Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
= CA 02745088 2011-05-30
Device and method for separating product parts of cut products
Description
The invention concerns an apparatus for separating product parts of cut
products, in particular
fish fillets, comprising a transport element for transporting the cut products
still lying together
in the transport direction T, means for transversely conveying product parts
in the transverse
direction Q transversely to the transport direction T. and a transport element
for carrying away
the separated product parts. Furthermore, the invention concerns a
corresponding method for
separating product parts of cut products.
Such apparatuses and methods are used in different areas of industry,
particularly in the food
industry. The fish industry serves as an example of such use. In particular in
the white fish
industry, the fish fillets are portioned. This means that the fish fillets,
which are usually
transported tail first, are cut by longitudinal and/or oblique and/or
transverse cuts into several
products parts, namely individual portions. After cutting, these portions are
still grouped
together on the transport element and must be separated and sorted. The aim is
to produce
product streams of a single type.
A fish fillet is usually cut into the so-called loin, belly and tail sections.
A liner division is
provided by cutting the fish fillet into the so-called long loin, belly, left
over and tail tip
sections. Due to the longitudinal cuts in the fish fillets, that is, cuts made
in the transport
direction T of the fish fillets, individual product parts lie adjacent to each
other in the
transport direction. By the example of fish fillets, e.g. the loin section and
the belly section lie
adjacent to each other.
The listing or naming of product parts is purely an example and not limited to
the named
product either. The same naturally also applies to other products in the food
industry, such as
e.g. poultry (here e.g. breast fillets), as well as products in other areas of
industry, such as e.g.
paper or the like.
Basically, apparatuses for sorting products are known. DIE 94 08 979 U I
describes, for
example, an apparatus which comprises product pushers, the product pushers
being movable
in vertical and horizontal directions. The product pushers serve to push
individual products
from a transport element onto a storage area or onto another transport
element. For this, the
CA 02745088 2012-11-29
2
product pusher pushes the product as a whole off the transport element, or
engages
completely over the product in order to pull it onto another transport
element. Many
products, in particular wet and/or sticky products, as e.g. fish fillets are,
are however not
suitable for pushing. Furthermore, the apparatus described in the named
document is only
suitable for moving the products as a whole in the transverse direction. In
other words, the
apparatus cannot separate individual product parts.
In order to separate individual product parts of cut products, the desired
product parts are first
taken off the conveyor belt manually. However, there are also possible ways of
at least
partially mechanically separating and sorting such products, that is, in
particular also fish
fillets, which have already been cut. This applies in particular to product
parts of the fish
fillet located one behind the other in the transport direction. These can be
pulled apart and
therefore separated and sorted e.g. using speed belts. But product parts
located adjacent to
each other, such as e.g. the loin section or long loin section, cannot be
separated and sorted in
this way.
It is therefore an object of the invention to provide an apparatus which
ensures the automatic
and careful separation of product parts located adjacent to each other in the
transport
direction.
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
apparatus for
separating product parts of cut products, comprising a transport element for
transporting the
cut products still lying together in the transport direction T, means for
transversely conveying
product parts in the transverse direction Q transversely to the transport
direction T, and a
transport element for carrying away the separated product parts, characterised
in that the
apparatus further comprises means for detecting the position of the products
on the transport
element and for capturing product-specific data and in that the means for
transverse
conveying has at least two product fingers which are designed to engage in
cutting grooves
between product parts and/or to rest on product parts and can be controlled in
accordance
CA 02745088 2012-11-29
2a
with the position of the products and the product-specific data accordingly
for transverse
conveying in the transverse direction Q.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a
method for
separating product parts of cut products, characterised by the following
steps:
delivery of the cut products still lying together in the transport direction T
by means
of a transport element,
detection of the position of the products on the transport element and capture
of
product-specific data,
Other objects, aspects, embodiments, variants and/or resulting advantages of
the present
invention, all being preferred and/or optional, are briefly summarized
hereinbelow.
20 For example, the device mentioned hereinbefore is advantageous by the
fact that the
apparatus comprises means for detecting the position of the products on the
transport element
and for capturing product-specific data and that the means for transverse
conveying has at
least two product fingers which are designed to engage in cutting grooves
between product
parts and/or to rest on product parts and can be controlled in accordance with
the position of
25 the products and the product-specific data accordingly for transverse
conveying in the
transverse direction Q. As a result of this construction according to the
invention, product
parts located adjacent to each other can be separated in the transverse
direction from the
product lying on the transport element, without damaging the other product
parts or altering
their position, by the fact that the product fingers can control or grip
individual product parts
CA 02745088 2012-11-29
2b
selectively and move them in the transport direction Q off the transport
element. Due to
knowledge of the exact product position and the individual product data (that
is, in particular
the geometric data and/or image data) on the one hand and cooperation of the
product fingers
with the product parts on the other hand, it is ensured that the product
parts, although they are
10
25/
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 3 -
conveyed continuously, can be separated to form streams of products or product
parts of a
single type (e.g. loin sections only or long loin sections only).
An appropriate development of the invention is distinguished in that the
product fingers are
constructed and designed to pull the product parts in the transverse direction
Q transversely to
the transport direction T. This ensures that even wet and sticky products or
product parts can
be moved off the transport element without damaging the product parts or
otherwise adversely
affecting them.
Advantageously, all of the product fingers are spring-loaded. Due to the fact
that force-
locking between the product fingers and the product is produced by the
springs, the products
are handled carefully.
A preferred embodiment of the invention is characterised in that all of the
product fingers are
disposed on a common support and designed to be movable out of a standby
position into a
work position and vice versa and the support has at least one further degree
of freedom for
performing the transverse movement in the transverse direction Q. In this way
a uniform
transverse pulling movement is ensured in a particularly simple and effective
manner. so that
the product parts to be pulled off the transport element remain unchanged in
their orientation.
Appropriately, the support is pivotable about an axis C which runs vertically
to the plane of
transport of the products, in such a way that the product fingers disposed on
the support can
be moved into different angular positions in relation to the transport
direction T. Thus
different positions of the product fingers relative to the product or product
parts can be
achieved within the plane of transport. If a product lies obliquely on the
transport element, the
product fingers can nevertheless be placed exactly in the cutting grooves or
on the
corresponding product parts. Furthermore, due to the pivot movement during the
transverse
movement, different mass inertias of the product parts. such as is the case
e.g. with a fish fillet
with the head and tail regions. can be compensated.
A preferred embodiment according to the invention provides that the product
fingers can be
controlled in groups, but preferably all individually. This allows individual
and careful
handling of the product, so that the precision and reliability during
separation of the product
parts are improved.
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 4 -
The object is also achieved by the method mentioned hereinbefore which is
characterised by
the following steps: delivery of the cut products still lying together in the
transport direction I
by means of a transport element, detection of the position of the products on
the transport
with the apparatus. To avoid repetition, reference is made to the
corresponding passages.
A particularly preferred method is characterised in that the product parts are
pulled off the
transport element, wherein the product fingers are pivoted about a vertical
axis C during the
apparent from the subsidiary claims and the description. A particularly
preferred embodiment
as well as the principle of the method are described in more detail with the
aid of the attached
drawings. The drawings show:
25 Figure 1 a top view of the apparatus according to the invention
with product fingers
which, for transverse conveying of the loin section, engage in a cutting
groove
between loin section and belly section, wherein the product fingers located
outside the loin section are in the standby position,
30 Figure 2 a top view of the apparatus with product fingers which,
for transverse convey-
ing of the long loin section, on the one hand engage in the cutting groove
between long loin section and belly section and on the other hand rest on the
long loin section,
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 5 -
Figure 3 a front view of the apparatus and
Figure 4 an individual product finger which is designed for force-
locking abutment
against product parts.
The apparatus shown is used to separate product parts of cut fish fillets.
Naturally, with this
device any other products from the food industry and other areas of industry
can be separated
as well.
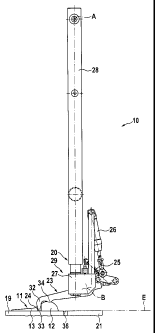
The apparatus 10 shown in the figures is used to separate product parts of cut
products 11, for
example fish fillets. The individual product parts of the fish fillets are
described in more detail
with the aid of Figures 1 and 2, wherein the number and description of the
product parts can
vary. A fish fillet is usually cut into the loin section 12, the belly section
13 and the tail
section 14 (see Figure 1) or the long loin section 15. the belly section 16,
the leftover section
17 and the tail tip section 18 (see Figure 2). These (or other) product parts
lie on a transport
element 19 for transporting the cut product parts still lying together in the
transport direction
T. The transport element 19 can be a revolving, ordinary suction belt. But
other designs of the
transport element 19, e.g. as a closed conveyor belt or the like, are possible
as well.
Particularly suitable are transport elements 19 with a smooth and slippery
surface, possibly
even supplied with water to achieve improved slipperiness. Associated with the
transport
element 19 is a means 20 for transversely conveying product parts in the
transverse direction
Q transversely to the transport direction T. Furthermore, the apparatus 10
comprises a
transport element 21 for carrying away the separated product parts. The
transport element 21
can be identical with the transport element 19. In other words, in such a case
a single transport
element is provided for delivery and carrying away. But preferably the
transport elements 19
and 21 are separate elements (see below on this point).
According to the invention, the apparatus 10 further comprises means (not
shown) for detect-
ing the position of the products 11 on the transport element 19 and for
capturing product-
specific data. Alternatively, the means could also form part of machines
mounted in front of
the apparatus 10, for example the machine for cutting the products 11. The
means is
preferably constructed and designed to capture or determine information on the
position of the
products 11 on the transport element 19 as well as geometric data and/or image
information
on the respective product 11, and to pass it on via suitable control means
(not shown) to the
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 6 -
means 20 for transverse conveying. The means 20 for transverse conveying
itself has at least
two product fingers 23 which are designed to engage in cutting grooves 24
between product
parts and/or for resting on product parts. The product Fingers 23 can in this
case be controlled
in accordance with the position of the products 11 and the product-specific
data for transverse
so that action on the products 11 or product parts can be performed from
above. The product
fingers 23 are constructed and designed to pull the product parts in the
transverse direction Q
transversely to the transport direction T. This applies in particular to the
product fingers 23
resting on the product part. But even the product fingers 23 which go over the
product part to
All of the product fingers 23 are spring-loaded. This means that the product
fingers 23 are
basically pulled down into the work position by spring elements 25, so that
they rest on the
Preferably, however, the product Fingers 23 can be controlled in groups, and
particularly
preferably individually.
All of the product fingers 23 ¨ preferably six product lingers 23 are
provided, wherein the
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 7 -
some other ordinary manner, e.g. by servo or step motors or the like.
Preferably the product
fingers 23 are mounted on the support 27 so as to be pivotable about an axis
B. The support
27 has at least one further degree of freedom for performing the transverse
movement in the
transverse direction Q. To put it another way, the support 27 is optionally
pivotable about at
least one further axis and/or linearly movable along at least one further
axis. Preferably the
support 27 is pivotable about an axis A which is located above the plane of
transport E and
runs in the transport direction T. For this purpose the support 27 is arranged
on a kind of
rocker arm 28, this being at the free end 29 of the rocker arm 28 opposite the
axis A. The
rocker arm 28 can be e.g. a lever or the like. But other embodiments of the
rocker arm 28 are
possible too. The pivot movement can preferably be performed by controlled
drive elements,
such as e.g. a servo motor or step motor. But other drive elements can be used
as well. Instead
of the pivot movements of the product fingers 23 and the rocker arm 28, the
movements can
also be performed by linear drive means, superimposed movements or in some
other manner.
In a further embodiment according to the invention, the support 27 can have a
further degree
of freedom. For example, the support 27 can be pivotable about an axis C which
runs
vertically to the plane of transport E of the products 11, such that the
product fingers 23 can
be brought into different angular positions within the plane of transport E in
relation to the
transport direction. For this purpose the support 27 is mounted rotatably or
pivotably at the
free end 29 of the rocker arm 28. Starting from the original position in which
the support 27 is
oriented substantially parallel to the transport element 19 or to the
transport direction T. a first
stage of the pivot capacity about the axis C can be provided e.g. by a
pneumatic cylinder 30.
By a further pneumatic cylinder 31 a further pivot capacity can be produced.
The pivot
movement is possible in both directions about the axis C. starting from the
original position.
But the pivot movement of the support 27 can also be infinitely adjustable.
All of the product fingers 23 can have the same construction. Preferable,
however, is a
construction of the product fingers 23 adapted to the product geometry and/or
position and
arrangement of the individual product parts relative to each other and/or
design of the cutting
grooves 24. Thus individual or several product fingers 23 can be designed to
produce
(predominantly) form-locking, while other product fingers 23 are designed to
produce
(predominantly) force-locking. As already mentioned above, all of the product
fingers 23
exert a certain degree of force-locking on the products 11 by the spring
elements 25, which
however
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 8 -
can be ignored in the case of smooth products 11, as the fish fillets show.
In the embodiment described in the figures, three product fingers 23 are given
a hooked shape
to produce form-locking with the product 11 (see e.g. Figure 3). This hooked
shape is
particularly suitable for engagement of the product fingers 23 in the cutting
grooves 24
between the product parts, wherein the cutting groove 24 between the loin
section 12 and the
belly section 13 is particularly wide on account of the so-called pin-bone
cut. The hook 32 of
the product fingers 23 which produces form-locking has an edge 33, the so-
called pulling
edge, for abutment against the product part to be moved transversely. With
this edge 33 the
product finger 23 engages in the cutting groove 24. Furthermore, on the side
facing towards
the upper side of the product parts the product finger 23 has a holding
element 34 which
simultaneously functions as a kind of hold-down device. Naturally, the design
of the product
fingers 23 can be different to produce the form-locking.
The other product fingers 23 which produce predominantly force-locking are
shown in detail
in Figure 4. These product fingers 23 are designed without the hook 32 and
have, on the side
facing towards the upper side of the product parts, a surface structure which
supports friction-
locking. This surface structure can be designed in different ways.
Particularly preferably,
several grooves 35 which run transversely to the transverse direction Q are
provided. These
grooves 35 form a non-slip surface structure or contact surface between the
product fingers 23
on the one hand and the product parts on the other hand. The shape or design
of the surface
structure, that is, in the practical example the grooves 35, is in particular
also selected from
the point of view of hygiene. This means that the grooves 35 of the surface
give a rough
structure which is particularly easy to clean. But the number and orientation
and also form of
the grooves 35 can be varied. The grooves 35 can also be replaced by other
structural
elements, such as e.g. spikes or the like. With respect to the length of the
product fingers 23,
these can all have the same length. Preferably the product lingers 23 for
producing force-
locking are however slightly shorter than the product fingers 23 for producing
form-locking.
As mentioned above, in addition to the transport element 19 for delivering and
transporting
the products 11, a further transport element 21 is provided for carrying away
the separated
product parts. The transport elements 19 and 21 are preferably arranged
adjacent to each other
and located approximately at the same height. To put it another way, the
transport elements
19,21 lie in the same plane of transport E. However, the transport elements
19,21 can also be
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 9 -
staggered in height from each other. The two transport elements 19, 21 are
preferably
arranged close together, so that the gap is kept small. Gaps which cannot be
avoided (but are
also deliberately chosen) can be bridged e.g. by an intermediate plate 36 or
the like, wherein
the intermediate plates 36 or equivalent elements assist the transverse
movement of the
product parts off the transport element 19 onto the transport element 21, or
at least do not
block it. With respect to the drive or transport direction T, the two
transport elements 19, 21
are preferably driven in the same direction. But an opposite drive direction
of the two
transport elements 19, 21 is possible as well.
As mentioned, the invention is not confined to the embodiment described. Thus
the means 20
for transverse conveying can also be arranged in a different position, e.g.
laterally of the
transport element 19. In the apparatus 10 described, the products 11, namely
the fish fillets.
are transported tail first. Naturally transport headfirst is possible as well.
But in the separation
of other products 11 or product parts, such as e.g. poultry, stacks of paper
or the like,
completely different positioning and orientation for transport are possible as
well. The
apparatus 10 is of course also suitable for separating or sorting complete
products 11 as a
whole or product parts which have been separated from the product 11 in a way
other than
cutting.
Below, the principle of the method is described in more detail with the aid of
the Figures. The
products 11 are transported along continuously on the transport element 19 by
the apparatus
10 and in the process in particular below the means 20 for transverse
conveying. But inter-
mittent conveying is also basically possible. On delivery to the apparatus 10,
the products 11
on the transport element 19, cut into several product parts but still lying
together. Optionally
the position of the product 11 as well as product-specific information are
detected and
captured or taken from a machine in front, for example a machine for cutting
the products 11.
To separate individual product parts, that is, dispatch them laterally or
transversely or separate
them from the rest of the product 11, the product fingers 23 are first moved
into the correct
position above the product 11. On the basis of the product-specific data and
with knowledge
of the position of the product 11 on the transport element 19. the product
Fingers 23 are
positioned exactly by pivoting about the axis A and/or axis C before they are
pivoted down-
wards about the axis B out of a standby position into a work position. In the
process the
product fingers 23 engage in the cutting groove 24 and/or rest on the product
part to be
separated. As soon as form-locking and/or force-locking is produced between
the product
CA 02745088 2011-05-30
- 10 -
fingers 23 and the product part, the product lingers 23 arranged on the
,:upport 27 pivot with
the support 27 by means of the rocker arm 28 about the axis A. so that the
product parts are
pulled in the transverse direction Q transversely to the transport direction T
to the side of the
transport element 19 or onto the further transport element 21 located adjacent
to the transport
element 19. Then the product fingers 23 are lifted back into the standby
position, so that the
product parts are released. The separated product parts are then carried away.
By the example of Figure 1, only the first three product fingers 23 in the
transport direction T,
which have the hooked shape, become engaged with the cutting groove 24 in
order to separate
the loin section 12. The other three, rear product fingers 23 in the transport
direction T are in
the standby position and at a distance from the product 11. By pivoting the
support 27 about
the axis A, the loin section 12 is separated. To separate the long loin
section 15 (see Figure 2).
all of the product fingers 23 are in the work position, that is, engaged with
and abutting
against the product part. By pivoting the support 27 about the axis A, the
long loin section 15
is separated. Optionally, the product lingers 23 or the support 27 can be
pivoted additionally
about a vertical axis C at least toward the end of the transverse movement, so
that different
mass inertias of the product part are compensated, and placement of the long
loin section 15
parallel to the transport direction T is achieved. In addition there is the
possibility, this being
due to the possibility of individual control of the product fingers 23, of
moving individual
product fingers 23 or the product fingers 23 which pull the section of the
product part with the
higher mass inertia out of engagement or out of contact earlier in time than
the product lingers
23 which pull the section of the product part with the lower mass inertia.
Moreover the product fingers 23 can be actuated independently of each other,
for example for
adaptation to different product sizes. The combination of the product lingers
23 which are
engaged or abutting and the length of time of engagement or abutment can be
chosen as
desired.