites combined were 0.08 and
0.15% of the
applied dose in the group using 75 mg (6 packets) for males and females,
respectively
following 3 applications per week for 16 weeks.
Systemic absorption of imiquimod was observed across the affected skin of 12
subjects
with genital/perianal warts, with an average dose of 4.6 mg. Mean peak drug
concentration
of approximately 0.4 ng/mL was seen during the study. Mean urinary recoveries
of imiquimod
and metabolites combined over the whole course of treatment, expressed as
percent of the
estimated applied dose, were 0.11 and 2.41% in the males and females,
respectively.
159
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) rat carcinogenicity study, imiquimod was administered to
Wistar
rats on a 2X/week (up to 6 mg/kg/day) or daily (3 mg/kg/day) dosing schedule
for 24
months. No treatment related tumors were noted in the oral rat carcinogenicity
study up to the
highest doses tested in this study of 6 mg/kg administered 2X/week in female
rats (87X
MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons), 4 mg/kg administered 2X/week in male
rats (75X
MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons) or 3 mg/kg administered 7X/week to male
and
female rats (153X MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons).
In a dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream (up to 5
mg/kg/application imiquimod or 0.3% imiquimod cream) was applied to the backs
of mice
3)C/week for 24 months. A statistically significant increase in the incidence
of liver adenomas
and carcinomas was noted in high dose male mice compared to control male mice
(251X
MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons). An increased number of skin papillomas
was
observed in vehicle cream control group animals at the treated site only. The
quantitative
composition of the vehicle cream used in the dermal mouse carcinogenicity
study is the same
as the vehicle cream used for Aklara Cream, minus the active moiety
(imiquimod).
In a 52-week dermal photoco-carcinogenicity study, the median time to onset of
skin
tumor formation was decreased in hairless mice following chronic topical
dosing (3X/week;
40 weeks of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation) with concurrent
exposure to UV
radiation (5 days per week) with the Aldarag Cream vehicle alone. No
additional effect on
tumor development beyond the vehicle effect was noted with the addition of the
active
ingredient, imiquimod, to the vehicle cream.
Imiquimod revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on
the
results of five in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma L5178Y
assay,
Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay, human lymphocyte
chromosome
aberration assay and SHE cell transformation assay) and three in vivo
genotoxicity tests (rat
and hamster bone marrow cytogenetics assay and a mouse dominant lethal test).
Daily oral administration of imiquimod to rats, throughout mating, gestation,
parturition and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility or
reproduction, at doses
up to 87X MRHD based on AUC comparisons.
160
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical studies, 436 subjects with AK
were
randomized to treatment with either Aldarag Cream or vehicle cream 2 times per
week for
16 weeks. The studies enrolled subjects with 4 to 8 clinically typical,
visible, discrete,
nonhyperkeratotic, nonhypertrophic AK lesions within a 25 cm2 contiguous
treatment area
on either the face or scalp. The 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area could be of
any dimensions
e.g., 5 cm x 5 cm, 3 cm by 8.3 cm, 2 cm by 12.5 cm. Study subjects ranged from
37 to 88
years of age (median 66 years) and 55% had Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. All
Aldarag-treated
subjects were Caucasians.
On a scheduled dosing day, the study cream was applied to the entire treatment
area
prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Twice
weekly
dosing was continued for a total of 16 weeks. The clinical response of each
subject was
evaluated 8 weeks after the last scheduled application of study cream.
Efficacy was
assessed by the complete clearance rate, defined as the proportion of subjects
at the 8-week
post-treatment visit with no (zero) clinically visible AK lesions in the
treatment area.
Complete clearance included clearance of all baseline lesions, as well as any
new or sub-
clinical AK lesions which appeared during therapy.
Complete and partial clearance rates are shown in the table below. The partial
clearance
rate was defmed as the percentage of subjects in whom 75% or more baseline AK
lesions
were cleared.
Table 11: Clearance Rates (AK)
Complete Clearance Rates (100% AK Lesions Cleared)
Study Aldarag Cream Vehicle
Study 46% (49/107) 3% (3/110)
AK1
Study 44% (48/108) 4% (4/111)
AK2
Partial and Complete Clearance Rates (75% or More Baseline AK
Lesions Cleared)
Study Aldarag Cream Vehicle
Study 60% (64/107) 10% (11/110)
AK1
161
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Study 58% (63/108) 14% (15/111)
AK2
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during
treatment
with Aldara Cream. During the course of treatment, 48% (103/215) of subjects
experienced an increase in AK lesions relative to the number present at
baseline within the
treatment area. Subjects with an increase in AK lesions had a similar response
to those with no
increase in AK lesions.
14.2 Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
In two double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical studies, 364 subjects with
primary
sBCC were treated with Aldara Cream or vehicle cream 5 times per week for 6
weeks.
Target tumors were biopsy-confirmed sBCC and had a minimum area of 0.5 cm2 and
a
maximum diameter of 2.0 cm (4.0 cm2). Target tumors were not to be located
within 1.0
cm of the hairline, or on the anogenital area or on the hands or feet, or to
have any atypical
features. The population ranged from 31-89 years of age (median 60 years) and
65% had
Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. On a scheduled dosing day, study cream was
applied to the
target tumor and approximately 1 cm (about 1/3 inch) beyond the target tumor
prior to
normal sleeping hours, and 5 times per week dosing was continued for a total
of 6 weeks.
The target tumor area was clinically assessed 12 weeks after the last
scheduled application
of study cream. The entire target tumor was then excised and examined
histologically for
the presence of tumor.
Efficacy was assessed by the complete response rate defined as the proportion
of subjects
with clinical (visual) and histological clearance of the sBCC lesion at 12
weeks post-
treatment.
Of Aldarao-treated subjects, 6% (11/178) who had both clinical and
histological
assessments post-treatment, and who appeared to be clinically clear had
evidence of tumor on
excision of the clinically-clear treatment area.
Data on composite clearance (defined as both clinical and histological
clearance) are
shown in the table below.
Table 12: Composite Clearance Rates at 12 Weeks Post-Treatment for
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
162
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Study A ldarat Vehicle
Cream Cream
Study 70% 2%
sBCC1 (66/94) (2/89)
Study 80% 1%
sBCC2 (73/91) (1/90)
Total 75% 2%
(139/185) (3/179)
A separate 5-year, open-label study is ongoing to assess the recurrence of
sBCC
treated with Aldara Cream applied once daily 5 days per week for 6 weeks.
Target tumor
inclusion criteria were the same as for the studies described above. At 12-
weeks post-
treatment, subjects were clinically evaluated for evidence of persistent sBCC
(no
histological assessment). Subjects with no clinical evidence of sBCC entered
the long-term
follow-up period. At the 12 week post-treatment assessment, 90% (163/182) of
the subjects
enrolled had no clinical evidence of sBCC at their target site and 162
subjects entered the
long-term follow-up period for up to 5 years. Two year (24 month) follow-up
data are
available from this study and are presented in the table below:
Table 13: Estimated Clinical Clearance Rates for Superficial Basal Cell
Carcinoma
Follow-up Period
Follow-up No. of No. of No. of Subjects Estimated Rate of
visit after 12- Subjects who Subjects who discontinued
Subjects who
week post- remained with sBCC at this visit with Clinically Cleared
and
treatment clinically recurrence no sBCCa remained Clear"
assessment clear
Month 3 153 4 5 87%
Month 6 149 85%
Month 12 143 4 0 84%
Month 24 139 79%
Reasons for discontinuation included death, non-compliance, entry criteria
violations, personal reasons, and
treatment of nearby sBCC tumor.
Estimated rate of subjects who clinically cleared and remained clear are
estimated based on the time to event
analysis employing the life table method begirming with the rate of clinical
clearance at 12 weeks post-treatment.
14.3 External Genital Warts
163
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, 209 otherwise healthy
subjects 18
years of age and older with genital/perianal warts were treated with Aldara
Cream or
vehicle control times per week for a maximum of 16 weeks. The median baseline
wart area
was 69 mm2 (range 8 to 5525 mm2). Subject accountability is shown in the
figure below.
Figure 1: Subject Accountability (External Genital Warts)
Enrolled
n=209
Aldara Cream Vehicle
n=109 n=100
Completed 16 Weeks Withdrew Completed 16 Weeks Withdrew
of Treatment n=19 of Treatment n=27
Not Clear Not Clear
n=36 n=62
Clear Clear
n=54 n=11
Completed 12 Weeks of Follow-up* Completed 12 Weeks of Follow-up*
Remained Clear Remained Clear
n=39 n=9
*The other subjects were either lost to follow-up or experienced recurrences.
Data on complete clearance are 1i4ted in the table below. The median time to
complete wart
clearance was 10 weeks.
Table 14: Complete Clearance Rates (External Genital Warts)- Study EGW1
Subjects with Subjects
Complete Subjects with
Treatment Clearance Without Warts
of Warts Follow-up Remaining
at Week 16
Overall
Aldara Cream (n =109) 54 (50%) 19 (17%)
36 (33%)
Vehicle (n =100) 11(11%) 27 (27%)
62 (62%)
Females
Aldara Cream (n =46) 33 (72%) 5 (11%) 8 (17%)
Vehicle (n =40) 8 (20%) 13 (33%)
19 (48%)
Males
Aldara Cream (n =63) 21(33%) 14 (22%)
28 (44%)
Vehicle (n =60) 3 (5%) 14 (23%) 43
(72%)
164
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5%, is supplied in single-use packets which contain
250
mg of the cream. Available as: box of 12 packets NDC 29336-610-12. Store at 4 -
25 C (39
- 77 F)
Avoid freezing.
Keep out of reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
( 1 7 .7)
17.1 General Information: All Indications
Aldara Cream should be used as directed by a physician. [see Dosage and
Administration (2)] Aldara Cream is for external use only. Contact with the
eyes, lips and
nostrils should be avoided. [see Indications and Usage (I) and Dosage and
Administration
(2)]
The treatment area should not be bandaged or otherwise occluded. Partially-
used
packets should be discarded and not reused. The prescriber should demonstrate
the proper
application technique to maximize the benefit of Aldara Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Aldara
Cream.
17.2 Local Skin Reactions: All Indications
Patients may experience local skin reactions during treatment with Aldara
Cream
(even with normal dosing). Potential local skin reactions include erythema,
edema,
vesicles, erosions/ulcerations, weeping/exudate, flaking/scaling/dryness, and
scabbing/crusting.
These reactions can range from mild to severe in intensity and may extend
beyond the
application site onto the surrounding skin. Patients may also experience
application site
reactions such as itching and/or burning. [see Adverse Reactions (6)]
Local skin reactions may be of such an intensity that patients may require
rest periods
from treatment. Treatment with Aldara Cream can be resumed after the skin
reaction has
subsided, as determined by the physician. Patients should contact their
physician promptly if
they experience any sign or symptom at the application site that restricts or
prohibits their daily
activity or makes continued application of the Aldara Cream difficult.
165
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Because of local skin reactions, during treatment and until healed, the
treatment area is
likely to appear noticeably different from normal skin. Localized
hypopigmentation and
hyperpigmentation have been reported following use of AldaraS Cream. These
skin color
changes may be permanent in some patients.
17.3 Systemic Reactions: All Indications
Patients may experience flu-like systemic signs and symptoms during treatment
with
Aldarat) Cream (even with normal dosing). Systemic signs and symptoms may
include malaise,
fever, nausea, myalgias and rigors. [see Adverse Reactions (6)1 An
interruption of dosing should
be considered.
17. 4 Patients Being Treated for Actinic Keratosis (AK)
Dosing is 2 times per week for a full 16 weeks, unless otherwise directed by
the
physician. However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond 16
weeks due to
missed doses or rest periods. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)1
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 8
hours
following AldaraS Cream application.
Most patients using AldaraS Cream for the treatment of AK experience erythema,
flaking/scaling/dryness and scabbing/crusting at the application site with
normal dosing. [see
Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
Use of sunscreen is encouraged, and patients should minimize or avoid exposure
to
natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using
AldaraS Cream.
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)1
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during
treatment and
may subsequently resolve. [see Clinical Studies (16.1)1
17.5 Patients Being Treated for Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma (sBCC)
Dosing is 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks, unless otherwise directed by
the
physician. However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond 6 weeks
due to
missed doses or rest periods. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)1
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 8
hours
following AldaraS Cream application. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]
166
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Most patients using Aldara Cream for the treatment of sBCC experience
erythema,
edema, induration, erosion, scabbing/crusting and flaking/scaling at the
application site with
normal dosing. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
Use of sunscreen is encouraged, and patients should minimize or avoid exposure
to
natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using
Aldara Cream.
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
The clinical outcome of therapy can be determined after resolution of
application site
reactions and/or local skin reactions.
Patients with sBCC treated with Aldara Cream should have regular follow-up to
re-
evaluate the treatment site. [see Clinical Studies (16.2)]
17.6 Patients Being Treated for External Genital Warts
Dosing is 3 times per week to external genital/perianal warts. Aldara Cream
treatment
should continue until there is total clearance of the genital/perianal warts
or for a maximum
of 16 weeks.
It is recommended that the treatment area he washed with mild soap and water 6-
10 hours
following Aldara Cream application.
It is common for patients to experience local skin reactions such as erythema,
erosion,
excoriation/flaking, and edema at the site of application or surrounding
areas. Most skin reactions
are mild to moderate.
Sexual (genital, anal, oral) contact should be avoided while Aldaraii) Cream
is on the
skin. Application of Aldara Cream in the vagina is considered internal and
should be avoided.
Female patients should take special care if applying the Aldara Cream at the
opening of the
vagina because local skin reactions on the delicate moist surfaces can result
in pain or
swelling, and may cause difficulty in passing urine.
Uncircumcised males treating warts under the foreskin should retract the
foreskin and
clean the area daily.
New warts may develop during therapy, as Aldara Cream is not a cure.
The effect of Aldara Cream on the transmission of genital/perianal warts is
unknown.
Aldara Cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms, therefore concurrent
use is not
recommended.
167
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Should severe local skin reaction occur, the Aldara Cream should be removed
by
washing the treatment area with mild soap and water.
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Patient Information
ALDARA [al dar' a] Cream, 5% (Imiquimod)
IMPORTANT: Not for mouth, eye, or vaginal use
Read the Patient Information that comes with Aldara Cream before you start
using
it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet
does not take
the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical
condition or treatment.
If you do not understand the information, or have any questions about Aldara
Cream, talk with
your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is Aldara Cream?
Aldara Cream is a skin use only (topical) medicine used to treat:
= external genital and perianal warts in people 12 years and older
= actinic keratosis in adults with normal immune systems. Actinic keratosis
is
caused by too much sun exposure.
= superficial basal cell carcinoma in adults with normal immune systems
when
surgical methods are less appropriate. This skin cancer needs to be diagnosed
by your healthcare
provider.
Aldara Cream is used in different ways for the three different skin
conditions it is
used to treat. It is very important that you follow the instructions for your
skin condition.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions.
Aldara Cream does not work for everyone. Aldara Cream will not cure your
genital
or perianal warts. New warts may develop during treatment with Aldara Cream.
It is not
known if Aldara Cream can stop you from spreading genital or perianal warts
to other
people. For your own health and the health of others, it is important to
practice safer sex.
Talk to your healthcare provider about safer sex practices.
Who should not use Aldara Cream?
= Aldara Cream has not been studied in children under 12 years old for
external
genital and perianal warts.
168
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Aldara Cream has not been studied in children under 18 years old for
actinic
keratosis or superficial basal cell carcinoma. Children usually do not get
actinic keratosis or
basal cell carcinoma.
Before using Aldara Cream, tell your healthcare provider:
= about all your medical conditions, including if you
o are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Aldara
Cream can harm your unborn baby.
o are breastfeeding. It is not known if Aldara Cream passes into your milk
and if it can harm your baby.
= about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-
prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Especially tell your
healthcare
provider if you have had other treatments for genital or perianal warts, or
actinic keratosis, or
superficial basal cell carcinoma. Aldara Cream should not be used until your
skin has
healed from other treatments.
How should I use Aldara Cream?
= Use Aldara Cream exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Aldara Cream is for skin use only. Do not take by mouth or use in or near
your eyes, lips or
nostrils. Do not use Aldara Cream unless your healthcare provider has taught
you the right
way to use it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
= Aldara Cream is used for several skin conditions. Use Aldara Cream only
on the area of your body to be treated. Your healthcare provider will tell you
where to
apply Aldara Cream and how often and for how long to apply it for your
condition. Do not use
Aldara Cream longer than prescribed. Using too much Aldara Cream, or using
it too
often, or for too long can increase your chances for having a severe skin
reaction or other side
effect. Talk to your healthcare provider if Aldara Cream does not work for
you.
For external genital and perianal warts, Aldara Cream is usually used once a
day for 3
days a week:
= Monday, Wednesday and Friday, or
= Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday
169
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
For these conditions, Aldara Cream is usually left on the skin for 6 to 10
hours.
Treatment should continue until the warts are completely gone, or up to 16
weeks.
For actinic keratosis, Aldara Cream is usually used once a day for 2 days a
week, 3 to
4 days apart, such as:
= Monday and Thursday, or
= Tuesday and Friday
For this condition, Aldara Cream is usually left on the skin for about 8
hours.
Treatment should continue for the full 16 weeks even if all actinic keratoses
appear to be gone,
unless you are told otherwise by your healthcare provider. The area you treat
with Aldara
Cream should be no larger than approximately the size of your forehead or one
cheek (for
example 2 inches by 2 inches), unless otherwise directed by your healthcare
provider.
For superficial basal cell carcinoma, Aldara Cream is usually used once a day
for 5
days a week:
= Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday
For this condition, Aldara Cream is usually left on the skin for about 8
hours. Your
healthcare provider will show you how much Aldara Cream to apply to your
superficial
basal cell carcinoma. You should also apply Aldara Cream to a small area of
skin all
around the superficial basal cell carcinoma. This small area of skin should be
about the size
of your fingertip. Treatment should continue for the full 6 weeks, even if the
superficial basal cell
carcinoma appears to be gone, unless you are told otherwise by your healthcare
provider.
Applying Aldara Cream
Aldara Cream should be applied just before your bedtime.
= Wash the area to be treated with mild soap and water. Allow the area to
dry.
0 Uncircumcised males treating warts under their penis foreskin must pull
their foreskin back and clean before treatment, and clean daily during the
weeks of treatment.
= Wash your hands
= Open a new packet of Aldara Cream just before use
170
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Apply a thin layer of Aldara Cream only to the affected area or areas to
be
treated. Do not use more Aldara Cream than is needed to cover the treatment
area.
= Rub the Aldara Cream in all the way to the affected area or areas.
o Do not get Aldara Cream in your eyes.
o Do not get Aldara Cream in the anus when applying to perianal warts.
0 Female patients treating genital warts must be careful when applying
Aldara Cream around the vaginal opening. Female patients should take
special care if applying the Aldara Cream at the opening of the vagina
because local skin reactions on the delicate moist surfaces can cause pain or
swelling, and may cause problems passing urine. Do not put Aldara Cream
in your vagina or on the skin around the genital wart.
= Do not cover the treated area with an airtight bandage. Cotton gauze
dressings
can be used. Cotton underwear can be worn after applying Aldara Cream to the
genital or
perianal area.
= Safely throw away the open packet of Aldara Cream so that children and
pets
cannot get it. The open packet should be thrown away even if all the Aldara
Cream was not
completely used.
= After applying Aldara Cream, wash your hands well.
= Leave the Aldara Cream on the affected area or areas for the time
prescribed by
your healthcare provider. The length of time that Aldara Cream is left on the
skin is not the
same for the different skin conditions that Aldara Cream is used to treat. Do
not bathe or
get the treated area wet before the right time has passed. Do not leave Aldara
Cream on
your skin longer than prescribed.
= After the right amount of time has passed, wash the treated area or areas
with
mild soap and water.
= If you forget to apply Aldara Cream, apply the missed dose of Aldara
Cream as
soon as you remember and then continue on your regular schedule.
= If you get Aldara Cream in your mouth or in your eyes rinse well with
water
right away.
What should I avoid while using Aldara Cream?
171
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Do not cover the treated site with bandages or other closed dressings.
Cotton
gauze dressings are okay to use, if needed. Cotton underwear can be worn after
treating the
genital or perianal area.
= Do not apply Aldara Cream in or near the eyes, lips or nostrils, or in
the
vagina or anus.
= Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight as much as
possible
during treatment with Aldara Cream. Use sunscreen and wear protective
clothing if you go
outside during daylight.
= Do not have sexual contact including genital, anal, or oral sex when
Aldara
Cream is on your genital or perianal skin. Aldara Cream may weaken condoms
and vaginal
diaphragms. This means they may not work as well to prevent pregnancy. For
your own health
and the health of others, it is important to practice safer sex. Talk to your
healthcare
provider about safer sex practices.
What are the possible side effects of Aldara Cream?
The most common side effects with Aldara Cream are skin reactions at the
treatment site
including:
= redness
= swelling
= a sore, blister, or ulcer
= skin that becomes hard or thickened
= skin peeling
= scabbing and crusting
= itching
= burning
= changes in skin color that do not always go away
Actinic Keratosis
During treatment and until the skin has healed, your skin in the treatment
area is likely to
appear noticeably different from normal skin. Side effects, such as redness,
scabbing, itching
and burning are common at the site where Aldara Cream is applied, and
sometimes the
172
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
side effects go outside of the area where Aldara Cream was applied. Swelling,
small open
sores and drainage may also be experienced with use of Aldara Cream. You may
also
experience itching and/or burning. Actinic keratoses that were not seen before
may appear
during treatment and may later go away. If you have questions regarding
treatment or skin
reactions, please talk with your healthcare provider.
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
During treatment and until the skin has healed, your skin in the treatment
area is likely
to appear noticeably different from normal skin. Side effects, such as
redness, swelling and
a sore are common at the site where Aldara Cream is applied. You may also
experience
itching or burning. Your healthcare provider will need to check the area that
was treated
after your treatment is finished to make sure that the skin cancer is gone.
Superficial basal
cell carcinoma can come back. The chances of it coming back are higher as time
passes. It
is very important to have regular follow-up visits with your healthcare
provider to check the
area to make sure your skin cancer has not come back. Ask your healthcare
provider how
often you should have your skin checked. Talk with your healthcare provider if
you have
questions about your treatment or skin reactions.
External Genital and Perianal Warts
Patients should be aware that new warts may develop during treatment, as
Aldara
Cream is not a cure. Many people see reddening or swelling on or around the
application site
during the course of treatment. If you have questions regarding treatment or
local skin
reactions, please talk with your healthcare provider.
You have a higher chance for severe skin reactions if you use too much Aldara
Cream or use it the wrong way. Stop Aldara Cream right away and call your
healthcare
provider if you get any skin reactions that affect your daily activities, or
that do not go
away. Sometimes, Aldara Cream must be stopped for a while to allow your skin
to heal.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about your treatment or
skin reactions.
Other side effects of Aldara Cream include headache, back pain, muscle aches,
tiredness,
flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, diarrhea, and fungal infections.
173
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
If the reactions seem excessive, if either skin breaks down or sores develop
during the
first week of treatment, if flu-like symptoms develop or if you begin to not
feel well at
anytime, contact your healthcare provider.
These are not all the side effects of Aldara Cream. For more information, ask
your
healthcare provider or pharmacist.
How do I store Aldara Cream?
= Store Aldara Cream at 39 - 77 F (4 - 25 C). Do not freeze.
= Safely throw away Aldara Cream that is out of date or that you do not
need.
= Keep Aldara Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Aldara Cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in
patient
information leaflets. Do not use Aldara Cream for a condition for which it
was not
prescribed. Do not give Aldara Cream to other people, even if they have the
same
symptoms you have.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Aldara Cream. If
you
would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask
your pharmacist
or healthcare provider for information about Aldara Cream that is written for
the
healthcare provider. If you have other questions about Aldara Cream, call 1-
888-2-
ALDARA.
What are the ingredients in Aldara Cream?
Active Ingredient: imiquimod
Inactive ingredients: isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white
petrolatum,
polysorbate 60, sorbitan monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water,
benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and propylparaben.
Manufactured by:
3M Health Care Limited
Loughborough LE1 1 lEP England
Distributed by:
Graceway Pharmaceuticals, LLC Bristol, TN 37620
174
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment IX
[000318] Zyclara Izi-clar-al (imiquimod) 3.75% Cream
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION FOR ACTINIC KERATOSIS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZYCLARA
Cream
safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Zyclarae Cream.
ZYCLARA (imiquimod), Cream, 3.75%
For topical use only
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
------------------------ INDICATIONS AND USAGE ---------------------------
ZYCLARA Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical
visible or
palpable actinic keratoses of the face or balding scalp in immunocompetent
adults. (1.1)
---------------------- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION -------------------------
ZYCLARA Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. (2)
= daily to the skin of the affected area (either the face or balding scalp)
for two 2-
week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period. (2.1)
-------------------- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS --------------------------
Cream, 3.75%, white to fainty yellow cream. (3)
-------------------------- CONTRAINDICATIONS -----------------------------
= None. (4)
---------------------- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS --------------------------
= Intense local inflammatory reactions can occur (e.g., skin weeping,
erosion).
Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.1, 6)
175
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Flu-like systemic signs and symptoms including fatigue, nausea, fever,
myalgias,
arthralgias, and chills. Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.2, 6)
= Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps (5.3). Wear sunscreen daily
(17.4).
= Avoid concomitant use of Zyclara Cream and any other imiquimod cream.
-------------------------- ADVERSE REACTIONS -----------------------------
Most common Adverse Reactions (incidence >50%) are local skin reactions,
erythema,
edema, weeping/exudate, flaking/scaling/dryness, scabbing/crusting and
erosion/ulceration (6.2).
Other reported reactions (occurring in 2% of ZYCLARAS-Treated Subjects)
include headache,
fatigue, nausea and fever (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Graceway Pharmaceuticals,
LLC at 1-800-328-0255 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or wwwfda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Issued" March 2010
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
1.2 Unevaluated Populations
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
176
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
5.2 Systemic Reactions
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
OVER DOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmaco dynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
177
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions for Administration
17.2 Local Skin Reactions
17.3 Systemic Reactions
17. 4 Recommended Administration
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not
listed
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Actinic Keratosis
ZYCLARA Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical
visible or palpable
actinic keratosis (AK), of the face or balding scalp in immunocompetent
adults.
1.2 Unevaluated Populations
Safety and efficacy have nor been established for ZYCLARA Cream in the
treatment of actinic
keratoses with more than one 2-cycle treatment course in the same area.
The safety and efficacy of ZYCLARA Cream in immunosuppressed patients have
not
been established.
The safety and efficacy have not been established for ZYCLARA Cream in the
treatment of patients with xeroderma pigmentosum.
The safety and efficacy have not been established for ZYCLARA Cream in the
treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma.
The safety and efficacy have not been established for ZYCLARA0 Cream in the
treatment of external genital warts.
ZYCLARA Cream should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing
autoimmune conditions.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
ZYCLARA Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
2.1 Actinic Keratosis
178
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
ZYCLARA Cream should be applied once daily before bedtime to the skin of the
affected area (either the face or balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment
cycles separated by a 2-
week no-treatment period. ZYCLARA Cream should be applied as a thin film to
the entire
treatment area and rubbed in until the Zyclara Cream is no longer visible. Up
to 2 packets of
ZYCLARA Cream may be applied to the treatment area at each application.
ZYCLARA
Cream should be left on the skin for approximately 8 hours, after which time
the cream should be
removed by washing the area with mild soap and water. The prescriber should
demonstrate the
proper application technique to maximize the benefit of ZYCLARA Cream
therapy.
Patients should wash their hands before and after applying ZYCLARA Cream.
Avoid use in or on the lips and nostrils. Do not use in or near the eyes.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are common. [see Adverse Reactions
(6.1,
6.2)] A rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's
discomfort or
severity of the local skin reaction. However, neither 2-week treatment cycle
should be extended
due to missed doses or rest periods. A transient increase in AK lesion counts
may be observed
during treatment. Response to treatment cannot be adequately assessed until
resolution of local
skin reactions. The patient should continue dosing as prescribed. Treatment
should continue for
the full treatment course even if all actinic keratoses appear to be gone.
Lesions that do not
respond to treatment should be carefully re-evaluated and management
reconsidered.
ZYCLARA Cream is packaged in single-use packets, with 28 packets supplied per
box.
Patients should be prescribed no more than 56 packets for the total 2-cycle
treatment course.
Unused packets should be discarded. Partially-used packets should be discarded
and not reused.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Cream, 3.75%, white to faintly yellow cream.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
179
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Intense local skin reactions including skin weeping or erosion can occur after
a few
applications of ZYCLARA Cream and may require an interruption of dosing. [see
Dosage and
Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. ZYCLARA Cream has the
potential to
exacerbate inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus
host disease.
Administration of ZYCLARA Cream is not recommended until the skin is healed
from
any previous drug or surgical treatment.
Concomittant use of ZYCLARA Cream and any other imiquimod cream, in the same
treatment area, should be avoided since they contain the same active
ingredient (imiquimod) and
may increase the risk for and severity of local skin reactions.
5.2 Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local skin
reactions and
may include fatigue, nausea, fever, myalgias, arthralgias, and chills. An
interruption of dosing
and an assessment of the patient should be considered. [see Adverse Reactions
(6)]
Lymphadenopathy occurred in 2% of subjects treated with ZYCLARA Cream [see
Adverse Reactions (6)]. This reaction resolved in all subjects by 4 weeks
after completion of
treatment.
The safety of concomitant use of ZYCLARA Cream and any other imiquimod creams
has not been established and should be avoided since they contain the same
active ingredient
(imiquimod) and may increase the risk for and severity of systemic reactions.
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
Exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) should be avoided or minimized
during use of
ZYCLARA Cream because of concern for heightened sunburn susceptibility.
Patients should
be warned to use protective clothing (e.g., a hat) when using ZYCLARA Cream.
Patients with
sunburn should be advised not to use ZYCLARA Cream until fully recovered.
Patients who
may have considerable sun exposure, e.g. due to their occupation, and those
patients with
inherent sensitivity to sunlight should exercise caution when using ZYCLARA
Cream.
In an animal photoco-carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream shortened the time
to skin
tumor formation [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. The enhancement of
ultraviolet
carcinogenicity is not necessarily dependent on phototoxic mechanisms.
Therefore, patients
should minimize or avoid natural or artificial sunlight exposure.
180
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse
reaction
rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to
rates in the clinical
trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience:
The data described below reflect exposure to ZYCLARA Cream or placebo in 319
subjects enrolled in two double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies. Subjects
applied up to two
packets of ZYCLARAS Cream or vehicle daily to the skin of the affected area
(either entire face
or balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-
treatment period.
Table 1: Selected Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 2% of ZYCLARAO-Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency Than With Vehicle in the Combined
Studies
ZYCLARAS Cream 3.75% Vehicle
Preferred Term (N=160) (N=159)
Headache 10 (6%) 5 (3%)
Application site pruritus 7 (4%) 1 (<1%)
Fatigue 7 (4%) 0 (0%)
Nausea 6 (3%) 2 (1%)
Application site irritation 5 (3%) 0 (0%)
Application site pain 5 (3%) 0 (0%)
Pyrexia 5 (3%) 0 (0%)
Anorexia 4 (3%) 0 (0%)
Dizziness 4 (3%) 0 (0%)
Herpes simplex 4 (3%) 1 (<1%)
Pain 4 (3%) 0 (0%)
Chest pain 3 (2%) 0 (0%)
Diarrhea 3 (2%) 0 (0%)
Lymphadenopathy 3 (2%) 0 (0%)
Table 2: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area in ZYCLARAO-Treated
181
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Subjects as Assessed by the Investigator
ZYCLARA Cream 3.75% Placebo
(N=160) (N=159)
All Grades* Severe All Grades*
Severe
Erythema 154 (96%) 40 (25%) 124 (78%) 0
(0%)
Scabbing/Crusting 149 (93%) 22 (14%) 72 (45%) 0
(0%)
Flaking/Scaling/Dryness 147 (92%) 13 (8%) 123 (77%) 2
(1%)
Edema 120 (75%) 9 (6%) 31(19%) 0
(0%)
Erosion/Ulceration 99(62%) 17(11%) 14(9%)
0(0%)
Weeping/Exudate 81(51%) 9 (6%) 6 (4%) 0
(0%)
*All Grades: mild, moderate or severe
Local skin reactions may extend beyond treatment area.
Overall, in the clinical trials, 11% (17/160) of subjects on ZYCLARA Cream
and 0%
on vehicle cream required rest periods due to adverse reactions.
Other adverse reactions observed in subjects treated with ZYCLARA Cream
include:
application site bleeding, application site swelling, arthralgia, cheilitis,
chills, dermatitis, herpes
zoster, influenza-like illness, insomnia, lethargy, myalgia, pancytopenia,
pruritus, squamous cell
carcinoma, and vomiting.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience: Dermal Safety Studies
There are currently no postmarketing adverse reactions reported for ZYCLARA
Cream.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use
of
Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5%. Because these reactions are reported
voluntarily from a
population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate
their frequency or
establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: angioedema.
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy,
pulmonary
edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial
fibrillation, palpitations),
chest pain, ischemia, myocardial infarction, syncope.
Endocrine: thyroiditis.
182
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders: abdominal pain.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience with Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5%
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use
of
Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5%. Because these reactions are reported
voluntarily from a
population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate
their frequency or
establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: angioedema.
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy,
pulmonary
edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, palpitations), chest
pain, ischemia,
myocardial infarction, syncope.
Endocrine: thyroiditis.
Hematological: decreases in red cell, white cell and platelet counts
(including idiopathic
thrombocytopenic purpura), lymphoma.
Hepatic: abnormal liver function.
Infections and Infestations: herpes simplex.
Neuropsychiatric: agitation, cerebrovascular accident, convulsions (including
febrile
convulsions), depression, insomnia, multiple sclerosis aggravation, paresis,
suicide.
Respiratory: dyspnea.
Urinary System Disorders: proteinuria, urinary retention, dysuria.
Skin and Appendages: exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme,
hyperpigmentation,
hypertrophic scar.
Vascular: Henoch-Schonlein purpura syndrome
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ZYCLARAO
Cream should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies
the potential risk to
the fetus.
Note: The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on daily
dose
comparisons for the reproductive toxicology studies described in this label.
The animal
183
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
multiples of human exposure were based on weekly dose comparisons for the
carcinogenicity
studies described in this label. For the animal multiple of human exposure
ratios presented in
this label, the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) was set at 2 packets
(500 mg
cream) per treatment of ZYCLARA Cream (imiquimod 3.75%, 18.75 mg imiquimod).
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits.
Oral doses
of 1, 5, and 20 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period of
organogenesis
(gestational days 6 ¨ 15) to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal
toxicity, fetal
effects noted at 20 mg/kg/day (190X MRHD based on AUC comparisons) included
increased
resorptions, decreased fetal body weights, delays in skeletal ossification,
bent limb bones, and
two fetuses in one litter (2 of 1567 fetuses) demonstrated exencephaly,
protruding tongues, and
low-set ears. No treatment related effects on embryofetal toxicity or
teratogenicity were noted at
mg/kg/day (32X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered
during the
period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 ¨ 18) to pregnant female rabbits.
No treatment-
related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 2
mg/kg/day (2.1X MRHD
based on BSA comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study, or 1
mg/kg/day (134X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
A combined fertility and pen- and post-natal development study was conducted
in rats.
Oral doses of 1, 1.5, 3, and 6 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered to male
rats from 70 days
prior to mating through the mating period and to female rats from 14 days
prior to mating
through parturition and lactation. No effects on growth, fertility,
reproduction, or post-natal
development were noted at doses up to 6 mg/kg/day (29X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons),
the highest dose evaluated in this study. In the absence of maternal toxicity,
bent limb bones
were noted in the Fl fetuses at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (29X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons).
This fetal effect was also noted in the oral rat embryofetal development study
conducted with
imiquimod. No treatment-related effects on teratogenicity were noted at 3
mg,/kg/day (14X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether imiquimod is excreted in human milk following use of
ZYCLARA Cream. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should
be
exercised when ZYCLARA Cream is administered to nursing women.
184
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
8.4 Pediatric Use
AK is not a condition generally seen within the pediatric population. The
safety and
efficacy of ZYCLARA Cream for AK in patients less than 18 years of age has
not been
established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 160 subjects treated with ZYCLARA Cream in the clinical studies, 78
subjects
were 65 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were
observed between
these subject and younger subjects.
OVER DOSAGE
Topical overdosing of ZYCLARA Cream could result in an increased incidence of
severe local skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
Hypotension was reported in a clinical trial following multiple oral imiquimod
doses of
>200 mg (equivalent to the ingestion of imiquimod content of >21 packets of
ZYCLARA
Cream). This resolved following oral or intravenous fluid administration.
11 DESCRIPTION
ZYCLARA Cream is intended for topical administration. Each gram contains 37.5
mg
of imiquimod in a white to faintly yellow oil-in-water vanishing cream base
consisting of
isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, polysorbate
60, sorbitan
monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water, benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and
propylparaben.
Chemically, imiquimod is 1 -(2-methylpropy1)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine
.
Imiquimod has a molecular formula of C141116N4 and a molecular weight of
240.3. Its structural
formula is:
NH 2
N
r C H
3
CH 3
185
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ZYCLARA Cream in treating AK lesions is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of ZYCLARA are unknown.
Imiquimod is a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist that activates immune cells.
Topical
application to skin is associated with increases in markers for cytokines and
immune cells.
In a study of 18 subjects with AK comparing Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5% to
vehicle, increases from baseline in week 2 biomarker levels were reported for
CD3, CD4, CD8,
CD11c, and CD68 for Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5% treated subjects; however,
the clinical
relevance of these findings is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following dosing with 2 packets once daily (18.75 mg imiquimod/day) for up to
three
weeks, systemic absorption of imiquimod was observed in all subjects when
ZYCLARA
Cream was applied to the face and/or scalp in 17 subjects with at least 10 AK
lesions. The mean
peak serum imiquimod concentration at the end of the trial was approximately
0.323 ng/mL.
The median time to maximal concentrations (T max) occurred at 9 hours after
dosing. Based on
the plasma half-life of imiquimod observed at the end of the study, 29.3 17.0
hours, steady-state
concentrations can be anticipated to occur by day 7 with once daily dosing.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) rat carcinogenicity study, imiquimod was administered to
Wistar rats
on a 2)C/week (up to 6 mg/kg/day) or daily (3 mg/kg/day) dosing schedule for
24 months. No
treatment related tumors were noted in the oral rat carcinogenicity study up
to the highest doses
tested in this study of 6 mg/kg administered 2X/week in female rats (8.2X MRHD
based on
weekly AUC comparisons), 4 mg/kg administered 2X/week in male rats (7.1X MRHD)
based on
weekly AUC comparisons) or 3 mg/kg administered 7X/week to male and female
rats (14X
MRHD based on weekly AUC comparisons).
186
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
In a dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream (up to 5
mg/kg/application
imiquimod or 0.3% imiquimod cream) was applied to the backs of mice 3)C/week
for 24 months.
A statistically significant increase in the incidence of liver adenomas and
carcinomas was noted
in high dose male mice compared to control male mice (24X MRHD based on weekly
AUC
comparisons). An increased number of skin papillomas was observed in vehicle
cream control
group animals at the treated site only.
In a 52-week dermal photo-carcinogenicity study, the median time to onset of
skin tumor
formation was decreased in hairless mice following chronic topical dosing
(3X/week; 40 weeks
of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation) with concurrent exposure to
UV radiation (5
days per week) with vehicle alone. No additional effect on tumor development
beyond the
vehicle effect was noted with the addition of the active ingredient,
imiquimod, to the vehicle
cream.
Imiquimod revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on
the
results of five in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma L5178Y
assay, Chinese
hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay, human lymphocyte chromosome
aberration
assay and SHE cell transformation assay) and three in vivo genotoxicity tests
(rat and hamster
bone marrow cytogenetics assay and a mouse dominant lethal test).
Daily oral administration of imiquimod to rats, throughout mating, gestation,
parturition
and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility or reproduction,
at doses up to 29X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Actinic Keratosis
In two double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical studies, 319
subjects with
AK were treated with ZYCLARA Cream, or vehicle cream. Studies enrolled
subjects >18
years of age with 5-20 typical visible or palpable AK lesions of the face or
scalp. Study cream
was applied to either the entire face (excluding ears) or balding scalp once
daily for two 2-week
treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period. Subjects then
continued in the study
for an 8-week follow-up period during which they returned for clinical
observations and safety
monitoring. Study subjects ranged from 36 to 90 years of age and 54% had
Fitzpatrick skin type
I or II. All ZYCLARA Cream-treated subjects were Caucasians.
187
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
On a scheduled dosing day, up to two packets of the study cream were applied
to the
entire treatment area prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for
approximately 8 hours.
Efficacy was assessed by AK lesion counts at the 8-week post-treatment visit.
All AKs in the
treatment area were counted, including baseline lesions as well as lesions
which appeared during
therapy.
Complete clearance required absence of any lesions including those that
appeared during
therapy in the treatment area. Complete and partial clearance rates are shown
in the tables
below. Partial clearance rate was defined as the percentage of subjects in
whom the number of
baseline AKs was reduced by 75% or more. The partial clearance rate was
measured relative to
the numbers of AK lesions at baseline.
Table 3: Rates of Subject with Complete Clearance at 8 Weeks Post Treatment
ZYCLARA Cream 3.75% Vehicle Cream
Study 1 25.9%(21/81) 2.5%(2/80)
Study 2 45.6%(36/79) 10.1%(8/79)
Table 4: Rates of Subjects with Partial Clearance W75%) at 8 Weeks Post
Treatment
ZYCLARA Cream 3.75% Vehicle Cream
Study 1 45.7%(37/81) 18.8%(15/80)
Study 2 73.4%(58/79) 26.6%(21/79)
During the course of treatment, 86% (138/160) of subjects experienced a
transient
increase in lesions evaluated as actinic keratoses relative to the number
present at baseline within
the treatment area.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ZYCLARA (imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%, is supplied in single-use packets which
contain 250 mg of the cream. Available as: box of 28 packets NDC 29336-710-28.
Store at 25 C
(77 F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30 C (59 to 86 F) [See USP Controlled
Room
Temperature].
Avoid freezing.
188
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Keep out of reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (17.7)
17.1 General Information:
ZYCLARA Cream should be used as directed by a physician. [see Dosage and
Administration (2)] ZYCLARA Cream is for external use only. Contact with the
eyes, lips and
nostrils should be avoided. [see Indications and Usage (1) and Dosage and
Administration (2)].
The treatment area should not be bandaged or otherwise occluded. Partially-
used packets
should be discarded and not reused. The prescriber should demonstrate the
proper application
technique to maximize the benefit of ZYCLARA Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
ZYCLARA
Cream.
17.2 Local Skin Reactions:
Patients may experience local skin reactions during treatment with ZYCLARA
Cream.
Potential local skin reactions include erythema, edema, erosions/ulcerations,
weeping/exudate,
flaking/scaling/dryness, and scabbing/crusting. These reactions can range from
mild to severe in
intensity and may extend beyond the application site onto the surrounding
skin. Patients may
also experience application site reactions such as itching, irritation or
pain. [see Adverse
Reactions (6)]
Local skin reactions may be of such an intensity that patients may require
rest periods
from treatment. Treatment with ZYCLARA Cream can be resumed after the skin
reaction has
subsided, as determined by the physician. However, each treatment cycle should
not be
extended beyond 2 weeks due to missed doses or rest periods. Patients should
contact their
physician promptly if they experience any sign or symptom at the application
site that restricts or
prohibits their daily activity or makes continued application of the ZYCLARA
Cream difficult.
Because of local skin reactions, during treatment and until healed, the
treatment area is
likely to appear noticeably different from normal skin. Localized
hypopigmentation and
hyperpigmentation have been reported following use of imiquimod cream. These
skin color
changes may be permanent in some patients.
17.3 Systemic Reactions:
189
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Patients may experience flu-like systemic signs and symptoms during treatment
with
ZYCLARA Cream. Systemic signs and symptoms may include fatigue, nausea,
fever, myalgia,
arthralgia, and chills. [see Adverse Reactions (6)] An interruption of dosing
and assessment of
the patient should be considered.
17. 4 Recommended Administration
Dosing is once daily before bedtime to the skin of the affected area (either
the full face or
balding scalp) for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-
treatment period.
However, the treatment period should not be extended beyond two 2-week
treatment cycles due
to missed doses or rest periods. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1).
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
ZYCLARA
Cream. Before applying the ZYCLARA Cream, the patient should wash the
treatment area
with mild soap and water and allow the area to dry thoroughly.
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water 8
hours
following ZYCLARA Cream application.
Most patients using ZYCLARA Cream for the treatment of AK experience
erythema,
flaking/scaling/dryness and scabbing/crusting at the application site with
normal dosing. [see
Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Use of sunscreen is encouraged, and patients should minimize or avoid exposure
to
natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using
ZYCLARA
Cream. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during
treatment and
may subsequently resolve. [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Patient Information
ZYCLARA [imiquimod] Cream, 3.75% (Imiquimod)
IMPORTANT: Not for mouth, eye, or vaginal use
Read the Patient Information that comes with ZYCLARA Cream before you start
using
it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet
does not take the
place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or
treatment. If you
190
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
do not understand the information, or have any questions about ZYCLARA Cream,
talk with
your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is ZYCLARA Cream?
ZYCLARA Cream is a skin use only (topical) medicine used to treat:
= actinic keratosis in adults with normal immune systems. Actinic keratosis
is
caused by too much sun exposure.
ZYCLARA Cream does not work for everyone.
Who should not use ZYCLARA Cream?
= ZYCLARA Cream has not been studied in children under 18 years old.
Children usually do not get actinic keratoses.
Before using ZYCLARA Cream, tell your healthcare provider:
= about all your medical conditions, including if you
o are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if
ZYCLARA Cream can harm your unborn baby.
o are breastfeeding. It is not known if ZYCLARA Cream passes into your
milk and if it can harm your baby.
= about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-
prescription
medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare
provider if you have
had other treatments for actinic keratosis. ZYCLARA Cream should not be used
until your
skin has healed from other treatments.
How should I use ZYCLARA Cream?
= Use ZYCLARA Cream exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
ZYCLARA Cream is for skin use only. Do not take by mouth or use in or near
your eyes, lips
or nostrils. Do not use ZYCLARA Cream unless your healthcare provider has
taught you the
right way to use it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any
questions.
= Your healthcare provider will tell you where to apply ZYCLARA Cream and
how often and for how long to apply it for your condition. Do not use ZYCLARA
Cream
longer than prescribed. Using too much ZYCLARA Cream, or using it too often,
or for too
191
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
long can increase your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side
effect. Talk to
your healthcare provider if ZYCLARAS Cream does not work for you.
= ZYCLARAS Cream is applied once a day for two-weeks. There is no treatment
for the next two weeks. ZYCLARAS Cream is then applied once a day for another
two-weeks.
ZYCLARAS Cream is usually left on the skin for about 8 hours. Treatment should
continue for the full treatment course even if all actinic keratosis appear to
be gone, unless you
are told otherwise by your healthcare provider. ZYCLARAS Cream should be used
to treat
either the whole face or balding scalp.
Applying ZYCLARAS Cream
ZYCLARAS Cream should be applied just before your bedtime.
= Wash the area to be treated with mild soap and water. Allow the area to
dry.
= Wash your hands
= Open a new packet(s) of ZYCLARAS Cream just before use
= Apply a thin layer of ZYCLARAS Cream only to the affected area or areas
to be
treated. Do not use more ZYCLARAS Cream than is needed to cover the treatment
area. Do not
use more than two packets for each application.
= Rub the ZYCLARAS Cream in all the way to the affected area or areas.
o Do not get ZYCLARAS Cream in or around your eyes.
= Safely throw away the open packet of ZYCLARAS Cream so that children and
pets cannot get it. The open packet should be thrown away even if all the
ZYCLARAS Cream
was not completely used.
= After applying ZYCLARAS Cream, wash your hands well.
= Leave the ZYCLARAS Cream on the affected area or areas for the time
prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not bathe or get the treated area
wet before the right
time has passed. Do not leave ZYCLARAS Cream on your skin longer than
prescribed.
= After about 8 hours, wash the treated area or areas with mild soap and
water.
= If you forget to apply ZYCLARAS Cream, continue on your regular schedule
and do not make up the missed dose(s).
= If you get ZYCLARAS Cream in your mouth or in your eyes rinse well with
water right away.
192
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
What should I avoid while using ZYCLARA Cream?
= Do not cover the treated site with bandages or other closed dressings.
Cotton
gauze dressings are okay to use, if needed.
= Do not apply ZYCLARA Cream in or near the eyes, lips or nostrils,.
= Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight as much as
possible
during treatment with ZYCLARA Cream. Use sunscreen and wear protective
clothing if you
go outside during daylight.
= What are the possible side effects of ZYCLARA Cream?
Side effects with ZYCLARA I1) Cream may include skin reactions at the
treatment site
such as:
= redness
= swelling
= a sore, blister, or ulcer
= skin that becomes hard or thickened
= skin peeling
= scabbing and crusting
= itching
= burning
= changes in skin color that do not always go away
During treatment and until the skin has healed, your skin in the treatment
area is likely to
appear noticeably different from normal skin. Side effects, such as redness,
scabbing, itching
and burning are common at the site where ZYCLARA Cream is applied, and
sometimes the
side effects go outside of the area where ZYCLARA Cream was applied.
Swelling, small open
sores and drainage may also be experienced with use of ZYCLARA Cream. You may
also
experience itching, irritation or pain. Actinic keratoses that were not seen
before may appear
during treatment and may later go away. If you have questions regarding
treatment or skin
reactions, please talk with your healthcare provider.
You have a higher chance for severe skin reactions if you use too much ZYCLARA
Cream or use it the wrong way. Stop ZYCLARA Cream right away and call your
healthcare
provider if you get any skin reactions that affect your daily activities, or
that do not go away.
193
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Sometimes, ZYCLARA Cream must be stopped for a while to allow your skin to
heal. Talk to
your healthcare provider if you have questions about your treatment or skin
reactions.
Other side effects of ZYCLARA Cream include headache, back pain, muscle
aches,
joint aches, tiredness, flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, nausea and
diarrhea.
If the reactions seem excessive, if either skin breaks down or sores develop
during the
first week of treatment, if flu-like symptoms develop or if you begin to not
feel well at anytime,
stop applying ZYCLARAO Cream and contact your healthcare provider.
These are not all the side effects of ZYCLARA Cream. For more information,
ask your
healthcare provider or pharmacist.
How do I store ZYCLARA Cream?
= Store ZYCLARA Cream at 39-77 F (4-25 C). Do not freeze.
= Safely throw away ZYCLARA Cream that is out of date or that you do not
need.
= Keep ZYCLARA Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about ZYCLARA Cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in
patient
information leaflets. Do not use ZYCLARA Cream for a condition for which it
was not
prescribed. Do not give ZYCLARA Cream to other people, even if they have the
same
symptoms you have.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about ZYCLARA Cream.
If
you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can
ask your
pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ZYCLARA Cream that is
written for
the healthcare provider. If you have other questions about ZYCLARA0 Cream,
call 1-800-328-
0255.
What are the ingredients in ZYCLARA Cream?
Active Ingredient: imiquimod
Inactive ingredients: isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white
petrolatum,
polysorbate 60, sorbitan monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water,
benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and propylparaben.
194
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Manufactured by
3M Health Care Limited
Loughborough LE11 lEP England
Distributed by
Graceway Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Bristol, TN 37620
195
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment X
[000319] Zyclara ki-clar-a] (imiquimod) 3.75% Cream
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION FOR GENITAL AND PERIANAL
WARTS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZYCLARA
Cream
safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Zyclara Cream.
ZYCLARA (imiquimod), Cream, 3.75%
For topical use only
Initial U.S. Approval:
-------------------------- INDICATIONS AND USAGE -------------------------
Zyclara Cream is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal
warts/condyloma acuminata in patients 12 years or older (11)
----------------------- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ------------------------
Zyclara Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, intra-anal or intravaginal use.(2)
= External Genital Warts: daily to the external genital/perianal warts
until total clearance or up
to 8 weeks (2.1)
---------------------- DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS ------------------------
Zyclara (imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%, is supplied in single-use packets 28 per
Dose
Pack, each of which contains 250 mg of the cream, equivalent to 9.4 mg of
imiquimod. (3)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
196
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Unevaluated Populations
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
5. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
5.2 Systemic Reactions
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
5.4 Unevaluation Uses: External Genital Warts
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Dermal Safety Trials Experience
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
------------------------- CONTRAINDICATIONS -------------------------------
= None (4)
---------------------- WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ---------------------------
= Intense local inflammatory reactions can occur (e.g., skin weeping,
erosion).
Dosing interruption may be required (2, 5.1, 6)
= Flue-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local skin
reactions and may include fatigue, fever, mylagia, malaise and nausea. Dosing
interruption may
be required (2, 5.2, 6)
= Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps to the affected areas (5.3).
= Treatment of urethral, intra-vaginal, cervical, rectal or intra-anal
viral disease is
not recommended. (5.)
197
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
---------------- ADVERSE REACTIONS ---------------------
Table 1: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area Assessed by the
Investigator, Table
1: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area Assessed by the Investigator
Table 2: Treatment
Related Adverse Reactions occurring in > 1% of Zyclara0 ¨ Treated Subjects and
at a Greater
Frequency than with Placebo in either gender. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Graceway Pharmaceuticals,
LLC at 1-800-328-0255 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or wwwfda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient
labeling.
8. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10. OVER DOSAGE
11. DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14. CLINICAL STUDIES
198
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions for Administration:
17.2 Local Skin Reactions:
17.3 Systemic Reactions:
17.4 Recommended Administration
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
*Sections or subsections omitted from the Full Prescribing Information are not
listed.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Zyclara Cream is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal
warts/condyloma acuminata, whether present at the start of therapy or emerging
during therapy,
in patients 12 years or older.
1.1 Unevaluated Populations
The safety and efficacy of Zyclara Cream in immunosuppressed patients have
not been
established.
Zyclara0 Cream should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing
autoimmune
conditions.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Zyclara Cream is not for oral, ophthalmic, infra-anal, or intravaginal use.
Zyclara
Cream should be applied once-a-day to the external genital/perianal warts.
Zyclarall) Cream
should be used for up to 8 weeks. Zyclara Cream should be applied prior to
normal sleeping
hours and left on the skin for approximately 8 hours, after which time the
Zyclarat, Cream
should be removed by washing the area with mild soap and water. The prescriber
should
demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the benefit of
Zyclara Cream
therapy.
199
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Zyclara
Cream.
A thin layer of Zyclara Cream should be applied to the areas of existing and
emerging
warts and rubbed in until the Zyclara Cream is no longer visible. The
application site should
not be occluded. Following the treatment period the Zyclara Cream should be
removed by
washing the treated area with mild soap and water.
Local skin reactions at the treatment site are common. [see Adverse Reactions
(6.2)1 A
rest period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's
discomfort or severity of the
local skin reaction. Treatment may resume once the reaction subsides. Non-
occlusive dressings
such as cotton gauze or cotton underwear may be used in the management of skin
reactions.
Zyclara Cream is packaged in single-use packets with 28 packets supplied per
box,
which contain sufficient Zyclara Cream to cover the wart areas; use of
excessive amounts of
Zyclara Cream should be avoided. Patients should be prescribed no more than 2
Dose Packs
(56 packets) for the treatment course. Unused packets should be discarded.
Partially-used
packets should be discarded and not reused.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Zyclara (imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%, is supplied in single-use packets each of
which
contains 250 mg of the cream, equivalent to 9.4 mg of imiquimod. Zyclara
Cream is supplied
in a Dose Pack of 28 packets each.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Skin Reactions
Intense local skin reactions including skin weeping or erosion can occur after
a few
applications of Zyclara Cream and may require an interruption of dosing. [see
Dosage and
Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6)] . Zyclara Cream has the
potential to exacerbate
inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus host
disease.
200
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Administration of Zyclara ii) Cream is not recommended until the skin is
healed from any
previous drug or surgical treatment.
5.2 Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local skin
reactions and
may include fatigue, fever, myalgia, malaise and nausea. An interruption of
dosing and an
assessment of the patient should be considered. [see Adverse Reactions (6)]
5.3 Ultraviolet Light Exposure
In an animal photo-carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream shortened the time
to skin
tumor formation [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)] . The enhancement of
ultraviolet
carcinogenicity is not necessarily dependent on phototoxic mechanisms.
Therefore, patients
should minimize or avoid natural or artificial sunlight exposure to the
affected areas.
5.4 Unevaluated Uses
Zyclara Cream has not been evaluated for the treatment of urethral, intra-
vaginal,
cervical, rectal, or intra-anal human papilloma viral disease.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions. Adverse
reaction rates
observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates
in the clinical trials
of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies for genital warts, 602
subjects applied up
to one packet of Zyclara 0 Cream or placebo daily for up to 8 weeks. The most
frequently
reported adverse reactions were local skin and application site reactions.
Overall, fewer than 1% (3/400) of the subjects treated with Zyclara Cream
discontinued
due to local skin/application site reactions. The incidence and severity of
local skin reaction
during controlled clinical studies are shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area Assessed by the
Investigator
Zyclara Cream Placebo
Females Males Females
Males
201
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
n=217 n=183 n=106
n=96
All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe All Grades* Severe
Erythema
74% 10% 78% 10% 23% 0% 37% 1%
Edema (induration) 41% 2% 48% 2% 8% 0% 9%
0%
Weeping/Exudate 35% 1% 39% 3% 5% 0% 0%
0%
Flaking/Scaling/ 26% 0% 39% 0% 11% 0% 11%
0%
Dryness
Scabbing/Crusting 18% <1% 34% 1% 6% 0% 2%
0%
Erosion/Ulceration 36% 13% 42% 10% 7% 1% 2%
0%
*Mild, Moderate, or Severe
Local skin reactions were recorded as adverse events if they extended beyond
the
treatment area, if they required any medical intervention, or they resulted in
patient
discontinuation from the study.
Selected treatment related adverse reactions are listed below.
Table 2: Treatment Related Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 1% of Zyclara ¨
Treated Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Placebo in either gender
Females Males
Zyclara Cream Placebo Zyclara Cream Placebo
Preferred Term n=217 n=106 n183
n=96
Application site pain 7.8% 0% 5.5%
1.0%
Application site irritation 5.5% 0.9% 6.0% 1.0%
Application site pruritus 3.2% 1.9% 1.6% 0%
Application site bleeding 1.4% 0.9% 1.5% 0%
Application site discharge 1.4% 0% 0.5% 0%
Application site erythema 1.4% 0% 0% 0%
Application site reaction 0.9% 0% 1.1% 0%
Application site rash 0.9% 0% 1.1% 0%
Scrotal pain 0% 0% 1.6% 0%
Application site excoriation 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
202
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Secretion discharge 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Scrotal erythema 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Scrotal ulcer 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Scrotal edema 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Pruritus genital 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Application site cellulitis 0% 0% 1.1% 0%
Systemic adverse reactions considered treatment related in clinical trials
involving
Zyclara Cream included pain, pyrexia (fever), influenza, and myalgia.
Adverse reactions seen in clinical trials for external genital warts involving
5%
imiquimod cream included: tinea cruris, application site soreness,
hypopigmentation, sensitivity,
stinging and tenderness.
Other systemic adverse reactions considered treatment related in clinical
trials for
external genital warts involving 5% imiquimod cream included: headache,
influenza-like
symptoms, fatigue, malaise, nausea, and diarrhea.
6.2 Dermal Safety Trials Experience
Provocative repeat insult patch test studies involving induction and challenge
phases
produced no evidence that imiquimod cream causes photoallergenicity or contact
sensitization in
healthy skin; however, cumulative irritancy testing revealed the potential for
imiquimod cream to
cause irritation, and application site reactions were reported in the clinical
studies. [see Adverse
Reactions (6)]
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use
of
Aldara (imiquimod) Cream, 5%. Because these reactions are reported
voluntarily from a
population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate
their frequency or
establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Application Site Disorders: tingling at the application site.
Body as a Whole: angioedema.
Cardiovascular: capillary leak syndrome, cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy,
pulmonary
edema, arrhythmias (tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, palpitations), chest
pain, ischemia,
myocardial infarction, syncope.
203
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Endocrine: thyroiditis.
Gastro-Intestinal System Disorders: abdominal pain.
Hematological: decreases in red cell, white cell and platelet counts
(including idiopathic
thrombocytopenic purpura), lymphoma.
Hepatic: abnormal liver function.
Infections and Infestations: herpes simplex.
Musculo-Skeletal System Disorders: arthralgia.
Neuropsychiatric: agitation, cerebrovascular accident, convulsions (including
febrile
convulsions), depression, insomnia, multiple sclerosis aggravation, paresis,
suicide.
Respiratory: dyspnea.
Urinary System Disorders: proteinuria.
Skin and Appendages: exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme,
hyperpigmentation,
hypertrophic scar.
Vascular: Henoch-Schonlein purpura syndrome.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C:
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Zyclara
Cream
should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the
potential risk to the
fetus.
Note: The animal multiples of human exposure calculations were based on daily
dose
comparisons in this label. For the animal multiple of human exposure ratios
presented in this
label, the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) was set at 1 packet (250 mg
cream)
per treatment of Zyclara Cream (imiquimod 3.75%, 9.375 mg imiquimod).
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits.
Oral
doses of 1, 5 and 20 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during the period
of organogenesis
(gestational days 6 ¨ 15) to pregnant female rats. In the presence of maternal
toxicity, fetal
effects noted at 20 mg/kg/day (375X MRHD based on AUC comparisons) included
increased
resorptions, decreased fetal body weights, delays in skeletal ossification,
bent limb bones, and
two fetuses in one litter (2 of 1567 fetuses) demonstrated exencephaly,
protruding tongues and
204
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
low-set ears. No treatment related effects on embryofetal toxicity or
teratogenicity were noted at
mg/kg/day (73X MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
Intravenous doses of 0.5, 1 and 2 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered during
the
period of organogenesis (gestational days 6 ¨ 18) to pregnant female rabbits.
No treatment
related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 2
mg/kg/day (2.1X MRHD
based on BSA comparisons), the highest dose evaluated in this study, or 1
mg/kg/day (234X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
A combined fertility and pen- and post-natal development study was conducted
in rats.
Oral doses of 1, 1.5, 3 and 6 mg/kg/day imiquimod were administered to male
rats from 70 days
prior to mating through the mating period and to female rats from 14 days
prior to mating
through parturition and lactation. No effects on growth, fertility,
reproduction or post-natal
development were noted at doses up to 6 mg/kg/day (50X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons),
the highest dose evaluated in this study. In the absence of maternal toxicity,
bent limb bones
were noted in the Fl fetuses at a dose of 6 mg/kg/day (50X MRHD based on AUC
comparisons).
This fetal effect was also noted in the oral rat embryofetal development study
conducted with
imiquimod. No treatment related effects on teratogenicity were noted at 3
mg/kg/day (24X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether imiquimod is excreted in human milk following use of
Zyclara
Cream. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be
exercised when
Zyc1arao3 Cream is administered to nursing women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in patients with external genital/perianal warts below the
age of 12
years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 399 subjects treated with Zyclara Cream in the EGW clinical studies, 5
subjects
(1%) were 65 years or older. Data were too sparse to evaluate treatment
effects in this
population. No other clinical experience has identified differences in
responses between the
elderly and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older
individuals cannot be ruled
out.
205
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
OVER DOSAGE
Topical overdosing of Zyclara Cream could result in an increased incidence of
severe
local skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
The most clinically serious adverse event reported following multiple oral
imiquimod
doses of >200 mg (equivalent to imiquimod content of > 21 packets of Zyclara
Cream) was
hypotension, which resolved following oral or intravenous fluid
administration.
11 DESCRIPTION
Zyclara Cream is a toll-like receptor agonist for topical administration.
Each gram
contains 37.5 mg of imiquimod in an off-white oil-in-water vanishing cream
base consisting of
isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, polysorbate
60, sorbitan
monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water, benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and
propylparaben.
Chemically, imiquimod is 1-(2-methylpropy1)-1H-imidazo [4,5-c] quinolin-4-
amine.
Imiquimod has a molecular formula of C141-116N4 and a molecular weight of
240.3. Its structural
formula is:
N
N
CH 3
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Zyclara Cream is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Imiquimod has no direct antiviral activity in cell culture. A study in 22
subjects with
genital/perianal warts comparing imiquimod cream 5% and vehicle shows that
imiquimod
induces mRNA encoding cytokines including interferon-a at the treatment site.
In addition
HPVL1 mRNA and HPV DNA are significantly decreased following treatment.
However, the
clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
206
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic absorption of imiquimod (up to 9.4 mg [one packet]) across the
affected skin of
18 subjects with EGW was observed with once daily dosing for 3 weeks. The mean
peak serum
drug concentration at Day 21 was 0.488 ng/mL.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) rat carcinogenicity study, imiquimod was administered to
Wistar rats
on a 2X/week (up to 6 mg/kg/day) or daily (3 mg/kg/day) dosing schedule for 24
months. No
treatment related tumors were noted in the oral rat carcinogenicity study up
to the highest doses
tested in this study of 6 mg/kg administered 2X/week in female rats (50X MRHD
based on AUC
comparisons), 4 mg/kg administered 2X/week in male rats (40X MRHD) or 3 mg/kg
administered 7X/week to male and female rats (25X MRHD).
In a dermal mouse carcinogenicity study, imiquimod cream (up to 5
mg/kg/application
imiquimod or 0.3% imiquimod cream) was applied to the backs of mice 3X/week
for 24 months.
A statistically significant increase in the incidence of liver adenomas and
carcinomas was noted
in high dose male mice compared to control male mice (96X MIRED based on AUC
comparisons). An increased number of skin papillomas was observed in vehicle
cream control
group animals at the treated site only.
In a 52-week dermal photo-carcinogenicity study, the median time to onset of
skin tumor
formation was decreased in hairless mice following chronic topical dosing
(3X/week; 40 weeks
of treatment followed by 12 weeks of observation) with concurrent exposure to
UV radiation (5
days per week) with vehicle alone. No additional effect on tumor development
beyond the
vehicle effect was noted with the addition of the active ingredient,
imiquimod, to the vehicle
cream.
Imiquimod revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on
the
results of five in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma L5178Y
assay, Chinese
hamster ovary cell chromosome aberration assay, human lymphocyte chromosome
aberration
assay and SHE cell transformation assay) and three in vivo genotoxicity tests
(rat and hamster
bone marrow cytogenetics assay and a mouse dominant lethal test).
207
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Daily oral administration of imiquimod to rats, throughout mating, gestation,
parturition
and lactation, demonstrated no effects on growth, fertility or reproduction,
at doses up to 57X
MRHD based on AUC comparisons.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies, 601
subjects with
EGW were treated with 3.75% imiquimod cream, or a matching placebo cream.
Studies enrolled
subjects aged from 15 to 81 years. The baseline wart area ranged from 6 to
5579 mm2 and the
baseline wart count ranged from 2 to 48 warts. Most subjects had two or more
treated anatomic
areas at Baseline. Anatomic areas included: inguinal, perineal, and perianal
areas (both genders);
the glans penis, penis shaft, scrotum, and foreskin (in men); and the vulva
(in women). Up to
one packet of study cream was applied once daily to each wart identified at
Baseline and any
new wart that appeared during the treatment period. The study cream was
applied to all warts
prior to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Subjects
continued
applying the study cream for up to 8 weeks or until they achieved complete
clearance of all
(baseline and new) warts in all anatomic areas. Subjects not achieving
complete wart clearance
by the Week 8 visit (end of treatment, EOT), were evaluated for up to 8 weeks
or until they
achieved complete clearance during an additional 8 week no-treatment period.
Subjects who
achieved complete clearance of all warts at any time until the Week 16 visit
entered a 12 week
follow-up for recurrence period.
Efficacy was assessed by wart counts (those present at Baseline and new warts
appearing
during the study) at EOS (i.e., up to 16 weeks from Baseline).
Complete clearance required clearance of all warts in all anatomic areas.
Partial
clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects with at least a 75%
reduction in the
number of baseline warts at EOS. Percent reductions were measured relative to
the numbers of
warts at Baseline. Complete and partial clearance rates, and percent
reductions in wart counts
from baseline are shown in the table below (by overall rate and by gender).
Table 3: Efficacy Endpoints
Zyclara Cream Placebo
208
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
3.75% Cream
Complete Clearance Rate
Overall 28.3% (113/399) 9.4%
(19/202)
Females 36.6% (79/216) 14.2%
(15/106)
Males 18.6%(34/183)
4.2%(4/96)
Partial Clearance Rate
Overall 38.3% (153/399) 11.9%
(24/202)
Females 47.7% (103/216) 17.0%
(18/106)
Males 27.3% (50/183) 6.3%
(6/96)
Percent Reduction of EGW (Median)
Overall 50.0% 0.0
Females 70.7% 0.0
Males 23.3% 0.0
The numbers of subjects who remained clear of EGW at the end of 12 week follow-
up for
recurrence period are shown in Table 4 below:
Table 4: Sustained Complete Clearance
Zyclara Cream Placebo
3.75% Cream
Cleared and entered Follow-up 102 13
Remained Clear 71 12
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Zyclara (imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%, is supplied in single-use packets which
contain
250 mg of the cream. Available as: Dose Pack of 28 packets NDC 29336-710-28.
Store at 25 C (77 F); excursions permitted to 150 to 30 C (59 to 86 F) [See
USP
Controlled Room Temperature].
Avoid freezing.
209
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Keep out of reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (1 7. 7)
17.1 Instructions for Administration:
Zyclara Cream should be used as directed by a physician. [see Dosage and
Administration (2)] Zyclara Cream is for external use only. Contact with the
eyes, lips and
nostrils should be avoided. [see Indications and Usage (I) and Dosage and
Administration (2)] .
The treatment area should not be bandaged or otherwise occluded. Partially-
used packets
should be discarded and not reused. The prescriber should demonstrate the
proper application
technique to maximize the benefit of Zyclara) Cream therapy.
It is recommended that patients wash their hands before and after applying
Zyclara
Cream.
17.2 Local Skin Reactions:
Patients may experience local skin reactions during treatment with Zyclara
Cream.
Potential local skin reactions include erythema, edema, erosions/ulcerations,
weeping/exudate,
flaking/scaling/dryness, and scabbing/crusting. These reactions can range from
mild to severe in
intensity and may extend beyond the application site onto the surrounding
skin. Patients may
also experience application site reactions such as itching, irritation or
pain. [see Adverse
Reactions (6)]
Local skin reactions may be of such an intensity that patients may require
rest periods
from treatment. Treatment with Zyclara Cream can be resumed after the skin
reaction has
subsided, as determined by the physician. Treatment should not be extended
beyond 8 weeks
due to missed doses or rest periods. Patients should contact their physician
promptly if they
experience any sign or symptom at the application site that restricts or
prohibits their daily
activity or makes continued application of the Zyclara Cream difficult.
Because of local skin reactions, during treatment and until healed, the
treatment area is
likely to appear noticeably different from normal skin. Localized
hypopigmentation and
hyperpigmentation have been reported following use of imiquimod cream. These
skin color
changes may be permanent in some patients.
210
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
17.3 Systemic Reactions:
Patients may experience flu-like systemic signs and symptoms during treatment
with
Zyclara Cream. Systemic signs and symptoms may include fatigue, fever,
myalgia, malaise,
and nausea. [see Adverse Reactions (6)] An interruption of dosing and
assessment of the patient
should be considered.
17.4 Recommended Administration
Dosing is once daily before bedtime to the skin of the affected wart areas.
Zyclara
Cream treatment should continue until there is total clearance of the
genital/perianal warts or for
up to 8 weeks.
It is recommended that the treatment area be washed with mild soap and water
approximately 8 hours following Zyclara Cream application.
It is common for patients to experience local skin reactions such as erythema,
erosion,
excoriation/flaking, and edema at the site of application or surrounding
areas. Most skin
reactions are mild to moderate.
Sexual (genital, anal, oral) contact should be avoided while Zyclara Cream is
on the
skin. Application of Zyclara Cream in the vagina is considered internal and
should be avoided.
Female patients should take special care if applying the Zyclara Cream at the
opening of the
vagina because local skin reactions on the delicate moist surfaces can result
in pain or swelling,
and may cause difficulty in passing urine.
Uncircumcised males treating warts under the foreskin should retract the
foreskin and
clean the area daily.
New warts may develop during therapy, as Zyclara Cream is not a cure.
The effect of Zyclara Cream on the transmission of genital/perianal warts is
unknown.
Zyclara Cream may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms, therefore concurrent
use
is not recommended.
Should severe local skin reaction occur, the Zyclara Cream should be removed
by
washing the treatment area with mild soap and water.
17.7 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
17.8 Patient Information
Zyclara [imiquimod] Cream, 3.75% (Imiquimod)
211
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
IMPORTANT: Not for mouth, eye, or vaginal use
Read the Patient Information that comes with Zyclara Cream before you start
using it
and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet
does not take the
place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or
treatment. If you
do not understand the information, or have any questions about Zyclara Cream,
talk with your
healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What is Zyclara Cream?
= Zyclara Cream is a skin use only (topical) medicine used to treat
external genital
and perianal warts in people 12 years and older.
Zyclara0 Cream does not work for everyone.
= Zyclara Cream may not completely cure your genital or perianal warts.
New
warts may develop during treatment with Zyclara Cream. It is not known if
Zyclara
Cream can stop you from spreading genital or perianal warts to other people.
For your
own health and the health of others, it is important to practice safer sex.
Talk to your
healthcare provider about safer sex practices.
=
Who should not use Zyclara Cream?
= Zyclara Cream has not been studied in children under 12 years old for
external
genital and perianal warts.
Before using Zyclara Cream, tell your healthcare provider:
= about all your medical conditions, including if you
o are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Zyclara
Cream can harm your unborn baby.
o are breastfeeding. It is not known if Zyclara Cream passes into your
milk
and if it can harm your baby.
= about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-
prescription
medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare
provider if
you have had other treatments for genital or perianal warts. Zyclara Cream
should not
be used until your skin has healed from other treatments.
How should I use Zyclara Cream?
212
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Use Zyclara Cream exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Zyclara Cream is for skin use only. Do not take by mouth and do not get
Zyclara
Cream in or near your eyes, lips or nostrils. Do not use Zyclara Cream unless
your
healthcare provider has taught you the right way to use it. Talk to your
healthcare
provider if you have any questions.
= Your healthcare provider will tell you where to apply Zyclara Cream and
how
often and for how long to apply it for your condition. Do not use Zyclara
Cream longer
than prescribed. Using too much Zyclara Cream, or using it too often, or for
too long
can increase your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side
effect. Talk to
your healthcare provider if Zyclara Cream does not work for you.
= Zyclara Cream is applied once a day.
Zyclara Cream is usually left on the skin for approximately 8 hours.
Treatment should
continue until the warts are completely gone or for up to 8 weeks.
Applying Zyclara Cream
Zyclara Cream should be applied just before your bedtime.
= Wash the area to be treated with mild soap and water. Allow the area to
dry.
Uncircumcised males treating warts under their penis foreskin must pull
their foreskin back and clean before treatment and clean daily during the
weeks of
treatment.
= Wash your hands
= Open a new packet of Zyclara Cream just before use.
= Apply a thin layer of Zyclara ii) Cream only to the affected area or
areas to be
treated. Do not use more Zyclara Cream than is needed to cover the treatment
area. Do
not use more than one packet for each application.
= Rub the cream in all the way to the affected area or areas.
= Do not get Zyclara Cream in or around your eyes or mouth.
= Do not get Zyclara Cream in the anus when applying to perianal warts.
= Female patients treating genital warts must be careful when applying
Zyclara
Cream around the vaginal opening. Female patients should take special care if
applying
213
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
the Zyclara Cream at the opening of the vagina because local skin reactions
on the
delicate moist surfaces can cause pain or swelling, and may cause problems
passing
urine. Do not put Zyclara Cream in your vagina.
= Do not cover the treated area with an airtight bandage. Cotton gauze
dressings
can be used. Cotton underwear can be worn after applying Zyclara Cream to the
genital or perianal area.
= Safely throw away the open packet of Zyclara Cream so that children and
pets
cannot get it. The open packet should be thrown away even if all the Zyclara
Cream
was not completely used.
= After applying Zyclara Cream, wash your hands well.
= Leave the Zyclara Cream on the affected area or areas for the time
prescribed by
your healthcare provider. Do not bathe or get the treated area wet before the
right time
has passed. Do not leave Zyclara Cream on your skin longer than prescribed.
= After about 8 hours, wash the treated area or areas with mild soap and
water.
= If you forget to apply Zyclara Cream, continue on your regular schedule
and do
not make up the missed dose(s).
= If you get Zyclara Cream in your mouth or in your eyes rinse well with
water
right away.
What should I avoid while using Zyclarag Cream?
= Do not cover the treated site with bandages or other closed dressings.
Cotton
gauze dressings are okay to use, if needed. Cotton underwear can be worn after
treating
the genital or perianal area.
= Do not get Zyclara Cream in or near the eyes, lips or nostrils.
= Do not put Zyclara Cream in your vagina or anus.
= Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight to the treated
area as
much as possible during treatment with Zyclara Cream.
= Do not have sexual contact including genital, anal, or oral sex when
Zyclara
Cream is on your genital or perianal skin. Zyclara Cream may weaken condoms
and
vaginal diaphragms. This means they may not work as well to prevent pregnancy.
For
your own health and the health of others, it is important to practice safer
sex. Talk to
214
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
your healthcare provider about safer sex practices.
What are the possible side effects of Zyclara Cream?
Side effects with Zyclara Cream may include skin reactions at the treatment
site such
as:
= redness
= swelling
= a sore, blister, or ulcer
= skin that becomes hard or thickened
= skin peeling
= scabbing and crusting
= itching
= burning
= changes in skin color that do not always go away
During treatment and until the skin has healed, your skin in the treatment
area is likely to
appear noticeably different from normal skin. Side effects, such as redness,
scabbing, itching
and burning are common at the site where Zyclara il) Cream is applied, and
sometimes the side
effects go outside of the area where Zyclara 0 Cream was applied. Swelling,
small open sores
and drainage may also be experienced with use of Zyclara Cream. You may also
experience
itching, irritation or pain. Patients should be aware that new warts may
develop during
treatment, as Zyclara Cream may not be a cure. Many people see reddening or
swelling on or
around the application site during the course of treatment. If you have
questions regarding
treatment or local skin reactions, please talk with your healthcare provider.
You have a higher chance for severe skin reactions if you use too much Zyclara
Cream
or use it the wrong way. Stop Zyclara Cream right away and call your
healthcare provider if
you get any skin reactions that affect your daily activities, or that do not
go away. Sometimes,
Zyclara Cream must be stopped for a while to allow your skin to heal. Talk to
your healthcare
provider if you have questions about your treatment or skin reactions.
Other side effects of Zyclara Cream include pain, fever, muscle aches, and
may also
include headache, back pain, joint aches, tiredness, flu-like symptoms,
nausea, and diarrhea.
215
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
If the reactions seem excessive, if either skin breaks down or sores develop
during the
first week of treatment, if flu-like symptoms develop or if you begin to not
feel well at anytime,
stop applying ZyclaraS Cream and contact your healthcare provider.
These are not all the side effects of ZyclaraS Cream. For more information,
ask your
healthcare provider or pharmacist.
How do I store Zyclara0 Cream?
= Store ZyclaraS Cream at 77 F (25 C). [59 to 86 F; 15 to 30 C]. Do not
freeze.
= Safely throw away ZyclaraS Cream that is out of date or that you do not
need.
= Keep Zyclara0 Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about ZyclaraS Cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in
patient
information leaflets. Do not use ZyclaraS Cream for a condition for which it
was not prescribed.
Do not give Zyclara0 Cream to other people, even if they have the same
symptoms you have.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about ZyclaraS Cream.
If you
would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask
your pharmacist
or healthcare provider for information about ZyclaraS Cream that is written
for the healthcare
provider. If you have other questions about Zyclara0 Cream, call 1-800-328-
0255.
What are the ingredients in ZyclaraS Cream?
Active Ingredient: imiquimod
Inactive ingredients: isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white
petrolatum,
polysorbate 60, sorbiran monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water,
benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and propylparaben.
Manufactured by:
3M Health Care Limited, Loughborough LE11 lEP England
Distributed by:
Graceway Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Bristol, TN 37620
216
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment XI
[000320] CANADA PRODUCT
MONOGRAPH
(Actinic Keratosis)
ZYCLARAS
(imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%
250 mg single-dose packet
Immune response modifier
Graceway Pharmaceuticals
252 Pall Mall St., Suite 302
London, Ontario
Canada
N6A 5P6
Date of Preparation:
January 13, 2009
Submission Control No: Not yet assigned
217
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART I: HEALTH PROFESSIONAL INFORMATION ....................................
219
SUMMARY PRODUCT INFORMATION ................................................
219
INDICATIONS AND CLINICAL USE ...............................................
219
CONTRAINDICATIONS ..........................................................
219
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ...................................................
219
ADVERSE REACTIONS ..........................................................
222
DRUG INTERACTIONS ..........................................................
224
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ..................................................
225
OVERDOSAGE .................................................................
226
ACTION AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ...........................................
226
STORAGE AND STABILITY ......................................................
227
DOSAGE FORMS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING ....................................
227
PART II: SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION ............................................
228
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION .................................................
228
CLINICAL TRIALS ............................................................
229
DETAILED PHARMACOLOGY ......................................................
231
TOXICOLOGY .................................................................
232
REFERENCES .................................................................
234
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION .............................................
237
218
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
ZYCLARA
(imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%
PART I: HEALTH PROFESSIONAL INFORMATION FOR ACTINIC KERATOSIS
SUMMARY PRODUCT INFORMATION
Route of Dosage Form / Clinically Relevant Nonmedicinal
Administration Strength Ingredients
Topical Cream / 9.4 mg For a complete listing see Dosage
imiquimod per 250 Forms, Composition and Packaging
mg single-dose section.
packet
(3.75 % w/w)
INDICATIONS AND CLINICAL USE
Zyclara Cream is indicated for the topical treatment of clinically typical
visible or
palpable actinic keratoses (AK) of the entire face or balding scalp in adults.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Zyclara Cream is contraindicated in individuals with a history of sensitivity
reactions to
any of its components. It should be discontinued if hypersensitivity to any of
its ingredients is
noted.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
General
The efficacy of Zyclara in the prevention of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
associated
with AK has not been established (see PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies).
Hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria) and erythema multiform have been
reported in
patients receiving imiquimod Cream. Causality has not been established and no
other reports of
219
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
similar cases have been reported in post-marketing surveillance. Zyclara o
Cream should be
discontinued immediately if these events occur.
The efficacy and safety of Zyclara Cream have not been established for
patients with
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome or Xeroderma Pigmentosum.
The safety and efficacy of Zyclaraii) Cream in immunosuppressed patients have
not been
established.
Local Skin Reactions
Intense local skin reactions including skin weeping or erosion can occur after
a few
applications of Zyclara Cream and may require an interruption of dosing. (see
Dosage and
Administration and Adverse Reactions) Zyclara Cream has the potential to
exacerbate
inflammatory conditions of the skin, including chronic graft versus host
disease.
Local skin reactions such as erythema, erosion, excoriation/flaking, and edema
are
common.
Should a severe local skin reaction occur, the Zyclara Cream should be
removed by
washing the treatment area with mild soap and water. Treatment with Zyclara
can be resumed
after the skin reaction has subsided.
Provocative repeat insult patch test studies involving induction and challenge
phases
produced no evidence that imiquimod cream causes photoallergenicity or contact
sensitization in
healthy skin; however, cumulative irritancy testing revealed the potential for
imiquimod cream to
cause irritation, and application site reactions were reported in clinical
studies (see Adverse
Reactions).
Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompany, or even precede, local skin
reactions and
may include fatigue, nausea, fever, myalgias, arthralgias, and chills. An
interruption of dosing
220
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
and an assessment of the patient should be considered. (see Adverse Reactions)
Ultraviolet Light Exposure
Exposure to sunlight (including sunlamps) should be avoided or minimized
during use of
Zyclara Cream because of concern for heightened sunburn susceptibility.
Patients should be
warned to use protective clothing (e.g. hat) when using Zyclara Cream.
Patients with sunburn
should be advised not to use Zyclara Cream until fully recovered. Patients
who may have
considerable sun exposure, e.g., due to their occupation, and those patients
with inherent
sensitivity to sunlight should exercise caution when using Zyclara Cream.
Phototoxicity has
not been adequately assessed for Zyclara Cream.
The enhancement of ultraviolet
carcinogenicity is not necessarily dependent on phototoxic mechanisms. Despite
the absence of
observed phototoxicity in humans (see PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies),
imiquimod cream
shortened the time to skin tumour formation in an animal photoco-
carcinogenicity study (see
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility). Therefore, it is
prudent for patients to
minimize or avoid natural or artificial sunlight exposure.
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Two-year bioassays in Wistar rats (up to 3 mg/kg orally per day) and CD-1 mice
(up to
4.5 mg/kg applied topically 3 times per week) showed no evidence of a
carcinogenic effect in
male and female rats and female mice. Liver tumours were increased in male
mice exposed to
the highest dose concentration, compared to the unexposed controls. However,
the number of
tumours was within the range seen historically for male CD-1 mice. It is
generally accepted that
an increase in liver tumours in male mice, in the absence of other neoplastic
responses in mice or
rats, is not indicative of a carcinogenic risk for humans.
In a photocarcinogenicity study in hairless mice, animals received Zyclara
Cream 3
times per week at imiquimod concentrations of 0.03%, 0.1% and 0.3% and were
irradiated with
solar ultraviolet light for 5 days each week for 40 weeks and observed an
additional 12 weeks.
Vehicle cream enhanced UVR-induced skin tumour development. Zyclara Cream had
no
additional effect on tumour development beyond the vehicle effect (i.e., the
addition of the active
ingredient, imiquimod, to the vehicle cream did not result in an additional
effect beyond the
221
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
vehicle effect on tumour development).
Special Populations
Pregnant Women: Imiquimod was not teratogenic in rat or rabbit teratology
studies. In
rats at a high maternally toxic dose (28 times human dose on a mg/m2 basis),
reduced pup
weights and delayed ossification were observed. However, there are no adequate
and well-
controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are
not always
predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only
if the potential
benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Women: It is not known whether topically applied imiquimod is excreted
in
human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be
exercised
when Zyclara Cream is administered to nursing women.
Pediatrics (< 18 years of age): Actinic keratosis is not a condition generally
seen within
the pediatric population. Safety and efficacy in patients below the age of 18
years have not been
established.
Geriatrics (> 65 years of age): Of the 160 subjects treated with Zyclara
Cream in the
clinical studies, 78 subjects were 65 years or older. No overall differences
in safety or
effectiveness were observed between these subject and younger subjects. No
other clinical
experience has identified differences in responses between the elderly and
younger subjects, but
greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Drug Reaction Overview
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse
reaction
rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to
rates in the clinical
trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trial Adverse Drug Reactions
222
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
The data described below reflect exposure to Zyclara Cream or placebo in 319
subjects
enrolled in two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Subjects applied
Zyclara Cream or
placebo daily to the skin of the affected area (either the entire face or
balding scalp) for two 2-
week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no treatment period.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 1% of Zyclara -Treated
Subjects and at a Greater Frequency than with Placebo in the Combined
Studies
Preferred Term Zyclara Cream, 3.75%
Placebo
(N=160) (N=159)
Headache 10 (6.3%) 5 (3.1%)
Application site pruritus 7 (4.4%) 1 (0.6%)
Fatigue 7 (4.4%) 0 (0%)
Nausea 6(3.8%) 2(1.3%)
Application site irritation 5 (3.1%) 0 (0%)
Application site pain 5 (3.1%) 0 (0%)
Pyrexia 5 (3.1%) 0 (0%)
Anorexia 4 (2.5%) 0 (0%)
Dizziness 4 (2.5%) 0 (0%)
Herpes simplex 4 (2.5%) 1 (0.6%)
Pain 4(2.5%) 0(0%)
Chest pain 3 (1.9%) 0 (0%)
Diarrhea 3 (1.9%) 0 (0%)
Lymphadenopathy 3 (1.9%) 0 (0%)
Application Site Swelling 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Arthralgia 2(1.3%) 0(0%)
Blood glucose increased 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Dermatitis 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Food poisoning 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Insomnia 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Seborrhoeic keratosis 2 (1.3%) 0 (0%)
Squamous cell carcinoma 2 (1.3%) 1 (0.6%)
Vomiting 2 (1.3%) 1(0.6%)
Table 2: Application Site Reactions in Zyclara -Treated Subjects as
Assessed by the Investigator
Included Term Zyclara - Cream, 3.75%*
Placebo*
(N=160) (N=159)
Any application site reaction 17 (10.6%) 2 (1.3%)
223
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Application site pruritus 7 (4.4%) 1 (0.6%)
Application site irritation 5 (3.1%) 0(0%)
Application site pain 5 (3.1%) 0(0%)
Application site swelling 2 (1.3%) 0(0%)
Application site paraesthesia 1 (0.6%) 1 (0.6%)
Application site scar 1 (0.6%) 0(0%)
* up to 2 packets daily
Local skin reactions were collected independently of the adverse event
"application site
reaction" in an effort to provide a better picture of the specific types of
local reactions that might
be seen. The most frequently reported local skin reactions were erythema,
flaking/scaling/dryness, and scabbing/crusting. The prevalence and severity of
local skin
reactions that occurred during controlled studies are shown in the following
table.
Table 3: Local Skin Reactions in the Treatment Area in Zyclara -
Treated Subjects as Assessed by the Investigator
Zyclara Cream, Placebo
3.75% (N=159)
(N=160)
All Grades Severe All Grades Severe
Erythema 154 (96.3%) 40 (25.2%) 124 (78.0%) 0
(0.0%)
Edema 120 (75.0%) 9 (5.7%) 31(19.5%) 0 (0.0%)
Weeping/Exudate 81(50.6%) 9 (5.7%) 6 (3.8%) 0 (0.0%)
Flaking/Scaling/Dryness 147 (91.9%) 13 (8.2%) 123 (77.4%) 2
(1.3%)
Scabbing/Crusting 149 (93.1%) 22 (13.8%) 72 (45.3%)
0 (0.0%)
Erosion/Ulceration 99 (61.9%) 17 (10.7%) 14 (8.8%)
0 (0.0%)
Other adverse events observed in subjects treated with Zyclaraol) Cream in
treatment
regimens other than two 2-week treatment cycles include: application site
bleeding, cheilitis,
chills, herpes zoster, influenza-like illness, lethargy, myalgia, pancytopenia
and pruritus.
Post-Market Adverse Drug Reactions
There is no post-marketing data available for the Zyclara Cream, 3.75%
product.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
224
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Overview
Interactions between Zyclara Cream with other drugs have not been
established.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dose and Dosage Adjustment
Zyclara Cream should be applied once daily before bedtime to the skin of the
affected
area (entire face or balding scalp) for two treatment cycles of 2 weeks each
separated by a 2-
week no-treatment period or as directed by physician.
Administration
Before applying the Zyclara Cream, the patient should wash the treatment area
with
mild soap and water and allow the area to dry thoroughly. Zyclara Cream
should be applied as
a thin film to the entire treatment area and rubbed in until the Zyclara
Cream is no longer
visible. Up to 2 packets of Zyclara Cream may be applied to the treatment
area at each
application. Zyclara Cream should be left on the skin for approximately 8
hours, after which
time the Zyclara Cream should be removed by washing the area with mild soap
and water. The
prescriber should demonstrate the proper application technique to maximize the
benefit of
Zyclara Cream therapy.
Use in or near the eyes, lips and nostrils should be avoided.
Local skin reactions in the treatment area are common. (see Adverse Reactions)
A rest
period of several days may be taken if required by the patient's discomfort or
severity of the local
skin reaction. However, each treatment cycle should not be extended beyond 2
weeks due to
missed doses or rest periods. Response to treatment cannot be adequately
assessed until
resolution of local skin reactions. Lesions that do not respond to treatment
should be carefully re-
evaluated and management reconsidered. Zyclarail) Cream is packaged in single-
use packets.
Partially-used packets should be discarded and not reused. The application
site is not to be
occluded.
225
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Missed Dose
Each treatment cycle should not be extended beyond 2 weeks due to missed doses
or rest
periods.
0 VERD 0 S AGE
Overdosage of Zyclara Cream in humans is unlikely due to minimal percutaneous
absorption. Animal studies reveal a rabbit dermal lethal imiquimod dose of
greater than
5000 mg/kg. Persistent topical overdosing of Zyclara Cream could result in an
increased
incidence of severe local skin reactions and may increase the risk for
systemic reactions.
The most clinically serious adverse event reported following multiple oral
imiquimod
doses of
200 mg was hypotension which resolved following oral or intravenous fluid
administration.
ACTION AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
In vitro studies have demonstrated that imiquimod induces the release of
interferon alpha
(IFN-a) and other cytokines from human monocytes/macrophages and
keratinocytes. The panel
of cytokines induced varied with the cell's tissue origin. Topical in vivo
application of
imiquimod cream on mouse skin resulted in increased concentrations of IFN and
tumour necrosis
factor (TNF) compared with skin of untreated mice.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of imiquimod in treating actinic keratosis (AK)
lesions is
unknown. While the following have been observed, the clinical significance of
these
observations in AK is not known. In a study of 58 patients with AK treated
with imiquimod 3
times per week, the response of biomarkers sensitive to imiquimod after 16
weeks of dosing
increased compared to the response after the first dose. For interleukin-1
antagonist, the median
concentration observed following multiple dosing was <2-fold higher than that
after single dose
administration, for interferon-a was _3-fold, and for T5'-oligoadenylate
synthetase was
226
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
approximately 3-fold.
Phannacokinetics
Percutaneous absorption of imiquimod has been studied through intact healthy
skin, the
skin of genital warts, and lesions of sun damaged skin. Percutaneous
absorption of
[14C]imiquimod was minimal in a study involving six healthy subjects treated
with a single
topical application (5 mg) of [14C]imiquimod in cream formulation. No
radioactivity was
detected in the serum (lower limit of quantitation is 1 ng/mL) and < 0.9% of
the radiolabelled
dose was excreted in the urine and feces following topical application.
Absorption: Zyclara Cream exhibited low systemic exposure to imiquimod and
its
metabolites when applied daily for 3 weeks (18.75 mg, 2 packets once daily) to
the entire face
and/or balding scalp (approximately 200 cm2) of patients with AK (N=17). A
mean (median)
peak serum drug concentration at the end of week 3 was approximately 0.323
ng/mL. Steady-
state levels were achieved in 2 weeks and Tmax ranged between 6 and 9 hours.
Excretion: The apparent half-life following topical dosing of 3.75% imiquimod
cream
was calculated as 29 hours after daily administration of 2 packets (18.75 mg)
for 3 weeks.
Special Populations and Conditions
Age: No formal pharmacokinetic study was conducted to examine age related
differences in the pharmacokinetic profile of imiquimod 3.75% cream.
Gender: During a 3 weeks treatment, the C.õõ and AUC0_24 on Day 21 appeared to
be
similar in female and male subjects and lower in male subjects who applied
Zyclara
(imiquimod) Cream, 3.75% balding scalp rather than the face.
STORAGE AND STABILITY
Store between 15-25 C. Avoid freezing.
DOSAGE FORMS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING
227
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Zyclara Cream is supplied in single-use packets which contain 250 mg of the
cream.
Available as box of XX packets.
Each gram of Zyclara contains 37.5 mg of imiquimod in an off-white oil-in-
water
vanishing cream base consisting of isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl
alcohol, white
petrolatum, polysorbate 60, sorbitan monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum,
purified water, benzyl
alcohol, methylparaben, and propylparaben.
PART II: SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Drug Substance
Proper name: Imiquimod (USAN, INN)
Chemical name: 1-(2-methylpropy1)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine
Molecular formula and molecular mass: C141116N4; MW = 240.3
Structural formula:
NH2
N
Physicochemical properties:
Physical Form:
Crystalline solid that varies in colour from white to off-white or
buff. The compound has no odour.
228
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Solubility: Practically insoluble in most common organic solvents
and in
aqueous systems except at extremely low pH conditions. It can be
made soluble to the extent of at least 100 mg/mL in methanol (as a
salt) upon the addition of a few drops of hydrochloric or acetic
acid. Soluble in fatty acids such as oleic acid and isostearic acid.
pKa Value: The ionization constant for imiquimod was determined
by
ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy and pH-solubility to be about 7.5.
Melting point: 297-299 C with sublimation.
CLINICAL TRIALS
Study demographics and trial design for studies considered pivotal are
presented in Table
4.
Table 4: Summary of Patient Demographics for Pivotal Clinical Trials
Study Study Duration of Application No. Sex Age in No.
Discontinued
Number Design Treatment Frequency/St Subjects in (M/F) Years
(2.5%/3.75%/Placebo)
udy Cream ITT Mean
(2.5%/3.75 (SD)
%/Placebo
No.
Subjects in
PP
(2.5%/3.75
%/Placebo)
GW01- Phase 3, 2 weeks Once daily 242 198/44
63.7 3/7/5
0702 1:1:1 treatment (81/81/80) (10.1)
Imiq 2.5%, followed
lmiq by 2 weeks 218
3.75%: of no (75/73/70)
Pla; treatment;
dbleblind, then, 2
parallel; weeks
subjects treatment
with followed
AK. by 8 weeks
of no
treatment
GW01- Phase 3, 2 weeks Once daily 237 191/46
65.1 3/4/4
0704 1:1:1 treatment (79/79/79) (9.9)
Imiq 2.5%, followed
229
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Imiq by 2 weeks 207
3.75%: of no (67/68/72)
Pla; treatment;
dbleblind, then, 2
parallel; weeks
subjects treatment
with followed
AK. by 8 weeks
of no
treatment
AK = actinic keratosis; Imiq = imiquimod; Pla = placebo
In two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies, 319
subjects with
AK were treated with 3.75% imiquimod cream, or a matching placebo cream.
Studies enrolled
subjects >18 years of age with 5-20 typical visible or palpable AK lesions of
the face or scalp in
an area that exceeded 25cm2. Study cream was applied to full face or balding
scalp once daily
for two 2-week treatment cycles separated by a 2-week no-treatment period.
Subjects then
continued in the study for an 8-week follow-up period during which they
returned for clinical
observations and safety monitoring. Study subjects ranged from 36 to 90 years
of age and 54%
had Fitzpatrick skin type I or II. All Zyclarail) Cream-treated subjects were
Caucasians.
On a scheduled dosing day, the study cream was applied to the entire treatment
area prior
to normal sleeping hours and left on for approximately 8 hours. Efficacy was
assessed by AK
lesion counts at the 8-week post-treatment visit. All AKs in the treatment
area were counted,
including baseline lesions as well as new or sub-clinical AK lesions which
appeared during
therapy.
Complete clearance required clearance of all lesions. The partial clearance
rate and
percent reductions were measured relative to the numbers of AK lesions at
Baseline. Partial
clearance rate was defined as the proportion of subjects in whom the number of
baseline AKs
was reduced by 75% or more. Complete and partial clearance rates, and percent
reductions in
AK counts from baseline are shown in the table below.
Table 5: Efficacy Endpoints a
Zyclaral3 Cream, Placebo p-value
230
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
3.75% Cream
Complete Clearance Rate 35.6% (57/160) 6.3%
(10/159) <0.001
Partial Clearance Rate 59.4% (95/160) 22.6% <0.001
(36/159)
Percent Reduction of AKs 81.8% 25.0% <0.001
(median)
a Studies GW01-0702 and GW01-0704
Sub-clinical AK lesions may become apparent in the treatment area during
treatment with
Zyclara Cream. During the course of treatment, >85% (138/160) of subjects
experienced an
increase in AK lesions relative to the number present at baseline within the
treatment area.
Subjects with an increase in AK lesions had a similar response to those with
no increase in AK
lesions.
DETAILED PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics: Imiquimod is an immune response modifier that is not a
nucleoside
analogue. Saturable binding studies suggest a membrane receptor for imiquimod
exists on
responding cells. In vitro studies have demonstrated that imiquimod induces
the production of
IFN and other cytokines from a variety of human and animal cells. In addition,
cytokines were
produced following dermal application and oral administration in various
laboratory animals and
in human studies following oral administration of imiquimod. In animal models
imiquimod is an
effective antiviral and antitumour agent whose activity is principally due to
induction of alpha
interferon but other cytokines are also involved. Imiquimod induced a local
immune response
and a decrease in HPV-DNA for genotypes 6 and 11 in patients treating external
genital/perianal
warts. The immune response was characterized by significant increases in mRNA
for IFN-a,
2'5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and IFN-y in wart tissue. Although these data
suggest a sequence
of immunologic events initiated by imiquimod therapy, the cause of wart
regression seen with
imiquimod therapy has not been established.
In vitro studies using isolated guinea pig myocardium, showed stimulation with
tachyphylaxis development after multiple doses. Moderate to marked inhibition
of agonist-
induced contractions was observed in isolated guinea pig tracheal strips.
Intravenous
231
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
administration of a bolus dose of imiquimod caused CNS and cardiac stimulation
in dogs. Little
activity was found in inflammatory rat models. Some local anaesthetic
activity, slight effect on
locomotor, and slight effect on hexobarbital induced sleep time were observed
in the mouse.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism: Animal and human dermal pharmacokinetic
results
indicate that minimal, if any, systemic absorption occurs following dermal
application of
imiquimod cream. Imiquimod was not quantifiable in the serum of rats dosed
topically three
times per week at 5 mg/kg for 4 weeks; low levels of metabolite were
quantifiable after the last,
but not after the first dose. In guinea pigs, after a single large (21 mg/kg)
topical dose of [14C]
imiquimod as a 5% cream, only low concentrations of imiquimod were
quantifiable in plasma.
Oral ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination) studies in
laboratory
animals, revealed extensive biotransformation followed by both urinary and
biliary excretion of
metabolites. Tissue distribution is rapid with clearance after 2 to 3 days
with the exception of
pigmented tissues - skin and uveal tract of the eye. No evidence of ocular
toxicity was found in
six month oral rat and monkey imiquimod toxicity studies conducted at high
daily doses.
Percutaneous absorption of 5% imiquimod cream following topical application
for 8-12
hours was observed across the intact skin of healthy subjects and the affected
skin of subjects
with either genital warts or AK. In subjects with AK, urinary recovery less
than 0.6% of the
applied dose was seen. Because of this low percutaneus absorption, serum
levels of imiquimod
and metabolites were low or undetectable in these subjects.
TOXICOLOGY
Acute Toxicity: Acute dermal toxicity studies in rabbits with unformulated
imiquimod
under occlusion did not reveal any toxic effects at very high dose levels -
5000 mg/kg. When
administered orally, intraperitoneally, subcutaneously or intravenously,
single dose studies
revealed that imiquimod produced central nervous system (CNS) stimulation and
convulsions at
lethal doses. However, signs of CNS toxicity did not occur when animals were
given lower
repeat doses (100 mg/kg or lower).
232
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Table 6
Species Route LD50 (mg/kg)
Mouse oral 403
intraperitoneal 879
Rat oral 1665
intraperitoneal 763
subcutaneous Ft, 20
Rabbit dermal > 5000
Monkey oral > 200
intravenous infusion 8
intravenous bolus > 6
Irritation/Sensitization Studies: Skin irritation studies in rabbits showed
that imiquimod
was non-irritating when dosed unformulated at 500 mg or formulated up to 250
mg per site.
Unformulated imiquimod produced mild or no eye irritation in rabbits when
applied
unformulated at 100 mg/eye or formulated up to 5 mg/eye. Formulated imiquimod
was not
irritating to rat or rabbit vaginal tract when applied every other day for 10
days at 10 and 50
mg/dose respectively. Dermal sensitization studies in guinea pigs showed that
the imiquimod
cream was not a dermal sensitizer. Comparison of the dermal reaction to
imiquimod cream in
animal species (rat, mouse, rabbit) with clinical study results, reveals that
mouse and rabbit
results are comparable to humans. The more severe dermal irritation seen in
the rat is not
predictive of human response.
Long-Term Toxicity: Two repeat dose dermal toxicity studies in rats showed a
compound
related but non-dose related dermal irritation. A dose-related decrease in
body weight of male
rats was also observed. No systemic toxicity was found at doses up to 5 mg/kg
three days per
week for 4 weeks or at doses up to 2.5 mg/kg three days per week for 16 weeks.
The adverse effects observed for the high doses (10-30 mg/kg) in repeat dose
oral toxicity
studies in rats and monkeys could be related to exaggerated pharmacological
effects of excessive
233
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
cytokines induction and lymphoid stimulation: reduced body weight gains,
anaemia, serum
protein changes and death. High repeat daily doses of imiquimod did not
produce necrosis in
any organ; the compound is not cytotoxic. Recovery animals demonstrated that
the adverse
effects were readily reversible. An oral no-adverse-effect level of 3
mg/kg/day was determined
in both rats and monkeys dosed daily for 6 months.
Carcinogenicity: Two-year bioassays in Wistar rats (up to 3 mg/kg orally per
day) and
CD-1 mice (up to 4.5 mg/kg applied topically 3 times per week) showed no
evidence of a
carcinogenic effect in male and female rats and female mice. Liver tumours
were increased in
male mice exposed to the highest dose concentration, compared to the unexposed
controls.
However, the number of tumours was within the range seen historically for male
CD-1 mice. It
is generally accepted that an increase in liver tumours in male mice, in the
absence of other
neoplastic responses in mice or rats, is not indicative of a carcinogenic risk
for humans.
In a photocarcinogenicity study in hairless mice, animals received imiquimod
cream 3
times per week at concentrations of 0.03%, 0.1% and 0.3% and were irradiated
with solar
ultraviolet light for 5 days each week for 40 weeks and observed an additional
12 weeks.
Vehicle cream enhanced UVR-induced skin tumour development. Imiquimod cream
had no
additional effect on tumour development beyond the vehicle effect (i.e., the
addition of the active
ingredient, imiquimod, to the vehicle cream did not result in an additional
effect beyond the
vehicle effect on tumour development).
Mutagenicity: Imiquimod was without effect in a series of eight mutagenicity
assays
including Ames, mouse lymphoma, CHO chromosome aberration, human lymphocyte
chromosome aberration, SHE cell transformation, rat and hamster bone marrow
cytogenetics,
and mouse dominant lethal test.
REFERENCES
1. Arany I, Tyring S, Stanley MA, Tomai MA, Miller RL, Smith MH et al.
Enhancement of the
innate and cellular immune response in patients with genital warts treated
with topical
imiquimod cream 5%. Antiviral Res 1999;43:55-63.
234
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
2. Berman B, Bienstock L, Kuritzky L, Mayeaux EJ, Jr., Tyring SK. Actinic
keratoses: sequelae
and treatments. Recommendations from a consensus panel. J Fam Pract. May
2006; 55(5)(suppl):1-8.
3. Bernstein DI, Harrison CJ. Effects of the Immunomodulating Agent R-837 on
Acute and
Latent Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Infections. Antimicro Agents and
Chemotherapy 1989;
33(9):1511-1515.
4. Bernstein DI, Miller RL, Harrison CJ. Effects of Therapy with an
Immunomodulator
(Imiquimod, R-837) Alone and with Acyclovir on Genital HSV-2 Infection in
Guinea-Pigs
When Begun After Lesion Development. Antiviral Res 1993; 20:45-55.
5. Dahl MV. Imiquimod: An immune response modifier. J Am Acad Dermatol
2000;43(1):S1-
5.
6. Edwards L. Imiquimod in clinical practice. J Am Acad Dermatol
2000;43(1):S12-17.
7. Edwards L, Ferenczy A, Eron L, Baker D, Owens ML, Fox TL et al. Self-
administered
topical 5% imiquimod cream for external anogenital warts. Arch Dermatol
1998;134:25-30.
8. Einspahr JG, Xu MJ, Warneke J, et al. Reproducibility and expression of
skin biomarkers in
sun-damaged skin and actinic keratoses. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prey. Oct
2006;15(10):1841-1848.
9. Gaspari AA, Sauder DN. Immunotherapy of basal cell carcinoma: evolving
approaches.
Dermatol Surg 2003;29(10):1027-1034.
10. Gollnick H, Barasso R, Jappe U, Ward K, Eul A, Carey-Yard M et al. Safety
and efficacy of
imiquimod 5% cream in the treatment of penile genital warts in uncircumcised
men when
applied three times weekly or once per day. Int J STD & AIDS 2001;12:22-28.
235
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
11. Harrison CJ, Miller RL, Bernstein DI. Posttherapy Suppression of Genital
Herpes Simplex
Virus (HSV) Recurrences and Enhancement of HSV-Specific T-Cell Memory by
Imiquimod
in Guinea Pigs. Antimicro Agents and Chemo 1994; 38(9):2059-2064.
12. Kende M, Lupton 11W, Canonico PG. Treatment of Experimental Viral
Infections with
Immuno-modulators. Adv Biosci 1988; 68:51-63.
13. Miller RL, Birmachu W, Gerster JF et al. Imiquimod Cytokine Induction and
Antiviral
Activity. Intl Antiviral News 1995; 3 (7):111-113.
14. Miller RL, Gerster JF, Owens ML, Slade HB, Tomai MA. Imiquimod applied
topically: a
novel immune response modifier and new class of drug. Int J Immunopharm
1999;21:1-14.
15. Quatresooz P, Pierard-Franchimont C, Paquet P, et al. Crossroads between
actinic keratosis
and squamous cell carcinoma, and novel pharmacological issues. Eur J Dermatol.
Jan-Feb
2008;18(1):6-10.
16. Sauder DN. Immunomodulatory and pharmacologic properties of imiquimods. J
Am Acad
Dermatol 2000;43(1):S6-11.
17. Stockfleth E, Ken l H. Guidelines for the management of actinic keratoses.
Eur J Dermatol.
Nov-Dec 2006;16(6):599-606.
18. Testerman TL, Gerster JF, Imbertson LM et al.
Cytokine Induction by the
Immunomodulators Imiquimod and S-27609. J Leuk Biol 1995; 58:365-372.
19. Tones A, Storey L, Anders M, et al. Microarray analysis of aberrant gene
expression in
actinic keratosis: effect of the Toll-like receptor-7 agonist imiquimod. Br J
Dermatol. Dec
2007;157(6):1132-47. Epub Oct 28 2007.
236
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
20. Tyring SK. Immune-response modifiers: A new paradigm in the treatment of
human
papillomavirus. Curr Ther Res 2000;60(9):584-596.
21. Tyring SK, Arany I, Stanley MA, Tomai MA, Miller RL, Smith MH et al. A
randomized,
controlled, molecular study of condylomata acuminata clearance during
treatment with
imiquimod. J Infect D is 1998 ;178(August):551 -555 .
22. Vatve M, Ortonne JP, Birch-Machin MA, Gupta G. Management of field change
in actinic
keratosis. Br J Dermatol. Dec 2007;157(s2):21-24.
23. Weeks CE, Gibson SJ. Induction of Interferon and Other Cytokines by
Imiquimod and its
Hydroxylated Metabolite R-842 in Human Blood Cells In Vitro. J Interferon Res
1994;
14:81-85.
24. Lebwohl M, Dinehart S, Whiting D, Lee PK, Tawfik N, Jorizzo J, Lee JH, Fox
TL et al.
Imiquimod 5% cream for the treatment of actinic keratosis: Results from two
phase III,
randomized, double-blind, parallel group, vehicle-controlled trials. J Am Acad
Dermatol
May 2004;50(5):714-21.
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION
Pr Zyclara
(imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%
This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when
Zyclara
was approved for sale in Canada and is designed specifically for Consumers.
This leaflet is a
summary and will not tell you everything about Zyclara . Contact your doctor
or pharmacist if
you have any questions about the drug.
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION
What the medication is used for:
237
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Zyclara is the brand name for imiquimod cream, 3.75%. It is used to treat
actinic
keratosis (AK) in adults with normal immune systems. Actinic keratosis may be
caused by too
much sun exposure.
What it does:
Zyclara cream is an immune response modifier. Zyclara Cream is a medicine
that
works by stimulating your body's own immune response.
When it should not be used:
Zyclara Cream can only be used if a doctor prescribes it for you.
Zyclara Cream should only be used on the skin.
What the medicinal ingredient is:
Zyclara Cream contains 37.5 mg of imiquimod per gram.
What the important nonmedicinal ingredients are:
Isostearic acid, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, white petrolatum, polysorbate
60, sorbitan
monostearate, glycerin, xanthan gum, purified water, benzyl alcohol,
methylparaben, and
propylparaben.
For a full listing of nonmedicinal ingredients see Part I of the product
monograph.
What dosage forms it comes in:
Zyclara Cream is supplied in single-use packets which contain 250 mg of the
cream. It
is available as boxes of XX packets.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
= Only use on the affected area of your skin.
= Use this Zyclarag Cream the way your doctor showed you.
238
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Do not rub Zyclara Cream in your eyes, lips or nostrils.
= If you get Zyclara Cream in your eyes, wash your eyes out with abundant
amounts of water.
= Wear a hat, long sleeves and use sunscreen if you must be out in the sun.
Avoid
natural or artificial sunlight, for example tanning salons, as much as
possible.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in
patient
information leaflets. Do not use Zyclara Cream for a condition for which it
was not prescribed.
Do not give Zyclara Cream to other people, even if they have the same
symptoms you have.
BEFORE you use Zyclara talk to your doctor or pharmacist if:
= you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to Zyclara Cream.
= you have any allergies.
= you are thinking about having a baby, pregnant (about to have a baby), or
breast-
feeding your baby.
= you have had any other treatment for your Actinic Keratosis:
- any prescription and over-the-counter drugs you have used.
- any other non-drug treatments you have had for your condition.
- for example, freezing or surgery.
Zyclara Cream should not be used while pregnant or breast-feeding unless your
doctor
tells you to.
INTERACTIONS WITH THIS MEDICATION
Drugs that may interact with Zyclara include: none.
PROPER USE OF THIS MEDICATION
Usual dose:
239
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Use Zyclara Cream exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Zyclara Cream is for skin use only. Do not take by mouth or use in or near
your eyes, lips or
nostrils. Do not use Zyclara Cream unless your healthcare provider has taught
you the right
way to use it. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
= Your healthcare provider will tell you where to apply Zyclara Cream and
how
often and for how long to apply it for your condition. Do not use Zyclara
Cream longer than
prescribed. Using too much Zyclara Cream, or using it too often, or for too
long can increase
your chances for having a severe skin reaction or other side effect. Talk to
your healthcare
provider if Zyclara Cream does not work for you.
= Zyclara Cream is applied once a day for two-weeks. There is no treatment
for
the next two weeks. Zyclarae Cream is then applied once a day for another two-
weeks.
= Do not cover the treated site with bandages or other closed dressings.
Cotton
gauze dressings are okay to use, if needed.
= Do not apply Zyclara Cream in or near the eyes, lips or nostrils.
= Do not use sunlamps or tanning beds, and avoid sunlight as much as
possible
during treatment with Zyclara Cream. Use sunscreen and wear protective
clothing if you go
outside during daylight.
Zyclara Cream is usually left on the skin for about 8 hours. Treatment should
continue
for the full treatment course even if all actinic keratoses appear to be gone,
unless you are told
otherwise by your healthcare provider. Zyclara Cream should be used to treat
either the whole
face or balding scalp.
Applying Zyclara Cream
Zyclara Cream should be applied just before your bedtime.
= Wash the area to be treated with mild soap and water. Allow the area to
dry.
= Wash your hands
= Open a new packet(s) of Zyclara Cream just before use
= Apply a thin layer of Zyclara Cream only to the affected area or areas
to be
treated. Do not use more Zyclara Cream than is needed to cover the treatment
area. Do not use
more than two packets for each application.
240
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= Rub the Zyclara Cream in all the way to the affected area or areas.
o Do not get Zyclara Cream in or around your eyes.
= Safely throw away the open packet of Zyclara Cream so that children and
pets
cannot get it. The open packet should be thrown away even if all the Zyclara
Cream was not
completely used.
= After applying Zyclara Cream, wash your hands well.
= Leave the Cream on the affected area or areas for the time prescribed by
your
healthcare provider. Do not bathe or get the treated area wet before the right
time has passed. Do
not leave Zyclara Cream on your skin longer than prescribed.
= After about 8 hours, wash the treated area or areas with mild soap and
water.
= If you forget to apply Zyclara Cream, continue on your regular schedule
and do
not make up the missed dose(s).
= If you get Zyclara Cream in your mouth or in your eyes rinse well with
water
right away.
= Use ZyclaraiD Cream daily for 2-week treatment cycles, unless otherwise
directed
by the physician.
= The treatment period should not be extended beyond two 2-week treatment
cycles
weeks due to missed does or rest periods.
Overdose:
Persistent topical overdosing of Zyclara Cream could result in an increased
incidence of
severe local skin reactions and may increase the risk for systemic reactions.
Missed Dose:
If you miss a dose of Zyclara Cream, wait until the next night to apply it.
SIDE EFFECTS AND WHAT TO DO ABOUT THEM
Side effects with Zyclara Cream may include skin reactions at the treatment
site such
as:
= redness
241
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
= swelling
= a sore, blister, or ulcer
= skin that becomes hard or thickened
= skin peeling
= scabbing and crusting
= itching
= burning
= changes in skin color that do not always go away
During treatment and until the skin has healed, your skin in the treatment
area is likely to
appear noticeably different from normal skin. Side effects, such as redness,
scabbing, itching
and burning are common at the site where Zyclara Cream is applied, and
sometimes the side
effects go outside of the area where Zyclara Cream was applied. Swelling,
small open sores
and drainage may also be experienced with use of Zyclara Cream. You may also
experience
itching, irritation or pain. Actinic keratoses that were not seen before may
appear during
treatment and may later go away. If you have questions regarding treatment or
skin reactions,
please talk with your healthcare provider.
You have a higher chance for severe skin reactions if you use too much Zyclara
Cream
or use it the wrong way. Stop Zyclara Cream right away and call your
healthcare provider if
you get any skin reactions that affect your daily activities, or that do not
go away. Sometimes,
Zyclara Cream must be stopped for a while to allow your skin to heal. Talk to
your healthcare
provider if you have questions about your treatment or skin reactions.
Other side effects of Zyclara Cream include headache, back pain, muscle
aches, joint
aches, tiredness, flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, nausea and diarrhea.
If the reactions seem excessive, if either skin breaks down or sores develop
during the
first week of treatment, if flu-like symptoms develop or if you begin to not
feel well at anytime,
stop applying Zyclara Cream and contact your healthcare provider.
242
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
These are not all the side effects of Zyclara Cream. For more information,
ask your
healthcare provider or pharmacist.
This is not a complete list of side effects. For any unexpected effects while
taking
Zyclara , contact your doctor or pharmacist.
HOW TO STORE IT
Store Zyclara Cream between 15-25 C. Do not freeze.
Safely throw away Zyclara Cream that is out of date or that you do not need.
Keep Zyclara Cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
REPORTING SUSPECTED SIDE EFFECTS
To monitor drug safety, Health Canada through the Canada Vigilance Program
collects
information on serious and unexpected effects of drugs. If you suspect you
have had a serious or
unexpected reaction to this drug you may notify Canada Vigilance:
Toll-free telephone: 1-866-234-2345
Toll-free fax: 1-866-678-6789
Online: www.healthcanada.gc.ca/medeffect
By email: CanadaVigilance@hcsc.gc.ca
By regular mail:
Canada Vigilance National Office
Marketed Health Products Safety and Effectiveness
Information Bureau
Marketed Health Products Directorate
Health Products and Food Branch
Health Canada
Tunney's Pasture, AL 0701C
Ottawa, ON KlA 0K9
243
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
NOTE: Should you require information related to the management of the side
effect,
please contact your healthcare provider before notiffing Canada Vigilance. The
Canada
Vigilance Program does not provide medical advice.
MORE INFORMATION
This document plus the full product monograph, prepared for health
professionals can be
found at:
http://www.gracewaypharma.ca or by contacting the sponsor, Graceway
Pharmaceuticals,
at: 1-800-328-0255
This leaflet was prepared by Graceway Pharmaceuticals, 252 Pall Mall St.,
Suite 302,
London, Ontario, N6A 5P6
Last revised: January 13, 2009
244
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Attachment XII
[000321] CANADA PRODUCT MONOGRAPH
(External Genital and Perianal Warts)
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH
ZYCLARA
(imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%
9.4 mg per 250 mg single-dose packet
Immune response modifier
Graceway Pharmaceuticals Date of Preparation:
252 Pall Mall St., Suite 302 March 24, 2010
London, Ontario
Canada
N6A 5P6
Submission Control No.:
TABLE OF CONTENTS
245
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
PART I: HEALTH PROFESSIONAL INFORMATION .................................... 3
SUMMARY PRODUCT INFORMATION ................................................ 3
INDICATIONS AND CLINICAL USE ............................................... 3
CONTRAINDICATIONS .......................................................... 4
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ................................................... 4
ADVERSE REACTIONS .......................................................... 6
DRUG INTERACTIONS .......................................................... 8
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION .................................................. 8
OVERDOSAGE .................................................................
10
ACTION AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ...........................................
10
STORAGE AND STABILITY ......................................................
11
DOSAGE FORMS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING ....................................
11
PART II: SCIENTIFIC INFORMATION ............................................
12
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION .................................................
12
CLINICAL TRIALS ............................................................
13
DETAILED PHARMACOLOGY ......................................................
15
TOXICOLOGY .................................................................
16
REFERENCES .................................................................
19
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION .............................................
21
Zyclara (imiquimod) Cream, 3.75%
PART I: HEALTH PROFESSIONAL INFORMATION
SUMMARY PRODUCT INFORMATION
Route of Dosage Form/ Clinically Relevant Nonmedicinal
Administration Strength Ingredients
Topical Cream / 9.4 mg For a complete listing see Dosage
imiquimod per 230 Forms, Composition and
mg single-close Packaging, section.
packet
(3.75 w/w)
INDICATIONS AND CLINICAL USE
Zyclara Cream is indicated for the treatment of external genital and perianal
warts/condyloma acuminate, whether present at the start of therapy or emerging
during therapy
in patients 12 years or older.
Geriatrics (>65 years of age)
246
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
Data from EGW clinical trials was too sparse to evaluate treatment effects in
this
population (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Geriatrics).
Pediatrics
Safety and efficacy in patients below the age of 12 years have not been
established (See
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Pediatrics).
Immunosuppressed
The safety and efficacy of Zyclarao Cream in immunosuppressed patients have
not been
established (SEE WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Immune).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Zyclara Cream is contraindicated in individuals with a history of sensitivity
reactions to
imiquimod or to any of the components in the formulation. It should be
discontinued if
hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients is noted (See WARNINGS AND
PRECAUTIONS,
Sensitivity).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
General
Zyclara Cream has not been evaluated for the treatment of urethral, intra
vaginal,
cervical, rectal, or intra-anal human papilloma viral disease.
Systemic Reactions
Flu-like signs and symptoms may accompanyõor even precede, local skin
reactions and
may include fatigue, nausea, fever, myalgias, arthralgias, and chills. An
interruption of dosing or
dose adjustment and an assessment of the patient should be considered (See
ADVERSE
REACTIONS)
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
In a hairless mouse photocarcinogenicity study with solar ultraviolet light
irradiation,
imiquimod cream enhanced UVR-induced skin tumour development, but not beyond
that of the
247
CA 02713777 2013-03-07
vehicle cream. Vehicle cream alone enhanced ultraviolet; induced skin tumour
development
(See TOXICOLOGY, Carcinogenicity). It is recommended that patients minimize or
avoid
natural or artificial sunlight exposure to the treatment area(s) during
treatment with Zyclara .
Immune
The safety and efficacy of Zyclara Cream in immunosuppressed patients have
not been
established.
Zyclara o topical Cream should be used with caution in patients with pre-
existing
autoimmune conditions (including thyroiditis, multiple sclerosis,
spondyloarthropathy, psoriasis,
ulcerative colitis) (See ADVERSE REACTIONS Post-Market Adverse, Drug
Reactions).
Sensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria) and erythema multiforme have been
reported in
patients receiving, imiquimod cream, however causality has not been
established. Zyclarao
Cream should be discontinued immediately if these events occur.
Skin
Local skin reactions such as erythema, scabbing/crusting,
flaking/scaling/dryness, and
edema are common.
Intense local skin reactions including erythema, scabbing/crusting and
erosion/ulceration
can occur after a few applications of Zyclara Cream and may require an
interruption of dosing
(See ADVERSE REACTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION)
ZyclaraiD Cream has the potential to exacerbate inflammatory conditions of the
skin,
including chronic graft versus host disease.
Administration of Zyclara Cream is not recommended until the skin is healed
from any
previous drug or surgical treatment.
248
DEMANDES OU BREVETS VOLUMINEUX
LA PRESENTE PARTIE DE CETTE DEMANDE OU CE BREVETS
COMPREND PLUS D'UN TOME.
CECI EST LE TOME 1 DE 2
NOTE: Pour les tomes additionels, veillez contacter le Bureau Canadien des
Brevets.
JUMBO APPLICATIONS / PATENTS
THIS SECTION OF THE APPLICATION / PATENT CONTAINS MORE
THAN ONE VOLUME.
THIS IS VOLUME 1 OF 2
NOTE: For additional volumes please contact the Canadian Patent Office.