Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
1
A 5-HYDROXY-QUINOLINE DERIVATIVE FOR OXIDATIVE DYEING OF KERATIN
FIBERS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a composition for the oxidative dyeing of
keratin fibers,
in particular human keratin fibers, comprising (A) a 5-hydroxy-quinoline
derivative as defined in
formula (I) hereafter, a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt
thereof, or mixtures thereof
and (B) an oxidizing agent.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The oxidative dyeing process using one or more oxidative hair coloring
precursors in
combination with one or more oxidizing agent is the most extensively used
method to color hair.
Commonly, the oxidative dyeing colorants are marketed as a two components kit.
One
component comprises the dye precursors and ammonia and the other is a
stabilized solution of
hydrogen peroxide. The two components are mixed immediately prior to use and
applied to the
hair. The dye precursors and peroxide diffuse into the hair where they undergo
rapid reaction,
which leads to the formation of higher molecular weight coloured materials.
The dyes precursors are divided into two classes: primary intermediates and
couplers. The
specific combination of these two classes of precursors, their amount and
their variety in the hair
dyeing composition lead to the achievement of a unique color.
Therefore, it is important to develop and search continuously for new dye
precursor
candidates in order to achieve new shades or better color results of the
already existing shades.
The aim of the invention is to develop a new hair dye composition providing a
strong hair
color intensity together with color-rich shades, good resistance against
shampooing and rubbing.
Indeed, it has surprisingly been found that the oxidative hair dyeing
composition
comprising at least a 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative of general formula (I)
provides strong hair
color intensity together with excellent properties of resistance to the
various treatments which
keratinous fibers may undergo.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to a first aspect, the present invention relates to a composition
for the oxidative
dyeing of keratin fibers, in particular human keratin fibers comprising (A) a
5-hydroxy-quinoline
derivative of the general formula (I) or a physiologically compatible water-
soluble salt thereof, or
mixtures thereof and (B) an oxidizing agent.
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
2
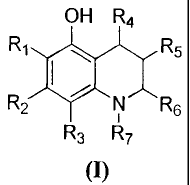
OH R4
R1 R5
R2 N R6
11
R3 R7
(I)
wherein R1 to R7 are as defined hereafter.
According to a second aspect, the present invention relates to a method of
dyeing hair
comprising the steps of:
(i) providing a tint component comprising (A) a 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative
of
formula (I), a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof, or
mixtures thereof;
(ii) providing a developer component comprising (B) an oxidizing agent;
(iii) mixing the tint component and the developer component to obtain a
composition for
the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers; and
(iv) applying said composition for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers onto
the hair.
According to a third aspect, the present invention relates to a kit
comprising: (i) a tint
component comprising (A) a 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative as defined in
formula (I), a
physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof, or mixtures thereof;
(ii) a developer
component comprising an (B) oxidizing agent.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
As used herein, the term "composition for the oxidative dyeing of keratin
fibers" means a
ready-to-use composition in a suitable carrier medium for dyeing keratin
fibers, in particular
human hair, comprising oxidative dye precursors (primary intermediates and
couplers) and an
oxidizing agent. These compositions can typically be the result of a mixture
of two compositions
namely a tint component comprising the dye precursors and usually an
alkalizing agent such as
ammonia and a developer component comprising the oxidizing agent.
As used herein, the term "keratin" refers to a scleroprotein found in
epidermal tissues and
modified into hard structures such as horns, hair, and nails. As used herein,
the term "hair" refers
to keratinous fibers on a living, e.g. a person, or non-living body, e.g. in a
wig, hairpiece, or other
aggregation of non-living keratinous fibers. Mammalian, preferably human, hair
is preferred.
Notably, hair, wool, fur, and other keratinous fibers are suitable substrates
for coloring by the
compounds and compositions described herein.
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
3
As used herein, the term "dye precursor" refers to compounds that may be used
in the
composition to act as primary intermediates, couplers, or both, in order to
provide the desired
color to ketatinous fibers.
It is to be understood that within the scope of this invention, numerous
potentially and
actually tautomeric compounds are involved. It is to be understood that when
this development
refers to a particular structure, all of the reasonable additional tautomeric
structures are included.
In the art, tautomeric structures are frequently represented by one single
structure and the
invention follows this general practice.
The present invention relates to a 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative of general
formula (I), a
physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof, or mixtures thereof:
OH R4
Ri R5
R2 N R6
R3 R7
(I)
wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are substituents selected independently of
each other
from the group consisting of:
(a) C-linked substituents selected from the group consisting of-
(i) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono- or poly- unsaturated, alkyl or heteroalkyl systems,
(ii) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono- or poly- unsaturated, aryl systems, and
(iii) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono- or poly- unsaturated, heteroaryl systems, and
wherein said systems of (i), (ii) and (iii) comprise from about I to 10 carbon
atoms and
from about 0 to 5 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of 0, F, N, P
and Si;
(b) S-linked substituents selected from the group consisting of SA', SO2A',
SO3A', SSA',
SOA', SO2NA'A2, SNA'A2, and SONA'A2;
(c) 0-linked substituents selected from the group consisting of OA', ONA'A2;
(d) N-linked substituents selected from the group consisting of NA'A2;
(NA'A2A3)+,
NA' SA2, NO2; NA' A2;
(e) substituents selected from the group consisting of COOA', CONA',
CONA'COA2,
C(=NA')NA'A2, CN, and X;
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
4
(f) fluoroalkyl substituents selected from the group consisting of mono-, poly-
, and per-
fluoro alkyl systems comprising from I to 12 carbon atoms and from 0 to 4
heteroatoms; and
(g) H;
wherein A', A2, and A3 are selected independently of each other from the group
consisting of: H; mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or
branched, saturated or
mono-or poly- unsaturated, alkyl or heteroalkyl systems; mono- or poly-
substituted or
unsubstituted, straight or branched, mono-or poly- unsaturated, aryl or
heteraryl systems; and
substituted or unsubstituted, mono-, poly-, or per-fluoro alkyl systems, or At
and A2 together with
nitrogen atoms to which they are bound form a ring; wherein said systems
comprise from 1 to 10
carbon atoms and from 0 to 5 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
0, S, N, P, and
Si; and wherein X is a halogen selected from the group consisting of F, Cl,
Br, and I; and
wherein R7 is a substituent selected independently of each other from the
group consisting
of:
(h) C-linked substituents selected from the group consisting of:
(i) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono-or poly- unsaturated, alkyl or heteroalkyl systems,
(ii) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono-or poly- unsaturated, aryl systems, and
(iii) mono- or poly- substituted or unsubstituted, straight or branched,
saturated or
mono-or poly- unsaturated, heteroaryl systems, and
wherein said systems of (i), (ii) and (iii) comprise from about 1 to 10 carbon
atoms and
from about 0 to 5 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of 0, F, N, P
and Si;
(i) substituents selected from the group consisting of COOA', CONA',
CONA'COA2,
C(=NA')NA'A2, CN; and
(j) H.
Suitable salts of formula (I) are also included such as chlorides, bromides,
sulfates, such
as hemisulfates, tartrates, lactates, malates and acetates.
In a preferred embodiment, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are selected
independently of each
other from the group consisting of a H; a halogen atom; an amino substituent,
a hydroxyl
substituent; a cyano substituent; a C1-C4 alkyl substituent; a trifluoromethyl
substituent; an
alkylamino substituent; a hydroxyalkylamino substituent; an acetylamido
substituent; a carboxyl
substituent or its esters; an alkoxy substituent; an alkoxyalkyl substituent;
a carbamoyl
substituent; an alkylcarbamoyl substituent; a hydroxyalkylcarbamoyl
substituent; an amido
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
substituent; an alkylarnido substituent; an alkylcarbonyl substituent; an
alkoxycarbonyl
substituent; an aryloxy substituent; an acyloxy substituent; an alkylthio
substituent; an arylthio
substituent; a heteroarylthio substituent; a heteroaryloxy substituent; a
thiocyano substituent; a 3-
, 4-, 5-, 6-, or 7- membered heterocycle having at least one nitrogen, oxygen
or sulfur atom; an
5 aryl substituent which is optionally substituted; a sulfonyl substituent; a
sulfinyl substituent; a
phosphonyl substituent; a sulfamoyl substituent; a siloxy substituent; an
acyloxy substituent; a
carbamoyloxy substituent; a sulphonamide substituent; an imide substituent; a
ureido substituent;
a sulfamoylamino substituent; an alkoxycarbonylamino substituent; an
aryloxycarbonylamino
substituent; an aryloxycarbonyl substituent; and a benzenesulfonamido
substituent.
In a preferred embodiment, R7 is selected independently of each other from the
group
consisting of a H; a Cl-C4 alkyl substituent; an alkylamino substituent; a
hydroxyalkylamino
substituent; an acetylamido substituent; a carboxyl substituent or its esters;
an alkoxy substituent;
an alkoxyalkyl substituent; a carbamoyl substituent; an alkylcarbamoyl
substituent; a
hydroxyalkylcarbamoyl substituent; an alkylamido substituent; an alkylcarbonyl
substituent; an
alkoxycarbonyl substituent.
In a preferred embodiment the 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative (I) is a compound
with
formula (1.1):
OH
N
H
(I.1)
In order to achieve the desired hair color, the 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative
of formula
(I) can be combined with one or more primary intermediate.
The primary intermediate may be a 4,5-diamino pyrazole derivative of the
general
formula (II) or a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof:
R8 NR9R10
N
N NR11R12
R13
(II)
wherein R3 has the same definition given above for R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6
and wherein
R9, R10, R11, R12 and R13 have the same definition given above for R7 of the 5-
hydroxy-quinoline
derivative of formula (I).
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
6
Rg, R9, R10, R11, R12 and R13 are substituents selected independently of each
other from
the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 hydroxalkyl, C2-C4 alkoxy
and mixtures
thereof.
In a preferred embodiment the 4,5-diamino pyrazole derivative (II) is a
compound of
formula (II.1):
NH2
NT
N\ NH2
OH
(11.1)
The primary intermediate may be a 1,4-diamino-benzene derivative of the
general
formula (III) or a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof-
NH2
R14 R16
R15 R17
NH2
(III)
wherein R14, R15, R16 and R17 have the same definition given above for R1, R2,
R3, R4, R5,
and R6 of the 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative of formula (I). Preferably R14,
R15, R16 and R17 are
selected independently of each other from the group consisting of hydrogen,
halogen, hydroxyl,
CI-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 hydroxalkyl, C2-C4 alkoxy and mixtures thereof.
The 1,4-diamino-benzene derivative (III) may be a compound of formula (111.1):
NH2
NH2
(III.1)
The 1,4-dialnino-benzene derivative (III) may be a compound of formula
(111.2):
NH2
NH2
(III.2)
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
7
The 1,4-diamino-benzene derivative (III) may be a compound of formula (111.3):
NH2
OH
NH2
(111.3)
The 1,4-diamino-benzene derivative (III) may be a compound of formula (111.4):
NH2
HO,-,~,~ N "-~OH
(111.4)
The primary intermediate may be a 4-amino-phenol derivative of the general
formula
(IV) or a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt thereof:
NH2
Res R20
Rig R21
OH
(IV)
wherein R18, R19, R20 and R21 have the same definition given above for R1, R2,
R3, R4, R5
and R6 of the 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative of formula (I). Preferably R18,
R19, R20 and R21 are
selected independently of each other from the group consisting of hydrogen,
halogen, hydroxyl,
C1-C6 alkyl, C2-C6 hydroxalkyl, C2-C4 alkoxy and mixtures thereof.
The 4-amino-phenol derivative (IV) may be a compound of formula (IV.1):
NH2
OH
(IV.!)
The 4-amino-phenol derivative (IV) may be a compound of formula (IV.2):
NH2
OH
(IV.2)
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
8
The primary intermediate may be 2,4,5,6-tetraaminopyrimidine or a
physiologically
compatible water-soluble salts thereof of formula (V):
NH2
HZN1-1-Y NH2
NYN
NH2
(V)
Oxidizing Agent
The compositions of the invention comprise an oxidizing agent. Typical
suitable
oxidizing agents for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers may be selected
from hydrogen
peroxide, sodium periodate, urea peroxide, melamine peroxide, perborates,
percarbonates,
perphosphates, persilicates, persulfates, oxidizing enzymes such as uricases,
oxidases, and
peroxidases, and mixtures thereof. Hydrogen peroxide, perborates, or
percarbonates may be
preferred.
Another potential oxidizing agent for use herein is a source of
peroxymonocarbonate
ions. Preferably, such a source is formed in situ from a source of hydrogen
peroxide and a
hydrogen carbonate ion source. Such an oxidizing agent has been found to be
particularly
effective at a pH of up to and including 9.5, preferably from about 7.5 to
about 9.5 more
preferably about pH 9. Moreover, this system is also particularly effective in
combination with a
source of ammonia or ammonium ions.
Accordingly, any source of these peroxymonocarbonate ions may be utilized.
Suitable
sources for use herein include sodium, potassium, guanidine, arginine,
lithium, calcium,
magnesium, barium or ammonium salts of carbonate, carbamate and hydrocarbonate
ions and
mixtures thereof. In particular, sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate,
potassium
carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate, guanidine carbonate, guanidine
hydrogen carbonate,
lithium carbonate, calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, barium carbonate,
ammonium
carbonate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and mixtures thereof may be preferred.
Percarbonate
salts may also be utilized to provide both the source of carbonate ions and as
an oxidizing agent.
Preferred sources of carbonate ions, carbamate and hydrocarbonate ions are
sodium hydrogen
carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate, ammonium carbonate, ammonium
carbamate, and
mixtures thereof.
The hair dyeing composition may usually comprise from about 1% to about 15%
by,
typically from about 1.5% to about 10% by weight, and more typically from
about 2% to about
8% by weight of the oxidizing agent relative to the total weight of the
composition.
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
9
The oxidizing agent may be provided in a developer component which is mixed to
a tint
component to obtain the composition of the invention. The developer component
may be based
on any desired formulation chassis, including any commercial product, for
example an oil-in-
water emulsion. Typical developer components comprise about 6% or about 9% of
the H202
relative to the total weight of the composition. A commercial example is the
Welloxon
Emulsion with respectively about. 6% and about 9% H202, marketed by Wella and
comprising as
INCI ingredients: Water, H202, Cetearyl Alcohol, Ceteareth-25, Salicylic Acid,
Phosphoric Acid,
Disodium Phosphate, Etidronic Acid.
The hair dyeing composition of the invention may be formed as thick liquid,
cream, gel,
emulsion, foam, aerosol mousse or as a solid form to which water is added to
generate the
oxidant and form a thickened vehicle suitable for hair coloring. They may
comprise in addition to
the ingredients indicated above further ingredients in order to further
enhance the properties of
the composition, including but not limited to: solvents; oxidative dyes,
direct dyes; oxidizing
agents; radical scavengers; thickeners and or rheology modifiers; chelants; pH
modifiers and
buffering agents; carbonate ion sources; peroxymonocarbonate ion sources;
anionic, cationic,
nonionic, amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants, or mixtures thereof;
anionic, cationic, nonionic,
amphoteric or zwitterionic polymers, or mixtures thereof; fragrances; enzymes;
dispersing
agents; peroxide stabilizing agents; antioxidants; natural ingredients, e.g.
proteins and protein
compounds, and plant extracts; conditioning agents including silicones and
cationic polymers,
ceramides, preserving agents; and opacifiers and pearling agents (such as
titanium dioxide and
mica). Some adjuvants referred to above, but not specifically described below,
which are suitable
are listed in the International Cosmetics Ingredient Dictionary and Handbook,
(8th ed.; The
Cosmetics, Toiletry, and Fragrance Association). Particularly, vol. 2,
sections 3 (Chemical
Classes) and 4 (Functions) are useful in identifying specific adjuvants to
achieve a particular
purpose or multipurpose. A few of these ingredients are discussed herein
below, whose
disclosure is of course non-exhaustive.
Alkalizing agent
The composition for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers may further
comprise,
generally in the tint component, an alkalizing agent as known in the art. Any
alkalizing agent
known in the art may be used such as ammonia, alkanolamines for example
monoethanolarnine,
diethanolamine, triethanolamine, monopropanolamine, dipropanolamine,
tripropanolamine, 2-
amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, 2-amino-2-methyl- l-propanol, and 2-amino-2-
hydroxymethyl-
1,3-propanediol, guanidium salts, alkali metal and ammonium hydroxides such as
sodium
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
hydroxide, alkali metal and ammonium carbonates, and mixtures thereof. Typical
alkalizing
agents are ammonia and/or monoethanolamine.
Typically, the compositions for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers
comprise from
about 0.1% to about 10%, preferably from about 0.5% to about 6%, more
preferably from about
5 1% to about 4% by weight of the alkalizing agent relative to the total
weight of the composition.
Primary intermediates
In addition to the pyrazole compounds of the invention, the hair dyeing
compositions of
the invention may comprise further primary intermediates. Suitable primary
intermediates for use
in the compositions described herein include, but are not limited to: toluene-
2,5-diamine, p-
10 phenylenediamine, N-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-p-
phenylenediamine, 2-hydroxyethyl-p-phenylenediamine, hydroxypropyl-bis-(N-
hydroxyethyl-p-
phenylenediamine), 2-methoxymethyl-p-phenylenediamine, 2-(I,2-dihydroxyethyl)-
p-
phenylenediamine, 2,2'-(2-(4-aminophenylamino)ethylazanediyl)diethanol, 2-(2,5-
diamino-4-
methoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol, 2-(7-amino-2H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazin-4(3H)-
yl)ethanol, 2-
chloro-p-phenylenediamine, p-aminophenol, p-(methylamino)phenol, 4-amino-m-
cresol, 2-
methoxy-p-phenylenediamine, 2,2'-methylenebis-4-aminophenol, 2,4,5,6-
tetraminopyrimidine,
2,5,6-triamino-4-pyrimidinol, I -hydroxyethyl-4,5-diaminopyrazole sulfate, 4,5-
diamino-l-
methylpyrazole, 4,5-diamino-l-ethylpyrazole, 4,5-diamino-l-isopropylpyrazole,
4,5-diamino-l-
butylpyrazole, 4,5-diamino-l-pentylpyrazole, 4,5-diamino-l-benzylpyrazole, 2,3-
diamino-6,7-
dihydropyrazolo[1,2-a]pyrazol-1(5H)-one dimethosulfonate, and mixtures
thereof.
Typically, the compositions for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers
comprise from
about 0.1% to about 10%, preferably from about 0.3% to about 6%, more
preferably from about
0.5% to about 4% by weight of the primary intermediates relative to the total
weight of the
composition.
Couplers
In addition to the pyrazole compounds of the invention, the hair dyeing
compositions of
the invention may comprise couplers to obtain various shades. Suitable
couplers for use in the
compositions described herein include, but are not limited to: resorcinol, 4-
chlororesorcinol, 2-
ch lororesorcinol, 2-methylresorcinol, 4,6-dichlorobenzene-1,3-diol, 2,4-
dimethylbenzene-1,3-
diol, m-aminophenol, 4-amino-2-hydroxytoluene, 2-methyl-5-
hydroxyethylaminophenol, 3-
am ino-2,6-dimethylphenol, 3-amino-2,4-dichlorophenol, 5-amino-6-chloro-o-
cresol, 5-amino-4-
chloro-o-cresol, 6-hydroxybenzomorpholine, 2-amino-5-phenylphenol, 2-amino-5-
methylphenol, 2-amino-6-rnethylphenol, 2-amino-5-ethoxyphenol, 5-methyl-2-
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
11
(methylamino)phenol, 2,4-diaminophenoxyethanol, 2-amino-4-
hydroxyethylaminoanisole, 1,3-
b1s-(2,4-diam1nophenoxy)-propane, 2,2'-(2-methyl-1,3-
phenylene)bis(azanediyl)diethanol,
benzene- 1,3 -diani in 2,2'-(4,6-diamino-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy)diethanol, 3-
(pyrrolidin-l-
yl)aniline, 1-(3-(dimethylamino)phenyl)urea, 1-(3-aminophenyl)urea, 1-
naphthol, 2-methyl-l-
naphthol, 1,5-naphthalenediol, 2,7-naphthalenediol or 1-acetoxy-2-
methylnaphthalene, 4-chloro-
2-methylnaphthalen- l -ol, 4-methoxy-2-methylnaphthalen- I -ol, 2,6-dihydroxy-
3,4-
dimethylpyridine, 2,6-dimethoxy-3,5-pyridinediamine, 3-amino-2-methylamino-6-
methoxypyridine, 2-amino-3-hydroxypyridine, 2,6-diaminopyridine, pyridine-2,6-
diol, 5,6-
dihydroxyindole, 6-hydroxyindole, 5,6-dihydroxyindoline, 3-methyl-l-phenyl-lH-
pyrazol-
5(4H)-one, 1,2,4-trihydroxybenzene, 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylamino)ethanol
(also known as
hydroxyethyl-3,4-methylenedioxyaniline), and mixtures thereof.
When the composition is obtained by mixing a tint component and a developer
component, additional primary intermediates and couplers may be preferably
incorporated in the
tint component.
Typically, the compositions for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers
comprise from
about 0.1% to about 10%, preferably from about 0.3% to about 6%, more
preferably from about
0.5% to about 4% by weight of the couplers relative to the total weight of the
composition.
Direct Dyes
The compositions of the present invention may also comprise compatible direct
dyes, in
an amount sufficient to provide additional coloring, particularly with regard
to intensity.
Typically, such an amount will range from about 0.05% to about 4%, by weight
of the direct dyes
relative to the total weight of the composition. When the composition is
obtained by mixing a tint
component and a developer component, the direct dyes are usually incorporated
in the tint
component.
The following direct dyes are commonly used: Acid dyes such as Acid Yellow 1,
Acid
Orange 3, Acid Black 1, Acid Black 52, Acid Orange 7, Acid Red 33, Acid Yellow
23, Acid
Blue 9, Acid Violet 43, HC Blue 16, Acid Blue 62, Acid Blue 25, Acid Red 4,
Basic Dyes such
as Basic Brown 17, Basic Red 118, Basic Orange 69, Basic Red 76, Basic Brown
16, Basic
Yellow 57, Basic Violet 14, Basic Blue 7, Basic Blue 26, Basic Red 2, Basic
Blue 99, Basic
Yellow 29, Basic Red 51, Basic Orange 31, Basic Yellow 87, 4-(3-(4-amino-9,10-
dioxo-9,10-
dihydroanthracen-l-ylamino)propyl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium-methylsuIfate, (E)-
1-(2-(4-(4,5-
dimethylthiazol-2-yl)diazenyl)phenyl)(ethyl)amino)ethyl)-3-methyl-1 H-imidazol-
3-ium chloride,
(E)-4-(2-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)diazenyl)-1-methyl-1 H-imidazol-3-ium-3-
yl)butane-l-
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
12
sulfonate, (E)-4-(4-(2-methyl-2-phenylhydrazono)methyl)pyridinium-l-yl)butane-
l-sulfonate,
N,N-dimethyl-3-(4-(methylamino)-9,10-dioxo-4a,9,9a,10-tetrahydroanthracen-l-
ylamino)-N-
propylpropan-1-aminium bromide, Disperse Dyes such as Disperse Red 17,
Disperse Violet 1,
Disperse Red 15, Disperse Violet 1, Disperse Black 9, Disperse Blue 3,
Disperse Blue 23,
Disperse Blue 377, Nitro Dyes such as 1-(2-(4-nitrophenylamino)ethyl)urea, 2-
(4-methyl-2-
nitrophenylamino)ethanol, 4-nitrobenzene-1,2-diamine, 2-nitrobenzene-1,4-
diamine, Picramic
acid, HC Red No. 13, 2,2'-(2-nitro-1,4-phenylene)bis(azanediyl)diethanol, HC
Yellow No. 5, HC
Red No. 7, HC Blue No.2, HC Yellow No. 4, HC Yellow No. 2, HC Orange No. 1, HC
Red No.
1, 2-(4-amino-2-chloro-5-nitrophenylamino)ethanol, HC Red No. 3, 4-amino-3-
nitrophenol, 4-(2-
hydroxyethylamino)-3-nitrophenol, 2-amino-3-nitrophenol, 2-(3-(methylamino)-4-
nitrophenoxy)ethanol, 3-(3-amino-4-nitrophenyl)propane-1,2-diol, HC Yellow No.
11, HC Violet
No. 1, HC Orange No. 2, HC Orange No. 3, HC Yellow No. 9, HC Red No. 10, HC
Red No. 11,
2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)-4,6-dinitrophenol, HC Blue No. 12, HC Yellow No. 6, HC
Yellow No.
12, HC Blue No. 10, HC Yellow No. 7, HC Yellow No. 10, HC Blue No. 9, 2-chloro-
6-
(ethylamino)-4-nitrophenol, 6-nitropyridine-2,5-diamine, HC Violet No. 2, 2-
amino-6-chloro-4-
nitrophenol, 4-(3-hydroxypropylamino)-3-nitrophenol, HC Yellow No. 13, 6-nitro-
1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroquinoxaline, HC Red No. 14, HC Yellow No. 15, HC Yellow No. 14, N2-
methyl-6-
nitropyridine-2,5-diamine, N1-allyl-2-nitrobenzene-1,4-diamine, HC Red No. 8,
HC Green No.1,
HC Blue No. 14, and Natural dyes such as Annato, Anthocyanin, Beetroot,
Carotene, Capsanthin,
Lycopene, Chlorophyll, Henna, Indigo, Cochineal.
Thickeners
The hair dyeing compositions of the present invention may comprise a thickener
in an
amount sufficient to provide the composition with a viscosity so that it can
be readily applied to
the hair without unduly dripping off the hair and causing mess. Typically,
such an amount will be
at least 0.05%, preferably at least 0.5%, more preferably at least 1%, by
weight of thickener
relative to the total weight of the composition. When the composition is
obtained by mixing
several components, the thickener may be present in any of the components.
Preferred for use herein are salt tolerant thickeners, including but not
limited to: xanthan,
guar, hydroxypropyl guar, scleroglucan, methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose
(available as
AQUACOTE(TM)), hydroxyethyl cellulose (NATROSOL(TM)), carboxymethyl cellulose,
hydroxypropyhnethyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxybutylmethyl
cellulose,
hydroxypropyl cellulose (available as KLUCEL(TM)), hydroxyethyl ethyl
cellulose, cetyl
hydroxyethyl cellulose (available as NATROSOL(TM)) Plus 330), N-
vinylpyrollidone (available
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
13
as POVIDONE(TM)), Acrylates/Ceteth-20 Itaconate Copolymer (available as
STRUCTURE(TM) 3001), hydroxypropyl starch phosphate (available as
STRUCTURE(TM)
ZEA), polyethoxylated urethanes or polycarbamyl polyglycol ester (e.g. PEG-
150/Decyl/SMDI
copolymer (available as ACULYN(TM) 44), PEG-150/Stearyl/SMDI copolymer
available as
ACULYN(TM) 46), Acrylates/Beheneth-25 Methacrylate Copolymer (available as
ACULYN(TM) 28), AcrylatesNinyl Neodecanoate Crosspolymer (available as
ACULYN(TM)
38), Acrylates/Steareth-20 Methacrylate Crosspolymer (available as ACULYN(TM)
88), PEG-
150 Distearate (available as ACULYN(TM) 60), trihydroxystearin (available as
THIXCIN(TM)),
acrylates copolymer (e.g. available as ACULYN(TM) 33) or hydrophobically
modified acrylate
copolymers (e.g. Acrylates/Steareth-20 Methacrylate Copolymer (available as
ACULYN(TM)
22), non-ionic amphophilic polymers comprising at least one fatty chain and at
least one
hydrophilic unit selected from polyether urethanes comprising at least one
fatty chain.
Also preferred for use herein are thickeners based on lamellar gel network
systems,
comprising at least one surfactant or amphophile having an HLB of 6 or less
and a melting point
of at least 30 C, preferably selected from fatty alcohols comprising from 14
to 30 carbon atoms,
or oxyethylenated fatty alcohols comprising from 16 to 30 carbon atoms and 2
units or less of
ethylene oxide, and further comprising at least one ionic or nonionic
surfactant, preferably
selected from:
anionic surfactants selected from C8-C30 alkyl sulfates, preferably C12-C18
alkyl
sulfates,
anionic surfactants according to the formula RõXmYM, wherein R is
independently selected from alkyl, alkenyl or alkylaryl groups having from 8
to 30 carbon atoms,
X is independently selected from polar groups comprising at least one carbon
atom and at least
one oxygen or nitrogen atom, Y is an anionic group selected from carboxylates,
sulfates,
sulfonates or phosphates, n and m are independently I or 2, and M is hydrogen
or a salt forming
cation and mixture thereof, most preferably selected from C8-C30 alkyl ether
phosphates having
from 1 to 20, preferably 2 to 10 ethylene oxide units (e.g. available as
CRODAFOS(TM) CES);
non-ionic surfactant comprising one or more polyethyleneoxide chains,
preferably each polyethyleneoxide chain having on average at least 50 ethylene
oxide units and
most preferably 100 to 200 ethylene oxide units (e.g. available as VOLPO(TM)
S200),
cationic surfactants selected from quaternary ammonium salts or amido-amines
having at least one fatty chain, preferably comprising at least 16 carbon
atoms and most
preferably at least 20 carbon atoms,
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
14
and mixture thereof.
Examples of such lamellar gel network systems are disclosed in EP1,832,273 and
EP2,103,299.
The composition preferably comprises a mixture of cetearyl alcohol and dicetyl
phosphate and ceteth-10 phosphate (e.g. available as CRODAFOS(TM) CES).
Chelants
The compositions of the present invention may comprise chelants in an amount
sufficient
to reduce the amount of metals available to interact with formulation
components, particularly
oxidizing agents, more particularly peroxides and percarbonates. Typically,
such an amount
range from at least 0.15%, preferably at least 0.25% by weight of the chelants
relative to the total
weight of the composition. Suitable chelants for use herein include but are
not limited to:
diethylenetriamine-N,N',N"-polyacids, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
(DTPA),
diethylenetriaminepenta(methylene phosphonic acid) (DTPMP), diamine-N,N'-
dipolyacids,
monoamine monoamide-N,N'-dipolyacids, N,N'-bis(2-hydroxybenzyl)ethylenediamine-
N,N'-
diacetic acid, EDDS (ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid), carboxylic acids
(preferably
aminocarboxylic acids), phosphonic acids (preferably aminophosphonic acids)
and
polyphosphoric acids (in particular straight polyphosphoric acids), their
salts and derivatives.
When the composition is obtained by mixing a tint component and a developer
component, the
chelants may be incorporated in the tint component or in the developer
component or in both. A
chelant is usually present in developer components for stability reason.
pH Modifiers
The compositions of the present invention may comprise in addition to the
alkalizing
agent discussed above a pH modifier and/or buffering agent in an amount that
is sufficiently
effective to adjust the pH of the composition to fall within a range from
about 3 to about 13,
preferably from about 8 to about 12, more preferably from about 9 to about 11.
Radical Scavengers
According to the present invention, the compositions may comprise a radical
scavenger.
As used herein the term radical scavenger refers to a species that can react
with a radical, to
convert the radical species by a series of fast reactions to an unreactive or
less reactive species.
The radical scavenger is also preferably selected such that it is not an
identical species as
the alkalizing agent and is present in an amount sufficient to reduce the
damage to the hair during
the coloring /bleaching process. The compositions of the present invention
comprise a radical
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
scavenger from about 0.1 % to about 10%, preferably from about I % to about 7%
by weight of
the radical scavenger relative to the total weight of the composition
Suitable radical scavengers for use herein may be selected from the classes of
alkanolamines, amino sugars, amino acids, esters of amino acids and mixtures
thereof. Suitable
5 compounds include 3-substituted-pyrazol-5-ones, 3 -carboxy- I H-pyrazol-5 -
one, 3-methyl-l-
phenyl-pyrazol-5-one, 3-methyl-l-p-tolyl-pyrazol-5-one, 3-methyl-l-(4-
sulfophenyl)-pyrazol-5-
one, 3-methyl- l -(4-sulfoamidophenyl)-pyrazol-5-one, 3-methyl -l-(3-
sulfophenyl)-pyrazol-5-one,
3-methyl-l-(3-sulfoam idophenyl)-pyrazol-5-one, 3-methyl-l-(2-chloro-5-
sulfophenyl)-pyrazol-
5-one, 3-methyl-1 -(2,5-dichloro-4-sulfophenyl)-pyrazol-5-one, 3-methyl-l-(4-
chlorophenyl)-
10 pyrazol-5-one, 3 -methyl- I -(4-carboxyphenyl)-pyrazol -5 -one, 3-carboxy-l-
phenyl -pyrazol-5-one,
3-carboxy-l-(4-sulfophenyl)-pyrazol-5-one, 1, 3 -d iphenyl-pyrazol-5 -one,
methyl pyrazol-5-one-
3-carboxylate, 3-amino-l-propanol, 4-amino-l-butanol,5-amino-l-pentanol, 1-
amino-2-propanol,
1-amino-2-butanol, 1-amino-2-pentanol, I-amino-3-pentanol, I-amino-4-pentanol,
3-amino-2-
methylpropan-1-ol, 1-amino-2-methylpropan-2-ol, 3-aminopropane-1,2-diol,
glucosamine, N-
15 acetylglucosamine, glycine, arginine, lysine, proline, glutamine,
histidine, sarcosine, serine,
glutamic acid, tryptophan, or mixtures thereof, or the salts, such as the
potassium, sodium, or
ammonium salts thereof, or mixtures thereof. In some embodiments, the
inventive compositions
may comprise glycine, sarcosine, lysine, serine, 2-methoxyethylamine,
glucosamine, glutamic
acid, morpholine, piperidine, ethylamine, 3-amino-l-propanol, or mixtures
thereof.
Method of hair dyeing
In order to use the dyeing composition, the tint component and developer
components are
usually mixed immediately prior to use and a sufficient amount of the mixture
is applied to the
hair, according to the hair abundance, generally from about 60 to about 250
grams. Upon such
preparation the composition is applied to the hair to be dyed and remains in
contact with the hair
for an amount of time effective to dye the hair. Typically, the hair dye
composition is allowed to
act on the hair from about 2 to about 60, preferably about 15 to about 45,
more preferably about
minutes, at a temperature ranging from 15 C to about 50 C. Thereafter, the
hair is rinsed
with water to remove the composition and dried. If necessary, the hair is
washed with a shampoo
and rinsed, e.g., with water or a weakly acidic solution, such as a citric
acid or tartaric acid
30 solution, and dried. Optionally, a separate conditioning product may also
be provided.
The method of dyeing hair with the composition may therefore comprise the
steps of-
(0 providing a tint component comprising (A) 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative as
defined
in formula (I), a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt, or mixtures
thereof,
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
16
(ii) providing a developer component comprising an (B) oxidizing agent;
(iii) mixing the tint component and the developer component to obtain a
composition for
the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers according to the composition of the
invention;
(iv) applying said composition for the oxidative dyeing of keratin fibers onto
the hair.
The method may further comprise waiting a period of time, typically between 2
minutes
and 60 minutes, and then rinsing the composition from the hair.
The compositions can be applied on hair via applicator bottle or brush. It can
be used on
full head or partly on single strands (highlight application) as common
highlight applicator foils,
caps and special applicators can be used, but also freehand techniques such as
balayage, with
brush and/or combs can be possible. The composition can also be applied as a
mousse via a
manual spray, a pressurized container or an aerosol mousse.
The composition may be dispensed as a solid form to which water is added to
generate
the oxidant and form a thickened vehicle suitable for hair coloring.
The dye combination of the invention may also be used in three components
system. See
for example disclosed US2010/0223739A2 assigned to L'Oreal. Such a process and
kit for
lightening or dyeing keratin fibers may comprise the following composition
applied to the hair
fibers: an aqueous cosmetic composition (A) comprising at least one fatty
substance and at least
one surfactant; a cosmetic composition (B) comprising at least one alkaline
agent and the
oxidative dyes of the invention and if present direct dyes and other oxidative
dyes, a cosmetic
composition (C) comprising at least one oxidizing agent, wherein the amount of
the at least one
fatty substance in composition (A) is greater than 20% by weight relative to
the total weight of
composition (A).
Methods of making - Kit
The composition, and its tint component and developer component, may be
manufactured
by conventional processes known in the art for manufacturing oxidative dyeing
products, and ad-
mixing the ingredients of each component composition in suitable vessels,
followed by
packaging in appropriate individual containers. The components may be for
example packaged in
plastic or aluminium bottles.
In particular, the present invention may be provided as a kit comprising
different
components to be mixed by the consumer or salon stylist to obtain a hair
dyeing composition
according to the invention. Such a kit may comprise:
(i) a tint component comprising (A) 5-hydroxy-quinoline derivative as defined
in formula
(1), a physiologically compatible water-soluble salt, or mixtures thereof;
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
17
(ii) a developer component comprising an (B) oxidizing agent.
The kit may be presented in a single package comprising separate containers
for the tint
component, the developer component, and optionally a conditioner, a color
refresher or other hair
treatment product, instructions for use, gloves. The instructions for use
include the steps of the
method described above and optionally provide visual cues or pictures for the
desired steps of the
method. Kits are usually sold in retail products with enough material in each
component for
preparing a hair dyeing composition for one use.
The composition may be dispensed as a foam using for example manually-
actuable, non-
aerosol dispenser such as a pump or squeeze foamers, aerosol mousse. See for
example EP
613,728 B1, WO 97/013585 Al, EP 1,716,933A1, US 3,709,437, US 3,937,364, US
4,022,351,
US 4,147,306, US 4,184,615, US 4,615,467 and FR 2,604,622. One particular
example of a
squeeze foamer useful herein is able to dispense from an upright or inverted
position such as the
one discussed in US 6,604,693 assigned to Taplast, and more specifically, at
column 2, line 65,
through column 4, line 67 of that patent.
The composition may be dispensed as a solid form to which water is added to
generate
the oxidant and form a thickened vehicle suitable for hair coloring.
EXAMPLES
The following are non-limiting examples of the compositions of the present
invention.
The examples are given solely for the purpose of illustration and are not to
be construed as
limitations of the present invention, as many variations thereof are possible
without departing
from the spirit and scope of the invention, which would be recognized by one
of ordinary skill in
the art. In the examples, all concentrations are listed as weight percent,
unless otherwise
specified.
The 5-hydroxy-quinoline of formula (1.1) can be synthesized following the
experimental protocol described by D. Roberts, J.A. Joule in Journal of
Organic Chemistry, 62
(1997) pages 568-577.
Example 1: Synthesis of 5-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline of the formula
(1.1) as
shown in the following scheme.
OH OH
NiC12/NaBH4
&N)
H
(1.1)
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
18
Examples 2 to 9: flair dyes (1:1 combinations)
1.25 mmol 5-hydroxyquinoline of the formula (1.1)
1.25 mmol primary intermediate substance as in table I
10.0 g lauryl ether sulfate (28 percent aqueous solution)
9.0 g ammonia (22 percent aqueous solution)
7.8 g ethanol
0.3 g ascorbic acid
0.3 g ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid disodium salt hydrate
ad 100.0 g water, dernineralized
10 g of the above dye solution were mixed directly prior to application with
10 g of a
6 percent hydrogen peroxide solution. The mixture was then applied to bleached
hair. After a
contact time of 30 minutes at 40 C, the hair was rinsed with water, washed
with a standard
commercial shampoo and dried. The resulting colorations are summarized in
table 1.
Table 1:
Primary intermediate substance
1.4-diamino- 2,5-Diamino- 2,5-Diamino- 4,5-Diamino-l- 4-Amino-
benzene toluene sulfate phenyl-ethanol (2'-hydroxy- phenol
(IIL1) (IIL2) sulfate (111.3) ethyl)pyrazole (IV.1)
sulfate (11.1)
Coupler dark brown dark brown dark brown dark red Brown
substance (Example 2) (Example 3) (Example 4) (Example 5) (Example 6)
(I.1)
Primary intermediate substance
4-Amino-3-methyl- N,N-Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)- 2,4,5,6-Tetraamino-
phenol (IV.2) p-phenylenediamine pyrimidine sulfate (V)
sulfate (111.4)
Coupler Beige dark violet Beige
substance (1.1) (Example 7) (Example 8) (Example 9)
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
19
Example 10: 1 lair colorants (multi-combinations)
0.1 g hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline derivative of the
formula (1): 1.1
0.3 g primary intermediate substance (1,4-diaminobenzene)
0.05 g coupler substance (3-aminophenol)
0.20 g coupler substance (1,3-dihydroxybenzene)
10.0 g lauryl ether sulfate (28 percent aqueous solution)
9.0 g ammonia (22 percent aqueous solution)
7.8 g ethanol
0.3 g ascorbic acid
0.3 g ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid disodium salt hydrate
ad 100.0 g water, demineralized
Directly prior to application 30 g of the above coloring solution were mixed
with 30 g of
a 6 percent aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution. The mixture was then applied
to bleached hair.
After a contact time of 30 minutes at 40 C, the hair was rinsed with water,
washed with a
standard commercial shampoo and dried. The coloring result is a blonde shade.
Except as otherwise noted, all amounts including part, percentages, and
proportions are
understood to be modified by the word "about", and amounts are not intended to
indicate
significant digits. Except as otherwise noted, the articles "a", "an", and
"the" mean "one or more".
All percentages, parts and ratios are based upon the total weight of the
compositions of
the present invention, unless otherwise specified. All such weights as they
pertain to listed
ingredients are based on the active level and, therefore, do not include
solvents or by-products
that may be included in commercially available materials, unless otherwise
specified. The term
"weight percent" may be denoted as "wt. %" herein.
The dimensions and values disclosed herein are not to be understood as being
strictly
limited to the exact numerical values recited. Instead, unless otherwise
specified, each such
dimension is intended to mean both the recited value and a functionally
equivalent range
surrounding that value. For example, a dimension disclosed as "40 mm" is
intended to mean
"about 40 mm."
Every document cited herein, including any cross referenced or related patent
or
application is hereby incorporated herein by reference in its entirety unless
expressly excluded or
otherwise limited. The citation of any document is not an admission that it is
prior art with
respect to any invention disclosed or claimed herein or that it alone, or in
any combination with
CA 02754962 2011-10-07
any other reference or references, teaches, suggests or discloses any such
invention. Further, to
the extent that any meaning or definition of a term in this document conflicts
with any meaning
or definition of the same term in a document incorporated by reference, the
meaning or definition
assigned to that term in this document shall govern.
5 While particular embodiments of the present invention have been illustrated
and
described, it would be obvious to those skilled in the art that various other
changes and
modifications can be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the
invention. It is
therefore intended to cover in the appended claims all such changes and
modifications that are
within the scope of this invention.