Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
TITLE
[0001] Vertical Axis Windmill
FIELD
[0002] There is described a vertical axis windmill.
BACKGROUND
[0003] United States Patent 325,025 (Teft) from 1885 and United States Patent
584,986
(Chapman) from 1897 are early examples of vertical axis windmills.
SUMMARY
[0004] There will now be described a vertical axis windmill that has a novel
structure.
According to the present invention there is provided a vertical axis windmill
that includes a
rotating support that rotates about a vertical axis. A plurality of horizontal
members extend
horizontally from the rotating support and a plurality of vertical members
extend vertically
between the horizontal members to form a structure defining a plurality of
openings. Sets of
pivotally mounted louvers are positioned in each opening of the structure.
Each set of louvers
pivot about vertical pivot axes between a closed position in which the louvers
are overlapping
to prevent passage of wind through the opening and an open position in which
the louvers are
in parallel spaced relation allowing wind to pass through. Each set of louvers
have a
connecting linkage so that they move in unison to the closed position when
moving with wind
and move in unison to the open position when moving against wind.
[0005] Although vertical axis windmill is effective with horizontal members
and vertical
members of any shape, better results are obtained when both the horizontal
members and the
vertical members have aerodynamic wing shaping to help channel wind toward the
openings
when the louvers are in the closed position and reduce wind resistance as wind
passes through
the openings when the louvers are in the open position.
[0006] Various types of materials may be used to manufacture horizontal
members and
vertical members, however better results are obtained with the use of foam
filled polymer
plastic shells which are lightweight.
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
2
[0007] Vertical axis windmill may be of any shape, however the shape is
preferably a
generally triangular structure with peripheral edges that are converging from
a base inwardly
and upwardly. The triangular shape provides a stable structure for the
windmill.
[0008] A generator may be positioned at the base of the structure of the
rotating support
to capture kinetic energy generated by rotation of the rotating support. The
generator allows
energy created by the rotation of the rotating support to be stored and used
later on or in other
locations.
[0009] Bearings may be used to facilitate rotation of the rotating support are
magnetic
bearing sets made of two magnets that repel each other. The use of magnetic
bearing sets
reduces the amount of friction created during rotation of the rotation
support.
[0010] A fixed vertical support may be used to maintain vertical axis windmill
in a
vertical orientation. Supporting cables are used to support the fixed vertical
support.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0011] These and other features will become more apparent from the following
description in which reference is made to the appended drawings, the drawings
are for the
purpose of illustration only and are not intended to be in any way limiting,
wherein:
[0012] FIG. 1 is a front elevation view of a vertical axis windmill.
[0013] FIG. 2 is a detailed front elevation view of one of the plurality of
openings in the
vertical axis windmill shown in FIG. 1, with louvers in an open position to
allow wind to pass
through.
[0014] FIG. 3 is a detailed top plan view, in section, of one of the plurality
of openings in
the vertical axis windmill shown in FIG. 1, with louvers in a closed position
to capture wind.
[0015] FIG. 4 is a detailed section view of one of the horizontal members
showing
aerodynamic wing shaping.
[0016] FIG. 5 is a detailed side elevation view of magnetic bearings used on
the vertical
axis windmill shown in FIG. 1.
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
3
[0017] FIG. 6 is a top plan view of the vertical axis windmill shown in FIG.
1.
[0018] FIG. 7 is a side elevation view, in section, of an arm of the vertical
axis windmill
shown in FIG.!.
[0019] FIG. 8 is a front perspective view, partially in section, of one of the
plurality of
openings in the vertical axis windmill shown in FIG. 1, with louvers in the
closed position to
prevent wind from passing through.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
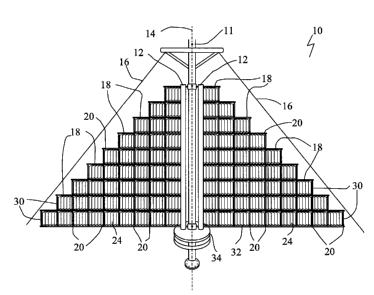
[0020] A vertical axis windmill generally identified by reference numeral 10,
will now be
described with reference to FIG. 1 through 8.
Structure and Relationship of Parts:
[0021] Referring to FIG. 1, a vertical axis windmill 10 has a rotating support
12 that
rotates about a vertical axis 14. In the embodiment shown, rotating support 12
is connected to
a fixed vertical support 11 which is maintained in a vertical orientation by
supporting cables
16. Referring to FIG. 6, a plurality of arms 13 extend outward from each
rotating support 12.
In the embodiment shown, four arms 13 are utilized, which keep windmill 10
rotating in the
presence of wind. It will be understood that different numbers of arms may be
utilized. The
number of arms 13 may be different at the top and bottom of windmill 10.
Reducing the
number of arms 13 at the bottom of windmill 10 allows for weight reduction and
less
resistance. Adjacent arms 13 are connected to each other by horizontal cables
17 which help
to maintain the shape of vertical axis windmill 10 in wind and provide
increased stability. In
this configuration, arms 13 support each other, as pressure upon one arm is
transmitted via
cables 17 to the other arms 13. Referring to FIG. 1, a plurality of horizontal
members 18
extend horizontally from rotating support 12 and a plurality of vertical
members 20 extend
vertically between horizontal members 18. Although beneficial results have
been obtained by
having a series of vertical members 20 along the length of horizontal members
18, it would
remain workable with vertical members 20 positioned only at the remote ends.
The longer the
span, the more advisable it is to provide multiple vertical members 20.
Referring to FIG. 7,
cables 15 run between horizontal members 18 and help maintain positioning of
horizontal
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
4
members 18. Cables 15 pass through horizontal members 18, but cable 15 is
fixed to each
horizontal members 18 to provide support. Referring to FIG. 2, horizontal
members 18 and
vertical members 20 form a structure defining a plurality of box shaped
openings 22. Sets of
pivotally mounted louvers 24 are positioned in each opening 22 of the
structure. Louvers 24
can be made from a strong and yet light materials such as plastic or carbon
fibre. Each set of
louvers 24 pivots about a vertical pivot axis 26 between a closed position,
shown in FIG. 8, in
which the louvers 24 are overlapping to prevent passage of wind through the
opening 22 and
an open position, shown in FIG. 2, in which the louvers 24 are in parallel
spaced relation
allowing wind to pass through. Referring to FIG. 8, when in the closed
position, openings 22
form a closed box. When louvers 24 are closed, air is captured in the closed
box and causes
vertical axis windmill 10 to rotate. Referring to FIG. 8, cables 15 run
through louvers 24 at
the vertical pivot axis 26. Cables 15 act as a hinge pin about which louvers
24 pivot. In order
to improve the pivotal action, a bushing can be inserted into the passage
through the louvers
24, so that louvers 24 pivot freely about cable 15 with little friction. In
addition, bearings can
be placed to reduce friction as louvers 24 move about cable 15 in response to
wind. At one
end a cables 15 is used to act as stop for the last louver 24 to create a
closed box when
louvers 24 are in the closed position. It will be understood that vertical
pivot axis 26 must be
positioned along one edge of each of louvers 24.. As shown in FIG. 8, cables
15 run through
louvers 24 at an edge of the louvers 24 and serve as pivot axis 26. Referring
to FIG. 2, each
set of louvers 24 has a connecting linkage 28 so that they move in unison to
the closed
position illustrated in FIG. 3 when moving with wind and move in unison to the
open
position illustrated in FIG. 2 when moving against wind. Openings 22 may be of
any size and
accommodate louvers 24 of any size. As an example, openings 22 may be large
enough to
contain a plurality of louvers 24 which measure four feet wide and twenty feet
long. When
large louvers 24 are used, several linkages 28 may be used to move louvers 24
in unison. It
will be understood that movement between an open position and a closed
position is a
movement over a range of roughly 90 degrees.
[0022] Referring to FIG. 4, horizontal members 18 and vertical members 20
preferably
have aerodynamic wing shaping. Referring to FIG. 3, aerodynamic wing shape
channels
wind toward the openings 22 in the closed position and, referring to FIG. 2,
reduces wind
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
5
resistance as wind passes through the openings 22 in the open position. It
will be understood,
however, that different shaped horizontal members 18 and vertical members 20
may be
utilized. Referring to FIG. 4, the horizontal members 18 and vertical members
20 may be
made of any material, however best results are seen when horizontal members 18
and vertical
members 20 are made of a light material such as foam filled polymer plastic
shells 21 with a
reinforcing tube 23 extending along its length.
[0023] Referring to FIG. 1, vertical axis windmill 10 may be of any general
shape,
however it is preferable that it be generally triangular with peripheral edges
30 that are
converging from a base 32 inwardly and upwardly. A generator34, may be
positioned at the
base 32 of the vertical axis windmill 10 of the rotating support 14 to capture
kinetic energy
generated by rotation of the rotating support 12.
[0024] Referring to FIG. 5, rotation of the rotating support 12 may be
facilitated by the
use of bearings 36. In particular, the use of a magnetic bearing set may be
used. Magnetic
bearing sets utilize two magnets 38 and 40 that repel each other and help to
reduce the amount
of friction in the bearings. It will be understood that a conventional
mechanical bearing could
be utilized.
Operation:
[0025] Referring to FIG. 1, vertical axis windmill 10 is placed in an area
where it can be
turned by wind power. Fixed vertical support 11 is stabilized by supporting
cables 16.
Referring to FIG. 3, as wind contacts louvers 24, they are moved into the
closed position to
prevent passage of the wind and cause rotation of the rotating support 12,
shown in FIG. 1.
Referring to FIG. 2, as the windmill 10 rotates and the wind is channelled
toward openings
22, the wind pushes louvers 24 back to the open position which allows the wind
to pass
through openings 22. This helps to reduce the drag caused by movement of the
windmill 10 as
louvers 24 contained within horizontal members 18 and vertical members 20 move
into the
wind. Disk generator 34 is used to capture kinetic energy that is generated by
rotation of the
rotating support 12. Referring to FIG. 4, the polymer shell 18 with foam
filler 21 is
extremely light weight. The triangular shape provides a stable structure,
which becomes even
CA 02758183 2011-11-08
6
more so when the weight of the generator is placed at the bottom. The
triangular structure
also provides room needed to install guide wires 16 to stabilize fixed
vertical support 11.
[0026] Advantages
[0027] 1. Windwills that utilize large propellers and associated gearing and
generators on
top of poles, require a substantial supporting structure. In contrast,
windmill 10 has the
gearing and generators at the bottom and can be made from very light weight
and relatively
inexpensive materials.
[0028] 2. With the gearing and generators positioned at the bottom, there is
improved
access for servicing.
[0029] 3. With the lighter weight, windmill 10 is more sensitive to lighter
winds that
would not move existing propellers.
[0030] 4. Windmill 10 acts like a sail and is very effective at catching a
large volume of
wind.
[0031] 5. One of the things that provides strength, while maintaining light
weight is the
use of cables 15. Cables 15 serving more than one purpose, to support vertical
members 18
and to serve as a pivot axis for louvers 24, and to serve as a pivotal stop of
the louver 24
which is positioned at one end.
[0032] 6. The triangular shape maintains the weight on the bottom and creates
a greater
stability to the structure.
[0033] 7. For a comparable performance, there is a greatly reduced cost.
[0034] In this patent document, the word "comprising" is used in its non-
limiting sense to
mean that items following the word are included, but items not specifically
mentioned are not
excluded. A reference to an element by the indefinite article "a" does not
exclude the
possibility that more than one of the element is present, unless the context
clearly requires that
there be one and only one of the elements.
[0035] The scope of the claims should not be limited by the illustrated
embodiments set
forth as examples, but should be given the broadest interpretation consistent
with the
description as a whole.