Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
DESCRIPTION
Title of Invention
DI S HWA SHING MACHINE
Technical Field
[0001] The present invention relates to a dishwashing machine for
washing dishes while jetting hot water accumulated in a tank on them.
Background Art
[0002] In Patent Document 1, a dishwashing machine is described, in
which hot water accumulated in a washing-water tank is jetted on dishes
contained in a washing room to wash them, and hot water accumulated
in a rinsing-water tank is jetted on the dishes to rinse them. In this
dishwashing machine, in order to improve contamination-removal
performance, washing is executed after the washing water in the
washing-water tank becomes 60 degree C or more. In addition, the
temperature of rinsing water in the rinsing-water tank is controlled by a
heater so as not to be always less than 80 degree C.
Citation List
Patent Literature
[0003] Patent Document 1: Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open
Publication No. 07-303592
Summary of Invention
Technical Problem
[0004] Energy consumed by a heater for heating hot water in a
washing-water tank or a rinsing-water tank occupies a large proportion
in consumption energy of the dishwashing machine. In particular,
since the dishwashing machine described in Patent Document 1 is used
1
CA 02729991 2015-10-15
for business application and is in a power-on state all day long, the
hot-water temperature in the tank is kept to be 80 degree C all the day.
Accordingly, the consumption energy becomes large, in some cases,
and the amount of CO2 emission (reduced value) may reach about
several tons per year.
Solution to Problem
[0005] Thus, an object of the present invention is to provide a
dishwashing machine capable of achieving energy saving.
[0006] Inventors of the present invention have developed a dishwashing
machine in view of the actual state where it is used for business
application in a kitchen. For example, a dishwashing machine
installed in a restaurant is powered-on before opening in the morning
and powered-off after closing in the afternoon. The dishwashing
machine is operated relatively continuously at busy periods of the day at
morning, noon and afternoon, but, during the time except for the busy
periods, in many cases, it is in a resting state without being operated.
[0007] Accordingly, it can be considered to turn off power in the resting
state for the purpose of energy saving. However, in this case, the
hot-water temperature in the tank may be lowered to thereby degrade
the washing performance when next operation is executed. In
particular, since one-cycle operation time of the dishwashing machine
for business application is short, there is a possibility that the operation
may be finished before the hot-water temperature in the tank is
sufficiently elevated. For this reason, the inventors of the present
invention has been invented a dishwashing machine capable of saving
energy while suppressing degradation of the washing performance and
2
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
the rinsing performance.
[0008] The dishwashing machine of the present invention capable of
executing a washing or rinsing step of jetting hot water accumulated in a
tank into a washing room, includes: a heater for heating hot water in a
tank; a temperature sensor for measuring the temperature of the hot
water in the tank; and a heater control unit for controlling the heater so
that the hot-water temperature in the tank becomes a set temperature,
based on the measured value of the temperature sensor. In the
dishwashing machine, the heater control unit is capable of controlling
the heater so that the hot-water temperature in the tank becomes a
waiting temperature that is lower than the set temperature, in a resting
state, in a quiescent operating state where the washing or rinsing step is
not executed.
[0009] In the dishwashing machine of the present invention, the
hot-water temperature in the tank is controlled so as to be the set
temperature during busy periods, and controlled so as to be the waiting
temperature that is lower than the set temperature during a quiescent
operating periods,. Thus, energy saving during a quiescent operating
periods can be achieved. Moreover, if the power supply is turned off
during a quiescent operating periodsõ it takes time to elevate the
hot-water temperature in the tank which was lowered up to
approximately room temperature, up to the set temperature when
executing the washing or rinsing step again. In contrast, according to
the present invention, since the hot-water temperature in the tank is
controlled so as to be the waiting temperature in a state where the power
supply is turned on, the temperature can be elevated to the set
3
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
temperature faster than ever, during executing the washing or rinsing
step. In addition, at the first operation to execute the washing or
rinsing step again after the dishwashing machine becomes a quiescent
operating state once, the washing or rinsing step can be executed at
higher hot-water temperature. Thus, degradation of the washing
performance and the rinsing performance can be prevented.
Furthermore, since heat quantity generated by the tank in the kitchen is
reduced during a quiescent operating period, getting hot in the kitchen
can be suppressed.
[0010] Preferably, the heater control unit, upon being provided with no
operation-start signal while the quiescent operating state has continued
for a predetermined time period, controls the heater so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank becomes the waiting temperature. In this case,
if the predetermined time period elapses without operation after the
quiescent operating state is started, the unit can switch control so that
the hot-water temperature in the tank automatically becomes the waiting
temperature from the set temperature.
[0011] Preferably, when the heater control unit is provided with the
operation start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank to be the waiting temperature, washing time is extended. If the
operation is started while the heater control unit is controlling the
hot-water temperature in the tank to be the waiting temperature, in the
washing step executed immediately after the start, washing may be
executed in a state where the hot-water temperature in the tank is still
lower than the set temperature, resulting in causing a possibility of
degradation of the washing performance. Therefore, by extending the
4
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
washing time in the washing step performed immediately after the start
of operation, to be longer than normal washing time, degradation of the
washing performance can be suppressed. Thus, the reliability of the
dishwashing machine can be improved.
[0012] Preferably, the heater control unit, if being provided with the
operation-start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank to be the waiting temperature, extends the washing time by preset
extension time. In this case, by suitably setting the extension time,
degradation of the washing performance due to temperature lowering of
the washing water can be suppressed.
[0013] Preferably, when the heater control unit is provided with the
operation-start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank to be the waiting temperature, the washing time is extended until
the hot-water temperature in the tank becomes a preset
washing-time-finishing temperature. In this case, by suitably setting
the washing-time-finishing temperature, degradation of the washing
performance due to temperature lowering of the washing water can be
suppressed.
[0014] Preferably, the washing-time-finishing temperature is set at the
start of the rinsing step so that the hot-water temperature in the tank for
rinsing becomes the set temperature. In this case, by automatically
extending the washing time until the hot-water temperature becomes the
washing-time-finishing temperature, the hot-water temperature in the
tank for rinsing can become the preset temperature at the start of the
rinsing step via temperature rising of the hot water during resting time
between the washing step and the rinsing step. Thus, since execution
5
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
of the rinsing step using low-temperature hot water can be prevented, a
sufficient sterilizing effect on dishes in the rinsing step can be ensured.
Furthermore, by considering temperature rising of the hot water during
the resting time, time required for the operation of the dishwashing
machine can be shorter than that of a case where the washing time is
extended until the hot-water temperature becomes the set temperature,
which contributes to energy saving of the dishwashing machine.
[0015] Preferably, when the heater control unit is provided with the
operation-start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank for rinsing to be the waiting temperature, the washing time is
extended for preset extended times of operation. If the quiescent
operating state of the dishwashing machine continues for a long time,
the hot water accumulated in a hot-water supply pipe connecting the
tank for rinsing and an external water heater is cooled to be lowered to
around normal temperature. Since the hot-water temperature in the
tank is significantly lowered every time when the cooled hot water is
supplied to the tank from the hot-water supply pipe, even for the second
or the later operation, there is a possibility that the rising of the
hot-water temperature may not in time for the start of the rinsing step.
Therefore, after the operation start signal has been input, executing
washing-time-extending operation during the preset extended times of
operation, allows the hot-water temperature in the tank to be surely the
set temperature at the start of the rinsing step, even if the hot-water
temperature is significantly lowered by supplying the cooled hot water
in the tank for a plurality times of operations, and thus, a sufficient
sterilizing effect on dishes can be ensured.
6
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
[0016] Preferably, the heater control unit, upon being provided with the
operation-start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank to be the waiting temperature, stops the heater when the hot water
in the tank reaches a preset heater-stopping temperature, which is set so
that hot-water temperature in the tank becomes the set temperature by
the thermal inertia of the stopped heater. In this case, by stopping
heating of the heater when the hot-water temperature has reached the set
temperature, the occurrence of excessive temperature rising of the hot
water exceeding the set temperature, that is, overshooting, can be
suppressed. Thus, as generation of unnecessary thermal energy can be
avoided, energy saving of the dishwashing machine can be achieved.
[0017] Preferably, the heater control unit, while controlling the
hot-water temperature in the tank to be the waiting temperature,
modifies the waiting temperature to be lower depending on period of
duration time of the quiescent operating state.
[0018] In this case, if being provided with no operation-start signal
within a predetermined time period while controlling the hot-water
temperature in the tank to be the waiting temperature, the unit controls
the hot-water temperature in the tank so as to be the lower waiting
temperature. In contrast, if being provided with the operation-start
signal within a predetermined time period while controlling the
hot-water temperature in the tank to be the waiting temperature, the unit
switches control so that the hot-water temperature in the tank becomes
the set temperature. Such control has the following advantages.
Since the quiescent operating state continues for a long time during
resting period, the unit controls the hot-water temperature in the tank to
7
= CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
be the waiting temperature, and then controls the waiting temperature to
be lower. Thus, energy saving in the quiescent operating state can be
surely achieved. Meanwhile, during transition period between busy
period and resting period, in some cases, one or two operations may be
executed with being intervened with a short resting state. During
transition period, the unit is controlling the hot-water temperature to be
the waiting temperature and, after one operation is executed, the unit
controls the waiting temperature to be the set temperature. Therefore,
the time required to reach the set temperature can be reduced compared
with a case where the hot-water temperature is controlled to be the set
temperature from the lower waiting temperature. Thus, degradation of
the washing performance can be further suppressed.
[0019] Preferably, the heater control unit, if being provided with the
operation-start signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the
tank to be the waiting temperature, modifies the waiting temperature to
be higher, and then elevates the waiting temperature to be close to the
set temperature depending on input frequency of the operation-start
signal.
[0020] In this case, the unit, if being provided with the operation start
signal while controlling the hot-water temperature in the tank to be the
waiting temperature, controls the hot-water temperature to be the higher
waiting temperature. Subsequently, if being provided with the
operation start signal by a predetermined number or more of times
within the predetermined time period, the unit controls the hot-water
temperature in the tank to be the set temperature. As described above,
during transition from resting period to busy period, the input frequency
8
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
of the operation start signal increases, and thus, the unit controls the
hot-water temperature in the tank so as to be closer to the set
temperature. In contrast, after the hot-water temperature in the tank is
controlled so as to be the higher waiting temperature, if being provided
with no operation start signal by the predetermined number or more of
times, the unit may switch control so that the hot-water temperature in
the tank becomes the original low waiting temperature. Thus, even in
a case where, the unit, by being provided with the operation start signal
while controlling the hot-water temperature in the tank to be the waiting
temperature, has switched control so that the hot-water temperature in
the tank becomes the higher waiting temperature, if being provided with
no operation start signal and the quiescent operating state continues for
a while, the unit can switch control so that the hot-water temperature in
the tank becomes the original waiting temperature. Therefore, further
energy saving can be achieved.
[0021] Preferably, the dishwashing machine includes a motion sensor
for detecting motion in surroundings of the dishwashing machine, and
the heater control unit controls the heater so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank becomes the waiting temperature when the
motion sensor does not detect the motion within a predetermined time
period. In this case, for example, when human's motion in the
surroundings of the dishwashing machine is not observed in
intermission time etc., the unit can switch control so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank automatically changes from the set temperature
to the waiting temperature.
[0022] Preferably, the dishwashing machine includes an illuminance
9
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
sensor for measuring illuminance in surroundings of the dishwashing
machine, and the heater control unit controls the heater so that the
hot-water temperature in the tank becomes the waiting temperature
when the illuminance sensor does not measure illuminance with a
predetermined value or more within the predetermined time period. In
this case, for example, when the illuminance in the surroundings of the
dishwashing machine is lowered by turning off illumination in
intermission time etc., the unit can switch control so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank automatically changes from the set temperature
to the waiting temperature.
[0023] Preferably, the dishwashing machine includes a sound sensing
sensor for detecting sound in surroundings of the dishwashing machine,
and the heater control unit controls the heater so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank becomes the waiting temperature when the
sound sensing sensor does not detect sound with a predetermined value
or more within the predetermined time period. In this case, if being
provided with no operation start signal within the predetermined time
period and the sound sensing sensor does not detect sound with sound
pressure exceeding a predetermined sound pressure, the unit switches
control so that the hot-water temperature in the tank changes from the
set temperature to the waiting temperature. Alternatively, if being
provided with no operation start signal within the predetermined time
period and accumulation value of sound pressure detected within the
predetermined time period does not exceed the predetermined value, the
unit switches control so that the hot-water temperature in the tank
changes from the set temperature to the waiting temperature.
CA 02729991 2015-10-15
Therefore, for example, if no sound is detected in the surroundings of
the dishwashing machine in intermission time etc., the unit can switch
control so that the hot-water temperature in the tank automatically
changes from the set temperature to the waiting temperature.
[0024] Preferably, the dishwashing machine includes a control section
for outputting a signal to the heater-control unit, for controlling the
heater so that the hot-water temperature in the tafflc becomes the waiting
temperature, and if the control section is operated, the heater-control
unit controls the heater so that the hot-water temperature in the tank
becomes the waiting temperature even if the predetermined time period
does not elapse. Thus, by user's operation of the control section
during the quiescent operating state, the signal is input to the
heater-control unit, and thus, the unit can surely switch control so that
the hot-water temperature in the tank changes from the set temperature
to the waiting temperature.
In one aspect, the invention provides a dishwashing machine capable of
executing a washing or rinsing step of jetting hot water accumulated in a
tank into a washing room, the dishwashing machine comprising:
a heater for heating the hot water in the tank;
a temperature sensor for measuring the temperature of the hot
water in the tank; and
a heater control unit for controlling the heater so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank becomes a set temperature, based on the
measured value of the temperature sensor,
11
CA 02729991 2015-10-15
wherein the heater control unit is capable of controlling the heater
so that the hot-water temperature in the tank becomes a waiting
temperature that is lower than the set temperature, in a quiescent
operating state in which the washing or rinsing step is not executed;
wherein the heater control unit, if being provided with no
operation-start signal and the quiescent operating state has continued for
a predetermined time period, controls the heater so that the hot-water
temperature in the tank becomes the waiting temperature.
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0025] According to the dishwashing machine of the present invention,
energy saving can be achieved.
Brief Description of Drawings
[0026]
Fig. 1 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to the present embodiment;
Fig. 2 is a schematic view illustrating the internal structure of
the dishwashing machine according to the present embodiment;
Fig. 3 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the present embodiment;
1 1 a
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
Fig. 4 is a graph illustrating the temperature in a washing-water
tank changing according to the motion of the dishwashing machine
according to the present embodiment;
Fig. 5 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a second modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 6 is a graph illustrating the temperature of a washing water
in the washing-water tank changing according to the motion of the
dishwashing machine according to the second modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 7 is another graph illustrating the temperature of the
washing water in the washing-water tank changing according to the
motion of the dishwashing machine according to the second modified
example of the present embodiment;
Fig. 8 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a third modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 9 is a graph illustrating the temperature of the washing
water in the washing-water tank changing according to the motion of
the dishwashing machine according to the third modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 10 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to a fourth modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 11 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the fourth modified example of the present
12
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
embodiment;
Fig. 12 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to a fifth modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 13 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the fifth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 14 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to a sixth modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 15 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the sixth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 16 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to a seventh modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 17 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the seventh modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 18 is another flowchart illustrating the motion of the
dishwashing machine according to the seventh modified example of the
present embodiment;
Fig. 19 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to an eighth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 20 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
13
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
machine according to a ninth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 21 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a tenth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 22 is a graph illustrating the temperature of a rinsing water
in washing-time-extending operation according to a eleventh modified
example of the present embodiment;
Fig. 23 is a graph illustrating the temperature of the rinsing
water in the washing-time-extending operation according to a twelfth
modified example of the present embodiment;
Fig. 24 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a thirteenth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 25 is a graph illustrating the temperature of the rinsing
water in the rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation according to the
thirteenth modified example of the present embodiment;
Fig. 26 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a fourteenth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 27 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of a dishwashing
machine according to a fifteenth modified example of the present
embodiment;
Fig. 28 is a perspective view illustrating the outline of a
dishwashing machine according to a sixteenth modified example of the
present embodiment; and
14
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
Fig. 29 is a flowchart illustrating the motion of the dishwashing
machine according to the sixteenth modified example of the present
embodiment.
Description of Embodiments
[0027] Hereinafter, with reference to drawings, embodiments of the
dishwashing machine according to the present invention will be
described in detail.
[0028] The dishwashing machine 1 illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2, is an
apparatus in which dishes P are washed with washing water containing
a detergent and then rinsed with clean rinsing water. The dishwashing
machine 1 includes a stainless-steel main body case 2. Partitioned
lower side in the case 2 has a function of a dishwashing machine room
3. In the dishwashing machine room 3, an electric component box 6
with a built-in microcomputer (hereinafter, referred to as "MC") 4 for
controlling the total movement of the dishwashing machine 1 is
contained. In contrast, the upper side of the main body case 2 has a
function of a washing room 5 and is provided with a door 7 vertically
moving to open/close the washing room 5. To the front of the door 7,
a handle 7a is attached so that a user can easily carry out the vertical
moving operation of the door 7.
[0029] In the washing room, a rack rail (not illustrated in figures) is
detachably arranged, and, on the rack rail, a lattice-shaped dish rack 8
on which dishes P such as dishes and china cups used for drinking and
eating are lined up, is placed. To the upper portion of the washing
room 5, an upper side washing nozzle 9 composed of radially extending
three arms and an upper side rinsing nozzle 11 composed of two arms
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
are rotatably arranged. Similarly, to the lower portion of the washing
room 5, a lower side washing nozzle 12 composed of radially extending
three arms and a lower side rinsing nozzle 13 composed of two arms are
rotatably arranged. Accordingly, onto the dishes P lined-up on the
dish rack 8, the washing water is jetted downward and upward by the
washing nozzles 9 and 12, respectively, in the washing step, and the
rinsing water is jetted downward and upward by the rinsing nozzles 11
and 13, respectively, in the rinsing step, and thus, efficient washing and
rinsing of the dishes P can be achieved.
[0030] To the bottom surface 5a of the washing room 5 configured as
mentioned above, a first filter 14 is detachably arranged, and, below the
first filter 14, a washing water tank 15 for accumulating the washing
water is formed. The inside of the tank 15 is provided with a
washing-water heater 16 for heating the washing water in order to
improve the washing performance and sterilizing performance and a
washing-water-temperature sensor 17 for detecting the temperature of
the washing water. A thermistor and a bimetal thermostat etc. can be
used as the washing-water-temperature sensor 17.
[0031] Furthermore, on the bottom surface 15a of the washing tank 15,
a second filter 18 that is finer in texture than the first filter 14 is
detachably arranged, and below the second filter 18, a depressed portion
19 is formed so that a part of the bottom surface 15a is depressed. To
the bottom surface 19a of the depressed portion 19, a drain pipe 20 is
connected, and to the drain pipe 20, the lower end portion of an
overflow pipe 21 whose upper end portion is positioned in the tank 15
through a cylindrical portion 18a of the second filter 18 is fitted.
16
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
Accordingly, excessive washing water flows into the overflow pipe 21
from an inflow port formed on the upper end portion of the pipe 21 and
discharged outside via the drain pipe 20, and thus, the level of the
washing water in the tank 15 is kept constant.
[0032] To the depressed portion 19 of the tank 15, a washing pump 23
is connected via a washing-water suction pipe 22. To a discharge port
of the washing pump 23, a washing-water discharge pipe 24 is
connected. The washing-water discharge pipe 24 is branched into a
first washing-water discharge pipe 25 and a second washing-water
discharge pipe 26, connected to the upper side washing nozzle 9 and the
lower side washing nozzle 12, respectively.
[0033] In addition, in the dishwashing machine room 3, a
rinsing-water tank 28, to which constant-temperature (about 43 degree
C) rinsing water is supplied via a hot-water supply pipe 27 from an
external water heater (not illustrated in figures), is arranged. In the
tank 28, a rinsing-water heater 29 for heating the rinsing water in order
to improve the sterilizing performance and a rinsing-water-temperature
sensor 31 for detecting the temperature of the rinsing water supplied
from the water heater, are installed. The heater 29 elevates the
temperature of the rinsing water supplied from the water heater up to a
preset temperature of 85 degree C. As the sensor 31, a thermistor and
a bimetal thermostat etc. can be used. Furthermore, in the tank 28, an
overflow pie 32 for discharging excessive rinsing water outside to keep
the level constant, is installed. Rinsing water flown into the pipe from
the upper end portion is discharged outside via the drain pipe 20.
[0034] To the tank 28, a rinsing pump 34 is connected via a
17
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
rinsing-water suction pipe 33. To a discharge port of the rinsing pump
34, a rinsing-water discharge pipe 36 is connected. The rinsing-water
discharge pipe 36 is branched into a first rinsing-water discharge pipe
37 and a second rinsing-water discharge pipe 38, connected to the upper
side rinsing nozzle 11 and the lower side rinsing nozzle 13, respectively.
[0035] Furthermore, in the dishwashing machine room 3, a detergent
tank 39 accumulating detergent W for being included in the washing
water in the tank 15, is arranged. To the detergent tank 39, a detergent
supply pump 42 is connected via a detergent suction pipe 41. To a
discharge port of the detergent supply pump 42, one end of a detergent
discharge pipe 43 is connected, and the other end of the detergent
discharge pipe 43 is located in the washing room 5 and is opened
downward.
[0036] The dishwashing machine 1 configured as described
above includes a operation panel 44, and a user manipulates the
dishwashing machine 1 via a power-supply switch 45 provided to the
panel 44.
[0037] In the dishwashing machine 1, when the power-supply switch 45
is turned on, by jetting hot water in the rinsing tank 28 into the washing
room 5 by using the rinsing pump 34, the hot water is supplied to the
tank 15. By this operation, initial hot-water supply is executed.
Then, detergent having the amount corresponding to the amount of the
initial hot-water supply is supplied to the tank 15, and concentration of
the detergent in the washing water in the tank 15 becomes a
predetermined concentration.
[0038] When a user racks the dishes P and closes the door 7 after the
18
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
initial hot-water supply, closing of the door 7 is detected by a door
switch 10, the operation start signal is input to MC 4, and then operation
is started. The "operation" here includes ones, such as a cycle
operation where one cycle including one washing step and one
subsequent rinsing step is executed, a one-cycle operation where one
cycle including one washing step, two subsequent rinsing steps, and a
subsequent drying step of drying the dishes by using a drying heater
arranged in the washing room 5 is executed, and a rinsing operation
where only a rinsing step is executed. That is, the operation executed
in the dishwashing machines 1 and 1A to 1B indicates washing or
rinsing movement.
[0039] If the operation start signal is input to the MC 4, the washing
pump 23 will be started, and the washing water accumulated in the tank
is pumped into the upper nozzle 9 and the lower nozzle 12 via the
15 washing-water discharge pipe 24 etc. to be jetted on the dishes P from
the nozzles 9 and 12. Since, at that time, the nozzles 9 and 12 are kept
to be rotated by the reaction of propellent force, the contamination of
the dishes P are effectively washed out.
[0040] While garbages etc. washed out from the dishes P by the first
filter 14 are being removed, the washing water jetted on the dishes P is
recovered in the washing-water tank 15. Furthermore, after small
garbages are removed by the second filter 18, the washing water is
circulated by the washing pump 23 and supplied to the washing room 5
again.
[0041] After such a washing step is executed for a predetermined time
period, the washing pump 23 is stopped and the rinsing pump 34 is
19
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
started. Therefore, rinsing water accumulated in the tank 28 is pumped
into the upper nozzle 11 and the lower nozzle 13 via the rinsing-water
discharge pipe 36 etc. to be jetted on the dishes P from the nozzles 11
and 13. Since, at that time, the nozzles 11 and 13 keep being rotated
by the reaction force of propellent force, the rinsing water is evenly
jetted on the dishes P, resulting in achieving efficient rinsing of the
dishes P.
[0042] The rinsing water jetted on the dishes P is recovered in the tank
via the first filter 14 to be mixed with the washing water so as to be
10 used as washing water of the next washing step. Excessive mixture is
discharged outside via the overflow pipe 21. After such a rinsing step
is executed for a predetermined time period, the rinsing pump 34 is
stopped and an one-cycle operation is completed.
[0043] In contrast, temperatures of the washing water and the rinsing
15 water are controlled as follows. If the power-supply switch 45 is
turned on, the MC 4, while executing on-off control of voltage applied
to the heater 29, controls the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 to
be 80 to 85 degree C which is a temperature sufficient for sterilizing the
dishes P.
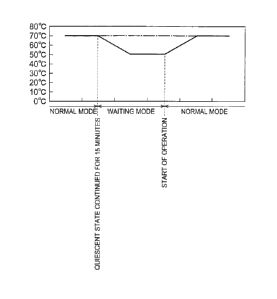
[0044] As illustrated in Fig. 3, the temperature of the washing water in
the tank 15 is controlled. If the power-supply switch 45 is turned on
(step Si), the MC 4 is set to be in a normal mode (step S2). The
"normal mode" is referred to as a mode in which the on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the
MC 4, based on the measured value of the washing-water temperature
sensor 17 so that the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
a set temperature (70 degree C).
[0045] In the normal mode, if being provided with no operation start
signal and a quiescent operating state in which operation is not executed
is continued for a predetermined time period (15 minutes) (YES in step
S3), the MC mode is set to a waiting mode from the normal mode (step
S4) by the MC 4. Here, the "quiescent operating state" is referred to as
a state in which the power supply is being turned on, and the washing
water is accumulated in the tank 15 and rinsing water is accumulated in
the tank 28, and if being provided with the operation start signal, the
operation can be started immediately. Until the quiescent operating
state continues for 15 minutes (NO in step S3), the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to become the set
temperature.
[0046] The "waiting mode" is referred to as a mode in which on-off
control of voltage to be applied to the heater 16 is executed by the MC 4,
based on the value measured by the sensor 17 so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes a waiting temperature (about 50
degree C) that is lower than the set temperature. Until being provided
with the operation start signal (NO in step S5), the MC mode is set to
the waiting mode. If being provided with the operation start signal
(YES in step S5), the MC mode is returned to the normal mode again
and the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to
be the set temperature.
[0047] In this way, when the temperature of the washing water in the
tank 15 is controlled as illustrated in Fig. 4, the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is kept to be about 70 degree C during a
21
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
period in which the MC mode is set to the initial normal mode, and if
the MC mode is set to the waiting mode, the temperature is lowered to
about 50 degree C and then kept to be 50 degree C. After that, if the
MC mode is returned to the normal mode, the temperature is elevated to
70 degree C from 50 degree C and then kept to be 70 degree C. A
conventional dishwashing machine has been controlled so that the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is kept to be always 70 degree
C. Thus, in the dishwashing machine 1 according to the present
invention, energy saving can be achieved further than in the
conventional dishwashing machine.
[0048] In a specific case where a 3.9 kW heater was used as the
washing-water heater 16, when 54 L washing-water in the
washing-water tank 15 was controlled to be 70 degree C, power
consumption per 1 hour was about 608 Wh. When the washing-water
temperature was controlled to be 60 degree C, power consumption of
the heater was able to be reduced by about 29%. When the washing
water temperature was controlled to be 50 degree C, power
consumption of the heater was able to be reduced by about 52%.
[0049] Moreover, in the dishwashing machine 1, since the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 was lowered in the waiting
mode, heat quantity dissipated by the tank 15 in a kitchen is reduced,
and thus, it is possible to prevent the inside of the kitchen from being
hot. Furthermore, since, the time to be exposed to high temperature is
reduced for components near the tank 15, reliability and product-life of
them can be improved. In addition, low cost energy saving can be
achieved only by control without adding new components.
22
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
[0050] Moreover, in the dishwashing machine 1 if being
provided with no operation start signal in a predetermined time period,
the MC mode is switched from the normal mode to the waiting mode,
and thus, if the predetermined time period elapses without operation
after the dishwashing machine 1 enters the quiescent operating state, the
MC mode can be automatically switched from the normal mode to the
waiting mode. This provides the following effects. In a practical use
environment, in the dishwashing machine 1, washing operation is
frequently executed during busy time, and the operation start signal is
frequently input. During the busy time, the MC 4 controls the
hot-water temperature in the tank 15 to be higher in the normal mode,
and thus, high-washing-performance operation can be executed. In
contrast, during time period except for busy period, a few washing
operations are executed, and a few operation start signals are input.
During the time period except for the busy period, the MC mode is
automatically switched to the waiting mode by the MC 4, in which the
hot-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled to be lower, thereby
enabling to save the consumption energy. As described above, since
the optimum mode is automatically selected by judging the usage of the
dishwashing machine 1, energy saving matching well with the usage
can be achieved without specific operation by a user.
[0051] Furthermore, since the hot-water temperature in the tank 15 is
controlled to be the waiting temperature, the hot-water temperature in
the tank 15 can be elevated in a shorter time than that required in a case
where the MC mode is returned to the normal mode from a state in
which the hot-water temperature in the tank 15 is room temperature due
23
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
to turning off the power supply. Thus, at the time when washing
operation is executed first, after the MC mode is returned to the nounal
mode, washing can be executed at a higher temperature, thereby
enabling to suppress degradation of the washing performance.
[0052] With regard to the dishwashing machine 1 according to the
present invention, various modifications can be considered.
Hereinafter first to tenth modified embodiments will be described. In
addition, the "tank" described in claims means both of the
washing-water tank 15 and the rinsing-water tank 28, and the "tank for
rinsing" means the rinsing-water tank 28. Moreover, the "hot water"
described in claims means both of the washing water and the rinsing
water.
[0053]
First Modified Example
According to the above mentioned embodiment, in the waiting
mode, the heater 16 is controlled so that the washing-water temperature
in the tank 15 becomes the waiting temperature (50 degree C) that is
lower than the set temperature (70 degree C). However, in the first
modified example, based on the measured value of the sensor 31, the
heater 29 is controlled so that the washing-water temperature in the tank
15 becomes a waiting temperature (60 degree C) that is lower than a set
temperature (80 degree C). In this case, power consumption of the
heater 29 can be reduced, and thus, energy saving can be achieved.
[0054] In addition, even for a case where a cycle operation is started
after the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 reached the waiting
temperature, it is also preferable to set temperature difference between
24
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
the set temperature and the waiting temperature to be about 5 to about
degree C so that the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 reaches
the set temperature before the rinsing step is started.
[0055] In the dishwashing machine 1, it takes about 25 seconds at room
5 temperature to elevate the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 with
a volume of 7.3 L from 80 degree C to 85 degree C by using the heater
29 of 6000 W. In the similar conditions, it takes about 52 seconds to
elevate the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 from 75 degree C to
85 degree C. In contrast, in the dishwashing machine 1, the total time
10 required from the start of the cycle operation to the end of the rinsing
step becomes about 51 seconds if exchange time of dishes is set to about
5 second, time for the washing step is set to 41 seconds, and resting time
between the washing step and the rinsing step is set to 5 seconds.
Accordingly, when the set temperature is 85 degree C, by setting the
waiting temperature to 75 to 85 degree C so that the temperature
difference becomes about 5 to about 10 degree C, the rinsing-water
temperature in the tank 28 can be elevated to the set temperature before
the rinsing step is started. In addition, the resting time is provided so
as to prevent washing-water dripping from the washing nozzles 9 and
12 after the washing step, so called "after dripping".
[0056] In a conventional case where the heater 29 was controlled so
that the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 was kept to 85 degree
C, power consumption was 493 W and heater conducting rate was 2.7%
per 3 hours. In contrast, when the heater 29 was turned off after the
cycle operation, and controlled so that the rinsing-water temperature in
the tank 28 was kept to the waiting temperature for 3 hours after the
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 reached the waiting
temperature, the following results were obtained. If the waiting
temperature was 80 degree C, the power consumption was reduced to
409 W, the heater conducting rate was reduced to 2.3%, and the power
consumption was able to be reduced by 17.1% than that of the
conventional case. If the waiting temperature was 75 degree C, the
power consumption was reduced to 373 W, the heater conducting rate
was reduced to 2.0%, and the power consumption was able to be
reduced by 24.4% than that of the conventional case. Here, the above
test was carried out in a state in which the rinsing water is filled in the
tank 28 with a volume of 7.3 L by using the heater 29 of 6000 W.
[0057] As described above, even in a case where the temperature
difference between the set temperature and the waiting temperature is
set to be in a small range of about 5 to 10 degree C, by controlling the
heater 29 so that the rinsing -water temperature in the tank 28 becomes
the waiting temperature in the quiescent operating state, energy saving
can be achieved. Moreover, by setting the temperature difference
between the set temperature and the waiting temperature to be small that
is an extent of 5 to 10 degree C, the rinsing-water temperature in the
tank 28 can be more surely elevated to the set temperature before the
rinsing step is started.
[0058] In order to reduce the power consumption of the rinsing-water
or washing-water heater, during period except for operation period, it
can be considered to control the temperature of the rinsing water in the
rinsing-water tank or the washing water in the washing-water tank to be
always the waiting temperature that is lower than the set temperature
26
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
during operation. In this case, if the rinsing water is heated
immediately after the operation start signal is input, the rinsing-water
temperature is elevated to the set temperature during the washing step.
However, when the difference between the set temperature and the
waiting temperature is large or when the room temperature is low, even
if the rinsing water in the rinsing-water tank is heated immediately after
the input of the operation start signal, the rinsing-water temperature
would not reach the set temperature during the washing step.
Therefore, the sterilizing effect during the rinsing step is degraded. In
addition, regarding to the washing water, if the washing step is started
immediately after the input of the operation start signal, washing must
be executed by using lowered-temperature washing water, and thus, the
washing performance during the washing step will be always degraded.
In contrast, in the present embodiment described above and the present
modified example, when the operation start signal is not input for a
predetermined time period, the MC mode is switched from the normal
mode to the waiting mode, and thus, energy saving can be achieved, and
simultaneously degradation of the washing performance including the
bactericidal performance can be suppressed.
[0059] In addition, in the waiting mode, it is also possible to control the
heater 16 so that the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes
the waiting temperature (50 degree C) that is lower than the set
temperature (70 degree C), and simultaneously control the heater 29 so
that the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 becomes the waiting
temperature (60 degree C) that is lower than the set temperature (80
degree C), based on the measured value of the sensor 31. In this case,
27
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
= FP09-0312-00
if being provided with the operation start signal of the cycle operation in
a state in which the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 and the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 are controlled to be the
respective waiting temperatures, the MC 4 controls the heaters 16 and
29 so that the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 and the rinsing
water in the tank 28 become the respective waiting temperatures.
Moreover, if being provided with the operation start signal only for the
rinsing operation in a state in which the washing-water temperature in
the tank 15 and the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 are
controlled to be the respective waiting temperatures, the MC 4 controls
the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 so as to be unchanged
waiting temperature, and switches control of the heater 29 so that the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 becomes the set temperature.
[0060]
Second Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 5, if the power switch 45 is turned on (step
S11), MC 4 according to the second modified example is set to be in the
normal mode (step S12). In the normal mode, on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by MC
4, based on the measured value of the sensor 17 so that the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature
(about 70 degree C).
[0061] In the normal mode, if an quiescent operating state in which the
operation start signal is not input and operation is not executed
continues for a predetermined time period (15 minutes) (YES in step
S13), the MC 4 sets its mode to a first waiting mode from the normal
28
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
mode (step S). Until the quiescent operating state continues for the
predetermined time period in the normal mode (NO in step S13), the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the
set temperature in the normal mode.
[0062] In the first waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be applied
to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the MC4, based on the
measured value of the washing-water-temperature sensor 17, so that the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes a first waiting
temperature (about 60 degree C) that is lower than the set temperature
(step S14). In the first waiting mode, if being provided with no
operation start signal for the predetermined time period (15 minutes)
and the quiescent operating state continues for the predetermined time
period (YES in step S15), the MC mode is controlled by the MC to be a
second waiting mode from the first waiting mode. Until the quiescent
operating state does not continue for the predetermined time period in
the first waiting mode (NO in step S15), the washing-water temperature
in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the first waiting temperature in
the first waiting mode.
[0063] In the second waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be
applied to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based
on the measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes a second waiting temperature (about
50 degree C) that is lower than the first waiting temperature (step S16).
Until being provided with the operation start signal (NO in step S17),
the MC mode is set to the second waiting mode. If being provided
with the operation start signal (YES in step S17), the MC mode is
29
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
returned to the normal mode again and the washing-water temperature
in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the set temperature.
[0064] When the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled
as described above, as illustrated in Fig. 6, the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is kept to be about 70 degree C during a
period in which the MC mode is set to the initial normal mode, and if
the mode is set to the waiting mode, the temperature is lowered to about
60 degree C and then kept to be 60 degree C. If the quiescent
operating state continues for the predetermined time period after being
set to the first waiting mode, the MC mode is set to the second waiting
mode, and the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is kept to be 50
degree C. After that, if the MC mode is returned to the normal mode,
the temperature is elevated from 50 degree C to 70 degree C and kept to
be 70 degree C.
[0065] In contrast, as illustrated in Fig. 7, if being provided with the
operation start signal before the quiescent operating state continues for
the predetermined time period after being set to the first waiting mode,
the MC is returned to be in the normal mode again, and the temperature
is elevated from 60 degree C to 70 degree C and kept to be 70 degree C.
In a conventional dishwashing machine, the washing-water temperature
in the tank 15 has been controlled so as to be always in 70 degree C.
Therefore, by executing control as described in the present modified
example, energy saving can be achieved further than in the conventional
dishwashing machine.
[0066] In addition, by executing control as described above, the
following advantages are provided. For example, during transition
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
period between busy period and resting period, in some cases, operation
may be executed one or two times with intervening a short resting state.
During transition period, the washing water is controlled in the waiting
mode to be in the first waiting temperature, and if the operation is
restarted, washing-water temperature is controlled to be the set
temperature from the first waiting temperature. The time At2 required
for rising the washing-water temperature from the first waiting
temperature to the set temperature is shorter than the time At 1 required
for rising the washing-water temperature from the second waiting
temperature to the set temperature when the operation is restarted while
controlling the washing-water temperature to be the second waiting
temperature. Accordingly, in first operation after the MC mode is
returned to the normal mode, washing can be executed using hot-water
in a higher temperature, and simultaneously, the washing-water
temperature can be elevated to the set temperature faster, and thus,
degradation of the washing performance can be suppressed further. In
contrast, in a case where the washing-water temperature is controlled so
as to be the first waiting temperature, and operation is not restarted
within the predetermined time period, the washing-water temperature is
controlled so as to be the second waiting temperature that is lower than
the first waiting temperature, and thus, energy saving in the quiescent
operating state can be surely achieved.
[0067] Moreover, in some cases, resting time may temporarily be long
during busy period. Even for such cases, since the temperature is
quickly returned to the set temperature when the operation start signal is
input, operation would have no trouble. Thus, control for energy
31
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
= FP09-0312-00
saving matching with the usage of the dishwashing machine 1 can be
executed.
[0068] In addition, although in the present modified example two steps
of waiting modes composed of the first waiting mode and the second
waiting mode are provided, three or more steps of waiting modes may
be provided.
[0069]
Third Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 8, if the power-supply switch 45 is turned
on (step S21), MC 4 according to the third modified example is set to be
in the normal mode (step S22). In the normal mode, on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based on
the measured value of the sensor 17 so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature (about 70
degree C).
[0070] In the normal mode, if being provided with no operation start
signal and an quiescent operating state in which operation is not
executed is continued for a predetermined time period (15 minutes)
(YES in step S23), the MC mode is set to the waiting mode from the
normal mode (step S24) by the MC 4. Until the quiescent operating
state does not continue for 15 minutes (NO in step S23), the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled in the normal
mode to be the set temperature.
[0071] In the waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be applied to
the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based on the
measured value of the washing-water temperature sensor 17, so that the
32
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes the waiting
temperature (about 50 degree C) that is lower than the set temperature
(step S24). Until being provided with the operation start signal (NO in
step S25), the MC mode is set to the waiting mode. If being provided
with the operation start signal (YES in step S25), the MC mode is set to
a semi-waiting mode (step S26).
[0072] In the semi-waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be
applied to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based
on the measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes a semi-waiting temperature (about
60 degree C) that is higher than the waiting temperature and lower than
the set temperature (step S26). If 5 minutes elapses after being
provided with the operation start signal during the waiting mode (YES
in step S27), and being provided with the operation start signal by n or
more times within a predetermined time period (5 minutes) (YES in step
S28), the MC mode is returned to the normal mode again and the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the
set temperature (about 70 degree C).
[0073] In contrast, if being not provided with the operation start signal
by n or more times within the predetermined time period (5 minutes)
(NO in step S28), the MC mode is returned to the waiting mode from
the semi-waiting mode.
[0074] When the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled
as described above, as illustrated in Fig. 9, the temperature in the tank
15 is kept to about 70 degree C during a period in which the MC mode
is set to the initial normal mode, and if the MC mode is set to the
33
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
waiting mode, the temperature is lowered to about 50 degree C and then
kept to 50 degree C. After that, if being provided with the operation
start signal during the waiting mode, the MC mode is set to the
semi-waiting mode, and the temperature in the tank 15 is kept to about
60 degree C, and if being provided with the operation start signal by n
or more times within the predetermined time period, the MC mode is
returned to the normal mode, and the temperature in the tank 15 is kept
to 70 degree C. In contrast, if being not provided with the operation
start signal by n or more times within the predetermined time period, the
MC mode is returned to be the waiting mode again, and the temperature
in the tank 15 is kept to 50 degree C. On the contrary, in the
conventional dishwashing machine the temperature in the tank 15 has
been controlled so as to be always 70 degree C. Therefore, by
executing control as described in the present modified example, energy
saving can be achieved further than in the conventional dishwashing
machine.
[0075] Moreover, in the dishwashing machine according to the third
modified example, if being provided with the operation start signal once
during the waiting mode, the MC mode is set to a semi-waiting mode.
And, if being provided with the operation start signal by a
predetermined number of times within the predetermined time period
after being in the semi-waiting mode, the MC mode is returned to the
normal mode from the semi-waiting mode. Therefore, if resting period
makes transition to busy period, the MC mode is returned to the normal
mode from the waiting mode via the semi-waiting mode so as to match
well with the transition, and thus, degradation of the washing
34
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
performance can be suppressed. In contrast, if being not provided with
the operation start signal by the predetermined number of times within
the predetermined time period after being in the waiting mode, the MC
mode is returned to the waiting mode. Therefore, if being operated
once after being set to the waiting mode, the MC mode is not returned
to the normal mode, and instead, it is returned to the waiting mode. In
addition, if being not operated for a while and being in a resting state,
the MC mode is switched from the semi-waiting mode to the waiting
mode again. That is, if being operated by many times, the dishwashing
machine is judged to be in busy period and the MC mode is set to the
normal mode, and if being operated by a few times, the dishwashing
machine is judged not to be in busy period and the MC mode returned to
the waiting mode instead of the normal mode. As described above, the
heater 16 is controlled depending on the usage, and thus, further energy
saving can be achieved.
[0076] In addition, in step S23, the time required for determining to
switch the MC mode from the normal mode to the waiting mode is set
to 15 minutes, and in step S27, the time required for determining to
whether mode among the normal mode and the waiting mode to switch
the mode from the semi-waiting mode is set to 5 minutes that is shorter
than the above one. Thus, the mode of destination is determined by
judging the usage in such a short time of five minutes after the mode is
switched to the semi-waiting mode.
[0077] In addition, in this modified example, by providing the
semi-waiting mode between the waiting mode and the normal so as to
elevate the hot-water temperature in a stepwise manner, the MC mode is
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode, however, it is also
possible for the mode to be returned to the normal mode from the
waiting mode by providing more steps. Moreover, timing when the
mode is returned to the normal mode from the semi-waiting mode, may
be a time point at which 5 minutes elapses after the operation-start
signal is input in the waiting mode, or may be a time point at which n-th
operation has been executed.
[0078]
Fourth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 10, a dishwashing machine 1A according
to the fourth modified example includes a motion sensor 47 for
detecting the motion of a human in the surroundings using infrared-rays
or microwaves. The sensor 47 may be fixed to the dishwashing
machine 1A itself, or it may be fixed to surrounding wall etc. of a place
in which the dishwashing machine 1A is arranged, while being
connected to the MC 4 of the dishwashing machine 1A.
[0079] As illustrated in Fig. 11, in the dishwashing machine 1A, if the
power switch 45 is turned on (step S31), the MC 4 is set to be in the
normal mode (step S32). In the normal mode, on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based on
the measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature (about 70
degree C).
[0080] In the normal mode, if in an quiescent operating state in which
the operation start signal is not input, and operation is not executed, the
motion sensor 47 does not detect a motion for a predetermined time
36
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
period (15 minutes) (YES in step S33), the MC 4 switches its mode
from the normal mode to the waiting mode (step S34). Until a state in
which the motion sensor 47 does not detect a motion in the quiescent
operating state continues for the predetermined time period in the
quiescent operating state (NO in step S43), the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the set temperature in
the normal mode.
[0081] In the waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be applied to
the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the MC4, based on the
measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water temperature
in the tank 15 becomes a temperature (about 50 degree C) that is lower
than the set temperature (step S34). The MC mode continues to be set
to the waiting mode until the sensor 47 detects a motion (NO in step
S35). If a motion is detected by the sensor 47 (YES in step S35), the
MC mode is returned to the normal mode again and the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to become the set
temperature.
[0082] In this case, for example, if operation enters a resting state and a
user leaves from the kitchen in intermission time etc., motion is not
detected by the sensor 47, and thus, the mode is automatically switched
from the normal mode to the waiting mode after the predetermined time.
If the user returns to the kitchen and carries out a motion such as a
cooking motion after the intermission time, and thus, user's motion is
detected by the sensor 47, the mode is returned to the normal mode from
the waiting mode. Therefore, by switching the mode to the normal
mode before operation is actually started again, the washing-water
37
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
= FP09-0312-00
temperature in the tank 15 can be elevated to the set temperature. That
is, by the time when the dishes P are washed after cooking and dining,
the washing-water temperature in the tank 15 can be surely elevated to
the set temperature. Therefore, degradation of the washing
performance when the mode is returned to the normal mode from the
waiting mode can be suppressed further.
[0083] In addition, it is preferable for sensitivity of the sensor 47 to be
adjustably configured according to installation location and conditions
etc. of the dishwashing machine 1. Moreover, as the turning point at
which the mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode
may be a time point at which the motion is detected by the sensor 47 by
a predetermined number or more of times within a predetermined time
period. Therefore, detection accuracy can be improved.
[0084]
Fifth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 12, a dishwashing machine 1B according to
the fifth modified example includes an illuminance sensor 48 for
detecting the illuminance of surroundings. The sensor 48 is fixed to
the operation panel 44 so as to surely measure the illuminance of
surroundings of the panel 44.
[0085] As illustrated in Fig. 13, in the dishwashing machine 1B, if the
power switch 45 is turned on (step S41), the MC 4 is set to be in the
normal mode (step S42). In the normal mode, on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based on
the measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature (about 70
38
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
degree C).
[0086] In the normal mode, if in an quiescent operating state in which
the operation start signal is not input, and operation is not executed, the
measured value by the sensor 48 is less than a predetermined value for a
predetermined time period (15 minutes) (YES in step S43), the MC 4
switches its mode from the normal mode to the waiting mode (step
S44). Until a state in which the measured value by the sensor 48 is
less than the predetermined value continues for the predetermined time
period in the quiescent operating state (NO in step S43), the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the
set temperature in the normal mode.
[0087] In the waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be applied to
the heater 16 is executed by the MC4, based on the measured value of
the sensor 17, so that the washing-water temperature in the tank 15
becomes a temperature (about 50 degree C) that is lower than the set
temperature (step S44). The MC mode continues to be set to the
waiting mode until the sensor 48 detects illuminance with a
predetermined value or more (NO in step S45). If illuminance with the
predetermined value or more is detected by the sensor 48 (YES in step
S45), the MC mode is returned to the normal mode again, and the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the
set temperature.
[0088] In this case, if light is turned off in intermission time and
operation enters a resting state, the mode is automatically switched to
the waiting mode from the normal mode. By automatically switching
the mode to the normal mode if activity in a kitchen is started again
39
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
after the intermission time is finished and light is turned on, the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 can be elevated before
operation is actually started again. Therefore, degradation of the
washing performance when the mode is returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode can be suppressed further.
[0089] In addition, in the case of the illuminance sensor 48, blind spots
are difficult to be generated than in the case of the motion sensor 47,
and thus, if activity in the kitchen is started again after the intermission
time is finished and light is turned on, the vicinity of the operation panel
44 is surely brightened. The mode can be returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode more surely before operation is actually started
again. The sensor 48 may be fixed to surrounding wall etc. of a place
in which the dishwashing machine 1B is arranged, while being
connected to the MC 4 of the dishwashing machine 1B. In addition, it
is preferable that the predetermined values mentioned above are set in
accordance to the installation environment of the dishwashing machine
1B .
[0090] Moreover, as the turning point at which the mode is returned to
the normal mode from the waiting mode may be a time point at which
the motion is detected by the sensor 48 by a predetermined number or
more of times within a predetermined time period. Therefore,
detection accuracy can be improved.
[0091]
Sixth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 14, a dishwashing machine 1C according to
the sixth modified example includes a sound sensing sensor 48 for
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
detecting the sound of surroundings. The sensor 49 has a function to
measure sound pressure.
[0092] As illustrated in Fig. 15, in the dishwashing machine 1C, if the
power switch 45 is turned on (step S51), the MC 4 is set to be in the
normal mode (step S52). In the normal mode, on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the heater 16 is executed by the MC 4, based on
the measured value of the sensor 17, so that the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature (about 70
degree C).
[0093] In the normal mode, if in an quiescent operating state in which
the operation start signal is not input, and operation is not executed, the
measured value by the sensor 49 is less than a predetermined value for a
predetermined time period (15 minutes) (YES in step S53), the MC 4
switches its mode from the normal mode to the waiting mode (step S54).
Until a state in which the measured value by the sensor 49 is less than
the predetermined value continues for the predetermined time period in
the quiescent operating state (NO in step S53), the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the set temperature in
the normal mode.
[0094] In the waiting mode, on-off control of voltage to be applied to
the heater 16 is executed by the MC4, based on the measured value of
the sensor 17, so that the washing-water temperature in the tank 15
becomes a temperature (about 50 degree C) that is lower than the set
temperature (step S54). The MC mode continues to be set to the
waiting mode until the sensor 49 detects sound pressure with a
predetermined value or more (NO in step S55). If sound pressure with
41
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
the predetermined value or more is detected by the sensor 49 (YES in
step S55), the MC mode is returned to the normal mode again, and the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is controlled so as to be the
set temperature (about 70 degree C).
[0095] In addition, it is also possible for the mode to be set to the
waiting mode in step S53, if accumulation value of sound pressure
detected by the sensor 49 within the predetermined time period is
smaller than the predetermined value, and to be set to the normal mode
in step S55, if accumulation value of sound pressure detected by the
sensor 49 within the predetermined time period is equal to or greater
than the predetermined value.
[0096] As described above, when the sound sensing sensor 49 is used,
if working sound in the kitchen disappears in intermission time etc., the
mode is automatically set to the waiting mode from the normal mode,
and if user's working sound is generated after the intermission time is
finished, the mode can be automatically returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode. That is, in the waiting mode, by detecting
sound in surroundings of the dishwashing machine 1C, operation
restarting can be predicted. Therefore, by switching the mode to the
normal mode before operation is started again, the washing-water
temperature in the tank 15 can be elevated before operation is started.
Accordingly, degradation of the washing performance when the mode is
returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode can be suppressed
further.
[0097] It is not necessary for the sound sensing sensor 49 to be installed
outside the dishwashing machine 1C in the same way as the motion
42
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
.
FP09-0312-00
sensor 47 and the illuminance sensor 48, and instead, the sensor 49 can
be installed inside the dishwashing machine 1C. Therefore, the sensor
49 is not easily affected by water, oil smoke, and contamination etc. in
the kitchen, and false detection can be suppressed. Moreover, since it
is not necessary for the sensor 49 to be added with components for
waterproofing and antifouling like the sensor 47 and the sensor 48, price
of the sensor 49 becomes more reasonable. In addition, it is preferable
that the predetermined values mentioned above are set in accordance
with the installation environment of the dishwashing machine 1C.
[0098]
Seventh Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 16, a dishwashing machine 1D according
to the seventh modified example includes a resting button 46 for
receiving user's setting of the waiting mode on the operation panel 44.
The button 46 , if being pushed down one time, is set so that the mode is
returned to the normal mode in one hour later, if being pushed down
two times, is set so that the mode is returned to the normal mode in 2
hours later, if being pushed down three times, is set so that the mode is
returned to the normal mode in 3 hours later, and if being pushed down
N times, is set so that the mode is returned to the normal mode in N
hours later.
[0099] As illustrated in Fig. 17, in the dishwashing machine 1B, if the
power switch 45 is turned on (step S61), the MC 4 is set to be in the
normal mode (step S62). In the normal mode, if the resting button 46
is pushed down N times (YES in step S63), the mode is set to the
waiting mode and set so as to be returned to the normal mode in N
43
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
hours later (step S64). Then, if N hours elapses after the mode is set to
the waiting mode (YES in step S65), the mode is returned to the normal
mode from the waiting mode.
[0100] In this case, when the dishwashing machine enters the quiescent
operating state, the mode, by being input from a user, can be surely
switched to the waiting mode from the normal mode. Further, if the
time set by the user elapses, the mode can be surely returned to the
normal mode.
[0101] Moreover, if the resting button is pushed down N times, it is
also possible for the mode to be set to the waiting mode, and
simultaneously to be set so as to be returned to the normal mode from
the waiting mode in 20 minutes before N hours, for example, so that the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 becomes the set temperature
in N hours later. Thus, when operation is started again, since the
washing-water temperature in the tank 15 is surely elevated to the set
temperature, degradation of the washing performance can be prevented.
In addition, since long time is required to elevate the temperature when
the ambient temperature is low, it is also possible to provide a
thermometer for detecting the ambient temperature so that the MC 4
calculates the timing at which the mode is returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode, using a correction value based on the ambient
temperature
[0102] Moreover, as illustrated in Fig. 18, it is also possible for the
mode to be returned to the normal mode when the operation-start signal
is input during the waiting mode. In this case, if the power-supply
switch 45 is turned on (step S71), the MC 4 is set to be in a normal
44
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
mode (step S72). In the normal mode, if the resting button is pushed
down N times (YES in step S73), the mode is set to the waiting mode
and set so as to be returned to the normal mode in N hours later (step
S74).
[0103] If the operation-resting signal is input during the waiting mode
(YES in step S75), the mode is returned to the normal mode. Even
when the operation-resting signal is input, if N time elapses after the
mode is set to the waiting mode (YES in step S76), the mode is returned
to the normal mode. In this case, since when operation is started again
earlier than predetermined time, the mode is automatically returned to
the normal mode, the convenience is improved.
[0104] In addition, as for an input button for receiving user's setting of
the waiting mode, it is not limited to the resting button 46 mentioned
above, instead, it may be configured with including an up-button, a
down-button, and determination button. In this case time can be set by
the up-button and the down-button, and the mode can be switched to the
waiting mode and set so as to be returned to the normal mode after the
set time elapsed by the determination button. Moreover, it is also
possible to carry out setting so that the mode is returned to the normal
mode from the waiting mode in fixed time later. In this case, it is also
possible to configure so that, if the resting button is pushed down 1
time, the mode switches from the normal mode to the waiting mode,
and, if the resting button is pushed down 2 times, the mode is returned
to the normal mode.
[0105]
Eighth Modified Example
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
As illustrated in Fig. 19, MC 4 according to the eighth modified
example, if being provided with the operation-start signal, is judged
whether it has been in the waiting mode (step S81). When the mode
entered the normal mode (NO in step S81), standard operation is
executed (step S82). The normal operation is referred to as operation
having washing time of about 41 seconds and rinsing time of about 6
seconds. When the mode entered the waiting mode (YES in step S81),
washing-time-extending operation of which washing time is extended is
executed (step S83).
[0106] In this case, if the operation-start signal is received during the
waiting mode, control of the washing-water heater 16 transitions to the
normal mode from the waiting mode. In contrast, as for operation,
washing-time-extending operation in which the washing time is
extended from 41 seconds to 61 seconds is executed. When the mode
is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode, in the washing
step executed for the first time, washing may be executed in a state in
which the washing-water temperature is still lower than the set
temperature, resulting in degradation of the washing performance.
Therefore, by extending the washing time in the washing step
immediately after the mode is returned to the normal mode than normal
washing time, degradation of the washing performance can be
suppressed. Thus, the reliability of the dishwashing machine can be
improved.
[0107] In addition, in the washing-time-extending operation, it is also
possible to extend the washing time by preset extending time. In this
case, In this case, by suitably setting the extension time, degradation of
46
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
the washing performance due to temperature lowering of the washing
water can be suppressed.
[0108] In addition, it is also possible to extend the time of the washing
step for operation executed by the predetermined number of times after
the mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode.
Moreover, it is also possible to execute operation by extending the
washing time when the measured value input from the washing-water
temperature sensor 17 is equal to or smaller than 60 degree C.
[0109]
Ninth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 20, MC 4 according to the ninth modified
example, if being provided with the operation-start signal, is judged
whether it has been in the waiting mode (step S91). When the mode
entered the normal mode (NO in step S91), standard operation is
executed (step S92). The normal operation is referred to as operation
having washing time of about 41 seconds and rinsing time of about 6
seconds. When the mode entered the waiting mode (YES in step S91),
rinsing-time-extending operation of which rinsing time is extended is
executed (step S93).
[0110] In this case, if the operation-start signal is received during the
waiting mode, control of the washing-water heater 16 transitions to the
normal mode from the waiting mode. In contrast, as for operation, the
rinsing time is extended from 6 seconds to 11 seconds. When the
mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode, in the
washing step executed for the first time, hot-water temperature jetted on
the dishes may be lower than the set temperature, resulting in
47
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
degradation of the sterilizing performance. However, since the rinsing
time in the rinsing step executed for the first time is extended than
normal rinsing time, degradation of the sterilizing performance by
heating can be suppressed. In addition, by extending the rinsing time,
heat-sterilization equivalent weight (3600HUE (Heat Unit Equivalent))
determined in NST-standard can be satisfied.
[0111] In addition, it is also possible to extend the time of the rinsing
step for operation executed by a predetermined number of times after
the mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode.
Moreover, it is also possible to execute operation by extending the
rinsing time when the measured value input from the sensor 17 is equal
to or smaller than 60 degree C.
[0112]
Tenth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 21, MC 4 according to the tenth modified
example, if being provided with the operation-start signal, is judged
whether it has been in the waiting mode (step S101). When the mode
entered the normal mode (NO in step S101), standard operation is
executed (step S102). The normal operation is referred to as operation
in which the washing pump 23 is operated at a preset output in the
washing step. When the mode entered the waiting mode (YES in step
S101), strong-washing operation in which the output of the pump 23 is
set to be larger than the preset output of the standard operation in the
washing step is executed (step S103).
[0113] In this case, if the operation-start signal is received during the
waiting mode, control of the heater 16 transitions to the normal mode
48
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
from the waiting mode. In contrast, as for operation, strong-washing
operation in which the output of the washing pump 23 is set to be larger
than that of the standard operation in the washing step is executed.
When the mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode,
in the washing step executed for the first time, although washing may be
executed in a state in which the washing-water temperature is still lower
than the set temperature, resulting in degradation of the washing
performance, since strong washing is executed in the washing step
executed for the first time after the mode is returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode, degradation of the washing performance can be
suppressed without extending the washing time.
[0114] In addition, it is also possible to use the strong-washing
operation for operation executed by the predetermined number of times
after the mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode.
Moreover, it is also possible to execute the strong-washing operation
when the measured value input from the sensor 17 is equal to or smaller
than 60 degree C.
[0115]
Eleventh Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 19, MC 4 according to the eleventh
modified example, if being provided with the operation-start signal
during the waiting mode, executes washing-time-extending operation
similarly to the eighth modified example.
Specifically, MC 4
according to the eleventh modified example, if being provided with the
operation-start signal, is judged whether it has been in the waiting mode
(step S81). When the mode entered the normal mode (NO in step
49
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
S81), standard operation is executed (step S82). The normal operation
is referred to as operation having washing time Tw of about 41 seconds,
resting time Tr of about 5 seconds, and rinsing time Ts of about 6
seconds. When the mode entered the waiting mode (YES in step S81),
washing-time-extending operation of which washing time Tw is
extended is executed (step S83).
[0116] As illustrated in Fig. 22, in the eleventh modified example, the
washing time Tw is extended so as to be finished when the
rinsing-water temperature H in the tank 28 has reached a
washing-step-finishing temperature (81 degree C) in the
washing-time-extending operation in step S83. The
washing-step-finishing temperature is a temperature preset so that the
rinsing-water temperature H becomes the set temperature (85 degree C)
at a time-point when the resting time Tr is finished, that is, when the
rinsing step is started, in consideration of temperature rising of the
rinsing water in resting time Tr.
[0117] In the eleventh modified, if the operation-start signal is input in
the MC 4 during the waiting mode, the washing time Tw is
automatically extended until the rinsing-water temperature becomes the
washing-step-finishing temperature. Moreover, after washing time Tw
is finished, the rinsing-ware is also heated during the resting time Tr,
and thus, the rinsing-water temperature becomes the set temperature at
the start of the rinsing step. Therefore, since the rinsing step by the
rinsing water in the set temperature is surely executed, rinsing of dishes
with a sufficient sterilizing effect can be ensured. In addition, the
rinsing-water heater 29 stops to heat the rinsing water the rinsing-water
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
temperature reaches to the set temperature. Moreover, by
automatically extending the washing time Tw until the rinsing-water
temperature reaches to the washing-step-finishing temperature while
considering rising of the rinsing water in the resting time Tr, time
required for operating the dishwashing machine can be reduced than the
case where the washing time Tw is extended until the rinsing-water
temperature reaches to the set temperature, which contributes to energy
saving for the dishwashing machine.
[0118]
Twelfth Modified Example
As illustrated in Figs. 19 and 23, MC 4 according to the twelfth
modified example, if being provided with the operation-start signal
during the waiting mode, extends the washing time Tw until the
rinsing-water temperature H reaches to the washing-step-finishing
temperature (81 degree C), similarly to the eleventh modified example.
The MC 4 according to the twelfth modified example, stops heating of
the rinsing-water heater 29 when the temperature H has reached a
heater-stopping temperature (81 degree C), by considering that even if it
stops heating of the heater 29 when the temperature H has reached the
set temperature (85 degree C), the rinsing-water is overheated by the
thermal inertia to be in a temperature overshot by ATd. The
heater-stopping temperature is preset so that, even if heating of the
heater 29 is stopped, the temperature H becomes the set temperature at
the start of the rinsing step by the thermal inertia.
[0119] In addition, it is not necessary for the heater-stopping
temperature to coincide with the washing-step-finishing temperature,
51
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
and the heater-stopping temperature is suitably set according to the
volume of the rinsing-water tank 28 and the heating performance of the
rinsing-water heater 29. That is, when the heating performance of the
heater 29 is strong, it is possible to set the heater-stopping temperature
to be lower than the washing-step-finishing temperature and to stop
heating of the heater 29 in midstream of the washing step. Moreover,
when the heating performance of the heater 29 is weak, it is possible to
set the heater-stopping temperature to be higher than the
washing-step-finishing temperature and to stop heating of the heater 29
during the resting time Tr. Furthermore, it is also possible to
determine the heater-stopping temperature and the
washing-step-finishing temperature by measuring the temperature rising
of the rinsing water during the washing-time-extending operation and
using the measured result and the duration of the resting time Tr.
[0120] In the twelfth modified example, by stopping heating of the
heater 29 when the rinsing-water temperature H has reached the
heater-stopping temperature, excessive temperature rising of the rinsing
water exceeding the set temperature, that is overshooting, can be
suppressed. Therefore, since the generation of unnecessary thermal
energy can be avoided, energy saving of the dishwashing machine can
be achieved.
[0121] Moreover, by suppressing the overshooting of the rinsing water
in the tank 28, bungle of a temperature-overheating-prevention device
such as a bimetal and a thermostat, provided in the tank 28, can be
avoided, which contributes to improve reliability of the dishwashing
machine. In addition, even if the above described control is applied to
52
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
the washing-water heater 16, other than the rinsing-water heater 29,
similar effects can also be obtained.
[0122]
Thirteenth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 24, MC 4 according to the thirteenth
modified example, if being provided with the operation-start signal, is
judged whether it has been in the waiting mode (step S111). When the
mode entered the normal mode (NO in step S111), standard operation is
executed (step S112). The normal operation is referred to as operation
having washing time Tw of about 41 seconds, resting time Tr of about 5
seconds, and rinsing time Ts of about 6 seconds. When the mode
entered the waiting mode (YES in step S81),
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation in which time from the start
point of the washing step to the start point of the rinsing step is extended
is executed (step S113).
[0123] As illustrated in Fig. 25, in the thirteenth modified example, in
the rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation in step S113, until the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 reaches to the set temperature
(85 degree C), time from the start of operation to the start point of the
rinsing step, that is the total time of the washing time Tw and the resting
time Tr, is extended.
[0124] As a specific description, a case will be considered, in which the
capacity of the heater 29 is 6000 W, the volume of the heater 29 is 6.6L,
and the thermal efficiency of the heater is 100%, in the dishwashing
machine. In this case, if the temperature difference AT1 between the
rinsing-water temperature H and the set temperature is 10 degree C,
53
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
time S1 required to elevate the temperature H to the set temperature is
expressed by the following formula (1):
Si = 1000 W /860 cal x 6.6L x 10 C/6000 W x 3600 sec
46 sec === (1)
[0125] As shown in formula (1), the time Si required to elevate the
rinsing-water temperature H from 75 degree C to the set temperature
(85 degree C) is substantially equal to the time from the start of
operation to the start point of the rinsing step in the standard operation,
that is, total time Tsuml (about 46 seconds) of washing time Tw (about
41 seconds) and resting time Tr (about 5 seconds), and thus, the time
extension is not substantially executed. In addition, even if the time
extension is not necessary by calculation, operation does not switch to
the standard operation, instead, the rinsing-step-start-time-extending
operation in which, until the rinsing-water temperature reaches to the set
temperature 85 degree C, the time from the start of operation to the start
point of the rinsing step is automatically extended is executed in
response to external influence such as ambient temperature.
[0126] Next, a case will be considered, in which the temperature
difference AT2 between rinsing-water temperature J and the set
temperature is 20 degree C. In this case, time S2 required to elevate
the temperature J to the set temperature is expressed by the following
formula (2):
S2 = 1000 W /860 cal x 6.6L x 20 C/6000 W x 3600 sec
r=1 92 sec =..( 2)
[0127] As shown in formula (2), time S2 required to elevate the
rinsing-water temperature J from 65 degree C to the set temperature (85
54
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
degree C) becomes Tsum2 (about 92 seconds), that is, the sum of total
time Tsumi (about 46 seconds) of washing time Tw (about 41 seconds)
and resting time Tr (about 5 seconds) in the standard operation, and 46
seconds. Therefore, the MC 4 according to the thirteenth modified
example, by extending washing time Tw or resting time Tr or both of
them, executes the rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation so that
the time from the start point of the washing step to the start point of the
rinsing step becomes Tsum2.
[0128] In the thirteenth modified example, since time from the start of
operation to the start point of the rinsing step is extended, rinsing step
using rinsing water in the set temperature capable of sufficiently
sterilizing dishes P is surely executed with no regard to external
influence such as ambient temperature. In addition, since rinsing step
using rinsing water in the set temperature, is surely ensured,
unnecessary extension of operation time can be avoided while setting
the waiting temperature of the rinsing water in the waiting mode to
lower temperature, which is advantageous for optimizing usage energy
with regard to the operation of the dishwashing machine, that is, energy
saving.
[0129]
Fourteenth Modified Example
As illustrated in Fig. 26, MC 4 according to the fourteenth
modified example, if operation (cycle operation, one-cycle operation) is
started during the waiting mode, during N (a preset number of
extension) times of operation, executes the
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation described above.
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
= FP09-0312-00
[0130] Specifically, the MC 4 according to the fourteenth modified
example, if operation is started, is judged whether it has been in the
waiting mode (step S121). When the mode entered the waiting mode
(YES in step S121), the preset extension number of times N is assigned
to a variable n (initial value: 0) for counting the number of operation
times (step S122). The extension number of times N is set according
to the amount of the rinsing water accumulated in the hot-water-supply
pipe 27 (refer to Fig. 2) for supplying the rinsing water to the tank 28
and the amount of the rinsing water used by one time of operation,
during the waiting mode. That is, by considering that, if the rinsing
water accumulated in the hot-water-supply pipe 27 is cooled and the
cooled water is supplied to the tank 28, for a plurality number of
operation times, the rinsing water in the tank 28, the rinsing-water
temperature in the tank 28 is lowered significantly, operation number of
times for using up the rinsing water accumulated in the pipe 27 is set as
the extension number of times N.
[0131] After that, the value of the variable n is decreased by one (step
S123), and the rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation is executed
(step S124). After the rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation,
next operation is executed by operation of a user (opening/closing of
door, and operation of an operation button).
[0132] In contrast, if operation is started during the normal mode (NO
in step S121), whether the variable n for counting operation number of
times is 0 is judged (step S125), if n is not 0 (YES in step S125), the
step advances to step S 123. Then, in step S123, the value of the
variable n is decreased by 1, and then the
56
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation is executed (step S124).
After that, by operation of the user, next operation is started.
[0133] In contrast, if n is 0 (NO in step S125), the standard operation is
executed (step S126). After that, by operation of the user, next
operation is started.
[0134] As described above, every time when
the
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation is executed in each
operation, after operation started during the waiting mode, the value of
the variable n is decreased by 1. If the value of the variable n becomes
0, the subsequent operation becomes the standard operation. In this
way, the MC 4 according to the fourteenth modified example, if
operation is started during the waiting mode, during N (a preset number
of extension) times of operation, executes the
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation described above. In
addition, the normal operation, similar to that in the thirteenth modified
example, is referred to as operation having washing time Tw of about
41 seconds, resting time Tr of about 5 seconds, and rinsing time Ts of
about 6 seconds.
[0135] If the waiting mode, that is, the quiescent operating state,
continues for a long period, the rinsing water in the hot-water-supply
pipe 27 for connecting the external water heater and the tank 28 is
cooled and the temperature is lowered to about normal temperature. If
the cooled rinsing water is supplied to the tank 28, the rinsing-water
temperature in the tank 28 is lowered significantly.
[0136] Specifically, such a dishwashing machine that uses the rinsing
water of 2L per one time of operation, will be considered. In this case,
57
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
= FP09-0312-00
if the length of the pipe 27 made of SS-steel pipe with nominal diameter
of 1/2B (JIS) becomes 8 m, the amount of the rinsing water
accumulated in the pipe during the quiescent operating state becomes
2.13 L, the amount exceeds the amount of the rinsing water used by one
time of operation. As a result, the cooled rinsing water in the pipe 27
is supplied to the tank 28 in the second operation, and thus, the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 is lowered significantly. As a
result, as in the thirteenth modified example, even if the
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation is executed only for the first
operation after operation is started during the waiting mode, the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 is lowered significantly every
time when the cooled rinsing water is supplied to the tank 28, and there
is a possibility that temperature rising of the rinsing water may not be in
time by the time the rinsing step is started.
[0137] Accordingly, in the fourteenth modified example, the
rinsing-step-start-time-extending operation is executed, in which time
from the start of operation to the start point of the rinsing step during N
(a preset number of extension) times of operation, after operation is
started during the waiting mode is extended. Thus, even if in the
second or later operation after operation is started during waiting mode,
the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 is lowered significantly by
the supply of the cooled rinsing water in the pipe 27, the rinsing-water
temperature can be surely elevated to the set temperature 85 degree C at
the start point of the rinsing step, and thus, a sufficient sterilizing effect
on dishes P can be ensured.
[0138] In addition, the dishwashing machine according to the
58
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
fourteenth modified example, if temperature difference between the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 and the set temperature is large
at a time point after the N times of rinsing-step-start-time-extending
operation is finished, may provided with a display section for alarming
anomaly around the dishwashing machine.
[0139]
Fifteenth Modified Example
The fifteenth modified example is a more specific example
regarding to the rinsing-water temperature control in the first modified
example. A dishwashing machine according to the fifteenth modified
example is a resting button for receiving setting of the waiting mode
from a user on the operation panel 44 (refer to Fig. 16).
[0140] As illustrated in Fig. 27, the MC 4, if the power-supply switch
45 is turned on (step S131), is set to be in a normal mode (step S132).
The normal mode is referred to as a mode in which on-off control of
voltage to be applied to the washing-water heater 16 is executed by the
MC 4, based on the measured value of the rinsing-water temperature
sensor 31 so that the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 becomes a
set temperature (80 degree C).
[0141] If a door 7 opened after a user racked dishes P is closed (YES in
step S133), the closing of the door is detected by a door switch 10, and
the operation-start signal is input in the MC 4. If the operation-start
signal is input in the MC 4, the washing step in step S142 is started.
[0142] In contrast, if the door 7 is not closed in the normal mode (No in
step S133), the operation-start signal is not input in the MC 4. Then, if
the quiescent operating state continues for 15 minutes or the resting
59
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
button 46 is pushed down (YES in step S135), the mode is set to the
waiting mode from the normal mode (step S135). The waiting mode is
referred to as a mode in which on-off control of voltage to be applied to
the rinsing-water heater 29 is executed by the MC 4, based on the
measured value of sensor 31 so that the rinsing-water temperature of the
rinsing water in the tank 28 becomes a waiting temperature (60 degree
C) that is lower than the set temperature. In addition, until the
quiescent operating state continues for 15 minutes (No in step S134),
the rinsing-water temperature is controlled so as to be the set
temperature, in the normal mode.
[0143] When the door 7 is closed in the normal mode (YES in step
S136), if the door 7 is closed (YES in step S137), the mode is set to the
normal mode from the waiting mode (step S138). After that, if the
door 7 is closed (YES in step S139), the operation-start signal is input
in the MC 4, and the washing step in step S142 is started.
[0144] In contrast, when the door 7 is opened in the waiting mode (No
in step S136), the operation-start signal is input in the MC 4, and the
mode is set to the normal mode from the waiting mode (step S141) by
the MC 4. Then, the washing step in step S142 is started.
[0145] In step S142, washing step is executed with the door 7 being
closed (the door switch is turned on). In the washing step, washing
water accumulated in the tank 15 is pumped to the washing nozzles 9
and 12 by the washing pump 23. Then, by being jetting with the
pumped water from the nozzles 9 and 12, dishes P are washed.
[0146] If the washing step is finished, the rinsing step is executed with
intervening resting time (step S143). In the rinsing step, rinsing water
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
accumulated in the tank 28 is pumped to the rinsing nozzles 11 and 13
by the rinsing pump 34. Then, by being jetting with the pumped water
from the nozzles 11 and 13, dishes P are washed.
[0147] If the door 7 is opened by the user after the rinsing step (YES in
step S144), the step returned to step S133, and by closing the door 7,
next cycle operation is started. In contrast, if a predetermined time
period (15 minutes) continues with the door 7 being closed, without
opening the door 7 (YES in step S145), the mode is set to the waiting
mode from the normal mode (step S146) by the MC 4. After that, the
step returned to step S136), next cycle operation is started by the user
according to the opening/closing of the door 7.
[0148] As described above, by controlling the rinsing-water
temperature in the tank 28, the rinsing-water temperature can be set to
the waiting temperature that is lower than the set temperature in the
quiescent operating state, and thus, power consumption of the heater 29
can be reduced. In addition, by lowering the rinsing-water temperature
in the tank 28 during the waiting mode, heat quantity dissipated by the
tank 28 in the kitchen is reduced, and thus, it is possible to prevent the
inside of the kitchen from being hot. Furthermore, since, time to be
exposed to high temperature is reduced for components near the tank
28, reliability and product-life of them can be improved. Therefore,
according to the dishwashing machine of the fifth modified example,
low cost energy saving can be achieved without adding new
components.
[0149] Moreover, in the dishwashing machine if being provided
with no operation start signal in a predetermined time period, the MC
61
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
mode is switched from the normal mode to the waiting mode, and thus,
if the predetermined time period elapses without operation after the
dishwashing machine enters in the quiescent operating state, the MC
mode can be automatically switched from the normal mode to the
waiting mode. Therefore, since optimum mode matching with the
usage is automatically selected, energy saving control without requiring
user's specific operation can be achieved. Further, when the
dishwashing machine enters the quiescent operating state, if the user
pushes down the button 46, the mode can be switched to the waiting
mode, without waiting for the passage of the predetermined time, and
thus, energy saving can be achieved further. In addition, in the
fifteenth modified example, although only the cycle operation is
described, this example can be preferably applied to one-cycle operation
in which a drying step is added further, and rinsing operation with the
rinsing step only.
[0150]
Sixteenth Modified Example
The sixteenth modified example, similar to the fifteenth
modified example, is a more specific example regarding to the
rinsing-water temperature control in the first modified example. As
illustrated in Fig. 28, a dishwashing machine 1E according to the
sixteenth modified example is mainly differs from the dishwashing
machine according to the fifteenth modified example in that an
operation button 50 for inputting the operation-start signal to the MC 4
therethrough is provided instead of the resting button 46. In the
sixteenth modified example, operation is started by manipulating the
62
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
operation button 50.
[0151] As illustrated in Fig. 29, the MC 4, if the power-supply switch
45 is turned on (step S151), is set to be in the normal mode (step S152).
If the operation button 50 is pushed down in the normal mode (YES in
step S153), the operation-start signal is input to the MC 4, and the
washing step in step S160 is started.
[0152] In contrast, if the button 50 is not pushed down in the normal
mode (NO in step S153), the quiescent operating state is held by the MC
4 without being provided with the operation-start signal. Then, if the
door is opened or closed for 15 minutes (YES in step S154), the mode is
set to the waiting mode from the normal mode (step S155). In
addition, counting of the predetermined time period in step S154, is
reset every time when the door 7 is closed/opened, and started again
from 0. Moreover, until the predetermined time period elapses, the
rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28 is controlled so as to be the set
temperature, in the normal mode.
[0153] When the door 7 is opened/closed in the waiting mode (YES in
step S156), the mode is set to the normal mode from the waiting mode
(step S157). In the normal mode, if the door is opened or closed for
the predetermined time period (YES in step S158), the step is returned
to step 5155 and the mode is set to the waiting mode again.
[0154] In contrast, if the button 50 is pushed down (YES in step S159)
before the door is opened or closed for the predetermined time period
(15 minutes) (No in step S158), the operation-start signal is input in the
MC 4, and the washing step in step S160 is started.
[0155] In step S160, washing step is executed with the door 7 being
63
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
closed (the door switch 10 is turned on). If the washing step is
finished, the rinsing step is executed with intervening resting time (step
S161). If the user opens the door 7 after the rinsing step (YES in step
S162), the step is returned to step S153. Then, next cycle is started by
user's operation of the button 50. In contrast, the predetermined time
period (15 minutes) elapses with the door 7 being not opened and
without opening the door 7 (YES in step S163), the mode is set to the
waiting mode from the normal mode by the MC 4 (YES in step S164).
After that, the step is returned to step S156, and next cycle is started by
user's opening/closing operation.
[0156] As described above, by controlling the rinsing-water
temperature in the tank 28, the dishwashing machine lE according to
the sixteenth modified embodiment can also obtain effects similar to
that of the fifteenth modified embodiment. Further, since input of the
operation-start signal to the MC 4 is executed by the operation of the
button 50 instead of the opening/closing operation of the door 7, it is
surely possible to prevent that operation is started by user's
opening/closing operation of the door 7, despite user's intentions.
[0157] As above, modified examples have been described, the
following matters can be modified.
[0158] In the above description, on-off control of the heaters 16 and 29
is executed by the MC 4, in addition to this, when the mode is returned
to the normal mode from the waiting mode, in order to execute rapid
rising of the temperature of the washing water or the rinsing water, the
washing ware or the rinsing water may be controlled by causing
magnitude of the output of the heater 16 or the heater 29 to be larger as
64
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
usual.
[0159] For example, as for the washing-water heater 16, the magnitude
of the output may be changed by including two heaters having different
output and by connecting either of them, or by including two heaters
having equal output and by switching between parallel connection of
them and series connection of them, or by switching the heater
connection between delta connection and star connection.
[0160] In these cases, when the mode is returned to the normal mode
from the waiting mode, hot-water temperature in the washing-water
tank or the rinsing-water tank is elevated faster at initial period of
operation, and thus, degradation of the washing performance and the
sterilizing performance can be prevented... In addition, when the water
temperature is controlled by using a heater with a large output, and by
causing the heater output during the waiting mode and the heater output
when mode is returned to the normal mode from the waiting mode to be
the same one, since frequency of on-off control of a relay connected to
the heater is increased, the product life of the relay is degraded. In
contrast, in case of changing the magnitude of the heater output,
frequency of on-off control of the relay is not increased, and thusõ
degradation of product life of the relay can be prevented.
[0161] In modified examples 2 to 10, although on-off control of the
heater 16 is executed so that the washing-water temperature in the tank
15 becomes a waiting temperature that is lower than the set temperature
in the waiting mode or the semi-waiting mode, control of the heater 29
may be executed so that the rinsing-water temperature in the tank 28
becomes a waiting temperature that is lower than the set temperature.
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
[0162] In the above cases, triggers to switch the mode from the normal
mode to the waiting mode (semi-waiting mode), are determined as
follows: that the operation-start signal is not provided within a
predetermined time period, that the motion sensor 47 does not detect a
motion within a predetermined time period, that the illuminance sensor
48 does not detect luminance being equal to or greater than a
predetermined value within a predetermined time period, and that the
sound sensing sensor 49 does not detect sound being equal to or greater
than a predetermined value. In contrast, triggers to switch the mode
from the waiting mode to the normal mode, are determined as follows:
that the operation-start signal is input, that the sensor 47 detects a
motion, that the sensor 48 detects luminance being equal to or greater
than a predetermined value, and that the sensor 49 detect sounds being
equal to or greater than a predetermined value. These triggers to
switch the mode from the waiting mode to the normal mode or vice
versa may be used by combining them.
[0163] In addition, the above embodiment and modified examples 1 to
10, it is configured that if the operation-start signal input, operation is
started immediately, however, it is also possible to start operation so
that operation is not executed until the washing or rinsing-water
temperature becomes the set temperature, and if the temperature has
reached the set temperature operation is started by driving the washing
pump 23 or the rinsing pump 34. Therefore, degradation of the
washing performance and the sterilizing performance at the start of
operation is prevented, and thus, the washing performance and the
sterilizing performance can be surely achieved.
66
CA 02729991 2011-01-05
FP09-0312-00
[0164] In addition, contents of each of the modified examples may be
used by suitably combining them.
Industrial Applicability
[0165] According to the dishwashing machines of the present invention,
energy saving can be achieved.
Reference Signs List
[0166]
1 DISHWASHING MACHINE
4 MC (HEATER CONTROL UNIT)
5 WASHING ROOM
WASHING WATER TANK
16 WASHING WATER HEATER
17 WASHING-WATER-TEMPERATURE SENSOR
28 RINSING WATER TANK
15 29 RINSING WATER HEATER
31 RINSING -WATER-TEMPERATURE SENSOR
44 OPERATION PANNEL
46 RESTING BUTTOM (OPERATION SECTION)
47 MOTION SENSOR
48 ILLUMINANCE SENSOR
49 SOUND SENSING SENSOR
67