Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 1 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
Patch transfer and inspection device
Description:
The invention relates to an interlinked device for
producing sealed packaging units, with a clocked
delivery device for web-like material, with a
separating device for separating in each case at least
one portion of the web-like material, with a clocked
packaging device, and with a sealing device, the sum of
the stoppage intervals per cycle of the delivery device
differing from the sum of the stoppage intervals per
cycle of the packaging device, and a method for
producing such a packaging unit.
Sealed packaging units, which are used for example for
therapeutic systems or for wafers containing active
substances, are in most cases produced in an
interlinked production process that ranges from the
manufacture of the systems to the packaging in
packaging units. For example, single-layer or multi-
layer material webs are produced, shaped cuts are
introduced, and the systems imprinted. During this
manufacture, a so-called release liner, for example, is
used as system carrier. It is only directly before the
packaging station that individual portions are
separated from this carrier for singulation of the
systems and are placed between the packaging material
webs. They are then carried along with the packaging
material webs and sealed within these by means of the
sealing device.
The individual separated portion may have geometric
defects or positioning errors. For example, it may be
too long or too short. It is also possible for narrow
portions to be inadvertently sealed in individually or
in addition to a geometrically correct portion. There
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 2 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
is also a danger of part of the separated portion
falling into the area of the sealing seam. Inspecting
the content of the packaging unit prior to the
packaging operation is not possible in the arrangement
used hitherto.
The object of the present invention is therefore to
develop a device and a method for producing packaging
units in an interlinked device, in which the content of
the packaging unit can be inspected.
This object is achieved by the features of the main
claim. To this end, the device comprises an
intermediate conveyor device which, in the material
flow, is arranged between the delivery device and the
packaging device. Moreover, an optical inspection
device is arranged on the intermediate conveyor device
and used at least for geometric inspection of the
separated portion.
In the production process, a web-like starting material
is delivered in a clocked manner. During a stoppage
interval of the delivery device, portions of the web-
like starting material are separated from the web-like
starting material by means of a separating device. An
optical inspection device inspects these portions at
least geometrically on an intermediate conveyor device
arranged downstream of the separating device in the
material flow. A lower packaging material web and an
upper packaging material web are delivered in a clocked
packaging device. The intermediate conveyor device
transfers the portions between the packaging material
webs. During a stoppage interval of the packaging
device, the packaging material webs are sealed in a
sealing device such that the packaging unit is closed
in a moisture-tight and aroma-tight manner.
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 3 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
Further details of the invention will become evident
from the dependent claims and from the following
description of schematically depicted embodiments.
Figure 1: device for producing packaging units;
Figure 2: path-time diagram of the delivery
device;
Figure 3: path-time diagram of the intermediate
conveyor device;
Figure 4: path-time diagram of the packaging
device.
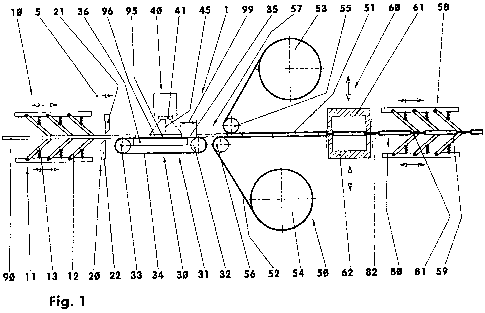
Figure 1 shows an interlinked device (1) for producing
packaging units (80), for example for medical products
such as transdermal therapeutic systems (95) or wafers
(95) containing active substances. The device (1)
comprises a delivery device (10), a separating device
(20), an intermediate conveyor device (30), an
inspection device (40), a packaging device (50), and a
sealing device (60). In this illustrative embodiment,
all of said parts (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60) of the
device (1) are rigidly interlinked one after another in
the material flow without buffers. This means that any
malfunction of a part (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60) or in a
part (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60) of the device (1)
adversely affects the material flow and the
availability of the whole device (1).
The starting material for the item (95) to be packaged
is a web-like material (90) which is conveyed by means
of the delivery device (10). The delivery device (10)
for this purpose comprises an intermittent conveyor
(11). The stroke cycle of an intermittent conveyor (11)
comprises a delivery stroke and a return stroke. The
return stroke is an idle stroke which runs counter to
the conveying direction (5) and in which the load-
bearing parts return to their starting position. In the
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 4 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
illustrative embodiment shown here, the intermittent
conveyor (11) comprises feeding pincers (12) which
engage the web-like material (90) from below and from
above, for example at its outer edges. Several feeding
pincers (12) have, for example, a common drive
mechanism for advancing the material. In the
illustrative embodiment, they are in each case clamped
with spring loading by a compression spring (13). If
appropriate, the clamping can also be effected via a
common drive mechanism, or a common drive mechanism can
effect both the clamping and the advancing movement.
Instead of using the feeding pincers (12), the web-like
material (90) can also be advanced by means of grippers
or other intermittent conveyors (11).
In the illustrative embodiment, the separating device
(20) comprises two intersecting knives (21, 22), of
which one (21) is arranged above, and the other (22)
below, the web-like material (90).
To convey the web-like material (90), it is first of
all clamped by means of the feeding pincers (12) . The
advancing drive mechanism, which has a predefined
stroke, for example, then pushes the web-like material
(90) in the direction of the separating device (20). As
soon as the end position of the stroke is reached, the
separating device (20) separates a portion (95) of the
web-like material (90). This portion (95) is, for
example, a transdermal therapeutic system (95) or a
wafer (95). During the separating operation, the
delivery device (10) is stopped. The feeding pincers
(11) are now opened and, by means of the advancing
drive mechanism, travel to the starting position
arranged away from the separating device (20). The next
conveying cycle of the intermittent conveyor (11) now
begins. If appropriate, the separating device (20) can
also be actuated only after every second advance cycle
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 5 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
or after another whole-number multiple of an advance
cycle. This results from the ratio of the length of a
wafer (95) to the advance stroke.
Figure 2 shows a path-time diagram of the advance
movement of the web-like material (90). In this
diagram, an abrupt change of speed is assumed for
reasons of simplicity, and the acceleration and
deceleration paths and times are not shown. The time
(t) is plotted on the abscissa, e.g. in seconds, and
the path traveled (s) is plotted on the ordinates, e.g.
in millimeters. The gradient of the resulting curve -
the mathematical first derivation of the path function
over time - is a measure of the speed of advance of the
delivery device (10).
The web-like material (90) is advanced, for example, at
constant speed as far as time point (121). From this
time point (121), the web-like material (90) is
stopped. For example, during a time interval (102) that
lasts up to time point (124), a portion (95) of the
web-like material (90) is separated and the feeding
pincers (12) are moved back to the starting position
relative to the device (1). They engage the web-like
material (90) in the next segment. Starting from time
point (124), the web-like material (90) is conveyed
onward in the direction of the separating device (20).
The conveying speed in the time interval . (103)
beginning at time point (124) corresponds to the
conveying speed in the time interval (101) between the
origin of the coordinates and time point (121).
As the web-like material (90) is being conveyed, it
passes through a cutting plane defined by the
separating device (20). The end lying at the front in
the conveying direction (5) places itself flat, for
example, on the moving intermediate conveyor device
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 6 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
(30) and is taken up by the latter. The conveying speed
of the intermediate conveyor device (30) corresponds,
for example, to the conveying speed of the delivery
device (10). After the time interval (102), which
corresponds for example to the quotient of the wafer
length and the conveying speed of the delivery device
(10), both the delivery device (10) and the
intermediate conveyor device (30) are stopped, and the
part of the web-like material (90) passing through the
cutting plane is cut off as portion (95).
The intermediate conveyor device (30) comprises a
continuous conveyor (31) which is driven by means of a
servo motor via a driving drum (32) and is guided by
means of a guide drum (33). In a continuous conveyor
(31), there is no reversal of the stroke direction. The
conveyor means is guided back during the conveying
operation to its starting point. The conveyor means
(34) of this continuous conveyor (31) is, for example,
a continuously circling endless conveyor belt (34). The
latter has, for example, a plurality of apertures, for
example having a mesh-like structure. A suction device
(36) is arranged below the upper load strand (35) of
the conveyor belt (34). In the area between the driving
drum (32) and the guide drum (33), this suction device
(36) sucks the portions (95) lying on the load strand
(35), which load portions (95) are thus pressed onto
the load strand (35) and are conveyed in the conveying
direction (5) without slip.
Figure 3 shows a simplified path-time diagram of the
portions (95) conveyed by means of the intermediate
conveyor device (30). The abscissa and ordinate scales
correspond for example to the corresponding scales in
Figure 2. Starting from the origin of the coordinates
(the origin of the time axis in Figure 3 corresponds,
for example, to the origin of the time axis in Figure
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 7 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
2), the path change per unit of time is constant up to
a time point (121), as a result of which the path-time
diagram is depicted as a straight line. The constant
gradient, which corresponds to a constant speed, is
identical, for example, to the gradient of the curve
shown in Figure 2 between the origin of the coordinates
and time point (121) and in the time interval (103)
following time point (124).
In the time interval (105) between time point (121) and
time point (122), the conveying operation of the
intermediate conveyor device (30) is interrupted. In
this time interval (105), the separating device (20)
cuts off a portion (95) of the web-like material (90).
Starting from time point (122), the intermediate
conveyor device (30) conveys the separated portion (95)
onward. In the following time interval (106) in which
the delivery device (10) is stopped, the separated
portion (95) travels a distance, for example, that
corresponds to the length difference of a packaging
unit (80) and of a portion (95). In this time interval
(106), the conveying speed of the portions (95) can be
higher or lower than the conveying speed of the web-
like material (90) outside of the stoppage times.
At time point (124), a new cycle then begins, for
example one that is constructed analogously to the
cycle beginning at the origin of the coordinates. The
cycle length of the delivery device (10) is identical
to the cycle length of the intermediate conveyor device
(30). The sum of conveying intervals (101; 103) and of
stoppage intervals (102) of the delivery device (10)
thus corresponds to the sum of the conveying intervals
(104, 106; 107) and stoppage intervals (105) of the
intermediate conveyor device (30).
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 8 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
Instead of a continuous conveyor (31), the intermediate
conveyor device (30) can also comprise an intermittent
conveyor. The return stroke times of an intermittent
conveyor then lie in the stoppage interval (105) of the
intermediate conveyor device (30) described.
An inspection device (40) is arranged above the load
strand (35). It comprises, for example, an optical
camera (41) which is connected, for example, to a
comparator unit (not shown here). By means of this
comparator unit, the geometric dimensions of the
surface (96) of each portion (95) lying on the conveyor
belt (34) are compared with a stored setpoint value
during the stoppage interval (105) of the intermediate
conveyor device (3 0) . If the inspected portion (95) is
too large or too small, or if it is lying askew on the
conveyor belt (34), it is marked, for example, or
ejected. The imprinting of the portion (95) can also be
monitored by means of this inspection device (40).
The inspection of a portion (95) takes place, for
example, in a stoppage interval during the cycle
following its separation stoppage interval (105).
Accordingly, the distance between the center line (45)
of the inspection device (40) and the separating device
(20) is the sum of the length of a packaging unit (80)
and half the length of a portion (95) or the sum of the
whole-number multiple of the length of a packaging unit
(80) and half the length of a portion (95). The
inspection device (40) can be adjusted in the
lengthwise direction of the device (1) in order to
adapt the latter to another length of packaging unit
(80) or to another portion length (95).
It is also conceivable for the inspection to be carried
out during the conveying of the intermediate conveyor
device (30). In this case, the position of the
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 9 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
inspection device (40) relative to the separating
device (20) can be chosen freely.
As soon as the portions (95) conveyed by means of the
intermediate conveyor device (30) have left the area of
influence of the suction device (36), they lie only
loosely on the load strand (35) of the conveyor belt
(34). On reaching the driving drum (32), they are
transferred, flat for example, onto the packaging
device (50). The individual portions (95) reach the
packaging device (50) in a clocked sequence. Here, the
time intervals between the times of arrival of the
individual portions (95) at the packaging unit (50) are
constant. Since, in this illustrative embodiment, each
portion (95) is received directly by the packaging
device (50), without waiting time, there is no buffer
and no waiting line.
The packaging device (50) comprises an upper packaging
material web (51), a lower packaging material web (52),
and an intermittent conveyor (58) with feeding pincers
(59). The upper and lower packaging material webs (51,
52) are each wound in lengths of several hundred meters
onto reels (53, 54) and each have a width of between
250 millimeters and 2500 millimeters depending on the
number of packaging units (80) produced in parallel.
The lower packaging material web (52) is guided from
the reel (54) to the transfer site (57), e.g. via a
guide roller (56). At a location offset from this in
the conveying direction (5), the upper packaging
material web (51) is guided via a guide roller (55)
into the conveying direction (5) parallel to the lower
packaging material web (52).
Next to the site of transfer to the packaging device
(50), the individual portion (95) lies on the lower
packaging material web (52). The feeding pincers (59),
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 10 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
configured analogously for example to the feeding
pincers (12) of the delivery device (10), convey the
packaging material webs (51, 52), equipped with the
portions (95), in the conveying direction (5) . In this
case, for example, an advance equal to the length of a
packaging unit (80) takes place in each cycle. The
feeding pincers (59) can also be configured such that
the advance equal to the length of a packaging unit
(80) takes place in two cycles or in several whole-
number cycles. The length of a packaging unit (80)
corresponds to the sum of the length of a portion (95)
and of both protruding areas of the packaging material
webs (51, 52), which protruding areas are oriented in
the longitudinal direction of the device (1) shown in
Figure 1 and are used for sealing.
During stoppage of the intermittent conveyor (58), the
feeding pincers (59) are moved back to their starting
position in order to continue conveying. As soon as the
conveying path corresponds to the length of a packaging
unit (80), the sealing device (60) is closed. For
example, by means of an upper part (61) and lower part
(62) of the sealing device (60), the upper and lower
packaging material webs (51, 52) are sealed together,
for example with simultaneous heating, to form a
moisture-tight and aroma-tight closure. In the
illustrative embodiment, the sealing is carried out at
four seams surrounding the individual portion (95),
resulting in what is called a four-edge sealed bag. The
latter is separated from the packaging material webs
(51, 52) in a downstream separating station not shown
here.
The position of the sealing device (60) relative to the
device (1) can be adjusted, for example. In this way,
the device (1) can be adapted to different portion
and/or package lengths.
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 11 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
Figure 4 shows a simplified path-time diagram of the
packaging device (50). The scales of the abscissa and
of the ordinates in this figure correspond, for
example, to the abscissa and ordinates scales of
Figures 2 and 3. The origin of the time axis in Figure
4 corresponds, for example, to the origin of the time
axis in Figures 2 and 3.
The transfer of a portion (95) between the packaging
material webs (51, 52) at the transfer site (57) is
described on the basis of the time interval (110 - 112)
delimited by time points (122) and (126).
After a stoppage, the conveying operation of the
packaging device (50) begins, for example, at time
point (122). Starting from time point (123), a portion
(95) is transferred to the packaging device (50) in the
conveying interval (111). This transfer ends, for
example, at time point (125). However, the intermittent
conveyor (58) continues to convey throughout the
subsequent time interval (112). The end position of the
stroke of the intermittent conveyor (58) is reached at
time point (126). The path covered by the packaging
webs (51, 52) throughout this conveying interval (110 -
112) corresponds to the length of a packaging unit
(80). The paths traveled in the time intervals (110)
and (112) in the illustrative embodiment correspond to
the length of the forward and rear sealing areas (81,
82) in the conveying direction (5). The path traveled
in the time interval (111) by the packaging material
webs (51, 52), which are moved in synchrony, for
example with a constant conveying speed, corresponds to
the length of a portion (95).
The time point (126) is followed by a stoppage interval
whose length corresponds to the stoppage interval
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 12 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
(109). The sealing of the packaging material webs (51,
52) and the return stroke of the intermittent conveyor
(58) take place, for example, during this stoppage
interval (109). This stoppage interval (109) is not
identical to the stoppage interval (102) of the
delivery device (10). It is shorter in the illustrative
embodiment. A new cycle of the packaging device (50)
begins after the stoppage interval (109).
The transfer of the portion (95) at the transfer site
(57) can also be interrupted by a stoppage of the
conveyor devices (30, 58).
The distances (99) between the portions (95) on the
intermediate conveyor device (30) correspond to the
length of two sealing areas (81, 82), which is the
difference between the length of the packaging unit
(80) and of an individual portion (95) . A sealing area
(81; 82) comprises the sealing seam and the protruding
area of the corresponding packaging materials (51, 52).
In relation to the delivery device (10), this means
that the stoppage interval (102) of the delivery device
(10) is equal to the sum of the stoppage interval (109)
of the packaging device (50) and the quotient of the
distance (99) and the conveying speed of the
intermediate conveyor device (30). The conveying speed
of the intermediate conveyor device (30) corresponds in
the illustrative embodiment to the conveying speed of
the packaging device (50) . These two speeds can differ
from each other, e.g. by 3 percent. They are therefore
at least approximately the same.
To control the device, the packaging device (50)
comprises, for example, an incremental sensor (not
shown here). By means of this incremental sensor, for
example, a clock signal of the packaging device (50),
e.g. the end of the sealing operation, is forwarded to
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 13 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
an evaluation device. From this signal, it is then
possible to derive a control signal, for example, for
the servomotor of the intermediate conveyor device
(30). This signal can also be used to control the ratio
between stoppage interval (102) and conveying interval
(101; 103) of the delivery device (10). Exact
positioning of the individual portion (95) between the
packaging material webs (51, 52) is thus ensured.
The intermediate conveyor device (30) can comprise a
buffer. For example, the suction device (36) then
covers only a partial area of the load strand (35). A
catch arranged outside the area of action of the
suction device (36), and controlled by the packaging
device (50) for example, then releases in each case one
portion (95) for further processing.
It is also conceivable for the individual conveyor
devices (10, 30, 50) to operate at different heights.
For example, the separating device (20) is then
arranged above the intermediate conveyor device (30),
and the intermediate conveyor device (30) is arranged
above the lower packaging material web (52). In such an
embodiment, the separated portion (95) then falls onto
the intermediate conveyor device (30) and from the
latter onto the lower packaging material web (52). In
such an embodiment, the conveying speeds of the
individual conveyor devices (10, 30, 50) can be
different. For example, the stoppage interval (109) of
the packaging device (50) can be greater than the
stoppage interval (102) of the delivery device (10).
However, the cycle interval - the sum of the respective
conveying interval. and of the respective stoppage
interval - at least of the packaging device (50) and of
the delivery device (10) is approximately equal.
Variations can be compensated, for example, by means of
the buffer described above.
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 14 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
If appropriate, the inspection device (40) can also
control the packaging device (50). In such an
embodiment, for example, the detection of 'a portion
(95) by means of the inspection device (40) triggers a
new cycle of the packaging device (50).
Combinations of the described illustrative embodiments
are also conceivable.
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 15 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
List of reference signs:
1 device
5 conveying direction
delivery device
11 intermittent conveyor
10 12 feeding pincers
13 compression spring
separating device
21 knife, top
15 22 knife, bottom
intermediate conveyor device
31 continuous conveyor
32 driving drum
20 33 guide drum
34 conveyor means, conveyor belt
load strand
36 suction device
25 40 inspection device
41 camera
center line
30 50 packaging device
51 upper packaging material web
52 lower packaging material web
53 reel
54 reel
35 55 guide roller
56 guide roller
57 transfer site
CA 02719090 2010-09-21
W02009/129888 - 16 -
PCT/EP2009/001447
58 intermittent conveyor
59 feeding pincers
60 sealing device
61 upper part of (60)
62 lower part of (60)
80 packaging units
81 seal area, forward
82 seal area, rear
90 web-like material
95 portions, transdermal therapeutic systems,
wafers, items to be packaged
96 surface
99 distances
101 time interval, conveying interval
102 stoppage interval
103 - 104 time interval, conveying interval
105 stoppage interval
106 - 108 time interval, conveying interval
109 stoppage interval
110 - 112 time interval, conveying interval
121 - 126 time points
s path
t time