Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
CHILD SAFETY SEAT
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0001] 1. Field of the Invention
[0002] The present invention relates to child seats suitable for use
in combination
with either a base and/or stroller structure.
[0003] 2. Description of the Related Art
[0004] Conventionally, an automobile vehicle has seatbelts provided at the
front and
rear seats. The seatbelt generally includes shoulder and lap straps that may
be fastened
with an anchor point of the vehicle to restrain and protect the occupant in
case of collision or
sudden stop of the vehicle. However, the use of the vehicle seatbelt is not
adapted for a
young child who has a smaller body and may not be able to sustain the pressure
applied by
the seatbelt. As a result, safety legislations require the use of a child
safety seat for seating
a young child in a vehicle. The seatbelt of the vehicle can be used to secure
the child safety
seat, which is more adapted to provide protection for the young child.
[0005] The child safety seat can include a seat portion and a base
connected
underneath the seat portion. To facilitate the use of the seat portion,
attachment structures
may be provided to allow the seat portion to attach with and be removed from
the base. In
particular, it is desirable that the foregoing attachment structures can hold
the seat portion
CA 02763906 2013-11-28
=
with the base in a more secure manner, and at the same time is easy to operate
when the seat
portion is to be removed from the base.
[0006] Therefore, there is a need for a child safety seat that can be
safe in use and
address at least the foregoing issues.
SUMMARY
[0007] The present application describes a child safety seat that can
provide safety in
use, and is easy to operate for removing the seat from a support structure,
such as a base or a
stroller structure. In one embodiment, the child seat can comprise a seat
shell having two
protruding rails extending at an underside of the seat shell, at least four
latches disposed in
two symmetric pairs adjacent to the two rails, wherein the latches are
operable to lock the
child seat with a base, and a release mechanism operable to drive the latches
to unlock from
the base.
[0007a] Accordingly, there is provided a child seat comprising: a seat
shell having two
protruding rails extending at an underside of the seat shell; at least four
latches symmetrically
disposed in two pairs adjacent to the two rails, wherein the latches are
operable to lock the
child seat with a base; and a release mechanism operable to drive the latches
to unlock from
the base, wherein the release mechanism includes two drive elements of
elongated shape
respectively assembled in the two rails, a first one of the two drive elements
being in contact
with two of the four latches, and a second one of the two drive elements being
in contact with
two other different ones of the four latches, and each of the drive elements
being movable
lengthwise along the rail to drive unlocking of the two latches associated
therewith.
2
CA 02763906 2013-11-28
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
100081 Figure 1 is a perspective view illustrating an embodiment of a
child safety seat
assembly;
[0009] Figure 2 is a bottom view of the child seat shown in Figure 1;
100101 Figure 3 is a schematic view illustrating how first and second
transverse shafts
are assembled with the rails in the child seat;
100111 Figure 4 is a schematic view of the base shown in Figure 1;
2a
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
[0012] Figure 5 is an enlarged view illustrating how a first latch of
the child seat can
engage with a catch in a first groove of the base;
[0013] Figure 6 is an enlarged view illustrating how a second latch
of the child seat
can engage with a catch in a second groove of the base;
[0014] Figure 7 is a schematic view illustrating one embodiment of a
release
mechanism operable to unlock the first and second latches shown in Figures 5
and 6;
[0015] Figure 8 is a top view illustrating the release mechanism
shown in Figure 7
assembled in the child seat;
[0016] Figure 9 is a partial cross-sectional view illustrating the
connection of the
release handle with an additional latch operable to attach with a tray of a
stroller;
[0017] Figure 10 is a bottom view illustrating another child seat
provided with a
variant attachment construction;
[0018] Figure 11 is a schematic view illustrating the assembly of a
plurality of
latches operable to attach the child seat shown in Figure 10 with a base;
[0019] Figure 12 is an enlarged view of a portion of Figure 11; and
[0020] Figure 13 is a schematic view illustrating a base adapted to
assemble with the
child seat shown in Figure 10.
3
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE EMBODIMENTS
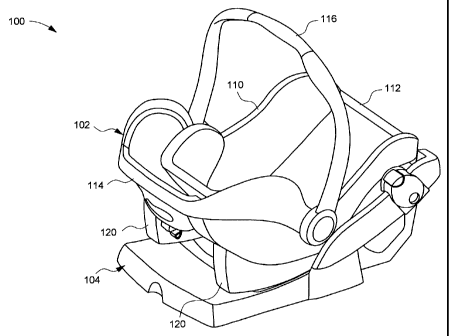
[0021] Figure 1 is a perspective view illustrating an embodiment of a
child safety
seat assembly 100. The child safety seat assembly 100 includes a child seat
102 and a base
104. The child seat 102 can include a seat shell 110 having a seat portion 112
and a
seatback 114. The seat shell 110, including the seat portion 112 and the
seatback 114, can
be formed in a single body by plastic molding. A handle 116 can be pivotally
connected
with two sides of the seat shell 110 to facilitate its carrying. In use, the
child seat 102 can
be either removed from the base 104, or attached herewith as shown in Figure
1. After it is
removed from the base 104, the child seat 102 can also be desirably mounted
with a stroller
apparatus. These different configurations of use can be secured via an
attachment
mechanism that can be adapted operable to fasten the child seat 102 with
either of the base
104 and a stroller apparatus. A first embodiment of this attachment mechanism
is
described hereafter with reference to Figures 2-9.
[0022] Figure 2 is a bottom view of the child seat 102. A bottom of
the child seat
102 can include two protruding rails 120, and a central recessed region 122
laterally
delimited between the two rails 120. The rails 120 can be formed at the
underside of the
seat portion 112, and extend to the rear of the seatback 114. A first
transverse shaft 124
can be pivotally mounted between the rails 120 across the recessed region 122
at a first
position adjacent to a front of the child seat 102. Two latches 126 can be
respectively
provided at two opposite end portions of the first transverse shaft 124,
adjacent to the
opposite inner sidewalls 120A of the rails 120. Each of the latches 126 can be
formed as a
sleeve 126A that can be affixed around the transverse shaft 124 and is
provided with a radial
4
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
engagement extension 126B oriented upward. A second transverse shaft 130 can
be
pivotally mounted between the rails 120 across the recessed region 122 at a
spaced-apart
second position behind the first transverse shaft 124. The second transverse
shaft 130 is
parallel to the first transverse shaft 124, and can have two opposite end
portions mounted
with latch elements 126 similar to those provided on the first transverse
shaft 124. While
the latches 126 have been described as parts assembled on the transverse
shafts 124 and 130,
alternate embodiments can also have the latches respectively formed integral
with the first
and second transverse shafts 124 and 130. The latches 126 exposed downward in
the
recessed region 122 can thereby form four attachment points disposed in two
symmetrical
pairs adjacent to the inner sidewalls 120A of the left and right side rails
120.
[0023] Figure 3 is a schematic view illustrating how the first and
second transverse
shafts 124 and 130 are assembled with the rails 120. Each of the rails 120 can
have a
hollow interior, and include first and second openings 132 and 134 through
which the end
portions of the first and second transverse shafts 124 and 130 can be
pivotally mounted.
The second opening 134 may have an oblong shape that permits relative back and
forth
floating movements of the second transverse shaft 130, which can accommodate
manufacturing tolerances and facilitate the movement and placement of the
second
transverse shaft 130 when the child seat 102 is installed on the base 104.
[0024] Figure 4 is a schematic view of the base 104. The base 104 can
include a
first portion 140 having an enlarged bottom to provide stable support, and a
second portion
142 rising from an upper side of the first portion 140 at an inclined angle.
An upper side of
the base 104 can include a support platform comprised of two protruding guide
rails 144 that
5
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
extend parallel in an axial direction of the base 104 and are adapted to
receive the placement
of the child seat 102. The guide rails 144 are symmetric in construction,
including first
grooves 146, and second grooves 148 axially spaced apart from the first
grooves 146. The
first and second grooves 146 and 148 can be formed as recesses in the upper
surfaces of the
guide rails 144, and are sized to receive and hold the end portions of the
transverse shafts
124 and 130 provided with the latches 126. Moreover, each of the first and
second grooves
146 and 148 can include catches 150 with which the latches 126 can engage to
lock the child
seat 102 with the base 104. In one embodiment, the catches 150 may be formed
at a same
side in each of the grooves 146 and 148, for example on the left side surface
as shown in
Figure 4.
[0025] Figures 5 and 6 are enlarged views illustrating how the
latches 126 can
respectively engage with the catches 150 in the first and second grooves 146
and 148. Each
of the catches 150 can have a hook shape having an upper angled surface 150A
and a lower
surface 150B. When the child seat 102 is disposed on the base 104, the angled
surface
150A can respectively push away the engagement extension 126B to rotate the
transverse
shaft 124 so that each of the latches 126 can be received in the associated
first and second
grooves 146 and 148. While the transverse shaft 124 is held in the first
grooves 146, the
preset manufacturing/assembly tolerance may result in difficulties of
engagement of the
second transverse shaft 130 in the second grooves 148. Thanks to the oblong
shape of the
second openings 134, the second transverse shaft 130 is allowed to self-adjust
for adequate
placement of the associated latches 126 in the second grooves 148. Once each
latch 126 is
held in the associated groove, forward and backward movements as well as
lateral
6
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
displacements of the child seat 102 relative to the base 104 can be blocked. A
torsion
spring 152 mounted with the latch 126 (better shown in Figure 7) can then bias
the latch 126
to rotate about the transverse axis defined by the transverse shaft 130 in a
first direction R1
to place the engagement extension 126B in locking engagement against the lower
surface
150B of the catch 150, whereby upward removal of the child seat 102 is also
blocked. The
child seat 102 can be thereby locked in position with the base 104. To unlock
the child seat
102, the latches 126 can be rotated in an opposite second direction R2 to
disengage the
engagement extensions 126B from the lower surface 150B of the catches 150.
Being
unlocked, the child seat 102 then can be pulled upward and separated from the
base 104.
For unlocking the latches 126, the child seat 102 can be provided with a
release mechanism
operable to drive rotation of the latches 126 in the direction R2 for
disengagement from the
catches 150. One embodiment of this release mechanism is described hereafter
with
reference to Figures 7 and 8.
[0026] Figure 7 is a schematic view illustrating one embodiment of a
release
mechanism 158 operable to unlock the latches 126, and Figure 8 is a top view
illustrating the
assembly of the release mechanism 158 in the child seat 102. The release
mechanism 158
can include two drive elements 160 coupled with the release handle 162. The
drive
elements 160 can be movably mounted in the interior of the rails 120, and are
respectively
connected with the latches 126. In one embodiment, the two drive elements 160
can be
formed as elongated strips made of plastic, and have bent shapes that
generally conform with
the profile of the rails 120 extending from the front of the child seat 102 to
a rear of the
seatback 114. Guiding structures 164 can be provided in the rails 120 to guide
movements
7
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
of the drive elements 160 between a normal position and a released position
along a
lengthwise axis of the child seat 102.
[0027] As better shown in Figure 7, each of the latches 126 can
include a lateral
protrusion 126C projecting in a transverse direction from the engagement
extension 126B.
The drive elements 160 can include a plurality of protruding fingers 166
respectively
connected with the lateral protrusions 126C. The fingers 166 can include
recesses into
which the lateral protrusions 126C can be movably engaged, so that a sliding
movement of
the drive elements 160 can drive rotation of the latches 126.
[0028] The release handle 162 is mounted to move relative to the seat
shell 110
generally along the inclination axis of the seatback 114. As shown, the
release handle 162
can have a generally U-shape including two side segments 168 respectively
connected with
end portions of the two drive elements 160, and a transverse segment 170
connected between
the two side segments 168. The transverse segment 170 can include a grip 172
that is
mounted through an opening 174 (better shown in Figure 9) formed at the rear
of the
seatback 114 for facilitating operation of the release handle 162. When the
release handle
162 is pulled upward, the drive elements 160 are moved to the released
position to drive the
latches 126 in rotation in the direction R2 (as shown in Figures 5 and 6) to
disengage the
engagement extensions 126B from the catches 150. The unlocked child seat 102
then can
be removed from the base 104.
[0029] In conjunction with Figure 7, Figure 9 is a partial cross-sectional
view
illustrating the connection of the release handle 162 with an additional latch
176 operable to
8
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
attach with a corresponding structure of a stroller, such as a tray 178. As
shown, the latch
176 may be pivotally connected with the seat shell 110 at a rear of the
seatback 114, and
include a hook 180 and an extension 182 projecting at opposite sides relative
to the pivot
axis of the latch 176. The release handle 162 can include an arm 184 adjacent
to the grip
172 and extending inward to couple with the extension 182 of the latch 176
such that the
user can operate the grip 172 to release the additional latch 176 as well. In
addition, the
child seat 102 can also include a rotation blocking portion 171 projecting
downward at the
rear of the seatback 114. The rotation blocking portion 171 can lie in front
of the hook 180
so as to define a gap between the rotation blocking portion 171 and the hook
180. When
the child seat 102 is installed on the stroller, a protruding portion of the
tray 178 can be
lodged in the gap between the latch 176 and the rotation blocking portion 171,
and the
rotation blocking portion 171 can abut against an inner surface 178A of the
tray 178 at a
position opposite to the latch 176. Moreover, the hook 180 of the latch 176
can engage
with an underside of the tray 178 to attach the rear of the child seat 102
with the stroller. A
biasing spring (not shown) may be used to maintain the latch 176 in this
locked state. In
this manner, the rear of the child seat 102 can be securely kept in place, and
the rotation
blocking portion 171 can prevent the child seat 102 from undesirable flipping
about the
region where the tray 178 is engaged with the hook 180.
[0030] When the release handle 162 is pulled upward (i.e., in the
same way as for
unlocking the latches 126 described previously), the arm 184 can pull on the
extension 182
to drive rotation of the latch 176 and cause the hook 180 to disengage from
the tray 178.
The child seat 102 then can be removed from the stroller.
9
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
[0031] With the foregoing attachment structure, the child seat 102
includes five
latches, four latches 126 provided symmetrically at left and right sides to
securely attach the
child seat 102 with the base 104, and one latch 176 to attach the rear of the
child seat 102
with a stroller. To remove the child seat 102 either from the base 104 or the
stroller, the
same release handle 162 can be operated to conveniently drive all of the
latches 126 and 176
in a concurrent manner.
[0032] Figure 10 is a bottom view illustrating another child seat 202
provided with a
variant attachment construction. Likewise, the child seat 202 can include a
seat shell 210
having a seat portion 212 and a seatback 214. A handle 216 can be pivotally
connected
with two sides of the seat shell 210 to facilitate its carrying. A bottom of
the child seat 202
can include two protruding rails 220, and a recessed region 222 delimited
between the two
rails 220. The rails 220 can be formed at the underside of the seat portion
212, and extend
to the rear of the seatback 214. Each of the rails 220 can be mounted with two
latches, one
latch 226 assembled through an opening at an inner sidewall 220A of the rail
220 (i.e.,
adjacent to the recessed region 222), and one latch 228 assembled through an
opening at an
opposite outer sidewall 220B of the rail 220 and spaced apart from the latch
226 along a
lengthwise axis of the rail 220. The latches 226 and 228, which are
constructed symmetric
with the two rails 220, can be operable to rotate in opposite directions when
the attachment
structure is switched from the locked to unlocked state, or reversely. The
pivot axes about
which the latches 226 and 228 rotate can extend generally along the lengthwise
axis of the
child seat 202.
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
100331 In conjunction with Figure 10, Figure 11 is a schematic view
illustrating the
assembly of the latches 226 and 228, and Figure 12 is an enlarged view of a
portion of
Figure 11. For clarity, certain portions of the seat shell 210 are omitted in
these figures to
better show the construction of the attachment structure. As shown in Figures
11 and 12,
each of the latches 226 can be placed at a rearward position (e.g., closer to
the release handle
244), and can be pivotally connected with the seat shell 210 via a fixed pivot
link 230 (such
as a pin or rivet) that define a pivot axis oriented in a lengthwise direction
of the seat shell
210 (i.e., from the rear to the front). The latch 226 can be formed in an
integral body
including a radial engagement extension 226A, a lever 226B projecting in a
transverse
direction from an inner side of the engagement extension 226A and located at a
position
upwardly offset from the pivot axis of the pivot link 230, and a stud 226C
projecting upward
from the lever 226B. A spring 232 can be interposed between a lower side of
the lever
226B and an inner bottom surface of the seat shell 210 (not shown).
100341 As shown in Figure 11, each of the latches 228 can be placed
at a forward
position(e.g., farther from the release handle 244) in front of the latch 226,
and can be
pivotally connected with the seat shell 210 via a fixed pivot link 234 (such
as a pin or rivet).
The latch 228 can be formed in an integral body including a radial engagement
extension
228A, and a lever 228B projecting transversal from an inner side of the
engagement
extension 228A and located at a position upwardly offset from the pivot axis
of the pivot
link 234. A spring 236 can be interposed between a lower side of the lever
228B and an
inner bottom surface of the seat shell 210 (not shown).
11
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
[0035] Referring again to Figures 11 and 12, the child seat 202 also
includes a
release mechanism that is coupled with the latches 226 and 228. The release
mechanism
can include two drive elements 240, a bar linkage 242 and a release handle
244. Each of
the drive elements 240 can be formed as an elongated part, and is assembled in
each of the
rails 220 for lengthwise movements along the rails 220. Axial springs 245 can
be provided
to bias the drive elements 240 forward to recover an initial normal position.
Each of the
drive elements 240 can include a rear portion 240A and a front portion 240B
respectively
adapted to interact with the latches 226 and 228 for actuating locking and
unlocking
operations.
[0036] As shown in Fig.12, The rear portion 240A can have a guide slot 246
through
which a fixed anchor 248 (pin or rivet) can be passed to guide lengthwise
displacements of
the drive element 240. The rear portion 240A can also include a surface that
extends above
the lever 226B and is provided with a slot 250 into which the stud 226C of the
latch 226 is
movably engaged. The slot 250 can have a tapered shape with a driving edge
250A that
extends gradually farther from the pivot axis of the pivot link 230 toward the
rear of the
drive element 240(toward the release handle 244). The biasing action of the
spring 232 can
keep the stud 226C constantly in contact with the driving edge 250A of the
slot 250.
[0037] The front portion 240B can be disposed to lie above the lever
228B, and
include an angled guide slot 252 through which a fixed anchor 254 (for example
rivet or pin)
can be passed at a position proximate to the latch 228. The biasing action of
the spring 236
can keep an upper side of the lever 228B constantly in contact with the front
portion 240B of
the drive element 240. The movable engagement of the fixed anchor 254 through
the guide
12
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
slot 252 can guide lengthwise displacement as well as downward and upward
deflections of
the front portion 240B relative to the seat shell 210 as the drive element 240
moves back and
forth along a lengthwise axis.
[0038] Referring to Figure 11, the bar linkage 242 can include a
generally U-shaped
linkage 256 and two links 258. The linkage 256 can be formed as an integral
body having
two side segments 256A and a transverse segment 256B. The linkage 256 can be
pivotally
connected with the seat shell 210 via pivot pins 260 provided on the side
segments 258A.
The two side segments 256A can be respectively connected with the two drive
elements 240
via the two links 258, each of which has a first end pivotally connected with
the rear portion
240A of one associated drive element 240 and a second end pivotally connected
with one
side segment 256A of the linkage 256.
[0039] The release handle 244 can be assembled through the rear of
the seatback 214,
and is assembled adjacent to the transverse segment 256B of the linkage 256.
Pins 262
may be provided to pivotally connect the release handle 244 with the seat
shell 210.
Moreover, the release handle 244 can also include an arm 264 that is coupled
with an
additional latch 266 configured to attach the rear of the child seat 202 with
a stroller, whose
mechanism is substantially the same as that of the previous embodiment.
[0040] Exemplary operation of the aforementioned attachment structure
is described
hereafter with reference to Figures 10 through 13. When the child seat 202 is
installed on a
base 304, the axial springs 245 can bias the drive elements 240 to return to
the normal
position. As a result, the interaction between the lever 226B and the spring
232 can drive
13
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
the associated latch 226 to rotate in a direction for bringing the engagement
extension 226A
to a position extending outward from the inner sidewall 220A of the rail 220.
Meanwhile,
the movable engagement of the fixed anchor 254 through the guide slot 252 at
the front
portion 240B of each drive element 240 can cause the drive element 240 to
deflect upward,
which allows the associated latch 228 biased by the spring 236 to rotate in a
direction for
bringing the engagement extension 228A to a position extending outward from
the outer
sidewall 220B of the corresponding rail 220. The latches 226 and 228 can be
thereby in
locking engagement against associated catch structures 346 and 348 provided on
the base
304 to block upward removal of the child seat 202.
100411 In conjunction with Figure 10, Figure 13 is a schematic view
illustrating a
base 304 provided with catch structures for attaching with the child seat 202.
The base 304
may include a support platform 306 comprised of two guide rails 344 that
extend parallel in
an axial direction of the base 304 and are adapted to receive the placement of
the child seat
202. The support platform 306 may include a plurality of catch structures 346
and 348
disposed symmetric in association with the latches 226 and 228 described
above. For
example, the catch structures 346 may be recesses symmetrically formed on the
outer
sidewalls 344A of the rails 344.
The catches structures 348 may be openings
symmetrically provided on an inner side of two sockets 350 projecting upward
from the
support platform 306 at outer sides of the rails 344. When the child seat 202
is installed on
the base 304, the inner sidewalls 220A of the rails 220 on the child seat 202
are respectively
placed adjacent to the outer sidewalls 344A of the rails 344 on the base 304,
whereas the
outer sidewalls 220B of the rails 220 are respectively adjacent to the inner
sides of the
14
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
sockets 350. The latches 226 and 228 can respectively engage with the catch
structures 346
and 348 to lock the child seat 202 with the base 304.
[0042] To unlock the child seat 202, the release handle 244 can be
pushed to rotate
upward, which pushes the linkage 256 in rotation in the same direction. The
rotation of the
linkage 256 can pull the two drive elements 240 rearward via the links 258,
which also
compress the axial springs 245. As each of the drive elements 240 move
rearward, the
interaction between the stud 226C of the latch 226 and the driving edge 250A
at the rear
portion 240A of the drive element 240 and can drive each latch 226 to rotate
in a direction
that retracts the engagement extension 226A inward and compresses the spring
232. In the
meantime, the movable engagement of the anchor 254 through the guide slot 252
at the front
portion 240B also causes the front portion 240B of the drive element 240 to
deflect
downward against the lever 228B, which in turn compresses the associated
spring 236 and
causes each latch 228 to rotate in a direction that retracts the engagement
extension 228A
inward. All of the latches 226 and 228 can thereby unlock in a concurrent
manner,
allowing upward removal of the child seat 202. Once the release handle 244 is
released,
the drive elements 240 can be biased to move forward to the normal position by
the axial
springs 245, and the elastic force applied by the springs 232 and 236 can
restore the initial
locking positions of the latches 226 and 228 respectively.
[0043] Similar to the previously described embodiment, the operation
of the release
handle 244 can also drive the latch 266 in rotation for disengaging the latch
266 from a tray
of a stroller.
CA 02763906 2012-01-10
[0044]
At least one advantage of the structures described herein is the ability to
securely attach the child seat with the base via four latches distributed
symmetrically along
two rails that extend lengthwise at the underside of the child seat. All of
the four latches
can be controllably driven to unlock concurrently via a release mechanism
integrated in the
child seat. In addition, the child seat also includes a latch that can attach
the rear of the
child seat with a stroller, and can be driven to unlock via the same release
mechanism.
[0045]
Realizations in accordance with the present invention therefore have been
described only in the context of particular embodiments. These embodiments are
meant to
be illustrative and not limiting.
Many variations, modifications, additions, and
improvements are possible. Accordingly, plural instances may be provided for
components
described herein as a single instance. Structures and functionality presented
as discrete
components in the exemplary configurations may be implemented as a combined
structure or
component. These and other variations, modifications, additions, and
improvements may
fall within the scope of the invention as defined in the claims that follow.
16