Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02747952 2016-01-13
54106-826
- 1 -
,
Electrical motor having rotor support shield
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates to an electrical motor with a
shaft on which a rotor is mounted and with a bearing unit by
means of which the shaft is mounted rotatably. The present
invention relates particularly to a permanent magnet generator
as an electrical motor of this type.
BACKGROUND
Where electrical motors are concerned, it is usually necessary
to exchange the bearing of the rotor at certain intervals. For
this purpose, the rotor has to be supported on another
component of the electrical motor or on a device intended
specifically for this. In permanent magnet-excited electrical
motors, the rotor adheres to the stator not only by gravity,
but also by additional magnetic force, when the rotor is
supported on the stator at the time of bearing exchange.
Tremendous forces are then necessary in order to release the
rotor from the stator again. This presents problems
particularly with regard to wind power plants which possess
relatively large generators.
Hitherto, and only in the case of separately excited
asynchronous generators, a bearing change has been carried out
with the aid of a lifting cylinder which is required for
supporting and raising the rotor. The rotor is then deposited
on the stator. Where permanent magnet generators are concerned,
a bearing change of this type can scarcely be carried out in
practice.
SUMMARY
The object of the present invention is, therefore, to propose
an electrical motor in which a bearing change can be carried
out more easily. In particular, a bearing change is to be
possible even in the case of permanent magnet generators.
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
PCT/EP2009/065733 - la -
2008P22372WOUS
According to the invention, this object is achieved by means of
an electrical motor with a shaft on which a rotor is mounted
and with a bearing unit by means of which the shaft is mounted
rotatably, and also with a rotor support shield, to which the
bearing unit is fastened,
õI
I
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 2 -
2008P22372WOUS
which is dimensioned such that it can support the shaft, with
the bearing unit removed, and which seals off a grease chamber
of the bearing unit with respect to the shaft.
Advantageously, the rotor support shield according to the
invention fulfils not only bearing shield functionality, but
also sealing functionality with regard to a grease chamber of
the bearing unit. On account of this sealing functionality in
which a grease chamber is sealed off with respect to the shaft,
the rotor support shield bears very closely against the shaft,
so that, in the event of an exchange of the bearing, the shaft
can readily be supported on the rotor support shield. As a
rule, the light gap is markedly smaller than the air gap
between the rotor and stator, so that, even in the case of a
permanent magnet generator (that is to say, a permanent magnet-
excited generator), bearing exchange is readily possible,
without the rotor coming into contact with the stator.
Preferably, the rotor support shield is formed as one part. It
is in this case shaped such that it forms virtually a bearing
shield onto which an internal grease chamber cover is formed in
one piece.
The bearing unit may, in particular, be a rolling bearing. In
rolling bearings of this type, exchange is necessary at regular
intervals.
Furthermore, the rotor support shield may have a peripheral
groove which forms part of a grease chamber for the bearing
unit. There is therefore no need for additional elements which
have to specially form a grease chamber.
The clearance between the rotor support shield and the shaft is
advantageously smaller than 0.5 mm in the operationally ready
state of the electrical motor. This low clearance is usually
smaller than the air gap between the rotor and stator,
II I
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 2a -
2008P22372WOUS
particularly in the case of large motors. The rotor
11
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 3 -
2008P22372WOUS
consequently does not come into contact with the stator even
when a bearing is removed from the electrical motor.
In particular, it is advantageous if a draw-off device is
arranged between the bearing outer ring and the rotor support
shield, so that the rolling bearing can be drawn off from the
shaft. It is thereby possible for the rolling bearing to be
drawn off without great effort.
In particular, the draw-off device may be of ring-shaped design
and have a plurality of threaded bores, into which can be
screwed, for drawing off the rolling bearing, screws which are
supported on the rotor support shield in order to generate an
axial draw-off force. Only a few screws therefore have to be
screwed into the draw-off device in order to draw off the
rolling bearing.
Furthermore, a hub for the bearing unit may be screwed to the
rotor support shield. A hub of this type, on the one hand,
ensures a stable mounting and, on the other hand, allows simple
bearing exchange.
Furthermore, an external grease chamber cover for sealing off
the grease chamber of the bearing unit outwardly may be screwed
to the hub. The external grease chamber cover, bearing unit,
hub and rotor support shield thus give rise as components to a
compact bearing unit with a grease chamber and with an easily
exchangeable bearing.
Moreover, it is advantageous if the rotor support shield
possesses a centering portion which ensures that the shaft with
bearing unit is centered in the rotor support shield when the
hub is screwed to the latter. The centering portion thus
ensures that, after the bearing change, the rotor lifts off
automatically from the rotor support shield during assembly and
is brought into the desired centered position.
CA 02747952 2016-01-13
54106-826
' - 4 -
As already indicated, it is especially advantageous if the
electrical motor outlined is designed as a permanent magnet
generator, since what should be avoided precisely in the case
of such a generator is that the rotor comes into contact with
the stator during the bearing exchange.
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is
provided an electrical motor, comprising: a shaft; a rotor
mounted on the shaft; a bearing unit for rotatably supporting
the shaft; a rotor support shield dimensioned to extend to the
shaft, with a gap being defined between confronting surfaces of
the rotor support shield and the shaft and being sufficiently
small to support the shaft, when the bearing unit is removed,
said rotor support shield shaped to bound a grease chamber and
to seal off the grease chamber with respect to the shaft, said
grease chamber adapted for lubrication of the bearing unit and
disposed axially outwards of the bearing unit; a hub connected
to the rotor support shield, with the bearing unit being
arranged axially inwards at a distance to the rotor support
shield between the hub and the shaft; an external cover
connected to the hub to seal the grease chamber against the
outside; and a draw-off device arranged between the bearing
outer ring of the bearing unit and the rotor support shield to
allow the bearing unit to be withdrawn from the shaft.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present invention, then, is explained in more detail by
means of the accompanying drawing which shows a cross section
through a bearing portion of an electrical motor.
The exemplary embodiments outlined in more detail below
constitute preferred embodiments of the present invention.
CA 02747952 2016-01-13
54106-826
. -4a-
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
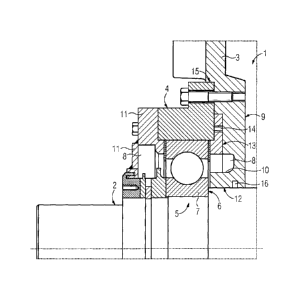
The figure shows a rotor support shield 1 which is typically
arranged on the end face of an electrical motor. It may
therefore be considered as being similar to a bearing shield as
part of the overall housing of the electrical motor. The figure
illustrates only that enlarged portion of the rotor support
shield 1 which is located in the center of the electrical
motor, that is to say in the vicinity of the shaft 2 of the
rotor, not illustrated in any more detail. The rotor support
shield 1 possesses a bearing shield portion 3 to which a hub 4
is screwed. A rolling bearing 5 is located between the hub 4
and a corresponding portion of the shaft 2. The inner ring 6 of
the rolling bearing 5 is pressed directly onto the shaft 2. The
outer ring 7 of the rolling bearing 5 is supported by the hub
4. The shaft 2 is consequently mounted via a hub 4 in the
conventional way.
Furthermore, the bearing is lubricated by the grease of a
grease chamber 8. The grease chamber 8 extends in the axial
direction on both sides of the rolling bearing 5. Inside the
electrical motor, the grease chamber 8 is sealed off, between
the shaft and rotor support shield, by an internal cover
portion 9 with seal (felt ring) which is connected in one part
to the bearing shield portion 3 and with the latter forms the
rotor support shield 1. So that a desired volume of grease
chamber 8
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 5 -
2008P22372WOUS
can be ensured, the internal cover portion 9 possesses a
peripheral groove 10 into which grease can be pressed. The
internal cover portion 9 extends virtually as far as a
corresponding portion of the shaft 2. Between the two
components a gap 12 remains, which cannot be seen in the figure
and which is usually smaller than 0.5 mm and amounts, for
example, to 0.3 mm. The grease chamber 8 is sealed off with
respect to the shaft 2 by means of the internal cover portion 9
as a result of this small gap 12 and the seal 16. Grease from
the grease chamber 8 therefore cannot penetrate into the inner
space of the electrical motor. The grease chamber 8 is closed
outwardly be means of an external cover 11. This external cover
11 of the grease chamber 8 is screwed axially onto the hub 4.
A draw-off device 13 is provided between the internal cover
portion 9, on the one hand, and the hub 4 and bearing outer
ring 7, on the other hand. In the assembled state, the draw-off
device 13, which is of ring-shaped design, has virtually no
effect. The draw-off device 13 is required only for drawing off
the rolling bearing 5. For this purpose, the draw-off device 13
possesses, for example distributed on the circumference,
threaded bores 14 into which screws (not illustrated) are
screwed for drawing off and are then supported on the internal
cover portion 9. The draw-off of the rolling bearing 5 is, of
course, possible only when the hub 4, including the external
cover 11, has been unscrewed from the rotor support shield 1.
The function of the rotor support shield according to the
invention is explained in more detail below. As already
indicated, in the exchange of the rolling bearing 5, first the
hub 4, including the external cover 11, is unscrewed from the
electrical motor (for example, a permanent magnet generator).
The rolling bearing 5 consequently loses radial support.
However, since the gap 12 is very small, with the hub 4 removed
the shaft is supported radially by the rotor support shield 1,
especially the internal cover portion 9. Since there is only a
I
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
=
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 5a -
2008P22372WOUS
clearance of 0.3 mm between the shaft 2 and internal cover
portion 9, there is no need to support the shaft 2 by means of
an additional appliance. Moreover,
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
=
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 6 -
2008P22372W0US
a rotor fitted with permanent magnets cannot come to bear
against the stator and remain adhering there with tremendously
high forces.
A rotor support shield 1 according to the invention which is of
this type can be used especially advantageously in wind power
plants. To be precise, a bearing change can thereby be carried
out in the gondola of a wind power plant having a permanent
magnet motor, without the rotor being capable of coming to bear
against the stator. The rotor could otherwise no longer be
released due to the high forces in the gondola.
It should be possible for the rolling bearing 5 to be drawn off
from outside, without the rotor having to be removed completely
from the stator. Since the rolling bearing 5 is pressed onto
the shaft 2, correspondingly high forces are necessary in order
to draw it off. In the present example, therefore, the ring-
shaped draw-off device 13 is integrated in the internal cover
portion 9. With the hub 4 removed, the threaded bores 14 of the
draw-off device 13 are accessible. As already indicated, the
axial forces for drawing off are generated by screws which are
supported on the internal cover portion 9. In this case, an
inner radial portion of the draw-off device 13 presses against
the bearing outer ring 7 of the rolling bearing 5. The rolling
bearing 5 can thus be pressed off from the shaft 2.
After a new bearing has been mounted on the shaft 2, the hub 4,
including the external cover 11, is screwed to the rotor
support shield 1 again. However, since the shaft 2 is supported
on the rotor support shield 1, said shaft has to be raised in
the radial direction in order to reach its operationally ready
position. For this purpose, a shaped slope 15 on the rotor
support shield 1 and a corresponding fit on the hub 4 serve as
a centering portion. The shaped slope 15 provides in the rotor
support shield 1 a conical depression which merges into a
cylindrical fit. When the hub 4 is fitted with its fit into
11
CA 02747952 2011-06-21
=
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 6a -
2008P22372WOUS
this depression, centering of the shaft 2 is thereby achieved
automatically. In a special case, by the hub 4 being screwed
on, raising of the shaft by the amount of
1,1
H
, CA 02747952 2011-06-21
,
,
PCT/EP2009/065733 - 7 -
2008P22372WOUS
0.3 mm and consequently self-centering of the shaft take place.
Alternatively, of course, a fit with a shaped slope on the hub
and a corresponding fit on the rotor support shield may also be
provided for the self-centering of the shaft. If appropriate, a
lifting cylinder may additionally be used in order to raise the
rotor.
The rotor support shield 1 according to the invention, by means
of which the rotor can be supported during a bearing change,
brings numerous advantages. On the one hand, costs and space
for additional appliances, such as an on-board crane in the
gondola of a wind power plant, can be saved. Furthermore, the
bearing shield or rotor support shield (for example, 250 kg)
does not have to be removed from the generator and set down on
the thin gondola wall, which would cause safety problems.
Moreover, a bearing change in the most confined possible space
is possible as a result of the rotor support shield according
to the invention.
,