Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
CUSHIONING DEVICE
Background of The Invention
The subject invention is directed to cushioning devices comprising a
pressure sensitive adhesive. In particular, the invention concerns the use of
pressure sensitive adhesive materials to improve the hold of soft gel
cushioning
devices. One of the key attributes of the footwear cushions is to prevent the
footwear from rubbing sensitive areas of skin, in particular in the heel area.
5 However, in order to achieve all the desired attributes of the cushion, the
cushion
needs to stay in place firmly during movement associated with normal use of
footwear. Cushioning devices made of soft gels are known in the art and are
desirable for their comfort, flexibility, durability and look. The assignee of
this
invention, Schering-Plough Healthcare Products, Inc., markets a cushioning
2 0 device under the trade name Dr. Scholl'sO Gel Heel Liner, which comprises
a
thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) film bonded to a polyurethane (PU) gel, where
the PU gel is produced in a way to have a sticky surface. However, no
additional
adhesive is used in this product. The Heel Liner is packaged with a release
film to
preserve the tackiness of the PU gel sticky surface, which is then applied to
the
25 shoe to hold the liner in place. The TPU film provides a nonstick surface
opposite
the sticky surface, which nonstick contacts the wearers foot, sock, or
hosiery.
It has now been determined, however, that the sticky PU gel does not hold
the liner in place for extended periods of use as may be desired for a
cushioning
element. Pressure sensitive adhesive materials have been used in the art.
0
30 However, direct modification of a sticky PU gel with a pressure sensitive
adhesive
did not produce a cushioning element with a stronger hold. Thus, a cushioning
device that provides the benefit of a gel and provides for long term hold in
the
shoe where placed would be desirable. Further, a method of manufacturing a gel
cushioning device with a pressure sensitive adhesive would also be desirable.
These and other advantages follow from the invention described and claimed
here.
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
2
Summary Of The Invention
The subject invention provides a cushioning device comprising a layer of
polyurethane gel material comprising top and bottom surfaces, at least one
layer
of thermoplastic polyurethane film material bonded to the one or both of said
top
and bottom surfaces thereof, and a layer of pressure sensitive adhesive bonded
to one of said at least one thermoplastic polyurethane film material, wherein
the
pressure sensitive adhesive is located on a surface of the thermoplastic
polyurethane film opposite to the surface contacting said bottom surface of
said
polyurethane gel material.
The subject invention also provides a get cushioning device comprising a
sticky surface, the device comprising a gel material bound to a thermoplastic
film
material having good compatibility with the gel material, wherein the
thermoplastic
film material further comprises a pressure sensitive adhesive located on a
surface
of the film material opposite to the surface that is bonded to the gel
material.
2 W The subject invention further provides gel cushioning device comprising a
sticky surface, the device comprising a layer of gel material having an upper
and
lower surface and two layers of thermoplastic film material, each film
material
comprising upper and lower surfaces, wherein the upper surface of the gel
material is bonded with the lower surface of one of said layers of film
material and
25 the lower surface of the gel material is bonded with the upper surface of
the other
of said layers of film material, wherein at least one of the layers of film
material
comprises a pressure sensitive adhesive on a surface opposite the surface
bonded to the gel material thereby providing the sticky surface of the device.
The subject invention also provides a method of constructing a gel
cushioning device comprising a sticky surface, which comprises loading gel
material into a mold cavity comprising at least one layer of thermoplastic
film
material, said at least one layer of thermoplastic film material comprising
upper
and lower surfaces, and curing the gel material to form a solid gel, such that
the
cured gel -.3terial is bonded with the fnl material and wherein said at least
one of
ti
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
3
on a surface opposite the surface bonded to the gel material thereby providing
the
sticky surface of the device.
Brief Description Of The Drawings
Figure 1A depicts a cross section of a prior art cushioning element.
Figure 1 B depicts a cross section of an example embodiment of the cushioning
element of the invention.
Figure 2 depicts a cross section of a second example embodiment of the
cushioning element of the invention.
Detailed Description
As depicted in Figure 1, the products of the invention comprise an advance
over prior art TPU/PU molded cushioning elements in that they provide for a
means to attach a pressure sensitive adhesive to a gel material to provide
extra
holding capabilities. Figure 1A shows a cross section of a prior art material
comprising gel material (104) bonded to a film material (102). The film
material
provides an exterior surface that resists friction to allow for smooth contact
with
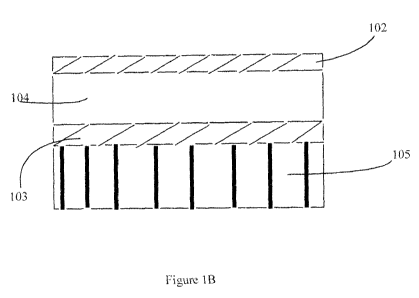
skin or articles of clothing. Figure 1 B shows a cross section of an example
embodiment of the subject invention wherein a layer of gel material having top
and bottom surfaces comprises two layers of film material (102, 103) bonded to
each surface of the gel material. In the practice of the invention, the gel
material
_ may comprise, for example polyurethane gel, styrenic based gels, or silicone
gels.
The gel materials useful in the invention may typically have a Shore 00
hardness
of between about 10 and about 80, preferably between about 30 and about 60. In
certain embodiments of the invention, the polyurethane gel materials are used
and may have a Shore 00 hardness of about 50. The gel material may typically
3 have a tN c ess of bet een 0.3 and 3 T e fÃI material may comnurse
.. ._ _.. ~- ... I I -.,.. Fps
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
cushion, the film material will likely comprise a thermoplastic polyurethane
film
material. Likewise, when an SEBS gel material is used in the cushion, the film
material will likely comprise SEES thermoplastic film. The film materials may
typically have a Shore A hardness of between about 40 to about 95 and may
typically have a thickness of between 0.025 mm and 0.25 mm. In certain
1u embodiments according to this invention where more than one layer of film
is
used, the individual layers of film will have the same thickness. In certain
additional embodiments according to this invention, individual layers of film
will
have different thicknesses. In practice, varying the thickness of the film
will affect
the softness and flexibility of the film and will likewise affect the softness
and
flexibility of the final gel cushion product. In certain embodiments, a
thermoplastic
polyurethane film is used and may be at least 0.025 mm thick.
As used herein polyurethane material will be understood to encompass
polymers that contain a plurality of urethane linkages and comprised of either
aliphatic or aromatic isocyanate prepolymers, and combinations thereof, both
with
200 either di or trifunctional polyol polymers or prepolymers. The
polyurethane
material may optionally also contain other kinds of chemical linkages formed
from
the reactions of polyisocyanates, including but not limited to urea linkages,
isocyanurate linkages, oxazolidone linkages, biuret linkages, allophanate
linkages, combinations of these, and the like. Polyurethane gel materials are
typically formed by reacting polyisocyanates with polyols. Examples of poly
isocyanates include those formed from aliphatic or aromatic isocyanate
prepolymers or combinations thereof. Examples of polyols include di or
trifunctional polyol polymers or prepolymers Examples of polyols used include
polyether polyols such as poly ethylene oxide) and poly(propylene oxide),
modified poiyether polyols, polytetram.ethylene glycol, co;- ler:sation
polyester
polyols produced by reacting dicarboxylic acids with diols, lactone-type
polyester
polyols produced by ring opening polymerization of epsilon-caprolactone or the
like, and polycarbonate polyols, vinyl polymers into which hydroxyl groups are
introduced s ch ac ;nlyols having pcYsobu r ylene as tho aft chain,
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
high levels of damping when tested by dynamic mechanical analysis performed in
the range of -50 degree Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius. Gels material can
include, but not limited to, the Kraton family of styrene-olefin-rubber block
copolymers, thermoplastic polyurethanes, thermoset polyurethanes,
thermoplastic
poly olefins, polyamides, polyureas, polyesters and other polymer materials
that
ILO reversibly soften as a function of temperature. The preferred elastomers
are a
Kraton block copolymer of styrene/ethylene-co-butylene/styrene (SEES) or
styrene/butadiene/styrene (SBS) with mineral oil incorporated into the matrix
as a
plasticizer.
As used herein, pressure sensitive adhesives (also known as contact
5 adhesives) are those that form viscoelastic bonds that are aggressively and
permanently tacky, adhere without the need of more than slight pressure, and
require no activation by water, solvent or heat. Pressure sensitive adhesives
are
typically available in solvent and latex or water based forms and are often
based
on non-crosslinked rubber adhesives, acrylics or polyurethanes.
In certain embodiments of the invention, the pressure sensitive adhesives
may comprise acrylic and methacrylate adhesives, rubber-based pressure
sensitive adhesives, styrene copolymers such as styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS)
and styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) copolymers with at least one tackifier,
and
silicones. Acrylic adhesives often use an acrylate system such as ethylene
ethyl
25- acrylate (EEA) or ethylene methyl acrylate (EMA) copolymers, which are
used to
form hot melt PSA adhesives. Natural rubber, synthetic rubber or elastomer
adhesives may typically comprise a variety of materials such as silicone,
polyurethane, chloroprene, butyl, polybutadiene, isoprene or neoprene. Rubber
and elastomers are characterized by their high degree of ""'ex'.Oility and
elasticity.
33 In certain embodiments, the pressure sensitive adhesive material may
comprise acrylate-based adhesive materials. The thickness of the layer of the
pressure sensitive adhesive material may be varied by those of ordinary skill
in
the art according to the adhesive material used and :rye desired tack. in the
p + of of the s s~ t'
e o. ce
: r _ y:.. ib fit . b tE 1.
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
6
An additional aspect of the invention comprises a method of manufacturing
a cushioning element comprising a polyurethane gel material, which method
comprises the step of bonding a polyurethane gel and a thermoplastic film
material, wherein the thermoplastic film material comprises a pressure
sensitive
adhesive. In preparation of one embodiment of the invention it was discovered
that the pressure sensitive adhesive layer cannot bond directly to the soft
polyurethane gel during the molding process. To overcome this limitation, a
layer
of thermoplastic film material comprising the pressure sensitive adhesive
layer
was added to the mold and bonded to the polyurethane gel.
In certain embodiments of the invention, the cushioning element is
prepared by a direct molding process where the gel material is applied
directly to
the mold, for example by injecting the gel prepolymer into the mold cavity.
During
a direct molding process, before the gel material is injected, the film
material layer
comprising the pressure sensitive adhesive is applied to the mold cavity with
the
adhesive on the side of the film material closest to the mold and then the PU
gel
2 material is injected into the mold over the film material. The mold can be
treated to
resist bonding of the pressure sensitive adhesive or a release liner material
can
be applied in the mold first before the film material is applied to the mold.
In
certain embodiments of the invention, the mold may be preheated to the desired
curing temperature prior to injecting the gel material or heated after all
materials
25 are loaded into the mold. For example, when using polyurethane gel
materials
according to the invention the mold temperature is typically between 85 -95C
and
the cycle time is approximately 8 min. The pressure is typically low and not
critical
for this type of operation provided that the pressure is high enough to fill
the
cavity-mold with polyurethane prepolymer.
As depicted in Figure 2, a release liner 106 is shown contacting the
exposed surface of the PSA layer depicted in Figure 1 S. In this example
embodiment of the invention, the gel cushion can be manufactured by direct
molding process. In this manner, the thin release liner laminate comprises the
C~ '7
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
film comprises the cover layer of the liner during the molding process. The
release liner can be kept on the product when packaged for sale and discarded
before applying the gel cushioning element to a surface, such as a shoe or
other
article of footwear. In certain embodiments the cushioning device may further
comprise a synthetic rubber foam, a woven cotton fabric, a synthetic fiber, a
knit
s fabric, a polyvinyl chloride film, and/or a synthetic non-woven fabric.
The products of the invention can be formed into any shape suitable for
use as a cushioning device, for example for insertion into footwear to prevent
rubbing between sensitive skin and hard or exposed surfaces of the footwear.
The cushioning elements can also be applied to other garments e.g., hats,
- = helmets, protective sporting gear such as elbow and knee pads and other
garments requiring extra padding for comfort, sizing and/or safety. Cushioning
elements according to the invention may also be applied to surfaces which come
in contact with body parts to provide protection from injury such as, e.g.,
chairs,
desks, cabinets, tables, doors and door frames, among others. Depending on the
2 0 size and shape of the object to which the cushioning element is applied,
certain
shapes will better protect different areas of the body from contact with the
object.
In certain example embodiments the products are molded in the shape of, e.g.,
circles, parabolas, stars, squares, rectangles, rounded rectangles, half-moon,
among others. The appropriate shape of the cushioning element can be
25 determined based on the size and surface of the object to which the
cushioning
element will be applied. In alternative example embodiments, the cushioning
element can be provided as a sheet of material that the user can cut to a
desired
shape. The sheet of material can also be provided with preformed shapes that
can be removed as desired for the appropriate protection from contact with the
30 object.
Experimental
A human wear test was conducted to compare the unmodified
ply 4. \r~-jesw~. -ac J i a .:'..1 - ..
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
invention would provide appropriate adhesion performance when compared to the
unmodified polyurethane gel heel liner. Prior to the wear test, a probe tack
test
was conducted on both devices according to ASTM D 2979-01 to measure the
force required to separate an adhesive and adherend shortly after they have
been
contacted under a defined load of known duration and at a specified
temperature.
The devices were also tested for shear hold according to PSTC-107 A, which
measures the adhesive material's ability to remain adhered under a constant
load
applied parallel to the surface of the material and substrate, in particular
measuring the shear adhesion when applied to a vertical standard steel panel.
The two devices were determined to have the following adhesion tack and shear
hold:
PU got without PSA PU gel with PSA. vW
Probe Tack (g) 449 +/- 9 422 +/- 39
Shear Hold (min) 445 +/- 220 325 +/- 173
Based on the results of the probe tack test and the shear hold test, those of
ordinary skill in the art would recognize that the two heel liner devices have
essentially the same adhesion tack and shear hold, and would be expected to
have the same adhesion performance in use, i.e., the ability to stay in place
in a
shoe under normal wear.
The adhesion performance of heel liner cushions formed according to the
invention was then evaluated in a wear test by volunteers who inserted the
devices into their shoes and wore them for three days of normal use. The test
L i
subjects were divided such that 23 subjects evaluated the unmodified heel e-s
while 22 subjects evaluated the heel liner modified with PSA. Both the
unmodified
heel liners and the modified heel liners were similar in appearance so the
test
subjects did not know which device they were wearing. After three days, the
test
subjects were asked to rate their agreement or disagreement with whether the
c f.-`hion stayed in place n normal use. rating acct to a sever; p6nt
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
9
Answer Rating
agree extremely 1 i
- - ----- - ------ - - -------- - ---------- -
agree moderately 2
agree slightly 3
neither agree or disagree 4
- - ------- - -----
-- - - -------- --------
disagree slightly 5
disagree moderately 6
disagree extremely 7
The sum of the top three rating answers indicated a positive feedback of the
performance of the heel liner cushion adhesion and the sum of the bottom three
rating answers indicated the negative feedback to the performance of the heel
liner cushion. The results were as follows:
Unmodified Modified
Top3box 13 21
Bottom 3 box 10 1
As shown, the modified heel liners produced according to the subject
invention containing the PSA produced an overwhelmingly positive feed back
from
users. Conversely, the unmodified heel liners showed equivocal results of
15 positive and negative feed back. The statistical analysis (p of 0.0041) of
the wear
test results indicated that the liners modified with PSA according to the
invention
provide a better adhesion performance during wear than the unmodified version,
which result was unexpected based on the probe tack and shear hold tests on
the
cushions.
%.
Several embodiments of the present invention are specifically described
herein. However, it wii. be appreciated that modifications and va,5ations of
the
appended c1a, s cep ai õtn fruffà Ua i cx à ate ScOpe of the
CA 02728540 2010-12-17
WO 2009/158560 PCT/US2009/048756
invention.