Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
1 ~
Panel saw with clamping jaw
The invention relates to a panel saw comprising a workpiece support surface
with
a saw slot disposed therein, a saw unit which can be moved horizontally along
the saw slot and which includes a rotatably mounted circular saw blade the
rotational axis of which is disposed below the workpiece support surface, and
at
least one workpiece clamping element disposed on a feeder carriage which is
displaceable in the plane of the workpiece support surface and which can
preferably be moved in a direction perpendicular to the saw slot.
Such panel saws are used to cut large-format panels, in particular panels made
of wood-based materials or solid wood, plastic panels, or panels made of light
metals. Panel saws of the kind specified by the invention have a horizontal
workpiece support surface onto which the workpiece can be placed by the user
or by an automatic feeder mechanism. The workpiece can be displaced on the
workpiece support surface, in particular by means of an air cushion or other
bearing devices, in order to be positioned in a defined manner relative to the
saw
unit and its direction of motion. In panel saws of the type specified in the
invention, the saw unit is disposed below the workpiece support surface. To
perform the cut, a peripheral section of the saw blade is passed upwards from
below through the saw slot, and the workpiece can then be cut by moving the
saw unit along the saw slot.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-2-
A panel saw of the kind initially specified is known from EP1990119A1. This
panel saw is characterised by having a lay-on edge disposed laterally on the
workpiece support surface, by means of which the workpiece can be positioned
in a defined manner relative to the saw slot or direction of motion of the saw
unit.
The prior art panel saw also has fixing and feeder carriages which are fitted
with
clamping elements for clamping the workpiece panel to be cut to shape and for
positioning it by moving the fixing and/or feeder carriages in a defined
manner.
With panel saws of the kind initially specified, it is basically possible to
cut large-
format workpieces to size in a time-efficient manner. However, it is desirable
that
such panel saws be further developed so that workpieces can be cut with a
variety of dimensions and from panels of various sizes. Another aim is to
provide
a workflow that is as time-efficient as possible.
The object of the invention is to develop a panel saw in such a way that it
permits
efficient working with workpiece panels of variable dimensions, also and in
particular with very small dimensions.
This object is achieved according to the invention by the workpiece clamping
element having a movable clamping jaw,
- which in a first position is disposed below the workpiece support surface,
- projects in a second position above the workpiece support surface and
- is configured on the one face such that in the second position it serves as
a
first stop face for a workpiece which is pushed against the clamping jaw
from a first direction aligned parallel to the workpiece support surface, and
- which is coupled to an actuator in such a way that the actuator exerts a
force on the clamping jaw, which moves the clamping jaw from the second
direction to the first position, thereby clamping a workpiece in the direction
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-3-
of the workpiece support surface, in particular against the workpiece
support surface, with a clamping face embodied on the clamping jaw.
By means of the panel saw according to the invention, it is possible to align
the
workpiece with a face of the clamping jaw and in this way to bring it into a
specific
and defined position. The stop face on the clamping jaw can only be used in
the
second position, in which the clamping jaw projects above the workpiece
support
surface, and in the first position, in which the clamping jaw is lowered to a
position below the workpiece support surface or is at least flush with the
latter,
the stop face is not in the way of displacing the workpiece on the workpiece
support surface. By virtue of this specific way of providing a stop face, it
is
possible for workpieces to be positioned, advanced and cut in a particularly
efficient manner, in that it is possible, firstly, to place the workpiece in a
defined
position at a stop face on the clamping jaw, and then by lowering the clamping
jaw into the first position to allow the workpiece to be displaced above the
lowered clamping jaw or to clamp the workpiece with the clamping jaw by
lowering the clamping jaw in the direction of the first position and
subsequently to
displace the clamped workpiece and in this way to set a defined cutting
dimension.
The stop face may be disposed on the clamping jaw in such a specific way that
a
workpiece which lies against the stop face can be clamped directly by moving
the
clamping jaw from the first position in the direction of the second position,
without
any horizontal displacement of the workpiece or the clamping jaw out of the
stop
position being necessary.
A stop face within the meaning of the invention is understood to be a surface
which is oriented in such a way that it references workpieces of any thickness
in
one and the same position. Such a stop face is preferably perpendicular to the
workpiece support surface or has at least one or several perpendicular regions
that are flush with one another. In order to lay workpieces with sensitive or
fragile
side edges in a defined manner against the stop face, without causing any
damage or inaccurate positioning, it is preferred that the workpiece edge and
the
stop face are fully in contact with each other. In certain kinds of
application,
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
= -4-
however, the stop face may be designed in such a way that it forms a linear
contact with the workpiece edge or, or even an approximately punctiform
contact.
The actuator provided in accordance with the invention and which is coupled to
the clamping jaw may preferably be an electromagnetic, electromotive,
pneumatically or hydraulically driven actuator which delivers a clamping force
sufficient for reliably clamping the workpiece. The actuator is also used
preferably
to move the clamping jaw from the first to the second position and vice versa,
and in this way to bring the clamping jaw into the position projecting above
the
workpiece support surface in order to position the stops, or into the lowered
position below or flush with the workpiece support surface in order to
displace the
workpiece on the workpiece support surface without damaging it.
Clamping against the workpiece support surface is understood to mean that the
workpiece is clamped against the surface forming the workpiece support surface
as counter-surface. This counter-surface may be provided in a fixed position
at
the panel saw, for example, or it may be movable so that the clamped workpiece
can still be moved, for example by moving the clamping jaw with the workpiece
clamped therein. The counter-surface can thus be embodied, for example, on the
fixing carriage on which the clamping jaw is disposed, so that the workpiece
in
the clamped position can be moved along with the fixing carriage by moving the
fixing carriage.
According to a first preferred embodiment of the invention, a second face is
embodied on the clamping jaw, which serves as a clamping face for a workpiece
and is disposed on the clamping jaw in such a way that a workpiece can be
clamped between the clamping face and the workpiece support surface when the
actuator moves the clamping jaw out of the second position in the direction of
the
first position. This configuration makes it possible to lay a workpiece
against the
clamping jaw in a defined manner and at the same time for the workpiece to be
subsequently clamped in this defined position by means of the clamping jaw,
which is highly advantageous for an efficient workflow. The clamping face
preferably lies in such a way that it has a portion on the opposite side from
the
workpiece support surface, which is placed onto the upper surface of the
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-5-
workpiece and which then presses the bottom surface of the workpiece onto the
workpiece support surface, thus causing the clamping procedure to occur. More
particularly, the clamping face may have a rounded shape for a gentle clamping
effect on the surfaces of workpieces of different material thicknesses, was is
advantageous whenever the clamping jaw is mounted as a swing arm or in some
other swivable manner in order to effect the movement from the first to the
second position and vice versa.
It is further preferred that a third face be disposed on the clamping jaw in
such a
way that it serves as a second stop face for a workpiece which is pushed
against
the against the clamping jaw from a second direction aligned parallel to the
workpiece support surface and preferably swivelled 180 relative to the first
direction. With this development of the invention, two stop faces are provided
on
the clamping jaw and disposed in such a way that a workpiece can be placed in
a
defined manner against the clamping jaw from two directions. In this way, it
is
possible to use the clamping jaw in a universal manner as a point of reference
for
defined positioning of a workpiece. More particularly, it is also possible
with this
configuration to position workpieces with large dimensions by means of the
first
stop face and to position workpieces with small dimensions by means of the
second stop face.
It is still further preferred that the first stop face lies parallel to and
spaced apart
from the second stop face. This configuration permits a stop movement along a
common directional axis at the two stop faces. The directional axis is
preferably
parallel to the rotational axis of the circular saw blade, such that the two
stop
faces lie parallel to the circular saw blade and thus provide a stop member in
the
advancement direction of the workpiece.
It is further preferred that at least one, preferably a plurality of vacuum
clamping
elements are disposed on the feeder carriage and are arranged in such a way
that they can clamp a workpiece lying on the workpiece support surface. In
particular, such vacuum clamping elements may be activated by a valve which is
actuated by a pin that is pressed in when a workpiece is placed onto the
vacuum
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-6-
clamping element. In this case, the workpiece is vacuum clamped to the feeder
carriage by the vacuum clamping element, which allows supporting fixing of the
workpiece relative to the feeder carriage, thus preventing any unwanted
slippage
of the workpiece during advancement or when the saw cut is being made. More
particularly, the feeder carriage may be designed as an elongate feeder
carriage
strip, along which a plurality of vacuum clamping elements are located.
A particularly preferred embodiment is one in which the feeder carriage can be
moved in a direction which is perpendicular to the saw slot. It should be
understood in this regard that the feeder carriage can preferably be moved in
a
direction which is parallel to the workpiece support surface, so that a
workpiece
clamped in the feeder carriage can be advanced perpendicularly to the circular
saw blade and that a desired cutting dimension can be adjusted in this way.
The panel saw according to the invention can be further developed by providing
a
plurality of feeder carriages which each have a clamping jaw with the kind of
construction described in the foregoing and which can be moved independently
of each other. It is possible with this configuration to align a workpiece
against the
stop faces of several clamping jaws. It should be understood in this regard
that
the plurality of feeder carriages can be displaced by means of an actuator and
that the stop faces of the respective clamping jaws on the feeder carriage can
thus be brought into predefined positions. In this way, a specific angle
relative to
the saw slot can be set when a workpiece is placed against the stop faces of
the
clamping jaws. It is specifically preferred in this regard that the stop face
is
swivably formed on the clamping jaw in order to permit flush contact against
the
workpiece edge at any angle.
Alternatively, in another preferred embodiment, a plurality of feeder
carriages
may be provided which each have at least one clamping jaw, in particular a
clamping jaw in their front end portion facing towards the saw slot and/or in
their
rear end portion facing away from the saw slot, the feeder carriages
preferably
being coupled to each other in such a way that they can be moved in common.
With this configuration, it is possible by means of the stop faces on the
clamping
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-7-
jaws to define a stop line on which the workpiece can be positioned as against
a
stop edge. By arranging clamping jaws in the end portion of the feeder
carriage
facing the saw slot, it is possible for narrow workpiece sections to be well
clamped and processed. The clamping jaws on the end facing away from the saw
slot are used, in contrast, for clamping large-format workpieces and permit
the
dimensioning of the panel saw to be fully utilised for the workpiece size. In
this
configuration, the feeder carriages can be directly coupled to each other
mechanically, or a control engineering coupling can be provided which
synchronously triggers the actuators of the plurality of feeder carriages,
thus
causing the coupled feeder carriages to move in synchrony. In the latter case,
in
particular, the control engineering coupling may also be removed and the
feeder
carriages moved independently of each other in order to thus provide the
advantages of the previously described embodiments.
It is further preferred that one, and preferably that all of the clamping jaws
clamp
against a face which is embodied on the respective feeder carriage on which
the
clamping jaw is disposed. This development of the invention allows a clamped
workpiece to be moved in common with the feeder carriage(s) on which the
clamping jaws clamping the workpiece are disposed. This is advantageous when
the feeder carriages are moved by means of one or more actuators, and then
permits the clamped workpiece to be positioned in a dimensionally accurate
manner.
In the case of the embodiments featuring a plurality of feeder carriages, it
is
further preferred that the feeder carriages are parallel to and spaced apart
from
each other. Such alignment of the feeder carriages results in an advancement
that is advantageous for many requirements in respect of saw cuts to be made.
The feeder carriages also ensure that the workpiece can be moved in a reliable
manner that the operator is able to understand arithmetically.
According to another preferred embodiment, the feeder carriage(s) is/are
coupled
to at least one carriage actuator for moving the feeder carriage(s), and the
clamping jaw(s) is/are coupled to at least one jaw actuator for moving the
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-8-
clamping jaw(s). This configuration is further characterised by a sensor in
the
region of the saw slot, said sensor being configured to detect the presence of
a
workpiece in a region above the saw slot, and by a machine controller which is
in
signal communication with the saw unit, the carriage actuator, the jaw
actuator
and the sensor and which is configured to actuate the jaw actuator to clamp a
workpiece, move the feeder carriage(s), when the workpiece is clamped, towards
the saw slot until the sensor detects the presence of the workpiece in the
region
above the saw slot, and following that step to actuate the saw unit to perform
a
trimming cut.
This development of the invention allows advantageous automated detection of a
workpiece edge which must be cut by means of a trimming cut. A trimming cut is
understood here to be a cut in which a narrow strip of material along a rough
or
undefined workpiece edge is cut away with one saw cut, thus producing a
defined
and clean workpiece edge. A trimming cut is typically used to define a large-
format workpiece panel which is to be cut to shape as having a specific length
along one edge, and then on the basis of this defined edge to perform further
saw
cuts parallel or at an angle to said edge. These additional saw cuts are then
made at an exact length and angle, clearly determined by the panel saw, to the
edge produced by the trimming cut. The machine controller according to the
invention works with a sensor, such as a photoelectric barrier which can
detect a
workpiece above the saw slot.
According to the invention, it is possible with a single sensor or with a
plurality of
sensors distributed along the saw slot to detect the presence of the workpiece
in
order, for example, to ensure by means of a plurality of sensors that the
workpiece lies above the saw slot along a specific portion of the saw slot. In
order
to bring the workpiece into such a defined position detected by the sensors,
it is
firstly clamped by the clamping jaws of the feeder carriages or in some other
way
and then moved onto the saw slot by moving the feeder carriages. This feeder
movement is not stopped until the workpiece lies above the saw slot. The
trimming cut can then be performed by moving the saw unit along the saw slot.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-9-
It is particularly preferred in this regard that the machine controller be
configured
to move the feeder carriage, with the clamped workpiece, in the direction of
the
saw slot by a predetermined distance, which can preferably be entered via a
user
interface, after the sensor has detected the presence of the workpiece in the
region above the saw slot, and following that step to actuate the saw unit to
perform the trimming cut. This development of the machine controller ensures
that the circular saw blade cuts away a strip of material with a specific
minimum
width when making the trimming cut and hence that its does not run too close
to
a workpiece edge or even go beyond the side of the workpiece, which can result
in a bad trimming cut. The amount by which the feeder carriage is advanced
after
the workpiece has been detected above the saw cut may be specified or may be
programmed by the user, according to the materials being processed, for
example, or the thickness of the materials being processed or the size of the
saw
slot, in order to effect an advancement that cuts away a strip that is
sufficiently
large not to fall into the saw slot. The machine controller may be
specifically
configured to calculate, from previously entered workpiece values, for example
the type of material and/or the thickness of the workpiece, the advancement
that
is required for a clean trimming cut, and to perform the trimming cut
accordingly.
It is still further preferred that the machine controller be configured to
actuate the
jaw actuator to clamp a workpiece, to move the feeder carriage with the
clamped
workpiece in the direction of the saw slot as long as the sensor detects the
presence of the workpiece in the region above the saw slot, then preferably to
move the feeder carriage with the clamped workpiece in the direction of the
saw
slot until the sensor detects the presence of the workpiece in the region
above
the saw slot, then to move the feeder carriage with the clamped workpiece,
after
the sensor has detected the presence of the workpiece in the region above the
saw slot, by a predetermined distance, which can preferably be entered via a
user interface, in the direction of the saw slot, and then to move the feeder
carriage with the clamped workpiece, after the sensor has detected the
presence
of the workpiece in the region above the saw slot, by a predetermined
distance,
which can preferably be entered via a user interface, in the direction of the
saw
slot, and following that step to actuate the saw unit to perform a trimming
cut.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-10-
Whereas it is necessary, in the previously described embodiments for detecting
the edge to be trimmed, that the workpiece be laid down in such a way that it
does not cover the saw slot, and the workpiece is subsequently guided to the
saw
slot, it is possible with this latest preferred embodiment for the workpiece
to be
laid on the workpiece support surface and be clamped by the fixing carriages
in
any way one wishes, regardless of whether the saw slot is already covered in
the
process, or not. The machine controller is then able to move the workpiece
into
place, depending on the signal from the sensor in the region of the saw slot,
in
such a way that the edges to be trimmed are detected. This is done by removing
the workpiece from the region above the saw slot, if necessary, firstly by
moving
the feeder carriage away from the saw slot, then advancing it again until the
overlap over the saw slot is the amount required for the trimming cut, after
which
the trimming cut can then be carried out.
According to another preferred embodiment of the machine controller provided
for carrying out the trimming cut, the machine controller can be configured
actuate the jaw actuator to clamp a workpiece, to move the feeder carriage
with
the clamped workpiece in the direction of the saw slot as long as the sensor
detects the presence of the workpiece in the region above the saw slot, then
to
move the feeder carriage(s) with the clamped workpiece, after the sensor has
no
longer detected the presence of the workpiece in the region above the saw
slot,
by a predetermined distance, which can preferably be entered via a user
interface, in the direction of the saw slot, and following that step to
actuate the
saw unit to perform a trimming cut. With this configuration, if the workpiece
is
lying above the saw slot after being laid down, it is initially displaced by
means of
the feeder carriage until it no longer lies above the saw slot, after which it
is
moved back by a predetermined amount, which may be selected by the user or
automatically adjusted by the machine controller, in order to produce
sufficient
overlapping of the saw slot for a clean trimming cut to be carried out.
The panel saw according to the invention may be further developed by coupling
the feeder carriage(s) to at least one carriage actuator for moving the feeder
carriage(s), coupling the clamping jaw(s) to at least one jaw actuator for
moving
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-11-
the clamping jaw(s), and by also providing a machine controller which is in
signal
communication with the carriage actuator, the jaw actuator and the sensor and
which is configured to a) actuate the jaw actuator to clamp a workpiece, b)
move
the feeder carriage(s) with the clamped workpiece by a cutting dimension which
can be entered via a user interface, c) following that step to actuate the saw
unit
to perform a format cut, and following that step to repeat steps b) and c) if
necessary, the feeder carriage being moved by the same or by a different
cutting
dimension.
It is possible with this preferred embodiment to perform one or more cuts on a
workpiece that are each carried out according to defined cutting dimensions
adjusted by moving the feeder carriage, thus cutting a large-format workpiece
panel into a plurality of strips of defined width. What is particularly
advantageous
about this development of the invention is that the operator can program the
width and number of strips beforehand via a user interface, and that the panel
saw can then perform the required saw cuts automatically and without further
intervention by the user. It should be understood in this regard that, before
making the first cut to produce the strips, it may be necessary to perform a
trimming cut in the manner described in the foregoing, in order to produce a
defined reference edge on the workpiece.
Another aspect of the invention relates to a fixing table for a panel saw,
comprising a) a workpiece support surface, b) coupling means for fixing the
fixing
table to a panel saw in such a way that the workpiece support surface of the
fixing table lies flush with a workpiece support surface of the panel saw and
c) at
least one workpiece clamping element disposed on a feeder carriage which can
be moved in the plane of the workpiece support surface. According to the
invention, the fixing table is characterised by the workpiece clamping element
having a movable clamping jaw which in a first position is disposed below the
workpiece support surface, projects in a second position above the workpiece
support surface, on which one face is embodied in such a way that in the
second
position it serves as a first stop face for a workpiece which is pushed
against the
clamping jaw from a first direction aligned parallel to the workpiece support
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-12-
surface, and which is coupled to an actuator in such a way that the actuator
exerts a force on the clamping jaw, which moves the clamping jaw from the
second direction to the first position, the workpiece thus being clamped by
the
clamping jaw.
Such a fixing table is particularly suitable for being used in combination
with a
panel saw, in that the fixing table is disposed alongside a workpiece support
surface having a saw slot with a circular saw unit therebelow. The fixing
table
according to the invention is characterised by clamping jaws that can be used
both for clamping and as stop faces. For a description of the advantages and
manner of operation of these clamping jaws of the fixing table, reference is
made
to the previous explanations in respect of the panel saw with suitably
configured
clamping jaws.
In addition to use in panel saws, the fixing table according to the invention
is also
suitable, in particular, for being used with other machine tools, such as
sliding
table saws with a stationary rotating circular saw blade, processing centres
comprising other cutting tools, such as cutting tools or planing tools and the
like.
The fixing table according to the invention can be further developed in a
manner
similar to that described above for the inventive panel saw and its clamping
jaws,
feeder carriage and machine controller.
Preferred embodiments of the invention shall now be described with reference
to
the attached Figures, in which
Fig. 1 shows a plan view of a first embodiment of a panel saw according to the
invention, comprising a fixing table with feeder carriages in a first
position,
Fig. 2 shows a plan view according to Fig. 1, with the feeder carriage in a
second
position,
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-13-
Fig. 3 shows a side elevation view of the fixing table of the panel saw shown
in
Fig. 1,
Fig. 4 shows a section from Fig. 3,
Fig. 5 shows a perspective view of the upper components of a vacuum clamping
element,
Fig. 6 shows a detail of a partly cut-away side view showing a vacuum clamping
element and a clamping jaw,
Fig. 7 shows a detail of a partly cutaway side view according to Fig. 6, in a
different sectional plane,
Fig. 8 shows a perspective view, seen at an angle from the front and above, of
a
second embodiment of the invention, and
Fig. 9 shows a perspective view, at an angle from above and behind, of the
embodiment shown in Fig. 8.
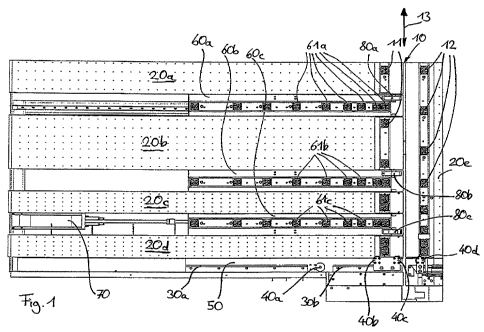
As can be seen from Fig. 1, a panel saw according to the invention includes a
saw slot 10, below which a saw unit (not shown) can move along the saw slot in
the direction shown by arrow 13, the saw unit typically projecting upwards out
of
the saw slot with part of the periphery of the circular saw blade during
movement
in a first direction, in order to perform the cut, and being disposed
completely
below the saw slot when moving back in the opposite direction. In the region
of
saw slot 10, a plurality of sensors (not shown) are disposed which detect the
presence of a workpiece above the saw slot.
A fixing table is disposed alongside the saw slot. A workpiece support surface
is
formed by a plurality of air cushion fields 20a-e. Said air cushion fields 20a-
d are
arranged on the fixing table, whereas air cushion field 20e is disposed at the
saw
slot. The air cushion fields are provided with a plurality of orifices through
which
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-14-
air can escape upwards in order to slightly raise a workpiece placed on the
air
cushion fields and thus to keep it easily displaceable for exact positioning.
In the forward region to the left of the saw cut, a stop bar 30a, b used as a
reference surface for laying-on a workpiece is disposed to the side of the
workpiece support surface 20a-e. Stop bar 30a, b lies above the workpiece
support surface and is perpendicular to saw slot 10.
In order to clamp the workpiece to be cut, a total of four saucer-shaped
clamping
elements are provided along the stop bar in this example. A single clamp 40a
is
disposed between two stop bar sections 30a and 30b of the stop bar. Two
clamping elements embodied double clamps 40b, c are arranged on the
immediate left of saw slot 10, and a single clamping element 40d is disposed
on
the right of saw slot 10 and lies in a line with clamping elements 40b, c.
Clamping
elements 40a-c are mounted jointly with stop bar 30a,b on a fixing carriage 50
and can be moved in a direction lying in the same plane as the workpiece
support
surface, which is perpendicular to saw slot 10. Clamping element 40d is
stationary and is used to hold that part of a workpiece that remains after
cutting.
Three feeder carriages 60a, b, c which can be moved parallel to and in common
with the fixing carriage are disposed in the workpiece support surface of the
panel saw. Feeder carriages 60a-c are likewise perpendicular to saw slot 10
and
are coupled to each other and to fixing carriage 50 by means of a frame (not
shown) lying below the workpiece support surface 20a-e, in order to move in
common. To effect this movement, a linear actuator 70 is coupled to the frame
in
the region of feeder carriage 60a which is closest to fixing carriage 50.
The surface of each feeder carriage is flush with the workpiece support
surface.
In this embodiment, each feeder carriage carries a total of nine vacuum
clamping
elements 61a-c which are used to clamp, by means of a vacuum, a workpiece
lying on top of the feeder carriage.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-15-
In = the plane of the workpiece support surface, there is also a plurality of
vacuum
clamping elements 11 arranged along a line to the left of the saw slot and
another
plurality of vacuum clamping elements 12 arranged along a line to the right of
the
saw slot. These vacuum clamping elements are used to fix the workpiece
securely during the saw cut. The vacuum clamping elements 12 are also used to
hold the part of the workpiece that is separated after the saw cut.
A clamping jaw 80a-c is disposed at the end of each feeder carriage 60a-c
facing
towards the saw slot. Each clamping jaw 80a-c can be swivelled into an upper
position, shown in Figures 3 and 4, above the workpiece support surface. A
clamping jaw 80a-c is configure in such a way that it can clamp a workpiece
lying
on the side of the clamping jaw facing towards the saw slot and at the same
time
provide a defined stop face 81c for that workpiece. Also embodied on the
clamping jaw, on the side of the clamping jaw facing away from the saw slot,
is a
second stop face 82c for a workpiece, against which a workpiece laying on this
side of the clamping jaw can be placed.
Whereas Fig. 1 shows the panel saw with feeder carriages in an advancement
position as close as possible to saw slot 10, feeder carriages 60a-c in Fig. 2
are
moved as far away from the saw slot as possible, i.e. to the left in the
Figure. By
comparing Figs. 1 and 2, one can see that feeder carriages 60a-c and fixing
carriage 50 with its clamping elements 40a-c and stop bar 30a, b can be moved
in common, thus allowing a workpiece in contact with stop bar 30a, b and
clamped by means of clamping elements 30a-c and vacuum clamping elements
61a-c to be displaced reliably, without this workpiece moving out of its
defined
positioning against stop bar 30a, b.
One can also recognise that the vacuum clamping elements 11, 12 to the left
and
right of saw slot 10 can be moved in common with the feeder carriages and the
fixing carriage. These vacuum clamping elements are merely used to fix the
workpiece in place while the saw cut is being performed, in order to ensure a
clean cut and to hold the severed workpiece section subsequently lying to the
right of saw slot 10.
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-16-
Fig. 3 shows a side view of the fixing table. The assembly accommodating the
circular saw module, saw slot 10, clamping elements 11, 12 and the air cushion
field 20e is omitted from Fig. 3. This assembly would be disposed and joined
to
the fixing table at the position marked 100.
Fig. 3 shows the fixing table with feeder carriages 60a-c moved as far as
possible
to the right towards the saw slot. Stop bar 30a, b can be seen, as can the
clamping elements 40b, c arranged as a pair, and a clamping jaw 80c disposed
in
front of the clamping elements in an extended position above the workpiece
support surface. Disposed below the workpiece support surface there is also a
fan 90 which serves to deliver air to the orifices in air cushion sections 20a-
d.
Fig. 4 shows in more detail the section which is circled in Fig. 3. As can be
seen,
each clamping element 40a-d has a clamping plate 41a-d. Clamping elements
40a-d are retracted, so clamping plates 41 a-d are in their upper position,
and a
workpiece could be arranged in a space below clamping plates 41a-d and could
be pressed against the workpiece support surface, which is substantially
formed
by air cushion fields 20a-e and the surface of feeder carriages 60a-c. In the
region between clamping elements 40a, b, a sensor 42 is disposed which can
measure the thickness of the workpiece in order to determine the feed rate of
the
saw unit and the amount by which the periphery of the saw blade must extend
out of the saw slot.
As can be seen well in Fig. 4, the clamping jaw 80c shown in the upwardly
extended position has a first stop face 81 c, against which a workpiece can be
laid
and positioned in a defined position on the side of the clamping jaw 80c
facing
towards saw slot 10. Parallel to and spaced apart from the first stop face
81c, a
second stop face 82c is disposed on the side of the clamping jaw facing away
from saw slot 10. A workpiece can be positioned in a defined position against
stop face 82c, on the side of the clamping jaw facing away from the saw slot.
Finally, a rounded clamping face 84c opposite workpiece support surface 20a-e
is disposed on a clamping jaw arm 83c which projects above the first stop face
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-17-
81c. When clamping jaw 80c is swivelled about a swivel 85c in an anti-
clockwise
direction in Fig. 4, clamping face 84c clamps a workpiece on the left of
clamping
jaw 80c between clamping face 84c and the workpiece support surface 20a-e.
Fig. 5 shows in greater detail a vacuum clamping element 61a-c and 11, 12. As
can be seen, such a vacuum clamping element has a vacuum plate 62, within
and above which a rubber gasket 63 with a circumferential, elastically
deformable
rim 64 is disposed. Circumferential rim 64 defines an interior vacuum zone in
which a plurality of fields 65 are arranged on which the bottom surface of a
workpiece comes to lie with frictional engagement when a vacuum is applied to
this defined zone.
In one corner region of the vacuum clamping element, a sensor pin 66 is
disposed which detects a workpiece in the region of the vacuum clamping
element and actuates a valve which causes a vacuum to be applied through a
plurality of orifices 67 within the zone defined by rim 64. The vacuum
clamping
element may be attached to the feeder carriage or to the area around the saw
slot by means of a central bore 68.
Fig. 6 shows a cutaway side view of the vacuum clamping element in Fig. 5. It
can be seen that the entire vacuum clamping element is inserted inside a frame
69 and can be displaced in the vertical direction inside the frame. This makes
it
possible for the peripheral rim 64 to be moved into a position below the
workpiece support surface when the vacuum clamping element is not being used
to clamp a workpiece, so that no damage occurs to the rubber rim 64 of the
vacuum clamping element. The vacuum clamping element can be raised from
this lowered position when a vacuum is applied, as a result of which it comes
into
contact with the bottom surface of the workpiece in order to clamp it.
In the sectional drawing of the vacuum clamping element in Fig. 7, one can see
sensor pin 66, which is shown in the pushed-in position and which is biased by
a
spring 66' in such a way that it contacts the bottom surface of a workpiece,
thus
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
= -18-
detecting the presence or absence of a workpiece above the vacuum clamping
element.
By means of the inventive panel saw, it is possible to perform trimming cuts
and
cutting of large-format panels in a particularly simple manner. To perform a
trimming cut, a workpiece is placed on the workpiece support surface and
positioned against stop bar 30a, b and stop face 82a-c. The workpiece is then
clamped by means of vacuum clamping elements 61a-c and clamping elements
40a-c and can be moved with the aid of the feeder carriages and the fixing
carriage. When the detectors in the region of the saw slot detect the presence
of
a workpiece above the saw slot, the feeder carriages and the fixing carriage
move to the left, and when the sensors do not detect such a workpiece above
the
saw slot, the feeder carriages and the fixing carriage move to the right. In
this
way, the edge of the workpiece can be detected. As soon as the workpiece edge
has been detected in the region of the saw slot by means of the sensors, the
carriage moves a defined amount to the right over and beyond the saw cut.
Vacuum clamping elements 11 clamp the workpiece additionally, and the
trimming cut is performed by moving the circular saw module along the saw
slot.
Once such a trimming cut has been made, other formatting cuts can be carried
out after releasing vacuum clamping elements 11, by moving the feeder carriage
and the fixing carriage by a defined cutting dimension to the right. In this
case,
clamping elements 11, 12 and clamping element 40d clamp the workpiece to
perform the cut, so that the workpiece section to be cut away is likewise
fixed
securely during and after the saw cut.
In the event that a narrow workpiece is to be cut, the workpiece can be
clamped
in the defined manner against stop face 81a-c of the clamping jaw, then
clamped
by means of the clamping jaw and the clamping faces 84c embodied thereon and
moved towards the saw slot 10 to perform a cut.
Figs. 8 and 9 show a second embodiment of the invention. This embodiment
comprises a total of five feeder carriages 160 a-e, which are likewise
arranged
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-19-
parallel to one another and recessed within a workpiece support surface 120.
Feeder carriage 160 a lies adjacent and parallel to a stop fence 130 at a
short
distance away from the stop fence. Feeder carriage 160 b lies at an equally
short
distance adjacent to feeder carriage 160 a. The distance of feeder carriage
160 c
to feeder carriage 160 b is greater than the distance between feeder carriages
160 b and a. Feeder carriage 160 d is further apart than the distance between
feeder carriages 160 b and c, and the distance between feeder carriages 160 d
and e is larger again than the distance between feeder carriage 160 c and d.
The
distance between feeder carriages 160 a-e is thus increased continuously from
stop fence 130. This makes it possible for both small and large workpieces to
cover at least two feeder carriages and thus for them to be securely fixed.
Each feeder carriage 160 a-e is mounted displaceably along a direction 100,
and
it should be understood that this displacement of feeder carriage 160 a-c runs
perpendicular to the orientation 101 of a saw slot along which a saw blade
moves. The saw blade and saw slot provided for it are not depicted in Figures
8
and 9 and would lie in the zone marked with reference sign 110.
Each feeder carriage 160 a-e has a first clamping jaw 180 a-e at its end which
faces the saw slot and which is configured so that it lies in a recessed
position
below the workpiece support surface 120 and projected above the latter when in
a raised position. On each clamping jaw 180 a-e there is a clamping face which
faces towards the workpiece support surface white and is disposed such that it
can clamp a workpiece lying on the workpiece support surface against a counter-
surface formed on the feeder carriage. It is possible in this way to clamp a
workpiece with one or more clamping jaws 180 a-e and to move it onto saw slot
110 by advancing the feeder carriage, or to move it away from the former.
Also disposed on each feeder carriage is a clamping jaw 181 a-e which is
placed
at the opposite end of the feeder carriage facing away saw slot 110. Clamping
jaws 181 a-e are constructionally configured in the same way as clamping jaws
180 a-e. Clamping jaws 181 a-e are used to clamp larger workpieces which cover
the entire workpiece support surface or a large part thereof and which are to
be
CA 02762345 2011-11-17
-20-
cut in such a way that they are placed to extend far in direction 100.
Providing
two clamping jaws on each feeder carriage, at the respective front and back
end
of the feeder carriage, makes it possible to clamp not only very narrow
workpieces, but also very large workpieces with the feeder carriage and the
clamping jaws disposed thereon, and to cut them to shape with the panel saw
according to the invention. To do this, it is not necessary that the feeder
carriages
can be laterally displaced beyond the workpiece support surface.
In this regard, it should be understood as a basic principle that when a
workpiece
is clamped with the rear clamping jaws 181 a-e, the front clamping jaws 180 a-
e
are in their recessed position below the workpiece support surface and are
covered by the workpiece being processed.
It should be understood, as a basic principle, that a workpiece is preferably
clamped by at least two clamping jaws, although by way of exception a
workpiece can also be securely clamped by a single clamping jaw and then
processed. According to the invention, a workpiece is clamped, depending on
its
dimensions, by all those clamping jaws which match its depth perpendicular to
the direction in which the stop fence extends and which are reached by the
workpiece.